Impact of Different Surfactants on Oral Bioavailability of Paclitaxel/HPMC-AS Amorphous Solid Dispersion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of PTX ASDs
2.2.2. Characterization of Intermolecular Interactions
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.2.3. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
Equilibrium Solubility of Crystalline PTX
Supersaturation Maintenance Assessment
ASD Dissolution Under Non-Sink Conditions
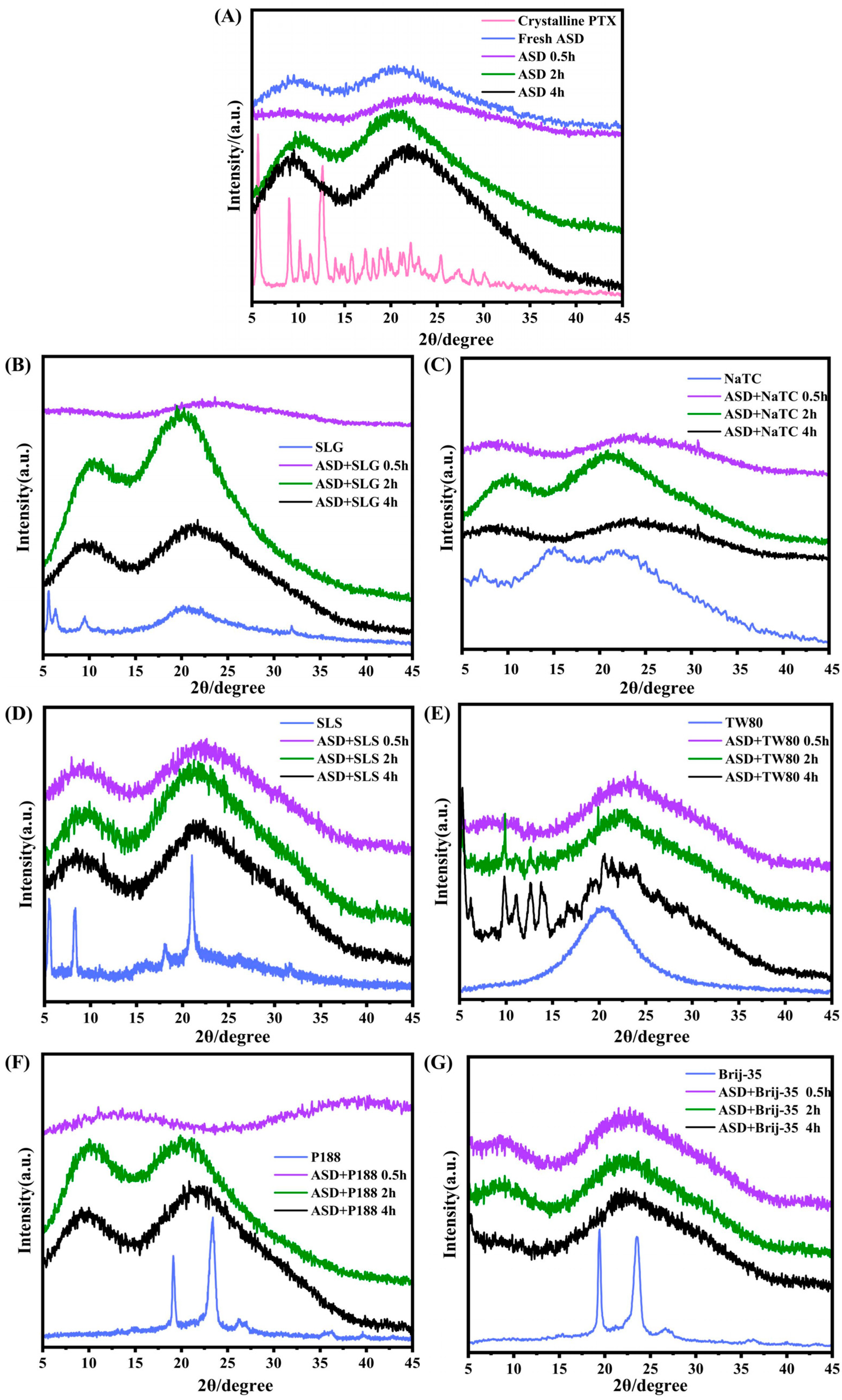
Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.2.4. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
Animals
Pharmacokinetic Protocol
2.2.5. Quantitative Determination Methods
HPLC-UV Analysis
LC-MS/MS Method
2.2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Interactions Between Drug, Polymer and Surfactant
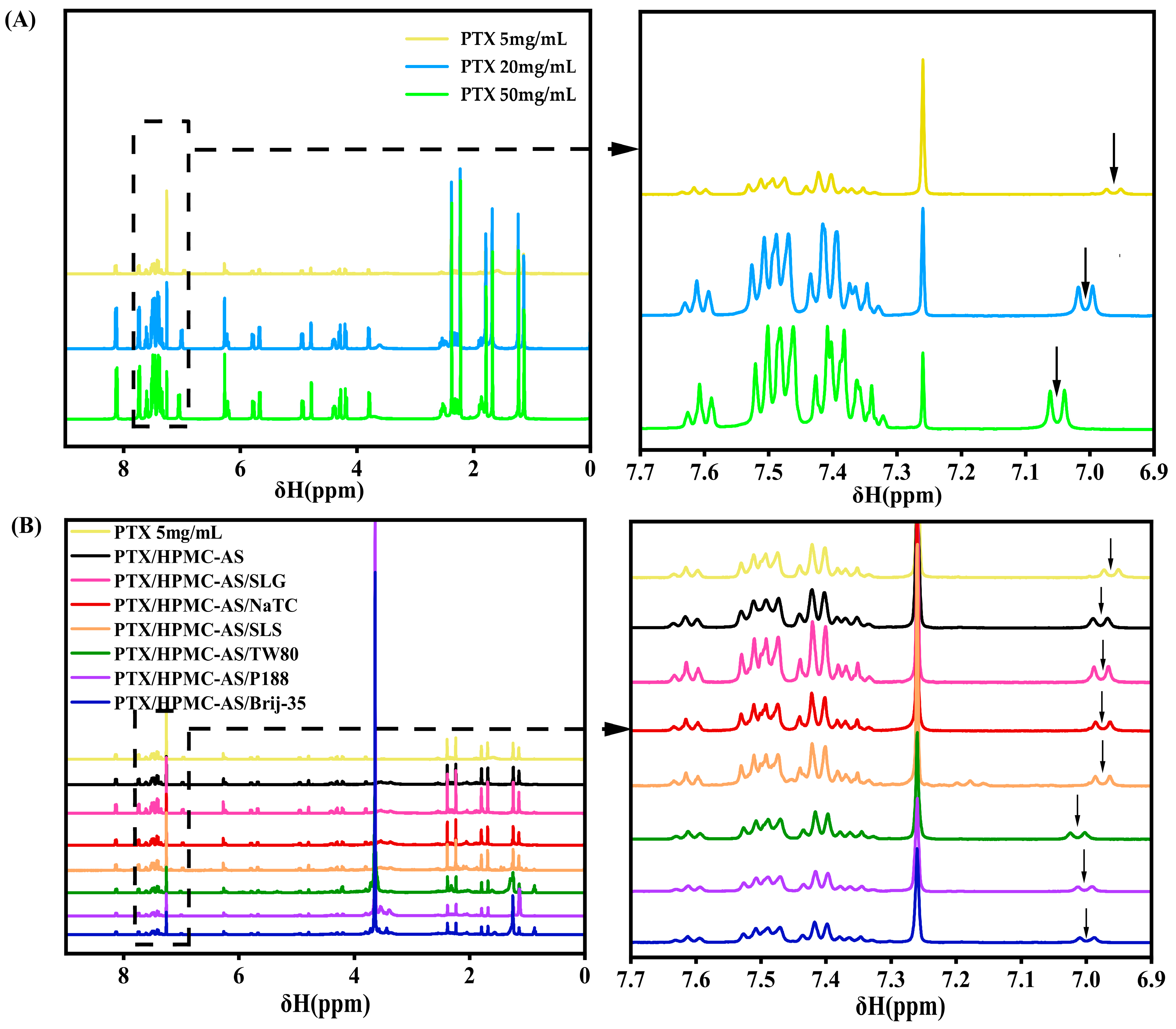
3.1.1. NMR Analysis of Intermolecular Interactions
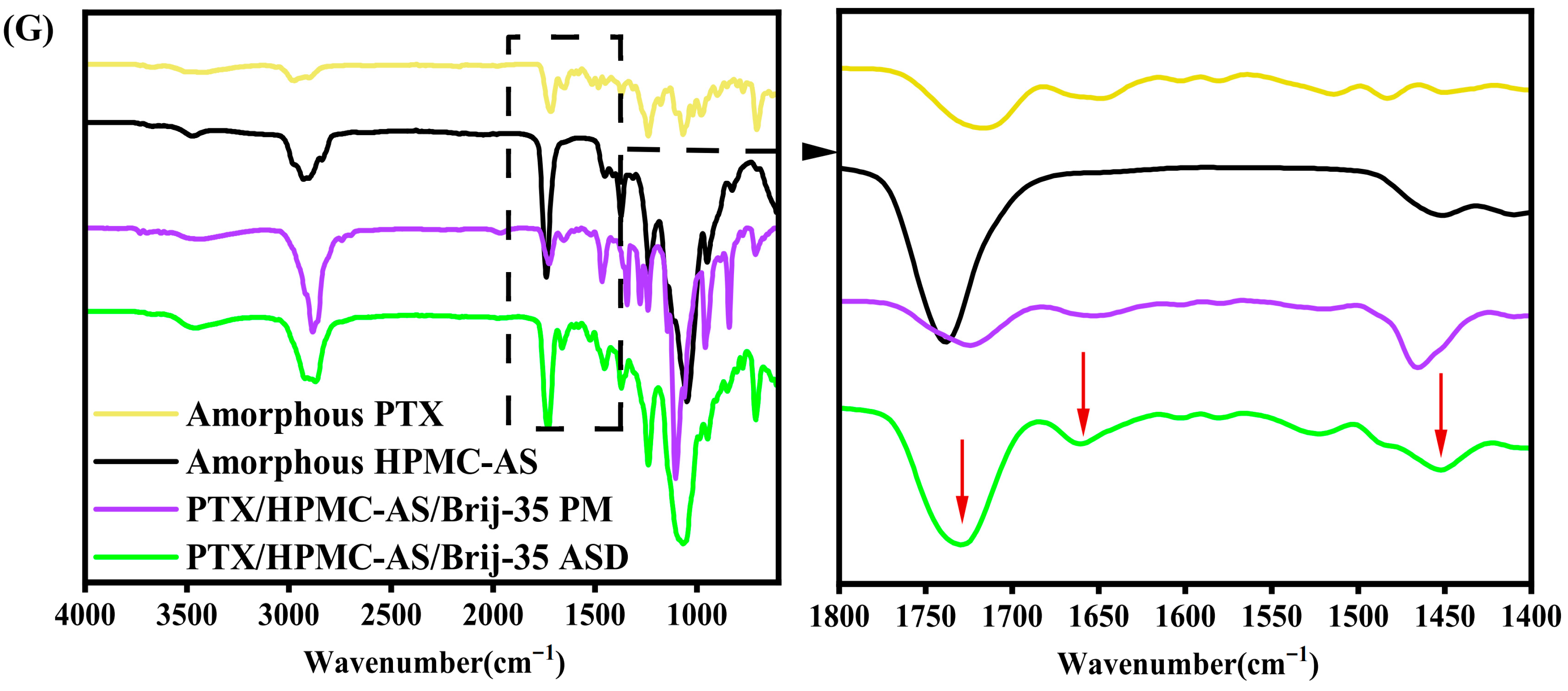
3.1.2. FT-IR Analysis of Intermolecular Interactions
3.2. In Vitro Dissolution Performance of PTX Formulations
3.2.1. Solubility of Crystalline PTX in PBS with Excipients
3.2.2. Effect of Excipients on PTX Supersaturation Maintenance
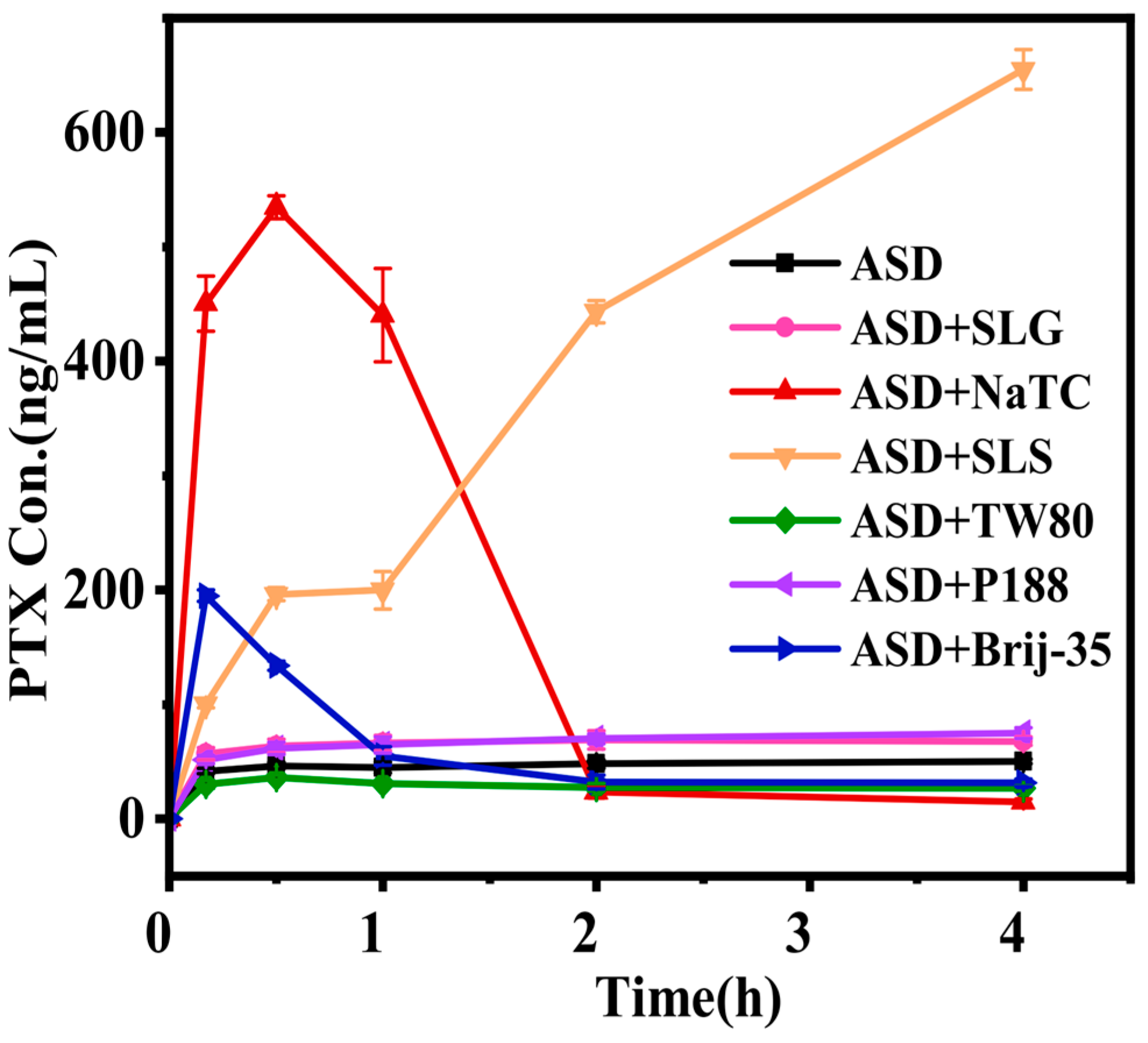
3.2.3. Dissolution Performance of PTX Formulations Under Non-Sink Conditions
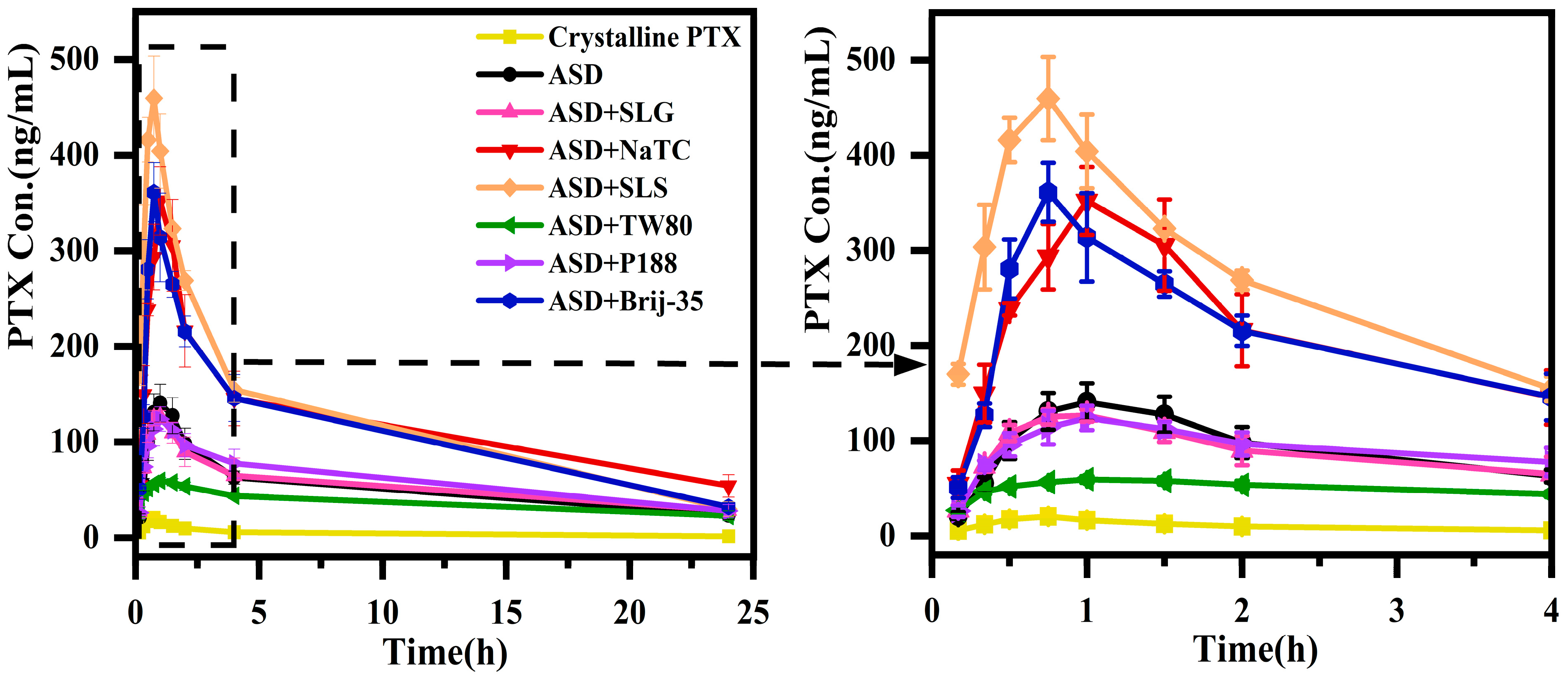
3.3. Pharmacokinetics of PTX Formulations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maurya, R.; Vikal, A.; Patel, P.; Narang, R.; Kurmi, B. Enhancing Oral Drug Absorption: Overcoming Physiological and Pharmaceutical Barriers for Improved Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Nutan, B.; Kumar, A.; Singh Chandel, A.K. Bioavailability Enhancement Techniques for Poorly Aqueous Soluble Drugs and Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujbal, S.V.; Mitra, B.; Jain, U.; Gong, Y.; Agrawal, A.; Karki, S. Pharmaceutical amorphous solid dispersion: A review of manufacturing strategies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2505–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittny, A.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Mechanisms of increased bioavailability through amorphous solid dispersions: A review. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D. Effects of Additives on the Physical Stability and Dissolution of Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiew, T.; Solomos, M.A.; Kafle, P.; Polyzois, H.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Punia, A. The importance of surface composition and wettability on the dissolution performance of high drug loading amorphous dispersion formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 114, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Purohit, H.S.; Taylor, L.S. Drug Release from Surfactant-Containing Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Mechanism and Role of Surfactant in Release Enhancement. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 2817–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.; Kuhn, R.; Hu, C.; Zhang, W.; Chiang, P.; Chen, J.Z. Impact of surfactant selection and incorporation on in situ nanoparticle formation from amorphous solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboo, S.; Bapat, P.; Moseson, D.E.; Kestur, U.S.; Taylor, L.S. Exploring the Role of Surfactants in Enhancing Drug Release from Amorphous Solid Dispersions at Higher Drug Loadings. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indulkar, A.S.; Lou, X.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Role of Surfactants on Release Performance of Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Ritonavir and Copovidone. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Liang, Y.; Pan, W.; Gou, J.; Yin, T.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Tang, X. Effect of supersaturation on the oral bioavailability of paclitaxel/polymer amorphous solid dispersion. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tres, F.; Posada, M.M.; Hall, S.D.; Mohutsky, M.A.; Taylor, L.S. Mechanistic understanding of the phase behavior of supersaturated solutions of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 543, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Han, W.; Shu, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Sui, X. Liquid–liquid phase separation drug aggregate: Merit for oral delivery of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Control. Release 2023, 353, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Peng, D.; Tian, B. Supersaturation and phase behavior during dissolution of amorphous solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Zhu, A.; Qian, F. Impact of Surfactants on Polymer Maintained Nifedipine Supersaturation in Aqueous Solution. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhalaweh, A.; Sayed, M.E.l.; Kovac, L.; Bergström, C.A.S. Impact of surfactants on solution behavior and membrane transport of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 114, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Mann, A.K.P.; Van, D.T.; Ormes, J.D.; Okoh, G.A.; Hermans, A. Drug Release and Nanodroplet Formation from Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Insight into the Roles of Drug Physicochemical Properties and Polymer Selection. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittny, A.; Philipp-Bauer, S.; Detampel, P.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Mechanistic insights into effect of surfactants on oral bioavailability of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Soto, C.E.; Gao, Y.; Indulkar, A.S.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Lynne, S.T. Role of surfactants in improving release from higher drug loading amorphous solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 625, 122120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Baak, J.P.A.; Chen, T.; Ye, H.; Liao, W.; Lv, H. Supersaturation and Precipitation Applicated in Drug Delivery Systems: Development Strategies and Evaluation Approaches. Molecules 2023, 28, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirvi, A.; Janjal, A.; Debaje, S.; Sangamwar, A.T. Influence of polymer and surfactant-based precipitation inhibitors on supersaturation-driven absorption of Ibrutinib from high-dose lipid-based formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 669, 125079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Benson, E.G.; Gui, Y.; Stelzer, T.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Yu, L. Surfactants Accelerate Crystallization of Amorphous Nifedipine by Similar Enhancement of Nucleation and Growth Independent of Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Roser, S.; Edler, K.J.; Piogliacelli, C.; Rogerson, M.; Weuts, I. Insights into the Role of Polymer-Surfactant Complexes in Drug Solubilisation/Stabilisation During Drug Release from Solid Dispersions. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Pui, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Serno, P.; Tonnis, W. Polymer mediated drug supersaturation controlled by drug-polymer interactions persisting in aqueous environment. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Müllers, W.; Serno, P.; Qian, F. Water-Resistant Drug−Polymer Interaction Contributes to the Formation of Nano-Species during the Dissolution of Felodipine Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Shan, W.; Liu, C.; Su, C.; Hageman, M. Sodium lauryl sulfate competitively interacts with HPMC-AS and consequently reduces oral bioavailability of Posaconazole/HPMC-AS amorphous solid dispersion. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, P.T.; Wakure, B.S.; Wakte, P.S. Oral Bioavailability Enhancement of Docetaxel by Preparation of Freeze-Dried Ternary Solid Dispersion Using Hydrophilic Polymer and Surfactant. J. Pharm. Innov. 2023, 18, 1669–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, E.; Cagel, M.; Lagomarsino, E.; Moretton, M.; Chiappetta, D.A. Paclitaxel: What has been done and the challenges remain ahead. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 474–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrie, L.; Ajjarapu, S.; Banda, S.; Parvathaneni, M.; Bolla, P.K.; Kommineni, N. HPMCAS-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersions in Clinic: A Review on Manufacturing Techniques (Hot Melt Extrusion and Spray Drying), Marketed Products and Patents. Materials 2023, 16, 6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Su, C.; Hageman, M.; Hussain, M. Drug-polymer-water interaction and its implication for the dissolution performance of amorphous solid dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookwala, M.; Wildfong, P.L.D. The Implications of Drug-Polymer Interactions on the Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 2963–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of Polymer Hygroscopicity on the Phase Behavior of Amorphous Solid Dispersions in the Presence of Moisture. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannachi, C.; Allen, E.; Egan, G.; Vucen, S.; Crean, A. Colyophilized Sugar–Polymer Dispersions for Enhanced Processing and Storage Stability. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y. Current and potential applications of simultaneous DSC-FTIR microspectroscopy for pharmaceutical analysis. J. Food Drug Anal. 2021, 29, 182–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cui, P.; Xing, L.; Lee, J.; Kim, D. Applications of π-π stacking interactions in the design of drug-delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, X.; Dong, S.; Chen, Y. Inhomogeneous Phase Significantly Reduces Oral Bioavailability of Felodipine/PVPVA Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, C.; Gao, Y.; Raina, S.A.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Paclitaxel Crystal Seeds with Different Intrinsic Properties and Their Impact on Dissolution of Paclitaxel-HPMCAS Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deac, A.; Qi, Q.; Indulkar, A.S.; Purohit, H.S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.G.Z. Dissolution Mechanisms of Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Role of Drug Load and Molecular Interactions. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Su, C.; Hageman, M. Initial Drug Dissolution from Amorphous Solid Dispersions Controlled by Polymer Dissolution and Drug-Polymer Interaction. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saboo, S.; Kestur, U.S.; Flaherty, D.P.; Taylor, L.S. Congruent Release of Drug and Polymer from Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Insights into the Role of Drug-Polymer Hydrogen Bonding, Surface Crystallization, and Glass Transition. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Duggirala, N.; Kumar, N.S.K.; Su, Y.; Suryanarayanan, R. Design of Ternary Amorphous Solid Dispersions for Enhanced Dissolution of Drug Combinations. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Paclitaxel Solubility (μg/mL) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | Without Surfactants | With Surfactants | SLG | NaTC | SLS | TW80 | P188 | Brij-35 |
| PBS | < 0.1 | 1mg/mL | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 3.6 ± 1.2 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.2 |
| 2mg/mL | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 3.4 | 17 ± 1.9 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | ||
| 4mg/mL | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 9.3 ± 1.7 | 15.4 ± 1.9 | 9 ± 1.4 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 1.3 | ||
| 2mg/mL HPMC-AS | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 1mg/mL | 7.9 ± 1.5 | 13.8 ± 1.0 | 20.9 ± 1.4 | 18.8 ± 1.4 | 6.9 ± 0.4 | 21.1 ± 3.1 |
| 4mg/mL HPMC-AS | 8.6 ± 1.8 | 2mg/mL | 11.2 ± 1.9 | 20.1 ± 3.6 | 73.9 ± 5.7 | 45.7 ± 8.6 | 8.2 ± 2.2 | 85.2 ± 8.2 |
| 8mg/mL HPMC-AS | 10.7 ± 1.6 | 4mg/mL | 12.0 ± 2.5 | 20.3 ± 2.0 | 177.3 ± 2.6 | 132.4 ± 27.1 | 10.6 ± 1.2 | 128.3 ± 19.5 |
| Solubility(μg/mL) |  | |||||||
| Formulation | Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax/(ng/mL) | Tmax/h | T1/2/h | AUC0-t(μg·h/L) | MRT0-t/h | |
| Crystalline PTX | 20.6 ± 2.7 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 3.7 ± 3.5 | 118.5 ± 22.7 | 5.9 ± 1.4 |
| ASD | 140.6 ± 19.9 ### | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 7.7 ± 3.8 | 1231.2 ± 118.3 ### | 7.2 ± 0.6 |
| ASD+SLG | 128.3 ± 7.6 ns | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 3.5 | 1281.3 ± 230.9 ns | 8.0 ± 0.7 |
| ASD+NaTC | 351.9 ± 35.7 *** | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 4.5 | 2849 ± 422.2 *** | 7.2 ± 0.8 |
| ASD+SLS | 459.6 ± 43.7 *** | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 3.3 ± 1.9 | 2899.8 ± 148.3 *** | 5.2 ± 0.5 |
| ASD+TW80 | 59.7 ± 2.2 *** | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 17.1 ± 4.1 | 865.8 ± 42.8 *** | 8.8 ± 0.8 |
| ASD+P188 | 124.0 ± 12.8 ns | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 11.5 ± 2.3 | 1420.4 ± 130.1 ns | 7.5 ± 1.2 |
| ASD+Brij-35 | 361.1 ± 21.6 *** | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 7.0 ± 1.9 | 2612.6 ± 261.8 *** | 5.8 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Mao, S.; Yuan, J.; Ma, X.; Xing, A.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Impact of Different Surfactants on Oral Bioavailability of Paclitaxel/HPMC-AS Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111487
Zhang C, Mao S, Yuan J, Ma X, Xing A, Liu X, Chen Y. Impact of Different Surfactants on Oral Bioavailability of Paclitaxel/HPMC-AS Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111487
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chenzhao, Siyi Mao, Jinhua Yuan, Xiuzhen Ma, Aiya Xing, Xiaoling Liu, and Yuejie Chen. 2025. "Impact of Different Surfactants on Oral Bioavailability of Paclitaxel/HPMC-AS Amorphous Solid Dispersion" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111487
APA StyleZhang, C., Mao, S., Yuan, J., Ma, X., Xing, A., Liu, X., & Chen, Y. (2025). Impact of Different Surfactants on Oral Bioavailability of Paclitaxel/HPMC-AS Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111487







