Translational Advances in Lipid Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy: Current Status and Future Horizons
Abstract
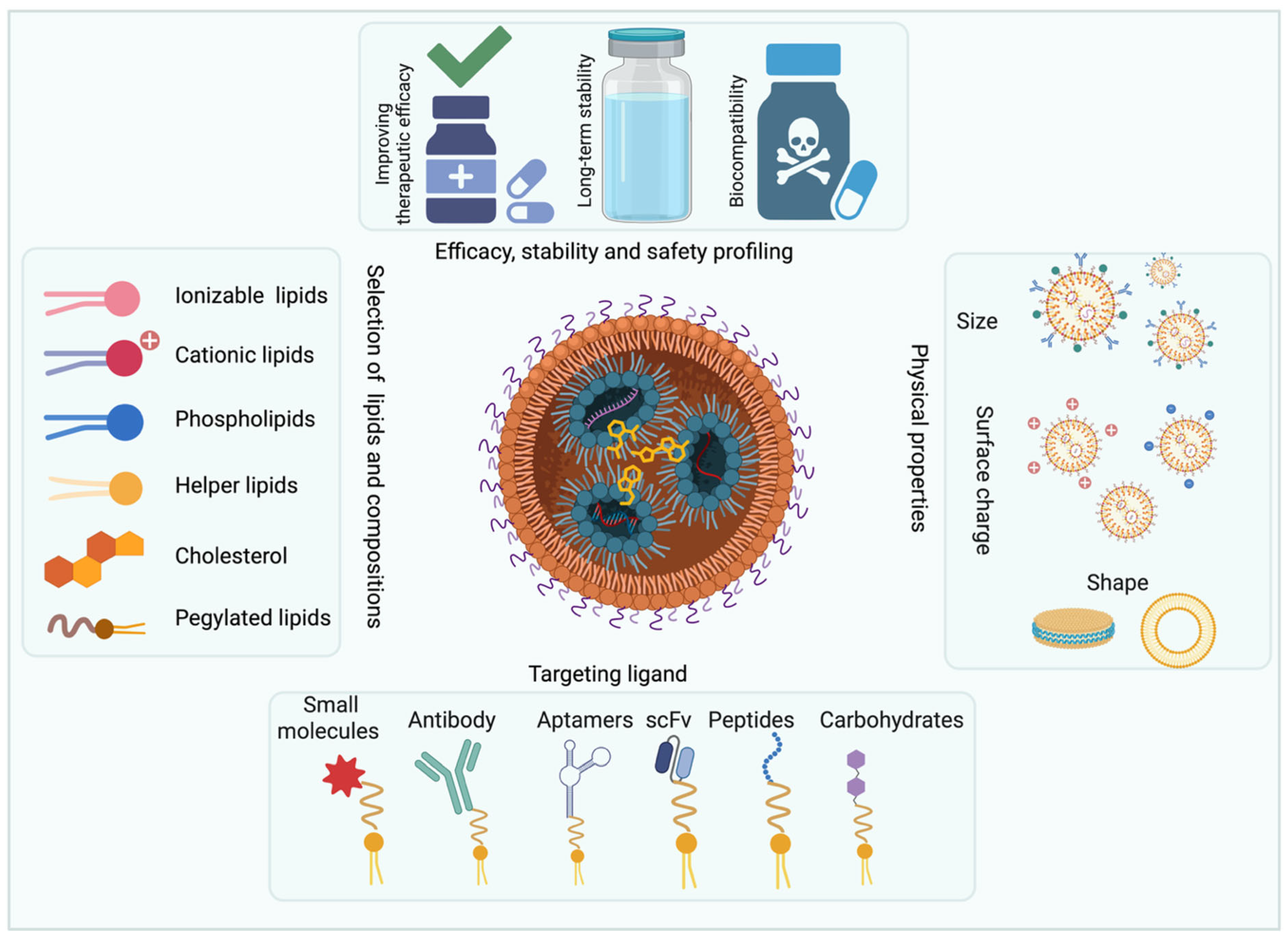
1. Introduction
2. LNP-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Melanoma
3. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Lung Cancer
4. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
5. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Liver Cancer
6. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
7. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
8. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Tumors and Neuroblastoma
9. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer
10. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Sarcoma
11. Lipid Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Leukemia
12. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.; Shan, X.; Ding, J.; Ma, B.; Li, B.; Huang, W.; Yang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J.; Song, C.; et al. Boosting RNA nanotherapeutics with V-ATPase activating non-inflammatory lipid nanoparticles to treat chronic lung injury. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, J.; Chakraborty, A.; Baysal, M.A.; Tsimberidou, A.M. Developments in nanotechnology approaches for the treatment of solid tumors. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 14, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurul, F.; Turkmen, H.; Cetin, A.E.; Topkaya, S.N. Nanomedicine: How nanomaterials are transforming drug delivery, bio-imaging, and diagnosis. Next Nanotechnol. 2025, 7, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, B.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, L.; Li, S. Targeting the tumor microenvironment with biomaterials for enhanced immunotherapeutic efficacy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lee, H.; Huang, R.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, W.; Chen, S. Harnessing nanotechnology for cancer treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1514890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, S.; Gonzalez, M.M.; Conejos-Sánchez, I.; Carreira, B.; Pozzi, S.; Acúrcio, R.C.; Satchi-Fainaro, R.; Florindo, H.F.; Vicent, M.J. Current hurdles to the translation of nanomedicines from bench to the clinic. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 500–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachamala, H.K.; Nakka, N.M.R.; Marepally, S. Advances in the preparation of lipid-based nanotechnologies: Contribution in expanding the horizons of therapeutic applications. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2025, 42, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachamala, H.K.; Nakka, N.M.R.; Angom, R.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Pal, K.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Dual Targeting of Syndecan-1 and Glucose Transporter-1 with a Novel Lipid-Based Delivery System Enhances Therapeutic Efficacy and Overcomes Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 160–163.e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nele, V.; Campani, V.; Alia Moosavian, S.; De Rosa, G. Lipid nanoparticles for RNA delivery: Self-assembling vs. driven-assembling strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 208, 115291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, N.; Mandal, T.K.; Joo, S.W. The Impact of COVID-19 on RNA Therapeutics: A Surge in Lipid Nanoparticles and Alternative Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachamala, H.K.; Madamsetty, V.S.; Angom, R.S.; Nakka, N.M.; Dutta, S.K.; Wang, E.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Pal, K. Targeting mTOR and survivin concurrently potentiates radiation therapy in renal cell carcinoma by suppressing DNA damage repair and amplifying mitotic catastrophe. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachamalla, H.K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Ahmad, A.; Sridharan, K.; Madamsetty, V.S.; Mondal, S.K.; Wang, E.; Dutta, S.K.; Jan, B.L.; Jinka, S.; et al. Enriched Pharmacokinetic Behavior and Antitumor Efficacy of Thymoquinone by Liposomal Delivery. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachamalla, H.K.; Mondal, S.K.; Deshpande, S.S.; Sridharan, K.; Javaji, K.; Jaggarapu, M.M.C.S.; Jinka, S.; Bollu, V.; Misra, S.; Banerjee, R. Efficient anti-tumor nano-lipoplexes with unsaturated or saturated lipid induce differential genotoxic effects in mice. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Keszei, A.F.A.; Kothari, S.; Liu, H.; Pan, A.; Kim, P.; Bu, J.; Kamanzi, A.; Dai, D.L.; Mazhab-Jafari, M.T.; et al. Lipid-siRNA Organization Modulates the Intracellular Dynamics of Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 10430–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anindita, J.; Tanaka, H.; Yamakawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Matsumoto, C.; Ishizaki, K.; Oyama, T.; Suzuki, S.; Ueda, K.; Higashi, K.; et al. The Effect of Cholesterol Content on the Adjuvant Activity of Nucleic-Acid-Free Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Teerdhala, S.V.; Padilla, M.S.; Joseph, R.A.; Li, J.J.; Haley, R.M.; Mitchell, M.J. Lipid nanoparticle-mediated RNA delivery for immune cell modulation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2024, 54, e2451008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Dai, Y. mRNA vaccines and SiRNAs targeting cancer immunotherapy: Challenges and opportunities. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wu, D.; Gu, Z.; Wang, D.; Ten Dijke, P. Lipid-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy. MedComm 2023, 4, e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, K.; Kotla, N.G.; Tunki, L.; Jayaraj, A.; Bhargava, S.K.; Hu, H.; Bonam, S.R.; Kurapati, R. Recent Advances in the Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of mRNA Vaccines. Vaccines 2023, 11, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Kon, E.; Sharma, P.; Peer, D. Endosomal escape: A bottleneck for LNP-mediated therapeutics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2307800120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargason, A.M.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. The evolution of commercial drug delivery technologies. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, G.; Rachamalla, H.K.; Arjunan, P.; Periyasami, Y.; M, S.; Thangavel, S.; Mohankumar, K.M.; Moorthy, M.; Velayudhan, S.R.; Srivastava, A. Optimization of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirion production in lentivirus backbone with a novel liposomal system. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 840727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Fobian, S.-F.; Gurrieri, E.; Amin, M.; D’Agostino, V.G.; Falahati, M.; Zalba, S.; Debets, R.; Garrido, M.J.; Saeed, M.; et al. Lipid-based nanosystems: The next generation of cancer immune therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, E.M.; Bahr, D.; Rachamala, H.K.; Madamsetty, V.S.; Shreeder, B.; Bagaria, S.; Escobedo, A.L.; Reid, J.M.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Liposomal Phenylephrine Nanoparticles Enhance the Antitumor Activity of Intratumoral Chemotherapy in a Preclinical Model of Melanoma. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 3412–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc, P.; Dams-Kozlowska, H.; Guzniczak, N.; Florczak-Substyk, A. Application of nanoparticles to target tumor blood vessels as a promising cancer treatment strategy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 186, 118038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Xie, Y.; Qin, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, C. Endo/Lysosomal-Escapable Lipid Nanoparticle Platforms for Enhancing mRNA Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadian Farsani, A.; Mokhtari, N.; Nooraei, S.; Bahrulolum, H.; Akbari, A.; Farsani, Z.M.; Khatami, S.; Ebadi, M.S.; Ahmadian, G. Lipid nanoparticles: The game-changer in CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.; Tam, Y.Y.; Cullis, P.R. Lipid nanoparticles for short interfering RNA delivery. Adv. Genet. 2014, 88, 71–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; More, K.R.; Ojha, A.; Jackson, C.B.; Quinlan, B.D.; Li, H.; He, W.; Farzan, M.; Pardi, N.; Choe, H. Effect of mRNA-LNP components of two globally-marketed COVID-19 vaccines on efficacy and stability. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, G.; Rachamalla, H.K.; Arjunan, P.; Karuppusamy, K.V.; Periyasami, Y.; Mohan, A.; Subramaniyam, K.; M, S.; Rajendran, V.; Moorthy, M.; et al. SMART-lipid nanoparticles enabled mRNA vaccine elicits cross-reactive humoral responses against the omicron sub-variants. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman Gonzalez, V.; Grunenberger, A.; Nicoud, O.; Czuba, E.; Vollaire, J.; Josserand, V.; Le Guével, X.; Desai, N.; Coll, J.-L.; Divita, G.; et al. Enhanced CRISPR-Cas9 RNA system delivery using cell penetrating peptides-based nanoparticles for efficient In Vitro and In Vivo applications. J. Control. Release 2024, 376, 1160–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Xia, G.; Adilijiang, N.; Li, Y.; Hou, Z.; Fan, Z.; Li, J. Recent Advances in Targeted Drug Delivery Strategy for Enhancing Oncotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, E.; Ahmed, A.; Naguib, Y.W. Advances in mRNA LNP-Based Cancer Vaccines: Mechanisms, Formulation Aspects, Challenges, and Future Directions. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, S.; Yang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Tang, R.; Wang, K. Targeted nano-drug delivery systems for tumor immunotherapy. J. Pharm. Anal. 2025, 15, 101408 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Qi, J.; Deng, W.; Hu, J.; Hasan, M.W.; Deng, F.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Z.; Deng, W.; et al. A lyophilizable LNP vaccine enables STING-reinforced postoperational adjuvant immunotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, A.E.I.; Filtjens, J.; Brabants, E.; Kancheva, D.; Debraekeleer, A.; Brughmans, J.; Jacobs, L.; Bardet, P.M.R.; Knetemann, E.; Lefesvre, P.; et al. Intratumoral delivery of lipid nanoparticle-formulated mRNA encoding IL-21, IL-7, and 4-1BBL induces systemic anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, D.; Wang, J.; Lim, J.M.; Xie, X.; Yu, X.; Zhao, D.; Maza, P.A.M.; Wang, Y.; Cyril-Remirez, D.; Young, K.H.; et al. Lipid nanoparticles deliver DNA-encoded biologics and induce potent protective immunity. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Han, H.; Yan, Z.; Lu, Y.; He, B.; Zhang, Q. Lipid-based nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy. Med. Rev. 2023, 3, 230–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Hu, C.; Chen, T.; Zhao, T.; Dai, X. Advancements in Cell Membrane-Derived Biomimetic Nanotherapeutics for Breast Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 6059–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujel, R.; Enkmann, V.; Burgstaller, H.; Maharjan, R. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Strategies for Targeted Delivery and Enhanced Stability of RNA-Based Lipid Nanoparticle Cancer Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samathoti, P.; Kumarachari, R.K.; Bukke, S.P.N.; Rajasekhar, E.S.K.; Jaiswal, A.A.; Eftekhari, Z. The role of nanomedicine and artificial intelligence in cancer health care: Individual applications and emerging integrations-a narrative review. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, K.; Jiang, T.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ying, H.; Yu, H.; Lu, J.; Lin, J.; Ouyang, D. Artificial intelligence-driven rational design of ionizable lipids for mRNA delivery. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ma, S.; Cui, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Gong, F.; Golubovic, A.; Zhou, M.; Wang, K.C.; Varley, A.; et al. AGILE platform: A deep learning powered approach to accelerate LNP development for mRNA delivery. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Data-balanced transformer for accelerated ionizable lipid nanoparticles screening in mRNA delivery. Brief Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, R.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, K.; Han, H.-K.; Jeong, S.H. Machine learning-driven optimization of mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine quality with XGBoost/Bayesian method and ensemble model approaches. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomari, M.M.; Ghantabpour, T.; Pourgholam, N.; Rostami, N.; Hatfield, S.M.; Namazifar, F.; Abkhiz, S.; Eslami, S.S.; Ramezanpour, M.; Darestanifarahani, M.; et al. Breaking barriers: Smart vaccine platforms for cancer immunomodulation. Cancer Commun. 2025, 45, 529–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, C.; Videira, M. Dual Approaches in Oncology: The Promise of siRNA and Chemotherapy Combinations in Cancer Therapies. Onco 2025, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimbo, J.F.; van Diest, E.; Murphy, D.E.; Ashoti, A.; Evers, M.J.W.; Narayanavari, S.A.; Vaz, D.P.; Rijssemus, H.; Zotou, C.; Saber, N.; et al. T cell-specific non-viral DNA delivery and In Vivo CAR-T generation using targeted lipid nanoparticles. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e011759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, G.T.; Mahiny, A.J.; Vlatkovic, I. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: Platforms and current developments. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1850–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Khezrabad, S.; Aghdasia, M.; Zare-Zardini, H.; Eslami, H.; Eskandari, F. CRISPR-Cas9-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles: A Promising Strategy for Targeted Gene Editing and Therapy. BioNanoScience 2025, 15, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylot, V.; Le, T.K.; Taïeb, D.; Rocchi, P.; Colleaux, L. Between hope and reality: Treatment of genetic diseases through nucleic acid-based drugs. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T.L.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Matsuda, D.; Riener, R.; Wang, A.; Li, J.J.; Soldevila, F.; Chu, D.S.H.; Nguyen, D.P.; et al. In Vivo CAR T cell generation to treat cancer and autoimmune disease. Science 2025, 388, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, N.; Senti, M.E.; Schiffelers, R.M. Lipid Nanoparticles for Nucleic Acid Delivery Beyond the Liver. Hum. Gene Ther. 2024, 35, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzun, T.; Moses, A.S.; Diba, P.; Sattler, A.L.; Taratula, O.R.; Sahay, G.; Taratula, O.; Marks, D.L. From Bench to Bedside: Implications of Lipid Nanoparticle Carrier Reactogenicity for Advancing Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomski, D.; Ji, A.; Kuzman, D.; Clenet, D.; Hieb, A.; Roberts, S.W.; Berry, J.; Lentes, C.; Weusten, J.; MacArthur, K.; et al. Predictive stability in biopharmaceuticals and vaccines: Perspectives and recommendations towards accelerating patient access. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 114, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X.; Guo, B.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F. Engineered lipid nanoparticles with synergistic dendritic cell targeting and enhanced endosomal escape for boosted mRNA cancer vaccines. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 34, 102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gong, L.; Wang, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, W. Recent Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivery of mRNA. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, T.; Dezfouli, S.A.; Pandey, L.M.; Uludag, H. siRNA Functionalized Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) in Management of Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfutaimani, A.S.; Alharbi, N.K.; Alahmari, A.S.; Alqabbani, A.A.; Aldayel, A.M. Exploring the landscape of Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs): A comprehensive review of LNPs types and biological sources of lipids. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 8, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parot, J.; Mehn, D.; Jankevics, H.; Markova, N.; Carboni, M.; Olaisen, C.; Hoel, A.D.; Sigfúsdóttir, M.S.; Meier, F.; Drexel, R.; et al. Quality assessment of LNP-RNA therapeutics with orthogonal analytical techniques. J. Control. Release 2024, 367, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P.; Blakney, A.K. Immune response to the components of lipid nanoparticles for ribonucleic acid therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 85, 103049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomani, A.; Saraswat, A.; Zhang, Y.; Parenky, A.C.; Kuo, C.-T.J.; Brown, H.; Hartford, S.; Rayaprolu, B.; Singh Bhupender Bhalla, A.; Shameem, M. RNA-lipid nanoparticle therapeutics for women’s health. Front. Nanotechnol. 2025, 7, 1475969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoudi, L.; Fobian, S.-F.; Oei, A.L.; Amin, M.; Jaafari, M.R.; ten Hagen, T.L.M. Applications of biomimetic nanoparticles in breast cancer as a blueprint for improved next-generation cervical cancer therapy. Nano Today 2023, 53, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haripriyaa, M.; Suthindhiran, K. Pharmacokinetics of nanoparticles: Current knowledge, future directions and its implications in drug delivery. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Kim, Y.; Kim, E.H.; Suk, J.S.; Yang, Y. mRNA: A promising platform for cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 199, 114993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe, C.A.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Cheng, M.H.Y.; An, K.; Witzigmann, D.; Cullis, P.R. Rational design of lipid nanoparticles for enabling gene therapies. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2025, 33, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, M.C.P.; Kont, A.; Kowalski, P.S.; O’Driscoll, C.M. Design of lipid-based nanoparticles for delivery of therapeutic nucleic acids. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.L. Nanomaterial-Based Molecular Imaging in Cancer: Advances in Simulation and AI Integration. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosma, M.; Mocan, T.; Sabau, L.I.; Pop, T.; Mosteanu, O.; Mocan, L. A Narrative Review on Functionalized Nanoparticles for the Treatment and Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, K.; Srinivasan, S.; Shanmugam, A. Review of the efficacy of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 5, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Melanoma of the Skin. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Tani, H. Recent Advances and Prospects in RNA Drug Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.A.; Gowda, R.; Sharma, A.; Park, E.J.; Adair, J.; Kester, M.; Smith, N.B.; Robertson, G.P. Targeting V600EB-Raf and Akt3 using nanoliposomal-small interfering RNA inhibits cutaneous melanocytic lesion development. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7638–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Nakase, M.; Inui, M.; Nakamura, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Tagawa, T. Bax mRNA therapy using cationic liposomes for human malignant melanoma. J. Gene Med. 2008, 10, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villares, G.J.; Zigler, M.; Wang, H.; Melnikova, V.O.; Wu, H.; Friedman, R.; Leslie, M.C.; Vivas-Mejia, P.E.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; et al. Targeting melanoma growth and metastasis with systemic delivery of liposome-incorporated protease-activated receptor-1 small interfering RNA. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9078–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Lung and Bronchus Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Canale, M.; Andrikou, K.; Priano, I.; Cravero, P.; Pasini, L.; Urbini, M.; Delmonte, A.; Crinò, L.; Bronte, G.; Ulivi, P. The Role of TP53 Mutations in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical Significance and Implications for Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahiman, N. Updates and current states on liposomal vehicles for tumor targeting: Precision therapy in the spotlight. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wong, B.C.K.; Chen, H.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Kashif Riaz, M.; Tyagi, D.; Lin, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Pulmonary delivery of triptolide-loaded liposomes decorated with anti-carbonic anhydrase IX antibody for lung cancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.L.; Ju, R.J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Fu, M.; Liu, J.J.; Gu, L.Y.; Li, X.T.; Cheng, L. Application of multifunctional targeting epirubicin liposomes in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7433–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Bhattacharyya, J.; Sagar, M.V.; Chaudhuri, A. Liposomally encapsulated CDC20 siRNA inhibits both solid melanoma tumor growth and spontaneous growth of intravenously injected melanoma cells on mouse lung. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.M.; Minko, T. Pharmacokinetics of inhaled nanotherapeutics for pulmonary delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 222–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarnick, E.; Andriyanov, A.V.; Han, H.; Eyal, S.; Barenholz, Y. PEGylated Liposomes Remotely Loaded with the Combination of Doxorubicin, Quinine, and Indocyanine Green Enable Successful Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tumors. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. In Vivo Analysis Techniques for Antibody Drug: Recent Advances and Methodological Insights. J. Pharm. Anal. 2025, 15, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Colorectal Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Xin, H.; Chang, Z.; Niu, M. Multifaceted Applications of Nanomaterials in Colorectal Cancer Management: Screening, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 7271–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chang, C.H.; Lan, K.L.; Ting, G.; Lee, T.W. Therapeutic efficacy of 188Re-liposome in a C26 murine colon carcinoma solid tumor model. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, B.; Phan, T.S.; Haddad, W.M.; Cason, A.; Mullis, J.; Price, L.; Bailey, J.M. Replicating human expertise of mechanical ventilation waveform analysis in detecting patient-ventilator cycling asynchrony using machine learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 97, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, T.; Porter, T.M. Thermosensitive liposomes for localized delivery and triggered release of chemotherapy. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, H.; Oryani, M.A.; Rezagholinejad, N.; Esparham, A.; Tajaldini, M.; Karimi-Shahri, M. RGD peptide in cancer targeting: Benefits, challenges, solutions, and possible integrin-RGD interactions. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, C.M.; Wu, Y.T.; Chen, L.C.; Ho, C.L.; Chang, T.J.; Lee, T.W.; Tsai, T.H. Correlation between radioactivity and chemotherapeutics of the (111)In-VNB-liposome in pharmacokinetics and biodistribution in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winifred Nompumelelo Simelane, N.; Abrahamse, H. Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery Systems in Photodynamic Therapy of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, T.; Yang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, N.; Garg, S. Development and evaluation of oxaliplatin and irinotecan co-loaded liposomes for enhanced colorectal cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, H.J.; Green, J.J.; Tzeng, S.Y. Cancer-Targeting Nanoparticles for Combinatorial Nucleic Acid Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1901081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Fan, J.; Deng, L.; Huang, B.; Zhou, B. Antitumor efficacy of cytosine deaminase-armed vaccinia virus plus 5-fluorocytosine in colorectal cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, N.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Jiang, H.; Piao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Co-delivery of IOX1 and doxorubicin for antibody-independent cancer chemo-immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, H.C.; Barten-van Rijbroek, A.D.; van der Wurff-Jacobs, K.M.G.; Bos, C.; Moonen, C.T.W.; Deckers, R. Tumor Drug Distribution After Local Drug Delivery by Hyperthermia, In Vivo. Cancers 2019, 11, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/livibd.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Sadrinasab, S.; Saket, S.; Pourmohammadi, N.; Khosravi, F.; Fakhr, M.S. Modern therapeutic approaches for hepatic tumors: Progress, limitations, and future directions. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Hynynen, K.; Allen, C. To heat or not to heat: Challenges with clinical translation of thermosensitive liposomes. J. Control. Release 2017, 249, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, M.A.; Filipczak, N.; Torchilin, V.P. Advances with Lipid-Based Nanosystems for siRNA Delivery to Breast Cancers. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Pan, G.; Ni, J.; Xie, F.; Jiang, B.; Wei, L.; Gao, J.; Zhou, W. Enhanced doxorubicin delivery to hepatocellular carcinoma cells via CD147 antibody-conjugated immunoliposomes. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliariello, V.; Masarone, M.; Armenia, E.; Giudice, A.; Barbarisi, M.; Caraglia, M.; Barbarisi, A.; Persico, M. Chitosan-coated liposomes loaded with butyric acid demonstrate anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyk, P.; Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Ziegler-Borowska, M.; Larrosa, I.; Goslinski, T. Sorafenib-Drug Delivery Strategies in Primary Liver Cancer. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Guo, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Bao, M. Prognostic genes of triple-negative breast cancer identified by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmuir, K.J.; Haynes, S.M.; Baratta, J.L.; Kasabwalla, N.; Robertson, R.T. Liposomal delivery of doxorubicin to hepatocytes In Vivo by targeting heparan sulfate. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opanasopit, P.; Sakai, M.; Nishikawa, M.; Kawakami, S.; Yamashita, F.; Hashida, M. Inhibition of liver metastasis by targeting of immunomodulators using mannosylated liposome carriers. J. Control. Release 2002, 80, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, D.; Cordeiro, R.A.; Mendonça, P.V.; Serra, A.C.; Coelho, J.F.J.; Faneca, H. Glycopolymers Mediate Suicide Gene Therapy in ASGPR-Expressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells in Tandem with Docetaxel. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Mythreye, K.; Lee, N.Y. Strength and duration of GIPC-dependent signaling networks as determinants in cancer. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Xiang, H.; Zeng, L.; Hou, L.; Li, K.; Fu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Hu, J.; Rosen-Zvi, M.; Zeng, X.; et al. A molecular video-derived foundation model for scientific drug discovery. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Paek, A.R.; Kim, S.Y.; You, H.J. GIPC mediates the generation of reactive oxygen species and the regulation of cancer cell proliferation by insulin-like growth factor-1/IGF-1R signaling. Cancer Lett. 2010, 294, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Y.; Hu, S.; Pan, L. Structural insights into the interaction and disease mechanism of neurodegenerative disease-associated optineurin and TBK1 proteins. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adel, I.M.; ElMeligy, M.F.; Abdelrahim, M.E.A.; Maged, A.; Abdelkhalek, A.A.; Abdelmoteleb, A.M.M.; Elkasabgy, N.A. Design and Characterization of Spray-Dried Proliposomes for the Pulmonary Delivery of Curcumin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2667–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagar, S.; Krishnadas, A.; Rubinstein, I.; Blend, M.J.; Onyüksel, H. VIP grafted sterically stabilized liposomes for targeted imaging of breast cancer: In Vivo studies. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Silva, J.; Fernandes, R.S.; Ramos Oda, C.M.; Ferreira, T.H.; Machado Botelho, A.F.; Martins Melo, M.; de Miranda, M.C.; Assis Gomes, D.; Dantas Cassali, G.; Townsend, D.M.; et al. Folate-coated, long-circulating and pH-sensitive liposomes enhance doxorubicin antitumor effect in a breast cancer animal model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, N.; Liu, J.; Chen, F.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D. Role of tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer metastasis and clinical advancements. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, J.; Elkhoury, K.; Velot, É.; Bianchi, A.; Acherar, S.; Francius, G.; Tamayol, A.; Grandemange, S.; Arab-Tehrany, E. Functionalized liposomes for targeted breast cancer drug delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 24, 401–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashihara, K.; Terai, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Maeda, K.; Tunetoh, S.; Sasaki, H.; Hayashi, M.; Ohmichi, M. Pharmacokinetic evaluation and antitumor potency of liposomal nanoparticle encapsulated cisplatin targeted to CD24-positive cells in ovarian cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1872–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Terai, Y.; Tanabe, A.; Ono, Y.J.; Hayashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Ashihara, K.; Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. CD24 expression is a marker for predicting clinical outcome and regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer via both the Akt and ERK pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3189–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Qiu, X.; Li, Y. Exosomes in ovarian cancer: Impact on drug resistance and advances in SERS detection techniques. J. Pharm. Anal. 2025, 15, 101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.J.; Wei, Y.F.; Wan, Y.Y.; Jiang, L.P.; Zhang, J.F.; Xin, H.B. Development of a novel liposomal nanodelivery system for bioluminescence imaging and targeted drug delivery in ErbB2-overexpressing metastatic ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Feng, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q. Gemcitabine-loaded RGD modified liposome for ovarian cancer: Preparation, characterization and pharmacodynamic studies. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 3281–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landen, C.N.; Merritt, W.M.; Mangala, L.S.; Sanguino, A.M.; Bucana, C.; Lu, C.; Lin, Y.G.; Han, L.Y.; Kamat, A.A.; Schmandt, R.; et al. Intraperitoneal delivery of liposomal siRNA for therapy of advanced ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, J.; Kamat, A.A.; Landen, C.N., Jr.; Han, L.Y.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Lin, Y.G.; Merritt, W.M.; Jennings, N.B.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Coleman, R.L.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase targeting using In Vivo short interfering RNA delivery in neutral liposomes for ovarian carcinoma therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4916–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Arreola, R.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Arana-Argáez, V.; Lara-Riegos, J.; Ramírez-Camacho, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Brain and Other Nervous System Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/brain.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Vagena, I.-A.; Malapani, C.; Gatou, M.-A.; Lagopati, N.; Pavlatou, E.A. Enhancement of EPR Effect for Passive Tumor Targeting: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yang, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Kalvakolanu, D.V.; Cong, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Utilization of nanotechnology to surmount the blood-brain barrier in disorders of the central nervous system. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhairiyah, F.; de Lange, E.C.M. Understanding Drug Delivery to the Brain Using Liposome-Based Strategies: Studies that Provide Mechanistic Insights Are Essential. AAPS J. 2021, 23, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, F.; Cunha, J.; Mendes, M.; Vitorino, C.; Sousa, J.J. Peptide-Hitchhiking for the Development of Nanosystems in Glioblastoma. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 16359–16394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tincu, C.-E.; Andrițoiu, C.V.; Popa, M.; Ochiuz, L. Recent Advancements and Strategies for Overcoming the Blood–Brain Barrier Using Albumin-Based Drug Delivery Systems to Treat Brain Cancer, with a Focus on Glioblastoma. Polymers 2023, 15, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangthem, V.; Yi, A.; Kim, Y.; Rehemtulla, A.; Lee, B.H.; Jeon, Y.H.; Singh, T.D.; Park, R.W. Therapeutic Effect of IL-4 Receptor-Targeting Pro-Apoptotic Peptide (AP1-ELP-KLAK) in Glioblastoma Tumor Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5039–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhai, B.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Yuan, Z.; Zhou, Y. Nanotechnology-Based Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Neuroblastoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 908713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Dolman, E.M.; Wieriks, R.; Sparidans, R.W.; Hennink, W.E.; Kok, R.J. Anti-GD2 Immunoliposomes for Targeted Delivery of the Survivin Inhibitor Sepantronium Bromide (YM155) to Neuroblastoma Tumor Cells. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Q.; Woodle, M.C.; Mixson, A.J. Targeted Delivery of siRNA Therapeutics to Malignant Tumors. J. Drug Deliv. 2017, 2017, 6971297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Orth, M.; Metzger, P.; Gerum, S.; Mayerle, J.; Schneider, G.; Belka, C.; Schnurr, M.; Lauber, K. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Biological hallmarks, current status, and future perspectives of combined modality treatment approaches. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahsavari, S.; Rad, M.B.; Hajiaghajani, A.; Rostami, M.; Hakimian, F.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Hasany, M.; Collingwood, J.F.; Aliakbari, F.; Fouladiha, H.; et al. Magnetoresponsive liposomes applications in nanomedicine: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 181, 117665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bharadwaj, U.; Zhai, Q.J.; Ahern, C.H.; Fisher, W.E.; Brunicardi, F.C.; Logsdon, C.D.; Chen, C.; Yao, Q. Down-regulation of ZIP4 by RNA interference inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and increases the survival of nude mice with pancreatic cancer xenografts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5993–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Lopez, C.B.; Timmerman, S.; Lorino, G.; Rogers, T.; Pyle, M.; Shrestha, T.B.; Basel, M.T. Thermosensitive Liposomes for Gemcitabine Delivery to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fite, B.Z.; Kheirolomoom, A.; Foiret, J.L.; Seo, J.W.; Mahakian, L.M.; Ingham, E.S.; Tam, S.M.; Borowsky, A.D.; Curry, F.E.; Ferrara, K.W. Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI detects changes in vascular transport rate constants following treatment with thermally-sensitive liposomal doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2017, 256, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Kimbrough, C.W.; Gomez-Gutierrez, J.G.; Burns, C.T.; Chuong, P.; Grizzle, W.E.; McNally, L.R. Tumor specific liposomes improve detection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma In Vivo using optoacoustic tomography. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad-Jabali, S.; Mahdinloo, S.; Farshbaf, M.; Sarfraz, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Atyabi, F.; Valizadeh, H. Transferrin receptor-mediated liposomal drug delivery: Recent trends in targeted therapy of cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitovic, D.; Kukovyakina, E.; Berdiaki, A.; Tzanakakis, A.; Luss, A.; Vlaskina, E.; Yagolovich, A.; Tsatsakis, A.; Kuskov, A. Enhancing Tumor Targeted Therapy: The Role of iRGD Peptide in Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. Cancers 2024, 16, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, R.; Rogers, S.C.; Lee, J.H.; Ramnaraign, B.; Sahin, I.; Fabregas, J.C.; Thomas, R.M.; Hughes, S.J.; Nassour, I.; Hitchcock, K.; et al. A phase II study of neoadjuvant liposomal irinotecan with 5-FU and oxaliplatin (NALIRIFOX) in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Future Oncol. 2023, 19, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Soft Tissue. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/soft.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Morya, V.K.; Magar, A.G.; Park, S.H.; Noh, K.C. Systemic strategies for osteosarcoma: Advances and future directions. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, E.; Ruocco, V.; Tornesello, M.L.; Gambardella, A.; Wolf, R.; Buonaguro, F.M. Kaposi’s sarcoma: Etiology and pathogenesis, inducing factors, causal associations, and treatments: Facts and controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinaty, P.E.; Lebbé, C.; Delyon, J. Endemic Kaposi’s Sarcoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/leuks.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Choi, H.-S.; Kim, B.S.; Yoon, S.; Oh, S.-O.; Lee, D. Leukemic Stem Cells and Hematological Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, J.A.B.; Pinheiro, P.S.; Kobetz, E.K. Epidemiology and Etiology of Leukemia and Lymphoma. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a034819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idres, Y.M.; Idris, A.; Gao, W. Preclinical testing of antiviral siRNA therapeutics delivered in lipid nanoparticles in animal models—A comprehensive review. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 3575–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdurashid, O.; Gulrukh, I.; Gulbaxor, U.; Nafisa, G.; Gullola, K.; Malokhat, J.; Shakhnoza, M.; Sultangazi, S.; Yorkinoy, R.; Muhriddin, A.; et al. CD19-Targeted Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivering Venetoclax and BCL2 siRNA in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Nanostruct. 2025, 15, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaafeen, B.H.; Ali, B.R.; Elkord, E. Combinational therapeutic strategies to overcome resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1546717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Aim | AI/ML Method | Key Outcome | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predict ionizable lipid properties and mRNA delivery | ML predictive models | Identified novel lipids with improved potency | Accelerates lipid library screening |
| Inverse design of LNP formulations | Transformer models | Predicted formulations with high transfection | Automates formulation discovery |
| Optimize microfluidic LNP manufacturing | XGBoost + Bayesian optimization | Improved size, EE%, potency reproducibility | Enhances scalability and CQA control |
| Predict biodistribution of NPs | QSAR + ML interpretability | Accurately forecasted organ/tumor uptake | Guides precision oncology delivery |
| Automated morphology analysis | Computer vision (LNP-MOD) | Linked cryo-EM features to efficacy | Enables theranostic optimization |
| Application Area | Example/Trial | Sponsor/Developer | Clinical Focus | Status/Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infectious Diseases (COVID-19) | mRNA-1273 (Moderna) BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) | Moderna; Pfizer/BioNTech | LNP-based mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 | Emergency/global approval; landmark success |
| Cancer Vaccines | BNT122 (BioNTech/Genentech) mRNA-4157 (Moderna/Merck) | BioNTech/Genentech; Moderna/Merck | Personalized mRNA neoantigen vaccines for melanoma and solid tumors | Phase I/II trials; promising immune responses |
| Gene Editing | NTLA-2001 (Intellia) | Intellia Therapeutics | In vivo LNP delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 for transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) | First-in-human CRISPR therapy; early clinical success |
| RNAi Therapies | Patisiran (ONPATTRO) | Alnylam Pharmaceuticals | siRNA delivery for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis | FDA/EMA approved; expanded use 2020–2025 |
| Cancer Immunotherapy/CAR-T | LNP-delivered immunomodulatory mRNA (preclinical to early trials) | Multiple (BioNTech, Moderna, academic consortia) | Enhancing CAR-T and immune checkpoint therapies | Early-phase, strong preclinical support |
| Autoimmune and Rare Diseases | Various pipeline candidates | Multiple developers | LNPs for autoimmune disorders, liver-targeted gene therapy | Ongoing early clinical trials |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rachamala, H.K. Translational Advances in Lipid Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy: Current Status and Future Horizons. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101315
Rachamala HK. Translational Advances in Lipid Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy: Current Status and Future Horizons. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101315
Chicago/Turabian StyleRachamala, Hari Krishnareddy. 2025. "Translational Advances in Lipid Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy: Current Status and Future Horizons" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101315
APA StyleRachamala, H. K. (2025). Translational Advances in Lipid Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy: Current Status and Future Horizons. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101315







