Navigating the Nose-to-Brain Route: A Systematic Review on Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Central Nervous System Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
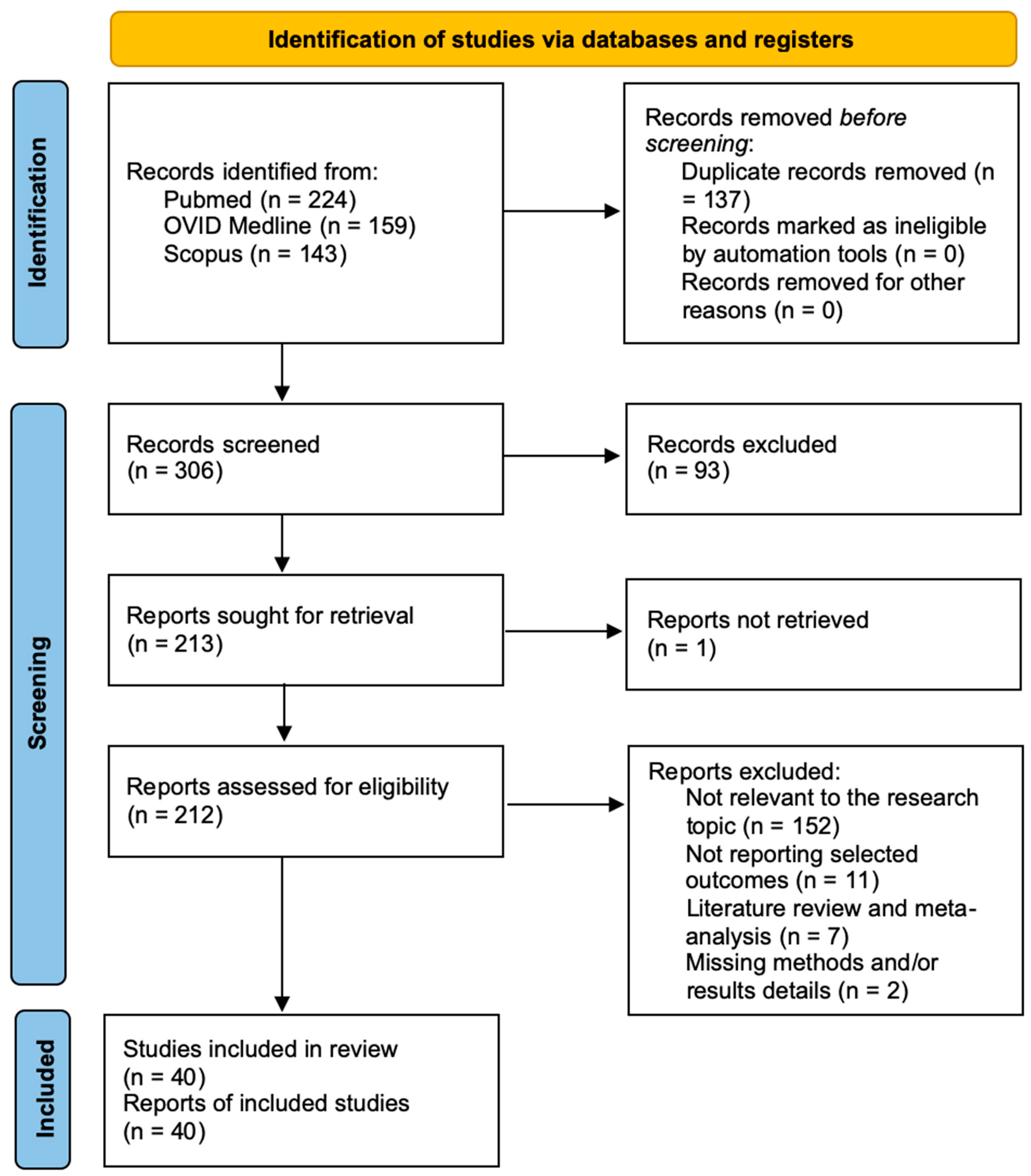
3.1. Literature Review
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. SLNs and NLCs for Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery
4.2. Intranasal Delivery of Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Neuro-Oncological Diseases
4.3. Intranasal Delivery of Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Neurodegenerative Disorders
4.4. Nose-to-Brain Delivery of SLNs and NLCs for Brain Diseases: In Vitro Studies
4.5. Nose-to-Brain Delivery of SLNs and NLCs for Brain Diseases: Ex Vivo Studies
4.6. Nose-to-Brain Delivery of SLNs and NLCs for Brain Diseases: In Vivo Studies
4.7. Advantages and Disadvantages of SLNs and NLCs
4.8. Challenges and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeshi, C.V.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Tekade, A.R.; Surana, S.J. Novel surface modified polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles as intranasal carriers for ropinirole hydrochloride: In vitro, ex vivo and in vivo pharmacodynamic evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 2101–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartziandia, O.; Herran, E.; Pedraz, J.L.; Carro, E.; Igartua, M.; Hernandez, R.M. Chitosan coated nanostructured lipid carriers for brain delivery of proteins by intranasal administration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Bhandari, S.; Deshmukh, R.; Yadav, A.K.; Mishra, N. Development and characterization of embelin-loaded nanolipid carriers for brain targeting. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhave, D.G.; Kokare, C.R. Nanostructured lipid carriers engineered for intranasal delivery of teriflunomide in multiple sclerosis: Optimization and in vivo studies. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.I.; Baboota, S.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, M.; Ali, J.; Sahni, J.K. Intranasal administration of nanostructured lipid carriers containing CNS acting drug: Pharmacodynamic studies and estimation in blood and brain. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, M.I.; Agu, R.U.; Verbeke, N.; Kinget, R. Nasal mucoadhesive drug delivery: Background, applications, trends and future perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1640–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, V.; Pavan, B.; Ferraro, L.; Beggiato, S.; Traini, D.; Reis, L.G.D.; Scalia, S.; Dalpiaz, A. Brain targeting of resveratrol by nasal administration of chitosan-coated lipid microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnik, A.; das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Mucoadhesive polymers in the design of nano-drug delivery systems for administration by non-parenteral routes: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 2030–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.C.C.; Chaves, L.L.; Pinheiro, S.; Pinheiro, M.; Lima, S.C.; Ferreira, D.; Sarmento, B.; Reis, S. Mucoadhesive chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for better management of tuberculosis. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Non-Randomized Studies in Meta-Analysis|Request PDF. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261773681_The_Newcastle-Ottawa_Scale_NOS_for_Assessing_the_Quality_of_Non-Randomized_Studies_in_Meta-Analysis (accessed on 19 July 2023).
- Madane, R.G.; Mahajan, H.S. Curcumin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for nasal administration: Design, characterization, and in vivo study. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Aqil, M.; Imam, S.S.; Ahad, A.; Sultana, Y.; Ali, A.; Khan, K. Temozolomide loaded nano lipid based chitosan hydrogel for nose to brain delivery: Characterization, nasal absorption, histopathology and cell line study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, F.; Dhaliwal, H.K.; Gattacceca, F.; Sarmento, B.; Amiji, M.M. Enhanced anti-angiogenic effects of bevacizumab in glioblastoma treatment upon intranasal administration in polymeric nanoparticles. J. Control Release 2019, 309, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintov, A.C. AmyloLipid Nanovesicles: A self-assembled lipid-modified starch hybrid system constructed for direct nose-to-brain delivery of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, P. Intranasal delivery of Paclitaxel encapsulated nanoparticles for brain injury due to Glioblastoma. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2020, 18, 2280800020977170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Algaleel, S.A.; Metwally, A.A.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Kassem, D.H.; Hathout, R.M. Synchronizing In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies for the Successful Nose to Brain Delivery of an Anticancer Molecule. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3763–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Khan, I.; Pandit, J.; Emad, N.A.; Bano, S.; Dar, K.I.; Alam Rizvi, M.M.; Ansari, M.D.; Aqil, M.; Sultana, Y. Brain targeted delivery of carmustine using chitosan coated nanoparticles via nasal route for glioblastoma treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandbhor, P.; Goda, J.; Mohanty, B.; Gera, P.; Yadav, S.; Chekuri, G.; Chaudhari, P.; Dutt, S.; Banerjee, R. Targeted nano-delivery of chemotherapy via intranasal route suppresses in vivo glioblastoma growth and prolongs survival in the intracranial mouse model. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 608–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yang, L. A simple self-assembly nanomicelle based on brain tumor-targeting peptide-mediated siRNA delivery for glioma immunotherapy via intranasal administration. Acta Biomater. 2023, 155, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, S.; Kause, S.; Belgamwar, V. Intranasal delivery of poly (d-glucosamine) encrusted self-assembled lipidic nanovesicles to enhanced brain uptake of thymoquinone for management of Glioblastoma Multiforme. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 90, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, N.; Hao, B.; Wang, X.; Kong, P. Pharmacokinetic behavior and efficiency of acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rat brain after intranasal administration of galanthamine hydrobromide loaded flexible liposomes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wu, K.; Lou, J.N.; Qi, X.R. Enhanced brain distribution and pharmacodynamics of rivastigmine by liposomes following intranasal administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Li, X.; Lu, C.T.; Lin, M.; Chen, L.-J.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Jin, R.-R.; Jiang, X.; Shen, X.-T.; et al. Gelatin nanostructured lipid carriers-mediated intranasal delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor enhances functional recovery in hemiparkinsonian rats. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.; Singh, D.; Prakash, A.; Mishra, N. Development, characterization and nasal delivery of rosmarinic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for the effective management of Huntington’s disease. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Khunt, D.; Bhatt, H.; Misra, M.; Padh, H. Application of quality by design approach for intranasal delivery of rivastigmine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Effect on formulation and characterization parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 78, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.C.; Srivastava, P.; Pandey, P.; Khan, W.; Prasad Panda, B. Nose to brain delivery of astaxanthin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Fabrication, radio labeling, optimization and biological studies. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10001–10010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntimadugu, E.; Dhommati, R.; Jain, A.; Challa, V.G.S.; Shaheen, M.; Khan, W. Intranasal delivery of nanoparticle encapsulated tarenflurbil: A potential brain targeting strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 92, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Posadino, A.M.; Pintus, G.; Sarmento, B.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Nose-to-brain delivery of BACE1 siRNA loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles for Alzheimer’s therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Cortesi, R.; Drechsler, M.; Fan, J.; Fu, B.M.; Calderan, L.; Mannucci, S.; Boschi, F.; Nastruzzi, C. Nanoformulations for dimethyl fumarate: Physicochemical characterization and in vitro/in vivo behavior. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 115, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Sara, U.V.S.; Chauhan, I.; Gaur, P.K.; Singh, A.P.; Puri, D.; Ameeduzzafar, A. Solid lipid nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery of donepezil: Formulation, optimization by Box–Behnken design, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojo, G.M.; Kuppusamy, G.; De, A.; Karri, V.V.S.N.R. Formulation and optimization of intranasal nanolipid carriers of pioglitazone for the repurposing in Alzheimer’s disease using Box-Behnken design. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.P.; Butani, S.B. Resveratrol anchored nanostructured lipid carrier loaded in situ gel via nasal route: Formulation, optimization and in vivo characterization. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaba, B.; Khan, T.; Haider, M.F.; Alam, T.; Baboota, S.; Parvez, S.; Ali, J. Vitamin E Loaded Naringenin Nanoemulsion via Intranasal Delivery for the Management of Oxidative Stress in a 6-OHDA Parkinson’s Disease Model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2382563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhai, W.; Zhuang, N.; Han, T.; Ding, Z. The Optimization Design of Lactoferrin Loaded HupA Nanoemulsion for Targeted Drug Transport Via Intranasal Route. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9217–9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Kumar, S.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Intranasal delivery of tetrabenazine nanoemulsion via olfactory region for better treatment of hyperkinetic movement associated with Huntington’s disease: Pharmacokinetic and brain delivery study. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2020, 230, 104917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Wong, L.R.; Xie, H.; Ho, P.C.L. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison of Curcumin-Encapsulated Chitosan-Coated Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles and Curcumin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes Administered Intranasally as Therapeutic Strategies for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 4256–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, T.; Di Benedetto, G.; Carbone, C.; Bonaccorso, A.; Amato, G.; Faro, M.J.L.; Burgaletto, C.; Puglisi, G.; Bernardini, R.; Cantarella, G. Intranasal Administration of a TRAIL Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Adsorbed in PLGA Nanoparticles and NLC Nanosystems: An In Vivo Study on a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Chavhan, S.; Soni, H.; Babbar, A.; Mathur, R.; Mishra, A.; Sawant, K. Brain targeting of risperidone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles by intranasal route. J. Drug Target 2011, 19, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, S.; Varshosaz, J.; Minaiyan, M.; Tabbakhian, M. Brain delivery of valproic acid via intranasal administration of nanostructured lipid carriers: In vivo pharmacodynamic studies using rat electroshock model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Patel, H.S.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Agrawal, A.; Tekade, A.R. Solid lipid nanoparticles of ondansetron HCl for intranasal delivery: Development, optimization and evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.P.; Saraf, S.K.; Saraf, S.A. SLN approach for nose-to-brain delivery of alprazolam. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2012, 2, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsi, N.M.; Ghorab, D.M.; Badie, H.A. Brain targeted solid lipid nanoparticles for brain ischemia: Preparation and in vitro characterization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kesarla, R.; Chotai, N.; Misra, A.; Omri, A. Systematic Approach for the Formulation and Optimization of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Efavirenz by High Pressure Homogenization Using Design of Experiments for Brain Targeting and Enhanced Bioavailability. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5984014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatouh, A.M.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Abdelbary, A. Agomelatine-based in situ gels for brain targeting via the nasal route: Statistical optimization, in vitro, and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Hidau, M.K.; Gautam, S.; Gupta, K.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, S.K. Glycol chitosan functionalized asenapine nanostructured lipid carriers for targeted brain delivery: Pharmacokinetic and teratogenic assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, H.; Tian, B.; Sai, S.; Gao, Y.; Lan, T.; Meng, Y.; Ding, C. Development of nose-to-brain delivery of ketoconazole by nanostructured lipid carriers against cryptococcal meningoencephalitis in mice. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.J.; Parikh, R.H. Intranasal delivery of topiramate nanoemulsion: Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and brain uptake studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, K.M. Nanosized Cubosomal Thermogelling Dispersion Loaded with Saquinavir Mesylate to Improve Its Bioavailability: Preparation, Optimization, in vitro and in vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5113–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Panciani, P.P.; Muntoni, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; De Bonis, P.; Mioletti, S.; Fontanella, M.; Swaminathan, S. Lipid nanoparticles for intranasal administration: Application to nose-to-brain delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuria, S.V.; Hanson, L.R.; Frey, W.H. Intranasal delivery to the central nervous system: Mechanisms and experimental considerations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1654–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illum, L. Nasal drug delivery: New developments and strategies. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Trotta, M.; Gallarate, M.; Carlotti, M.E.; Zara, G.P.; Bargoni, A. Solid lipid nanoparticles formed by solvent-in-water emulsion-diffusion technique: Development and influence on insulin stability. J. Microencapsul. 2007, 24, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M. Lipid nanoparticles: State of the art, new preparation methods and challenges in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Woensel, M.; Wauthoz, N.; Rosière, R.; Amighi, K.; Mathieu, V.; Lefranc, F.; Van Gool, S.W.; De Vleeschouwer, S. Formulations for Intranasal Delivery of Pharmacological Agents to Combat Brain Disease: A New Opportunity to Tackle GBM? Cancers 2013, 5, 1020–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, M.A.; Daviau, A.; Marcos, B.; Faucheux, N. Nanoparticle-mediated growth factor delivery systems: A new way to treat Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control Release 2015, 206, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Souto, E.B.; Singh, K.K. Advances in brain drug targeting and delivery: Limitations and challenges of solid lipid nanoparticles. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 889–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Md, S.; Mustafa, G.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Nanoneurotherapeutics approach intended for direct nose to brain delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devkar, T.B.; Tekade, A.R.; Khandelwal, K.R. Surface engineered nanostructured lipid carriers for efficient nose to brain delivery of ondansetron HCl using Delonix regia gum as a natural mucoadhesive polymer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivadasu, P.; Gowda, D.V.; Siddaramaiah, H.; Hemalatha, S. Ziprasidone hydrochloride loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCS) for intranasal delivery: Optimization and in vivo studies. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 12, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorulla, K.M.; Yasir, M.; Muzaffar, F.; Roshan, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Almurshedi, A.S.; Tura, A.J.; Alshehri, S.; Gebissa, T.; Mekit, S.; et al. Intranasal delivery of chitosan decorated nanostructured lipid carriers of Buspirone for brain targeting: Formulation development, optimization and In-Vivo preclinical evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Gupta, U.; Ujjwal, R.R.; Yadav, A.K. Nano-lipidic formulation and therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease via intranasal route. J Microencapsul. 2021, 38, 572–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathure, D.; Madan, J.R.; Gujar, K.N.; Tupsamundre, A.; Ranpise, H.A.; Dua, K. Formulation and Evaluation of Niosomal in situ Nasal Gel of a Serotonin Receptor Agonist, Buspirone Hydrochloride for the Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018, 6, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazuli, I.; Annu null Nabi, B.; Moolakkadath, T.; Alam, T.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Optimization of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Lurasidone Hydrochloride Using Box-Behnken Design for Brain Targeting: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palagati, S.; Sv, S.; Kesavan, B.R. Application of computational tools for the designing of Oleuropein loaded nanostructured lipid carrier for brain targeting through nasal route. Daru 2019, 27, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Du, J.; Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Hu, K. Improved brain delivery of pueraria flavones via intranasal administration of borneol-modified solid lipid nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 2105–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivadasu, P.; Gowda, D.V.; Subramani, N.K.; Malgur, B.; Vishweshwaraiah, S.S.; Hatna, S. Direct brain targeted nanostructured lipid carriers for sustained release of schizophrenic drug: Formulation, characterization and pharmacokinetic studies. Brain 2020, 9, 12. Available online: https://www.ijper.org/sites/default/files/IndJPhaEdRes_54_1-73.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2024). [CrossRef]

| Author (Year) | Drug Category | Drug | LN Type | Lipid Employed | Assays Performed |
| Madane et al. (2014) [13] | Phytochemical antiblastic | Curcumin | NLC | Lipids, Precirol, Capmul MCM | Cytotoxicity assay on astrocytoma–glioblastoma cell line U373MG; histopathological studies on sheep nasal mucosa; biodistribution studies on male Wistar rats |
| Khan et al. (2018) [14] | Antiblastic | Temozolomide | Nanolipid chitosan hydrogel | Gelucire 44/14, vitamin E | Nasal-diffusion study on goat nasal mucosa; brain/plasma uptake studies performed on Wistar rats; cytotoxicity studies on Clone-6 rat glioma cell line |
| Sousa et al. (2019) [15] | Anti-angiogenic monoclonal antibody | Bevacizumab | PLGA nanoparticles | PLGA | Intranasal bevacizumab efficacy studies in xenograft intracerebral glioblastoma nude mice model |
| Sintov et al. (2020) [16] | Antiblastic, anti-AD, anti-inflammatory | Curcumin | ALN | Polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, CB, tetraglycol, and glyceryl oleate | In vivo administration of curcumin-loaded nanoparticles into Sprague-Dawley rats’ brains |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [17] | Antiblastic | Paclitaxel | PLGA nanoparticles | PLGA | Cytotoxicity studies on U87MG cells; biodistribution studies in male BALB/c mice |
| Abd-algaleel et al. (2021) [18] | Antiblastic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory | Sesamol | SLN, PN | GMS, SA, tristearin, TP, PCL | In vivo pharmacokinetics study on male albino rats |
| Ahmad et al. (2022) [19] | Antiblastic | Carmustine | Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles | PLGA | Ex vivo permeation study on fresh goat nasal mucosa; pharmacokinetic study in Albino Wistar rats |
| Sandbhor et al. (2022) [20] | Antiblastic | Paclitaxel and miltefosine | SLN | SPC | Brain retention and biodistribution of intranasal nanoparticles on tumor-free Sprague Daley rats; in vivo anti-glioma efficacy evaluation in orthotopic GBM mice model |
| Tang et al. (2022) [21] | Nucleic acid drug | siRNA | Nanomicelles | T7-C | Biodistribution of siRNA delivered by T7-C in normal and tumor-bearing mice; creation of an in situ model of GL261 glioma and its therapeutic impact |
| Trivedi et al. (2023) [22] | Phytochemical with anticancer and antioxidant activity | Thymoquinone | Poly (D-glucosamine) self-assembled lipidic nanovesicles | cholesterol, DSPC | Ex vivo drug permeation study on porcine nasal mucosa of a goat; ex vivo biocompatibility study on goat nasal mucosa; brain uptake study in Albino Wistar rats |
| Author (Year) | Drug Category | Drug | LN Type | Lipid Employed | Assays Performed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. (2012) [23] | Anti-AD | Galantamine hydrobromide | liposomes | Soya phosphatidylcholine, cholesterol | Rat brain pharmacokinetic behavior, determination cytotoxicity in rat pheochromocytoma PC-12 cell line |
| Yang et al. (2013) [24] | Anti-AD | Rivastigmine | Liposomes, CPP liposomes | EPC, DSPE-PEG-CPP | Pharmacodynamic study in male Sprague-Dawley rats, evaluation of nasal toxicity |
| Pardeshi et al. (2013) [2] | Anti-PD | Ropinirole hydrochloride | CASLN | Trimyristin | Ex vivo mucosal toxicity studies on sheep nasal mucosa; anti-tremor activity in albino mice model |
| Zhao et al. (2013) [25] | Anti-PD | bFGF | GNL | N/A | Pharmacodynamics of intranasal delivery of bFGF-GNLs in hemiparkinsonian rats |
| Bhatt et al. (2014) [26] | Anti-HD | Rosmarinic acid | SLN | GMS | Functional tests in HD Wistar rat models |
| Shah et al. (2015) [27] | Anti-AD | Rivastigmine | SLN | Compritol 888 ATO, TPGS | Ex vivo permeation and toxicity studies on sheep nasal mucosa |
| Chandra Bhatt et al. (2016) [28] | Anti-AD | Astaxanthin | SLN | SA | Biodistribution in male albino Wistar rats |
| Muntimadugu et al. (2016) [29] | Anti-AD | Tarenflurbil | SLN | Glycerol monostearate, SA, soya lecithin | Biodistribution studies in Sprague-Dawley rats |
| Rassu et al. (2017) [30] | Anti-AD | BACE1 siRNA | CASLN | Witepsol E 85 solid triglycerides | Permeability studies on Caco-2 cell culture |
| Esposito et al. (2017) [31] | Anti-MS | Dimethyl fumarate | SLN, CASLN | Tristearin | Biodistribution studies in mice |
| Yasir et al. (2017) [32] | Anti-AD | Donepezil | SLN | GMS | In vitro release and release kinetic studies; pharmacokinetic and biodistribution in male albino Wistar rats |
| Gadhave et al. (2019) [5] | Anti-MS | Teriflunomide | NLC | Compritol 888 ATO, Maisine 35–1, Gelucire 44/14 | Ex vivo permeation of nanoparticles on nasal mucosa; subacute toxicity evaluation in male Wistar rats |
| Jojo et al. (2019) [33] | Anti-AD | Pioglitazone | NLC | TP, Capmul MCM | Ex vivo permeation study and nasal ciliotoxicity studies on sheep nasal mucosa; biodistribution study in male Wistar rats |
| Rajput et al. (2019) [34] | Anti-AD | Resveratrol | NLC | palmitate, Capmul MCM | Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies on rats |
| Gaba et al. (2019) [35] | Anti-PD | Vitamin E | NRG NE | Labrasol, different oils (namely soybean oil, almond oil, olive oil, vitamin E, grape seed oil, rice bran oil, and linseed oil) | In vitro release study, ex vivo permeation study on nasal mucosa; pharmacokinetic and brain-targeting studies in Wistar rats |
| Jiang et al. (2019) [36] | Anti-AD | Huperzine A | NE, NE modified with lactoferrin | soybean oil, isopropyl myristate, Capryol 90 | In vitro studies in hCMEC/D3; test for nasal toxicity in Wistar rats; drug distribution in rat brain |
| Arora et al. (2020) [37] | Anti-HD | Tetrabenazine | NE | different oil (Capmul MCM, soya bean oil, grape seed oil, and vitamin E) | Ex vivo nasal mucosa permeation study on porcine nasal mucosa; pharmacokinetic and brain delivery study in Wistar rats |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [38] | Anti-AD | Curcumin | Chitosan-coated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles | acetic acid, ethyl acetate | Cytotoxicity and cellular uptake studies in SH-SY5Y cells and BV-2 cells; biodistribution studies in male C57BL/6 mice |
| Musumeci et al. (2022) [39] | Anti-AD | Anti-TRAIL monoclonal antibody | lipid and polymeric nanocarriers | Cetyl palmitate, glyceryl monooleate, isopropyl stearate | In vivo studies in 3xTg-AD mice and wild type mice: experimental groups and intranasal drug administration |
| Author (Year) | Drug Category | Drug | LN Type | Lipid Employed | Assays Performed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patel et al. (2011) [40] | Antipsychotic | Risperidone | SLN | Glyceryl behenate | Biodistribution and paw test in BALB/c mice |
| Eskandari et al. (2011) [41] | Antiepileptic | Valproic acid | NLC | Cetyl palmitate | Biodistribution and MES seizure test in Wistar rats |
| Joshi et al. (2012) [42] | Antiemetic | Ondansetron | SLN | GMS | Biodistribution in New Zealand rabbit; histological studies on isolated sheep nasal mucosa |
| Singh et al. (2012) [43] | Sedative | Alprazolam | SLN | GMS | Biodistribution in New Zealand rabbit |
| Morsi et al. (2013) [44] | Anti-ischemic | Vinpocetine | SLN bioadhesive | GMS | Ex vivo bioadhesive strength, histopathological, and permeation studies; biodistribution and pharmacokinetics |
| Gupta et al. (2017) [45] | Antiviral | Efavirenz | SLN | TP, tristearin glyceryl monostearate, glyceryl behenate | Biodistribution in Wistar rats |
| Fatouh et al. (2017) [46] | Antidepressant | Agomelatine | SLN | TP | Biodistribution in rats |
| Singh et al. (2017) [47] | Antipsychotic drug | Asenapine maleate | GC-ANLC | GMS, oleic acid | Pharmacokinetic study in Charles Foster rats; embryo fetal toxicity study |
| Du et al. (2019) [48] | Antifungal drug | Ketoconazole | NLC | Miglyol 812 N, Compritol 888 ATO | In vitro antifungal activity; animal studies in female C57BL/6 mice |
| Patel et al. (2020) [49] | Antiepileptic | Topiramate | NE | Capmul MCM C8 | Pharmacokinetic study and brain drug uptake study in Wistar albino rats |
| Hosny et al. (2020) [50] | Antiviral | Saquinavir mesylate | Cubosomes | Monoolein | Ex vivo permeation study; in vivo evaluation in albino male rabbits. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agosti, E.; Zeppieri, M.; Antonietti, S.; Battaglia, L.; Ius, T.; Gagliano, C.; Fontanella, M.M.; Panciani, P.P. Navigating the Nose-to-Brain Route: A Systematic Review on Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Central Nervous System Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030329
Agosti E, Zeppieri M, Antonietti S, Battaglia L, Ius T, Gagliano C, Fontanella MM, Panciani PP. Navigating the Nose-to-Brain Route: A Systematic Review on Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Central Nervous System Disorders. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(3):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030329
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgosti, Edoardo, Marco Zeppieri, Sara Antonietti, Luigi Battaglia, Tamara Ius, Caterina Gagliano, Marco Maria Fontanella, and Pier Paolo Panciani. 2024. "Navigating the Nose-to-Brain Route: A Systematic Review on Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Central Nervous System Disorders" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 3: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030329
APA StyleAgosti, E., Zeppieri, M., Antonietti, S., Battaglia, L., Ius, T., Gagliano, C., Fontanella, M. M., & Panciani, P. P. (2024). Navigating the Nose-to-Brain Route: A Systematic Review on Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Central Nervous System Disorders. Pharmaceutics, 16(3), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030329












