Active Tablet Coating with Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Ibuprofen–HPMCAS from Organic Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Drug–Polymer Solutions in Organic Solvents for Coatings
2.2. Flow Rate and Kinematic Viscosity of Solutions
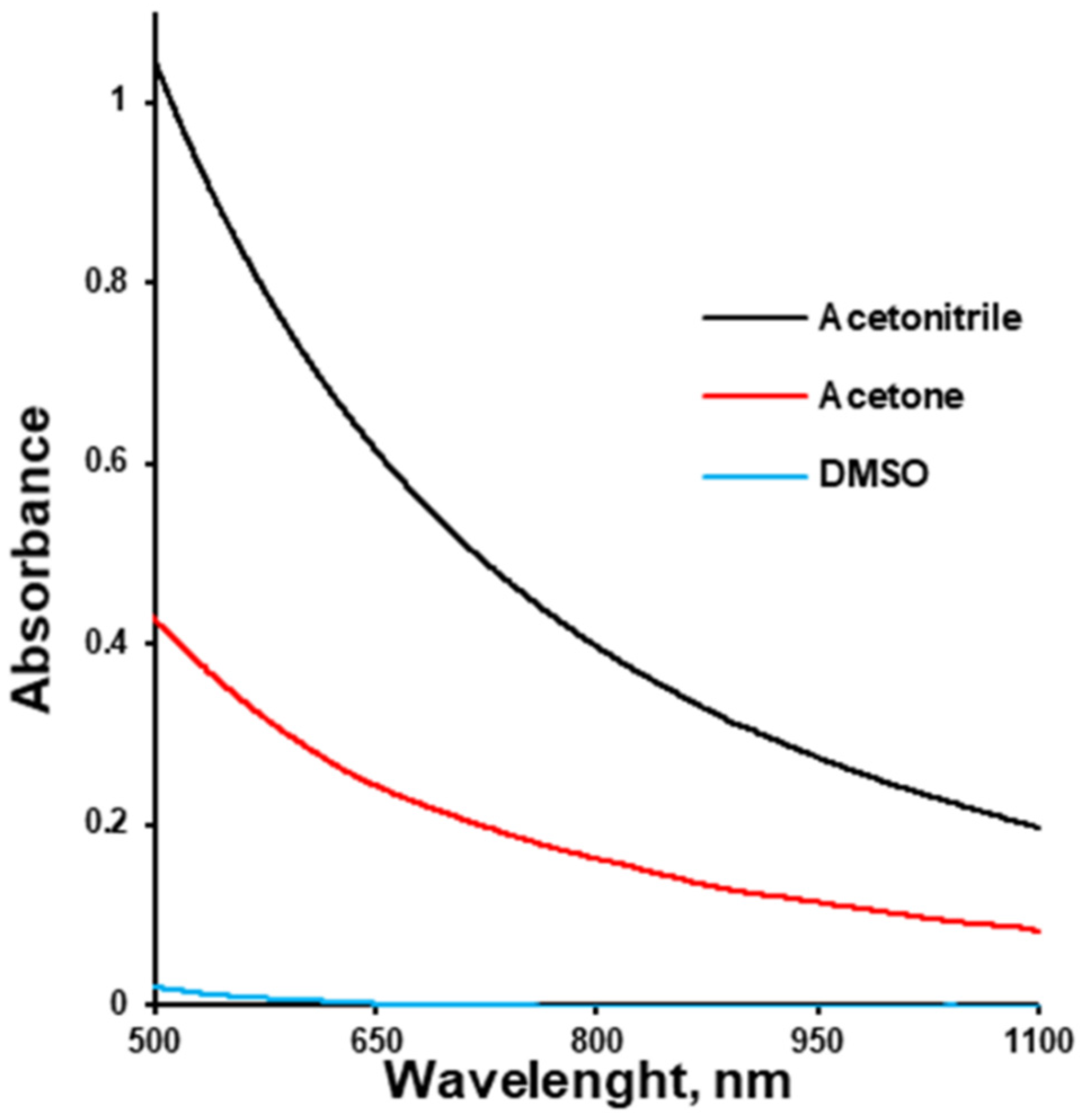
2.3. Turbidity Measurement
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.5. Placebo Tablet Preparation
2.6. Surface Area and Specific Surface Area of Tablets
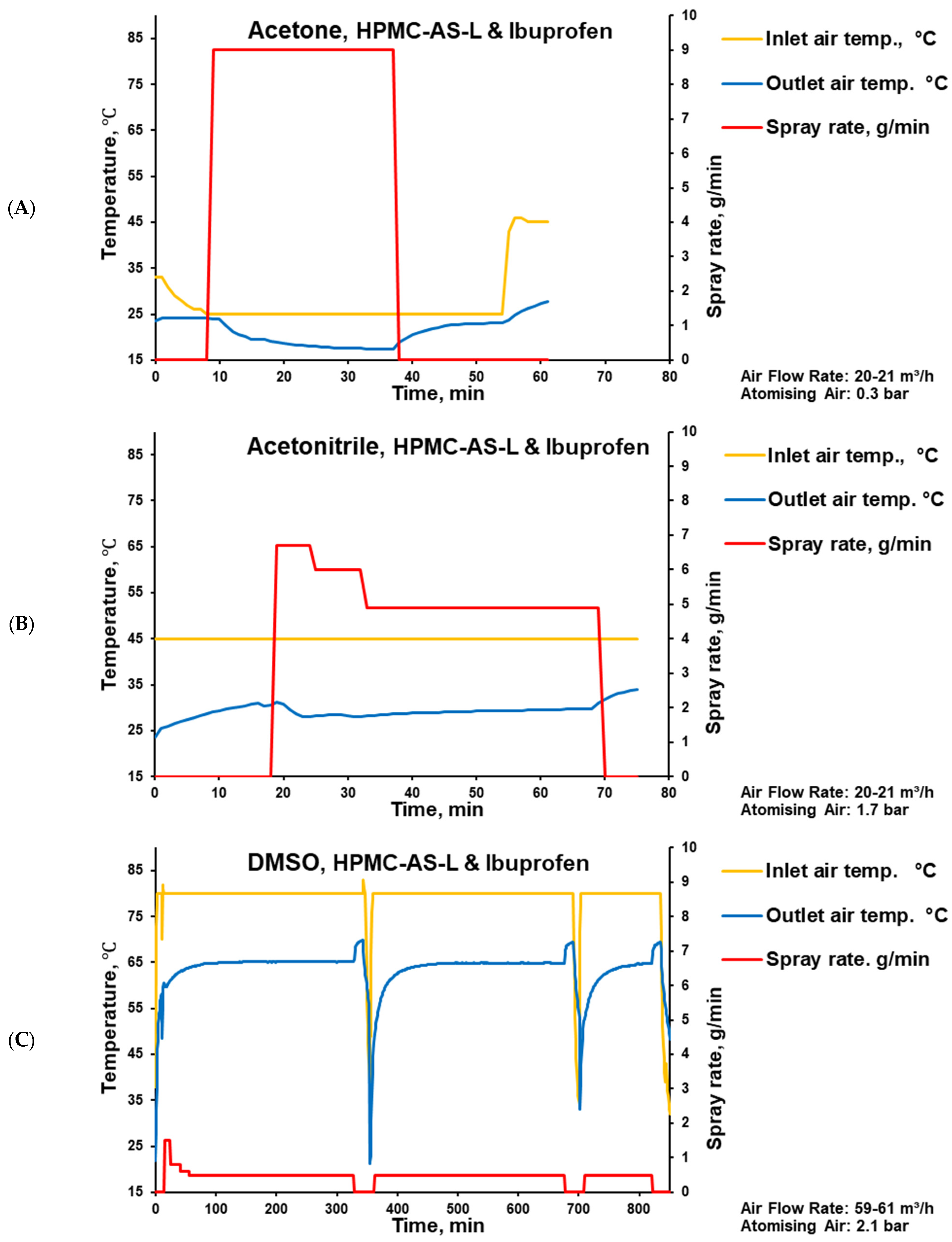
2.7. Tablet Coating
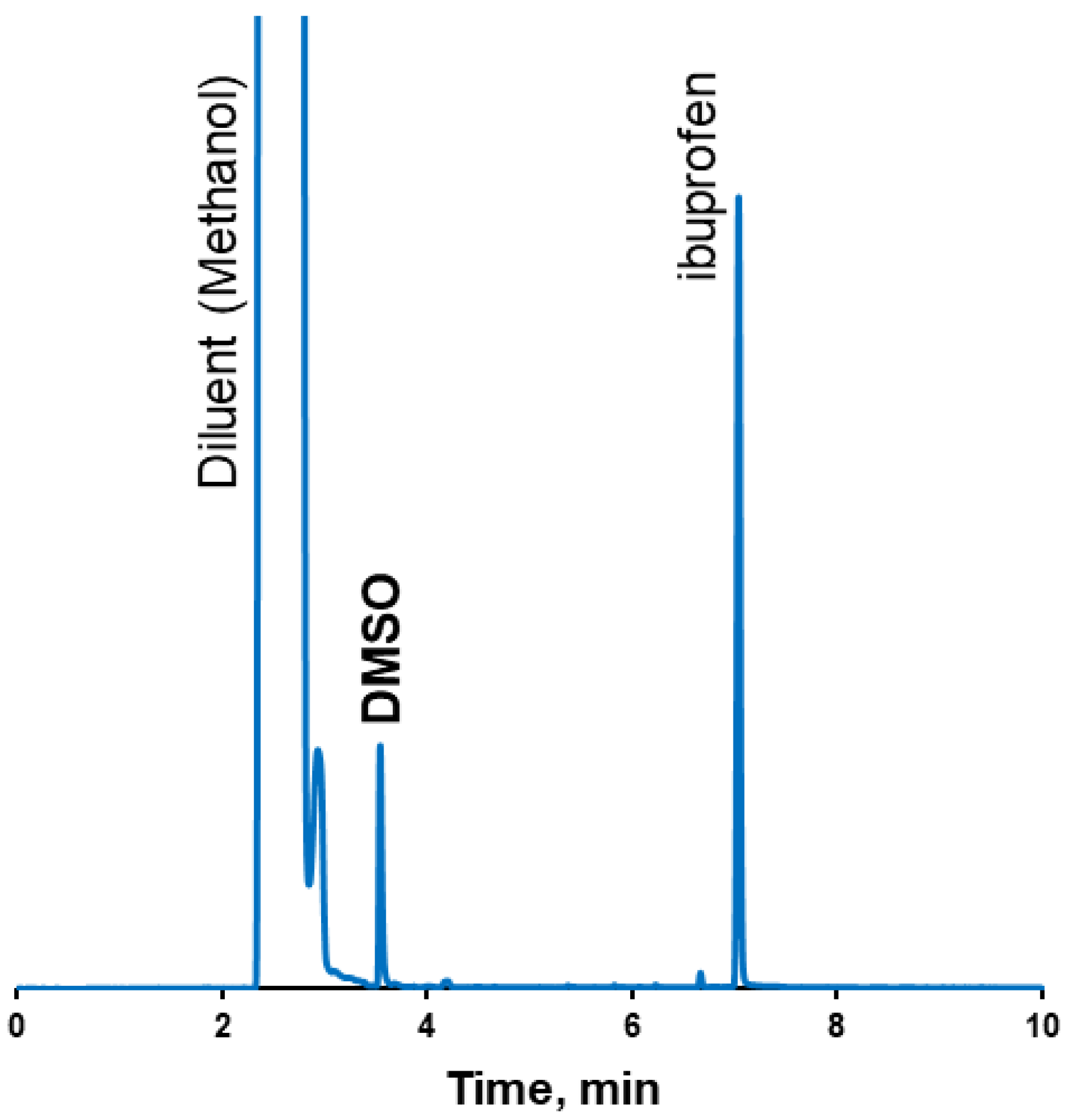
2.8. Gas Chromatography (GC) Method for Residual Solvent Quantification
2.9. Determination of Drug Content in Tablets
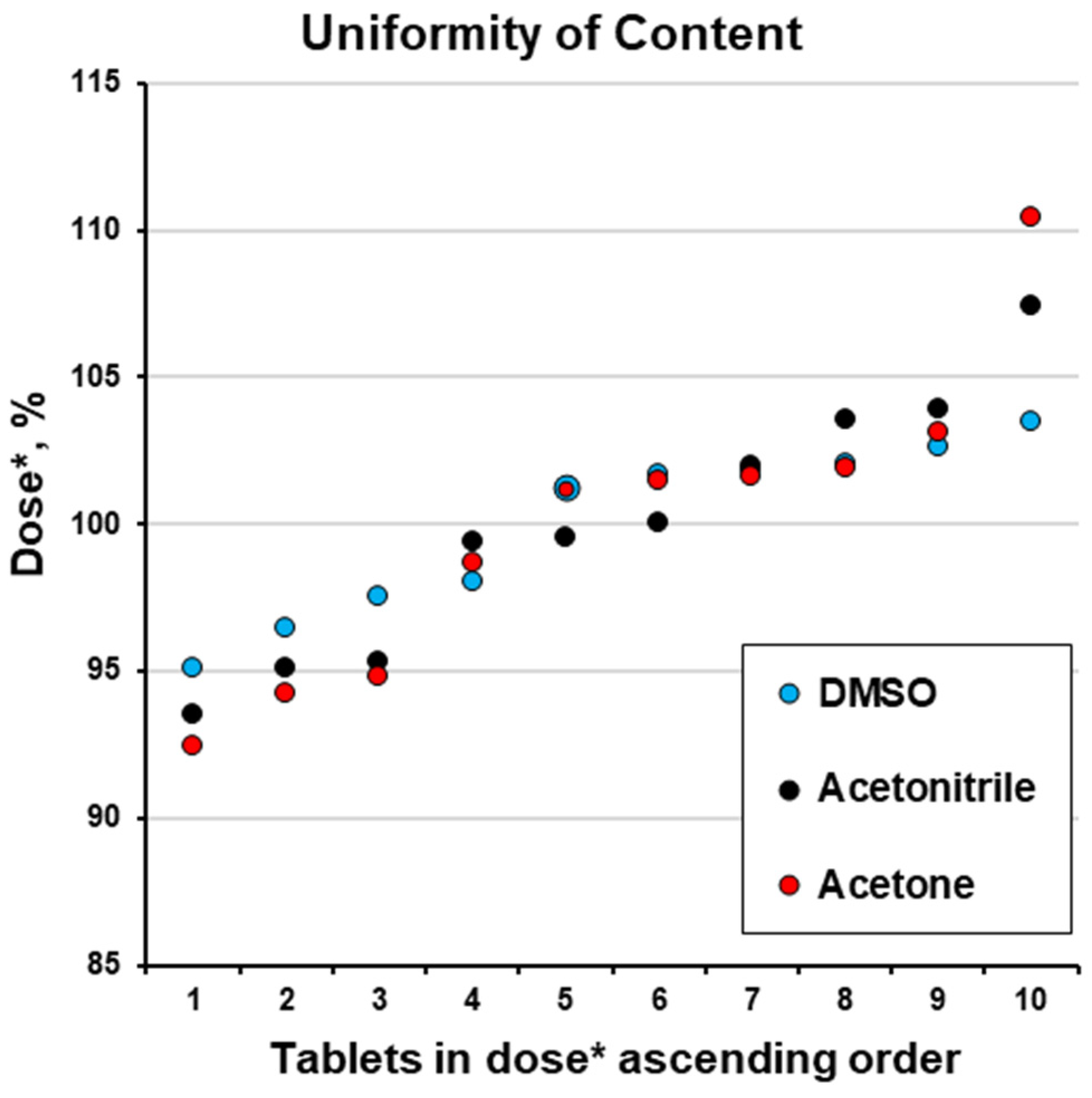
2.10. Uniformity of Dosage Forms: Test for the Uniformity of Content
2.11. Drug–Polymer Film Behaviour in Different Media
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leane, M.; Pitt, K.; Reynolds, G.; Manufacturing Classification System Working Group. A proposal for a drug product Manufacturing Classification System (MCS) for oral solid dosage forms. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 20, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, Z.M.; Grundsteins, K.; Radzins, O.; Kons, A.; Berzins, A.; Viter, R.; Lamprou, D.A.; Mohylyuk, V. FDM 3D-printed oral dosage form of prednisolone—Improvement of printability and influencing drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 673, 125391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberger, J.; Butler, J.; Dressman, J. A Refined Developability Classification System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.M.; Dressman, J.B. The developability classification system: Application of biopharmaceutics concepts to formulation development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4940–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsume, Y.; Mudie, D.M.; Langguth, P.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The Biopharmaceutics Classification System: Subclasses for in vivo predictive dissolution (IPD) methodology and IVIVC. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Weon, K.Y. Pharmaceutical application and development of fixed-dose combination: Dosage form review. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Mohan, S. Application of Process Analytical Technology for Pharmaceutical Coating: Challenges, Pitfalls, and Trends. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.; Rao, V.; Guo, H.; Li, D.; Stein, D.; Hu, F.Y.; Kiesnowski, C. An active film-coating approach to enhance chemical stability of a potent drug molecule. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.; Wang, J.; Wen, H.; Li, X.; Timmins, P. Formulation design, challenges, and development considerations for fixed dose combination (FDC) of oral solid dosage forms. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, L.A. Aqueous Polymeric Coatings for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Felton, L.A.; Porter, S.C. An update on pharmaceutical film coating for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salawi, A. Pharmaceutical Coating and Its Different Approaches, a Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boel, E.; Reniers, F.; Dehaen, W.; Van den Mooter, G. The Value of Bead Coating in the Manufacturing of Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Comparative Evaluation with Spray Drying. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwirth, M.; Kappes, S.K.; Hartig, M.U.; Wagner, K.G. Amorphous Solid Dispersions Layered onto Pellets-An Alternative to Spray Drying? Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han Won, D.; Park, H.; Seo, J.W.; Woo Jang, S.; Ha, E.S.; Kim, M.S. Active coating of immediate-release evogliptin tartrate to prepare fixed dose combination tablet with sustained-release metformin HCl. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Desai, D.; Chang, S.Y.; Kiang, S.; Lyngberg, O. A Strategy for Tablet Active Film Coating Formulation Development Using a Content Uniformity Model and Quality by Design Principles. In Comprehensive Quality by Design for Pharmaceutical Product Development and Manufacture; Wiley-AIChE: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 193–233. [Google Scholar]
- Mohylyuk, V.; Styliari, I.D.; Novykov, D.; Pikett, R.; Dattani, R. Assessment of the effect of Cellets’ particle size on the flow in a Wurster fluid-bed coater via powder rheology. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Porter, S.C.; Macht, B.; Meisen, A. Novel Coating Uniformity Models for Tablet Pan Coaters. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaese, A.N. Investigation of the Effect of Coating Time on the Inter-Tablet Coating Uniformity, Using Bohle Lab Coater. Master’s Thesis, Heinrich-Heine Universitat Dusseldorf, Dusseldorf, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Just, S.; Toschkoff, G.; Funke, A.; Djuric, D.; Scharrer, G.; Khinast, J.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. Optimization of the inter-tablet coating uniformity for an active coating process at lab and pilot scale. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hemenway, J.; Chen, W.; Desai, D.; Early, W.; Paruchuri, S.; Chang, S.Y.; Stamato, H.; Varia, S. An evaluation of process parameters to improve coating efficiency of an active tablet film-coating process. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 427, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Boukouvala, F.; Keyvan, G.; Hsia, R.; Saranteas, K.; Brone, D.; Misra, T.; Ierapetritou, M.G.; Muzzio, F.J. Improvement of tablet coating uniformity using a quality by design approach. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Munoz, S.; Gierer, D.S. Coating uniformity assessment for colored immediate release tablets using multivariate image analysis. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 395, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chang, S.Y.; Kiang, S.; Marchut, A.; Lyngberg, O.; Wang, J.; Rao, V.; Desai, D.; Stamato, H.; Early, W. Modeling of pan coating processes: Prediction of tablet content uniformity and determination of critical process parameters. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3213–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbag, A.; Wassgren, C. Inter-tablet coating variability: Tablet residence time variability. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 2705–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbag, A.; Wassgren, C.; Sumana Penumetcha, S.; Pérez-Ramos, J.D. Inter-tablet coating variability: Residence times in a horizontal pan coater. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 2881–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.S.; Liew, C.V.; Er, D.Z.; Liu, X.; Wigmore, A.J.; Heng, P.W. Study of coat quality of tablets coated by an on-line Supercell coater. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiska, S.; Kleinebudde, P. Coating uniformity and coating efficiency in a Bohle Lab-Coater using oval tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rege, B.D.; Gawel, J.; Kou, J.H. Identification of critical process variables for coating actives onto tablets via statistically designed experiments. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 237, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficzere, M.; Meszaros, L.A.; Kallai-Szabo, N.; Kovacs, A.; Antal, I.; Nagy, Z.K.; Galata, D.L. Real-time coating thickness measurement and defect recognition of film coated tablets with machine vision and deep learning. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Markl, D.; Williams, B.M.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zeitler, J.A. Measurement of the Intertablet Coating Uniformity of a Pharmaceutical Pan Coating Process With Combined Terahertz and Optical Coherence Tomography In-Line Sensing. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, E.; Chaudhuri, B. Experimental and modeling approaches in characterizing coating uniformity in a pan coater: A literature review. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Hsia, R.; Saranteas, K.; Brone, D.; Misra, T.; Muzzio, F.J. Effect of speed, loading and spray pattern on coating variability in a pan coater. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 5107–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.; Liu, P.; Berchielli, A.; Doshi, P.; Saxena, U.; Khan, M.; Suryawanshi, T.; Kasat, G. Prediction of the finished tablet coating variability in pan coaters by coupling CFD-DEM and Monte Carlo simulations: Method development and validation. Powder Technol. 2024, 445, 120141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschkoff, G.; Just, S.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P.; Funke, A.; Djuric, D.; Scharrer, G.; Khinast, J.G. Modeling of an Active Tablet Coating Process. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 4082–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzzi, D.; Toschkoff, G.; Radl, S.; Machold, D.; Fraser, S.D.; Glasser, B.J.; Khinast, J.G. DEM simulation of continuous tablet coating: Effects of tablet shape and fill level on inter-tablet coating variability. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 69, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzzi, D.; Radl, S.; Khinast, J.G. Local analysis of the tablet coating process: Impact of operation conditions on film quality. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 5699–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, L.; Sommerfeld, M.; Muramulla, P.; Yuan, F.-L.; Gopireddy, S.; Urbanetz, N.; Profitlich, T. Tablet coating in lab-scale drum coaters: Combining DEM simulations and spray experiments to predict tablet coating. Powder Technol. 2023, 427, 118683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohrn, S.; Luebbert, C.; Lehmkemper, K.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Degenhardt, M.; Sadowski, G. Phase behavior of pharmaceutically relevant polymer/solvent mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 577, 119065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boel, E.; Van den Mooter, G. The impact of applying an additional polymer coating on high drug-loaded amorphous solid dispersions layered onto pellets. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mare, E.J.; Punia, A.; Lamm, M.S.; Rhodes, T.A.; Gormley, A.J. Data-Driven Design of Novel Polymer Excipients for Pharmaceutical Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Bioconjugate Chem. 2024, 35, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DIN 53211-1987; Determination of Flow Time Using DIN Flow Cups for Paints, Varnishes and Similar Coating Materials. Deutsche Institut fur Normung EV (DIN): Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987.
- Mohylyuk, V.; Bandere, D. High-speed tableting of high drug-loaded tablets prepared from fluid-bed granulated isoniazid. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.H. Coated Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Fundamentals, Manufacturing Techniques, Biopharmaceutical Aspects, Test Methods, and Raw Materials, 1st ed.; Medpharm Scientific; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Commission and European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare: Council of Europe. Chapter 2.9.40. Uniformity of Dosage Units European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur. 11.8); Commission and European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare: Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2025; pp. 421–423. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Trasi, N.S.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Taylor, L.S. Surface area normalized dissolution to study differences in itraconazole-copovidone solid dispersions prepared by spray-drying and hot melt extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 540, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Q3C (R9) Guideline on Impurities: Guideline for Residual Solvents; International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH): Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]


| Pan Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pan type | Fully perforated side-vented coating pan | ||
| Pan diameter, cm | 30 | ||
| Pan width, cm | 11 | ||
| Coating Composition | |||
| Solvent | acetone | acetonitrile | DMSO |
| Drug-to-polymer ratio, w/w | 25:75 | 25:75 | 25:75 |
| Solid content, % w/v | 10.09 | 10.24 | 7.40 |
| Polymer content, % w/v | 7.57 | 7.68 | 5.55 |
| Volume of coating solution, mL | 278.6 | 274.7 | 380.3 |
| Run Objectives | |||
| Theoretical weight gain, wt.% | 7.66 | ||
| Theoretical drug load, wt.% | 1.91 | ||
| Theoretical drug load, mg/tab. | 12.63 | ||
| Tablet charge, g | 350 | ||
| Single tablet weight (Av.), mg | 660 | ||
| Tablet shape and size | Biconvex, D = 13 mm, hemisphere r = 6.5 mm, H = 6 mm | ||
| Gun Configuration and Settings | |||
| Number of guns | 1 | ||
| Gun type | Schlick nozzle (970/0 S75 ABC-Technology®) | ||
| Spray pattern | Oval flat spray pattern | ||
| Nozzle diameter, mm | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Gun to bed distance, cm | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| Atomized air pressure, bar | 0.3 | 1.7 | 2.1 |
| Pattern air pressure, bar | 0 | 0 | 1.4 |
| Other Process Parameters | |||
| Pan speed, rpm | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Intel air flow rate, m3/h | 20.5 | 20.8 | 60 |
| Intel air temperature, °C | 25 | 45 | 80 |
| Outlet air temperature, °C | 24–17 | 30 | 60–65 |
| Spray rate, g/min | 9.0 | 6.7–4.9 | 0.5 |
| Coating time, min | 28 | 50 | 739 |
| Setting for Residual Solvents | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Acetonitrile or Acetone | DMSO |
| for HS-20NX | ||
| Oven | 80 °C | |
| Sample line temperature | 180 °C | |
| Transfer line temperature | 180 °C | |
| Precondition and time | Shaking for 60 min | Shaking for 20 min |
| Run time | 45 min | 10 min |
| for Nexis GC-2030 | ||
| Column | Restek Rxi-5 ms (30 m × 0.32 mm, 0.25 µm film thickness column). | |
| Injector | 200 °C, split ratio 1:10 (splitless) | 250 °C, splitless |
| Detector | FID, 250 °C | |
| Carrier gas | constant flow of helium (He) at 1 mL/min | |
| Thermal conditions of column | Initial isothermal temperature hold at 40 °C for 20 min; followed by temperature increase 10 °C/min up to 250 °C | Initial isothermal temperature hold at 70 °C for 1 min; temperature increase of 50 °C/min up to 130 °C; isothermal temperature hold at 130 °C for 1 min; followed by temperature increase of 50 °C/min up to 220 °C; and isothermal hold at 220 °C for 5 min |
| Solvents in Tablet Coating | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | Acetonitrile | Acetone | ||||
| Sample Solution | In Coating | Sample Solution | In Coating | Sample Solution | In Coating | |
| Units | ppm | wt. % | ppm | wt. % | ppm | wt. % |
| run #1 | 13,469 | 1.3 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| run #2 | 16,953 | 1.7 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| run #3 | 15,224 | 1.5 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Av. | 15,215 | 1.5 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| S.D. | 1742 | 0.2 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Method-related information | ||||||
| Retention time, min | 3.5 min | 2.9 min | 2.9 min | |||
| LOQ concentration | 0.038 mg/mL (38 ppm) | 0.02 mg/mL (20 ppm) | 0.03 mg/mL (30 ppm) | |||
| LOD concentration | 0.013 mg/mL (13 ppm) | 0.007 mg/mL (7 ppm) | 0.01 mg/mL (10 ppm) | |||
| Linearity range | 0.038–1.15 mg/mL 38–1493 ppm | 0.04–0.5 mg/mL 40–494 ppm | 0.05–0.6 mg/mL 50–589 ppm | |||
| Recovery, % | 98.2 | 101.8 | 103.2 | |||
| Calibration eq. | Peak area = 69.7 × 104·CDMSO − 9.98 × 104 | Peak area = 2 × 106·CACN − 4 × 106 | Peak area = 2 × 107·CAcetone − 3 × 106 | |||
| Regression Coeff. (R2) | 0.997 | 0.986 | 0.991 | |||
| Determined Values | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | Acetonitrile | Acetone | DMSO | Acetonitrile | Acetone | ||||
| mg/tabl | mg/tabl | mg/tabl | % of Dose * | Dev. a | % of Dose * | Dev. | % of Dose * | Dev. | |
| Tablet #1 | 6.17 | 12.53 | 12.21 | 101.7 | 1.7 | 103.6 | 3.6 | 98.7 | 1.3 |
| Tablet #2 | 5.77 | 12.11 | 12.56 | 95.1 | 4.9 | 100.1 | 0.1 | 101.5 | 1.5 |
| Tablet #3 | 5.86 | 11.53 | 12.58 | 96.5 | 3.5 | 95.3 | 4.7 | 101.6 | 1.6 |
| Tablet #4 | 6.23 | 12.03 | 11.44 | 102.6 | 2.6 | 99.4 | 0.6 | 92.4 | 7.6 |
| Tablet #5 | 6.28 | 12.57 | 11.74 | 103.5 | 3.5 | 103.9 | 3.9 | 94.8 | 5.2 |
| Tablet #6 | 6.18 | 12.05 | 11.66 | 101.9 | 1.9 | 99.6 | 0.4 | 94.2 | 5.8 |
| Tablet #7 | 6.20 | 12.34 | 12.76 | 102.0 | 2.0 | 102.0 | 2.0 | 103.1 | 3.1 |
| Tablet #8 | 5.95 | 11.32 | 13.67 | 98.0 | 2.0 | 93.6 | 6.4 | 110.5 | 10.5 |
| Tablet #9 | 6.15 | 13.00 | 12.53 | 101.2 | 1.2 | 107.5 | 7.5 | 101.2 | 1.2 |
| Tablet #10 | 5.92 | 11.51 | 12.61 | 97.6 | 2.4 | 95.1 | 4.9 | 101.9 | 1.9 |
| Mean value () | 6.07 | 12.10 | 12.38 | 100.0 | – | 100.0 | – | 100.0 | – |
| Target dose (M) | 12.63 | 12.63 | 12.63 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Sample S.D. (s) | 0.18 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 2.93 | – | 4.42 | – | 5.25 | – |
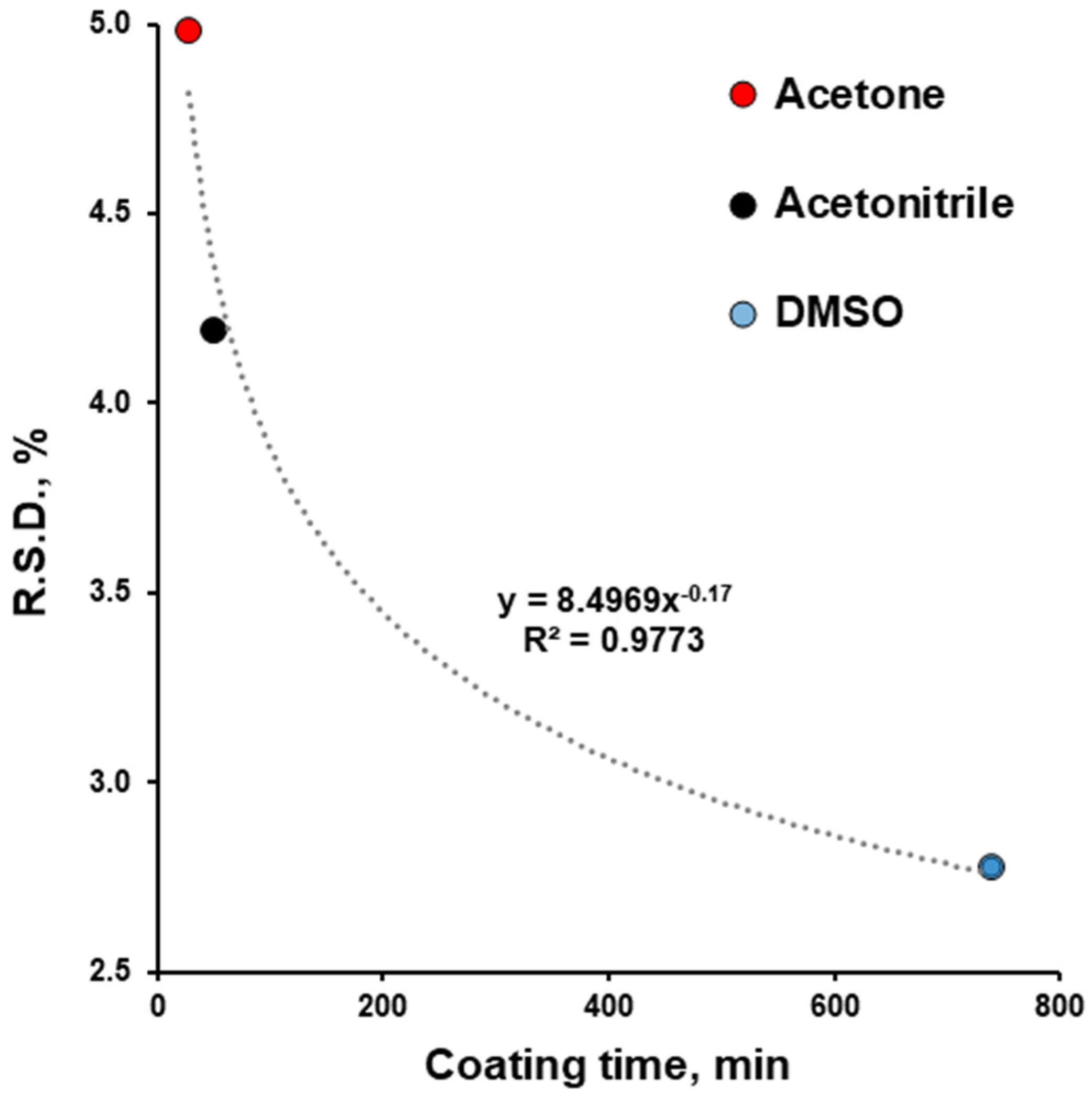
| R.S.D., % | 2.93 | 4.42 | 5.25 | 2.93 | – | 4.42 | – | 5.25 | – |
| – | – | – | 7.03 | passed | 10.60 | passed | 12.60 | passed | |
| Max allowed AV = 15% (or 1.90 mg) b | did not pass 51.9% > 15% | Passed 4.2% < 15% | passed 2.0% < 15% | 15.00 | passed | 15.00 | passed | 15.00 | passed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raciborska, L.; Buczkowska, E.M.; Kukuls, K.; Pētersone, L.; Mohylyuk, V. Active Tablet Coating with Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Ibuprofen–HPMCAS from Organic Solution. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121514
Raciborska L, Buczkowska EM, Kukuls K, Pētersone L, Mohylyuk V. Active Tablet Coating with Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Ibuprofen–HPMCAS from Organic Solution. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(12):1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121514
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaciborska, Liene, Elżbieta Maria Buczkowska, Kirils Kukuls, Līga Pētersone, and Valentyn Mohylyuk. 2025. "Active Tablet Coating with Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Ibuprofen–HPMCAS from Organic Solution" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 12: 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121514
APA StyleRaciborska, L., Buczkowska, E. M., Kukuls, K., Pētersone, L., & Mohylyuk, V. (2025). Active Tablet Coating with Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Ibuprofen–HPMCAS from Organic Solution. Pharmaceutics, 17(12), 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121514








