Multifunctional Bioactivity Electrospinning Nanofibers Encapsulating Emodin Provide a Potential Postoperative Management Strategy for Skin Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Coaxial Electrospinning Nanofibers
2.3. Characterization of Electrospinning Nanofibers
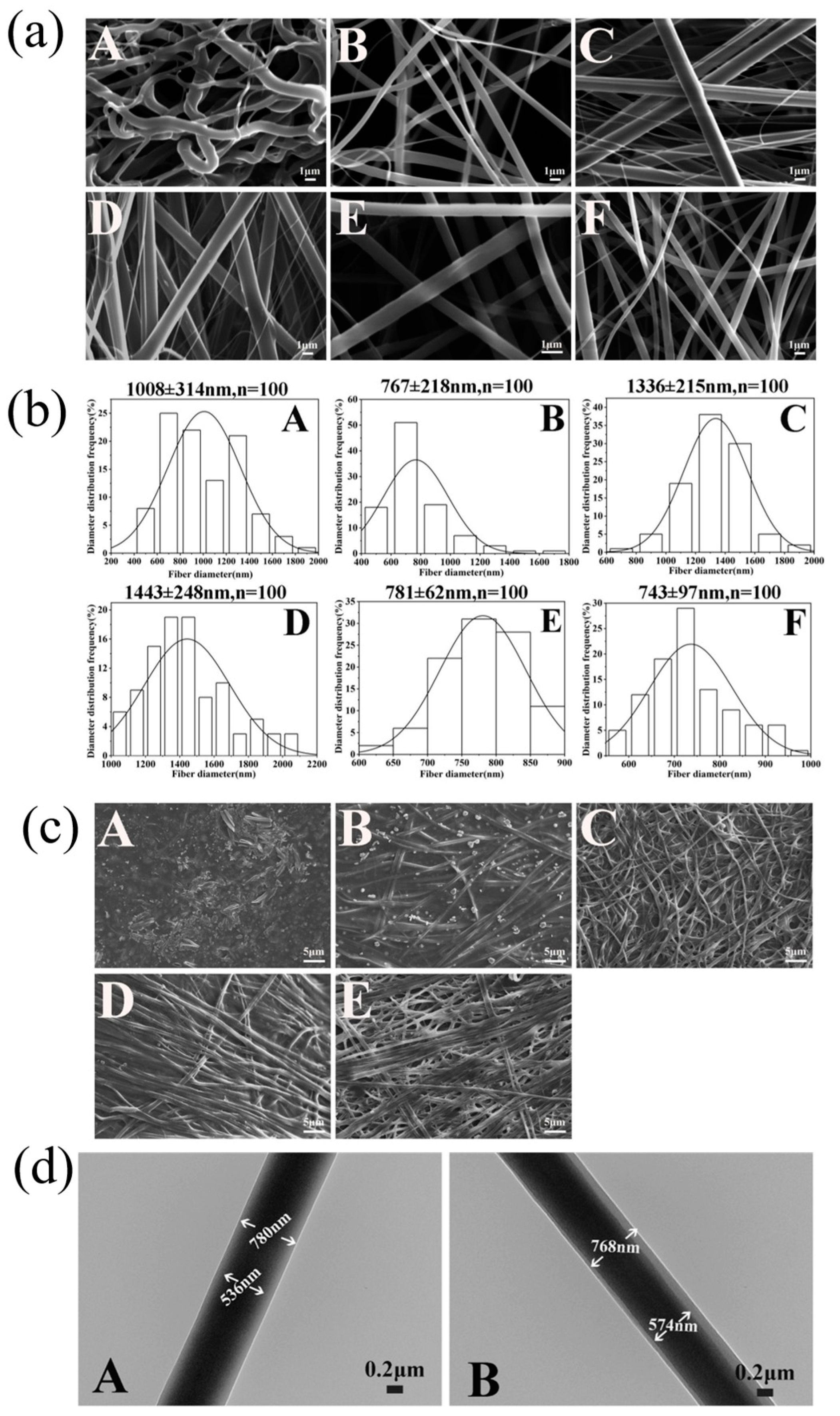
2.3.1. Morphologies
2.3.2. Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectra Analysis
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction
2.3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.3.5. Wettability and Swelling Ratio
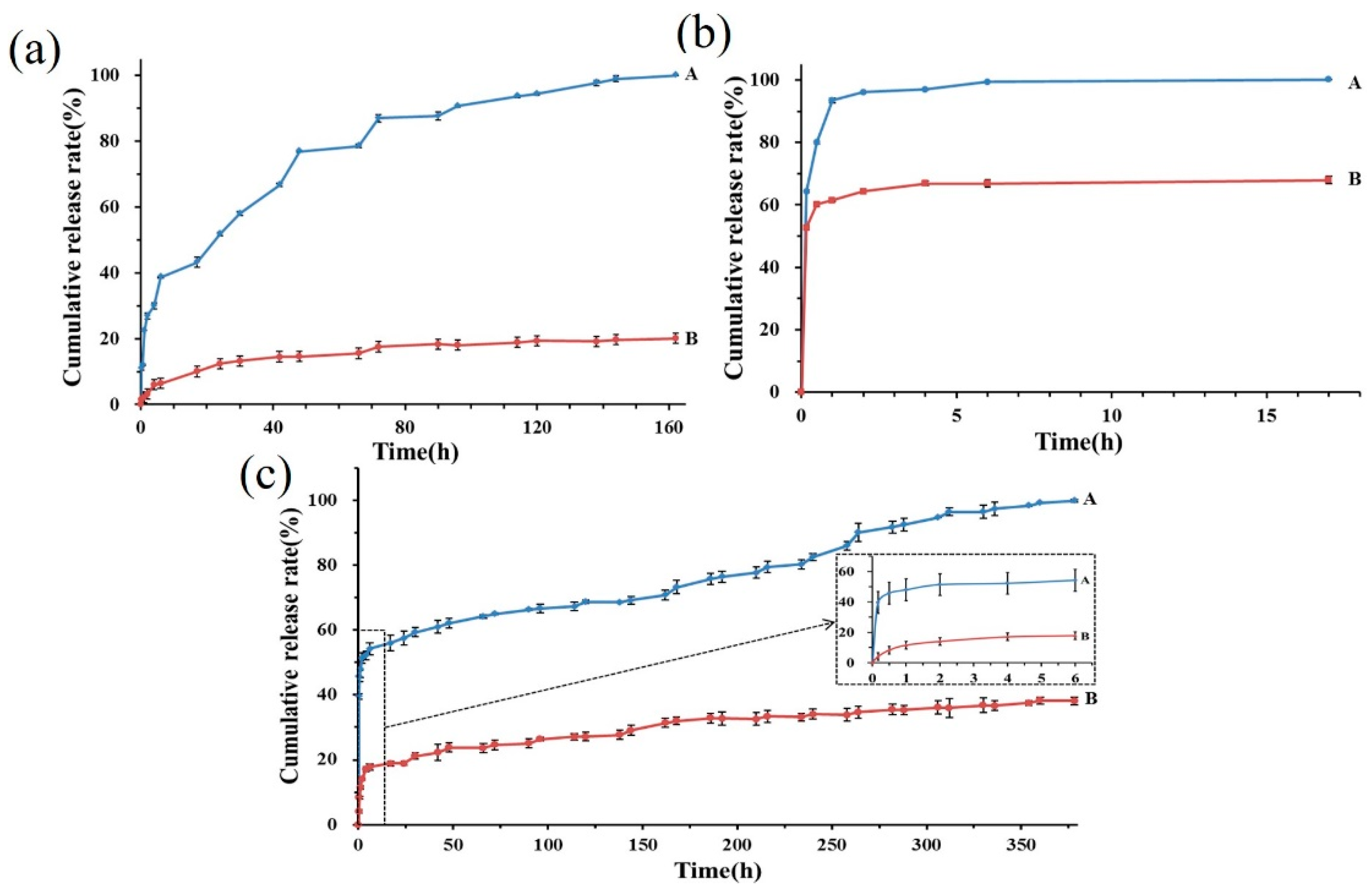
2.3.6. Encapsulation Efficiency and Drug Release Profiles
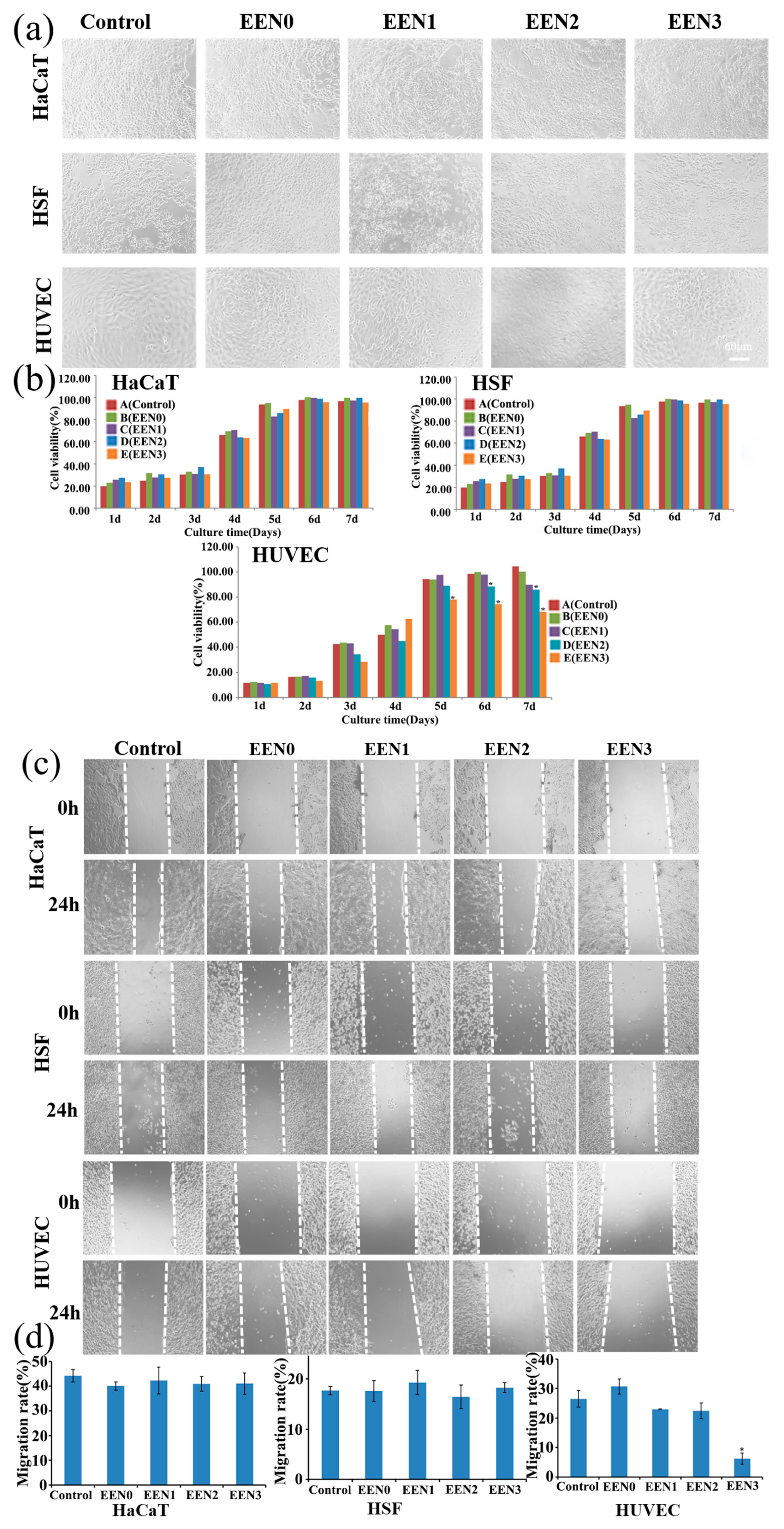
2.4. Cytocompatibility
2.5. Anti-Cancer Effects
2.6. Mechanism of Anti-Cancer Effects
2.6.1. Cell Death Inhibitors
2.6.2. MDA Level
2.6.3. ROS Level
2.7. Anti-Bacterial Activities
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimized Electrospinning Conditions
3.2. Characterization
3.2.1. Morphology
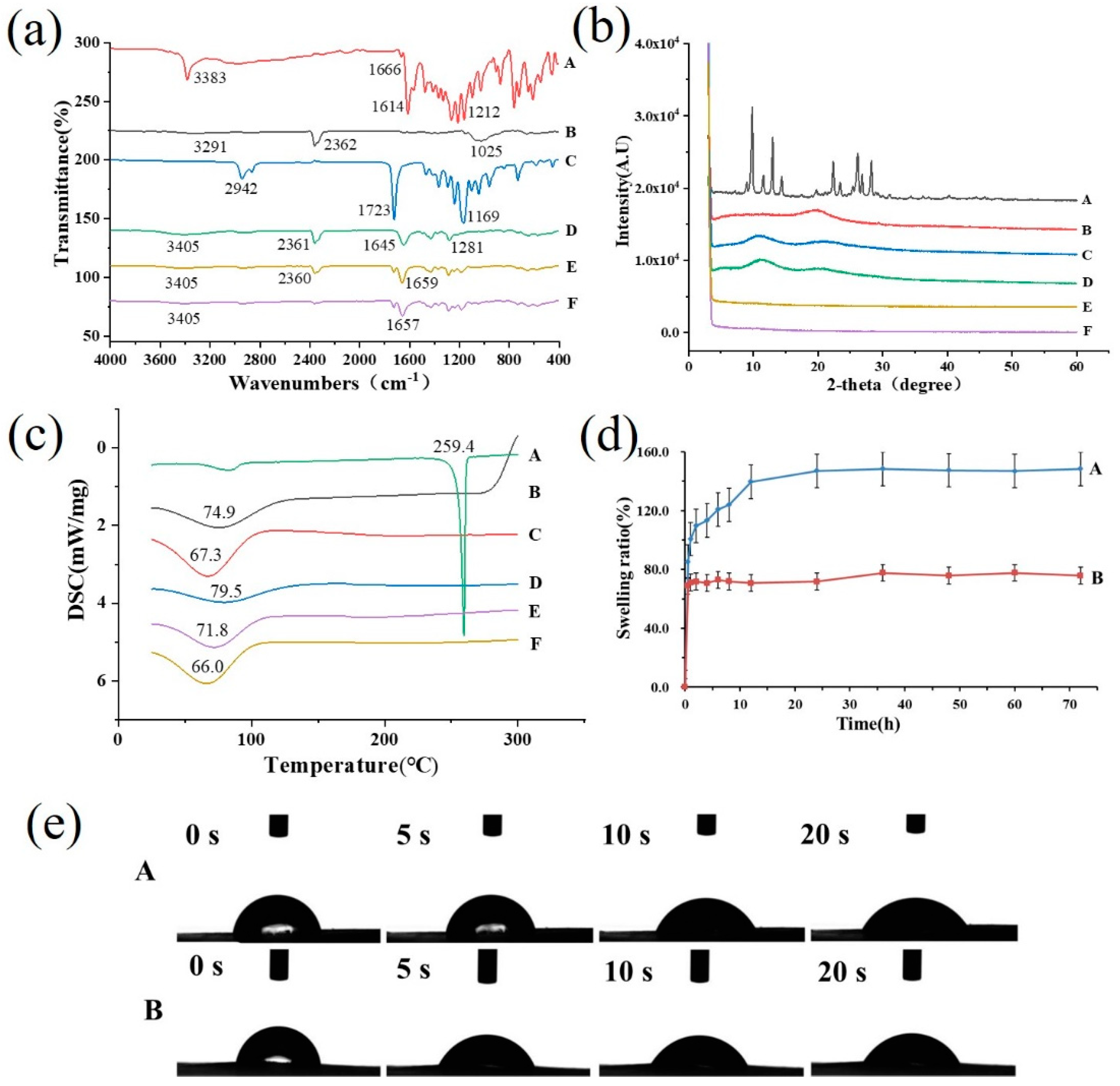
3.2.2. ATR-FTIR Spectra Analysis
3.2.3. X-ray Diffraction
3.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.2.5. Swelling Ratio and Contact Angle
3.2.6. Encapsulation Efficiency and Release Profiles
3.3. Cytocompatibility with Normal Cells
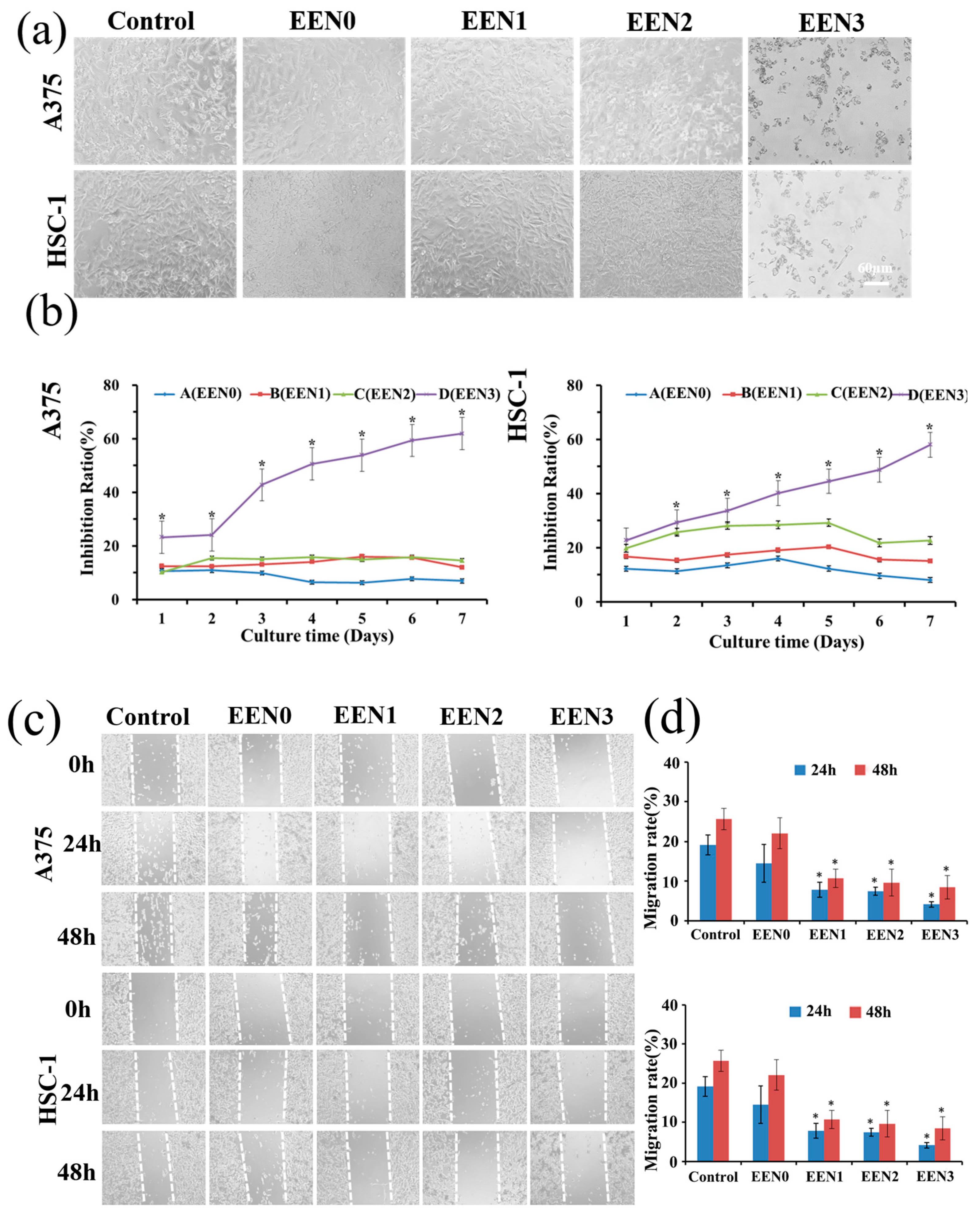
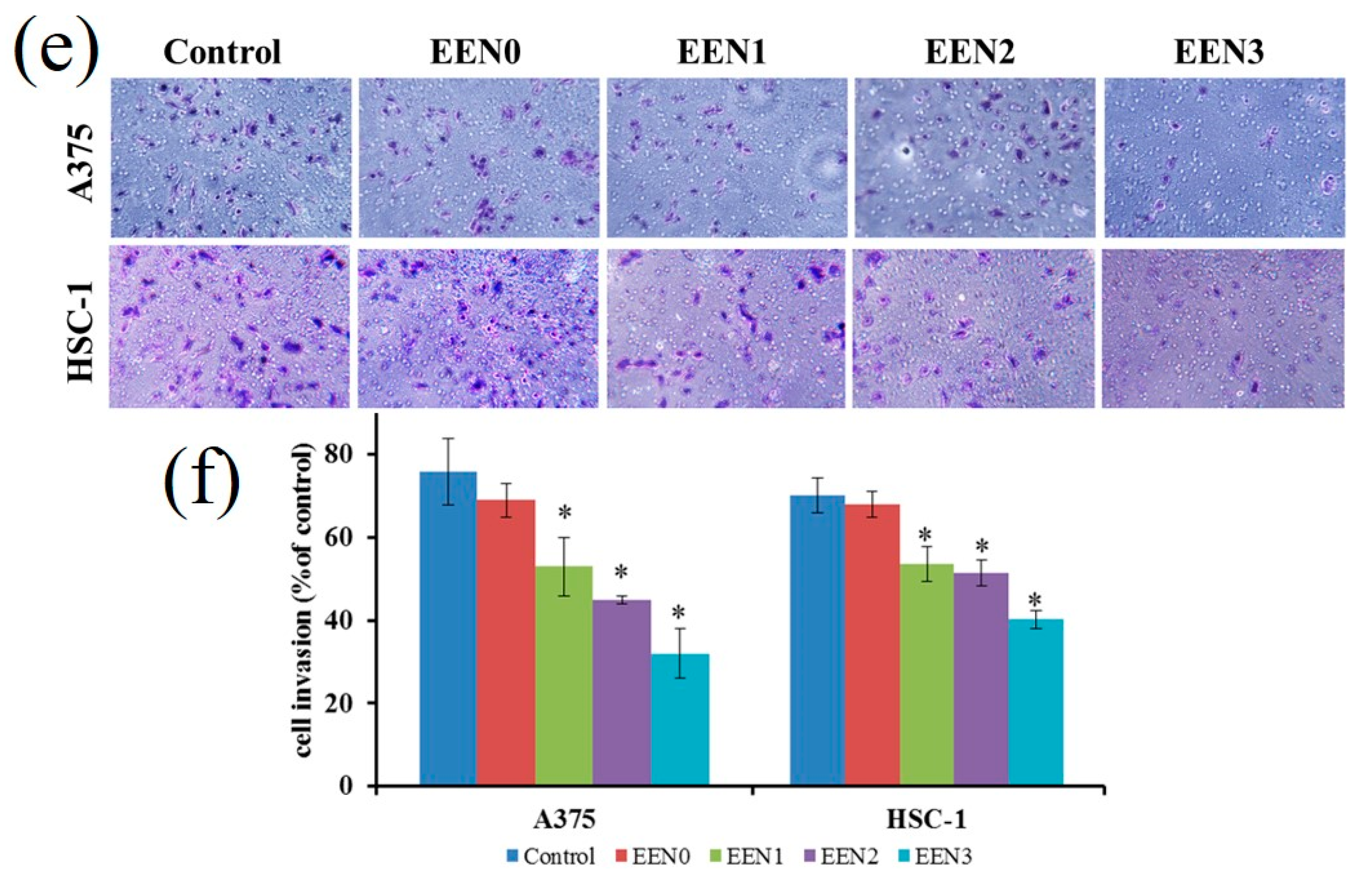
3.4. Anti-Cancer Effects
3.5. Anti-Cancer Effect Mechanism
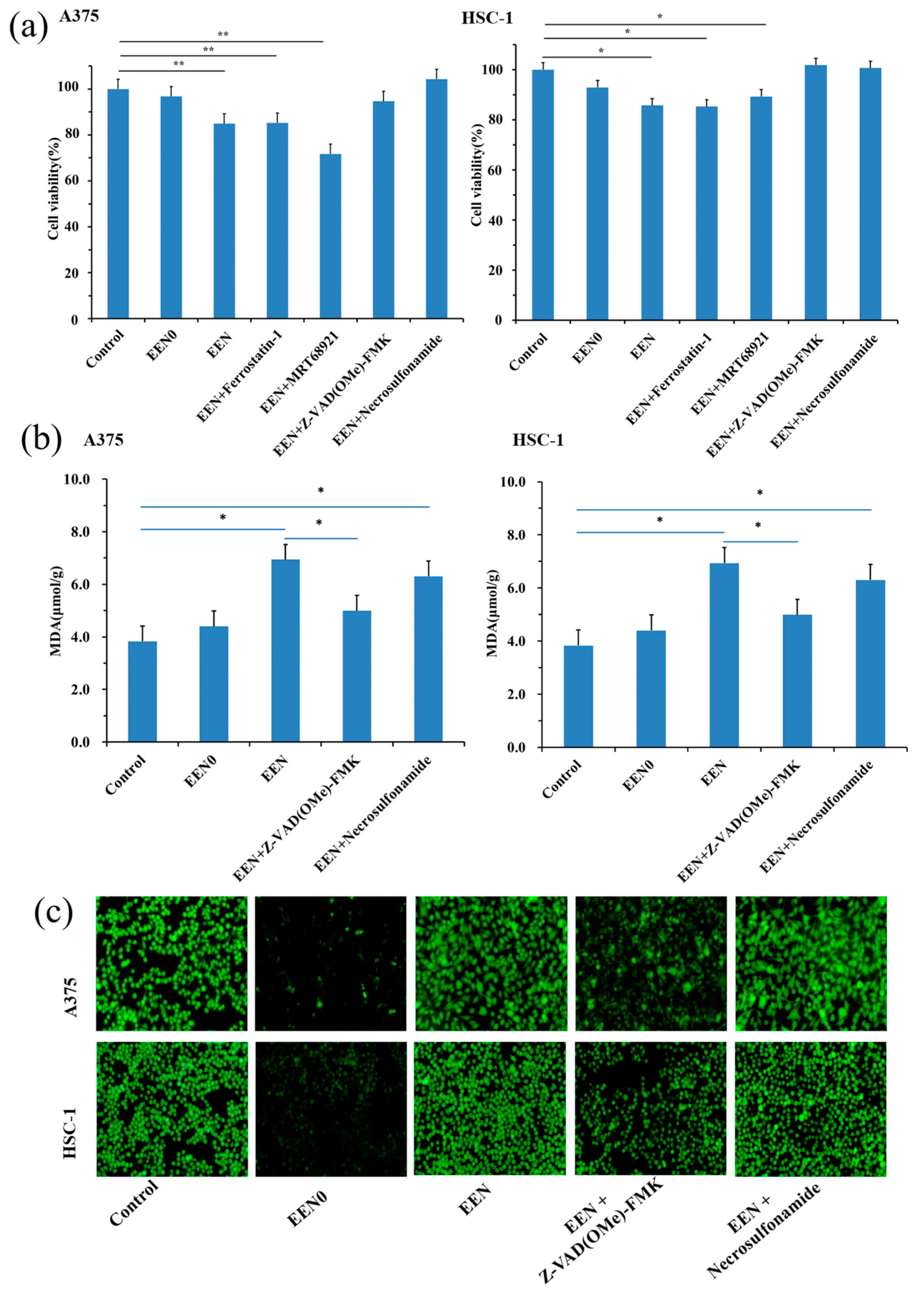
3.5.1. Inhibit Cancer Cell Proliferation via Necroptosis and Apoptosis Pathway
3.5.2. MDA Level in Tumor Cells
3.5.3. ROS Level in Tumor Cells
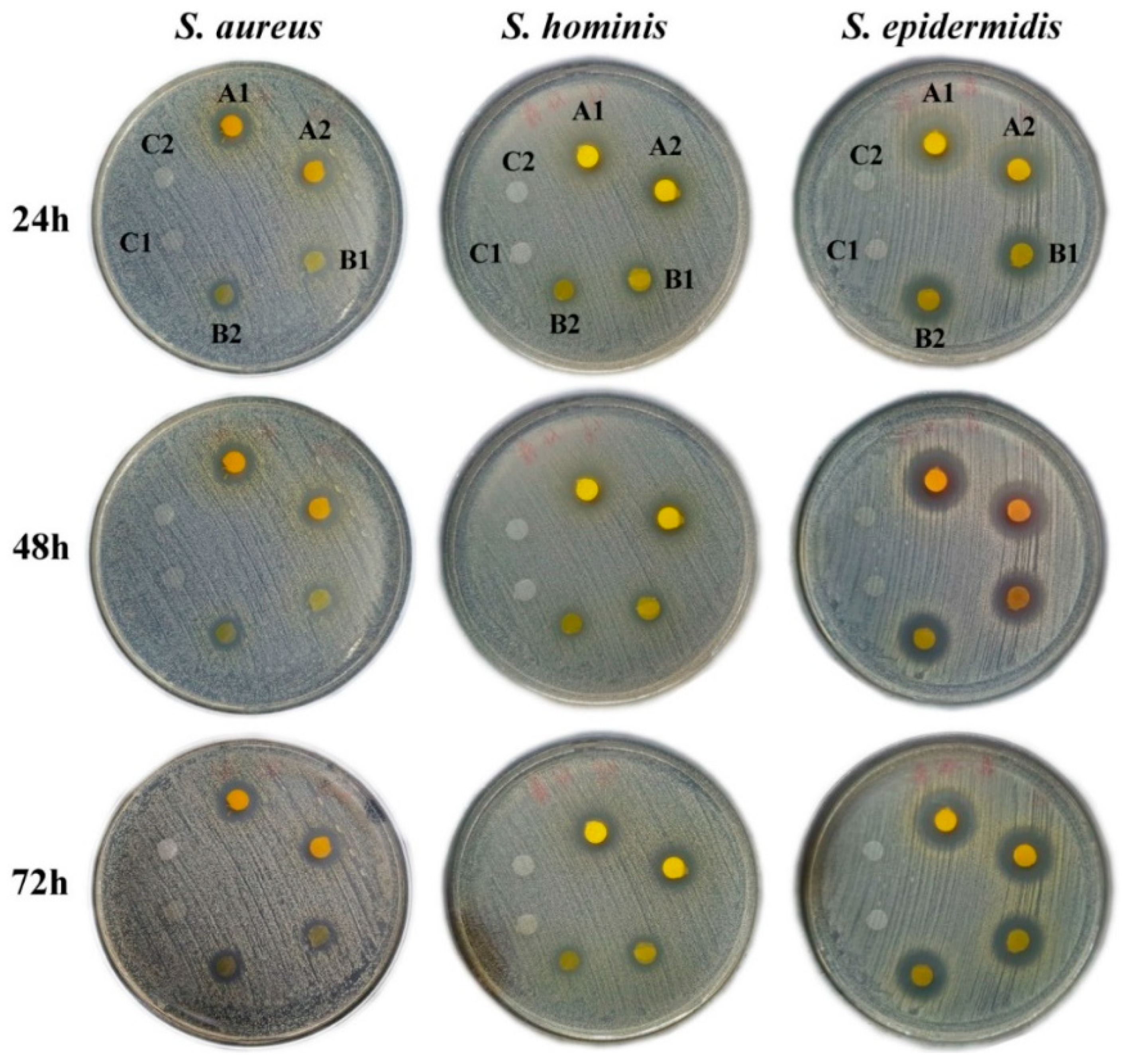
3.6. Anti-Bacterial Activities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Jin, J. Screening and Prevention of Skin Cancer. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2023, 329, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, K.D.; Perez, M.E.; Marchetti, M.A.; Nichols, A.J.; Penedo, F.J.; Jaimes, N. Skin cancer: Primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Part II. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Chua, D.; Tan, N.S. Reactive oxygen species: A volatile driver of field cancerization and metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, K. HIV and skin cancer risk. Nat. Med. 2022, 24, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yu, Q.; Qu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C. Manganese silicate nanospheres-incorporated hydrogels: Starvation therapy and tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4558–4567. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, Y.; Ge, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Niu, W.; Cheng, W.; Xue, Y.; Lin, C.; Lei, B. Bioactive Anti-inflammatory, Antibacterial, Antioxidative Silicon-Based Nanofibrous Dressing Enables Cutaneous Tumor Photothermo-Chemo Therapy and Infection-Induced Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2904–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xu, Q.; Hao, R.; Wang, C.; Que, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Chang, J. Multi-functional wound dressings based on silicate bioactive materials. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Perlak, M.; Bromke, M.A.; Ziolkowski, P.; Wozniak, M. The Comparison of the Efficiency of Emodin and Aloe-Emodin in Photodynamic Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Wei, S.; Luo, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, A.; Wei, F. Long-Term Effect against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus of Emodin Released from Coaxial Electrospinning Nanofiber Membranes with a Biphasic Profile. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yao, J.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Tang, W.; Liu, J.; Wan, M. Emodin attenuates severe acute pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury by suppressing pancreatic exosome-mediated alveolar macrophage activation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3986–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumit, V.I.; Zerbes, R.M.; Kaeser-Pebernard, S.; Rackiewicz, M.; Wall, M.T.; Gretzmeier, C.; Kuttner, V.; van der Laan, M.; Braun, R.J.; Dengjel, J. Respiratory status determines the effect of emodin on cell viability. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37478–37490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hodge, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Singh, U.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, D.; Ai, W.; et al. Emodin reduces Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis by suppressing Macrophage-induced Breast Cancer Cell Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and Cancer Stem Cell formation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8365–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmeeta, A.; Adhikary, S.; Dharshnaa, V.; Swarnamughi, P.; Ummul, M.Z.; Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Plant-derived bioactive compounds in colon cancer treatment: An updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, S.; Bramanti, A.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Kaluderovic, G.N.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D. Naturally occurring compounds in differentiation based therapy of cancer. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, T.D.; Huang, J.T.; Chou, C.H.; Huang, C.H.; Yang, M.H.; Ho, C.T. Emodin represses TWIST1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting the beta-catenin and Akt pathways. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, C.S.; Hou, Y.C.; Tsai, S.Y.; Huieh, P.H.; Leu, Y.L.; Chao, P.D. Differences in pharmacokinetics and ex vivo antioxidant activity following intravenous and oral administrations of emodin to rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Cai, Z.; Xia, B.; Zhang, J.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z. Species and Gender Differences Affect the Metabolism of Emodin via Glucuronidation. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, E.; Park, M.; Jeong, S.; Kwon, T.; Kim, E.H.; Jung, K.; Kim, A. Poloxamer-Based Thermoreversible Gel for Topical Delivery of Emodin: Influence of P407 and P188 on Solubility of Emodin and Its Application in Cellular Activity Screening. Molecules 2017, 22, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Dong, D.; Lu, D.; Wang, S.; Wu, B. Cremophor EL-based nanoemulsion enhances transcellular permeation of emodin through glucuronidation reduction in UGT1A1-overexpressing MDCKII cells. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2016, 501, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Sun, R.; Mo, Z.; Jin, G.; Wei, F.; Hu, J.; Guan, W.; Zhong, N. Preparation of lung-targeting, emodin-loaded polylactic acid microspheres and their properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6241–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.Y.; Nie, W.; Wang, Y.C.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Gan, S.J. Electrospun emodin polyvinylpyrrolidone blended nanofibrous membrane: A novel medicated biomaterial for drug delivery and accelerated wound healing. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirbagheri, M.S.; Akhavan-Mahdavi, S.; Hasan, A.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jafari, S.M. Chitosan-based electrospun nanofibers for diabetic foot ulcer management; recent advances. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 313, 120512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, R.D.; Powell, J.D. Metabolism of immune cells in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 516–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinones, E.D.; Lu, T.Y.; Liu, K.T.; Fan, Y.J.; Chuang, E.Y.; Yu, J. Glycol chitosan/iron oxide/polypyrrole nanoclusters for precise chemodynamic/photothermal synergistic therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, H.S.; Yadav, P.N. Anticancer Activity of Chitosan, Chitosan Derivatives, and Their Mechanism of Action. Int. J. Biomater. 2018, 2018, 2952085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Mu, M.; Fan, R.; Zou, B.; Guo, G. Functionalized chitosan as a promising platform for cancer immunotherapy: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2022, 290, 119452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiki, Y.; Iskandar, A.; Wong, T.W. Functionalized chitosan for cancer nano drug delivery. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 67, 108200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, X.; Shiu, B.C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Ye, Y.; Fang, R. Chitosan-Urushiol nanofiber membrane with enhanced acid resistance and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 312, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, C.; Thompson, Z.; Bhattarai, N. 15—Electrospun chitosan fibers. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Afshari, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 371–398. [Google Scholar]
- Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M.; Morariu, S. Biomaterials of PVA and PVP in medical and pharmaceutical applications: Perspectives and challenges. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Gao, J.; Yang, R.; Yuan, C.; Wang, R.; Zou, Q.; Zuo, Y.; Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Man, Y.; et al. A baicalin-loaded coaxial nanofiber scaffold regulated inflammation and osteoclast differentiation for vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulmalik, S.; Gallo, J.; Nip, J.; Katebifar, S.; Arul, M.; Lebaschi, A.; Munch, L.N.; Bartly, J.M.; Choudhary, S.; Kalajzic, I.; et al. Nanofiber matrix formulations for the delivery of Exendin-4 for tendon regeneration: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 25, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailincai, D.; Cibotaru, S.; Anisiei, A.; Coman, C.G.; Pasca, A.S.; Rosca, I.; Sandu, A.I.; Mititelu-Tartau, L.; Marin, L. Mesoporous chitosan nanofibers loaded with norfloxacin and coated with phenylboronic acid perform as bioabsorbable active dressings to accelerate the healing of burn wounds. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 318, 121135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Song, Y.; He, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Hydrogel-Functionalized Bandages with Janus Wettability for Efficient Unidirectional Drug Delivery and Wound Care. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 3468–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, B. Electrospun PCL/mupirocin and chitosan/lidocaine hydrochloride multifunctional double layer nanofibrous scaffolds for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5287–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Im, J.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H. Electro-responsive transdermal drug delivery behavior of PVA/PAA/MWCNT nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grada, A.; Otero-Vinas, M.; Prieto-Castrillo, F.; Obagi, Z.; Falanga, V. Research Techniques Made Simple: Analysis of Collective Cell Migration Using the Wound Healing Assay. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Hussain, T.; Nazir, A.; Zahir, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Hameed, M.; Khenoussi, N. Enhanced antibacterial activity of PEO-chitosan nanofibers with potential application in burn infection management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 1222–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Li, X.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Liu, D.; Wu, Y.Q.; Hou, F.F.; Ye, L.; Wu, C.J.; Feng, X.D.; et al. Novel Double-Layer Dissolving Microneedles for Transmucosal Sequential Delivery of Multiple Drugs in the Treatment of Oral Mucosa Diseases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13892–13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrimali, D.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Zhang, J.; Tan, B.K.H.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. Targeted abrogation of diverse signal transduction cascades by emodin for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 341, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, M.; Biziato, D.; Petrova, T.V. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, V.; Kamran, M.Z.; Ranjan, A.; Nimesh, H.; Singh, M.; Tandon, V. Akt1/NFkappaB signaling pathway activation by a small molecule DMA confers radioprotection to intestinal epithelium in xenograft model. Free Radic. Bio Med. 2017, 108, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wang, P.; Huang, C.; Zhou, S. The crosstalk between reactive oxygen species and noncoding RNAs: From cancer code to drug role. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Tian, R.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, G.; Yu, P.; Chang, J.; Chen, X. Beyond Photo: Xdynamic Therapies in Fighting Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2007488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, P.; Yusufu, R.; Guan, Z.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lu, J.; Luo, M.; Wei, F. Multifunctional Bioactivity Electrospinning Nanofibers Encapsulating Emodin Provide a Potential Postoperative Management Strategy for Skin Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091131
Ye P, Yusufu R, Guan Z, Chen T, Li S, Feng Y, Zeng X, Lu J, Luo M, Wei F. Multifunctional Bioactivity Electrospinning Nanofibers Encapsulating Emodin Provide a Potential Postoperative Management Strategy for Skin Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(9):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091131
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Peiwen, Reyisha Yusufu, Zhenfeng Guan, Tiantian Chen, Siyi Li, Yanping Feng, Xiaoyan Zeng, Jingya Lu, Muxiang Luo, and Fenghuan Wei. 2024. "Multifunctional Bioactivity Electrospinning Nanofibers Encapsulating Emodin Provide a Potential Postoperative Management Strategy for Skin Cancer" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 9: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091131
APA StyleYe, P., Yusufu, R., Guan, Z., Chen, T., Li, S., Feng, Y., Zeng, X., Lu, J., Luo, M., & Wei, F. (2024). Multifunctional Bioactivity Electrospinning Nanofibers Encapsulating Emodin Provide a Potential Postoperative Management Strategy for Skin Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 16(9), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091131





