Designing Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Core-Shell Alginate Particles through Electro-Fluid Dynamic Atomization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
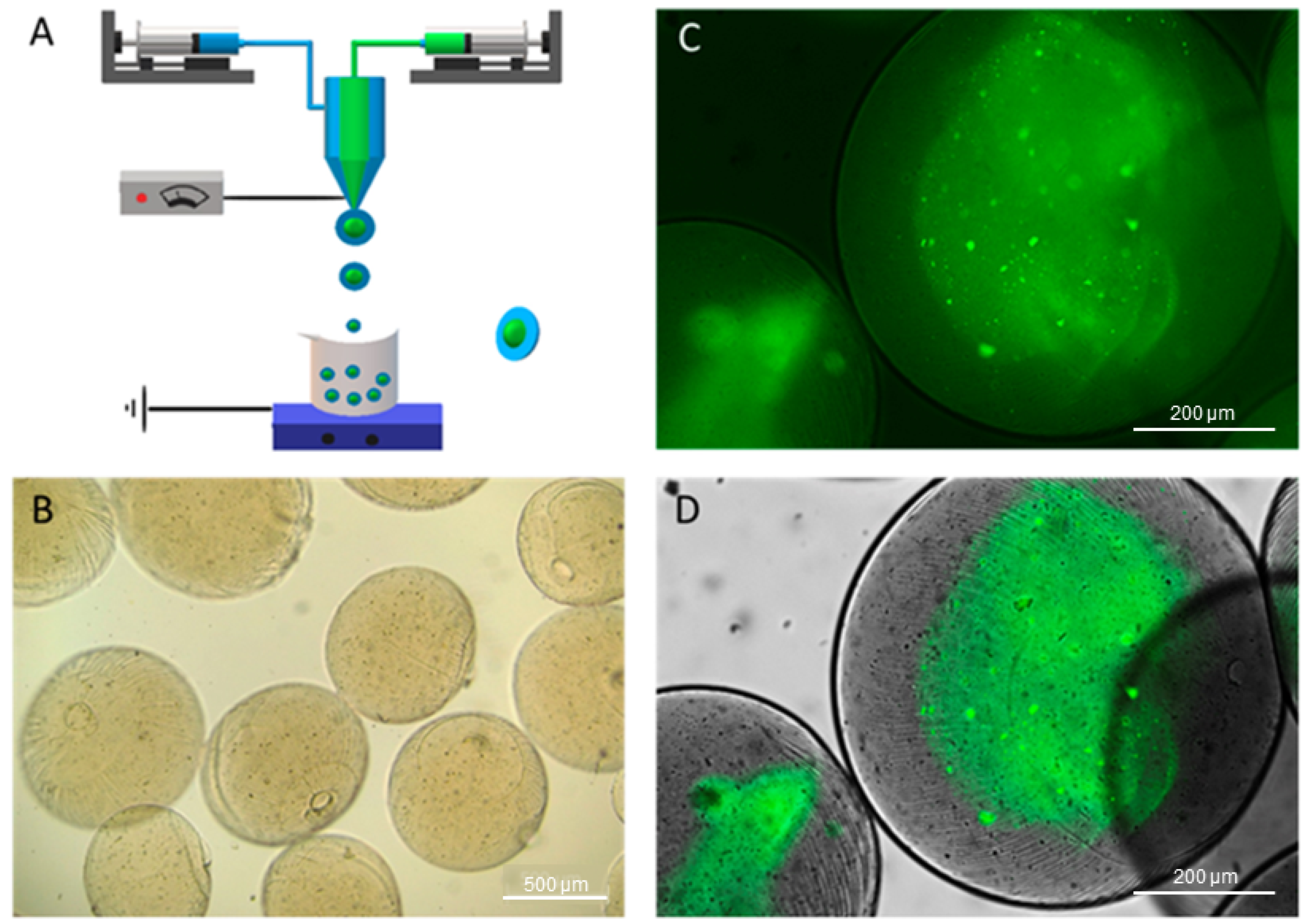
2.1. Preparation of Alginate Microparticles
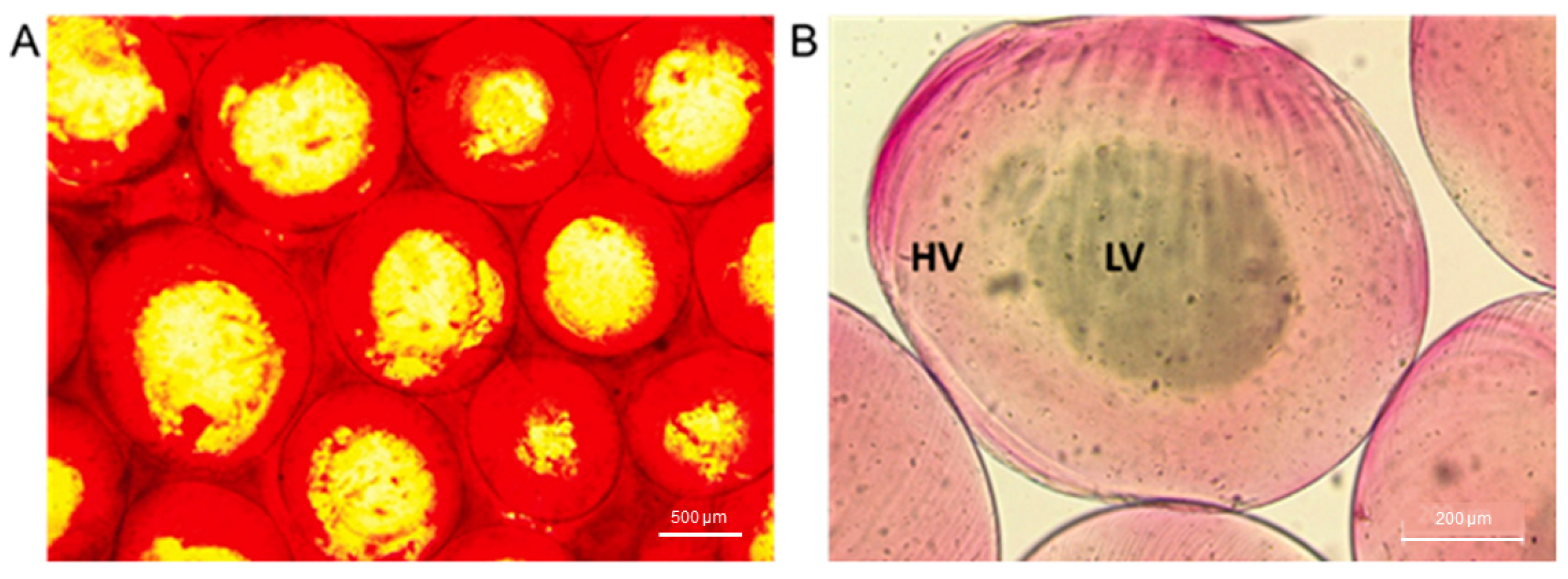
2.2. Microparticle Characterization
2.3. Rheological Setup
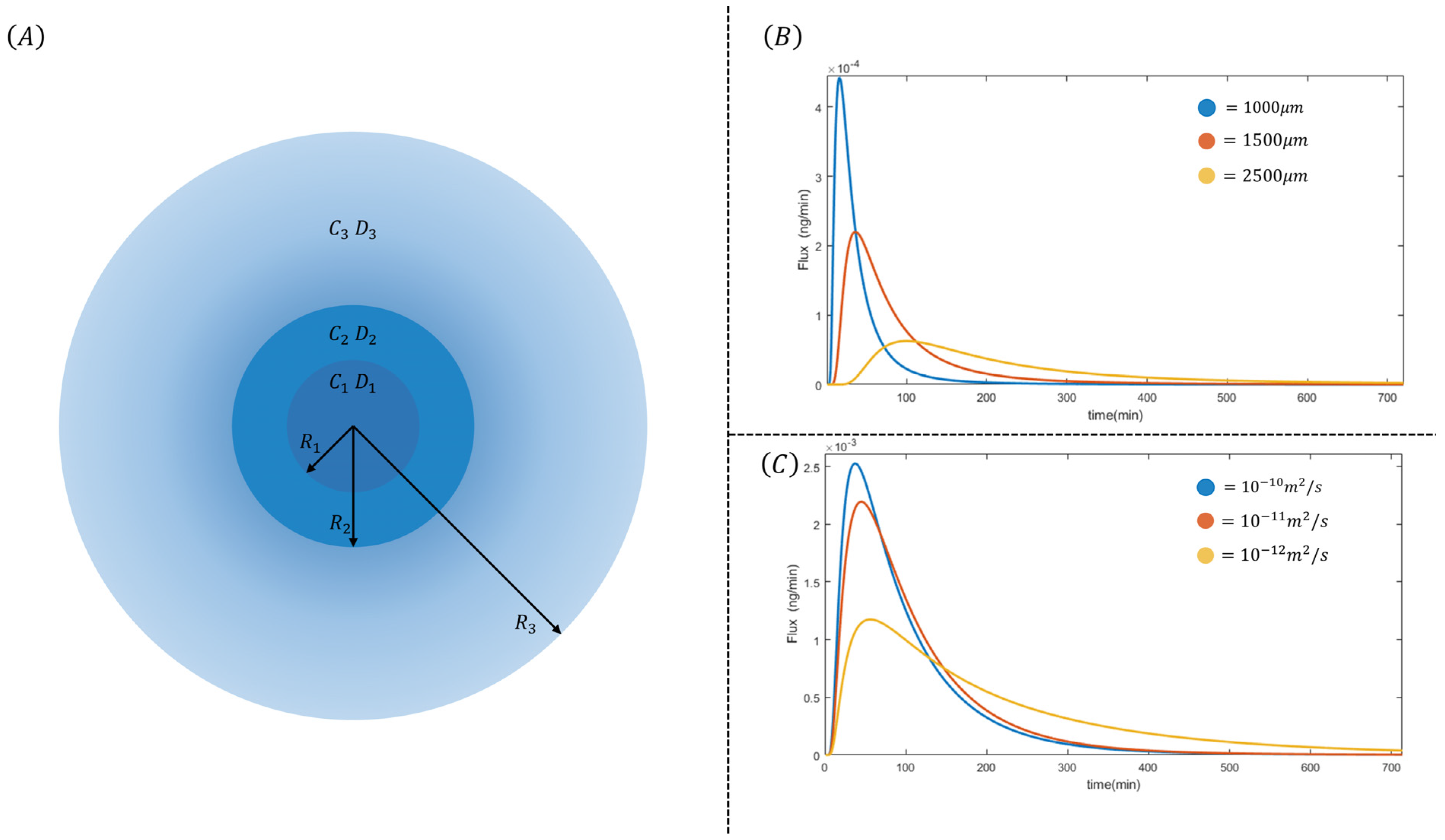
2.4. Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faheem, A.M.; Abdelkader, D.H. Novel drug delivery systems. In Engineering Drug Delivery Systems; Seyfoddin, A., Dezfooli, S.M., Greene, C.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Romana, B.; Hassan, M.M.; Sonvico, F.; Garrastazu Pereira, G.; Mason, A.F.; Thordarson, P.; Bremmell, K.E.; Barnes, T.J.; Prestidge, C.A. A Liposome-Micelle-Hybrid (LMH) Oral Delivery System for Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs: Enhancing Solubilisation and Intestinal Transport. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Zare, M.; Thomas, V.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Conventional Drug Delivery Routes, Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Med. Drug Discov. 2022, 15, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Luo, C.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ruan, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Sun, T.; Li, N.; Han, L.; et al. Advances of Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems for Disease Diagnosis and Treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Jannat, F.T.; Ashfaq, T.; Santulli, C.; Rizwan, M.; Najda, A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Hussain, S.; et al. A Critical Review on the Synthesis of Natural Sodium Alginate Based Composite Materials: An Innovative Biological Polymer for Biomedical Delivery Applications. Processes 2021, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M.; Mehta, M.; Satija, S.; Aljabali, A.A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Anand, K.; Sharma, N.; Dureja, H.; Jha, N.K.; et al. Current-Status and Applications of Polysaccharides in Drug Delivery Systems. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 42, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüero, L.; Zaldivar-Silva, D.; Peña, L.; Dias, M.L. Alginate Microparticles as Oral Colon Drug Delivery Device: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyadi, D.M.; Islam, N. Current Status of Alginate in Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 2020, 8886095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyhani, M.; Mak, S.Y.; Sammut, S.; Shum, H.C.; Hwang, D.K.; Tsai, S.S.H. Controlled Electrospray Generation of Nonspherical Alginate Microparticles. ChemPhysChem 2018, 19, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.-J. Chapter 3—Algae-Based Alginate Biomaterial: Production and Applications. In Biomass, Biofuels, and Biochemicals; Ngo, H., Guo, W., Pandey, A., Chang, J.-S., Lee, D.-J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 37–66. ISBN 978-0-323-96142-4. [Google Scholar]
- Altobelli, R.; Guarino, V.; Ambrosio, L. Micro- and Nanocarriers by Electrofludodynamic Technologies for Cell and Molecular Therapies. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Khodir, W.K.W.A.; Ambrosio, L. Biodegradable Microparticles and Nanoparticles by Electrospraying Techniques. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2012, 10, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Xie, Y.-J.; He, W. Research Progress on Chemical Modification of Alginate: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, J.; Afrose, A.; Islam, N. Formulation and Delivery Strategies of Ibuprofen: Challenges and Opportunities. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayehrad, A.T.; Wondie, G.B.; Marew, T. Different Nanotechnology Approaches for Ciprofloxacin Delivery Against Multidrug-Resistant Microbes. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. The Molecular Structure and Self-Assembly Behavior of Reductive Amination of Oxidized Alginate Derivative for Hydrophobic Drug Delivery. Molecules 2021, 26, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Nie, X.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liao, M.; Li, S. A Sodium Alginate-Based Sustained-Release IPN Hydrogel and Its Applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 39722–39730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourehab, M.A.S.; Rajendran, R.R.; Singh, A.; Pramanik, S.; Shrivastav, P.; Ansari, M.J.; Manne, R.; Amaral, L.S.; Deepak, A. Alginate as a Promising Biopolymer in Drug Delivery and Wound Healing: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Wang, F. PLGA-Based Micro/Nanoparticles: An Overview of Their Applications in Respiratory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpamalar, J.; Sathasivam, T.; Gugler, M.C. Hydrogel BeadsBeads of Natural PolymersPolymers as a Potential Vehicle for Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery. In BT—Bio-Carrier Vectors: Methods and Protocols; Narayanan, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 171–182. ISBN 978-1-0716-0943-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gali, L.; Pirozzi, A.; Donsì, F. Biopolymer- and Lipid-Based Carriers for the Delivery of Plant-Based Ingredients. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sun, R.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, C. PLGA-Based Biodegradable Microspheres in Drug Delivery: Recent Advances in Research and Application. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1397–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A. Electrohydrodynamic Microencapsulation Technology. In Encapsulations; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–45. ISBN 978-0-12-804307-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, C.; Yue, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, P.; Wu, A.; Chen, C.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, C. Application Advance of Electrosprayed Micro/Nanoparticles Based on Natural or Synthetic Polymers for Drug Delivery System. Mater. Des. 2022, 220, 110850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Maya, I.; Guarino, V. 3D Scaffolds Fabrication via Bicomponent Microgels Assembly: Process Optimization and In Vitro Characterization. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Maya, I.; Altobelli, R.; Alvarez-Perez, M.A.; Guarino, V. Mineralized Microgels via Electrohydrodynamic Atomization: Optimization and In Vitro Model for Dentin Pulp Complex. Gels 2023, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Maya, I.; Altobelli, R.; Marrese, M.; Guarino, V. Design of Alginate Based Micro-gels via Electro Fluid Dynamics to Construct Microphysiological Cell Culture Systems. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentería-Ortega, M.; Salgado-Cruz, M.D.L.P.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Alamilla-Beltrán, L.; Farrera-Rebollo, R.R.; Valdespino León, M.; Calderón-Domínguez, G. Effect of Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Conditions on Morphometric Characteristics and Mechanical Resistance of Chia Mucilage-Alginate Particles. CyTA-J. Food 2020, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Caputo, T.; Calcagnile, P.; Altobelli, R.; Demitri, C.; Ambrosio, L. Core/shell Cellulose-Based Microspheres for Oral Administration of Ketoprofen Lysinate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, Q.; Zhou, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, R.; Lenders, V.; Manshian, B.B.; Hua, D.; Soenen, S.J.; et al. Core-Shell Microparticles: From Rational Engineering to Diverse Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 299, 102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Altobelli, R.; Caputo, T.; Ambrosio, L.; Caserta, S.; Calcagnile, P.; Demitri, C. Mono- and Bi-Phasic Cellulose Acetate Micro-Vectors for Anti-Inflammatory Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Stride, E.; Edirisinghe, M. One-Step Electrohydrodynamic Production of Drug-Loaded Micro- and Nanoparticles. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 7, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Mathematical Modeling of Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Maya, I.; Zuppolini, S.; Zarrelli, M.; Mazzotta, E.; Borriello, A.; Malitesta, C.; Guarino, V. Polydopamine-Coated Alginate Microgels: Process Optimization and In Vitro Validation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, R.; Caserta, S. SLE3S-Water System: A Linear Rheological Characterisation. Rheol. Acta 2023, 62, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, H.; Song, D.W.; Kwak, H.W.; Yun, H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. Effect of Shear Viscosity on the Preparation of Sphere-like Silk Fibroin Microparticles by Electrospraying. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, S.; Si, T.; Gai, M.; Frueh, J.; He, Q. Hydrodynamic Electrospray Ionization Jetting of Calcium Alginate Particles: Effect of Spray-Mode, Spraying Distance and Concentration. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 24243–24249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Rheological Properties of Sodium Alginate Solutions in the Presence of Added Salt: An Application of Kulicke Equation. Rheol. Acta 2020, 59, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Sodium Alginate Solutions: Correlation between Rheological Properties and Spinnability. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8034–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.C.; Walker, J. The Stokes-Einstein Law for Diffusion in Solution. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1997, 106, 724–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, A.B.; Mishra, S.; Kulkarni, R.D.; Naik, J.B. Influence of Different Viscosity Grade Ethylcellulose Polymers on Encapsulation and in Vitro Release Study of Drug Loaded Nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 7, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.-C.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, C.-H. Coaxial Electrohydrodynamic Atomization toward Large Scale Production of Core-Shell Structured Microparticles. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 5303–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kooij, R.S.; Steendam, R.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. An Overview of the Production Methods for Core–Shell Microspheres for Parenteral Controlled Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 170, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadou, D.; Evans, R.E.; Atkinson, E.; Abdalla, A.; Gavins, F.K.H.; Boyd, A.S.; Williams, G.R.; Knowles, J.C.; Roberton, V.H.; Phillips, J.B. An Alginate-Based Encapsulation System for Delivery of Therapeutic Cells to the CNS. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 4005–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cu, Y.; Saltzman, W.M. Mathematical Modeling of Molecular Diffusion through Mucus. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, B.; Gåserød, O.; Paus, D.; Mikkelsen, A.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Toffanin, R.; Vittur, F.; Rizzo, R. Inhomogeneous Alginate Gel Spheres: An Assessment of the Polymer Gradients by Synchrotron Radiation-Induced x-Ray Emission, Magnetic Resonance Microimaging, and Mathematical Modeling. Biopolymers 2000, 53, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, S.; Barnard, E.; Hyatt, B.; Rathinam, M.; Zustiak, S.P. Predicting Drug Release From Degradable Hydrogels Using Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy and Mathematical Modeling. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axpe, E.; Chan, D.; Offeddu, G.S.; Chang, Y.; Merida, D.; Hernandez, H.L.; Appel, E.A. A Multiscale Model for Solute Diffusion in Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 6889–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccavo, D. An Overview on the Mathematical Modeling of Hydrogels’ Behavior for Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Lumpkin, J.A.; Rosenblatt, J. Mathematical Modeling of Drug Release from Hydrogel Matrices via a Diffusion Coupled with Desorption Mechanism. J. Control. Release 1994, 32, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembczynski, R.; Jankowski, T. Characterisation of Small Molecules Diffusion in Hydrogel-Membrane Liquid-Core Capsules. Biochem. Eng. J. 2000, 6, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabardo, S.; Rech, R.; Ayub, M.A.Z. Determination of Lactose and Ethanol Diffusion Coefficients in Calcium Alginate Gel Spheres: Predicting Values To Be Used in Immobilized Bioreactors. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 2305–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puguan, J.M.C.; Yu, X.; Kim, H. Diffusion Characteristics of Different Molecular Weight Solutes in Ca–Alginate Gel Beads. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øyaas, J.; Storrø, I.; Svendsen, H.; Levine, D.W. The Effective Diffusion Coefficient and the Distribution Constant for Small Molecules in Calcium-Alginate Gel Beads. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 47, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Shimono, K. Molecular Modeling to Estimate the Diffusion Coefficients of Drugs and Other Small Molecules. Molecules 2020, 25, 5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrami, M.; Marizza, P.; Zecchin, F.; Bertoncin, P.; Marson, D.; Lapasin, R.; de Riso, F.; Posocco, P.; Grassi, G.; Grassi, M. Theoretical Importance of PVP-Alginate Hydrogels Structure on Drug Release Kinetics. Gels 2019, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, G.; Donati, I.; Grassi, M.; Marchioli, G.; Lapasin, R.; Paoletti, S. Mechanical Spectroscopy and Relaxometry on Alginate Hydrogels: A Comparative Analysis for Structural Characterization and Network Mesh Size Determination. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offeddu, G.S.; Axpe, E.; Harley, B.A.C.; Oyen, M.L. Relationship between Permeability and Diffusivity in Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogels. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmann, M.S.; Skeens, K.M.; Kharkar, P.M.; Ford, E.M.; Maverakis, E.; Lee, K.H.; Kloxin, A.M. Tuning and Predicting Mesh Size and Protein Release from Step Growth Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3131–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diclofenac. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00586 (accessed on 22 December 2023).
- Gombotz, W.R.; Wee, S.F. Protein Release from Alginate Matrices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshi, M.A.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Hasan, N.; Im, E.; Jung, Y.; Yoo, J.-W. PH-Responsive Alginate-Based Microparticles for Colon-Targeted Delivery of Pure Cyclosporine A Crystals to Treat Ulcerative Colitis. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, T.; Narayana, S.N.G.H.; Pal, K.; Pramanik, K.; Giri, S.; Banerjee, I. Calcium Alginate-Carboxymethyl Cellulose Beads for Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, H.; Su, W.; Wang, H.; Tan, M. Tuning the Microstructures of Electrospray Multicore Alginate Microspheres for the Enhanced Delivery of Astaxanthin. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 41537–41547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, A.M.; Kadkhodaee, R.; Ghorani, B.; Razzaq, H.; Tucker, N. Electrospray-Assisted Encapsulation of Caffeine in Alginate Microhydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Maya, I.; Schiavone, C.; Ferraro, R.; Renkler, N.Z.; Caserta, S.; Guarino, V. Designing Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Core-Shell Alginate Particles through Electro-Fluid Dynamic Atomization. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020193
Cruz-Maya I, Schiavone C, Ferraro R, Renkler NZ, Caserta S, Guarino V. Designing Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Core-Shell Alginate Particles through Electro-Fluid Dynamic Atomization. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(2):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020193
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Maya, Iriczalli, Carmine Schiavone, Rosalia Ferraro, Nergis Zeynep Renkler, Sergio Caserta, and Vincenzo Guarino. 2024. "Designing Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Core-Shell Alginate Particles through Electro-Fluid Dynamic Atomization" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 2: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020193
APA StyleCruz-Maya, I., Schiavone, C., Ferraro, R., Renkler, N. Z., Caserta, S., & Guarino, V. (2024). Designing Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Core-Shell Alginate Particles through Electro-Fluid Dynamic Atomization. Pharmaceutics, 16(2), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020193









