Emerging Trends in Bilosomes as Therapeutic Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
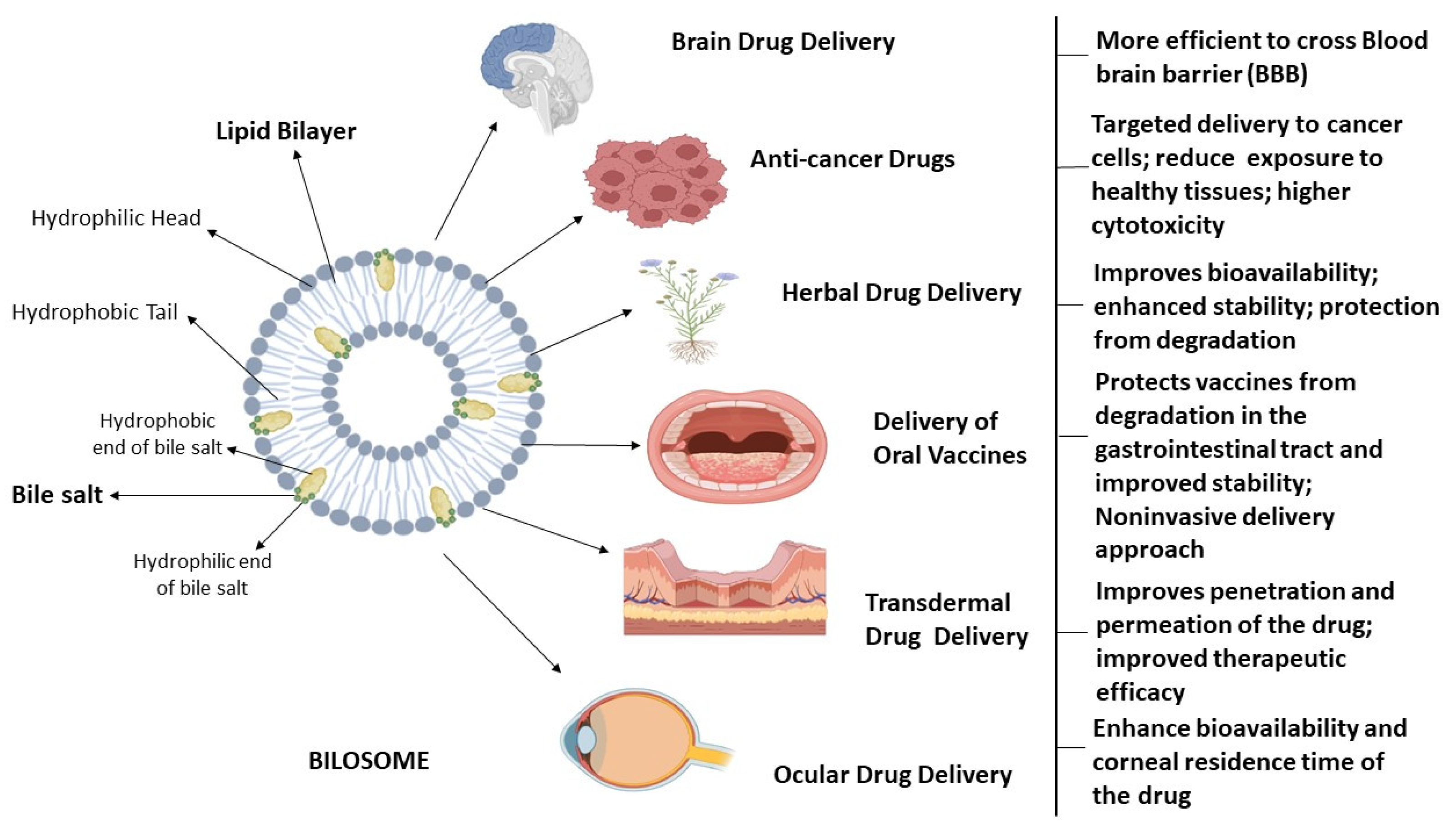
3. Bilosomes: Structural Aspects
3.1. Lipids as a Component of Bilosomes
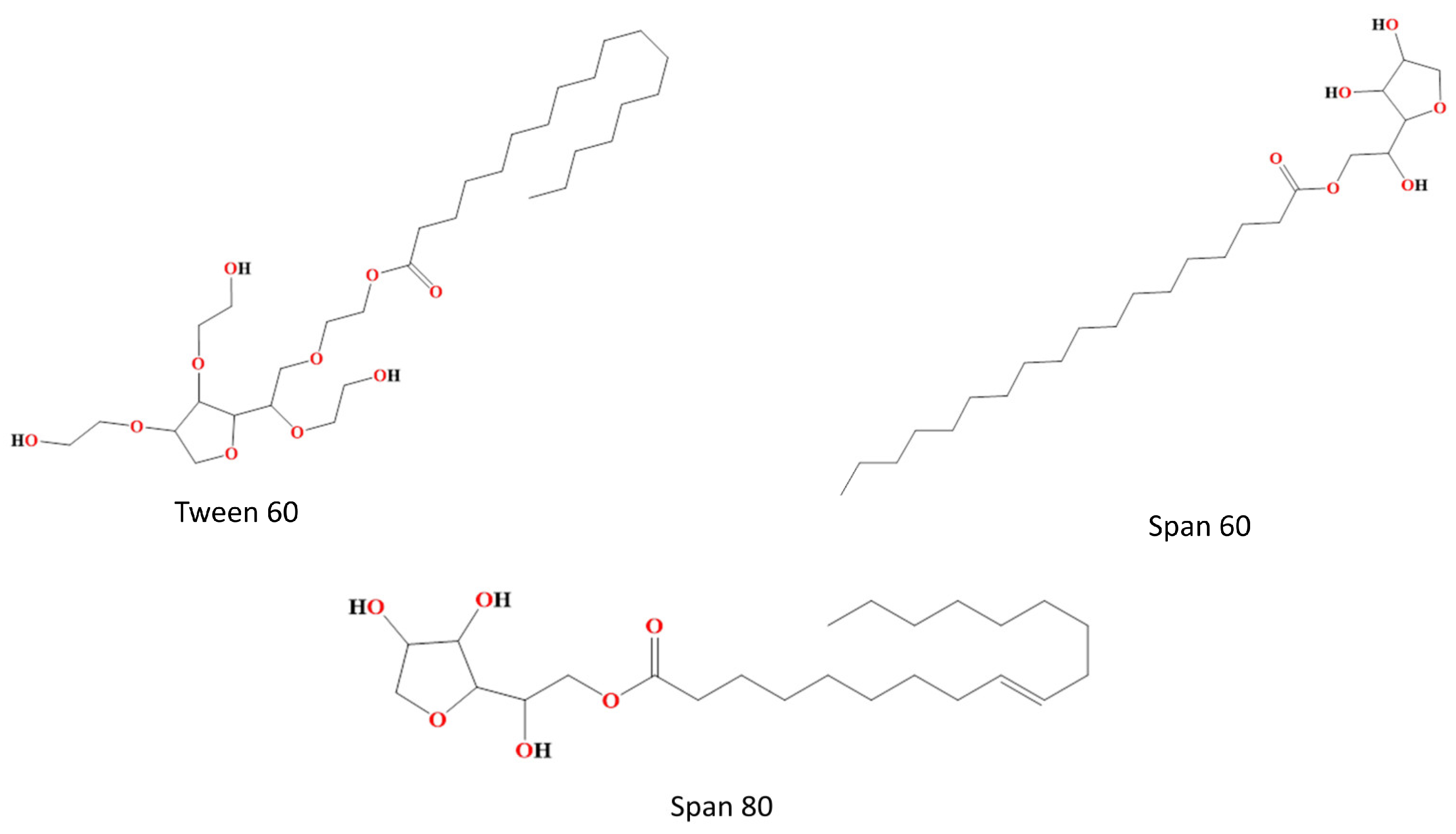
3.2. Non-Ionic Surfactant as a Component of Bilosomes
3.3. Bile Salts as a Component of Bilosomes
4. Bilosomes as Nanocarrier Drug Delivery System for Treating Various Disorders
4.1. Bilosomes as Drug Delivery System for Brain Disorders
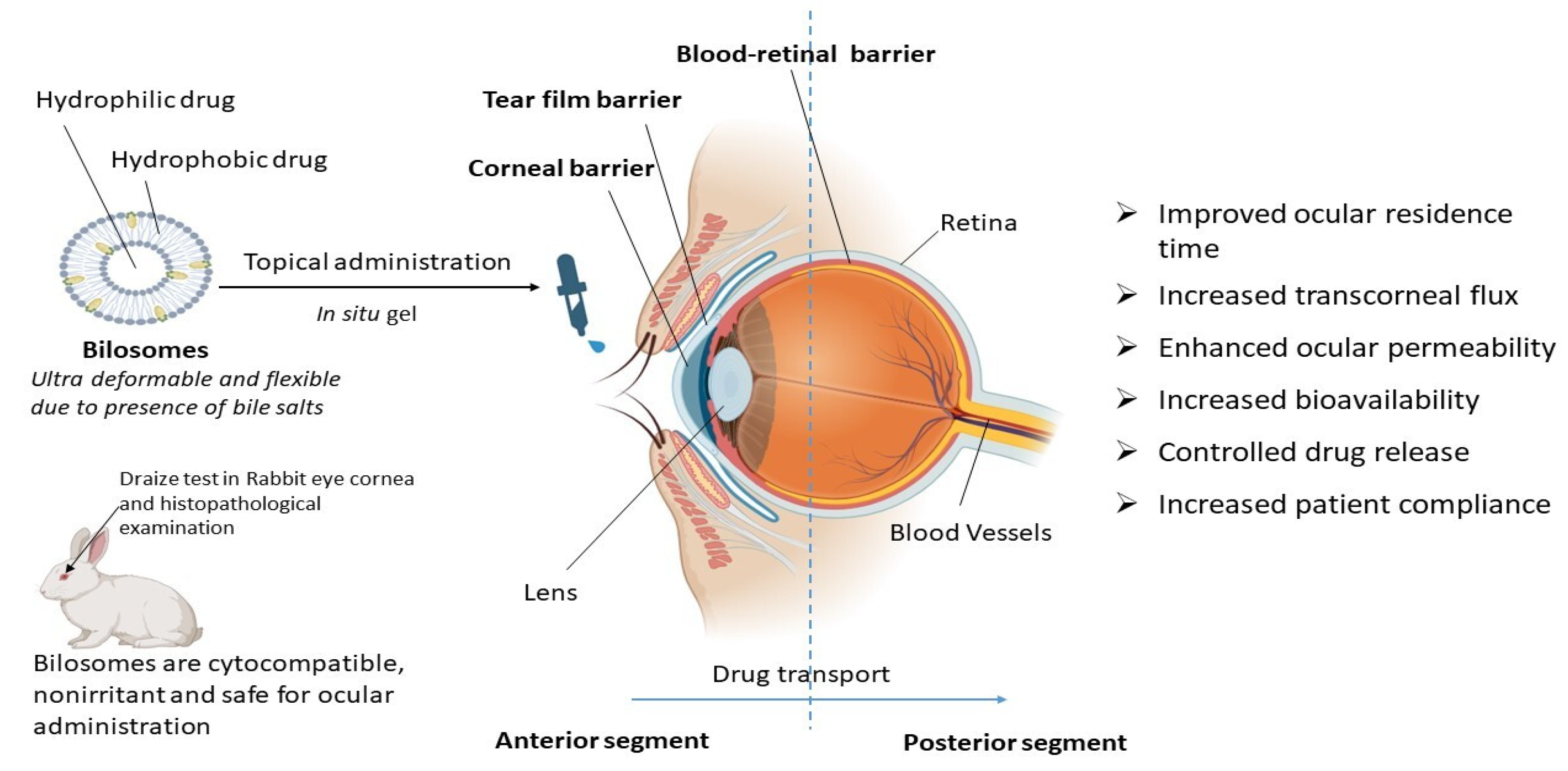
4.2. Bilosomes as an Ocular Drug Delivery System
4.3. Bilosomes for Delivery of Oral Vaccines
4.4. Bilosomes for Delivery of Proteins and Peptides
4.5. Bilosomes as Transdermal Drug Delivery System
| No. | Drug | Formulation | Therapeutic Problem | Study Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diacerin (DCN) | Bilosomes | Poorly bioavailable (35–56%) osteoarthritic drug with gastrointestinal side effects on oral administration | Bilosomes were found to be superior than niosomes and pure suspension for enhancing DCN flow through the skin | [11] |
| 2 | Olmesartan medoxomil (OLM) | PEGylated bilosomes | Poor oral bioavailability of 26% which limits its therapeutic efficacy | Higher OLM deposition in rat’s skin from bilosomal formulation compared to transethosomes and OLM suspension was found as per in vivo skin deposition studies | [24] |
| 3 | Tizanidine HCL (TZN) | Bilosomes | Poor bioavailability | Enhanced transdermal permeation compared to plain drug | [64] |
| 4 | Terbutaline sulfate (TBN) | TBN chitosan-coated bilosomes (TBN-CTS-BLS) | Poor oral bioavailability due to hepatic first-pass metabolism | 2.33-fold increase in TBN bioavailability and t1/2 was increased to 6.21 ± 0.24 h when using the optimized TBN-CTS-BLS formulation compared to the oral TBN solution in the rat model | [65] |
| 5 | Lornoxicam | Bilosomes | Poor aqueous solubility and rapid clearance, GIT toxicity | In vivo pharmacodynamic activity in male rats and mice model demonstrated enhanced anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity compared to that of the oral marketed product | [66] |
| 6 | Dapsone (DPS) | Bilosomes | Low solubility and toxicity through oral administration | Ex vivo deposition study of optimized DPS-loaded bilosomes showed 170.57 ± 55.12 μg/mL DPS retention compared to 120.24 ± 10.7 μg/mL from DPS alcoholic solution | [68] |
| 7 | Sildenafil citrate (SC) | Nanobilosomes | Poor bioavailability | In vivo study in Sprague Dawley rats revealed 2-folds increase in intromission frequency and intromission ratio compared to untreated group | [69] |
| 8 | Teroconazole (TCZ) | Highly deformable bilosomes (HBs) | Poor permeability | In vivo studies showed improvement in terconazole skin deposition compared to typical bilosomal formulation and TCZ suspension | [70] |
| 9 | Diclofenac sodium (DNa) | Bilosomal gel | Gastrointestinal side effects on oral administration | Ex vivo permeation studies of optimized formulation showed a 2.5-fold increase in skin permeability than DNa solution, In vivo studies in paw edema rat model also revealed significant suppression of inflammatory mediators and reduction in paw edema | [71] |
| 10 | Metformin HCL | Bilosomes | Adverse effects | Permeation flux was found to be enhanced (198.79–431.91 ng cm −2 h−1) in comparison to the plain drug (154.26 ng cm −2 h−1). | [72] |
| 11 | Miconaole nitrate (MN) | Chitosan–carbopol bilosomal gel | Poor water solubility | Enhanced antifungal activity compared to pure drug against Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger | [73] |
| 12 | Simvastatin (SMV) | Bilosomal gel | Poor bioavailability due to water insolubility and hepatic first-pass effect. | 3-fold increase in SMV transdermal flux from SMV-loaded bilosomal gel compared to plain drug suspension. Bioavailability of SMV-BS gel was also found to be ~2-fold and ~3-fold higher than those of oral SMV suspension and SMV gel, respectively | [74] |
| 13 | Dronedarone hydrochloride (DRN) | Bilosomal nanogel | Poor bioavailability | Bilosomal gel demonstrated enhanced release (57.0 ± 8.68% of DRN compared to only 13.3 ± 1.2% released from drug suspension after 12 h) and enhanced skin permeation | [75] |
4.6. Bilosomes as Cancer Drug Delivery System
| No. | Drug | Formulation | Therapeutic Problem | Study Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cisplatin | Cytostatic bile acid incorporated liposomes | Cisplatin resistance in cancer cell lines | Enhanced ability of anticancer drug to be taken up by cancer cell due to the presence of cytostatic bile acids. | [77] |
| 2 | Silymarin | Dextrose-modified bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | Dextrose bilosomes loaded with silymarin were tested in vivo for treating Diethyl nitrosamine (DEN)-induced hepatic malignancy. The mice had longer lifespans and less tumor load, suggesting more therapeutic potential. | [78] |
| 3 | Lead acrylamide molecules | Lead acrylamide molecules utilizing 4e-charged PEGylated bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | Cytotoxicity testing showed that compounds 4e and 5d were effective against MCF-7 cells. After integration into the nano-PEGylated bilosomal system, the drug’s cytotoxic activity was increased. | [79] |
| 4 | Icariin and Melittin | Icariin-loaded bilosomes-melittin (ICA-BM) | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | ICA-BM showed a lower IC50 than blank-BM and ICA-pure. ICA-BM formulation increased icariin’s effectiveness against malignant pancreatic cells. | [80] |
| 5 | Luteolin | PEGylated bilosomes (LL-BLs) | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | LL-BLs showed greater cell viability than the pure drug on MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. It was found that the IC50 values for MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cancer cells were 390 M and 510 M, respectively. | [82] |
| 6 | Sulfated polysaccharide–protein complexes | Bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | Substantial decrease in serum α-fetoprotein, endoglin, lipocalin-2, and heat shock protein 70 levels. The photomicrographs of rat liver tissue slices showed a focal area of pleomorphic hepatocytes that had deteriorated, together with fine fibrosis emanating from the portal region. | [83] |
| 7 | Curcumin (CUR) analogue 3,5-bis(4-bromobenzylidene)-1-propanoylpiperidin-4-one | Nano-bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and permeability | Antitumor selectivity index of CUR analogue-loaded bilosomes recorded 420.55 against liver cancer cells when compared to a CUR suspension. | [85] |
| 8 | Apigenin | Chitosan-coated bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | Antimicrobial and cell viability analyses demonstrated better outcomes with regard to inhibition and cell line assessment against two MCF-7 breast cancer and A549 lung cancer cell lines. | [87] |
| 9 | Pitvaststin | Bilosomes | Poor bioavailability | Improvement in the cytotoxicity of HepG2 spheroids, which was 44 times greater than that of pitavastatin (PIT) solution. | [88] |
| 10 | Quercetin | Chitosan-coated quercetin-bilosomes | Low bioavailability | 1.61-fold higher cytotoxicity of surface-modified chitosan-coated quercetin-bilosomes against MFC7 and 1.44-fold higher cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 than pure quercetin. | [89] |
| 11 | Psoralidin (Ps) | Chitosan-coated bilosomes | Water insoluble, dose-dependent toxicity | Apoptotic and necrotic potential of the developed formulation was evaluated in human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7) and human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines (A549), in which a significant increase in the percentages of the apoptotic and necrotic cells was found compared to the control and free Ps. | [91] |
| 12 | Doxorubicin (DOX) | Bilosomes | High dose-related toxicity | Formulation showed improved DOX cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells (MCF-7) and the reduced IC50 value from 13.3 μM to 0.1 μM. A 4.5–6 and 1.8–2.5-fold increase in drug absorption from jejuno-ileum and colon was demonstrated. | [18] |
4.7. Bilosomes for Delivery of Herbal Drugs
| No | Drug | Formulation | Therapeutic Problem | Outcome of Study | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Silymarin | Bilosomes | Poor water solubility and stability | Ex vivo intestinal uptake study revealed the superiority of bilosomes compared to liposomes for strong hepatoprotective effect | [12] |
| 2 | Berberine (BER) and curcumin (CUR) | Bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and biodistribution | In vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation of bilosomal formulation in mice model showed improved and synchronized oral bioabsorption of both BER and CUR | [15] |
| 3 | Apigenin (AG) | Bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | In vivo permeation and pharmacokinetic studies showed that the free AG-dispersion had a 4.49 times higher flux and a 4.67 folds higher AUC0–t | [95] |
| 4 | Piperine | Bilosomes | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | Piperine-loaded bilosomes had higher oral bioavailability than piperine suspension. Additionally, the optimized formula’s antiviral activity and safety margin were much higher than those of the drug suspension | [96] |
| 5 | Berberine (BER) | Chitosan-coated bilosomal gel | Poor bioavailability and low solubility | In comparison to the BER solution, formulation showed greater stability and sustained release of BER. In vivo study, formulation significantly reduced blood sugar, with a maximum drop of 41%, compared to BER-blood SOL’s sugar reduction of only 19% | [16] |
| 6 | Resveratrol (RSV) | Nanobilosomes | Poor bioavailability | Caco-2 cell lines study showed 4.7 fold increase in cellular uptake compared to RSV dispersion | [100] |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kecman, S.; Škrbić, R.; Badnjevic Cengic, A.; Mooranian, A.; Al-Salami, H.; Mikov, M.; Golocorbin-Kon, S. Potentials of human bile acids and their salts in pharmaceutical nano delivery and formulations adjuvants. Technol. Health Care 2020, 28, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburahma, M.H. Bile salts-containing vesicles: Promising pharmaceutical carriers for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs and peptide/protein-based therapeutics or vaccines. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1847–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, C.; Serafim, C.; Rijo, P.; Reis, C.P. Bile acids and bile acid derivatives: Use in drug delivery systems and as therapeutic agents. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimipour, E.; Ameri, A.; Handali, S. Absorption-Enhancing Effects of Bile Salts. Molecules 2015, 20, 14451–14473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, N.; Goločorbin-Kon, S.; Ðanić, M.; Stanimirov, B.; Al-Salami, H.; Stankov, K.; Mikov, M. Bile Acids and Their Derivatives as Potential Modifiers of Drug Release and Pharmacokinetic Profiles. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojančević, M.; Pavlović, N.; Goločorbin-Kon, S.; Mikov, M. Application of bile acids in drug formulation and delivery. Front. Life Sci. 2013, 7, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.O.; Mohamed, M.I.; Tadros, M.I.; Fouly, A.A. High frequency ultrasound mediated transdermal delivery of ondansetron hydrochloride employing bilosomal gel systems: Ex-vivo and in-vivo characterization studies. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Ahad, A.; Waheed, A.; Aqil, M.; Al-Jenoobi, F.I.; Al-Mohizea, A.M. Bilosomes: A novel platform for drug delivery. In Systems of Nanovesicular Drug Delivery; Nayak, A.K., Hasnain, M.S., Aminabhavi, T.M., Torchilin, V.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 293–309. [Google Scholar]
- Palekar-Shanbhag, P.; Lande, S.; Chandra, R.; Rane, D. Bilosomes: Superior Vesicular Carriers. Curr. Drug Ther. 2020, 15, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conacher, M.; Alexander, J.; Brewer, J.M. Oral immunisation with peptide and protein antigens by formulation in lipid vesicles incorporating bile salts (bilosomes). Vaccine 2001, 19, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, D.E.; Abdelbary, A.A.; Elassasy, A.I. Investigating superiority of novel bilosomes over niosomes in the transdermal delivery of diacerein: In vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo skin deposition study. J. Liposome Res. 2019, 29, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, A.M.; Asfour, M.H.; Salama, A.A.A. Improved hepatoprotective activity of silymarin via encapsulation in the novel vesicular nanosystem bilosomes. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premanand, B.; Prabakaran, M.; Kiener, T.K.; Kwang, J. Recombinant baculovirus associated with bilosomes as an oral vaccine candidate against HEV71 infection in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Jing, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, H. Bilosomes as effective delivery systems to improve the gastrointestinal stability and bioavailability of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, R.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Huang, J.; Shen, X.; et al. Improving the ameliorative effects of berberine and curcumin combination via dextran-coated bilosomes on non-alcohol fatty liver disease in mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Elmowafy, M.; Shalaby, K.; Zafar, A.; Ahmad, N.; Alsalahat, I.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Eissa, E.M.; Eid, H.M. Surface-Modified Bilosomes Nanogel Bearing a Natural Plant Alkaloid for Safe Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Lu, Y.; Hovgaard, L.; Guan, P.; Tan, Y.; Lian, R.; Qi, J.; Wu, W. Hypoglycemic activity and oral bioavailability of insulin-loaded liposomes containing bile salts in rats: The effect of cholate type, particle size and administered dose. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, A.A.; Saad, G.A.; El Maghraby, G.M. Permeation enhancers loaded bilosomes for improved intestinal absorption and cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waglewska, E.; Maliszewska, I.; Bazylińska, U. Antimicrobial phyto-photodynamic activity inducing by polyphenol-supported Methylene Blue co-loaded into multifunctional bilosomes: Advanced hybrid nanoplatform in the skin infections treatment? J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2023, 240, 112650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-moneum, R.; Abdel-Rashid, R.S. Bile salt stabilized nanovesicles as a promising drug delivery technology: A general overview and future perspectives. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 79, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarenezhad, E.; Marzi, M.; Abdulabbas, H.T.; Jasim, S.A.; Kouhpayeh, S.A.; Barbaresi, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Ghasemian, A. Bilosomes as Nanocarriers for the Drug and Vaccine Delivery against Gastrointestinal Infections: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.; Shakir, E.; Carter, K.C.; Mullen, A.B.; Alexander, J.; Ferro, V.A. Lipid vesicle size of an oral influenza vaccine delivery vehicle influences the Th1/Th2 bias in the immune response and protection against infection. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3643–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Kreutzberger, A.J.B.; Lee, J.; Kiessling, V.; Tamm, L.K. The role of cholesterol in membrane fusion. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2016, 199, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albash, R.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Refai, H.; Abdelbary, A.A. Tailoring of PEGylated bilosomes for promoting the transdermal delivery of olmesartan medoxomil: In-vitro characterization, ex-vivo permeation and in-vivo assessment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6555–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.S.; Srivastava, V.; Bhavana, V.; Yadav, R.; Rajana, N.; Singh, S.B.; Mehra, N.K. Exploring Penetration Ability of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor-Loaded Ultradeformable Bilosome for Effective Ocular Application. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifi, Z.; Rizwanullah, M.; Mir, S.R.; Amin, S. Bilosomes nanocarriers for improved oral bioavailability of acyclovir: A complete characterization through in vitro, ex-vivo and in vivo assessment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.P.; Rajeshwarrao, P. Nonionic surfactant vesicular systems for effective drug delivery—An overview. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2011, 1, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbari, M.A.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Abdelbary, A.A.; Mosallam, S. Implementing Nanovesicles for Boosting the Skin Permeation of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wei, M.; He, S.; Yuan, W.E. Advances of Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) and Their Application in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkhu, J.S.; McNeil, S.E.; Anderson, D.E.; Perrie, Y. Characterization and optimization of bilosomes for oral vaccine delivery. J. Drug Target 2013, 21, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilkwar, R.N.; Nanjwade, B.K.; Nwaji, M.S.; Idris, S.A.M.; Mohamied, A.S. Bilosomes Based Drug Delivery System. J. Chem. Appl. 2015, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Mandal, R.P.; De, S. Addressing the Superior Drug Delivery Performance of Bilosomes—A Microscopy and Fluorescence Study. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3896–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaurav, H.; Kapoor, D.N. Implantable systems for drug delivery to the brain. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. Blood-brain barrier delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabh, P.; Braun, A.; Nedergaard, M. The blood-brain barrier: An overview: Structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaurav, H.; Kapoor, D.N.; Upadhyay, N.K. Bilosomes in brain drug delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2023, 14, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmela, I.; Correia, L.; Silva, R.F.; Sasaki, H.; Kim, K.S.; Brites, D.; Brito, M.A. Hydrophilic bile acids protect human blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from disruption by unconjugated bilirubin: An in vitro study. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Gad, H.A.; Khattab, M.A.; Mansour, M. The Tragedy of Alzheimer’s Disease: Towards Better Management via Resveratrol-Loaded Oral Bilosomes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Resveratrol: A Double-Edged Sword in Health Benefits. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Refai, H.; El Sayed, N.; Rashed, L.A.; Mousa, M.R.; Zewail, M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide loaded chitosan coated bilosomes for magnetic nose to brain targeting of resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Taweel, M.M.; Aboul-Einien, M.H.; Kassem, M.A.; Elkasabgy, N.A. Intranasal Zolmitriptan-Loaded Bilosomes with Extended Nasal Mucociliary Transit Time for Direct Nose to Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, M.A.; El-Feky, Y.A.; Al-Sawahli, M.M.; Ali, M.E.; Fayez, A.M.; Abbas, H. A Brain-Targeted Approach to Ameliorate Memory Disorders in a Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model via Intranasal Luteolin-Loaded Nanobilosomes. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, V.A.; Sharma, A.; Rajesh, K.S.; Arunraj, T.R.; Gururaj, M.P.; Parasuraman, S.; John, A. Bilosomes as a Potential Carrier to Enhance Cognitive Effects of Bacopa monnieri Extract on Oral Administration. J. Health Allied Sci. NU 2022, 13, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, Y.; Jain, R.; Aqil, M.; Ali, A. Review of ocular drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Singh, V.; Kumar Khatri, D.; Kumar Mehra, N. Recent trends and updates on ultradeformable and elastic vesicles in ocular drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gote, V.; Sikder, S.; Sicotte, J.; Pal, D. Ocular Drug Delivery: Present Innovations and Future Challenges. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 602–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbary, A.A.; Abd-Elsalam, W.H.; Al-Mahallawi, A.M. Fabrication of novel ultradeformable bilosomes for enhanced ocular delivery of terconazole: In vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo safety assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janga, K.Y.; Tatke, A.; Balguri, S.P.; Lamichanne, S.P.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Maria, D.N.; Jablonski, M.M.; Majumdar, S. Ion-sensitive in situ hydrogels of natamycin bilosomes for enhanced and prolonged ocular pharmacotherapy: In vitro permeability, cytotoxicity and in vivo evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, A.M.; Salama, A.; Kassem, A.A. Development of acetazolamide loaded bilosomes for improved ocular delivery: Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemr, A.A.; El-Mahrouk, G.M.; Badie, H.A. Hyaluronic acid-enriched bilosomes: An approach to enhance ocular delivery of agomelatine via D-optimal design: Formulation, in vitro characterization, and in vivo pharmacodynamic evaluation in rabbits. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, M.G.; El-Zahaby, S.A.; Al-Mahallawi, A.M.; Ghorab, D.M. Fabrication of betaxolol hydrochloride-loaded highly permeable ocular bilosomes (HPOBs) to combat glaucoma: In vitro, ex vivo & in vivo characterizations. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 82, 104363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaidan, O.A.; Zafar, A.; Yasir, M.; Alzarea, S.I.; Alqinyah, M.; Khalid, M. Development of Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Bilosomes In-Situ Gel for Ocular Delivery: Optimization, In-Vitro Characterization, Ex-Vivo Permeation, and Antimicrobial Study. Gels 2022, 8, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Alsaidan, O.A.; Imam, S.S.; Yasir, M.; Alharbi, K.S.; Khalid, M. Formulation and Evaluation of Moxifloxacin Loaded Bilosomes In-Situ Gel: Optimization to Antibacterial Evaluation. Gels 2022, 8, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Mishra, V.; Kesharwani, P. Bilosomes in the context of oral immunization: Development, challenges and opportunities. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B.; Vyas, S.P. M-cell targeted delivery of recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen using cholera toxin B subunit conjugated bilosomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Indulkar, A.; Harde, H.; Agrawal, A.K. Oral mucosal immunization using glucomannosylated bilosomes. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 932–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Singhal, M.; Amin, S.; Rizwanullah, M.; Akhter, S.; Kamal, M.A.; Haider, N.; Midoux, P.; Pichon, C. Bile Salt Stabilized Vesicles (Bilosomes): A Novel Nano-Pharmaceutical Design for Oral Delivery of Proteins and Peptides. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Niu, M.; Hu, F.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Yin, Z.; Wu, W. Integrity and stability of oral liposomes containing bile salts studied in simulated and ex vivo gastrointestinal media. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Tan, Y.; Guan, P.; Hovgaard, L.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Lian, R.; Li, X.; Wu, W. Enhanced oral absorption of insulin-loaded liposomes containing bile salts: A mechanistic study. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallamothu, B.; Kuche, K.; Ghadi, R.; Chaudhari, D.; Jain, S. Enhancing oral bioavailability of insulin through bilosomes: Implication of charge and chain length on apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT) uptake. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Elias, P.M.; Franz, T.J.; Schmuth, M.; Tsai, J.-C.; Menon, G.K.; Holleran, W.M.; Feingold, K.R. Skin Barrier and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Dermatology 2012, 3, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, K.S.; Milewski, M.; Swadley, C.L.; Brogden, N.K.; Ghosh, P.; Stinchcomb, A.L. Challenges and opportunities in dermal/transdermal delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Laithy, H.M.; Basalious, E.B.; El-Hoseiny, B.M.; Adel, M.M. Novel self-nanoemulsifying self-nanosuspension (SNESNS) for enhancing oral bioavailability of diacerein: Simultaneous portal blood absorption and lymphatic delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.M.; Abdelbary, A.; Kocova El-Arini, S.; Basha, M.; El-Hashemy, H.A. Evaluation of bilosomes as nanocarriers for transdermal delivery of tizanidine hydrochloride: In vitro and ex vivo optimization. J. Liposome Res. 2019, 29, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Menshawe, S.F.; Aboud, H.M.; Elkomy, M.H.; Kharshoum, R.M.; Abdeltwab, A.M. A novel nanogel loaded with chitosan decorated bilosomes for transdermal delivery of terbutaline sulfate: Artificial neural network optimization, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kassem, M.A.; Sayed, S. Bilosomes as Promising Nanovesicular Carriers for Improved Transdermal Delivery: Construction, in vitro Optimization, ex vivo Permeation and in vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9783–9798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahiem, B.; Shamma, R.; Salama, A.; Refai, H. Magnetic targeting of lornoxicam/SPION bilosomes loaded in a thermosensitive in situ hydrogel system for the management of osteoarthritis: Optimization, in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo studies in rat model via modulation of RANKL/OPG. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Shamma, R.N.; Farouk, F.; Nasralla, S.M. Bilosomes as a novel carrier for the cutaneous delivery for dapsone as a potential treatment of acne: Preparation, characterization and in vivo skin deposition assay. J. Liposome Res. 2020, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelalim, L.R.; Abdallah, O.Y.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R. High efficacy, rapid onset nanobiolosomes of sildenafil as a topical therapy for erectile dysfunction in aged rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 591, 119978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallam, S.; Sheta, N.M.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Abdelbary, A.A. Fabrication of Highly Deformable Bilosomes for Enhancing the Topical Delivery of Terconazole: In Vitro Characterization, Microbiological Evaluation, and In Vivo Skin Deposition Study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, T.M.; Nafady, M.M.; Farouk, H.O.; Mahmoud, D.M.; Ahmed, Y.M.; Zaki, R.M.; Hamad, D.S. Novel Bile Salt Stabilized Vesicles-Mediated Effective Topical Delivery of Diclofenac Sodium: A New Therapeutic Approach for Pain and Inflammation. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.F.; Nafady, M.M.; Ali, A.A.; Khalil, N.M.; Elsisi, A.A. Evaluation of Metformin Hydrochloride Tailoring Bilosomes as an Effective Transdermal Nanocarrier. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1185–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, S.S.; Gilani, S.J.; Zafar, A.; Jumah, M.N.B.; Alshehri, S. Formulation of Miconazole-Loaded Chitosan-Carbopol Vesicular Gel: Optimization to In Vitro Characterization, Irritation, and Antifungal Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khafagy, E.S.; Almutairy, B.K.; Abu Lila, A.S. Tailoring of Novel Bile Salt Stabilized Vesicles for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Simvastatin: A New Therapeutic Approach against Inflammation. Polymers 2023, 15, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teaima, M.H.; Alsofany, J.M.; El-Nabarawi, M.A. Clove Oil Endorsed Transdermal Flux of Dronedarone Hydrochloride Loaded Bilosomal Nanogel: Factorial Design, In vitro Evaluation and Ex vivo Permeation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, S.; Alharbi, K.S.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Alotaibi, N.H.; Almalki, W.H.; Alenezi, S.K.; Altowayan, W.M.; Alshammari, M.S.; Rahman, M. Nanotherapeutic systems for delivering cancer vaccines: Recent advances. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briz, O.; Macias, R.I.; Vallejo, M.; Silva, A.; Serrano, M.A.; Marin, J.J. Usefulness of liposomes loaded with cytostatic bile acid derivatives to circumvent chemotherapy resistance of enterohepatic tumors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, P.; Rana, P.; Dwivedi, M.; Saraf, S.A. Dextrose modified bilosomes for peroral delivery: Improved therapeutic potential and stability of silymarin in diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic carcinoma in rats. J. Liposome Res. 2019, 29, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, I.; Abou-Elkhair, R.A.; Abu Almaaty, A.H.; AAbu Ali, O.; Fayad, E.; Ahmed Gaafar, A.G.; Zakaria, M.Y. Design and Synthesis of Newly Synthesized Acrylamide Derivatives as Potential Chemotherapeutic Agents against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line Lodged on PEGylated Bilosomal Nano-Vesicles for Improving Cytotoxic Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Alharbi, W.S.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Al-Hejaili, O.D.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Eid, B.G.; Bakhaidar, R.; Drago, F.; Caraci, F.; et al. Development of an Icariin-Loaded Bilosome-Melittin Formulation with Improved Anticancer Activity against Cancerous Pancreatic Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Caruso, G.; Al-Rabia, M.W.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Asfour, H.Z.; Alshehri, S.; Alzaharani, S.H.; Alhamdan, M.M.; Rizg, W.Y.; et al. Piceatannol-Loaded Bilosome-Stabilized Zein Protein Exhibits Enhanced Cytostatic and Apoptotic Activities in Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Imam, S.S.; Alsaidan, O.A.; Yasir, M.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshehri, S.; Anwer, M.K.; Almurshedi, A.S.; Alanazi, A.S. Development and evaluation of luteolin loaded pegylated bilosome: Optimization, in vitro characterization, and cytotoxicity study. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 2562–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matloub, A.A.; Salama, A.H.; Aglan, H.A.; AbouSamra, M.M.; ElSouda, S.S.M.; Ahmed, H.H. Exploiting bilosomes for delivering bioactive polysaccharide isolated from Enteromorpha intestinalis for hacking hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, S.I.; Priya, A.; Balasubramaniam, B.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Sivasankar, C.; Selvaraj, A.; Valliammai, A.; Jothi, R.; Pandian, S. Biomedical Applications and Bioavailability of Curcumin-An Updated Overview. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, H.; El-Feky, Y.A.; Al-Sawahli, M.M.; El-Deeb, N.M.; El-Nassan, H.B.; Zewail, M. Development and optimization of curcumin analog nano-bilosomes using 2(1).3(1) full factorial design for anti-tumor profiles improvement in human hepatocellular carcinoma: In-vitro evaluation, in-vivo safety assay. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, H.; Amin, M.M.; Fayad, W.; Zakaria, M.Y. TPGS surface modified bilosomes as boosting cytotoxic oral delivery systems of curcumin against doxorubicin resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 619, 121717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Altamimi, M.A.; Almalki, R.K.H.; Hussain, A.; Bukhari, S.I.; Mahdi, W.A.; Qamar, W. Formulation of Chitosan-Coated Apigenin Bilosomes: In Vitro Characterization, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Assessment. Polymers 2022, 14, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharouba, M.; El-Kamel, A.; Mehanna, R.; Thabet, E.; Heikal, L. Pitavastatin-loaded bilosomes for oral treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A repurposing approach. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2925–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alruwaili, N.K.; Zafar, A.; Alsaidan, O.A.; Yasir, M.; Mostafa, E.M.; Alnomasy, S.F.; Rawaf, A.; Alquraini, A.; Alomar, F.A. Development of surface modified bilosomes for the oral delivery of quercetin: Optimization, characterization in-vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial, and cytotoxicity study. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 3035–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Kamiloglu, S.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Beyatli, A.; Alfred, M.A.; Salehi, B.; Calina, D.; Docea, A.O.; Imran, M.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; et al. Pharmacological Activities of Psoralidin: A Comprehensive Review of the Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 571459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youness, R.A.; Al-Mahallawi, A.M.; Mahmoud, F.H.; Atta, H.; Braoudaki, M.; Fahmy, S.A. Oral Delivery of Psoralidin by Mucoadhesive Surface-Modified Bilosomes Showed Boosted Apoptotic and Necrotic Effects against Breast and Lung Cancer Cells. Polymers 2023, 15, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrikumar, S.; Ravi, T. Approaches towards development and promotion of herbal drugs. Pharmacog. Rev. 2007, 1, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Abrol, S.; Trehan, A.; Katare, O.P. Comparative study of different silymarin formulations: Formulation, characterisation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waglewska, E.; Pucek-Kaczmarek, A.; Bazylińska, U. Self-assembled bilosomes with stimuli-responsive properties as bioinspired dual-tunable nanoplatform for pH/temperature-triggered release of hybrid cargo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 215, 112524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, A.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Imam, S.S.; Hadal Alotaibi, N.; Alharbi, K.S.; Afzal, M.; Ali, R.; Alshehri, S.; Alzarea, S.I.; Elmowafy, M.; et al. Bioactive Apigenin loaded oral nano bilosomes: Formulation optimization to preclinical assessment. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.Y.; Fayad, E.; Althobaiti, F.; Zaki, I.; Abu Almaaty, A.H. Statistical optimization of bile salt deployed nanovesicles as a potential platform for oral delivery of piperine: Accentuated antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity in MERS-CoV challenged mice. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1150–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Hao, J.; Fan, D. Biological properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhadi, E.; Rezaee, M.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Nano strategies for berberine delivery, a natural alkaloid of Berberis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Eid, H.M.; Elmowafy, M.; Shalaby, K.; Zafar, A.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Rateb, M.E.; Ali, M.R.A.; Alsalahat, I.; Abou-Taleb, H.A. Bilosomes as a promising nanoplatform for oral delivery of an alkaloid nutraceutical: Improved pharmacokinetic profile and snowballed hypoglycemic effect in diabetic rats. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2694–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.Y.; Abd El-Halim, S.M.; Beshay, B.Y.; Zaki, I.; Abourehab, M.A.S. Poly phenolic phytoceutical loaded nano-bilosomes for enhanced caco-2 cell permeability and SARS-CoV-2 antiviral activity: In-vitro and insilico studies. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2162157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaurav, H.; Tripathi, M.; Kaur, S.D.; Bansal, A.; Kapoor, D.N.; Sheth, S. Emerging Trends in Bilosomes as Therapeutic Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060697
Kaurav H, Tripathi M, Kaur SD, Bansal A, Kapoor DN, Sheth S. Emerging Trends in Bilosomes as Therapeutic Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(6):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060697
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaurav, Hemlata, Meenakshi Tripathi, Simran Deep Kaur, Amit Bansal, Deepak N. Kapoor, and Sandeep Sheth. 2024. "Emerging Trends in Bilosomes as Therapeutic Drug Delivery Systems" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 6: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060697
APA StyleKaurav, H., Tripathi, M., Kaur, S. D., Bansal, A., Kapoor, D. N., & Sheth, S. (2024). Emerging Trends in Bilosomes as Therapeutic Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics, 16(6), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060697








