In-Situ Forming Polyester Implants for Sustained Intravesical Oxybutynin Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Oxybutynin Base
2.3. Preparation of ISFI-Solutions
2.4. Viscosity of ISFI-Solutions
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.6. In Vitro Drug-Release Testing
2.7. Degradation of PLGA
2.8. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis
2.9. Gas Chromatography (GC)
2.10. Visualization of Implants
2.11. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
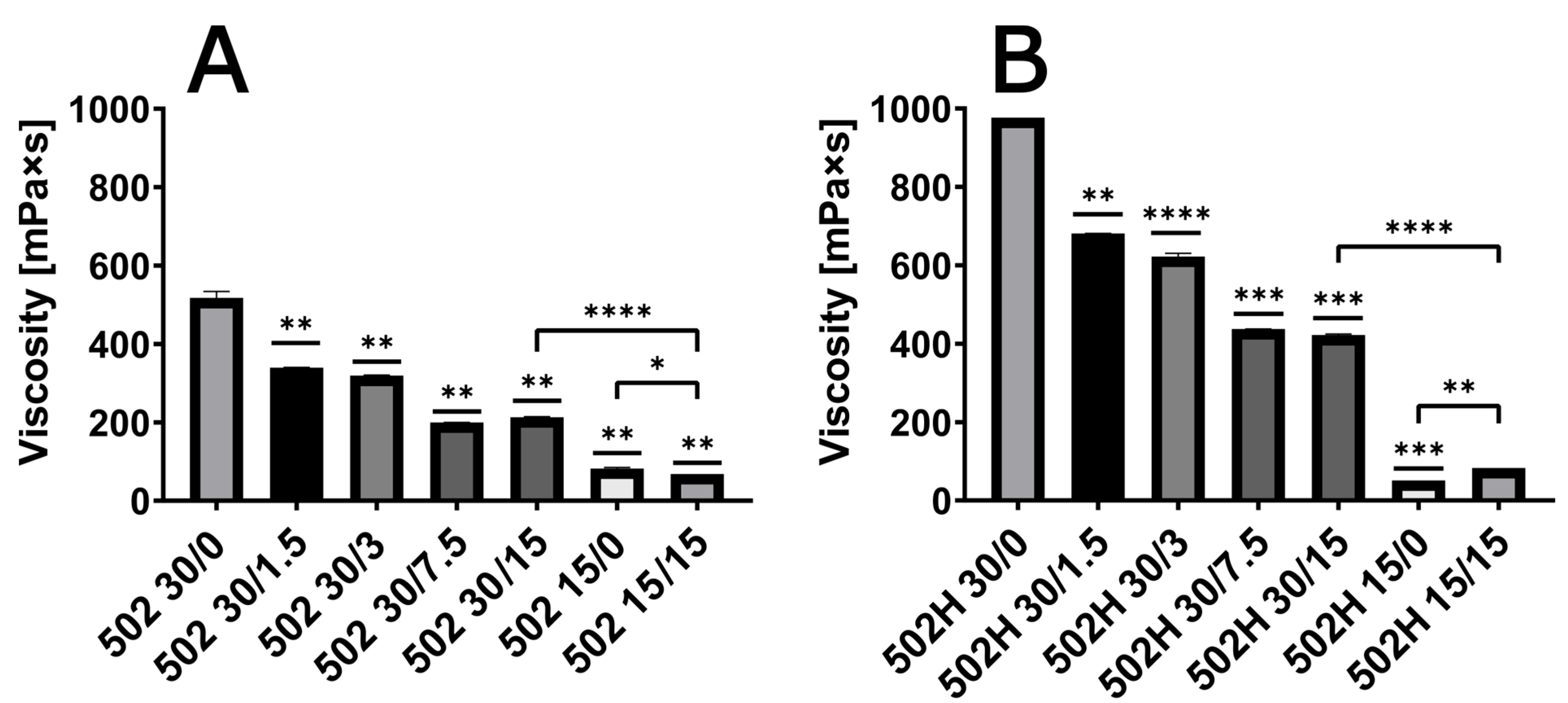
3.1. Viscosity of ISFI Solutions
3.2. Glass Transition Temperature of ISFI
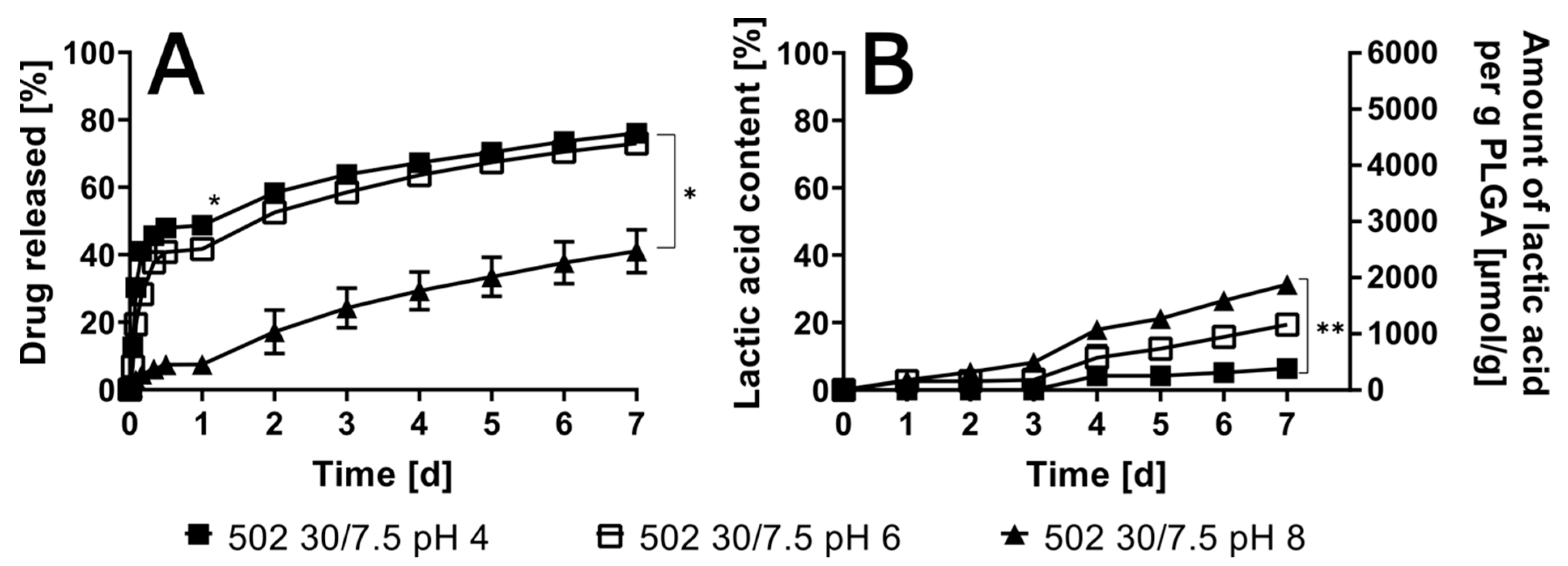
3.3. Impact of Variable pHs of Artificial Urine
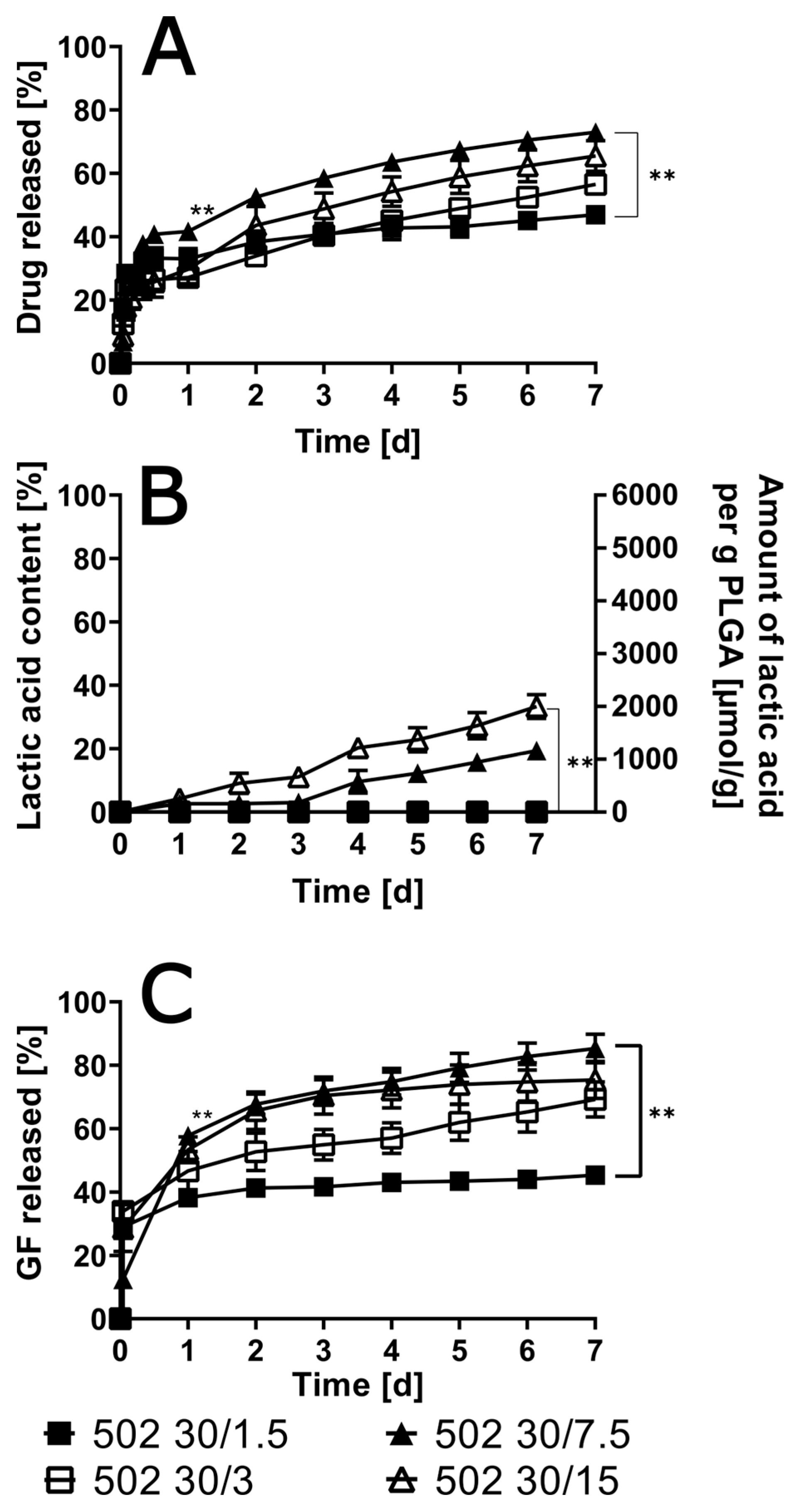
3.4. Variation of Drug Load in the ISFIs
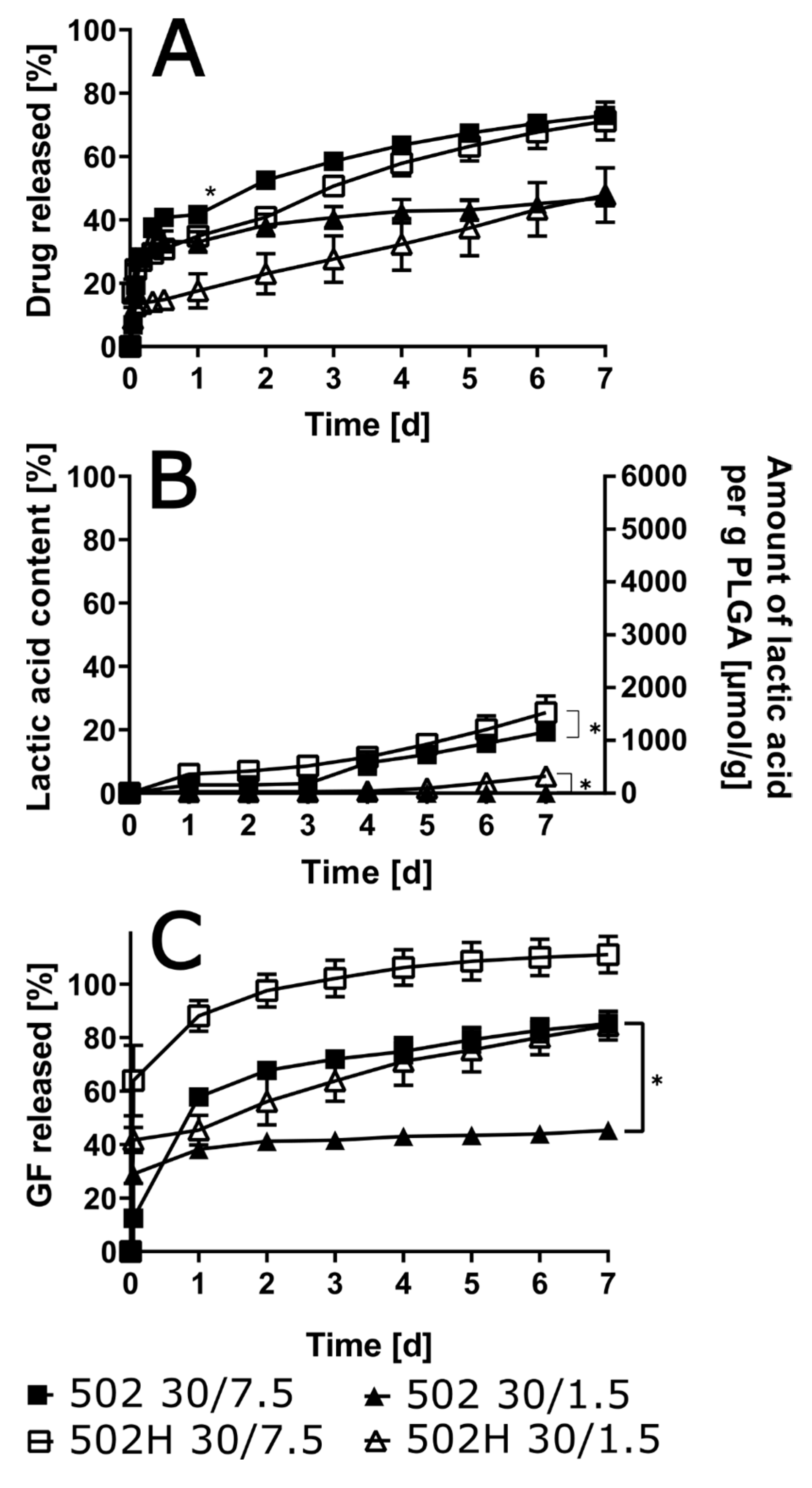
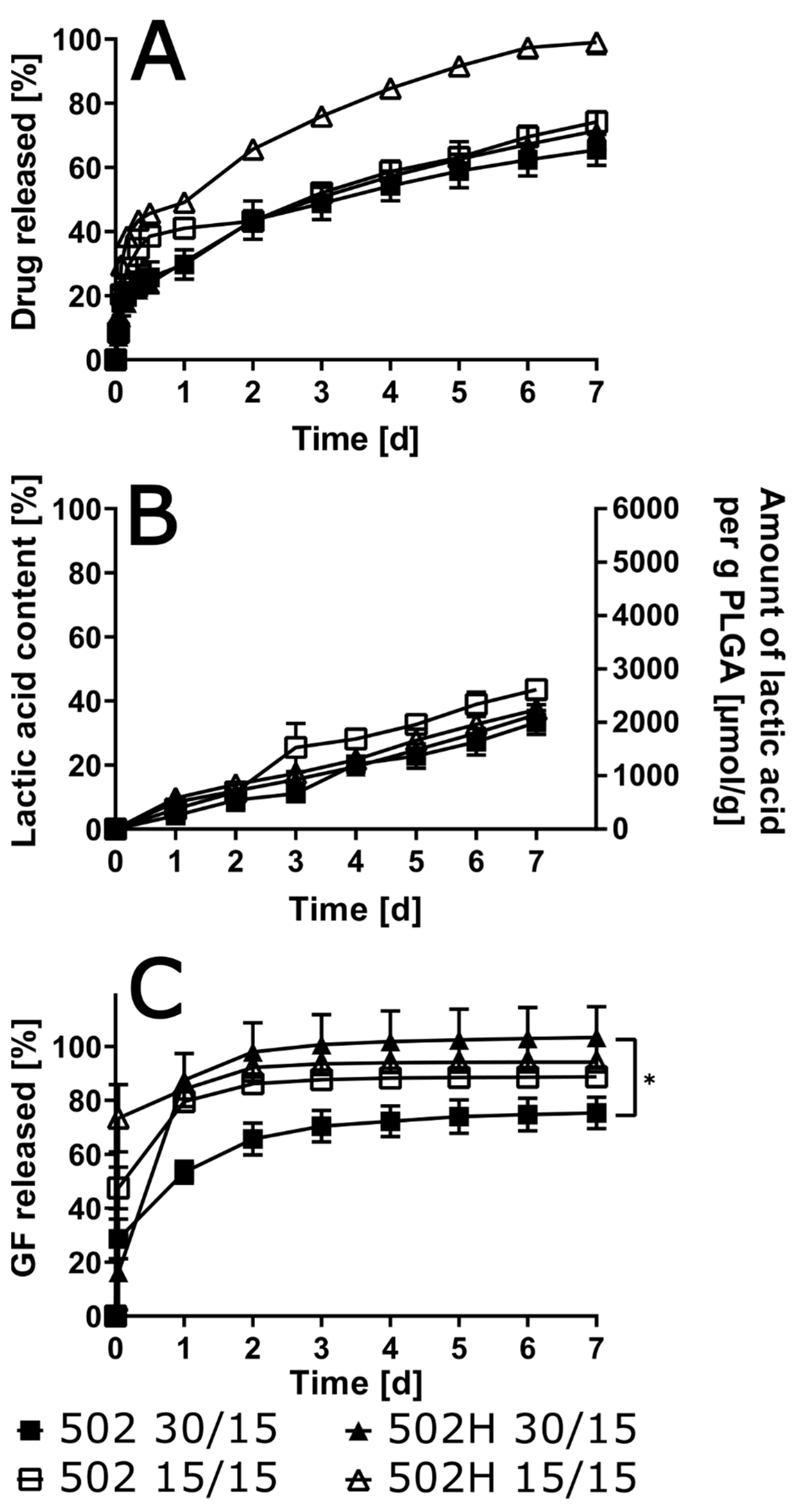
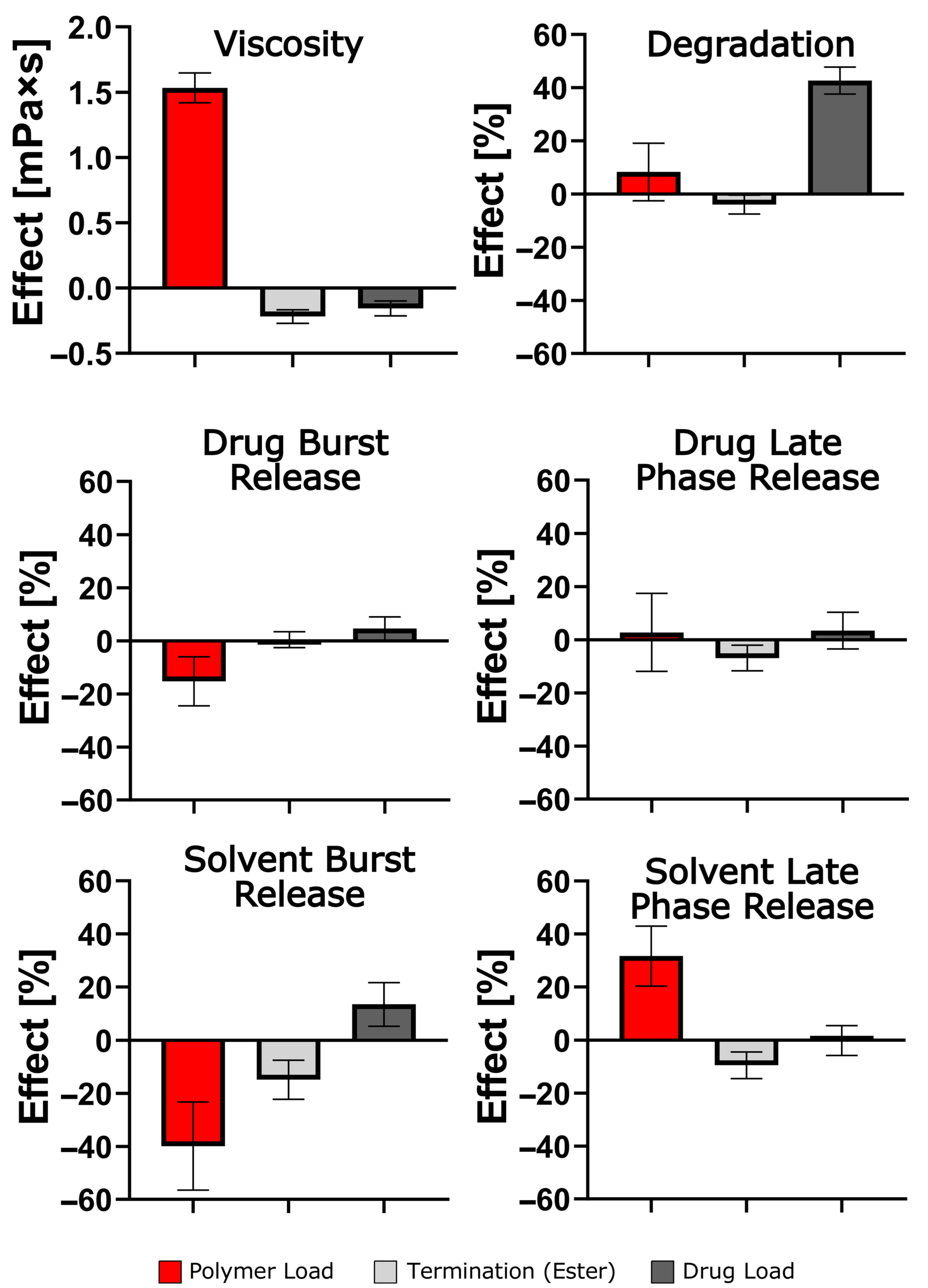
3.5. Influence of Polymer Grade and Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kempe, S.; Mäder, K. In situ forming implants—An attractive formulation principle for parenteral depot formulations. J. Control Release Off. J. Control Release Soc. 2012, 161, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-A.; Wen, K.-C.; Liu, J.-H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Li, F.-Q. Strategies for intravesical drug delivery: From bladder physiological barriers and potential transport mechanisms. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 4738–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, I.; Kushwah, V.; Alva, C.; Koutsamanis, I.; Rattenberger, J.; Schroettner, H.; Mayrhofer, C.; Modhave, D.; Braun, M.; Werner, B.; et al. Paudel, Influence of plga end groups on the release profile of dexamethasone from ocular implants. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 1307–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlomke, C.; Barth, M.; Ma, K. Polymer degradation induced drug precipitation in plga implants—Why less is sometimes more. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machatschek, R.; Lendlein, A. Fundamental insights in plga degradation from thin film studies. J. Control Release 2020, 319, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford Versypt, A.N.; Pack, D.W.; Braatz, R.D. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery from autocatalytically degradable plga microspheres—A review. J. Control Release 2013, 165, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, F.; Willart, J.; Neut, C.; Agossa, K.; Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. In-situ forming plga implants: Towards less toxic solvents. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 657, 124121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Lin, X.; Zhou, L.; Xue, A.; Gosselin, E.; Chothe, P.; Darji, M.; Lu, X.; Yang, W. Evaluation of the impact of the polymer end groups and molecular weight on in vitro and in vivo performances of plga based in situ forming implants for ketoprofen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 114, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredenberg, S.; Wahlgren, M.; Reslow, M.; Axelsson, A. The mechanisms of drug release in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based drug delivery systems—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Meng, S.; Zhang, W.; Meng, S. Effect of polymer permeability and solvent removal rate on in situ forming implants: Drug burst release and microstructure. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Yang, T.-X.; Fang, K.-W.; Wang, G.; Li, P. Efficacy, according to urodynamics, of onabotulinumtoxina compared with antimus-carinic drugs, for neurogenic detrusor overactivity: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Kimura, Y.; Tsounapi, P.; Hikita, K.; Saito, M.; Takenaka, A. Long-term efficacy, safety, and tolerability of modified intravesical oxybutynin chloride for neurogenic bladder in children. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2019, 11, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Albrecht, U.; Schnitker, J.; Reitz, A.; Stein, R. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of intravesically administered 0.1% oxybutynin hydrochloride solution in adult patients with neurogenic bladder: A randomized, prospective, controlled multi-center trial. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2015, 35, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palugan, L.; Cerea, M.; Cirilli, M.; Moutaharrik, S.; Maroni, A.; Zema, L.; Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Filippin, I.; Foppoli, A.; et al. Intravesical drug delivery approaches for improved therapy of urinary bladder diseases. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmand, S.; Kamat, A.M.; Shore, N.D.; Meeks, J.J.; Galsky, M.D.; Jacob, J.M.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Williams, S.B.; Powles, T.; Chang, S.S.; et al. Development of tar-200: A novel targeted releasing system designed to provide sustained delivery of gemcitabine for patients with bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2025, 43, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gindy, A. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of oxeladin citrate and oxybutynin hydrochloride and their degradation products. Il Farm. 2005, 60, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, M.; Nouvel, C.; Ko, M.; Sapin, A.; Maincent, P.; Boudier, A. Plga in situ implants formed by phase inversion: Critical physicochemical parameters to modulate drug release. J. Control Release Off. J. Control Release Soc. 2013, 172, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhrushina, E.; Sakharova, P.; Konogorova, P.; Pyzhov, V.; Kosenkova, S.; Bardakov, A.; Zubareva, I.; Krasnyuk, I. Burst release from in situ forming plga-based implants: 12 effectors and ways of correction. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, H.; Khodaverdi, E.; Kaffash, E.; Saffari, A.; Nesa, S.; Shiadeh, R.; Nokhodchi, A.; Hadizadeh, F. Optimization and in vitro evaluation of injectable sustained-release of levothyroxine using plga-peg-plga. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 16, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Chen, S.; Etzler, F. Rheological characterization of hydroxypropylcellulose gels. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1999, 25, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhabbour, R.; Kovarova, M.; Jones, C.; Copeland, D.; Shrivastava, R.; Swanson, M.; Sykes, C.; Ho, P.; Cottrell, M.; Sridharan, A.; et al. Ultra-long-acting tunable biodegradable and removable controlled release implants for drug delivery. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, C.; Kranz, H.; Siepmann, F.; Siepmann, J. In-situ forming plga implants for intraocular dexamethasone delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorio, L.; Olear, A.; Hamilton, J.; Patel, R.; Beiswenger, A.; Wallace, J.; Zhou, H.; Exner, A. Noninvasive characterization of the effect of varying plga molecular weight blends on in situ forming implant behavior using ultrasound imaging. Theranostics 2012, 2, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kost, B.; Basko, M.; Bednarek, M.; Socka, M.; Kopka, B.; Łapienis, G.; Biela, T.; Kubisa, P.; Brzeziński, M. The influence of the functional end groups on the properties of polylactide-based materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 130, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Chanda, N. Formulation of plga nano-carriers: Specialized modification for cancer therapeutic applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 837–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussain, R.; Adebisi, A.; Conway, B.R.; Asare-Addo, K. Electrospun nanofibers: Exploring process parameters, polymer selection, and recent applications in pharmaceuticals and drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 90, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, H.; Bodmeier, R. Structure formation and characterization of injectable drug loaded biodegradable devices: In situ implants versus in situ microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, F.; Le Brun, V.; Siepmann, J. Drugs acting as plasticizers in polymeric systems: A quantitative treatment. J. Control Release 2006, 115, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, S.; Faraj, J.; Dorati, R.; Deluca, P. Enhanced degradation of lactide-co-glycolide polymer with basic nucleophilic drugs. Adv. Pharm. 2015, 2015, 154239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Lv, F.; Liu, T. A pro-angiogenic degradable mg-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) implant combined with rhbfgf in a rat limb ischemia model. Acta Biomater. 2017, 64, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, J.; Prasher, A.; Young, I.; Kim, J.; Shrivastava, R.; Maturavongsadit, P.; Benhabbour, R. Effects of drug physicochemical properties on in-situ forming implant polymer degradation and drug release kinetics. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DrugBank, Oxybutynin (db01062). 2024. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01062 (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Liu, J.; Yang, T.; Dai, L.; Shi, K.; Hao, Y.; Chu, B.; Hu, D.; Bei, Z.; Yuan, L.; Pan, M.; et al. Intravesical chemotherapy synergize with an immune adjuvant by a thermo-sensitive hydrogel system for bladder cancer. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 31, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 502 | 502H | |
|---|---|---|
| NEAT | 39.0 °C ± 2.6 °C | 42.5 °C ± 3.6 °C |
| 30/0 | 23.9 °C ± 1.6 °C | 18.3 °C ± 8.2 °C |
| 30/1.5 | 17.9 °C ± 4.7 °C | 16.3 °C ± 1.9 °C |
| 30/3 | 14.9 °C ± 4.0 °C | 13.1 °C ± 4.3 °C |
| 30/7.5 | 6.5 °C ± 0.8 °C | 7.5 °C ± 0.9 °C |
| 30/15 | <5 °C | <5 °C |
| 15/0 | 23.2 °C ± 0.5 °C | 16.8 °C ± 3.2 °C |
| 15/15 | <5 °C | <5 °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hartig, M.U.; Appelhaus, J.; Vollenbröker, M.; Lamprecht, A. In-Situ Forming Polyester Implants for Sustained Intravesical Oxybutynin Release. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111369
Hartig MU, Appelhaus J, Vollenbröker M, Lamprecht A. In-Situ Forming Polyester Implants for Sustained Intravesical Oxybutynin Release. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111369
Chicago/Turabian StyleHartig, Michael Uwe, Jan Appelhaus, Marc Vollenbröker, and Alf Lamprecht. 2025. "In-Situ Forming Polyester Implants for Sustained Intravesical Oxybutynin Release" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111369
APA StyleHartig, M. U., Appelhaus, J., Vollenbröker, M., & Lamprecht, A. (2025). In-Situ Forming Polyester Implants for Sustained Intravesical Oxybutynin Release. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111369







