A Systematic Intelligent Optimization Framework for a Sustained-Release Formulation Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Feature Selection Methods
2.2.2. Quadratic Inference Function
2.2.3. Exterior Penalty Function Method
2.2.4. Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithm
2.2.5. Multi-Objective Optimization Evaluation
2.2.6. Function Transformation
2.2.7. Software and Parameter Settings
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Feature Selection
3.2. Results of the QIF Modeling
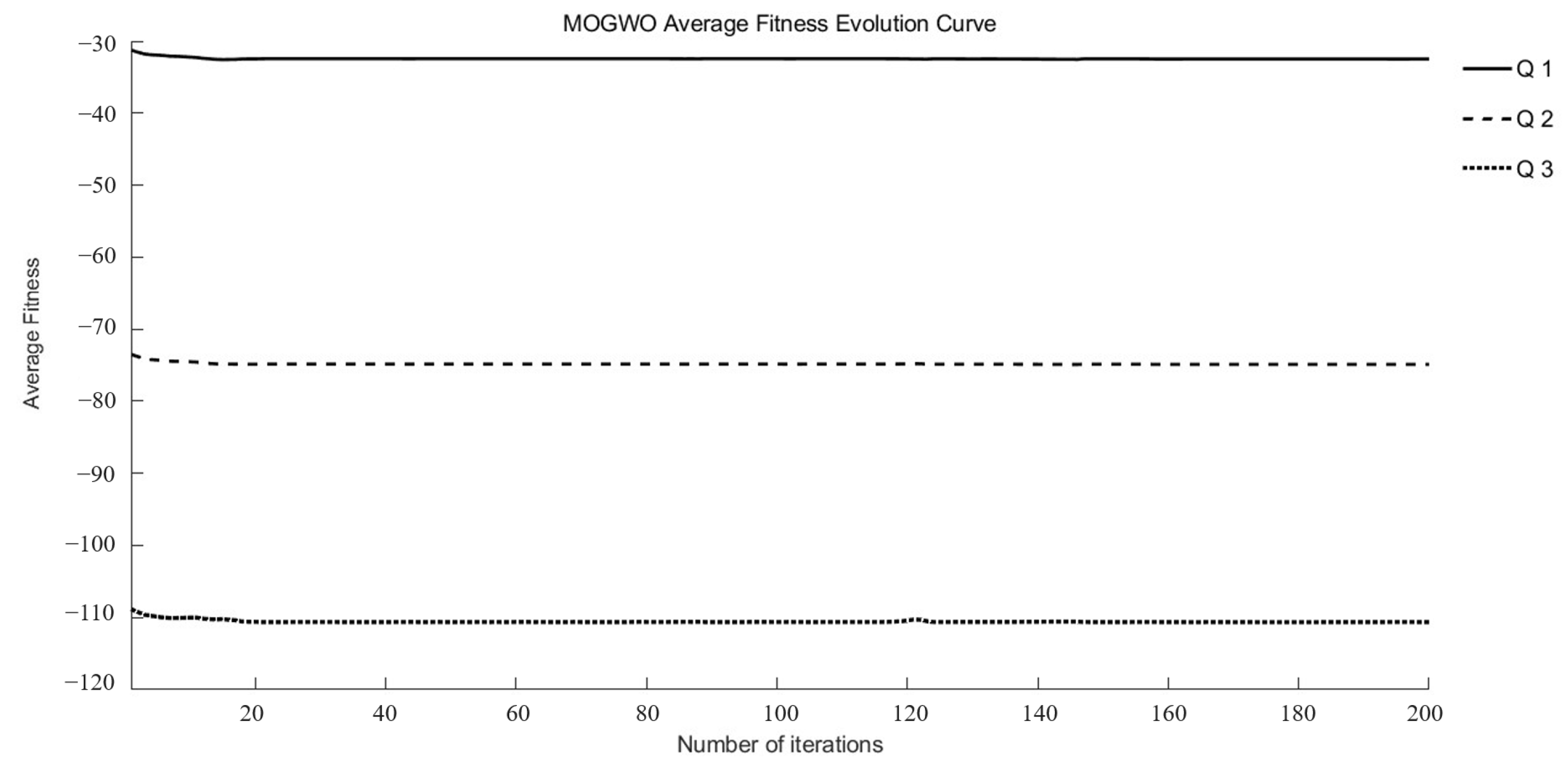
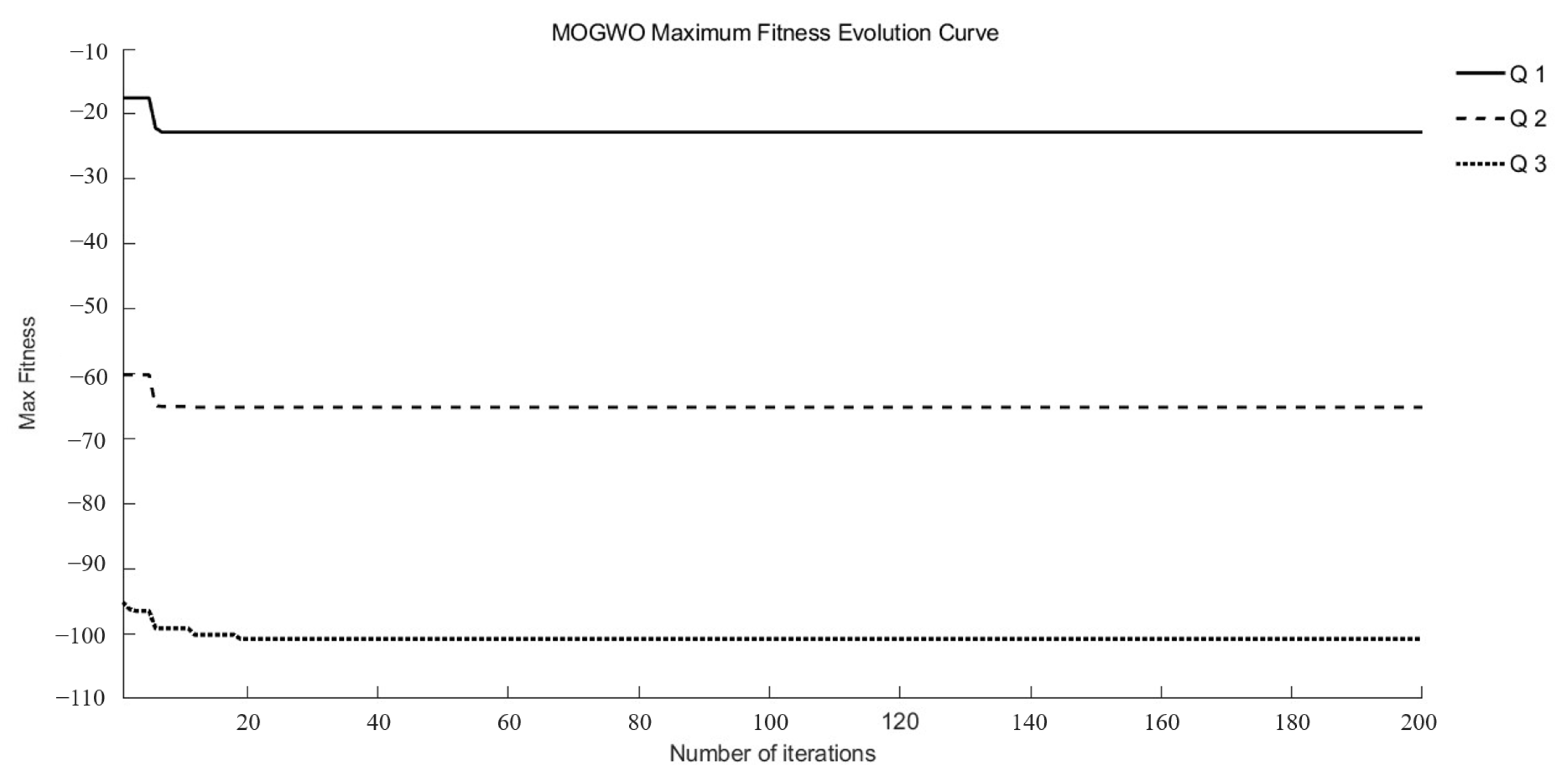
3.3. Results of the Multi-Objective Algorithm Optimization
3.4. Results of the Entropy Weight-TOPIS Method Optimization Evaluation
3.5. Comparison of Optimization Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunawardana, M.; Remedios-Chan, M.; Miller, C.S.; Fanter, R.; Yang, F.; Marzinke, M.A.; Hendrix, C.W.; Beliveau, M.; Moss, J.A.; Smith, T.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of long-acting tenofovir alafenamide (GS-7340) subdermal implant for HIV prophylaxis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandave, S.S.; Sawant, S.V.; Joshi, S.S.; Bansal, Y.K.; Kadam, S.S. Comparative bioequivalence studies of tramadol hydrochloride sustained-release 200 mg tablets. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2010, 4, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwerfalli, A.M.; Al-Kinani, A.; Alany, R.G.; ElShaer, A. Nano-engineering chitosan particles to sustain the release of promethazine from orodispersables. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberkt, C.A.; van den Beuken-van Everdingen, M.H.J.; Schols, J.; Hameleers, N.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Janssen, D.J.A. Effect of Sustained-Release Morphine for Refractory Breathlessness in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease on Health Status: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuboshi, S.; Imai, S.; Kizaki, H.; Hori, S. Comparison of different sustained-release opioids and acute respiratory conditions in patients with cancer and chronic kidney disease. Pharmacotherapy 2024, 44, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.H.; Boland, J.W.; Kochovska, S.; Honson, A.; Phillips, J.L.; Currow, D.C. Patients’ and caregivers’ experiences of driving with chronic breathlessness before and after regular low-dose sustained-release morphine: A qualitative study. Palliat. Med. 2020, 34, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Cui, Y.; Ren, J.; Hao, C.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; et al. A study on the preparation conditions of lidocaine microemulsion based on multi-objective genetic algorithm. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1272454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Kang, S.; Wu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Han, M.; Lou, Y.; Tian, Q.; Qiu, L. Application of multi-objective optimization algorithm to the preparation of polycaprolactone microsphere formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 681, 125859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Tsai, Y.H.; Yang, W.C.; Chang, J.S.; Wu, P.C. Optimization of sustained-release propranolol dosage form using factorial design and response surface methodology. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1626–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.L.; Bruns, R.E.; Ferreira, H.S.; Matos, G.D.; David, J.M.; Brandão, G.C.; da Silva, E.G.; Portugal, L.A.; dos Reis, P.S.; Souza, A.S.; et al. Box-Behnken design: An alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, N.; Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Cox’s Proportional Hazards Model via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibshirani, R.; Bien, J.; Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Simon, N.; Taylor, J.; Tibshirani, R.J. Strong rules for discarding predictors in lasso-type problems. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2012, 74, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Lv, J. Non-Concave Penalized Likelihood with NP-Dimensionality. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 5467–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breheny, P.; Huang, J. Coordinate Descent Algorithms for Nonconvex Penalized Regression, with Applications To Biological Feature Selection. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2011, 5, 232–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offorha, B.C.; Walters, S.J.; Jacques, R.M. Analysing cluster randomised controlled trials using GLMM, GEE1, GEE2, and QIF: Results from four case studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2023, 23, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhou, L.; Song, P.X. Real-Time Regression Analysis of Streaming Clustered Data With Possible Abnormal Data Batches. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2023, 118, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odueyungbo, A.; Browne, D.; Akhtar-Danesh, N.; Thabane, L. Comparison of generalized estimating equations and quadratic inference functions using data from the National Longitudinal Survey of Children and Youth (NLSCY) database. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2008, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y. Longitudinal data analysis for rare variants detection with penalized quadratic inference function. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Deb, K.; Thiele, L. Comparison of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: Empirical results. Evol. Comput. 2000, 8, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, Z.; Mandal, A.; Wong, W.K. Using Differential Evolution to Design Optimal Experiments. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 199, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagal, I.; Ibrahim, A.W.; Harrison, A.; Mbasso, W.F.; Hourani, A.O.; Zaitsev, I. Hierarchical multi step Gray Wolf optimization algorithm for energy systems optimization. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Wang, L. Hybrid Tabu-Grey wolf optimizer algorithm for enhancing fresh cold-chain logistics distribution. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Huang, J.; Lin, H.; Xie, Y. Optimization the formulation of pH-independent sustained release tablets of glipizide using D-optimal mixture design. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 2018, 34, 547–553. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Breheny, P.; Ma, S. A Selective Review of Group Selection in High-Dimensional Models. Stat. Sci. 2012, 27, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westgate, P.M. Criterion for the simultaneous selection of a working correlation structure and either generalized estimating equations or the quadratic inference function approach. Biom. J. 2014, 56, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, L.B.; Altan, S.; Coppenolle, H. Correction to “Mixture Experimentation in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Tutorial”. Pharm. Stat. 2025, 24, e70017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilil, H.; Aniba, G.; Gharavi, H. Dynamic Appliances Scheduling in Collaborative MicroGrids System. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 2276–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kim, Y.; Li, R. Calibrating Non-Convex Penalized Regression in Ultra-High Dimension. Ann. Stat. 2013, 41, 2505–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Liu, J.; He, J. Multi-objective winter wheat irrigation strategies optimization based on coupling AquaCrop-OSPy and NSGA-III: A case study in Yangling, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 157104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison of multi-objective evolutionary algorithms applied to watershed management problem. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Coelho, L.d.S. Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: A novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 47, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaness, M.A.A.; Helmi, A.M.; Dahou, A.; Elaziz, M.A. The Applications of Metaheuristics for Human Activity Recognition and Fall Detection Using Wearable Sensors: A Comprehensive Analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Zamani, H.; Asghari Varzaneh, Z.; Mirjalili, S. A Systematic Review of the Whale Optimization Algorithm: Theoretical Foundation, Improvements, and Hybridizations. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 4113–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangir, P.; Jangir, N. Non-Dominated Sorting Whale Optimization Algorithm (NSWOA): A Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithm for Solving Engineering Design Problems. Glob. J. Res. Eng. 2017, 17, 15–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hadka, D.; Reed, P. Borg: An auto-adaptive many-objective evolutionary computing framework. Evol. Comput. 2013, 21, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Kang, Y.; Lu, J.F.; Yu, X.Z. Using the TOPSIS method to select the best low-toxicity organic cosolvent for rice-based toxicity tests. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, B.R.; Zuffo, A.M.; Aguilera, J.G.; Steiner, F.; Ancca, S.M.; Flores, L.A.P.; Gonzales, H.H.S. Selection of Soybean Genotypes under Drought and Saline Stress Conditions Using Manhattan Distance and TOPSIS. Plants 2022, 11, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Niu, Y. Improving marginal hazard ratio estimation using quadratic inference functions. Lifetime Data Anal. 2023, 29, 823–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabat, F.; Pundir, M.; Mohabatpour, F.; Lobanova, L.; Koutsopoulos, S.; Hadjiiski, L.; Chen, X.; Papagerakis, P.; Papagerakis, S. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems for Oral Cancer Treatment-Current Status and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrinidis, G.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A. Multi-objective optimization methods in novel drug design. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Higuchi equation: Derivation, applications, use and misuse. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanjickal, D.G.; Lopina, S.T. Modeling of drug release from polymeric delivery systems—A review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2004, 21, 345–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Kaushik, D. Design and optimization of candesartan loaded self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for improving its dissolution rate and pharmacodynamic potential. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, A.; Cvetkovic, N.; Ibric, S.; Trajkovic, S.; Djuric, Z.; Popadic, D.; Popovic, R. Application of mixture experimental design in the formulation and optimization of matrix tablets containing carbomer and hydroxy-propylmethylcellulose. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2009, 32, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, E.; Matsumoto, C.; Okuyama, S.; Takada, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Shimomura, Y. Quantification of metamorphopsia in a macular hole patient using M-CHARTS. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2007, 85, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.; Coomans, D.; Smeyers-Verbeke, J.; Massart, D.L. Non-linear mixed effects models for the evaluation of dissolution profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 240, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Deb, K. An Evolutionary Many-Objective Optimization Algorithm Using Reference-Point Based Nondominated Sorting Approach, Part II: Handling Constraints and Extending to an Adaptive Approach. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2014, 18, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Sun, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, L. Optimization of a Screw Centrifugal Blood Pump Based on Random Forest and Multi-Objective Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm. Micromachines 2023, 14, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, X. A Balanced Whale Optimization Algorithm for Constrained Engineering Design Problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 71, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yu, Y.; Tao, T. A comprehensive evaluation of liposome/water partition coefficient prediction models based on the Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to an Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) method: Challenges from different descriptor dimension reduction methods and machine learning algorithms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443 Pt A, 130181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witten, D.M.; Tibshirani, R.J. Extensions of sparse canonical correlation analysis with applications to genomic data. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, B.A.; Abdeltawab, N.F.; Salah Ad-Din, I. D-optimal mixture design for optimization of topical dapsone niosomes: In vitro characterization and in vivo activity against Cutibacterium acnes. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Schemes | Pharmaceutical Components (%) | Cumulative Release Degree (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPMC K4M (X1) | HPMC K100LV (X2) | MgO (X3) | Lactose (X4) | Anhydrous CaHPO4 (X5) | 2 h (Y2) | 8 h (Y8) | 24 h (Y24) | |
| 1 | 29.5 | 22.6 | 7.2 | 16.4 | 7.1 | 17.1 | 64.4 | 98.1 |
| 2 | 25.2 | 27.8 | 2.0 | 22.8 | 5.0 | 17.5 | 54.4 | 87.3 |
| 3 | 41.4 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 16.4 | 5.0 | 16.0 | 59.8 | 102.3 |
| 4 | 38.3 | 14.4 | 4.5 | 17.8 | 7.8 | 19.3 | 61.2 | 93.2 |
| 5 | 32.5 | 17.5 | 5.0 | 22.8 | 5.0 | 17.7 | 58.8 | 92.5 |
| 6 | 29.0 | 27.8 | 6.0 | 15.0 | 5.0 | 19.2 | 69.8 | 100.4 |
| 7 | 45.4 | 10.0 | 2.0 | 20.4 | 5.0 | 14.9 | 64.2 | 95.0 |
| 8 | 25.0 | 26.3 | 4.8 | 18.4 | 8.4 | 13.7 | 63.8 | 100.8 |
| 9 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 10.0 | 17.8 | 5.0 | 19.3 | 62.5 | 90.6 |
| 10 | 45.4 | 10.0 | 2.0 | 15.0 | 10.4 | 23.2 | 60.2 | 89.0 |
| 11 | 32.5 | 17.5 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 7.8 | 17.4 | 59.6 | 93.9 |
| 12 | 34.0 | 18.7 | 4.3 | 17.8 | 7.8 | 15.3 | 59.8 | 103.0 |
| 13 | 25.2 | 27.8 | 2.0 | 15.0 | 12.8 | 19.6 | 55.1 | 83.8 |
| 14 | 40.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 15.0 | 12.8 | 26.3 | 60.5 | 91.2 |
| 15 | 25.2 | 27.8 | 2.0 | 22.8 | 5.0 | 20.3 | 58.2 | 89.0 |
| 16 | 29.5 | 21.8 | 3.2 | 20.3 | 7.9 | 23.8 | 64.4 | 94.7 |
| 17 | 25.2 | 27.8 | 2.0 | 15.0 | 12.8 | 20.8 | 55.3 | 84.5 |
| 18 | 47.8 | 13.0 | 2.0 | 15.0 | 5.0 | 18.2 | 65.1 | 95.3 |
| 19 | 45.4 | 10.0 | 2.0 | 20.4 | 5.0 | 16.3 | 63.8 | 99.5 |
| 20 | 32.5 | 17.5 | 2.0 | 18.0 | 12.8 | 16.0 | 61.9 | 98.7 |
| 21 | 41.4 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 16.4 | 5.0 | 16.7 | 58.8 | 87.4 |
| 22 | 40.4 | 20.4 | 2.0 | 15.0 | 5.0 | 20.1 | 60.7 | 87.4 |
| 23 | 33.0 | 27.8 | 2.0 | 15.0 | 5.0 | 19.7 | 56.0 | 86.5 |
| 24 | 40.0 | 10.0 | 2.0 | 22.8 | 8.0 | 19.0 | 56.7 | 91.2 |
| 25 | 40.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 15.0 | 12.8 | 22.5 | 58.4 | 90.6 |
| Feature/Criterion | LASSO | SCAD | MCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed by/Year | Tibshirani, 1996 | Fan & Li, 2001 | Zhang, 2010 |
| Penalty Type | Convex (L1) | Non-convex | Non-convex |
| Main Idea | Adds L1 penalty to achieve coefficient shrinkage and variable selection | Strongly shrinks small coefficients, weakly penalizes large ones | Gradually reduces penalty for large coefficients via concavity parameter (γ) |
| Key Advantages | Simple, interpretable, efficient for high-dimensional data (p > n) | Oracle property, avoids over-shrinkage, handles correlated variables well | Balanced sparsity and unbiasedness, faster convergence, robust under non-saturated data |
| Main Limitations | Equal shrinkage causes group selection bias; sensitive to penalty parameter | May trap in local optima; high computational cost | Requires tuning of γ; may show instability under high correlation |
| Computation Complexity | Low | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | Pharmaceutical modeling, gene screening, financial prediction | Pharmaceutical and epidemiological modeling | High-dimensional optimization, machine learning, formulation studies |
| Feature/Criterion | GEE | QIF |
|---|---|---|
| Proposed by/Year | Liang & Zeger, 1986 | Qu et al., 2000 |
| Core Idea | Estimates parameters using specified working correlation matrix | Approximates inverse of correlation matrix via linear combination of basis matrices |
| Handling of Correlation | Relies on correct specification of working correlation matrix | Robust to misspecification of correlation structure |
| Efficiency | May be inefficient with small sample size or complex correlation | Generally more efficient under finite sample or complex correlation conditions |
| Goodness-of-Fit Assessment | Limited; requires additional methods | Naturally incorporates model fit tests via quadratic construction |
| Computational Complexity | Moderate | Higher for very large/high-dimensional data due to matrix operations |
| Typical Applications | Longitudinal and repeated measures studies | Repeated measures modeling, formulation optimization, complex longitudinal data |
| Parameters | Estimated Value | Standard Error | Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 4.2711 | <0.0001 | 6,839,553.34 | <0.0001 |
| X24 | −0.0111 | 0.0002 | −50.01 | <0.0001 |
| X25 | −0.0097 | 0.0001 | −145.17 | <0.0001 |
| X35 | −0.6140 | <0.0001 | −194,734.95 | <0.0001 |
| X134 | −0.0017 | 0.0004 | −4.20 | <0.0001 |
| X135 | 0.0108 | <0.0001 | 243.54 | <0.0001 |
| X12345 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | 12.97 | <0.0001 |
| X3t | 0.0247 | <0.0001 | 1488.84 | <0.0001 |
| X5t | −0.0005 | <0.0001 | −7.16 | <0.0001 |
| t*t | −0.2199 | <0.0001 | −7196.43 | <0.0001 |
| time | 9.0864 | <0.0001 | 2,702,798.87 | <0.0001 |
| Optimization Methods | Schemes | Pharmaceutical Ingredients | Cumulative Release Degree | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | Y2 | Y8 | Y24 | ||
| NSGA-III | 1 | 36.786 | 11.010 | 9.126 | 19.382 | 6.497 | 18.421 | 61.084 | 97.463 |
| 2 | 33.465 | 20.442 | 2.953 | 20.694 | 5.247 | 19.610 | 61.360 | 95.307 | |
| 3 | 25.217 | 23.427 | 7.792 | 15.251 | 11.115 | 19.378 | 61.829 | 97.645 | |
| 4 | 30.039 | 21.690 | 3.386 | 20.997 | 6.690 | 20.154 | 61.965 | 96.071 | |
| 5 | 30.066 | 15.112 | 2.690 | 22.218 | 12.714 | 20.332 | 62.021 | 95.805 | |
| 6 | 25.199 | 18.156 | 6.158 | 21.725 | 11.563 | 20.638 | 62.845 | 98.010 | |
| 7 | 31.293 | 15.830 | 7.244 | 22.492 | 5.941 | 20.606 | 62.991 | 98.630 | |
| 8 | 27.350 | 17.315 | 9.844 | 20.670 | 7.622 | 20.312 | 63.078 | 99.733 | |
| 9 | 28.589 | 15.035 | 5.915 | 21.651 | 11.612 | 20.912 | 63.083 | 98.152 | |
| 10 | 34.957 | 12.257 | 4.536 | 20.992 | 10.060 | 21.492 | 63.463 | 97.999 | |
| 11 | 27.365 | 20.745 | 8.401 | 15.921 | 10.370 | 21.092 | 63.636 | 99.698 | |
| 12 | 31.423 | 18.737 | 4.185 | 16.744 | 11.714 | 22.102 | 64.016 | 98.399 | |
| 13 | 34.848 | 16.477 | 3.089 | 16.782 | 11.606 | 22.268 | 64.020 | 97.970 | |
| 14 | 26.544 | 22.193 | 4.914 | 20.584 | 8.566 | 22.127 | 64.159 | 98.856 | |
| 15 | 30.737 | 17.228 | 6.657 | 20.785 | 7.396 | 22.456 | 64.749 | 100.145 | |
| MOGWO | 16 | 25.000 | 27.800 | 10.000 | 15.000 | 5.000 | 18.685 | 61.481 | 98.218 |
| 17 | 26.845 | 16.251 | 9.996 | 22.169 | 7.539 | 18.940 | 61.729 | 98.444 | |
| 18 | 37.269 | 18.310 | 2.990 | 19.033 | 5.198 | 20.144 | 61.900 | 95.862 | |
| 19 | 35.501 | 17.066 | 2.656 | 20.937 | 6.642 | 20.396 | 62.098 | 95.916 | |
| 20 | 25.437 | 21.107 | 8.909 | 21.144 | 6.204 | 20.406 | 63.039 | 99.339 | |
| 21 | 30.350 | 25.226 | 3.143 | 16.339 | 7.743 | 20.871 | 62.643 | 96.645 | |
| 22 | 45.380 | 12.056 | 2.000 | 15.000 | 8.364 | 21.171 | 62.771 | 96.316 | |
| 23 | 42.505 | 11.207 | 2.000 | 15.241 | 11.847 | 21.210 | 62.799 | 96.317 | |
| 24 | 43.351 | 13.841 | 3.193 | 16.317 | 6.099 | 21.309 | 63.092 | 97.127 | |
| 25 | 41.335 | 17.011 | 2.685 | 15.009 | 6.761 | 21.458 | 63.164 | 96.993 | |
| 26 | 33.684 | 13.244 | 8.600 | 18.226 | 9.046 | 21.465 | 64.042 | 100.193 | |
| 27 | 27.207 | 23.936 | 5.577 | 19.627 | 6.453 | 21.618 | 63.754 | 98.729 | |
| 28 | 37.560 | 19.496 | 5.629 | 15.115 | 5.001 | 21.994 | 64.142 | 99.149 | |
| 29 | 34.682 | 19.649 | 8.314 | 15.000 | 5.156 | 22.160 | 64.703 | 100.765 | |
| 30 | 37.852 | 14.293 | 3.695 | 15.123 | 11.838 | 23.019 | 64.860 | 99.049 | |
| NSWOA | 31 | 36.758 | 12.245 | 3.426 | 21.961 | 8.411 | 21.083 | 62.894 | 97.004 |
| 32 | 37.177 | 14.354 | 5.786 | 16.485 | 9.004 | 21.186 | 63.346 | 98.384 | |
| 33 | 37.834 | 13.160 | 5.379 | 16.507 | 9.925 | 21.352 | 63.448 | 98.318 | |
| 34 | 37.957 | 13.310 | 5.828 | 16.589 | 9.121 | 21.475 | 63.640 | 98.694 | |
| 35 | 37.477 | 12.039 | 5.400 | 19.884 | 8.001 | 21.579 | 63.684 | 98.578 | |
| 36 | 37.765 | 13.067 | 5.553 | 16.845 | 9.574 | 21.797 | 63.920 | 98.862 | |
| 37 | 37.337 | 13.923 | 5.741 | 16.795 | 9.008 | 21.858 | 64.011 | 99.031 | |
| 38 | 38.468 | 12.654 | 5.799 | 16.442 | 9.440 | 22.337 | 64.497 | 99.537 | |
| 39 | 38.084 | 15.617 | 5.117 | 16.204 | 7.782 | 22.371 | 64.435 | 99.218 | |
| 40 | 37.991 | 13.178 | 5.806 | 16.710 | 9.119 | 22.384 | 64.546 | 99.591 | |
| 41 | 39.069 | 12.346 | 5.239 | 16.276 | 9.873 | 22.492 | 64.568 | 99.383 | |
| 42 | 38.803 | 12.318 | 5.419 | 16.442 | 9.821 | 22.498 | 64.600 | 99.487 | |
| 43 | 39.331 | 12.360 | 5.208 | 16.550 | 9.352 | 22.607 | 64.679 | 99.486 | |
| 44 | 38.198 | 13.213 | 5.766 | 16.474 | 9.152 | 22.741 | 64.898 | 99.927 | |
| 45 | 38.422 | 13.513 | 6.275 | 17.068 | 7.523 | 22.747 | 64.983 | 100.227 | |
| Schemes | Optimal Ideal Solution Distance D+ | Negative Ideal Solution Distance D− | Relative Proximity C | Sorting Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 0.009 | 0.129 | 0.932 | 1 |
| 29 | 0.013 | 0.128 | 0.908 | 2 |
| 15 | 0.014 | 0.123 | 0.901 | 3 |
| 44 | 0.014 | 0.125 | 0.898 | 4 |
| 43 | 0.022 | 0.117 | 0.839 | 5 |
| 40 | 0.023 | 0.115 | 0.834 | 6 |
| 42 | 0.023 | 0.115 | 0.831 | 7 |
| 38 | 0.024 | 0.113 | 0.823 | 8 |
| 41 | 0.025 | 0.114 | 0.819 | 9 |
| 30 | 0.028 | 0.118 | 0.809 | 10 |
| 39 | 0.029 | 0.109 | 0.79 | 11 |
| 26 | 0.03 | 0.109 | 0.782 | 12 |
| 28 | 0.035 | 0.102 | 0.747 | 13 |
| 14 | 0.038 | 0.101 | 0.728 | 14 |
| 37 | 0.038 | 0.098 | 0.72 | 15 |
| Schemes | Pharmaceutical Ingredients | Cumulative Release Degree | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | Y2 | Y8 | Y24 | |
| Original document optimal scheme | 40.000 | 10.000 | 5.000 | 15.000 | 12.800 | 20.900 | 59.500 | 91.500 |
| Scheme 45 | 38.422 | 13.513 | 6.275 | 17.068 | 7.523 | 22.747 | 64.983 | 100.227 |
| Change amount | −1.578 | 3.513 | 1.275 | 2.068 | −5.277 | 1.847 | 5.483 | 8.727 |
| Rate of Change (%) | −3.945 | 35.130 | 25.500 | 13.787 | −41.227 | 8.837 | 9.215 | 9.538 |
| Schemes | Pharmaceutical Ingredients | Cumulative Release Degree | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | Y2 | Y8 | Y24 | |
| Original document optimal scheme | 40.000 | 10.000 | 5.000 | 15.000 | 12.800 | 20.900 | 59.500 | 91.500 |
| 45 | 38.422 | 13.513 | 6.275 | 17.068 | 7.523 | 22.747 | 64.983 | 100.227 |
| 29 | 34.682 | 19.649 | 8.314 | 15.000 | 5.156 | 22.160 | 64.703 | 100.765 |
| 15 | 30.737 | 17.228 | 6.657 | 20.785 | 7.396 | 22.456 | 64.749 | 100.145 |
| 44 | 38.198 | 13.213 | 5.766 | 16.474 | 9.152 | 22.741 | 64.898 | 99.927 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Han, M.; Ren, H.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Lou, Y.; Hao, C.; Feng, Q.; Qiu, L. A Systematic Intelligent Optimization Framework for a Sustained-Release Formulation Design. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111419
Qiao Y, Wu Y, Han M, Ren H, Cui Y, Wang X, Lou Y, Hao C, Feng Q, Qiu L. A Systematic Intelligent Optimization Framework for a Sustained-Release Formulation Design. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111419
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Yuchao, Yijia Wu, Mengchen Han, Hao Ren, Yu Cui, Xuchun Wang, Yiming Lou, Chongqi Hao, Quan Feng, and Lixia Qiu. 2025. "A Systematic Intelligent Optimization Framework for a Sustained-Release Formulation Design" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111419
APA StyleQiao, Y., Wu, Y., Han, M., Ren, H., Cui, Y., Wang, X., Lou, Y., Hao, C., Feng, Q., & Qiu, L. (2025). A Systematic Intelligent Optimization Framework for a Sustained-Release Formulation Design. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111419






