Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives as Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Antagonists for Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
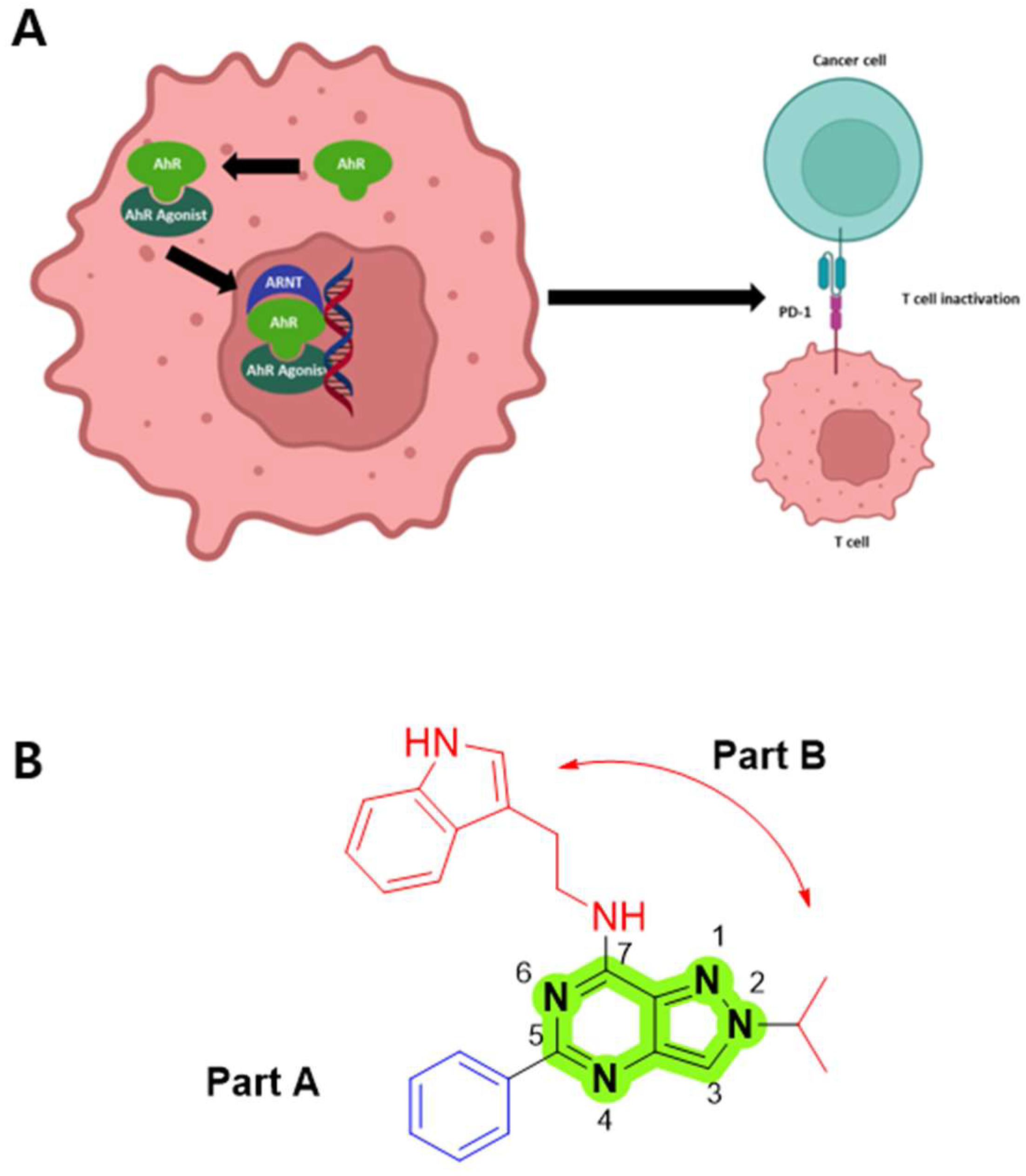
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Method
2.2. Biology
2.2.1. Animals
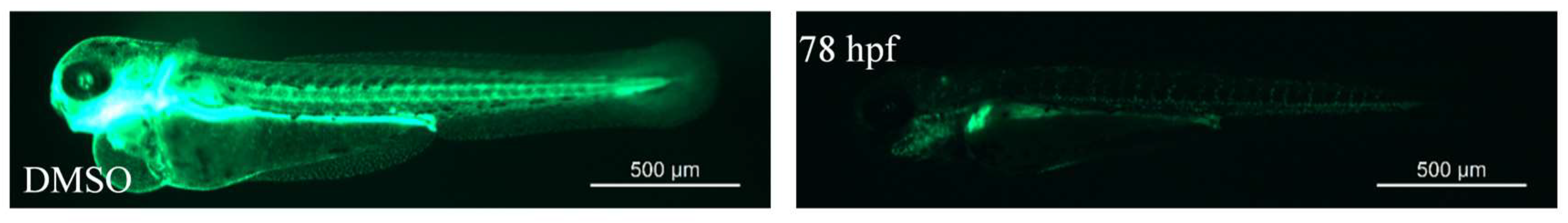
2.2.2. Zebrafish
2.2.3. Cells
2.2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.2.5. qRT-PCR
2.2.6. Cell Nucleus and Cytoplasmic Protein Isolation
2.2.7. Western Blot
2.2.8. Cell-Cycle Analysis
2.2.9. Apoptosis Analysis
2.2.10. Clonogenic Assay
2.2.11. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.2.12. Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte (CTL) Assay
2.2.13. In Vivo Therapy
2.2.14. Molecular Docking Studies of the Synthesized Compounds with Human AhR
2.2.15. Pharmacokinetic Study in Mouse
2.2.16. AhR Antagonist Screening Using Tg(cyp1a:egfp) Zebrafish
2.2.17. Determination of the Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) of Compounds
3. Results
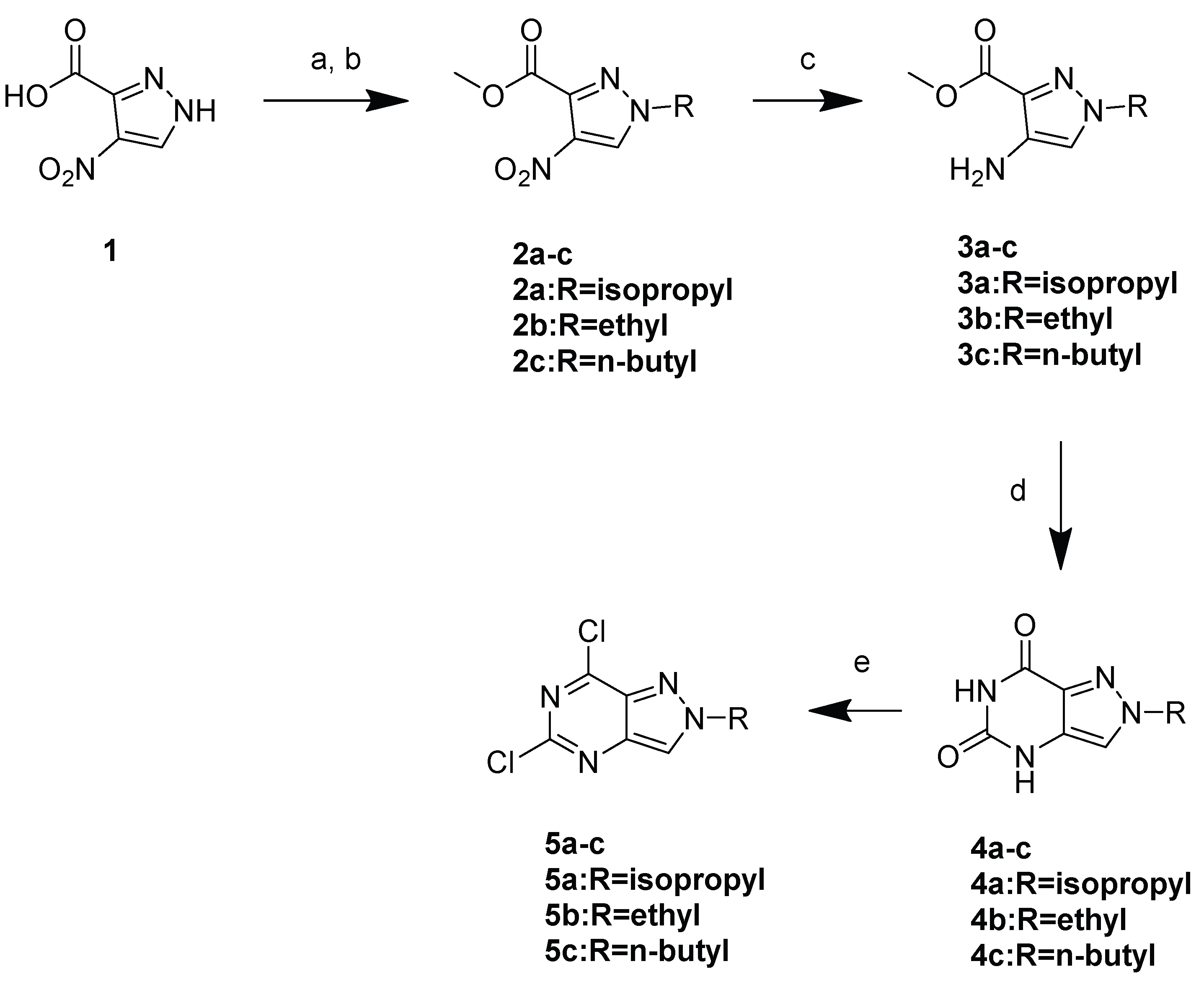
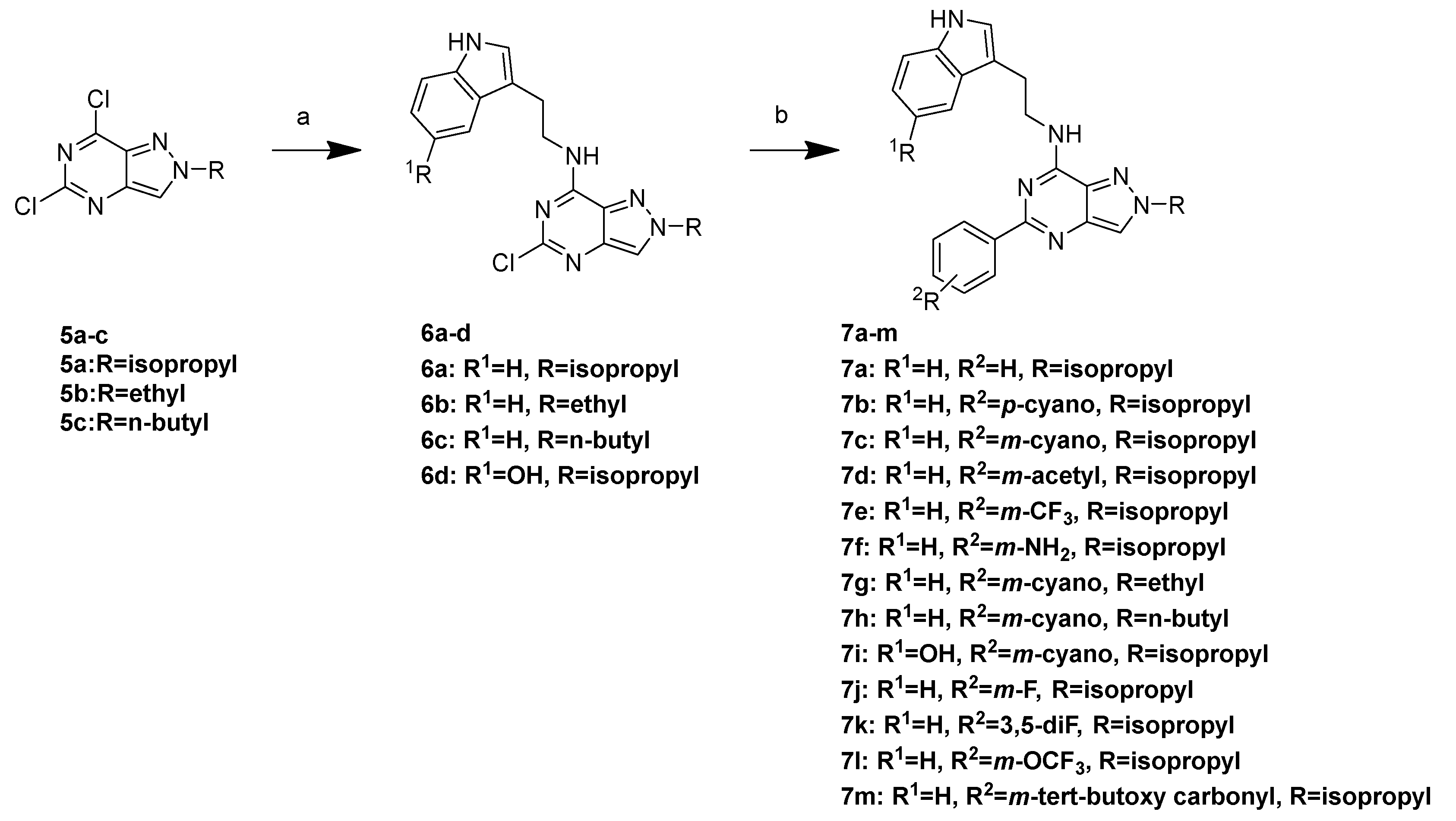
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. SAR Data of AhR Antagonists
3.3. PK Data of 7k
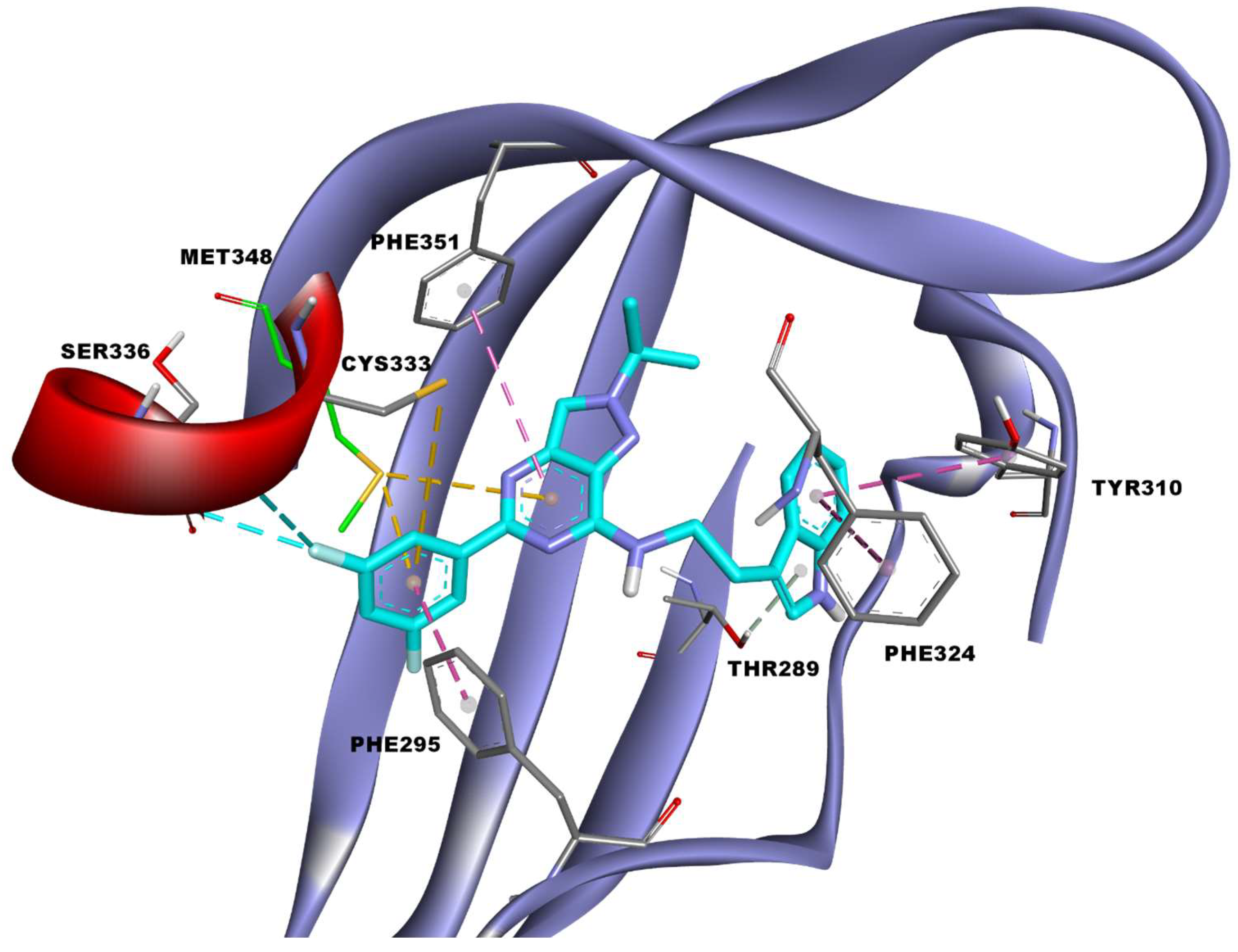
3.4. Docking Study
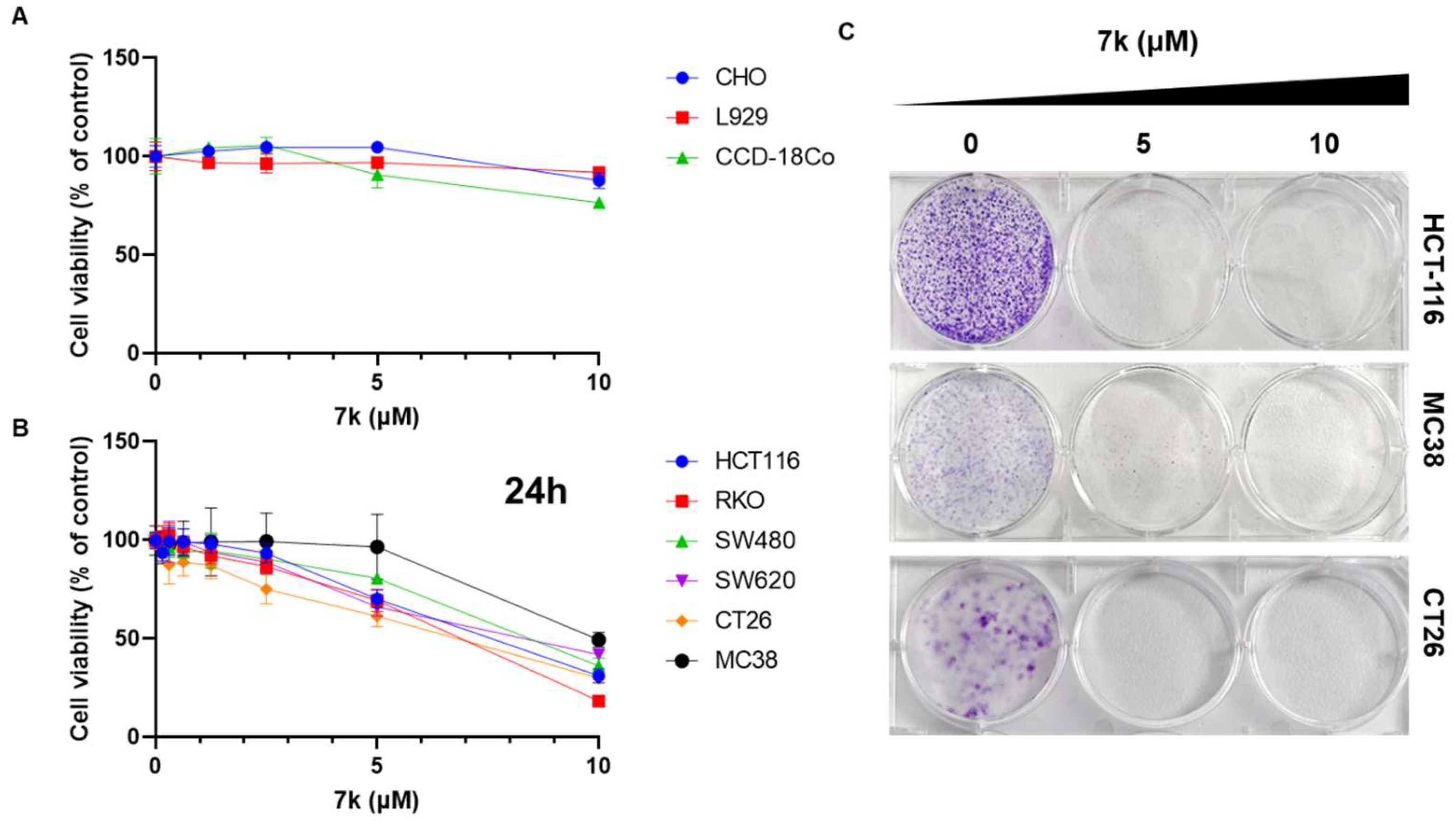
3.5. Antiproliferative Effects in Colorectal Cancer Cells and Not in Normal Cells
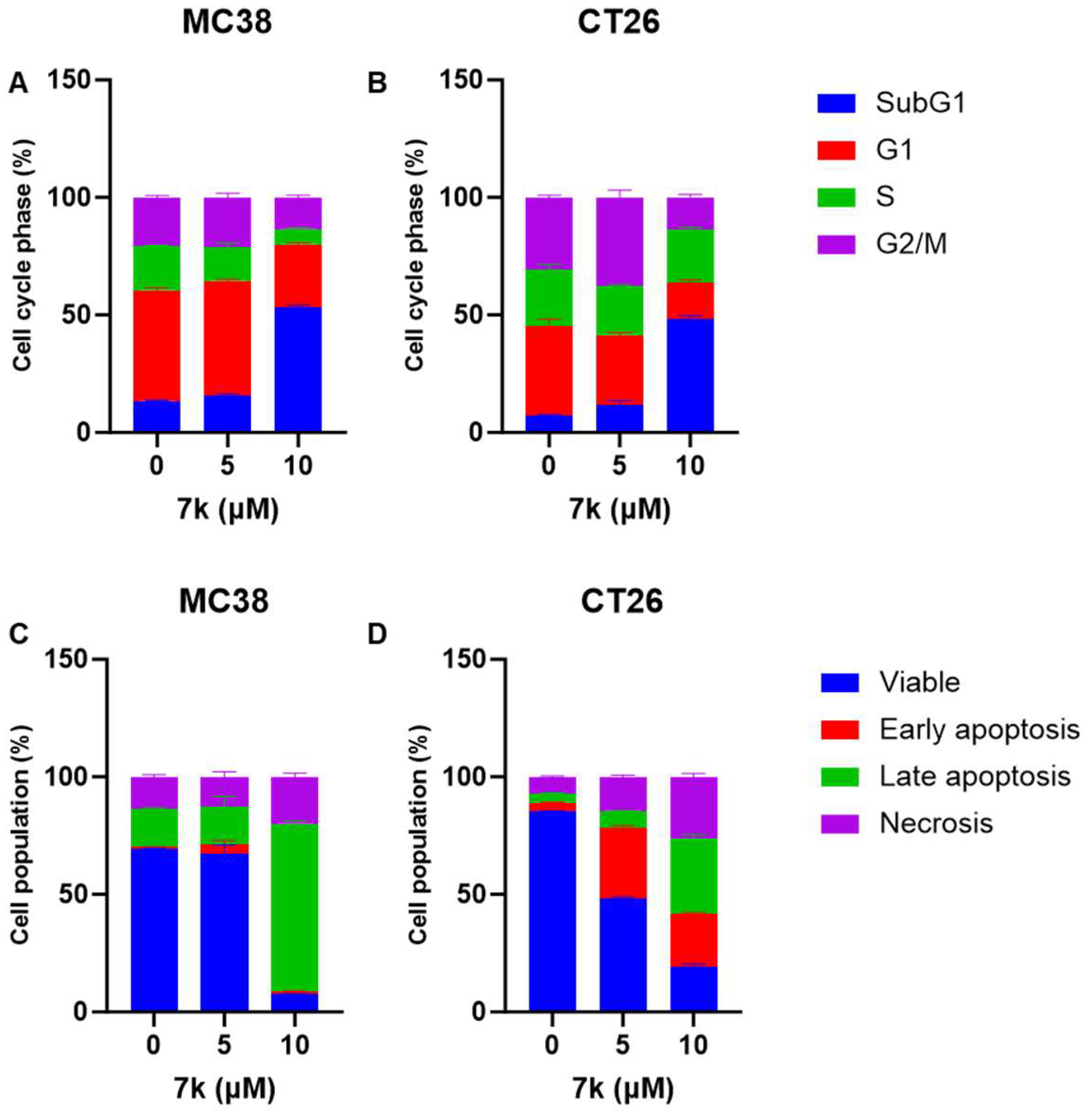
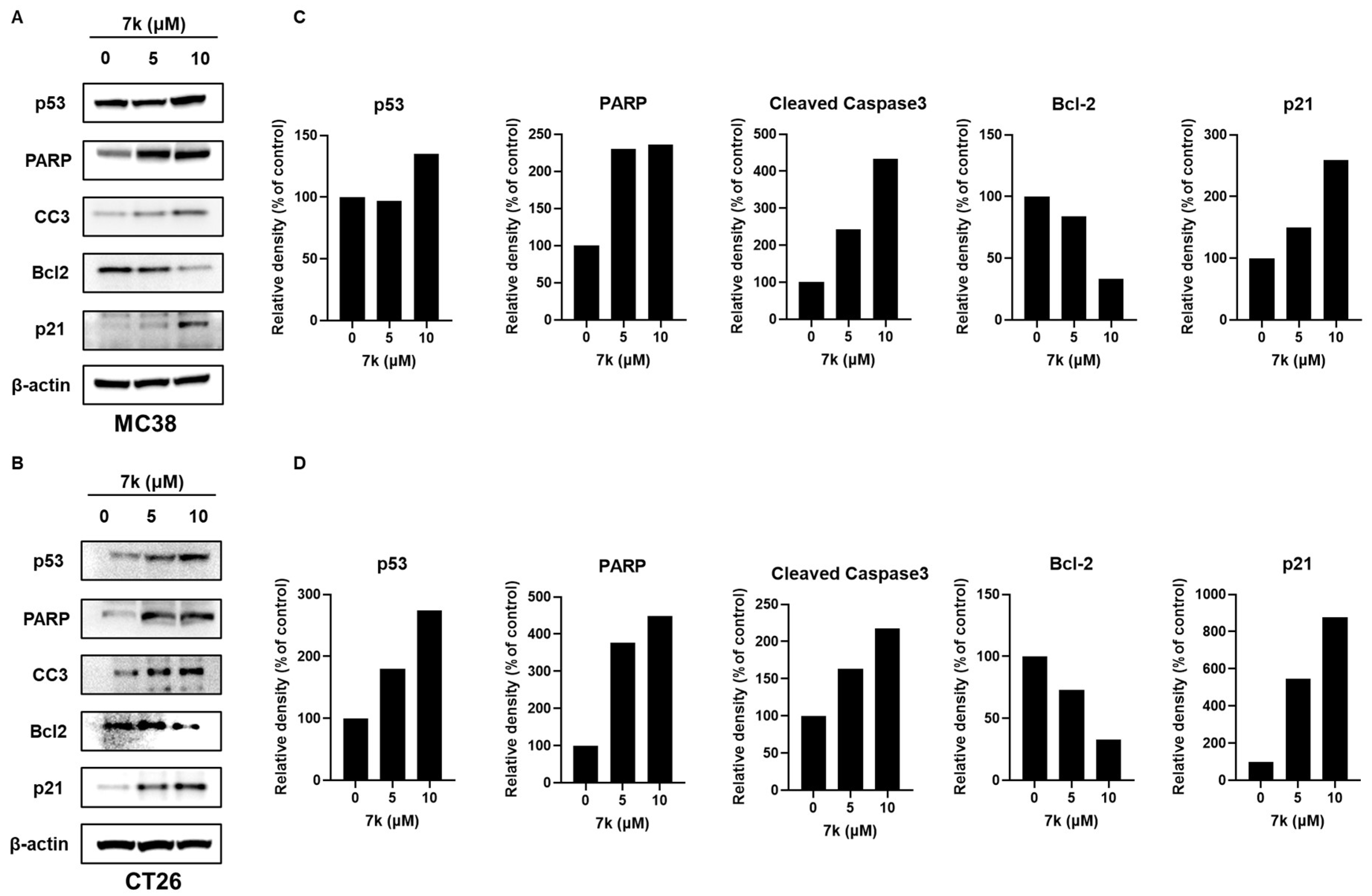
3.6. 7k-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Activation in Colorectal Cancer Cells
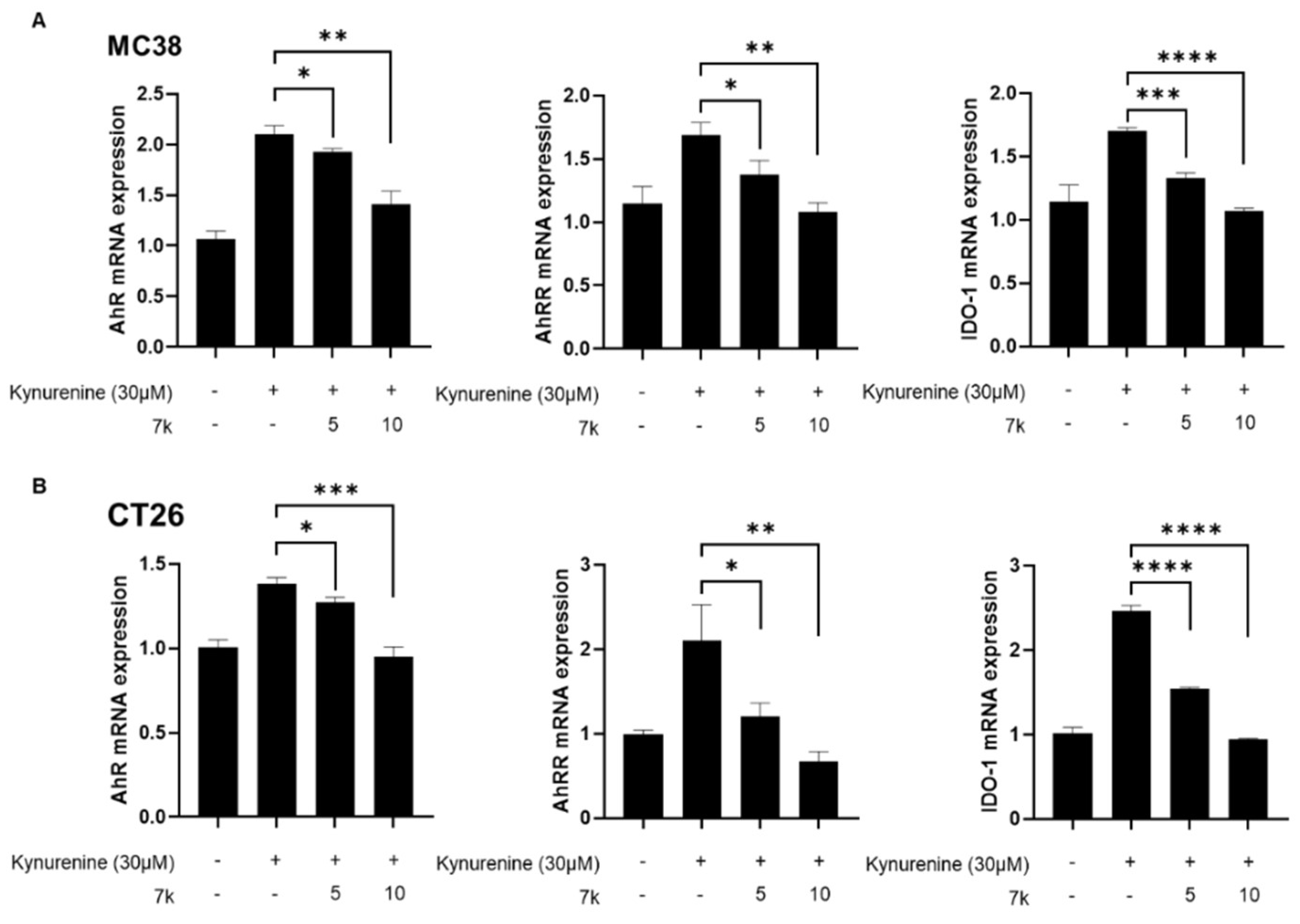
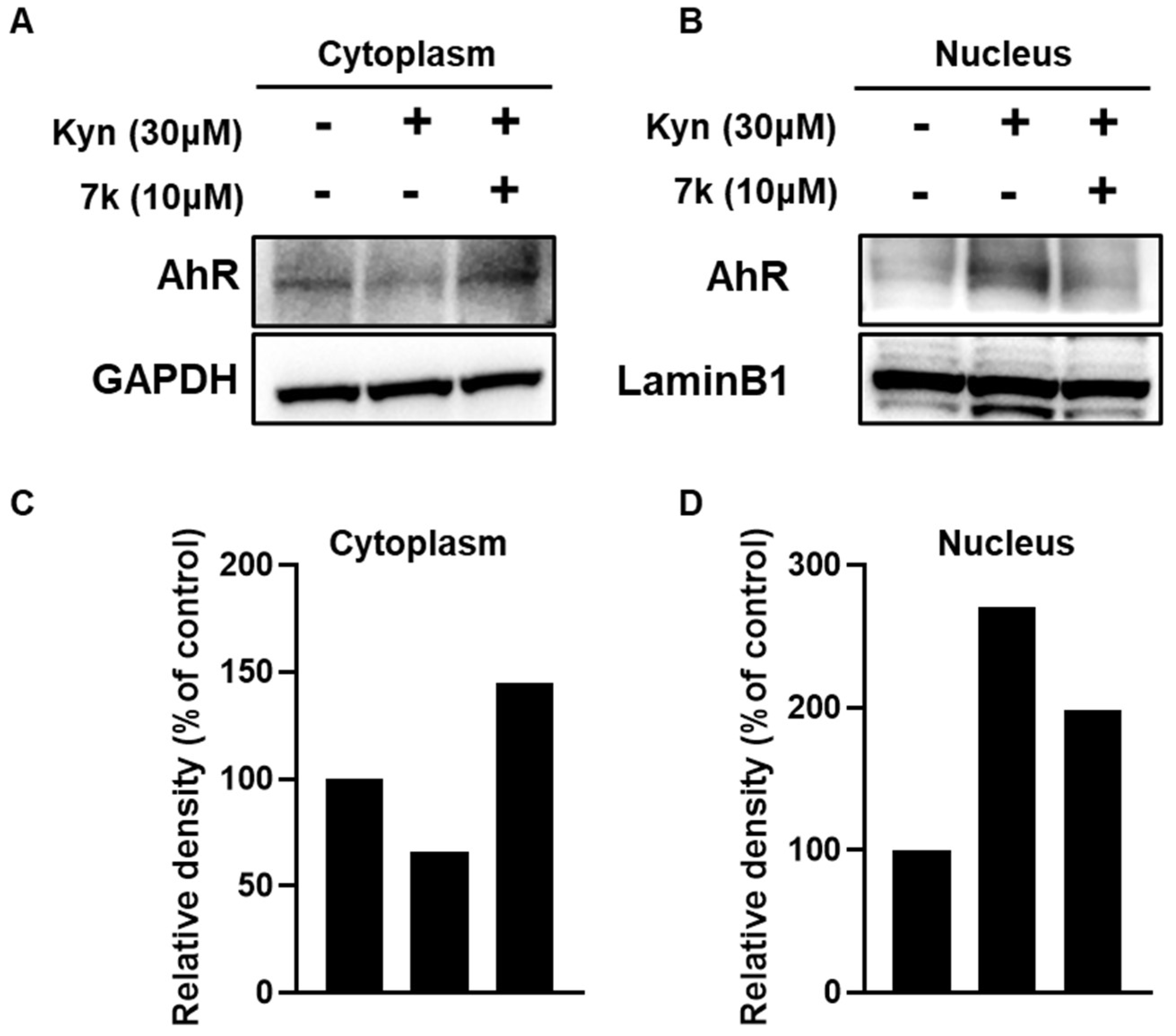
3.7. Inhibition of Kynurenine-Induced AhR Downstream Gene Expression and Its Nuclear Translocation by 7k
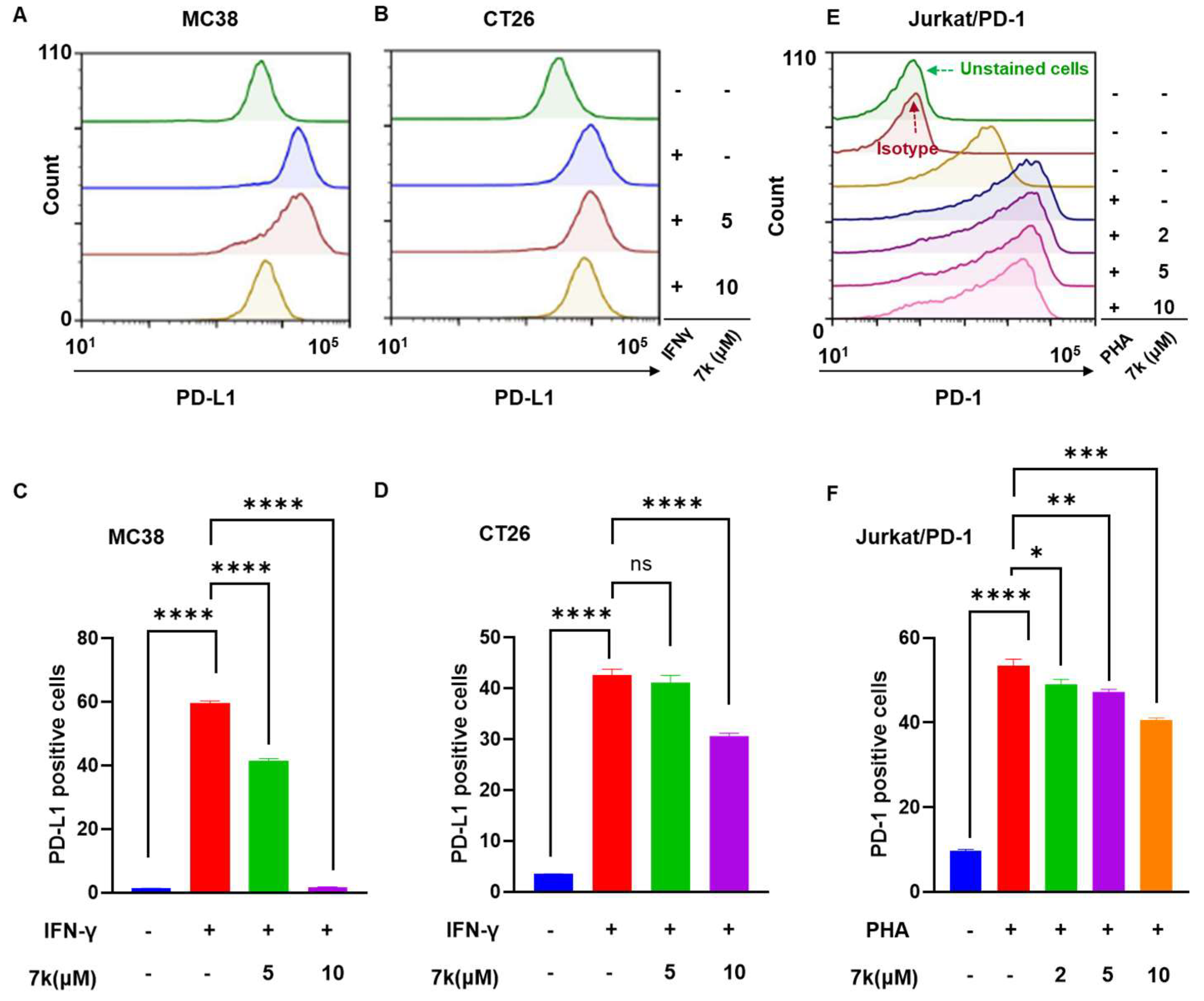
3.8. 7k-Mediated Suppression of PD-1/PD-L1 Protein Expression
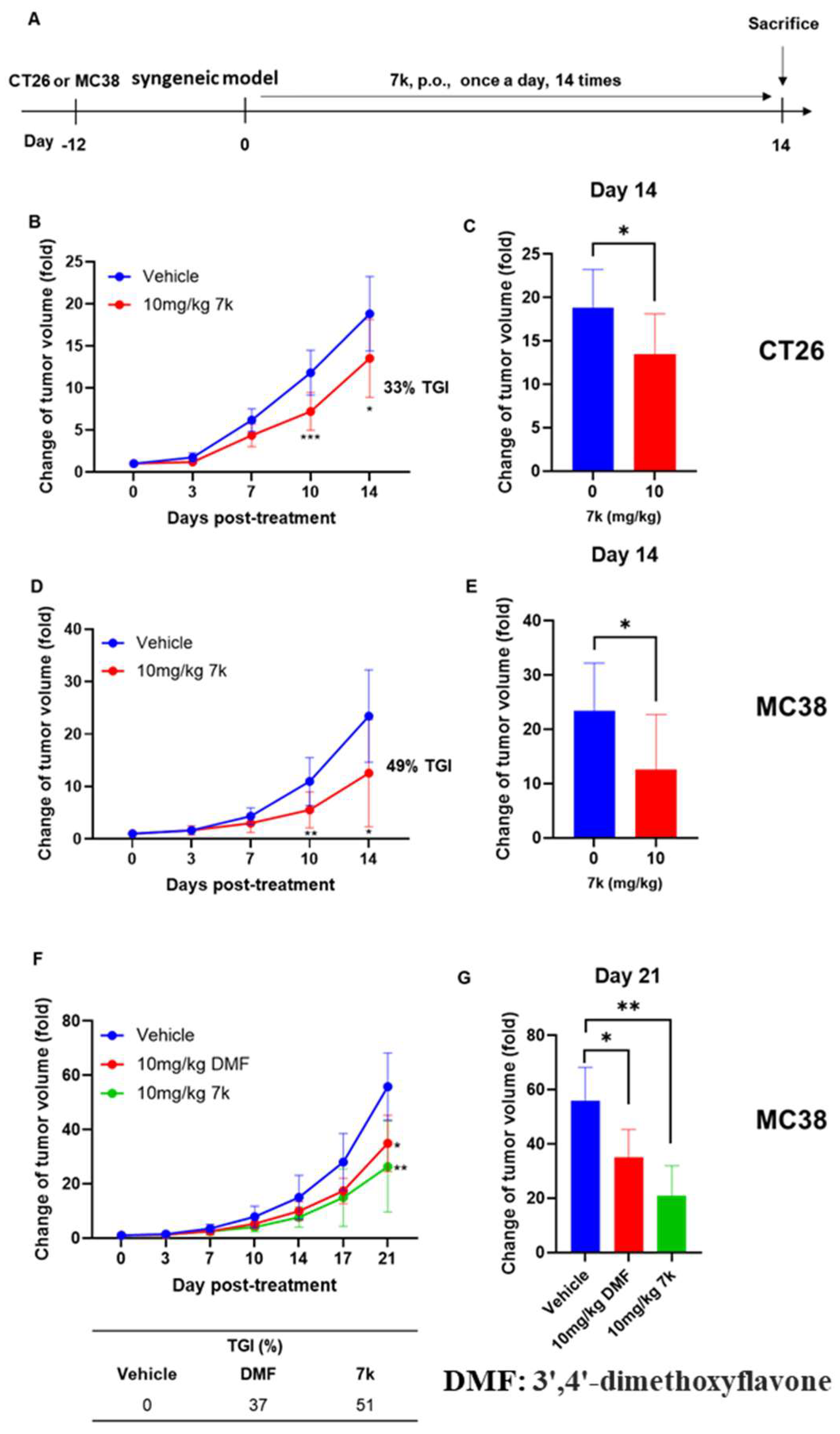
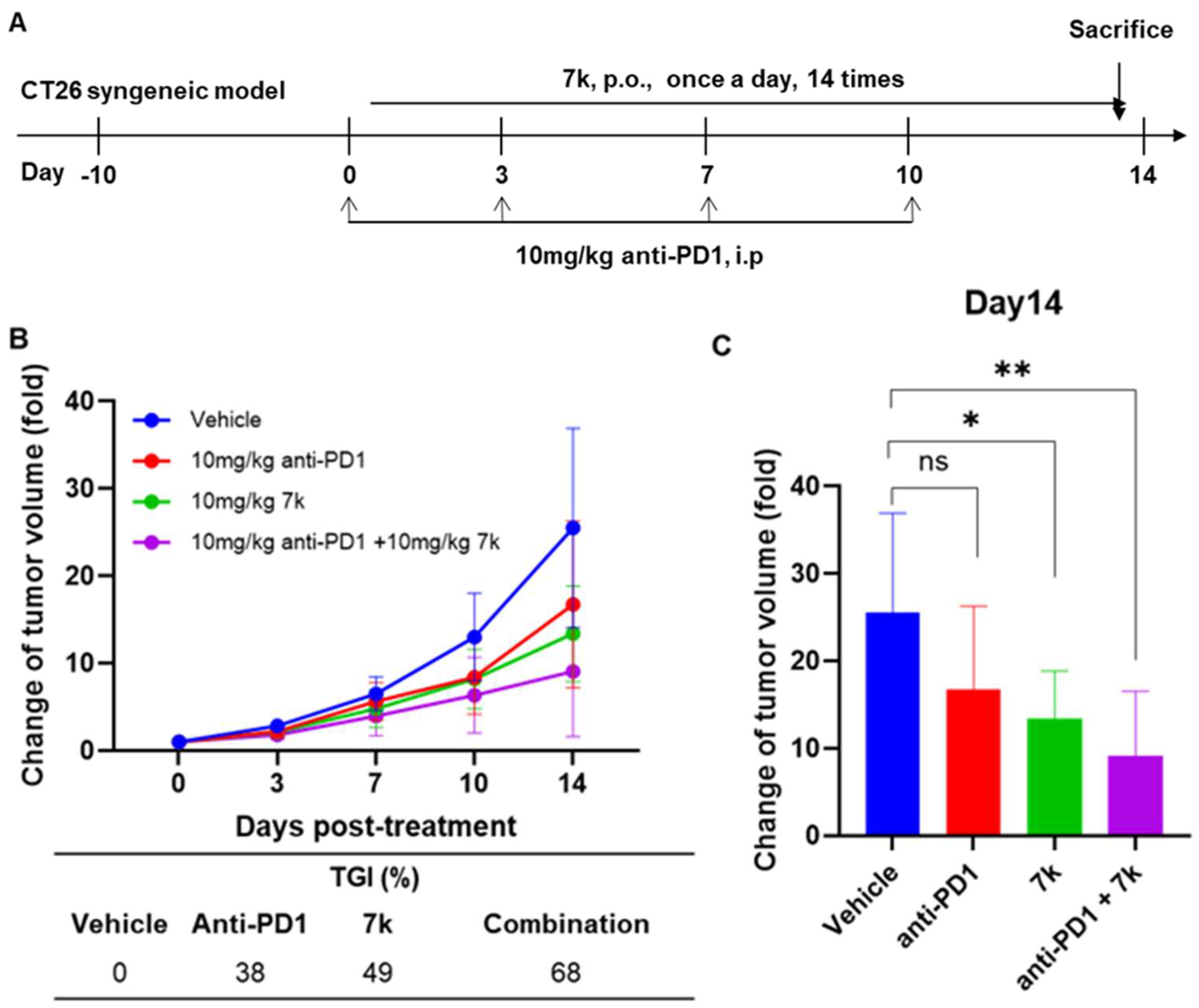
3.9. Antitumor Activity of 7k in Immunocompetent Mice with Colorectal Cancer
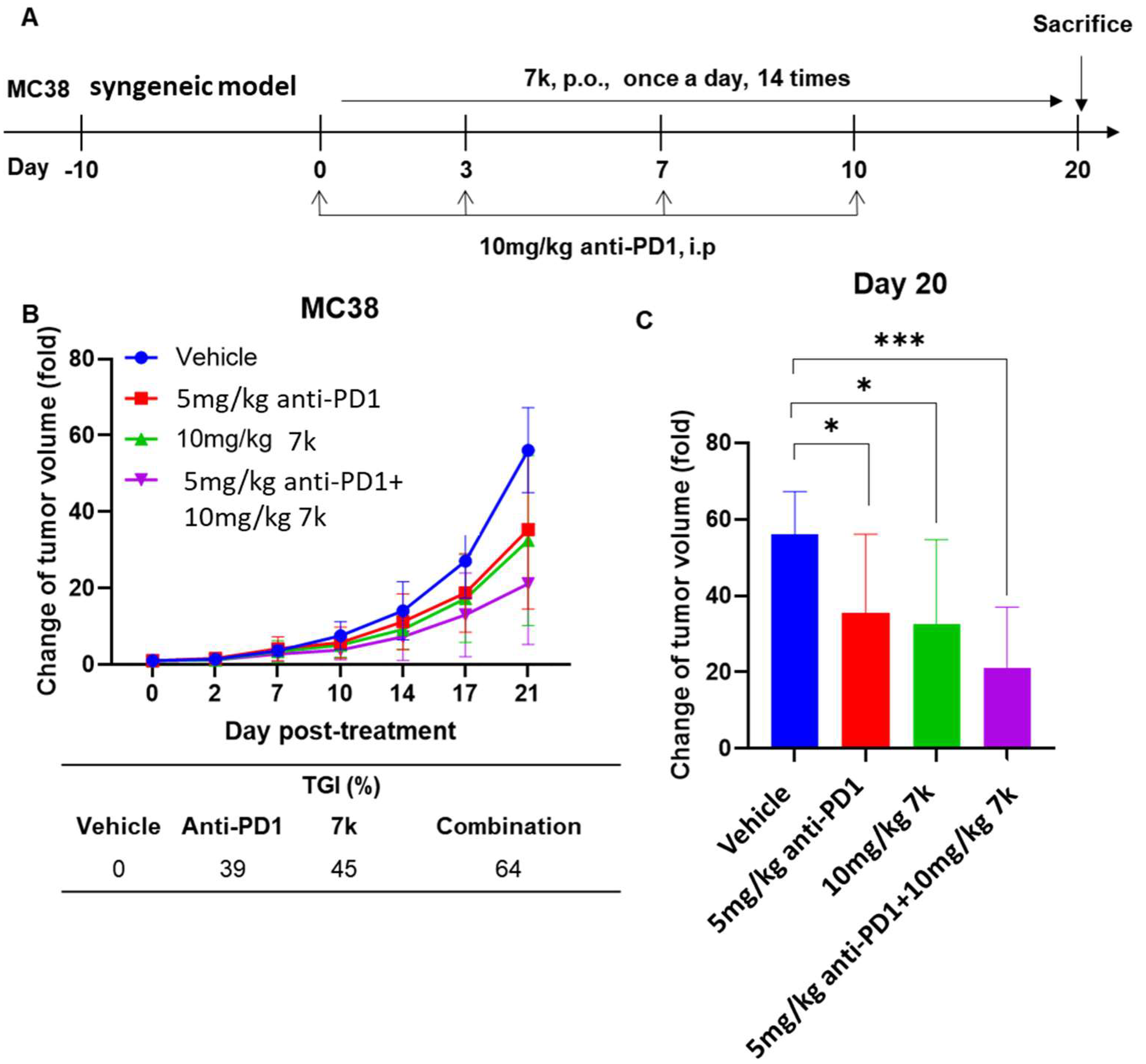
3.10. Antitumor Activity of Combination with 7k and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Anti-PD1 in Immunocompetent Mice with Colorectal Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, A.M.; Laversanne, M.; Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Parkin, D.M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. The GLOBOCAN 2022 cancer estimates: Data sources, methods, and a snapshot of the cancer burden worldwide. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 156, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.B.; Smyth, M.J. Immune surveillance of tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Sauer, A.G.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasová, M.; Procházková, J.; Tylichová, Z.; Fedr, R.; Ciganek, M.; Machala, M.; Dvořák, Z.; Vyhlídalová, B.; Zůvalová, I.; Ehrmann, J.; et al. Inhibition of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) Expression Disrupts Cell Proliferation and Alters Energy Metabolism and Fatty Acid Synthesis in Colon Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersten, D.C.; Sullivan, A.E.; Peet, D.J.; Whitelaw, M.L. bHLH-PAS proteins in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okey, A.B. Special contribution—An aryl hydrocarbon receptor odyssey to the shores of toxicology: The deichmann lecture, international congress of toxicology-XI. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 98, 5–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebert, D.W. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): “Pioneer member” of the basic-helix/loop/helix per-Arnt-sim (bHLH/PAS) family of “sensors” of foreign and endogenous signals. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 67, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soshilov, A.; Denison, M.S. Role of the Per/Arnt/Sim Domains in Ligand-dependent Transformation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 32995–33005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNatale, B.C.; Schroeder, J.C.; Perdew, G.H. Ah Receptor Antagonism Inhibits Constitutive and Cytokine Inducible IL6 Production in Head and Neck Tumor Cell Lines. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashibara, T.; Yamada, Y.; Mori, N.; Harasawa, H.; Sugahara, K.; Miyanishi, T.; Kamihara, S.; Tomonaga, M. Possible involvement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) leukemogenesis: Constitutive activation of AhR in ATL. Biochem. Bioph Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, D.H.; Monti, S. The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in normal and malignant B cell development. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opitz, C.A.; Litzenburger, U.M.; Sahm, F.; Ott, M.; Tritschler, I.; Trump, S.; Schumacher, T.; Jestaedt, L.; Schrenk, D.; Weller, M.; et al. An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature 2011, 478, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Dai, C.F.; Patankar, M.S.; Song, J.S.; Zheng, J. An endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand inhibits proliferation and migration of human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 340, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.T.; Chang, H.; Chen, P.H.; Lin, S.L.; Lin, P.P. Requirement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor overexpression for CYP1B1 up-regulation and cell growth in human lung adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, X.A.; Zhang, F.; Han, L.; Bao, G.; He, X.; Xu, Z. AhR expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Mol. Histol. 2013, 44, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolluri, S.K.; Jin, U.H.; Safe, S. Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in carcinogenesis and potential as an anti-cancer drug target. Arch Toxicol 2017, 91, 2497–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepechaeva, M.L.; Grishanova, A.Y. The Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) in Brain Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.A.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer: Friend and foe. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. Recent advances in the development of AHR antagonists in immuno-oncology. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Dong, W.; Fang, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, T.; Fiskesund, R.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Yin, X.; et al. Tumor-Repopulating Cells Induce PD-1 Expression in CD8+ T Cells by Transferring Kynurenine and AhR Activation. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 480–494.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashida, H.; Fukuda, I.; Yamashita, T.; Kanazawa, K. Flavones and flavonols at dietary levels inhibit a transformation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor induced by dioxin. Febs Lett. 2000, 476, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitano, A.; Cooke, M.; Pan, S.; Schultz, P.G.; Tellew, J.; Wan, Y.; Wan, X. Compounds that Expand Hematopoietic Stem Cells. U.S. Patent 9,580,426, 28 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stockinger, B.; Veldhoen, M. Inhibitors of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor for Modulating the Immune Response. WO Patent No. WO2009115807A1, 24 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Kim, M.; Pagire, S.H.; Dighe, M.; Choi, E.Y.; Bak, S.M.; Kim, E.Y.; et al. Identification of new aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) antagonists using a zebrafish model. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 115014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitano, A.; Cooke, M.; Goncalves, K.A.; Hoban, M. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Antagonists and Methods of Use Thereof for Treating Various Diseases. WO Patent No. WO2020051207, 12 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zorn, L.; Roehn, U.; Gutcher, I.; Roese, L.; Bader, B.; Kober, C.; Carretero, R.; Stoeckigt, D.; Platten, M. Sulphur substituted 3-oxo-2,3-dihydropyridazine-4-carboxamides. WO Patent No. WO2019101642, 31 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, A.C. N-Heteroaryl-tetrahydrocarbazolamines as AHR inhibitors and their preparation. WO Patent No. WO2020081636, 23 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio); University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Williams, D.R.; Kim, M.K.; Jung, Y.D.; Teraoka, H.; Park, H.C.; Choy, H.E.; et al. Cyp1a reporter zebrafish reveals target tissues for dioxin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 134, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitano, A.E.; Wang, J.; Romeo, R.; Bouchez, L.C.; Parker, A.E.; Sutton, S.E.; Walker, J.R.; Flaveny, C.A.; Perdew, G.H.; Denison, M.S.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonists promote the expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells. Science 2010, 329, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting p53 pathways: Mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yuan, J. Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6194–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, M.J.; McPherson, A.C.; Phelps, C.M.; Pandey, S.P.; Laughlin, C.R.; Shapira, J.H.; Medina Sanchez, L.; Rana, M.; Richie, T.G.; Mims, T.S.; et al. Dietary tryptophan metabolite released by intratumoral Lactobacillus reuteri facilitates immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. Cell 2023, 186, 1846–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, K.; Castro, A.C.; Cavanaugh, J.; Coma, S.; Walsh, M.; Tchaicha, J.; Syed, S.; Natarajan, P.; Manfredi, M.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of a Novel Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Inhibitor, IK-175, and Its Inhibitory Activity on Tumor Immune Suppression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenison, J.E.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, K.K.; Snyder, M.; Quintana, F.J.; Sherr, D.H. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor suppresses immunity to oral squamous cell carcinoma through immune checkpoint regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2012692118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer List | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
| AhR | AGCCGGTGCAGAAAACAGTAA | AGGCGGTCTAACTCTGTGTTC |
| AhRR | ACATACGCCGGTAGGAAGAGA | GGTCCAGCTCTGTATTGAGGC |
| IDO-1 | GCTTTGCTCTACCACATCCAC | CAGGCGCTGTAACCTGTGT |
| GAPDH | AGCTTGTCATCAACGGGAAG | TTTGATGTTAGTGGGGTCTCG |
| Compound | Structure | AhR Antagonist Activity at 100 nM | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7a | 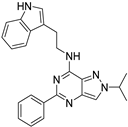 | + | |
| 7b | 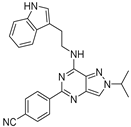 | ++ | |
| 7c | 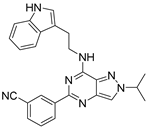 | ++++ | 170.93 |
| 7d | 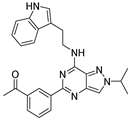 | - | |
| 7e | 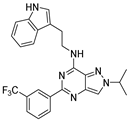 | - | |
| 7f | 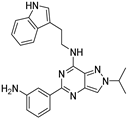 | - | |
| SR-1 (Reference) | +++ | 198.14 |
| Compound | Structure | AhR Antagonist Activity at 100 nM | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7c | 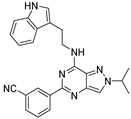 | ++++ | 170.93 |
| 7g | 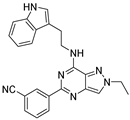 | +++ | |
| 7h | 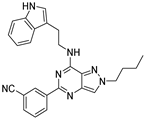 | +++ | |
| 7i | 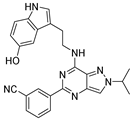 | - | |
| SR-1 (Reference) | +++ | 198.14 |
| Compound | Structure | AhR Antagonist Activity at 100 nM | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7c | 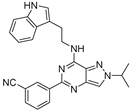 | ++++ | 170.93 |
| 7j | 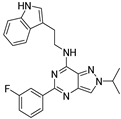 | ++++ | 412.86 |
| 7k | 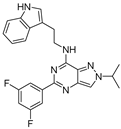 | +++++ | 13.72 |
| 7l | 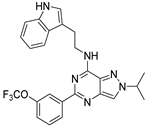 | +++ | 301.12 |
| 7m | 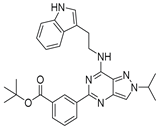 | - | |
| SR-1 (Reference) | +++ | 198.14 |
| Parameters | IV, 5 mg/kg | PO, 10 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|
| Tmax (h) Cmax (µg/mL) T1/2 (h) | NA NA 4.54 ± 0.65 | 0.67 ± 0.29 2.38 ± 1.25 3.77 ± 0.76 |
| AUCt (µg∙h/mL) AUC∞ (µg∙h/mL) CL (L/h/kg) Vss (L/kg) Ft (%) | 5.75 ± 0.74 5.86 ± 0.75 0.86 ± 0.11 3.91 ± 0.81 NA | 8.16 ± 3.67 8.23 ± 3.67 NA NA 71.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, B.W.; Lee, J.-E.; Jeon, D.B.; Kim, P.; Lee, G.B.; Parameswaran, S.; Jang, J.Y.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, G.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives as Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Antagonists for Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101359
Choi BW, Lee J-E, Jeon DB, Kim P, Lee GB, Parameswaran S, Jang JY, Chandrasekaran G, Jeong SY, Park G, et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives as Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Antagonists for Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101359
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Byeong Wook, Jae-Eon Lee, Da Bin Jeon, Pyeongkeun Kim, Gwi Bin Lee, Saravanan Parameswaran, Ji Yun Jang, Gopalakrishnan Chandrasekaran, So Yeon Jeong, Geumi Park, and et al. 2025. "Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives as Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Antagonists for Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101359
APA StyleChoi, B. W., Lee, J.-E., Jeon, D. B., Kim, P., Lee, G. B., Parameswaran, S., Jang, J. Y., Chandrasekaran, G., Jeong, S. Y., Park, G., Min, K.-j., Moon, H., Yoon, J., Heo, Y., Kim, D., Ahn, S. H., Choi, Y. J., Kim, S. S., Yang, J. Y., ... Ahn, J. H. (2025). Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives as Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Antagonists for Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101359








