Amphotericin B Encapsulation in Polymeric Nanoparticles: Toxicity Insights via Cells and Zebrafish Embryo Testing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PNP Production
2.2. Characterization of Produced PNP
2.3. Cell Viability Assessment by MTT Assay
2.4. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.5. Zebrafish Embryo–Larval Acute Toxicity Test (ZELT)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PNP Characterization
3.2. MTT Assays
3.3. Zebrafish Embryo–Larvae Toxicity (ZELT) Assessment
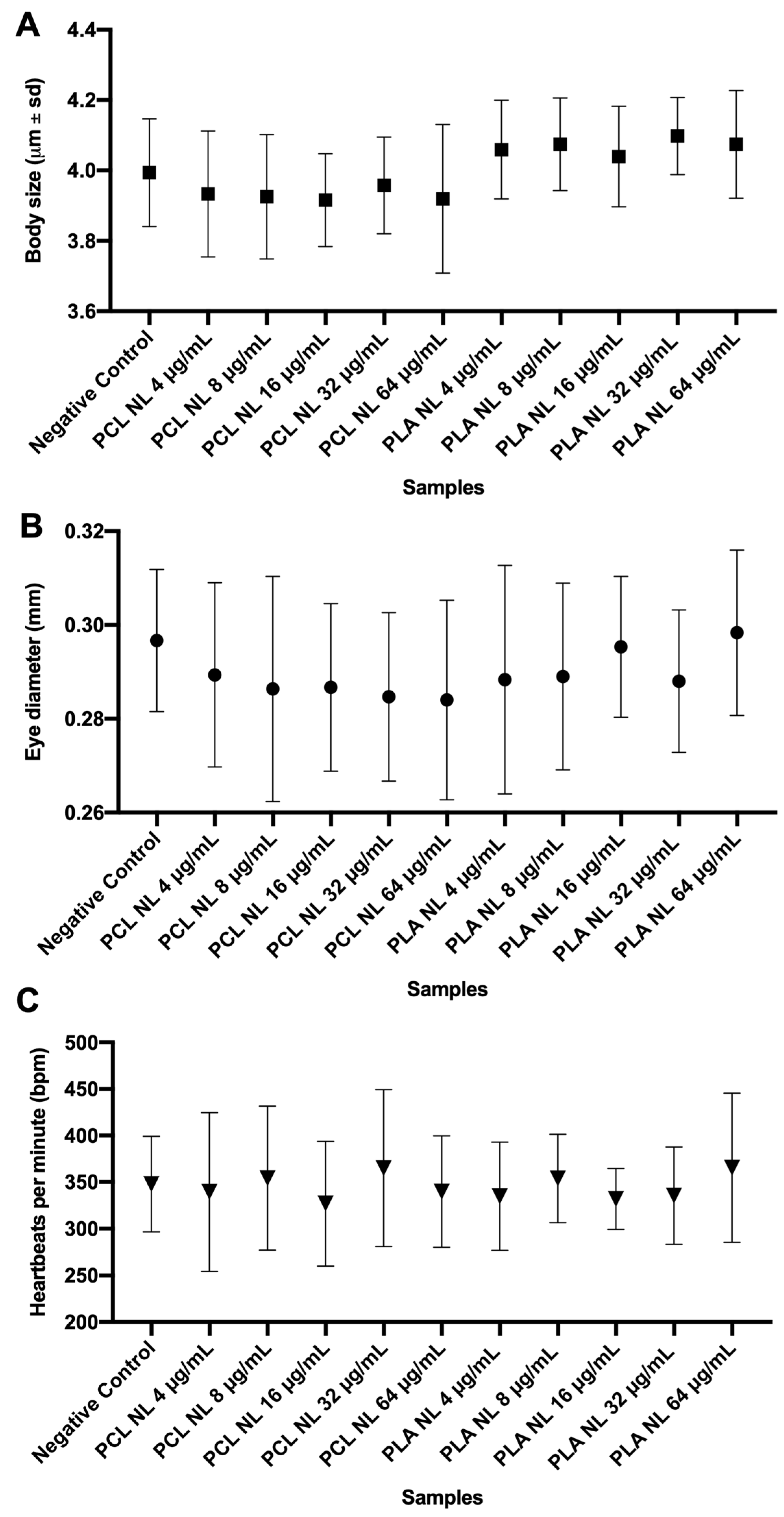
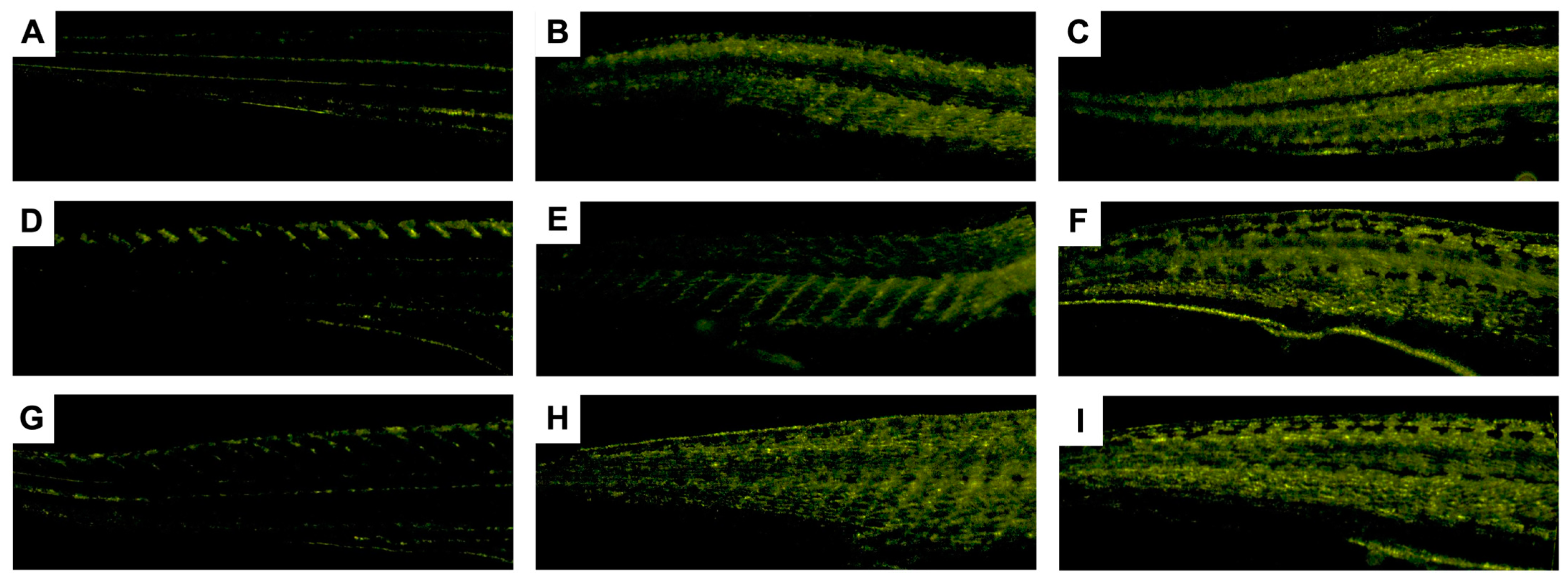
3.3.1. Effects of Non-Loaded PNPs on Zebrafish Embryos
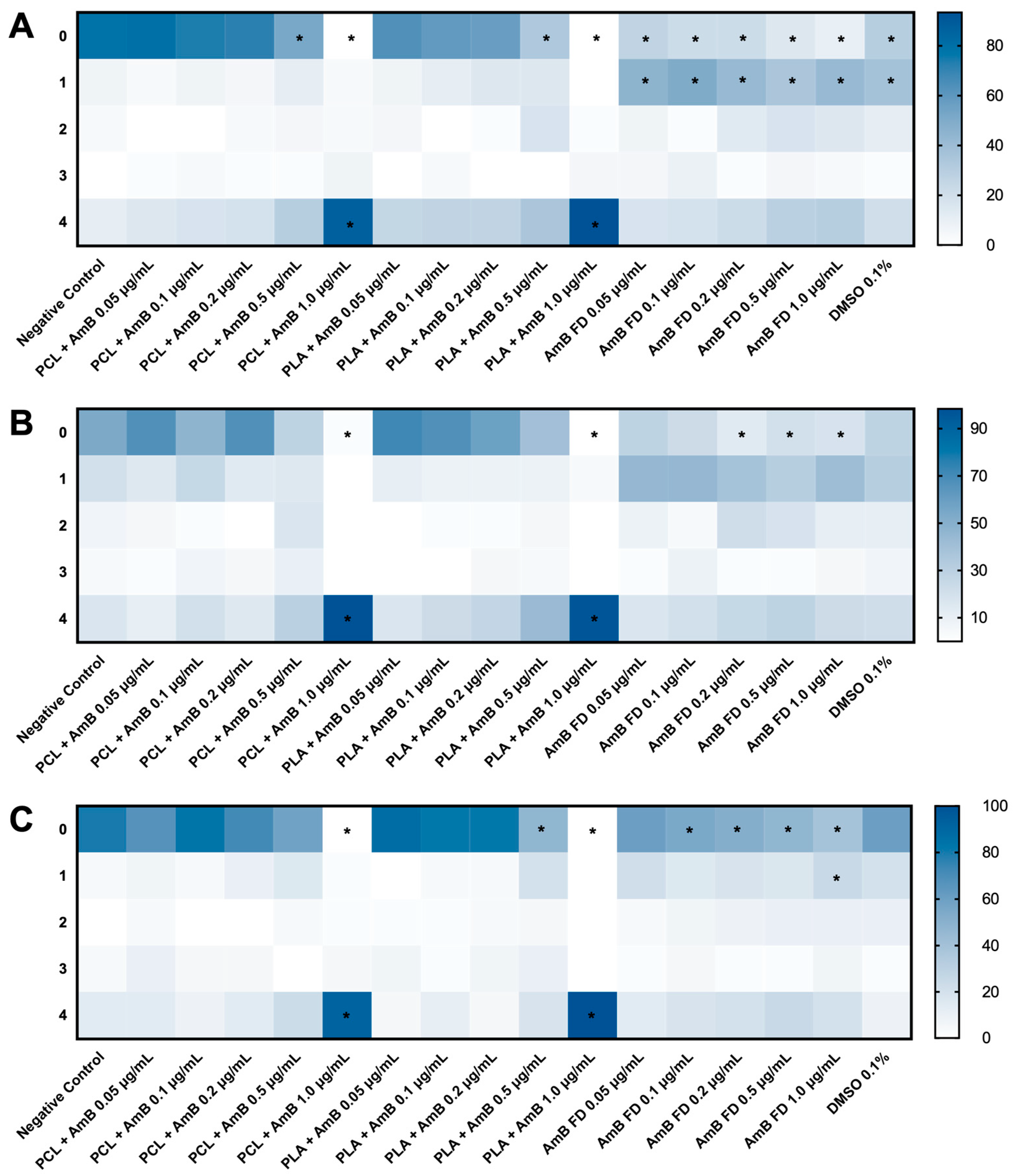
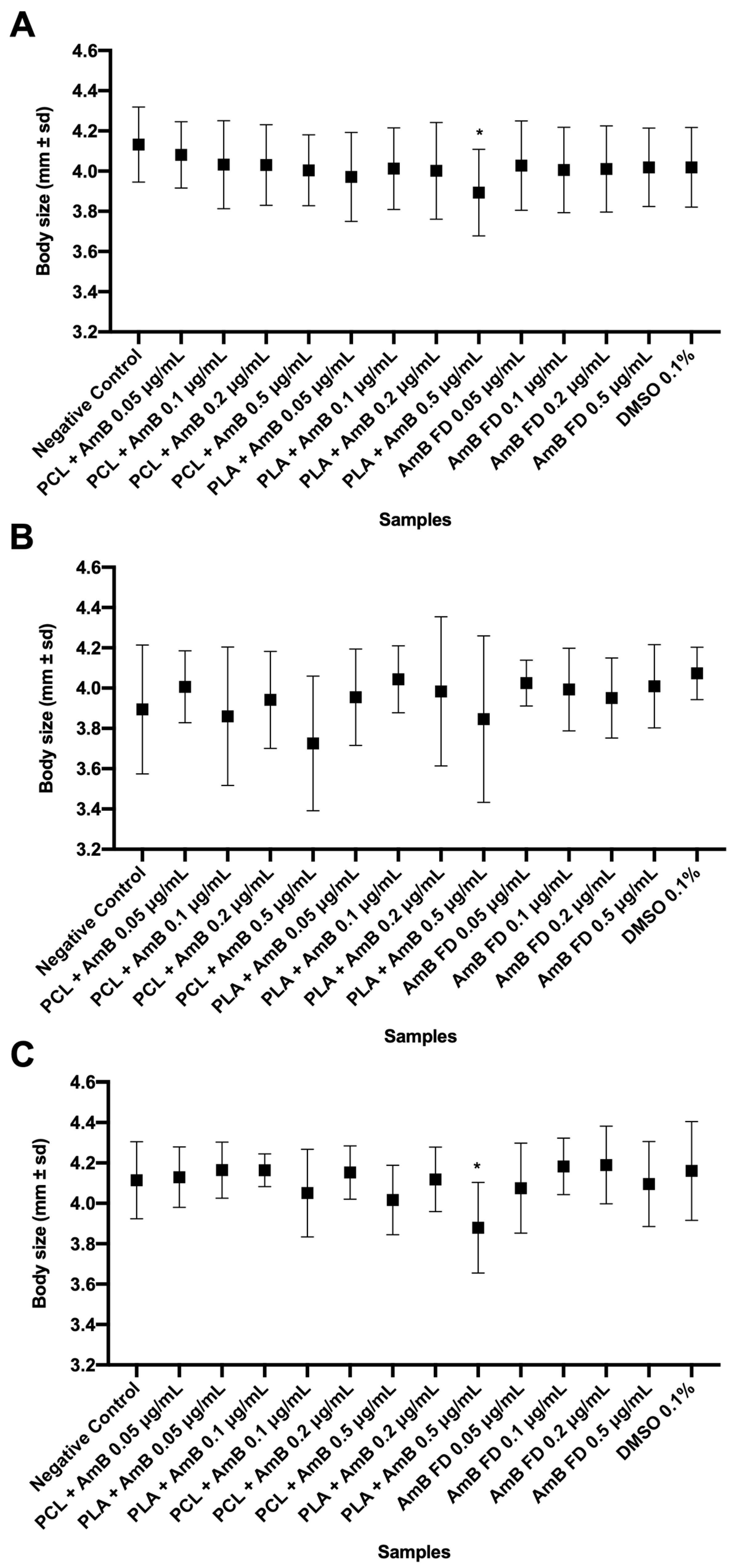
3.3.2. Impacts of AmB-Loaded PNPs and Free Drug on Zebrafish Embryos
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavassin, F.B.; Bau-Carneiro, J.L.; Vilas-Boas, R.R.; Queiroz-Telles, F. Sixty years of Amphotericin B: An Overview of the Main Antifungal Agent Used to Treat Invasive Fungal Infections. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadi, R.; Dand, N. BCS class IV drugs: Highly notorious candidates for formulation development. J. Control. Release 2017, 248, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill, R.J. Amphotericin B formulations: A comparative review of efficacy and toxicity. Drugs 2013, 73, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, M.B.; Desai, P.P.; Patel, P.A.; Patravale, V.B. Solid lipid nanoparticles of amphotericin B (AmbiOnp): In vitro and in vivo assessment towards safe and effective oral treatment module. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.A.; Patravale, V.B. AmbiOnp: Solid lipid nanoparticles of amphotericin B for oral administration. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Quadeib, B.T.; Radwan, M.A.; Siller, L.; Horrocks, B.; Wright, M.C. Stealth Amphotericin B nanoparticles for oral drug delivery: In vitro optimization. Saudi Pharm. J. 2015, 23, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipper, C.P.; Atukunda, M.; Stadelman, A.; Engen, N.W.; Bangdiwala, A.S.; Hullsiek, K.H.; Abassi, M.; Rhein, J.; Nicol, M.R.; Laker, E.; et al. Phase I EnACT Trial of the Safety and Tolerability of a Novel Oral Formulation of Amphotericin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00838-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Chang, J.H.; Barroso, E.; Espina, M.; Kuhne, B.A.; Barenys, M.; Auladell, C.; Folch, J.; Souto, E.B.; et al. Dual-drug loaded nanoparticles of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG)/Ascorbic acid enhance therapeutic efficacy of EGCG in a APPswe/PS1dE9 Alzheimer’s disease mice model. J. Control. Release 2019, 301, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Ettcheto, M.; Lopez-Machado, A.; Espina, M.; Souto, E.B.; Galindo, R.; Camins, A.; Garcia, M.L.; Turowski, P. Current advances in the development of novel polymeric nanoparticles for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1239–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mohammad, I.S.; Fan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Nurunnabi, M.; Sallam, M.A.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yin, L.; He, W. Delivery strategies of amphotericin B for invasive fungal infections. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2585–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Essa, M.M.; Lin, F.H.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A.; Caccamo, M.T. Smart Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Application: Development of Versatile Nanocarrier Platforms in Biotechnology and Nanomedicine. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh Mehrizi, T.; Mosaffa, N.; Vodjgani, M.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H. Advances in nanotechnology for improving the targeted delivery and activity of amphotericin B (2011–2023): A systematic review. Nanotoxicology 2024, 18, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.C.; Ananthakrishnan, G.; Jandhyam, S.; Dukhande, V.V.; Bhushan, A.; Gokhale, M.; Daniels, C.K.; Leung, S.W. Treatment of human astrocytoma U87 cells with silicon dioxide nanoparticles lowers their survival and alters their expression of mitochondrial and cell signaling proteins. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel-Magalhães, M.; Medeiros, R.J.; Bravin, J.S.; Patricio, B.F.C.; Rocha, H.V.A.; Paes-de-Almeida, E.C.; Santos, L.M.G.; Jacob, S.C.; Savignon, T.C.M.; Amendoeira, F.C. Evaluation of acute toxicity and copper accumulation in organs of Wistar rats, 14 days after oral exposure to copper oxide (II) nano- and microparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2019, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, I.F.; Paumgartten, F.J.R. Current challenges in toxicological research: Evaluation of the developmental toxicity of manufactured nanomaterials. Vigilância Sanitária Debate 2013, 1, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, S.; Grossen, P.; Bussmann, J.; Campbell, F.; Kros, A.; Witzigmann, D.; Huwyler, J. Zebrafish as a preclinical in vivo screening model for nanomedicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 151–152, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO/TR 16197:2014; Nanotechnologies—Compilation and Description of Toxicological Screening Methods for Manufactured Nanomaterials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Sobanska, M.; Scholz, S.; Nyman, A.M.; Cesnaitis, R.; Gutierrez Alonso, S.; Kluver, N.; Kuhne, R.; Tyle, H.; de Knecht, J.; Dang, Z.; et al. Applicability of the fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test (OECD 236) in the regulatory context of Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahle, U.; Scholz, S.; Geisler, R.; Greiner, P.; Hollert, H.; Rastegar, S.; Schumacher, A.; Selderslaghs, I.; Weiss, C.; Witters, H.; et al. Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments--a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, M.J.; Temprana, C.F.; del Rio Zabala, N.E.; Marotta, C.H.; Alonso Sdel, V. Optimization and in vitro toxicity evaluation of G4 PAMAM dendrimer-risperidone complexes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos, G. Desenvolvimento, Caracterização e Avaliação Biológica de Nanopartículas Poliméricas Contendo Anfotericina B. Master’s Thesis, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test. No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricio, B.F.d.C. Desenvolvimento e Caracterização Biofísica E Toxicológica de Nanopartículas Poliméricas de Ácido Poli-Láctico e Poli-Etileno Glicol. Ph.D. Thesis, Carlos Chagas Filho Institute of Biophysics, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, N.; Gayet, P.; Benoit, J.P.; Saulnier, P. Nano-emulsions and nanocapsules by the PIT method: An investigation on the role of the temperature cycling on the emulsion phase inversion. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 344, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes Profirio, D.; Pessine, F.B.T. Formulation of functionalized PLGA nanoparticles with folic acid-conjugated chitosan for carboplatin encapsulation. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K. Zeta potential measurement. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 697, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Ganem-Quintanar, A.; Allemann, E.; Fessi, H.; Doelker, E. Influence of the stabilizer coating layer on the purification and freeze-drying of poly(D,L-lactic acid) nanoparticles prepared by an emulsion-diffusion technique. J. Microencapsul. 1998, 15, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqib, M.; Ali Bhatti, A.S.; Ahmad, N.M.; Ahmed, N.; Shahnaz, G.; Lebaz, N.; Elaissari, A. Amphotericin B Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles for Treatment of Leishmania Infections. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Garcia, R.; Munoz-Garcia, J.C.; Wallace, M.; Fabian, L.; Gonzalez-Burgos, E.; Gomez-Serranillos, M.P.; Raposo, R.; Bolas-Fernandez, F.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Healy, A.M.; et al. Self-assembling, supramolecular chemistry and pharmacology of amphotericin B: Poly-aggregates, oligomers and monomers. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyson, N.; Pathak, A.; Jain, K. One Platform Comparison of Polymeric and Lipidic Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Amphotericin B. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeiro, V.S.; Silva-Carvalho, R.; Martins, D.; Parpot, P.; Grotto, D.; Chaud, M.V.; da Gama, F.M.P.; Jozala, A.F. Alginate-amphotericin B nanocomplexes covered by nanocrystals from bacterial cellulose: Physico-chemical characterization and in vitro toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameen, F.; Alsarraf, M.J.; Abalkhail, T.; Stephenson, S.L. Evaluation of resistance patterns and bioremoval efficiency of hydrocarbons and heavy metals by the mycobiome of petroleum refining wastewater in Jazan with assessment of molecular typing and cytotoxicity of Scedosporium apiospermum JAZ-20. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedda, M.R.; Madhukar, P.; Vishwakarma, A.K.; Verma, V.; Kushwaha, A.K.; Yadagiri, G.; Mudavath, S.L.; Singh, O.P.; Srivastava, O.N.; Sundar, S. Evaluation of Safety and Antileishmanial Efficacy of Amine Functionalized Carbon-Based Composite Nanoparticle Appended With Amphotericin B: An in vitro and Preclinical Study. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Fang, T.; Chen, S.M.; Hu, X.; Song, L.; Shen, H.; Dong, H.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Zou, Z.; et al. Turning weakness into strength: Albumin nanoparticle-redirected amphotericin B biodistribution for reducing nephrotoxicity and enhancing antifungal activity. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlottfeldt Fdos, S.; Fernandes, S.M.; Martins, D.M.; Cordeiro, P.; Fonseca, C.D.; Watanabe, M.; Vattimo Mde, F. Prevention of amphotericin B nephrotoxicity through use of phytotherapeutic medication. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 2015, 49, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laniado-Laborin, R.; Cabrales-Vargas, M.N. Amphotericin B: Side effects and toxicity. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2009, 26, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzidic-Krivic, A.; Sher, E.K.; Kusturica, J.; Farhat, E.K.; Nawaz, A.; Sher, F. Unveiling drug induced nephrotoxicity using novel biomarkers and cutting-edge preventive strategies. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 388, 110838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Mathai, M.; Zulli, A. Cytoprotective remedies for ameliorating nephrotoxicity induced by renal oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2023, 318, 121466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.K.; Benival, D.; Jindal, A.B. Formulation Strategies to Overcome Amphotericin B Induced Toxicity. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 5392–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadini, M.C.; Fernandes, F.S.; Ozelin, S.D.; de Melo, M.R.S.; Mansur, A.L.; de Toledo, T.B.; de Albuquerque, N.C.P.; Tavares, D.C.; Marquele-Oliveira, F.; de Oliveira, A.R.M. Pharmacokinetic study of AmB-NP-GR: A new granule form with amphotericin B to treat leishmaniasis and fungal infections. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 173, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; van Mil, H.G.; Richardson, M.K. Large-scale assessment of the zebrafish embryo as a possible predictive model in toxicity testing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igartúa, D.E.; Martinez, C.S.; Alonso, S.d.V.; Chiaramoni, N.S.; Prieto, M.J. Toxicity assessment of free and dendrimer-complexed curcumin in zebrafish larvae. PharmaNutrition 2020, 13, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wei, Z.; Xu, M.; Xi, L.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.M.; Ge, W.; Zheng, Y. Particle Integrity and Size Effect on the Journey of Polymeric Nanocarriers in Zebrafish Model and the Correlation with Mice. Small 2021, 17, e2103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, A.I.S.; Campos, E.V.R.; Oliveira, J.L.; Vallim, J.H.; Proença, P.L.F.; Castanha, R.F.; de Castro, V.; Fraceto, L.F. Ecotoxicity evaluation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded with ascorbic acid for fish nutrition in aquaculture. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wen, L.; Feng, X. Effects of microplastic exposure on the early developmental period and circadian rhythm of zebrafish (Danio rerio): A comparative study of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 258, 114994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraher, D.; Sanigorski, A.; Mellett, N.A.; Meikle, P.J.; Sinclair, A.J.; Gibert, Y. Zebrafish Embryonic Lipidomic Analysis Reveals that the Yolk Cell Is Metabolically Active in Processing Lipid. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, R.; de Pablo, E.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Serrano, D.R. Unmet clinical needs in the treatment of systemic fungal infections: The role of amphotericin B and drug targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszecki, W.I.; Gagos, M.; Herec, M. Dimers of polyene antibiotic amphotericin B detected by means of fluorescence spectroscopy: Molecular organization in solution and in lipid membranes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2003, 69, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguayo Frías, E.T.; Maza Vega, D.; Calienni, M.N.; Lillo, C.; Vazquez, D.S.; Alonso, S.d.V.; Montanari, J. Enhanced skin delivery of vismodegib-loaded rigid liposomes combined with ethosomes. OpenNano 2023, 14, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.P.; Chang, Y.; Hu, C.Q. A newly identified derivative of amphotericin B: Isolation, structure determination and primary evaluation of the activity and toxicity. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrado, J.J.; Espada, R.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Amphotericin B formulations and drug targeting. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2405–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.M.; Clay, M.C.; Cioffi, A.G.; Diaz, K.A.; Hisao, G.S.; Tuttle, M.D.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Comellas, G.; Maryum, N.; Wang, S.; et al. Amphotericin forms an extramembranous and fungicidal sterol sponge. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, A.; Soutar, C.P.; Greenwood, A.I.; Nimerovsky, E.; De Lio, A.M.; Holler, J.T.; Hisao, G.S.; Khandelwal, A.; Zhang, J.; SantaMaria, A.M.; et al. Fungicidal amphotericin B sponges are assemblies of staggered asymmetric homodimers encasing large void volumes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Devarajan, P.V. Enhancing Safety and Efficacy by Altering the Toxic Aggregated State of Amphotericin B in Lipidic Nanoformulations. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.A.; de Oliveira, H.C.; Agreda-Mellon, D.; Lucio, J.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S.; Garcia-Cambero, J.P.; Zaragoza, O. Identification of Off-Patent Drugs That Show Synergism with Amphotericin B or That Present Antifungal Action against Cryptococcus neoformans and Candida spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01921-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavic, A.; Stojanovic, Z.; Pekmezovic, M.; Veljovic, D.; O’Connor, K.; Malagurski, I.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Polyenes in Medium Chain Length Polyhydroxyalkanoate (mcl-PHA) Biopolymer Microspheres with Reduced Toxicity and Improved Therapeutic Effect against Candida Infection in Zebrafish Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Browning, L.M.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Desai, T.; Cherukuri, P.K.; Xu, X.H. In vivo quantitative study of sized-dependent transport and toxicity of single silver nanoparticles using zebrafish embryos. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Browning, L.M.; Osgood, C.J.; Xu, X.H. In vivo imaging of transport and biocompatibility of single silver nanoparticles in early development of zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezanujjaman, M.; Pachoensuk, T.; Forhad Hossain, M.; Maisum Sarwar Jyoti, M.; Rubel Rana, M.; Tsutsumi, E.; Mouri, T.; Bramastri Susilo, M.; Wanlada, K.; Yamamoto, C.; et al. Zebrafish prss59.1 is involved in chorion development. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2024, 349, 114453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


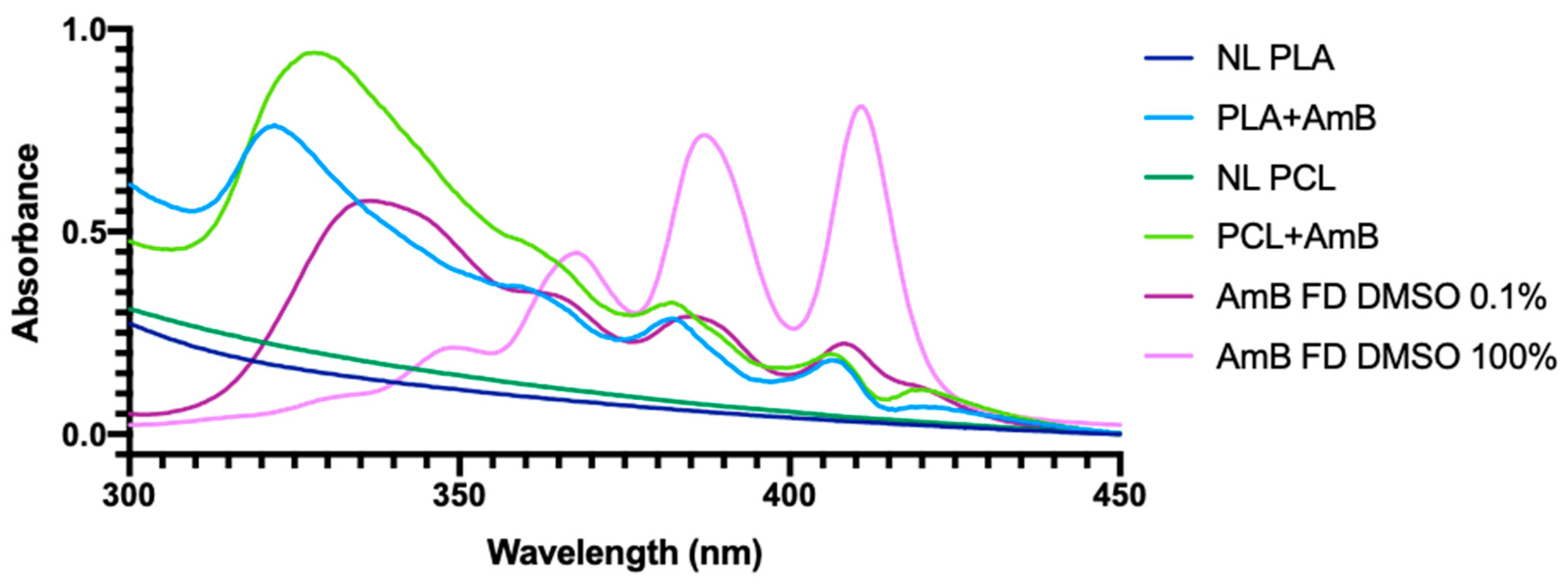





| PNP NL | PNPs Loaded with AmB | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | PdI | Zeta Potential (mV) | Size (nm) | PdI | Zeta Potential (mV) | [AmB] (mg/mL) | EE (%) | DL (%) | |
| PCL | 114.6 ± 10.2 | 0.126 ± 0.021 | −29.0 ± 7.6 | 163.4 ± 1.8 | 0.142 ± 0.033 | −24.6 ± 3.0 | 160.50 ± 8.14 | 21.66 ± 10.04 | 5.41 ± 2.51 |
| PLA | 171.9 ± 5.9 | 0.118 ± 0.018 | −31.8 ± 9.6 | 202.4 ± 16.1 | 0.114 ± 0.030 | −28.2 ± 8.5 | 165.64 ± 9.43 | 27.15 ± 14.96 | 6.79 ± 3.74 |
| PLA NL PNP | PCL NL PNP | PLA + AmB PNP | PCL + AmB PNP | AmB FD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEK293 | 4.775 μg/mL | 7.839 μg/mL | 3.759 μg/mL | 6.758 μg/mL | >10 μg/mL |
| HepG2 | >10 μg/mL | >10 μg/mL | >10 μg/mL | >10 μg/mL | >10 μg/mL |
| J774 A1 | >10 μg/mL | 1.082 μg/mL | 1.633 μg/mL | 0.2406 μg/mL | 1462 μg/mL |
| PLA + AmB PNP | PCL + AmB PNP | AmB FD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 hpf | TC50 | 0.1536 μg/mL | 0.3204 μg/mL | 1.034 μg/mL |
| LC50 | 0.3982 μg/mL | 0.5575 μg/mL | <1.5 μg/mL | |
| 6 hpf | TC50 | 0.3497 μg/mL | 0.3940 μg/mL | <1.5 μg/mL |
| LC50 | 0.4040 μg/mL | 0.5776 μg/mL | <1.5 μg/mL | |
| 24 hpf | TC50 | 0.5454 μg/mL | 0.5582 μg/mL | <1.5 μg/mL |
| LC50 | 0.5584 μg/mL | 0.6254 μg/mL | <1.5 μg/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maciel-Magalhães, M.; Medeiros, R.J.; Guedes, N.C.d.C.; Brito, T.M.d.; Souza, G.F.d.; Canabarro, B.R.; Ferraris, F.K.; Amendoeira, F.C.; Rocha, H.V.A.; Patricio, B.F.d.C.; et al. Amphotericin B Encapsulation in Polymeric Nanoparticles: Toxicity Insights via Cells and Zebrafish Embryo Testing. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010116
Maciel-Magalhães M, Medeiros RJ, Guedes NCdC, Brito TMd, Souza GFd, Canabarro BR, Ferraris FK, Amendoeira FC, Rocha HVA, Patricio BFdC, et al. Amphotericin B Encapsulation in Polymeric Nanoparticles: Toxicity Insights via Cells and Zebrafish Embryo Testing. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaciel-Magalhães, Magno, Renata Jurema Medeiros, Nayara Cecília do Couto Guedes, Thais Morais de Brito, Gabriele Fátima de Souza, Beatriz Rodrigues Canabarro, Fausto Klabund Ferraris, Fábio Coelho Amendoeira, Helvécio Vinicius Antunes Rocha, Beatriz Ferreira de Carvalho Patricio, and et al. 2025. "Amphotericin B Encapsulation in Polymeric Nanoparticles: Toxicity Insights via Cells and Zebrafish Embryo Testing" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010116
APA StyleMaciel-Magalhães, M., Medeiros, R. J., Guedes, N. C. d. C., Brito, T. M. d., Souza, G. F. d., Canabarro, B. R., Ferraris, F. K., Amendoeira, F. C., Rocha, H. V. A., Patricio, B. F. d. C., & Delgado, I. F. (2025). Amphotericin B Encapsulation in Polymeric Nanoparticles: Toxicity Insights via Cells and Zebrafish Embryo Testing. Pharmaceutics, 17(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010116







