Validated LC-MS/MS Assay for the Quantitative Determination of Fenretinide in Plasma and Tumor and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study in Mice of a Novel Oral Nanoformulation of Fenretinide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Preparation of Standard and Quality Control Solutions and Samples
2.4. Preparation of Plasma Samples
2.5. Preparation of Tumor Homogenate Samples
2.6. Liquid Chromatographic Conditions
2.7. Mass Spectrometry Conditions
| Analyte | Q1 (m/z) | Q3 (m/z) | CE (eV) |
| 4-HPR | 392.3 | 283.3 | 16 |
| 4-oxo-4-HPR | 406.2 | 297.1 | 16 |
| 4-MPR | 406.3 | 283.2 | 16 |
| DH-4-HPR | 390.2 | 281.1 | 16 |
| [2H4]-4-HPR | 396.3 | 283.2 | 18 |
2.8. Validation Procedures
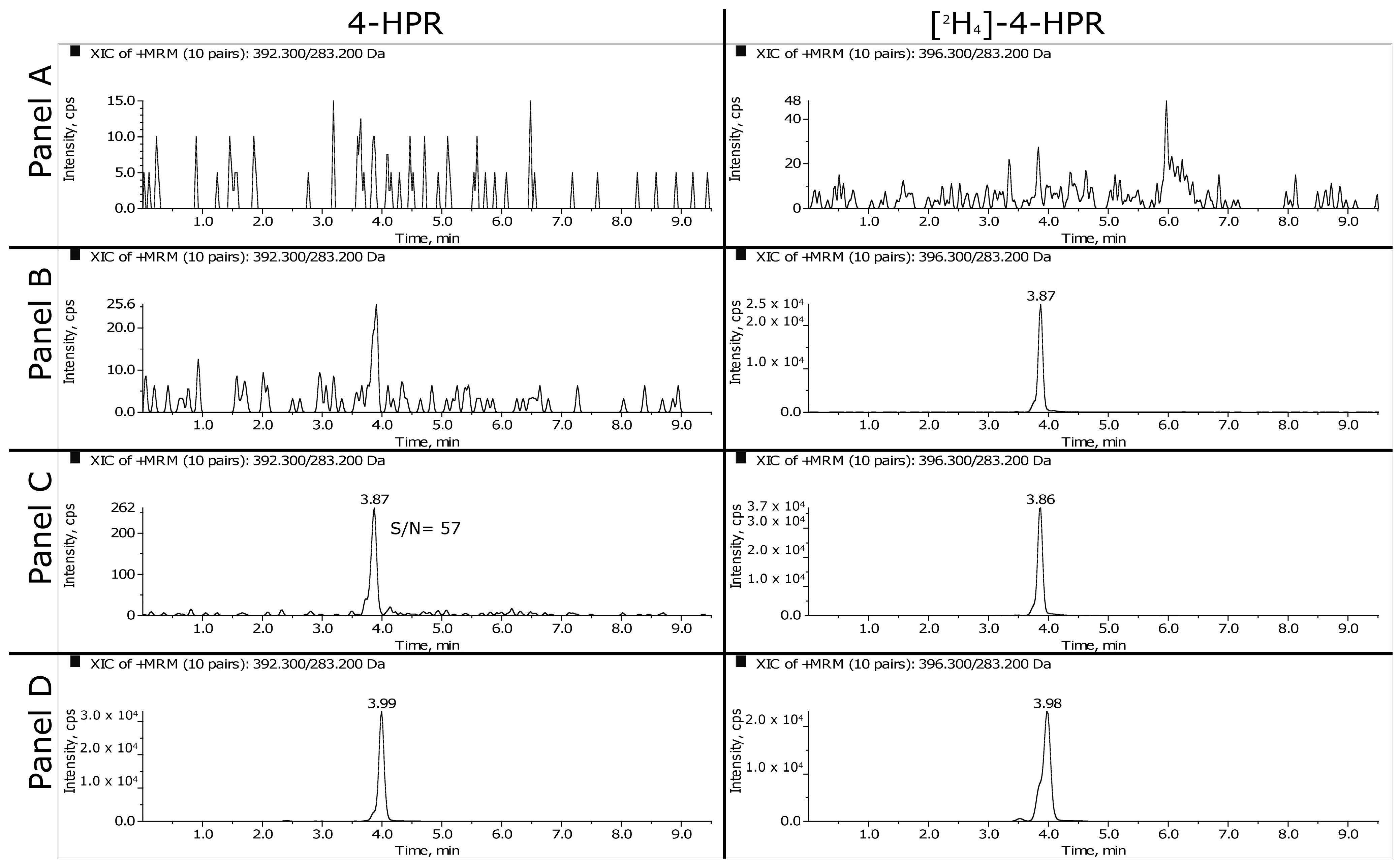
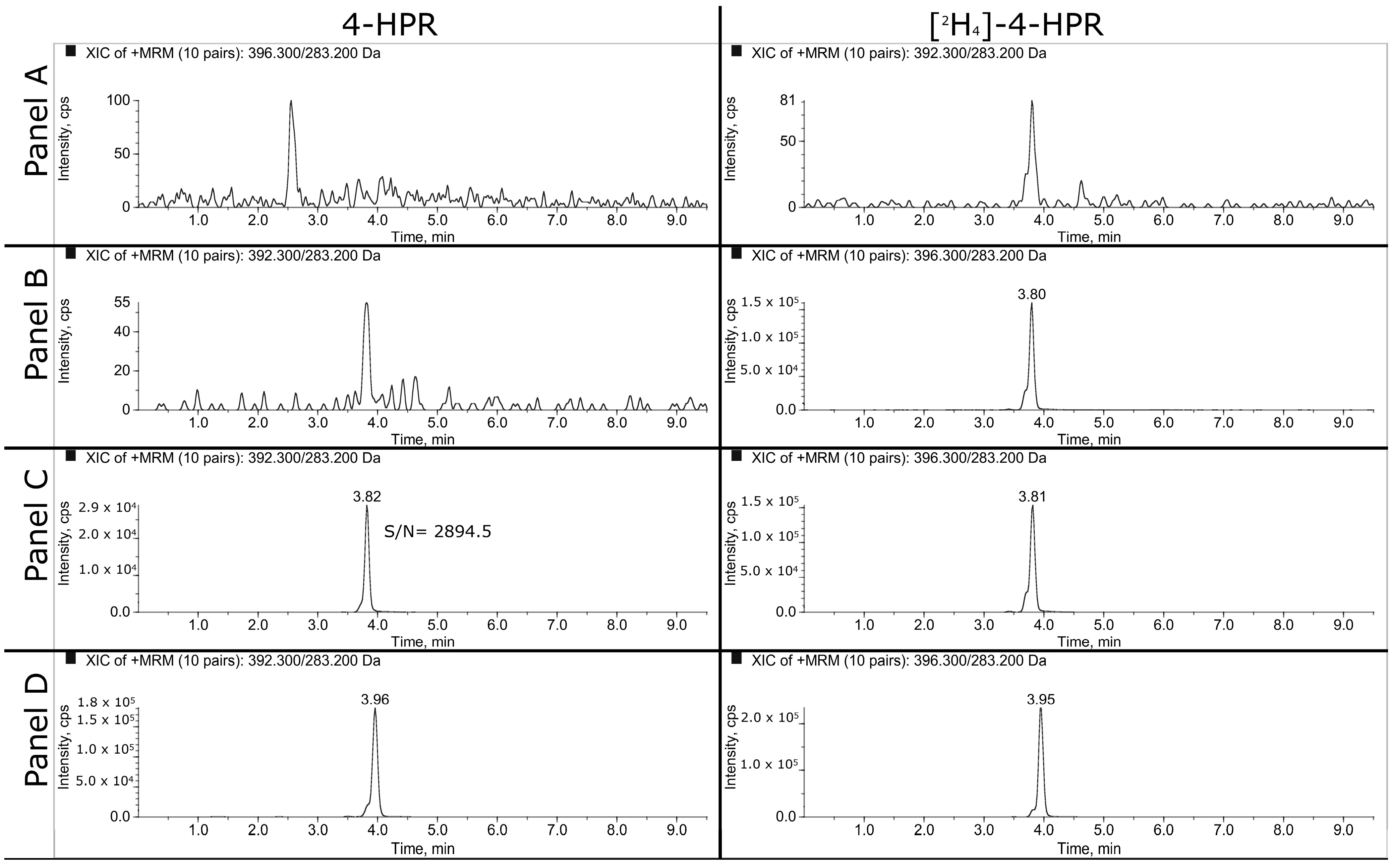
2.8.1. Limit of Quantification, Matrix Effect and Recovery
2.8.2. Linearity
2.8.3. Accuracy and Precision
2.8.4. Stability
2.8.5. Application to the Pharmacokinetic Study
3. Results
3.1. Method Development and Validation
3.1.1. HPLC-MS/MS
3.1.2. LLOQ, Matrix Effect and Recovery
3.1.3. Linearity
3.1.4. Accuracy and Precision
3.1.5. Stability
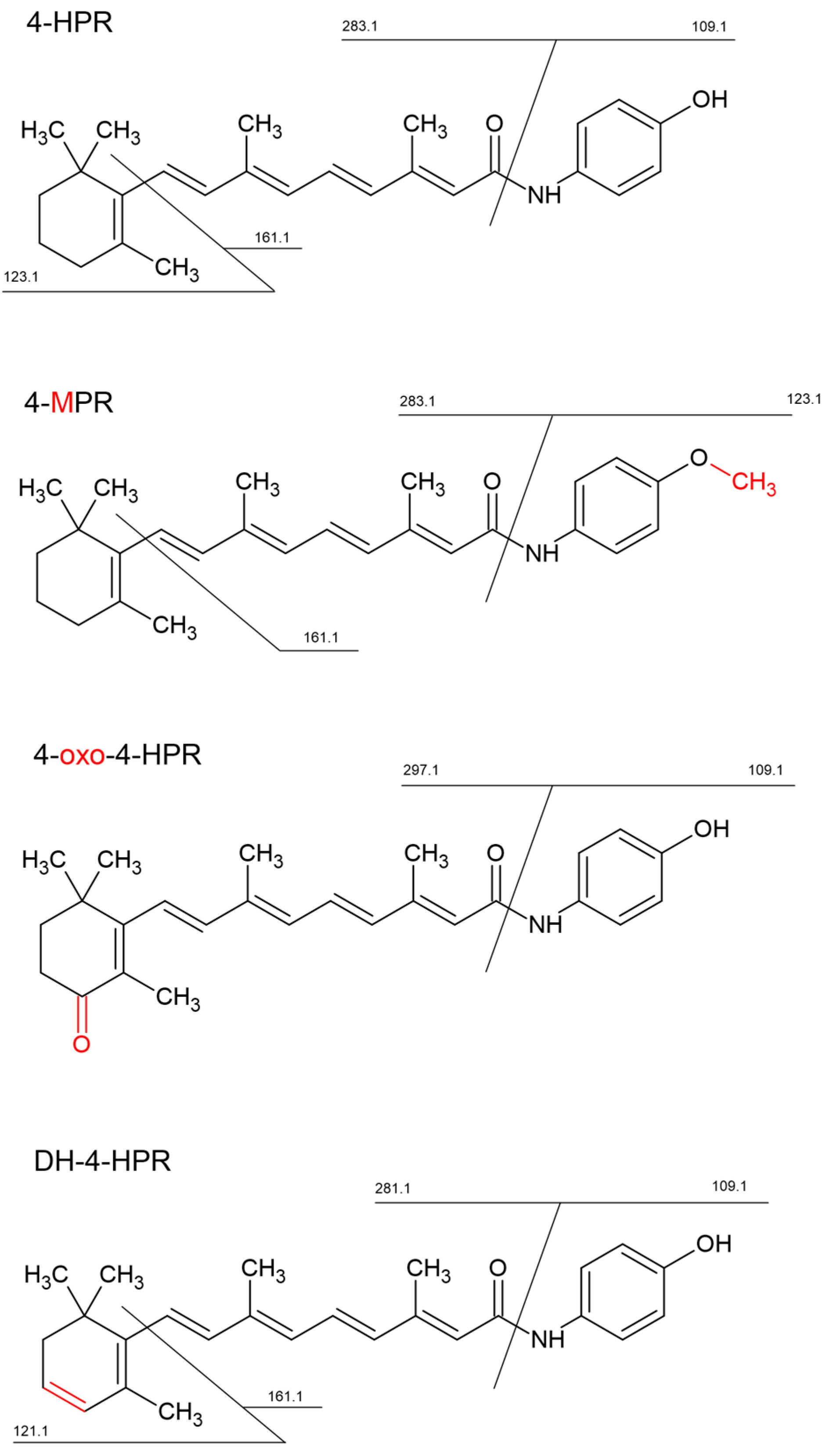
3.2. Identification of 4-HPR Metabolites
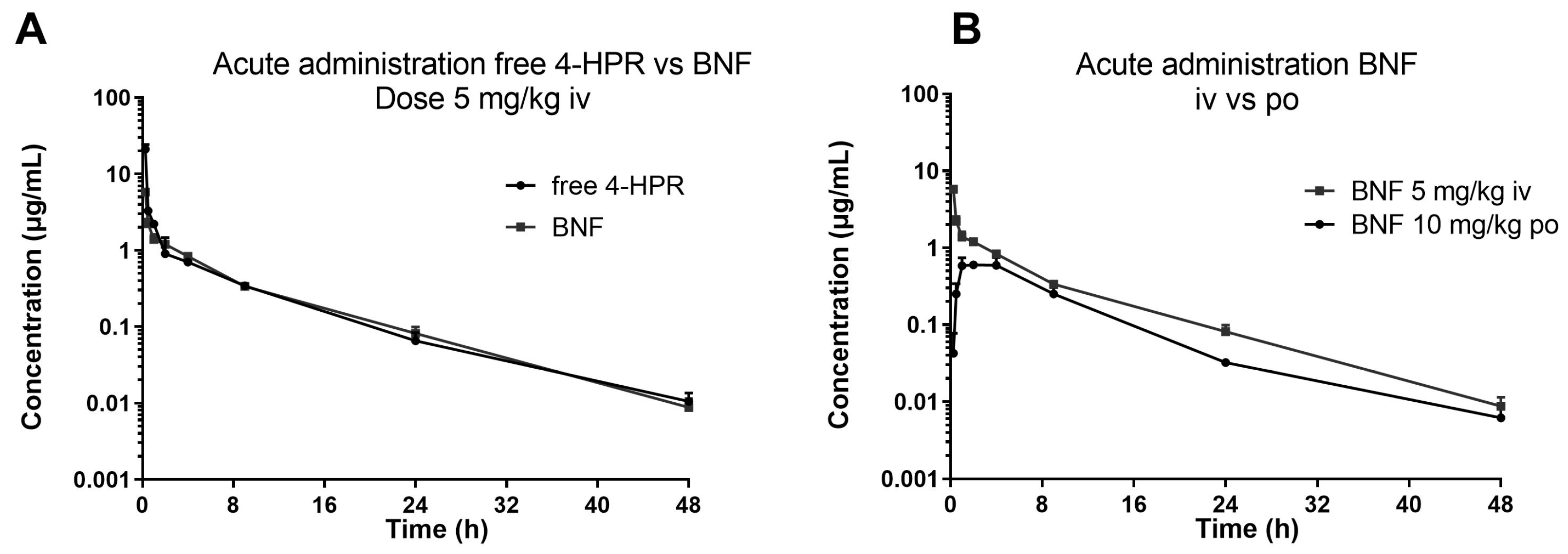
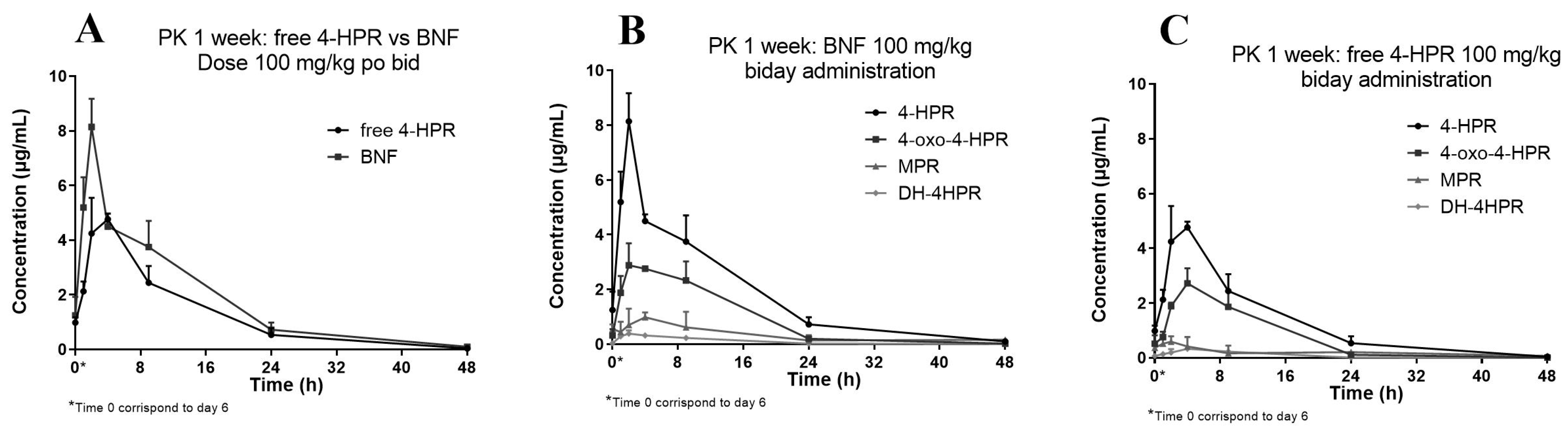
3.3. Application to the Pharmacokinetic Study
3.4. Application to the Activity Study
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barua, A.B.; Olson, J.A. Preparation of Retinamides by Use of Retinoyl Fluoride. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Companioni, O.; Mir, C.; Garcia-Mayea, Y.; LLeonart, M.E. Targeting Sphingolipids for Cancer Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 745092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenza, R.L.; Lodeserto, P.; Orienti, I. Fenretinide in Cancer and Neurological Disease: A Two-Face Janus Molecule. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.P.; Reynolds, C.P.; Cho, H.; Kang, M.H. Clinical Development of Fenretinide as an Antineoplastic Drug: Pharmacology Perspectives. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orienti, I.; Francescangeli, F.; De Angelis, M.L.; Fecchi, K.; Bongiorno-Borbone, L.; Signore, M.; Peschiaroli, A.; Boe, A.; Bruselles, A.; Costantino, A.; et al. A New Bioavailable Fenretinide Formulation with Antiproliferative, Antimetabolic, and Cytotoxic Effects on Solid Tumors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orienti, I.; Salvati, V.; Sette, G.; Zucchetti, M.; Bongiorno-Borbone, L.; Peschiaroli, A.; Zolla, L.; Francescangeli, F.; Ferrari, M.; Matteo, C.; et al. A Novel Oral Micellar Fenretinide Formulation with Enhanced Bioavailability and Antitumour Activity against Multiple Tumours from Cancer Stem Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rühl, R. Method to Determine 4-Oxo-Retinoic Acids, Retinoic Acids and Retinol in Serum and Cell Extracts by Liquid Chromatography/Diode-Array Detection Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionisation Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, T.E.; Bastani, N.E.; Blomhoff, R. Quantitative High-Throughput Determination of Endogenous Retinoids in Human Plasma Using Triple-Stage Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Ni, K.-Y.; Shen, Y.; Ma, P.-C.; Cao, L.; Wang, W.-P.; Wang, Y. Development and Validation of a LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Viaminate in Human Plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 856, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.I.; Nguyen, V.T.; Chen, M.-L.; Adamson, P.C. A Rapid, Sensitive and Selective Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Determination of Fenretinide (4-HPR) in Plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 862, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karppi, J.; Nurmi, T.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Granado-Lorencio, F.; Nyyssönen, K. Simultaneous Measurement of Retinol, α-Tocopherol and Six Carotenoids in Human Plasma by Using an Isocratic Reversed-Phase HPLC Method. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 867, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formelli, F.; Clerici, M.; Campa, T.; Di Mauro, M.G.; Magni, A.; Mascotti, G.; Moglia, D.; De Palo, G.; Costa, A.; Veronesi, U. Five-Year Administration of Fenretinide: Pharmacokinetics and Effects on Plasma Retinol Concentrations. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 2036–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vratilova, J.; Frgala, T.; Maurer, B.J.; Patrick Reynolds, C. Liquid Chromatography Method for Quantifying N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)Retinamide and N-(4-Methoxyphenyl)Retinamide in Tissues. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 808, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.E.; Min, H.K. Analysis of Fenretinide and Its Metabolites in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Its Application to Clinical Pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry; Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2018; p. 44.
- European Medicines Agency. Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/bioanalytical-method-validation (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An Add-in Program for Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Data Analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani, M.G.; Appierto, V.; Cavadini, E.; Bettiga, A.; Prinetti, A.; Clagett-Dame, M.; Curley, R.W.; Formelli, F. 4-Oxo-Fenretinide, a Recently Identified Fenretinide Metabolite, Induces Marked G2-M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Fenretinide-Sensitive and Fenretinide-Resistant Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3238–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.P.; Hwang, K.; Singh, H.; Wang, D.; Reynolds, C.P.; Curley, R.W.; Williams, S.C.; Maurer, B.J.; Kang, M.H. Fenretinide Metabolism in Humans and Mice: Utilizing Pharmacological Modulation of Its Metabolic Pathway to Increase Systemic Exposure. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illingworth, N.A.; Boddy, A.V.; Daly, A.K.; Veal, G.J. Characterization of the Metabolism of Fenretinide by Human Liver Microsomes, Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| (A) Plasma 4-HPR Concentration (ng/mL) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Calibration Curve | ||||||||||
| 1 | 5 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 500 | Intercept | Slope | R2 | |
| Day 1 | 1.02 | 5.05 | 9.92 | 23.88 | 52.48 | 96.14 | 256.10 | 503.90 | −0.001 | 0.008 | 0.9992 |
| Day 2 | 1.01 | 4.81 | 10.25 | 24.95 | 50.39 | 102.60 | 255.20 | 477.70 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.9996 |
| Day 3 | 1.01 | 5.02 | 9.24 | 25.24 | 47.91 | 100.30 | 254.20 | 539.00 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.9989 |
| Day 4 | 1.02 | 4.55 | 9.58 | 25.26 | 49.73 | 102.40 | 260.00 | 520.30 | −0.001 | 0.008 | 0.9989 |
| Day 5 | 1.01 | 4.78 | 10.22 | 23.87 | 48.59 | 103.58 | 253.70 | 518.24 | −0.001 | 0.007 | 0.9993 |
| Mean (N = 5) | 1.01 | 4.84 | 9.84 | 24.64 | 49.82 | 101.00 | 255.84 | 511.83 | −0.001 | 0.008 | 0.99918 |
| SD | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 0.71 | 1.77 | 2.97 | 2.50 | 22.80 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 |
| Precision (%) | 0.83 | 4.13 | 4.40 | 2.88 | 3.56 | 2.94 | 0.98 | 4.45 | |||
| Accuracy (%) | 101.3 | 96.8 | 98.4 | 98.6 | 99.6 | 101.0 | 102.3 | 102.4 | |||
| (B) Tumor 4-HPR Concentration (ng/mL) | |||||||||||
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Calibration Curve | ||||||||||
| 50 | 100 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | Intercept | Slope | R2 | |||
| Day 1 | 50.02 | 100.57 | 245.98 | 495.24 | 1018.50 | 2002.10 | −0.012 | 0.002 | 0.9999 | ||
| Day 2 | 50.33 | 100.06 | 237.33 | 514.37 | 999.17 | 2031.10 | −0.009 | 0.003 | 0.9994 | ||
| Day 3 | 49.66 | 102.49 | 237.32 | 530.11 | 964.49 | 2015.70 | −0.014 | 0.003 | 0.9988 | ||
| Day 4 | 51.49 | 94.66 | 245.00 | 503.32 | 971.29 | 2131.30 | −0.015 | 0.003 | 0.9986 | ||
| Mean (N = 4) | 50.38 | 99.45 | 241.41 | 510.76 | 988.36 | 2045.05 | −0.012 | 0.003 | 0.99918 | ||
| SD | 0.79 | 3.36 | 4.73 | 15.10 | 25.08 | 58.71 | 0.0026 | 0.0007 | 0.0006 | ||
| Precision (%) | 1.57 | 3.37 | 1.96 | 2.96 | 2.54 | 2.87 | |||||
| Accuracy (%) | 100.8 | 99.4 | 96.6 | 102.2 | 98.8 | 102.3 | |||||
| Plasma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | ||||
| 1 | 8 | 80 | 400 | |
| Intraday | ||||
| Measured Concentration | ||||
| Day 1 | 1.02 | 7.29 | 71.13 | 357.70 |
| 1.08 | 6.93 | 71.45 | 362.90 | |
| 1.08 | 6.82 | 71.21 | 348.70 | |
| 0.99 | 7.83 | 71.05 | 360.70 | |
| 1.05 | 7.35 | 75.61 | 368.90 | |
| Mean (N = 5) | 1.05 | 7.24 | 72.09 | 359.78 |
| SD | 0.04 | 0.40 | 1.97 | 7.43 |
| Precision (%) | 3.64 | 5.48 | 2.74 | 2.07 |
| Accuracy (%) | 104.6 | 89.7 | 90.1 | 89.9 |
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | ||||
| 8 | 80 | 400 | ||
| Interday | ||||
| Measured Concentration | ||||
| Day 1 | 7.95 | 83.70 | 418.90 | |
| 8.54 | 85.59 | 429.70 | ||
| 8.27 | 83.97 | 422.80 | ||
| Day 2 | 7.88 | 79.15 | 385.60 | |
| 8.02 | 89.30 | 382.00 | ||
| 8.15 | 80.78 | 432.30 | ||
| Day 3 | 7.88 | 79.15 | 385.60 | |
| 8.02 | 89.30 | 382.00 | ||
| 8.15 | 80.78 | 432.30 | ||
| Day 4 | 8.46 | 83.99 | 424.00 | |
| 8.78 | 88.70 | 421.80 | ||
| 8.77 | 87.37 | 432.30 | ||
| Day 5 | 8.10 | 81.46 | 388.83 | |
| 8.11 | 80.78 | 416.33 | ||
| 8.59 | 81.50 | 388.90 | ||
| Mean (N = 20) | 7.99 | 80.80 | 397.11 | |
| SD | 0.55 | 6.08 | 28.71 | |
| Precision (%) | 6.86 | 7.53 | 7.23 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 99.9 | 101.0 | 99.3 | |
| Tumor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | ||||
| 50 | 150 | 750 | 900 | |
| Intraday | ||||
| Measured Concentration | ||||
| Day 1 | 50.11 | 153.64 | 782.42 | 946.53 |
| 54.68 | 154.76 | 815.42 | 940.77 | |
| 54.27 | 157.04 | 776.70 | 981.73 | |
| 55.52 | 155.51 | 789.85 | 976.63 | |
| 50.04 | 153.39 | 813.89 | 969.83 | |
| Mean (N = 5) | 52.92 | 154.87 | 795.66 | 963.10 |
| SD | 2.64 | 1.49 | 17.97 | 18.36 |
| Precision (%) | 4.99 | 0.96 | 2.26 | 1.91 |
| Accuracy (%) | 105.8 | 103.3 | 106.1 | 107.0 |
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | ||||
| Interday | 150 | 750 | 900 | |
| Measured Concentration | ||||
| Day 1 | 150.34 | 765.33 | 939.23 | |
| 150.75 | 779.29 | 946.53 | ||
| 155.54 | 743.97 | 933.29 | ||
| 154.22 | 756.63 | 935.50 | ||
| 149.82 | 753.52 | 921.24 | ||
| 150.91 | 755.05 | 932.49 | ||
| Day 2 | 149.62 | 796.99 | 986.29 | |
| 154.88 | 788.64 | 974.25 | ||
| 150.35 | 807.83 | 1000.80 | ||
| Day 3 | 154.34 | 766.09 | 905.20 | |
| 157.20 | 754.69 | 911.21 | ||
| 150.03 | 775.60 | 986.18 | ||
| Day 4 | 152.64 | 811.27 | 936.07 | |
| 152.56 | 748.20 | 1002.00 | ||
| 160.44 | 776.32 | 911.66 | ||
| Mean (N = 20) | 153.40 | 777.89 | 951.87 | |
| SD | 2.93 | 22.72 | 30.40 | |
| Precision (%) | 1.91 | 2.92 | 3.19 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 102.3 | 103.7 | 105.8 | |
| (A) BNF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Cmax ± SD (µg/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC0–last (h*µg/mL) | R% * | HL (h) | |
| 4-HPR | 8.14 | ±1.029 | 2 | 86.28 | - | 7.5 |
| oxo-4-HPR | 2.88 | ±0.809 | 2 | 43.40 | 50% | 6.1 |
| MPR | 0.98 | ±0.179 | 4 | 14.82 | 17% | 16.6 |
| DH-4-HPR | 0.38 | ±0.125 | 2 | 4.73 | 5% | 6.2 |
| (B) Free 4-HPR | ||||||
| Parameter | Cmax ± SD (µg/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC0–last (h*µg/mL) | R% * | HL (h) | |
| 4-HPR | 4.76 | ±0.205 | 4 | 60.94 | - | 6.6 |
| oxo-4-HPR | 2.72 | ±0548 | 4 | 34.30 | 56% | 5.3 |
| MPR | 0.59 | ±0.193 | 2 | 9.60 | 16% | 21.7 |
| DH-4-HPR | 0.33 | ±0.068 | 4 | 4.09 | 7% | 5.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matteo, C.; Orienti, I.; Eramo, A.; Zeuner, A.; Ferrari, M.; Passoni, A.; Bagnati, R.; Ponzo, M.; Bello, E.; Zucchetti, M.; et al. Validated LC-MS/MS Assay for the Quantitative Determination of Fenretinide in Plasma and Tumor and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study in Mice of a Novel Oral Nanoformulation of Fenretinide. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030387
Matteo C, Orienti I, Eramo A, Zeuner A, Ferrari M, Passoni A, Bagnati R, Ponzo M, Bello E, Zucchetti M, et al. Validated LC-MS/MS Assay for the Quantitative Determination of Fenretinide in Plasma and Tumor and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study in Mice of a Novel Oral Nanoformulation of Fenretinide. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(3):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030387
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatteo, Cristina, Isabella Orienti, Adriana Eramo, Ann Zeuner, Mariella Ferrari, Alice Passoni, Renzo Bagnati, Marianna Ponzo, Ezia Bello, Massimo Zucchetti, and et al. 2024. "Validated LC-MS/MS Assay for the Quantitative Determination of Fenretinide in Plasma and Tumor and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study in Mice of a Novel Oral Nanoformulation of Fenretinide" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 3: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030387
APA StyleMatteo, C., Orienti, I., Eramo, A., Zeuner, A., Ferrari, M., Passoni, A., Bagnati, R., Ponzo, M., Bello, E., Zucchetti, M., & Frapolli, R. (2024). Validated LC-MS/MS Assay for the Quantitative Determination of Fenretinide in Plasma and Tumor and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study in Mice of a Novel Oral Nanoformulation of Fenretinide. Pharmaceutics, 16(3), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030387







