Engineered Fenretinide- and Tocilizumab-Releasing Janus Nanoparticles for Site-Directed Immunochemoprevention of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Modeling to Assess Capacity of 4HPR to Function as a Competitive Inhibitor for the ATP-Binding Sites of the PD-L1 Phosphorylating Kinases, JAK1 and CK2
2.2. Determination of the Impact of 4HPR Treatment on Janus Kinase 1 (JAK1) and Casein Kinase 2 (CK2) Functional Activity
2.3. Human Cell Lines
2.4. Evaluation of 4HPR and TCZ Treatment on the Transcriptome of Premalignant Human Lung Epithelial HBEC-KTRL53 Cells
2.5. Impact of TCZ on IL6-Mediated STAT3 Activation and Nuclear Translocation
2.6. Formulation and Characterization of the 4HPR-TCZ Human Serum Albumin-Chitosan Janus Nanoparticles
2.7. Encapsulation and Assessment of Bioactive 4HPR and TCZ Release from JNPs
2.8. Confirmation of JNP-Released TCZ Bioactivity
2.9. Impact of 4HPR and TCZ Following IL6 Challenge on PD-L1 Intracellular Localization
2.10. In Vivo Chemoprevention Studies
3. Results
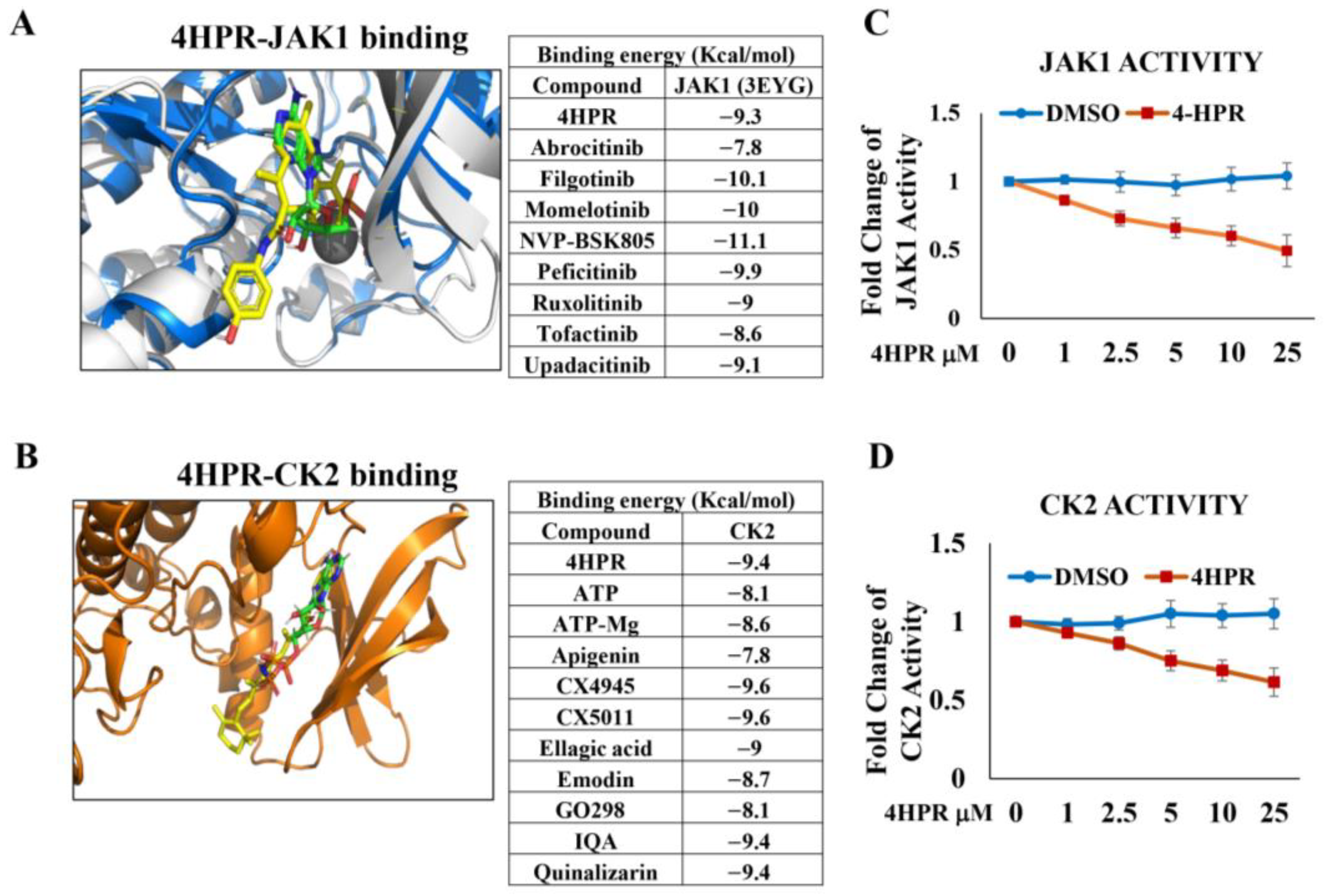
3.1. 4HPR Functions as a Competitive Inhibitor for ATP Binding at the JAK1 and CK2 Active Sites and Inhibits Function of Both Kinases in a Dose-Dependent Fashion
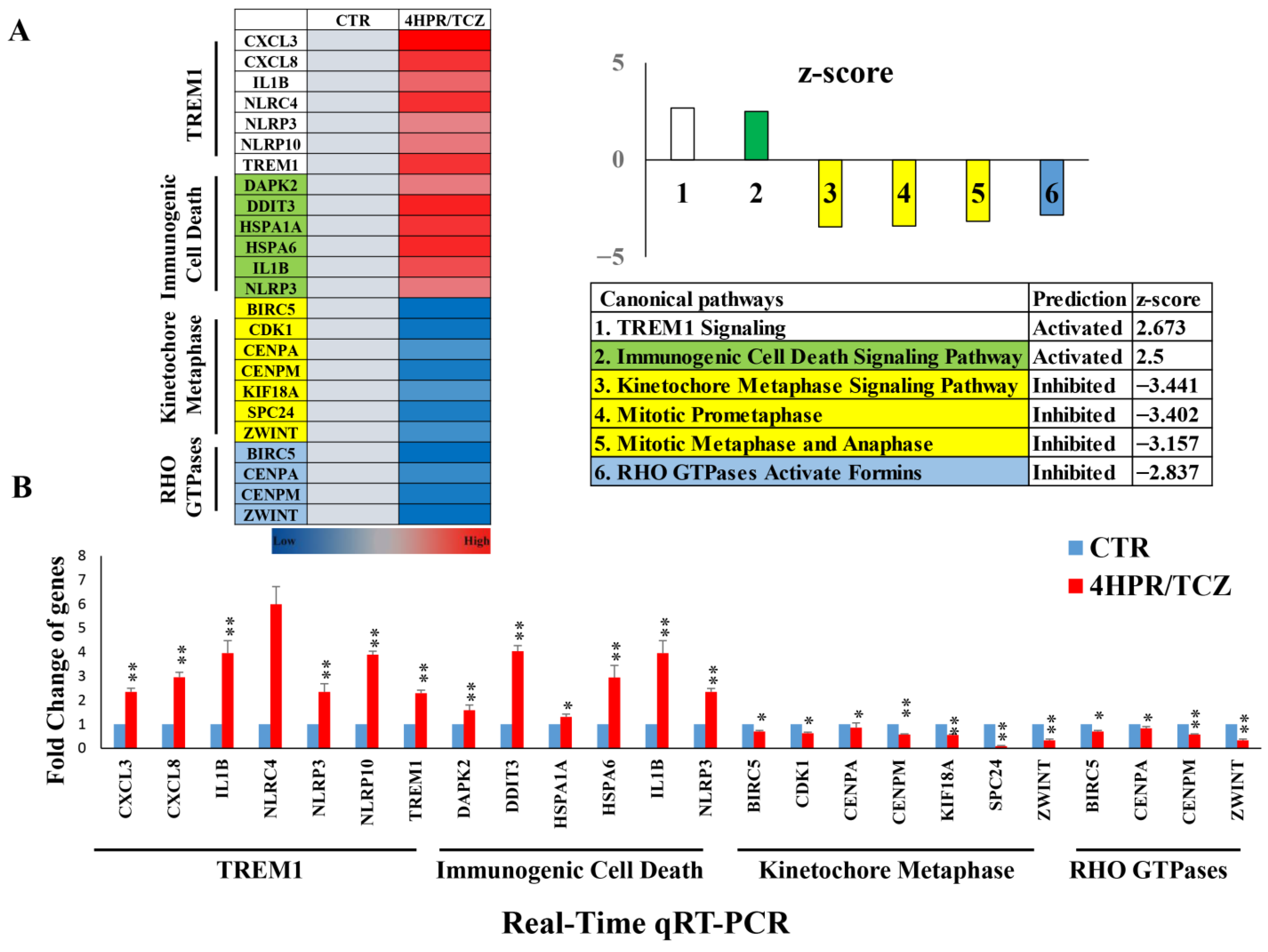
3.2. Combined Treatment with 4HPR and TCZ Reduced Expression of Pro-Proliferative Genes with Concurrent Increased Expression of Immune-Enhancing Genes in Premalignant Lung (PML) (HBEC-KTRL53) Cells
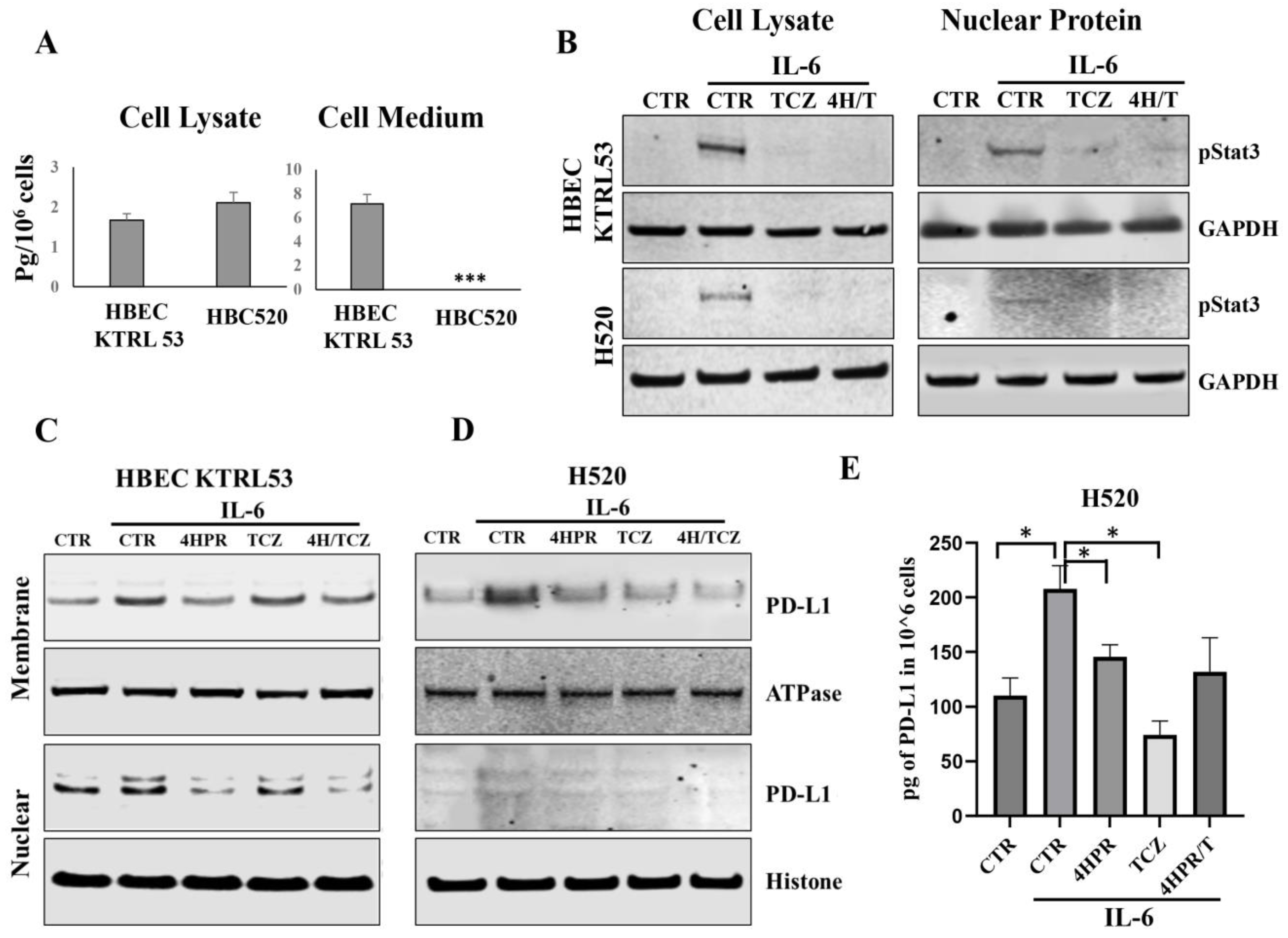
3.3. Pretreatment with 4HPR and TCZ Reduced STAT3 Signaling, Nuclear Translocation, and PD-L1 Levels and Localization in Human PML and LUSC Cells
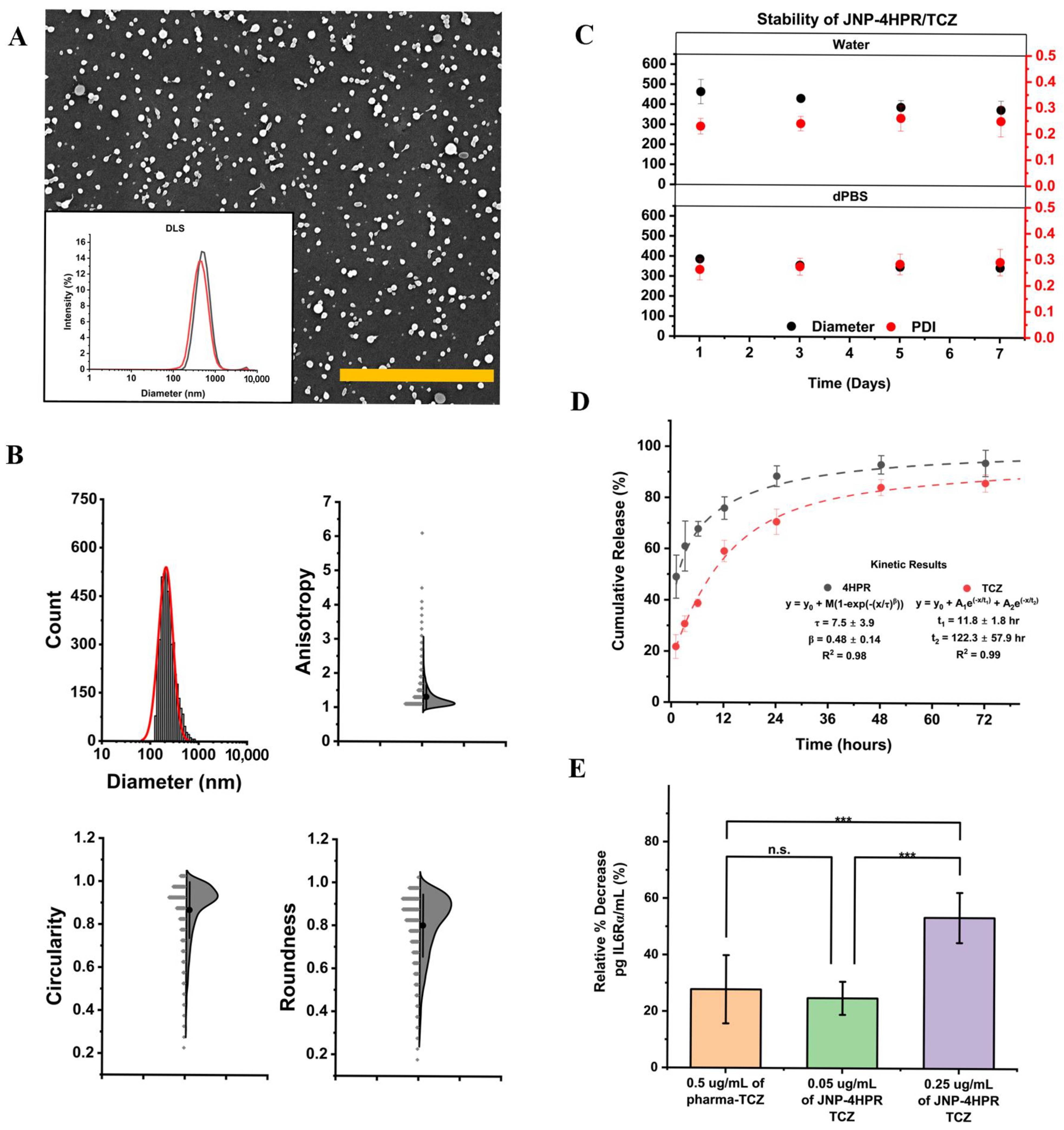
3.4. JNP-4HPR/TCZ Characterization Confirmed a Low Polydispersity Index, Excellent Nanoparticle Stability in Suspension, Controlled and Sustained Agent Release, and Retention of Bioactivity
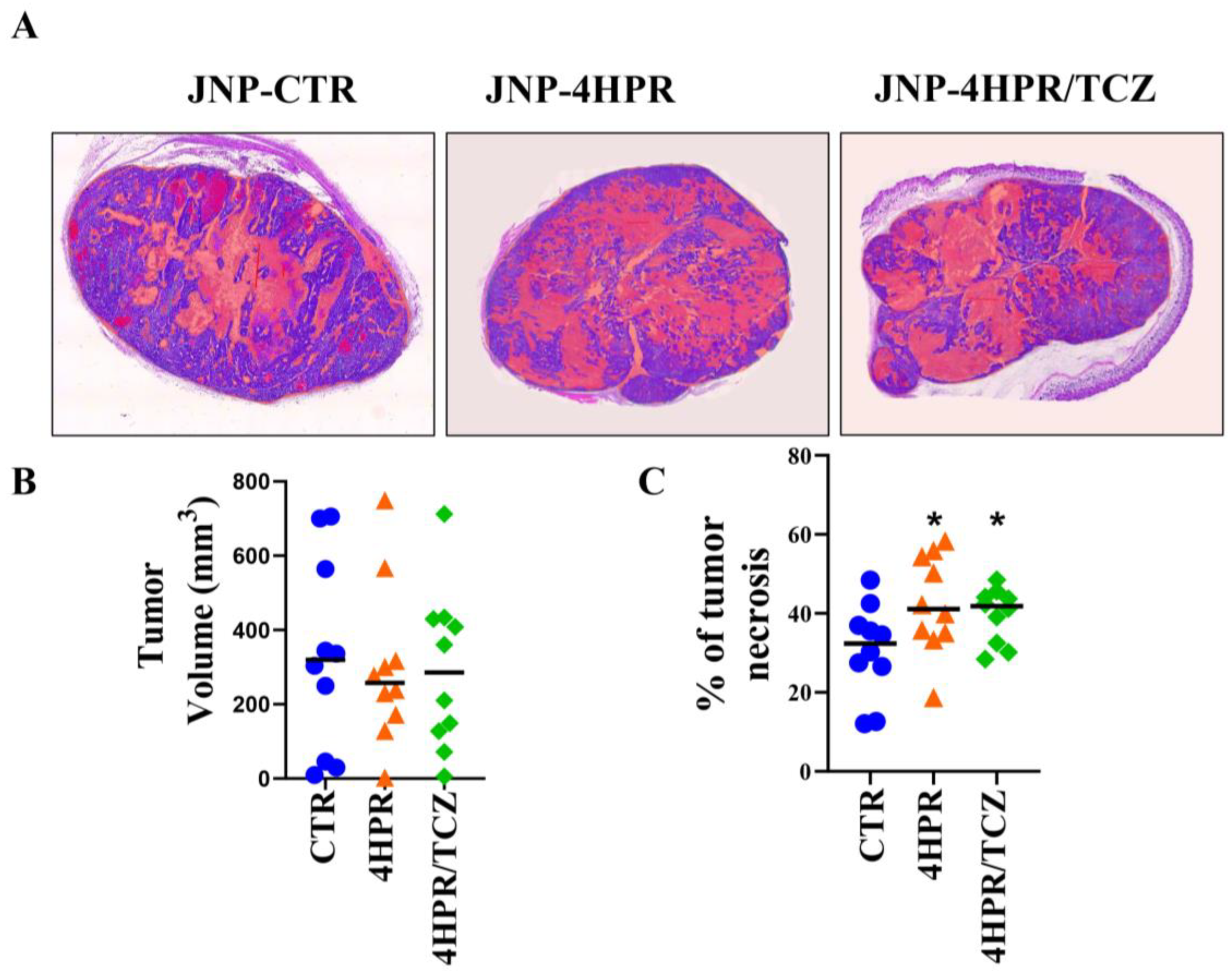
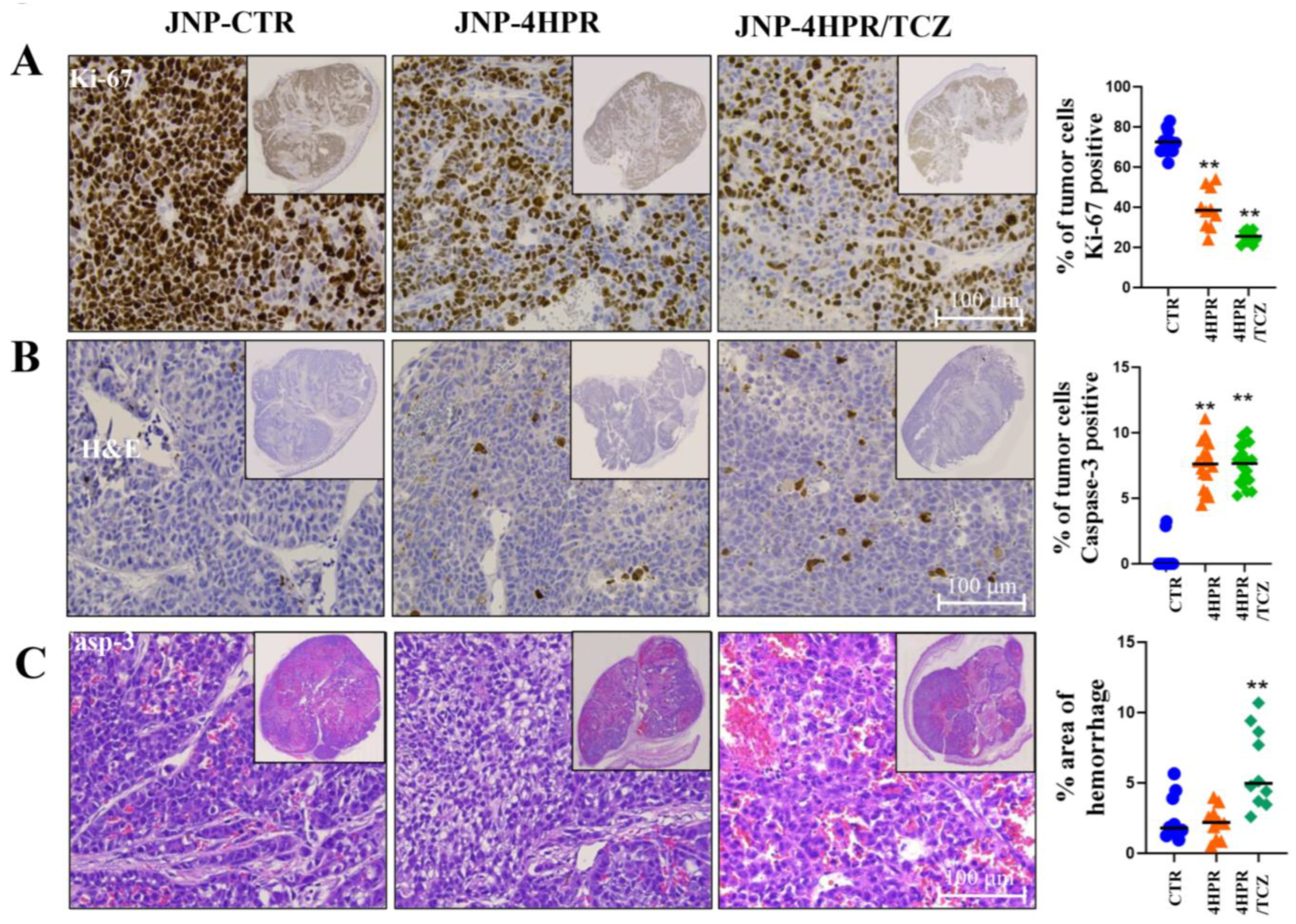
3.5. Local Delivery of TCZ-HPR JNPs Inhibited NCI-H520 LUSC Tumorigenesis In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, S.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society Cancer Facts & Figures. 2025. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2025-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Gao, J.; Karp, J.M.; Langer, R.; Joshi, N. The Future of Drug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Jung, H.; Li, X. Drug Delivery Approaches in Addressing Clinical Pharmacology-Related Issues: Opportunities and Challenges. Amer. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. (AAPS) 2015, 17, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.V.; Kadiyala, P.; Doherty, R.; Cadena, M.; Habeel, S.; Ruoslahti, E.; Lowenstein, P.R.; Castro, M.G.; Lahann, J. Systemic brain tumor delivery of synthetic protein nanoparticles for glioblastoma therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Bissonnette, C.; Pei, P.; Wang, D.; Chang, A.; Raymond, J.E.; Lahann, J.; Mallery, S.R. Mucopenetrating Janus Nanoparticles for Field Coverage Oral Cancer Chemoprevention. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Mauser, A.; Ko, Y.; Lahann, J. Protein Nanoparticles: Uniting the Power of Proteins with Engineering Design Approaches. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Christau, S.; Ochyl, L.J.; Fan, Z.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Kuehnhammer, M.; Zhang, M.; Helgeson, M.; von Klitzing, R.; Moon, J.J.; et al. Engineered Ovalbumin Nanoparticles for Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Ther. 2020, 10, 2000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.C.M.; Pan, Y.; Velcheti, V.; Wong, K.K. Squamous cell lung cancer: Current landscape and future therapeutic options. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denisov, E.V.; Schegoleva, A.A.; Gervas, P.A.; Ponomaryova, A.A.; Tashireva, L.A.; Boyarko, V.V.; Bukreeva, E.B.; Pankova, O.V.; Perelmuter, V.M.; Schegolevaa, A.A.; et al. Premalignant lesions of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: The molecular make-up and factors affecting their progression. Lung Cancer 2019, 135, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdara, A.F.; Brambilla, E. Preneoplasia of lung cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2010, 9, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, A.; Bhatt, A.N. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumor. Biol. 2016, 37, 11553–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.D.; Cheng, M.; Shang, P.P.; Yang, Y.Q. Role of IL-6 in dendritic cell functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 111, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Fujieda, K.; Senju, S.; Ikeda, T.; Oshiumi, H.; Nishimura, Y. Immune-suppressive effects of interleukin-6 on T-cell mediated anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.C.; Li, C.W.; Xia, W.; Hsu, J.M.; Lee, H.H.; Cha, J.H.; Wang, H.L.; Yang, W.H.; Yen, E.Y.; Chang, W.C.; et al. IL-6/JAK1 pathway drives PD-L1 Y112 phosphorylation to promote cancer immune evasion. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3324–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, D.T. Sequencing the Events That Mediate Progression of Premalignant Lung Lesions. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4811–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysan, K.; Tran, M.L.; Dubinett, S.M. Immunosurveillance and regression in the context of squamous pulmonary premalignancy. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1442–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallery, S.R.; Wang, D.; Santiago, B.; Pei, P.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Nieto, K.; Spinney, R.; Tong, M.; Koutras, G.; Han, B.; et al. Benefits of Multifaceted Chemopreventives in the Suppression of the Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) Tumorigenic Phenotype. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, C.; Moon, C.; Wang, L.; Hittelman, W.N.; Jang, S.J.; Sun, S.; Lee, J.J.; Liu, D.; Kurie, J.M.; Morice, R.C.; et al. Effects of N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)retinamide on hTERT Expression in the Bronchial Epithelium of Cigarette Smokers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Pei, P.; Shea, F.; Spinney, R.; Chang, A.; Lahann, J.; Mallery, S.R. Growth modulatory effects of fenretinide encompass keratinocyte terminal differentiation: A favorable outcome for oral squamous cell carcinoma chemoprevention. Carcinogenesis 2024, 45, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Pei, P.; Shea, F.F.; Bissonnette, C.; Nieto, K.; Din, C.; Liu, Y.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Lin, Y.X.; Spinney, R.; et al. Fenretinide combines perturbation of signaling kinases, cell–extracellular matrix interactions and matrix metalloproteinase activation to inhibit invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Protein Data Bank. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/ (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2022.02 Chemical Computing Group ULC, 910-1010 Sherbrooke St. W., Montreal, QC H3A 2R7. 2024. Available online: https://www.chemcomp.com/en/Products.htm (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Krieger, E.; Koraimann, G.; Vriend, G. Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA-A self-parameterizing force field. Proteins 2002, 47, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Molnar, L.F.; Jung, Y.; Kussmann, J.; Ochsenfeld, C.; Brown, S.T.; Gilbert, A.T.; Slipchenko, L.V.; Levchenko, S.V.; O’Neill, D.P.; et al. Advances in methods and algorithms in a modern quantum chemistry program package. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 3172–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. Comp. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PyMOL. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 2.5.2; Schrödinger, LLC: Singapore, 2019.
- Sun, H.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Jia, J.; Guo, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, T.; et al. Discovery and Design of Tricyclic Scaffolds as Protein Kinase CK2 (CK2) Inhibitors through a Combination of Shape-Based Virtual Screening and Structure-Based Molecular Modification. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.selleckchem.com/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Mulshine, J.L.; Ujhazy, P.; Antman, M.; Burgess, C.M.; Kuzmin, I.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Johnson, B.E.; Roth, J.A.; Pass, H.I.; Ross, S.M.; et al. From clinical specimens to human cancer preclinical models-A journey the NCI-cell line database-25 years later. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 121, 3986–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Mae, B.; Pei, P.; Shea, F.; Wang, D.; Raymond, J.; Mallery, S.R.; Lahann, J. Electrohydrodynamic Jetting of Mucoadhesive Protein Nanoparticles as a Chemopreventive Strategy for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Macromol. Biosci. 2025, 25, e00661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Mauser, A.; Raymond, J.E.; Lahann, J. Systematic studies into uniform synthetic protein nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euhus, D.M.; Hudd, C.; LaRegina, M.C.; Johnson, F.E. Tumor measurement in the nude mouse. J. Surg. Oncol. 1986, 31, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, R.B.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases: Regulation and roles in cancer cell biology. Small GTPases 2016, 7, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroemer, G.; Galassi, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Galluzzi, L. Immunogenic cell stress and death. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L. Immunogenic Cell Death in Cancer Therapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajith, A.; Mamouni, K.; Horuzsko, D.D.; Musa, A.; Dzutsev, A.K.; Fang, J.R.; Chadli, A.; Zhu, X.; Lebedyeva, I.; Trinchieri, G.; et al. Targeting TREM1 augments antitumor T cell immunity by inhibiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells and restraining anti–PD-1 resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, 6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juric, V.; Mayes, E.; Binnewies, M.; Lee, T.; Canaday, P.; Pollack, J.L.; Rudolph, J.; Du, X.; Liu, V.M.; Dash, S.; et al. TREM1 activation of myeloid cells promotes antitumor immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadd9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Cao, Z.; Lu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Sethi, G.; You, Y. Interleukin-6 (IL-6)-associated tumor microenvironment remodelling and cancer immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025, 85, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Sommer, J.; Monhasery, N.; Schwanbeck, R.; Keil, E.; Finkenstädt, D.; Pfeffer, K.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J.; Garbers, C. Inhibition of protein kinase II (CK2) prevents induced signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1/3 and constitutive STAT3 activation. Oncotarget 2014, 30, 2131–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.; Chu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Hsu, J.M.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, C.; Hsu, J.L.; Chang, W.C.; Yang, R.; et al. Phosphorylation and Stabilization of PD-L1 by CK2 Suppresses Dendritic Cell Function. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Abbaszadeh, M.; Fouladseresht, H.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Eskandari, N. PD-L1 importance in malignancies comprehensive insights into the role of PD-L1 in malignancies: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 25, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arter, C.; Trask, L.; Ward, S.; Yeoh, S.; Bayliss, R. Structural features of the protein kinase domain and targeted binding by small-molecule inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.Y.; Wilder, E.T.; Chipuk, J.E.; Lane, M.A. Retinol decreases phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in colon cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2008, 47, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; King, F.J.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Canedy, C.J.; Hayashi, J.; Zhong, Y.; Chang, M.W.; Pache, L.; Wong, J.L.; et al. Drug target prediction through deep learning functional representation of gene signatures. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucikova, J.; Kepp, O.; Kasikova, L.; Petroni, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Spisek, R.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hail, N.; Chen, P.; Wempe, M.F. The hydroxyl functional group of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide mediates cellular uptake and cytotoxicity in premalignant and malignant human epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, G.S. Hall of Fame among Pro-inflammatoryinters cytokines: Interleukin-6 Gene and Its Transcriptional Regulation Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Smith, M.A.; Doshi, P.; Sasser, K.; Fulp, W.; Altiok, S.; Haura, E.B. Antitumor Efficacy of the Anti-Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Antibody Siltuximab in Mouse Xenograft Models of Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardalan, A.A.; Khalili-Tanha, G.; Shoari, A. Shaping the Landscape of Lung Cancer: The Role and Therapeutic Potential of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 4, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hinsbergh, V.W.; Koolwijk, P. Endothelial sprouting and angiogenesis: Matrix metalloproteinases in the lead. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 78, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, G.; Brindle, S.D.; Greengard, P. The route of absorption of intraperitoneally administered compounds. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1971, 178, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgovanovic, D.; Song, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Roles of IFN-γ in tumor progression and regression: A review. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Jin, J.; Lou, J.; Qian, C.; Lin, J.; Xu, A.; Liu, B.; Zhang, M.; Tao, H.; Yu, W. The nuclear transportation of PD-L1 and the function in tumor immunity and progression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Chang, A.; Shea, F.; He, Y.; Spinney, R.; Whitsett, J.D.; Lahann, J.; Mallery, S.R. Engineered Fenretinide- and Tocilizumab-Releasing Janus Nanoparticles for Site-Directed Immunochemoprevention of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111471
Wang D, Chang A, Shea F, He Y, Spinney R, Whitsett JD, Lahann J, Mallery SR. Engineered Fenretinide- and Tocilizumab-Releasing Janus Nanoparticles for Site-Directed Immunochemoprevention of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111471
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Daren, Albert Chang, Fortune Shea, Yifei He, Richard Spinney, Jonathan D. Whitsett, Joerg Lahann, and Susan R. Mallery. 2025. "Engineered Fenretinide- and Tocilizumab-Releasing Janus Nanoparticles for Site-Directed Immunochemoprevention of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111471
APA StyleWang, D., Chang, A., Shea, F., He, Y., Spinney, R., Whitsett, J. D., Lahann, J., & Mallery, S. R. (2025). Engineered Fenretinide- and Tocilizumab-Releasing Janus Nanoparticles for Site-Directed Immunochemoprevention of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111471






