Evaluation of the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Saxagliptin through Reactive Metabolite Identification in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Stability Assay of DPP-4 Inhibitors after Incubation with Cysteine
2.3. Metabolite Profiling in Rat Liver Microsomes
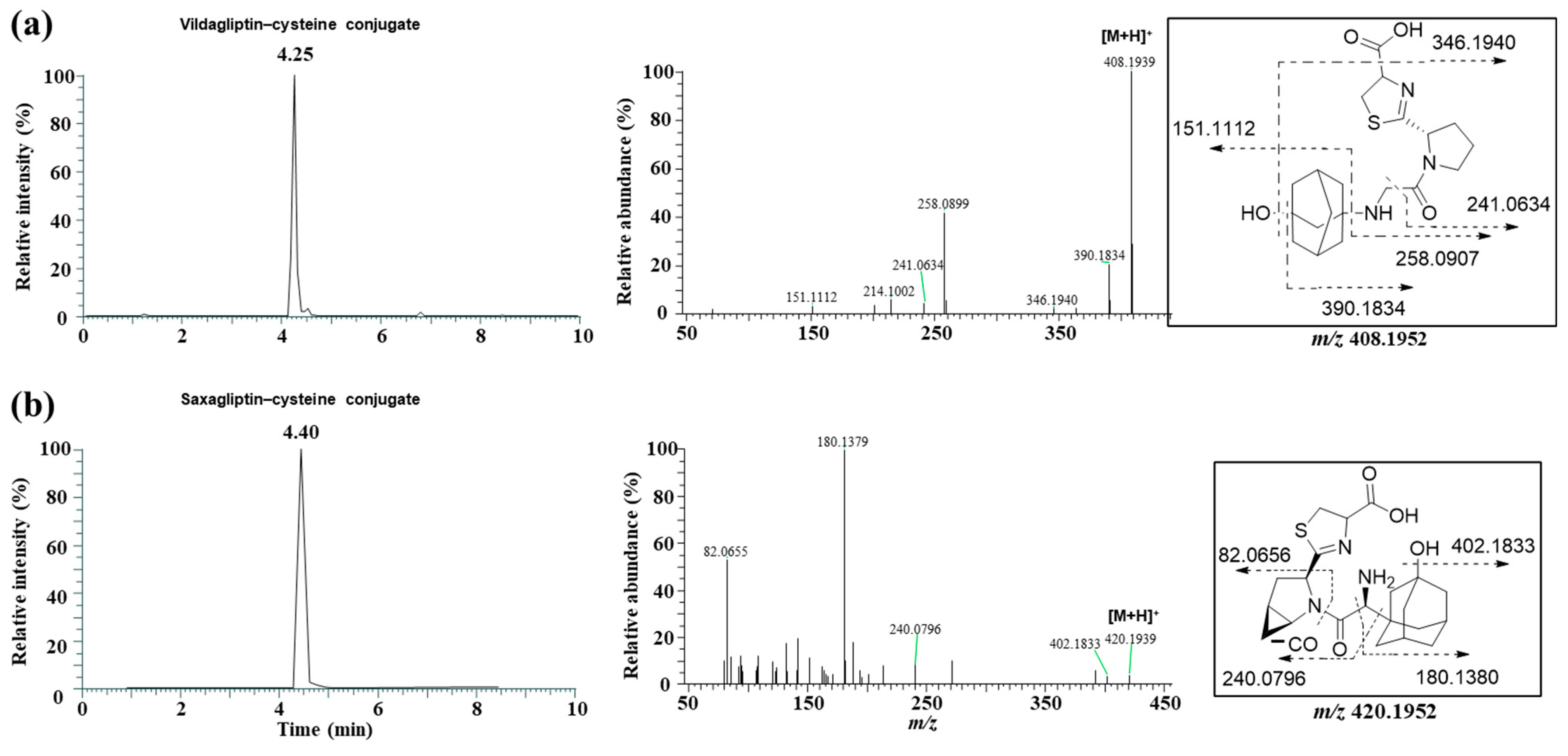
2.4. Cysteine and Glutathione Adduct Identification of 5-Hydroxysaxagliptin
2.5. Metabolite Profiling in Rats
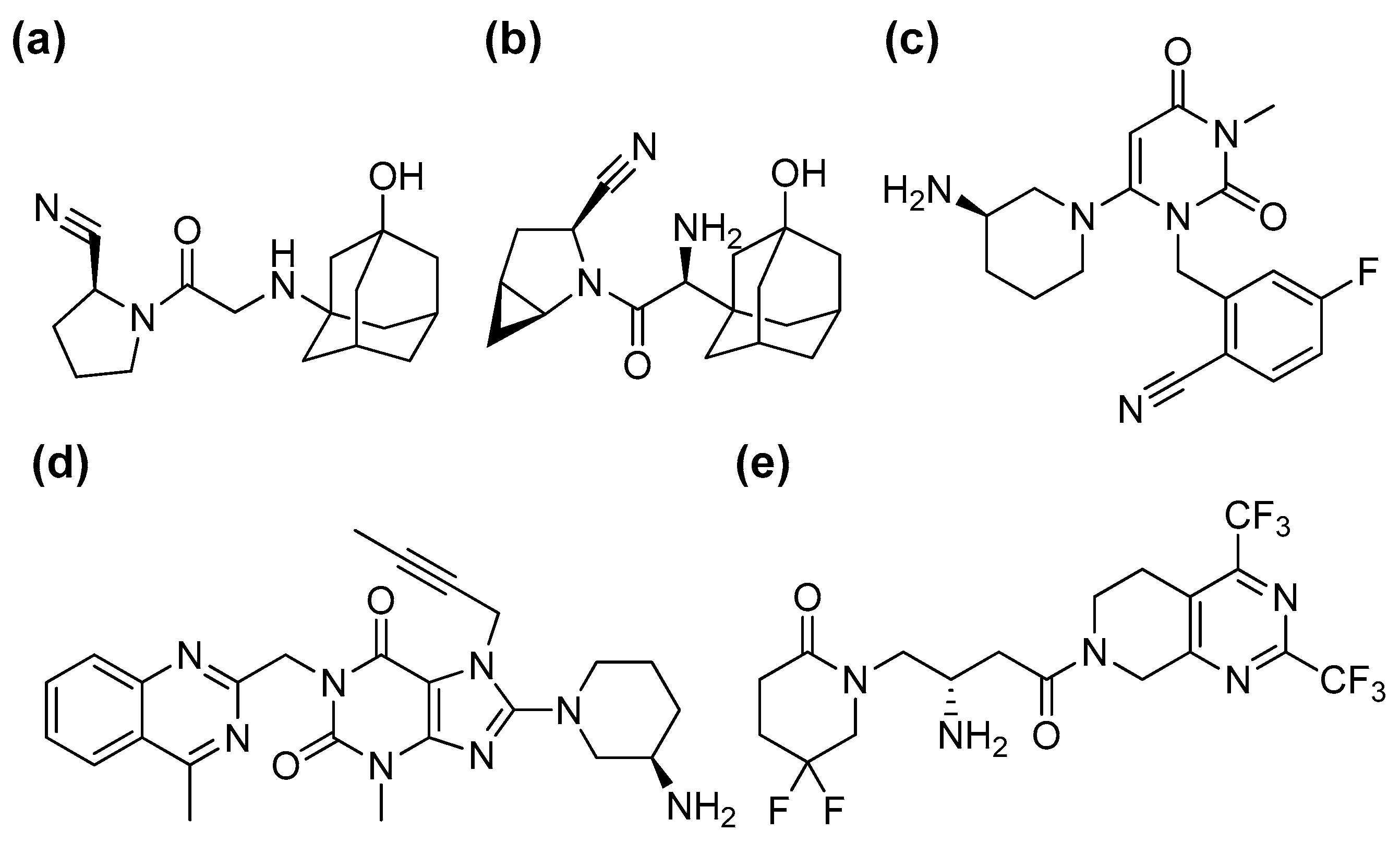
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Stability of DPP-4 Inhibitors under Nonenzymatic Conditions
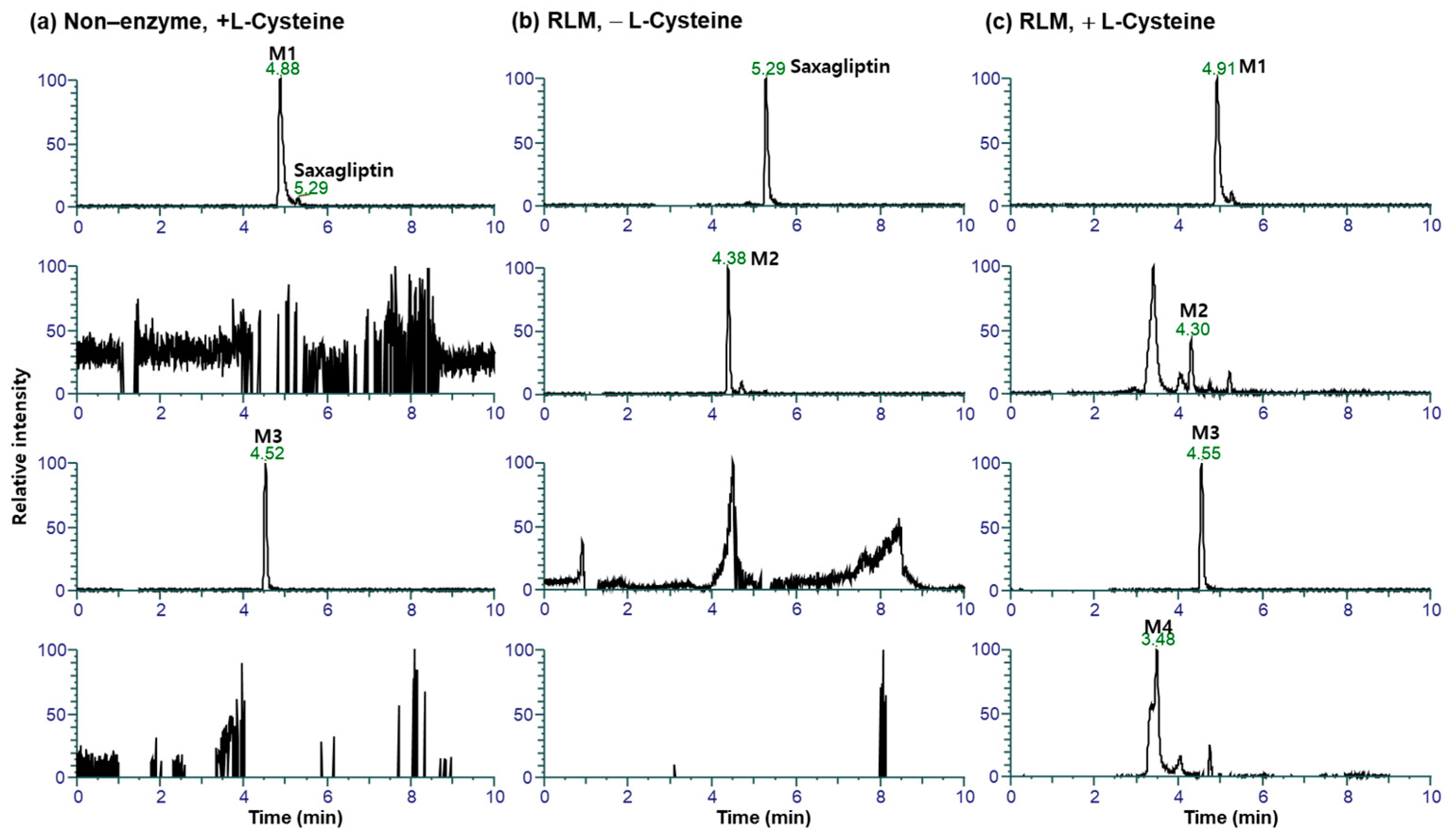
3.2. Metabolite Profiling in Rat Liver Microsomes
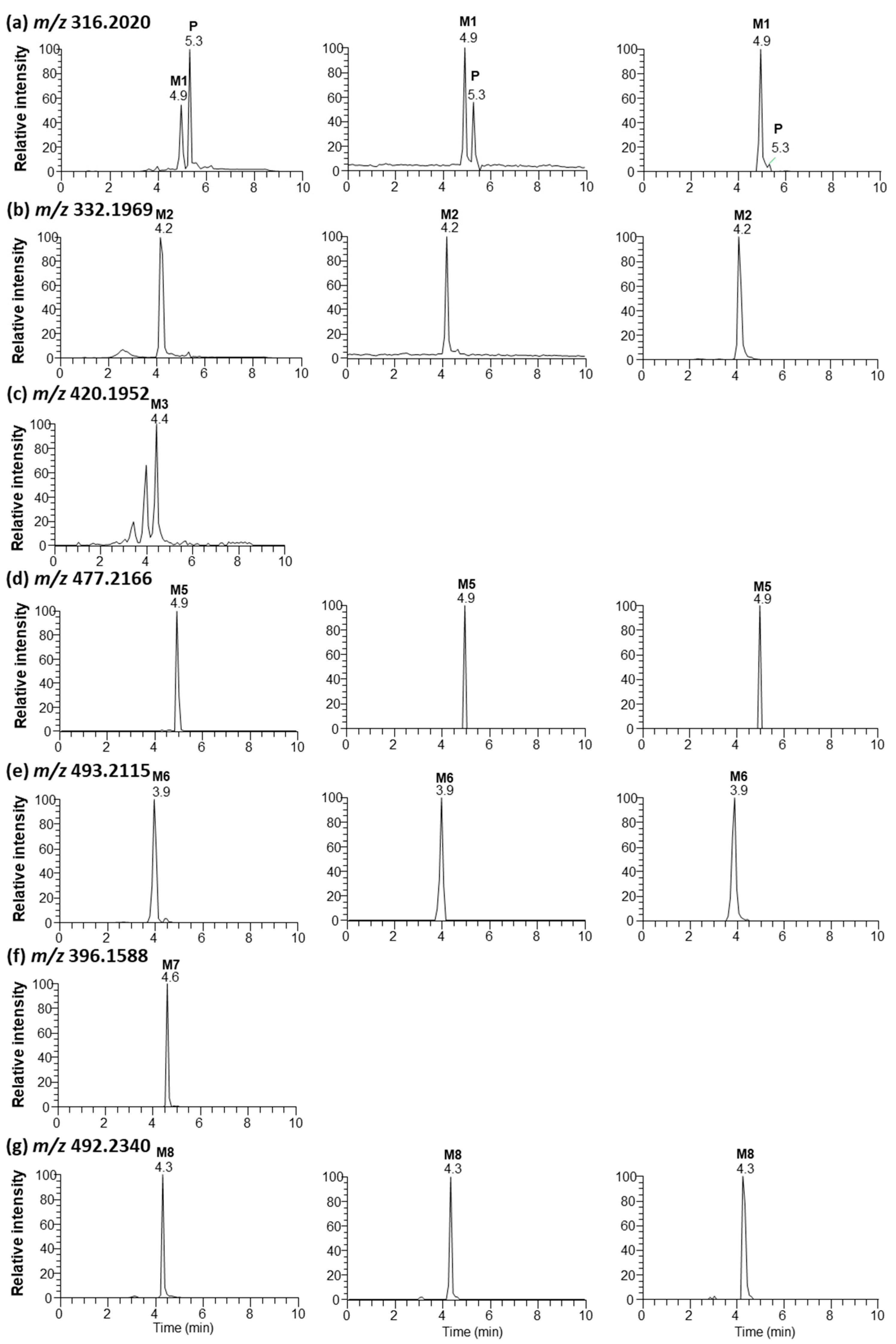
3.3. Metabolite Profiling in Rat Plasma, Bile, and Liver
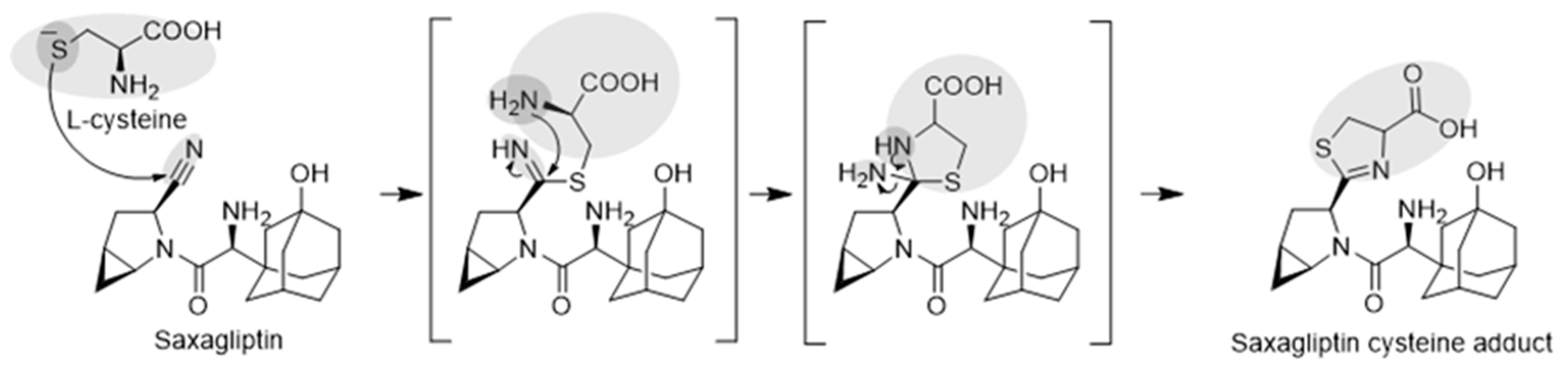
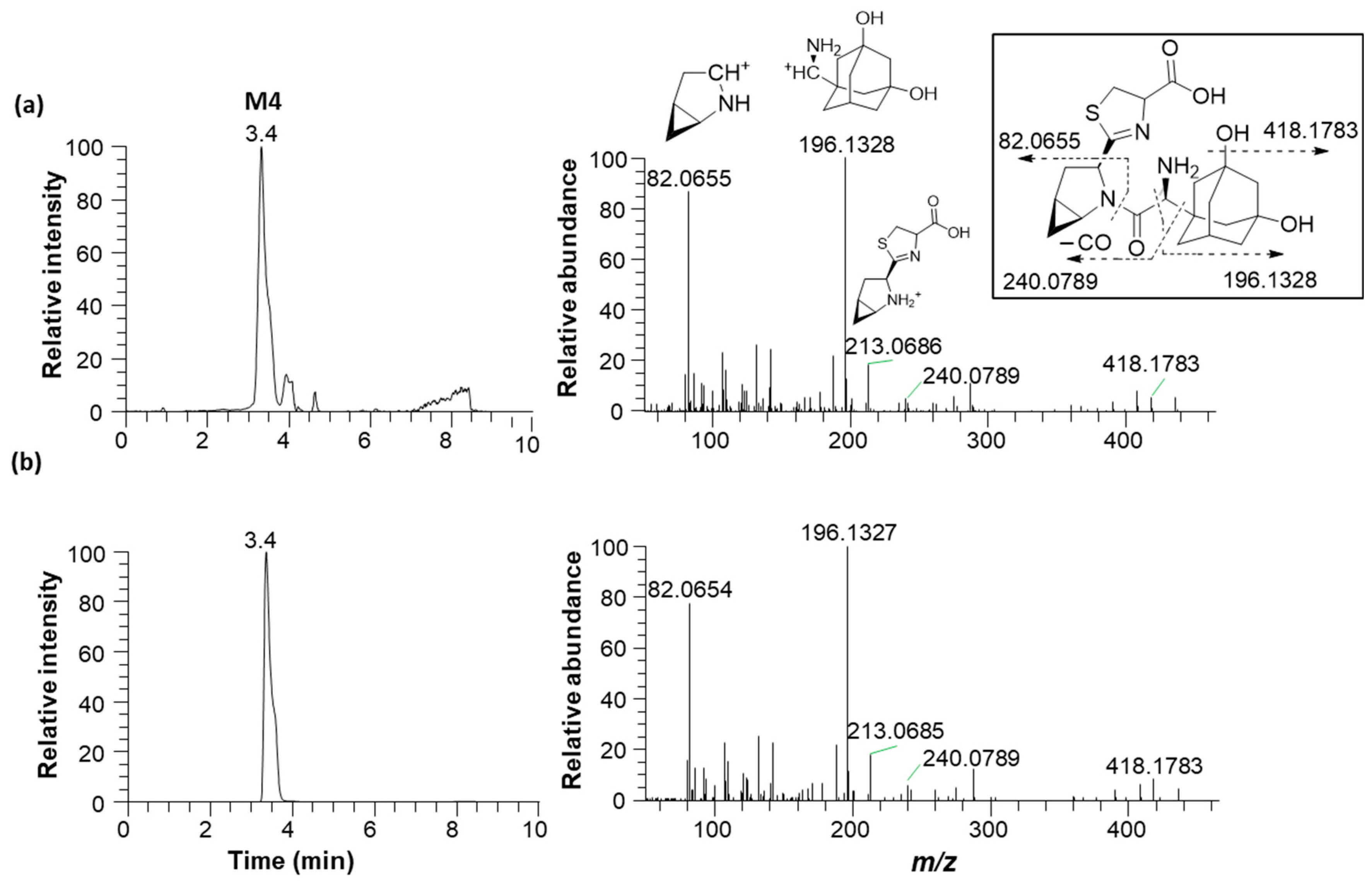
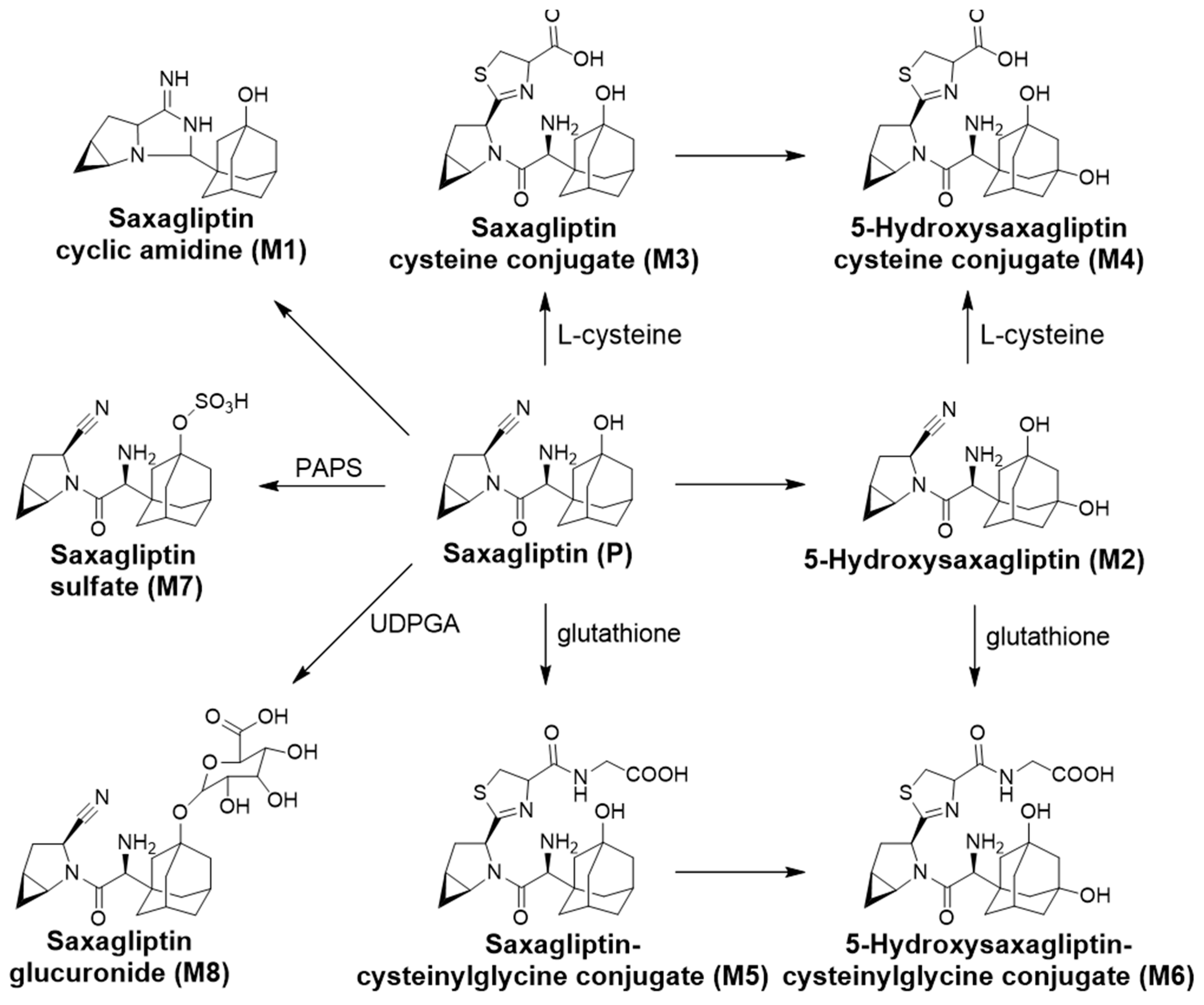
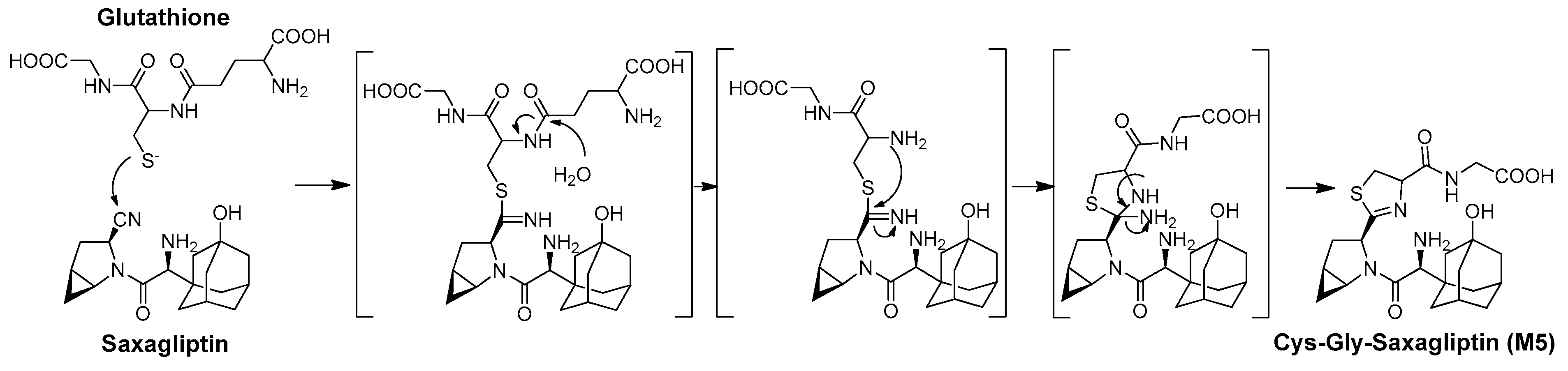
3.4. Identification of the Reactive Metabolites
3.5. Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Chen, F.; Gao, S.; Pei, J.; Lai, L. Deep Learning for Drug-Induced Liver Injury. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakatis, M.Z.; Reese, M.J.; Harrell, A.W.; Taylor, M.A.; Baines, I.A.; Chen, L.; Bloomer, J.C.; Yang, E.Y.; Ellens, H.M.; Ambroso, J.L.; et al. Preclinical strategy to reduce clinical hepatotoxicity using in vitro bioactivation data for >200 compounds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2067–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Umehara, K.; Nakajima, M. Identification of Novel Metabolites of Vildagliptin in Rats: Thiazoline-Containing Thiol Adducts Formed via Cysteine or Glutathione Conjugation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2019, 47, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Umehara, K.; Nakajima, M. Identification of a novel metabolite of vildagliptin in humans: Cysteine targets the nitrile moiety to form a thiazoline ring. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, W.G. Investigating the link between drug metabolism and toxicity. In Overcoming Obstacles in Drug Discovery and Development; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Samanta, I.; Mondal, A.; Liu, W.R. Covalent Inhibition in Drug Discovery. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Lechon, M.J.; Tolosa, L.; Donato, M.T. Metabolic activation and drug-induced liver injury: In vitro approaches for the safety risk assessment of new drugs. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 752–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Boulton, D.W.; Barros, A., Jr.; Wang, L.; Cao, K.; Bonacorsi, S.J., Jr.; Iyer, R.A.; Humphreys, W.G.; Christopher, L.J. Characterization of the in vitro and in vivo metabolism and disposition and cytochrome P450 inhibition/induction profile of saxagliptin in human. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, N.; Ito, T.; Shimizu, S.; Hirata, T.; Uchihara, H. Idiosyncratic liver injury induced by vildagliptin with successful switch to linagliptin in a hemodialyzed diabetic patient. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, e198–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dina Halegoua-De Marzio, V.J.N. Hepatotoxicity of Cardiovascular and Antidiabetic Drugs. In Drug-Induced Liver Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 519–540. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.W.; He, Z.X.; Zhou, Z.W.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.X.; Duan, W.; Zhou, S.F. Clinical pharmacology of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors indicated for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 42, 999–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, M.G.; Zaki, M.; Said, E. Nephroprotective effect of saxagliptin against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity, emphasis on anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptic effects. Life Sci. 2018, 208, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalha, A.M.; Mahadeva, S.; Boon Tan, A.T.; Mun, K.S. Kombiglyze (metformin and saxagliptin)-induced hepatotoxicity in a patient with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JGH Open 2018, 2, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, L.; Tou, C.K.; Patel, C.G.; Zhao, J. Pharmacokinetic study of saxagliptin in healthy Chinese subjects. Clin. Drug Investig. 2012, 32, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fura, A.; Khanna, A.; Vyas, V.; Koplowitz, B.; Chang, S.Y.; Caporuscio, C.; Boulton, D.W.; Christopher, L.J.; Chadwick, K.D.; Hamann, L.G.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor saxagliptin in rats, dogs, and monkeys and clinical projections. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.E.; Seo, H.J.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, G.M.; Ji, S.B.; Park, S.Y.; Wu, Z.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Liu, K.H. In Vitro Metabolism of Donepezil in Liver Microsomes Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betti, M.; Ciacci, C.; Abramovich, S.; Frontalini, F. Protein Extractions from Amphistegina lobifera: Protocol Development and Optimization. Life 2021, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruczynska, W.M.; Szlinder-Richert, J.; Malesa-Ciecwierz, M.; Warzocha, J. Assessment of PAH pollution in the southern Baltic Sea through the analysis of sediment, mussels and fish bile. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepan, A.F.; Walker, D.P.; Bauman, J.; Price, D.A.; Baillie, T.A.; Kalgutkar, A.S.; Aleo, M.D. Structural alert/reactive metabolite concept as applied in medicinal chemistry to mitigate the risk of idiosyncratic drug toxicity: A perspective based on the critical examination of trends in the top 200 drugs marketed in the United States. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1345–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oballa, R.M.; Truchon, J.F.; Bayly, C.I.; Chauret, N.; Day, S.; Crane, S.; Berthelette, C. A generally applicable method for assessing the electrophilicity and reactivity of diverse nitrile-containing compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berteotti, A.; Vacondio, F.; Lodola, A.; Bassi, M.; Silva, C.; Mor, M.; Cavalli, A. Predicting the reactivity of nitrile-carrying compounds with cysteine: A combined computational and experimental study. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tran, P.; Yin, H.; Smith, H.; Batard, Y.; Wang, L.; Einolf, H.; Gu, H.; Mangold, J.B.; Fischer, V.; et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of [14C]vildagliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blech, S.; Ludwig-Schwellinger, E.; Grafe-Mody, E.U.; Withopf, B.; Wagner, K. The metabolism and disposition of the oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, linagliptin, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, J.C.; Joo, J.; Lee, T.; Kim, N.D.; Liu, K.-H. DC23, a Triazolothione Resorcinol Analogue, Is Extensively Metabolized to Glucuronide Conjugates in Human Liver Microsomes. Mass Spectrom. Lett. 2018, 9, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Damsten, M.C.; Commandeur, J.N.; Fidder, A.; Hulst, A.G.; Touw, D.; Noort, D.; Vermeulen, N.P. Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry detection of covalent binding of acetaminophen to human serum albumin. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, B.R.; Wienkers, L.C.; Rock, D.A. Time-dependent inactivation of P450 3A4 by raloxifene: Identification of Cys239 as the site of apoprotein alkylation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, U.P.; Obach, R.S.; Gilbert, A.M. Benchmarking in vitro covalent binding burden as a tool to assess potential toxicity caused by nonspecific covalent binding of covalent drugs. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Metabolites | tR (min) | [M+H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | Reaction Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Measured | |||||
| P | Saxagliptin | 5.3 | 316.2020 | 316.2017 | −0.95 | |
| M1 | Saxagliptin cyclic amidine | 4.9 | 316.2020 | 316.2017 | −0.95 | cyclization |
| M2 | 5-Hydroxysaxagliptin | 4.2 | 332.1969 | 332.1965 | −1.2 | hydroxylation |
| M3 | Saxagliptin–cysteine conjugate | 4.4 | 420.1952 | 420.1931 | −4.99 | cysteine conjugation |
| M4 | 5-Hydroxysaxagliptin–cysteine conjugate | 3.5 | 436.1901 | 436.1895 | −1.40 | Hydroxylation and cysteine conjugation |
| M5 | Saxagliptin–cysteinylglycine conjugate | 4.7 | 477.2166 | 477.2163 | −0.63 | glutathione conjugation |
| M6 | 5-Hydroxysaxagliptin–cysteinylglycine conjugate | 3.9 | 493.2115 | 493.2113 | −0.41 | Hydroxylation and glutathione conjugation |
| M7 | Saxagliptin-O-sulfate | 4.6 | 396.1588 | 396.1581 | −1.77 | sulfation |
| M8 | Saxagliptin-O-glucuronide | 4.3 | 492.2340 | 492.2335 | −1.01 | glucuronidation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-Y.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, E.-J.; Jeon, J.-H.; Song, I.-S.; Liu, K.-H. Evaluation of the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Saxagliptin through Reactive Metabolite Identification in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010106
Kim K-Y, Jeong Y-J, Park S-Y, Park E-J, Jeon J-H, Song I-S, Liu K-H. Evaluation of the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Saxagliptin through Reactive Metabolite Identification in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ki-Young, Yeo-Jin Jeong, So-Young Park, Eun-Ji Park, Ji-Hyeon Jeon, Im-Sook Song, and Kwang-Hyeon Liu. 2024. "Evaluation of the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Saxagliptin through Reactive Metabolite Identification in Rats" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 1: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010106
APA StyleKim, K.-Y., Jeong, Y.-J., Park, S.-Y., Park, E.-J., Jeon, J.-H., Song, I.-S., & Liu, K.-H. (2024). Evaluation of the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Saxagliptin through Reactive Metabolite Identification in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 16(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010106







