Therapeutic Potential of Big-Belly Seahorse Derived Peptide in Blood Pressure Regulation and Protection Against Aortic, Renal, and Cardiac Injuries on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Peptide Synthesis
2.3. Animal Care and Experimental Treatment
2.4. Measurement of SBP, DBP, MAP
2.5. Blood Biochemical Assay for Serum ACE, Ang Ⅱ, ACE2
2.6. Histology and H&E Staining
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Pressure Regulatory Effect of Long-Term IGTGIPGIW Administration in SHR
3.2. Effect of IGTGIPGIW on Serum ANG and ACE Levels in SHR
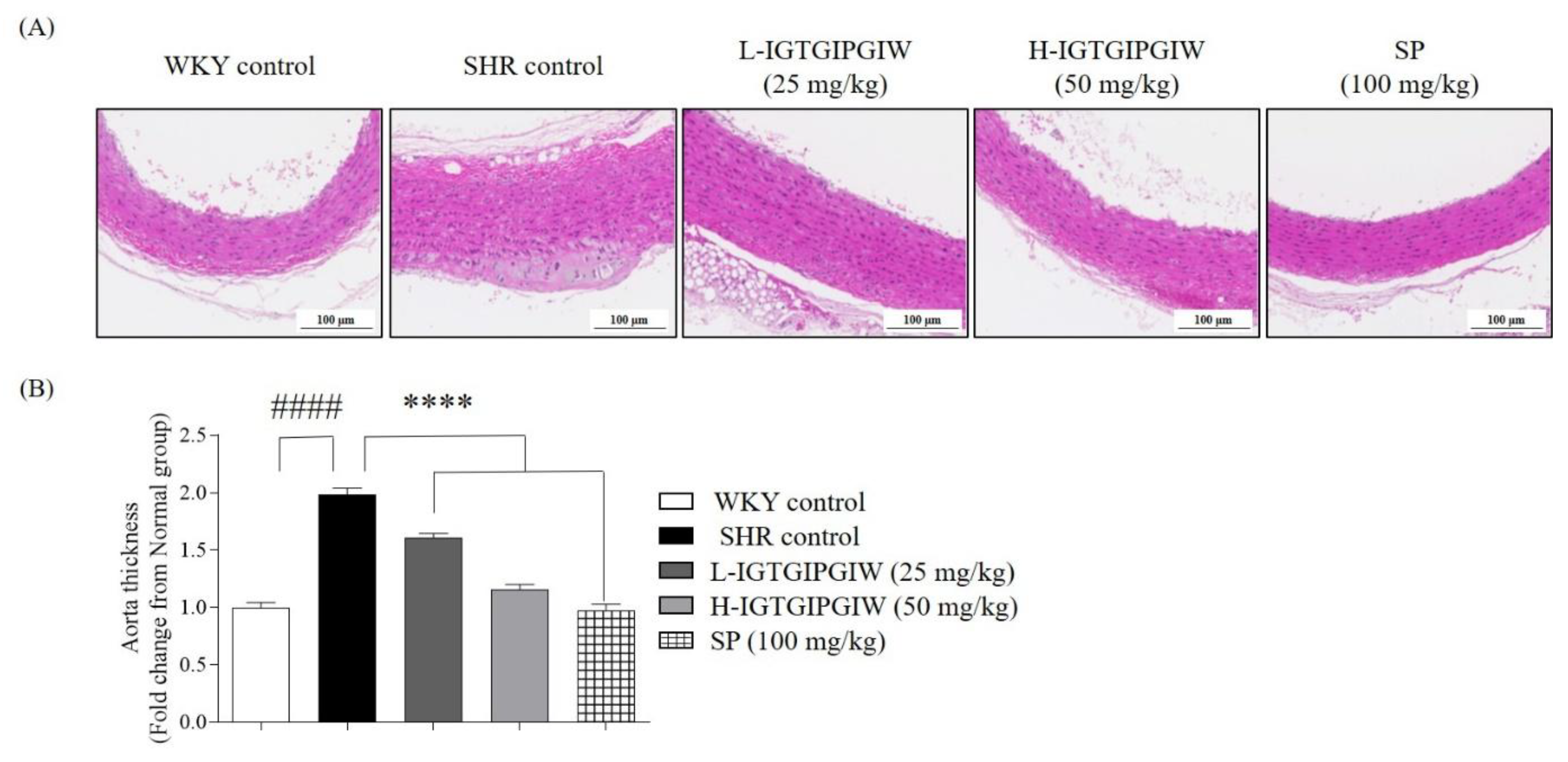
3.3. Protective Effect of IGTGIPGIW on Hypertension-Induced Aortic Wall Damage in SHR
3.4. Protective Effect of IGTGIPGIW on Hypertension-Induced Kidney Damage in SHR
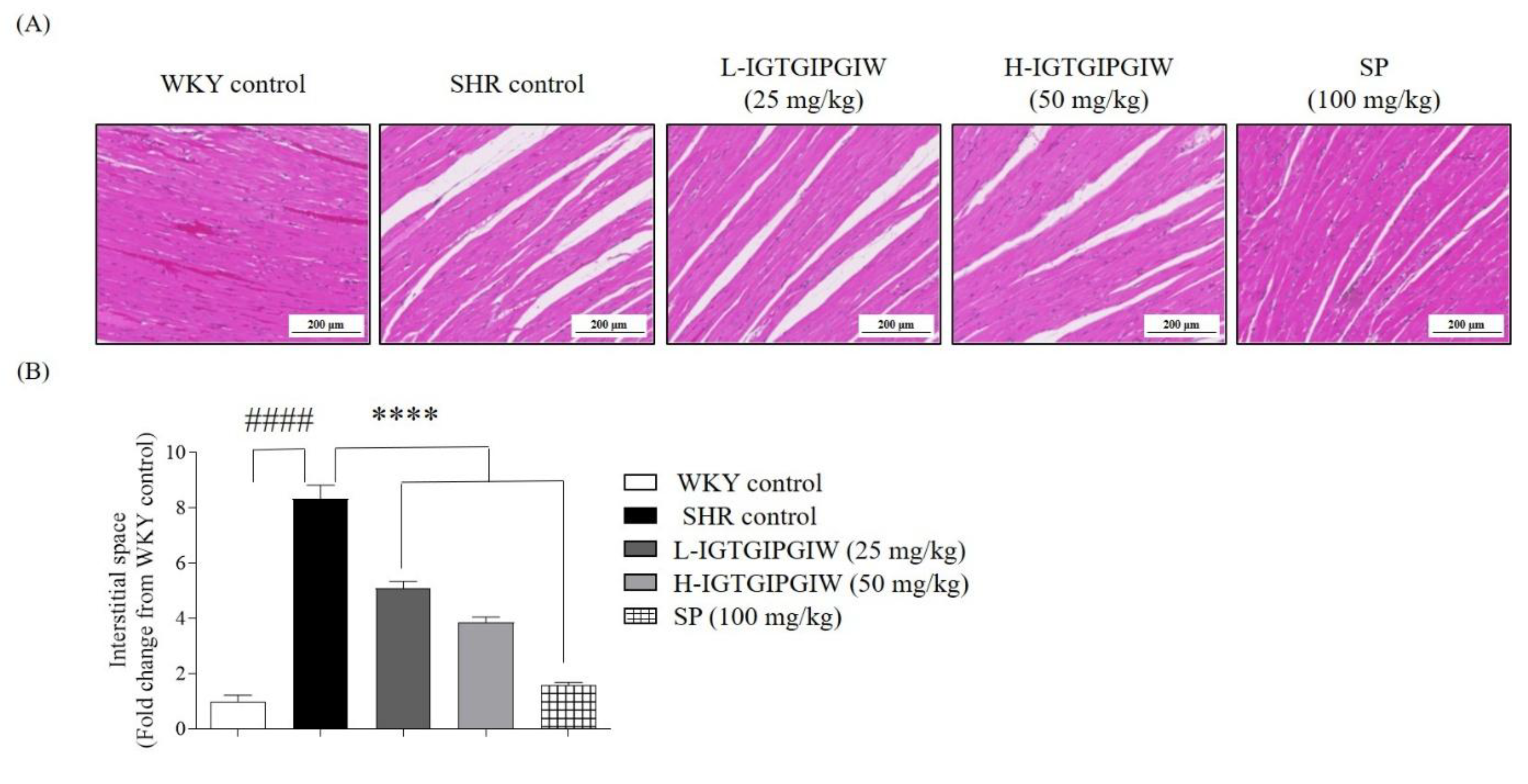
3.5. Protective Effect of IGTGIPGIW on Hypertension-Induced Heart Damage in SHR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carey, R.M.; Whelton, P.K.; 2017 ACC/AHA Hypertension Guideline Writing Committee. Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Synopsis of the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Hypertension Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2025, 168, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, E.; Pereira, C.; Ximenes, L.; Pires, C.M. Analysis of Secondary Data Utilization for Hypertension Prevention in Maubara Community Health Centre, Liquiça Municipality. Int. J. Sci. Multidiscip. Res. 2025, 3, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Joseph, P.; Rangarajan, S.; Islam, S.; Mente, A.; Hystad, P.; Brauer, M.; Kutty, V.R.; Rahman, O.; Zatonska, K.; et al. Modifiable Risk Factors, Cardiovascular Disease, and Mortality and Low-Income Countries (PURE): A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, S.I.; Aarsland, D.; Day, S.; Sønnesyn, H. Hypertension Is a Potential Risk Factor for Vascular Dementia: Systematic Review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debora, C.; Tolimba, C.; Palunggi, S.; Siregar, D.; Harefa, L. Risk Factors for Hypertension Among Adults Living in A Rural Area, Minahasa. J. Keperawatan Indones. 2023, 26, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Ying, S.; Yin, W.; Wei, C.; Fei, M. New Flavonoid-Based Compound Synthesis Strategy for Antihypertensive Drug Development. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.M. Effect of Combined Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Therapies on Cognitive Function: A New Treatment Strategy? Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.H.; Loffing, J. Thiazide Effects and Adverse Effects Insights from Molecular Genetics. Hypertension 2009, 6, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Nayak, A.K. Bioactive Natural Products for Pharmaceutical Applications; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; ISBN 9783030540265. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Andrade, P.B.; Nicosia, A.; Cuttitta, A.; Rotter, A.; Rotter, A.; Bacu, A.; Barbier, M.; Bertoni, F.; Bones, A.M.; et al. A New Network for the Advancement of Marine Biotechnology in Europe and Beyond. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 278, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, H.; Czajkowska, K.; Cichowska, J.; Lenart, A. Trends in Food Science & Technology What’ s New in Biopotential of Fruit and Vegetable by-Products Applied in the Food Processing Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajaria, T.K.; Suthar, P.; Baghel, R.S.; Balar, N.B.; Sharnagat, P.; Mantri, V.A.; Reddy, C.R.K. Bioresource Technology Integration of Protein Extraction with a Stream of Byproducts from Marine macroalgae: A Model Forms the Basis for Marine Bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, M.Z.; Rodr, D.; Javier, F.; Rubilar, O.; Alvear, M.; Encina-montoya, F.; Vidal, G. Composting as an Alternative for the Treatment of Solid Waste from the Kraft Pulp Industry. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayilara, M.S.; Olanrewaju, O.S.; Babalola, O.O. Waste Management through Composting: Challenges and Potentials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, A.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. By-Products of Plant Food Processing as a Source of Functional Compounds—Recent Developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 12, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Seafood Processing By-Products; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781461495895. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Wijesekara, I. Development and Biological Activities of Marine-Derived Bioactive Peptides: A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczek, K.; Tkaczewska, J.; Migdał, W. Antioxidant and Antihypertensive Protein Hydrolysates in Fish Products—A Review. Czech J. Food Sci. 2018, 36, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.C.; Harnedy, P.A.; Kee, M.B.O.; Alashi, M.A.; Aluko, R.E.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Peptide Identification in a Salmon Gelatin Hydrolysate with Antihypertensive, Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activities. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yathisha, U.G.; Bhat, I.; Karunasagar, I.; Mamatha, B.S. Antihypertensive Activity of Fish Protein Hydrolysates and Its Peptides. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walquist, M.J.; Eilertsen, K.-E.; Elvevoll, E.O.; Jensen, I.-J. Marine-Derived Peptides with Anti-Hypertensive Properties: Prospects for Pharmaceuticals, Supplements, and Functional Food. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Shi, Q. High Throughput Identification of Antihypertensive Peptides from Fish Proteome Datasets. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; San, S. Efficacy of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptide from Sargassum maclurei in Hypertension and Reduction of Intracellular Endothelin-1. Nutrients 2020, 12, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Mohan, A. Mechanisms of Food Protein-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides Other than ACE Inhibition. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 8, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, J.E.; Woo, S.Y.; Jin, H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Ham, H.; Chung, I.M. Evaluation of Antihypertensive Polyphenols of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Seedlings via Their Effects on Angiotensin—Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibition. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.N.; Dagogo-jack, S. Comorbidities of Diabetes and Hypertension: Mechanisms and Approach to Target Organ Protection. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolla, M.J.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Chan, S. The Importance of Comorbidities in Ischemic Stroke: Impact of Hypertension on the Cerebral Circulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metaboloism 2018, 38, 2129–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Deswal, A.; Dunbar, S.B.; Francis, G.S.; Horwich, T.; Jessup, M.; Kosiborod, M.; Pritchett, A.M.; Ramasubbu, K.; et al. Contributory Risk and Management of Comorbidities of Hypertension, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperlipidemia, and Metabolic Syndrome in Chronic Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e535–e578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.G.; Kim, H.S.; An, H.; Baek, K.; Lee, J.M.; Yim, M.J.; Ko, S.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, G.W.; Je, J.G.; et al. Antihypertensive Effects of IGTGIPGIW Peptide Purified from Hippocampus Abdominalis: P-ENOS and p-AKT Stimulation in EA.Hy926 Cells and Lowering of Blood Pressure in SHR Model. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, H.; Lin, Q.; Lu, J.; Gao, Y.; Shen, L.; Cai, J.; Luo, J. Effects of Food, The Effect of Temperature on Gonad, Embryonic Development and Survival Rate of Juvenile Seahorses, Hippocampus Kuda Bleeker. Aquaculture 2019, 254, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldewey, H.J.; Martin-smith, K.M. Review Article A Global Review of Seahorse Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, K.; Ho, J.; You, K.; Jeon, J.; Rho, S. Effects of Sea Horse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-Derived Protein Hydrolysate on Skeletal Muscle Development. Food Sci. 2017, 60, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, K.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H. Bigbelly Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-Derived Peptides Enhance Skeletal Muscle Differentiation and Endurance Performance via Activated P38MAPK/AKT Signalling Pathway: An In Vitro and In Vivo Analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Nagahawatta, D.P.; Yang, F.; Jayawardhana, H.H.A.C.K.; Liyanage, N.M.; Lee, D.; Min, J.; Yim, M.; Ko, S.; Kim, J.; et al. Antioxidant Potential of Hydrolysate-Derived Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) Peptide: Protective Effects against AAPH-Induced Oxidative Damage In Vitro and In Vivo. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo, H.; Jun, K.; Je, G.; Ryu, B.; Kang, N.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Young, J.; Tae, O.; et al. Antioxidant and Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Hippocampus Abdominalis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 1, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Oh, J.; An, Y.; Wang, L.; Rho, S.; Jeon, Y. Low-Molecular Weight Peptides Isolated from Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) Improve Vasodilation via Inhibition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme In Vivo and In Vitro. Process Biochem. 2020, 95, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kim, S.; Rho, S.; Ko, J.; Jeon, Y. Anti-Fatigue Activity of a Mixture of Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) Hydrolysate and Red Ginseng. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Q.; Xue, B.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Ou, S.; Peng, X. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activities and In Vivo Antihypertensive Effects of Sardine Protein Hydrolysate. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, 2831–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-yahia, D.; Madani, S.; Savelli, J.; Prost, J.; Bouchenak, M.; Belleville, J. Dietary Fish Protein Lowers Blood Pressure and Alters Tissue Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Composition in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients 2003, 19, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Sheikh, A.R.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Sun, N.; Su, X. Understanding the Mechanism for the Structure–Activity Relationship of Food-Derived ACEI Peptides. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1751–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Ou, S.; Zhang, L.; Peng, X. Combinative Effect of Sardine Peptides and Quercetin Alleviates Hypertension Through Inhibition of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Activity and Inflammation. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100 Pt 1, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-G.; Nagahawatta, D.P.; Liyanage, N.M.; Choe, Y.R.; Oh, J.-Y.; Jung, W.-K.; Park, S.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-S. Potential Blood Pressure Regulatory Effect of Low Molecular Weight α-Chymotrypsin Extract and Its Peptides from Stichopus japonicus: Peptide–ACE Interaction Study via In Silico Molecular Docking. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 123, 106551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Prada, J.A.; Ferreira, A.J.; Katovich, M.J.; Shenoy, V.; Qi, Y.; Santos, R.A.S.; Castellano, R.K.; Lampkins, A.J.; Gubala, V.; Ostrov, D.A.; et al. Structure-Based Identification of Small-Molecule Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Activators as Novel Antihypertensive Agents. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeffe, M.O.; Oterhals, Å.; Anja, L.; Vikøren, S.; Drotningsvik, A.; Mellgren, G.; Halstensen, A.; Gudbrandsen, O.A. Dietary Fish Intake Increased the Concentration of Soluble ACE2 in Rats: Can Fish Consumption Reduce the Risk of COVID-19 Infection through Interception of SARS-CoV-2 by Soluble ACE2? Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 130, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Oh, J.; Chung, D.; Seo, M.; Park, S.; Jeon, Y.; Ryu, B. Utility of a Hydrolysate from Overproduced Paralichthys Olivaceus for Hypertension Treatment: Correlation Between Physical Properties and Potent Anti-Hypertensive Activities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Je, J.-G.; Sim, J.; Lee, H.-G.; Kim, C.-Y.; Roh, Y.; Choe, Y.R.; Park, S.-H.; Heo, S.-J.; Jung, W.-K.; Jeon, Y.-J.; et al. Investigation of the Regulatory Effect of α-Chymotrypsin-Assisted Hydrolysate from Sebastes schlegelii on Blood Pressure through In Vitro, In Silico ACE Inhibitory Activity, and In Vivo Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Model. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 121, 106431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Zou, S.; Yu, J.; Wei, Y. Positive Effect of a Pea—Clam Two-Peptide Composite on Hypertension and Organ Protection in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Oh, S.; Choi, J.; Jang, J.T.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Attenuating Effects of Dieckol on Hypertensive Nephropathy in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, K.; Yildiz, V.; Xiao, M.; Medipally, A.; Hemminger, J.; Scarl, R.; Satoskar, A.A.; Hebert, L.; Ivanov, I.; Biederman, L.; et al. Hypertension and the Kidney: Reduced Kidney Mass Is Bad for Both Normotensive and Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, 34, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Nithiyanantham, S.; Ying, J. Bioactive Peptides Attenuate Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Hearts. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 28, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Groups | Ang II (pg/mL) | ACE (ng/mL) | ACE 2 (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WKY control | 1155.25 ± 48.04 # | 8.62 ± 0.02 #### | 0.45 ± 0.07 ## |
| SHR control | 1323.20 ± 15.76 | 9.46 ± 0.12 | 0.70 ± 0.03 |
| L-IGTGIPGIW | 1291.39 ± 5.85 | 8.88 ± 0.42 **** | 0.69 ± 0.02 |
| H-IGTGIPGIW | 1209.75 ± 6.36 * | 8.66 ± 0.32 **** | 0.88 ± 0.02 *** |
| SP | 1178.37 ± 9.93 ** | 8.63 ± 0.08 **** | 0.96 ± 0.02 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-G.; Wijerathne, H.D.T.U.; Kim, T.; Park, S.-H.; Jung, W.-K.; Oh, J.-Y.; Yim, M.-J.; Lee, J.M.; Ko, S.-C.; Lee, D.-S.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Big-Belly Seahorse Derived Peptide in Blood Pressure Regulation and Protection Against Aortic, Renal, and Cardiac Injuries on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111449
Lee H-G, Wijerathne HDTU, Kim T, Park S-H, Jung W-K, Oh J-Y, Yim M-J, Lee JM, Ko S-C, Lee D-S, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Big-Belly Seahorse Derived Peptide in Blood Pressure Regulation and Protection Against Aortic, Renal, and Cardiac Injuries on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111449
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyo-Geun, Habaragoda Dewage Tharushi Udayangani Wijerathne, Taeho Kim, Si-Hyeong Park, Won-Kyo Jung, Jae-Young Oh, Mi-Jin Yim, Jeong Min Lee, Seok-Chun Ko, Dae-Sung Lee, and et al. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of Big-Belly Seahorse Derived Peptide in Blood Pressure Regulation and Protection Against Aortic, Renal, and Cardiac Injuries on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111449
APA StyleLee, H.-G., Wijerathne, H. D. T. U., Kim, T., Park, S.-H., Jung, W.-K., Oh, J.-Y., Yim, M.-J., Lee, J. M., Ko, S.-C., Lee, D.-S., & Kim, H.-S. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Big-Belly Seahorse Derived Peptide in Blood Pressure Regulation and Protection Against Aortic, Renal, and Cardiac Injuries on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111449








