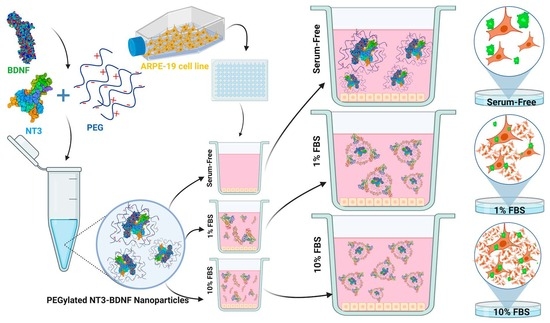
The Impact of Serum Protein Adsorption on PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles—Distribution, Protein Release, and Cytotoxicity in a Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cell Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles
2.1.1. BDNF and NT-3
2.1.2. PEG
2.1.3. PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles
2.1.4. FITC-PEGylated Neurotrophin Nanoparticles
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of PEGylated NTs’ Nanoparticles
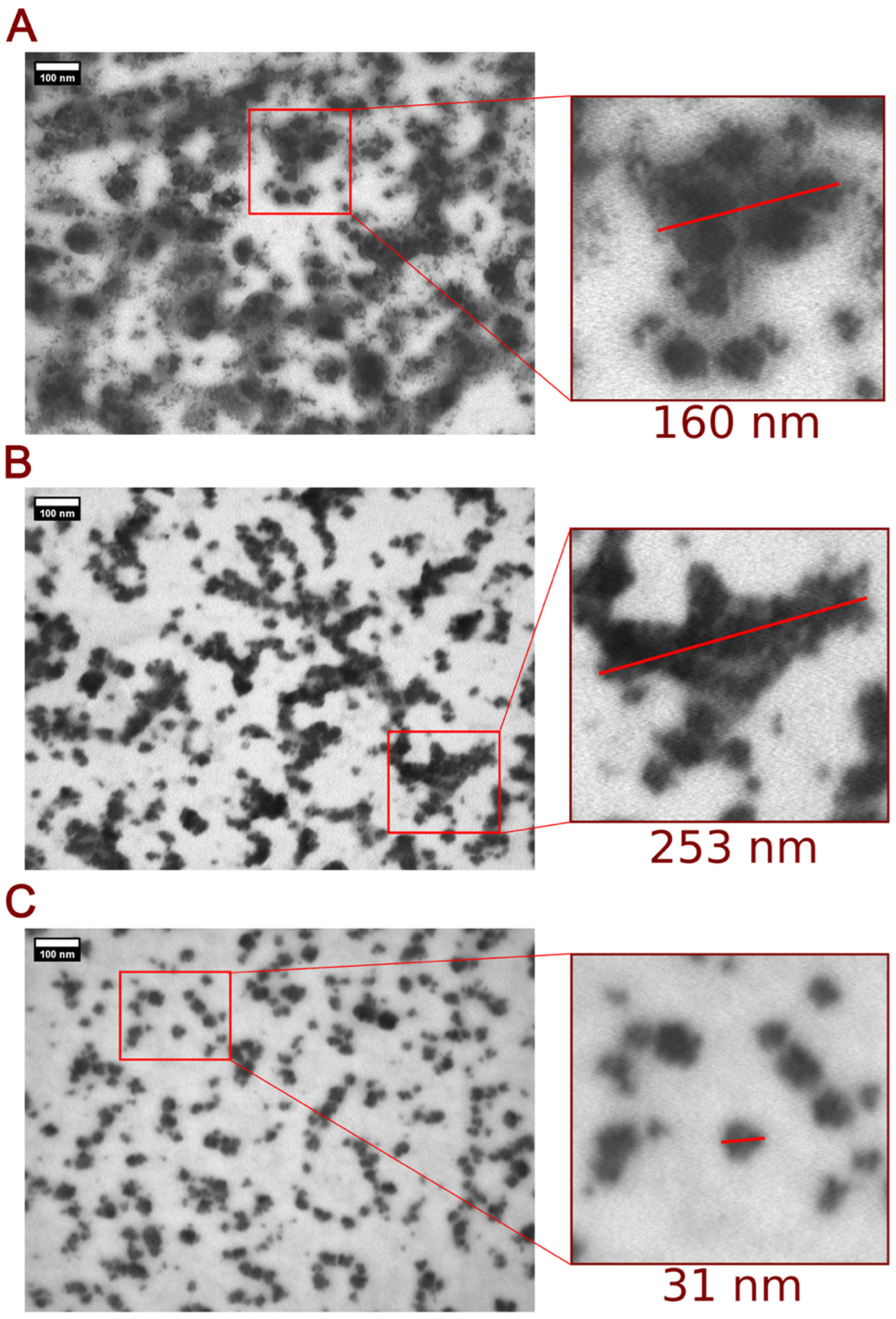
2.2.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
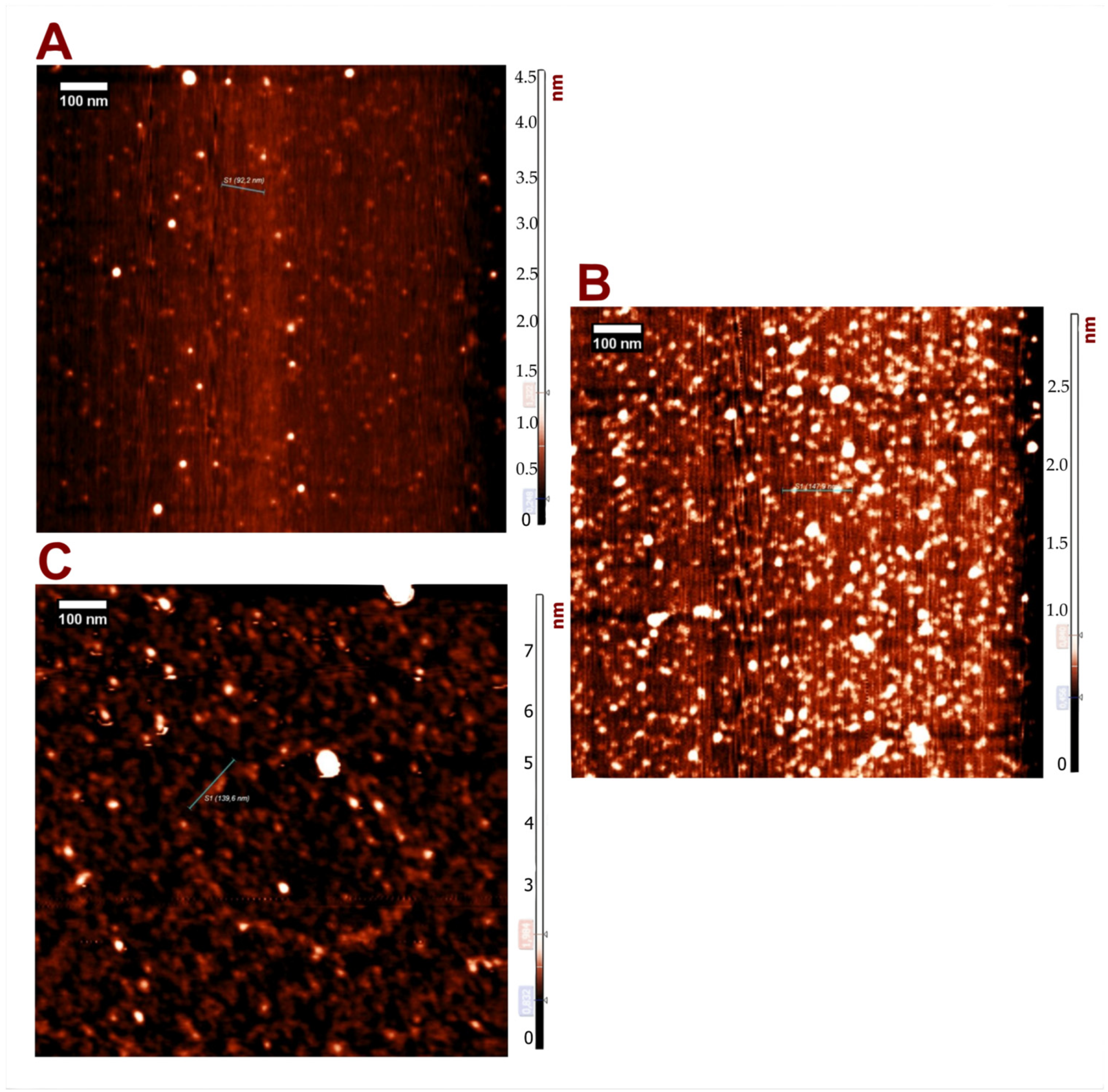
2.2.2. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
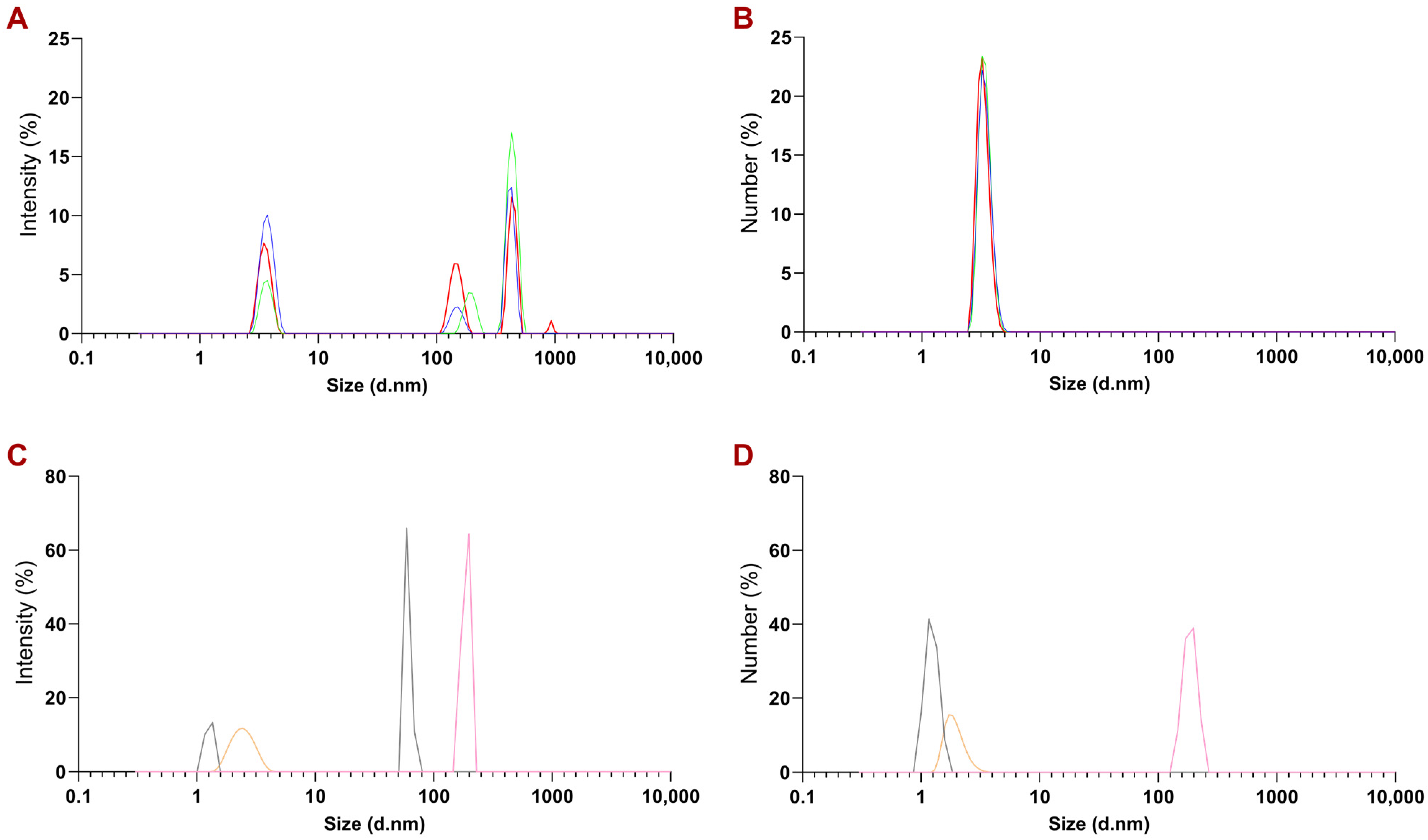
2.2.3. Size Measurement of PEGylated NTs with Multi-Angle Dynamic Light Scattering (MADLS)
2.2.4. Nanoparticle Zeta (ζ) Potential Determination
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. In Vitro BDNF and NT3 Release Profile Quantification in Serum-Free and Serum-Rich Environments
2.5.1. Release Profile Quantification and Nanoparticle Size Distribution in a Cell-Free System
2.5.2. In Vitro Release Profile in Cell Culture
2.6. Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles with Various Neurotrophins’ Concentrations in PBS
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles with Various Neurotrophin Concentrations in FBS
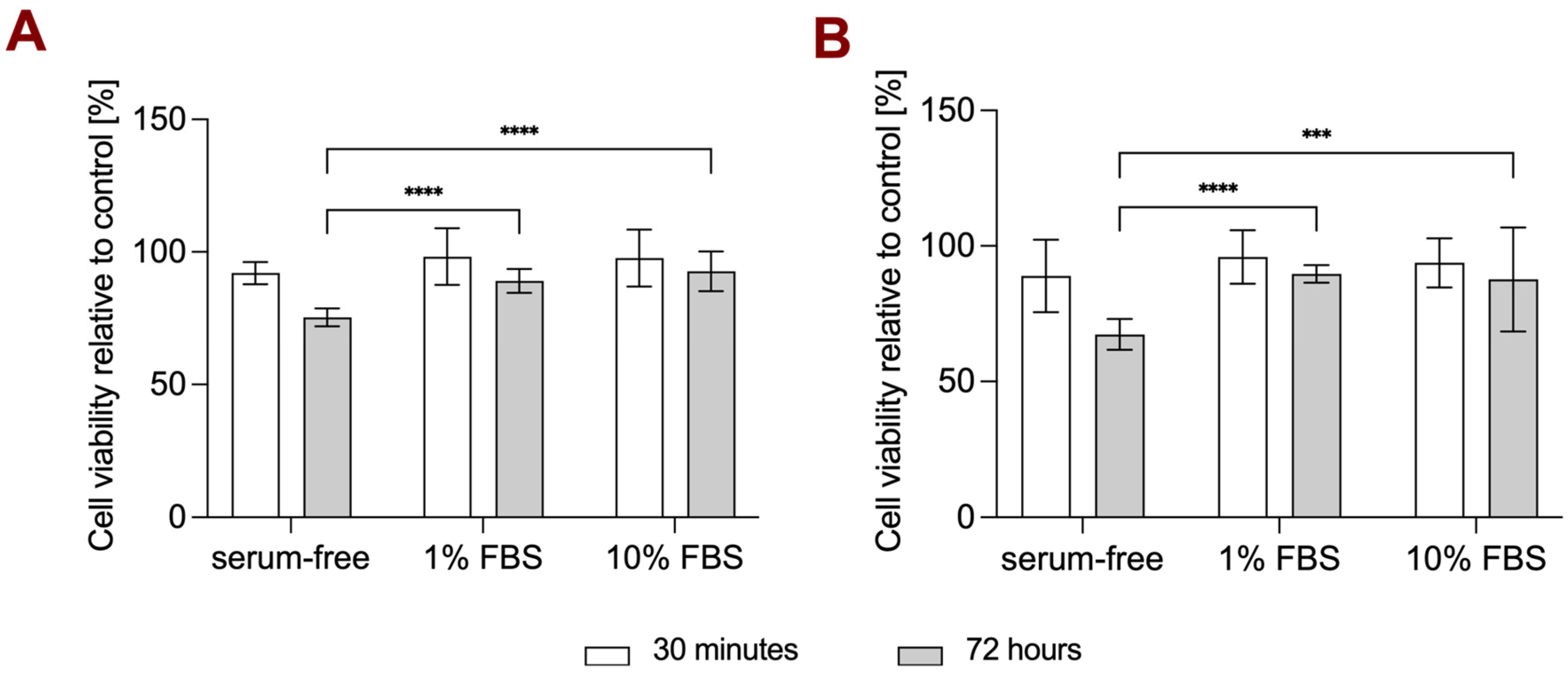
3.3. Cell Viability Study in Different Media Conditions
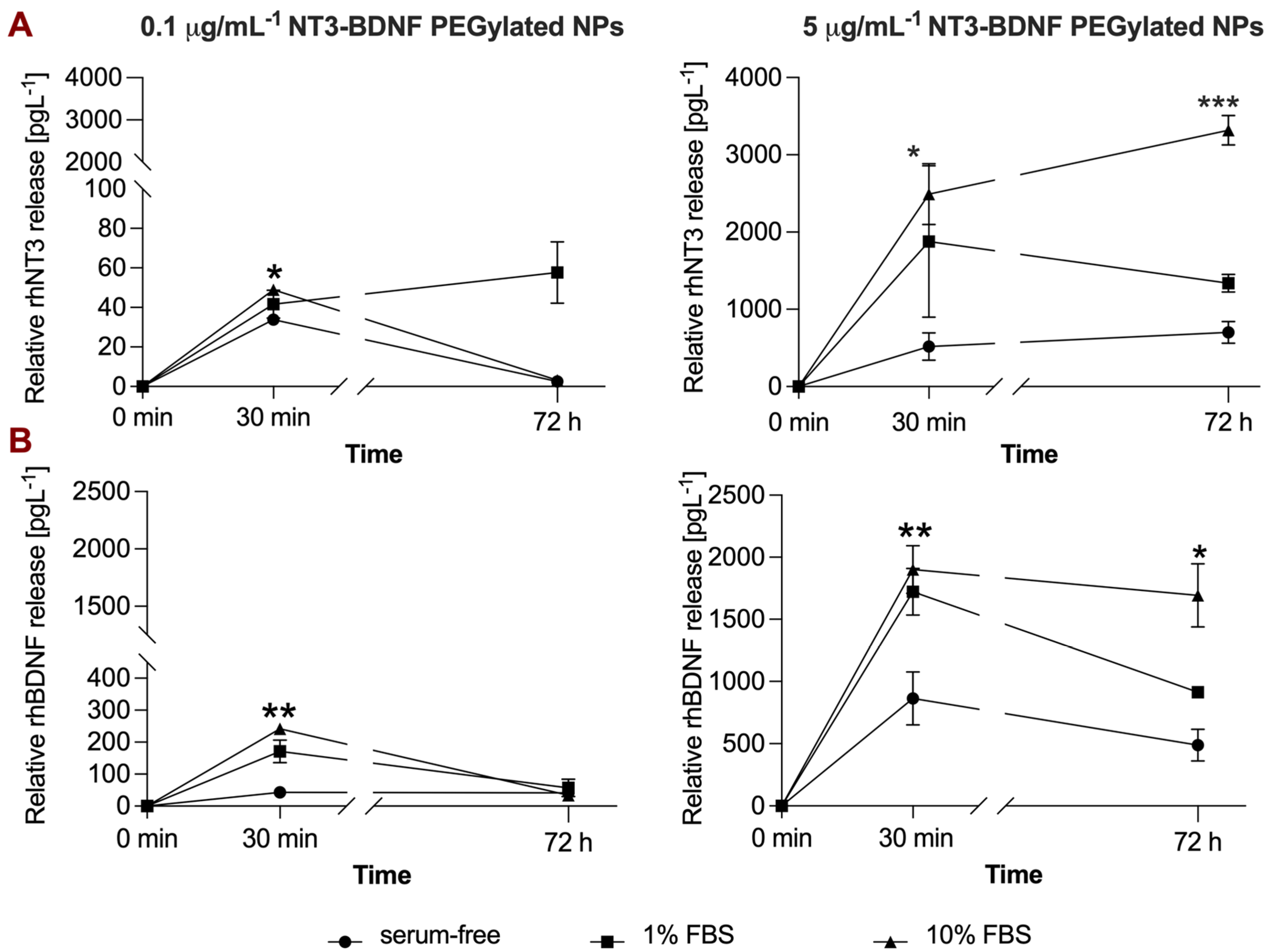
3.4. rhBDNF and rhNT3 Release Study under Sink Conditions in a Cell-Free System
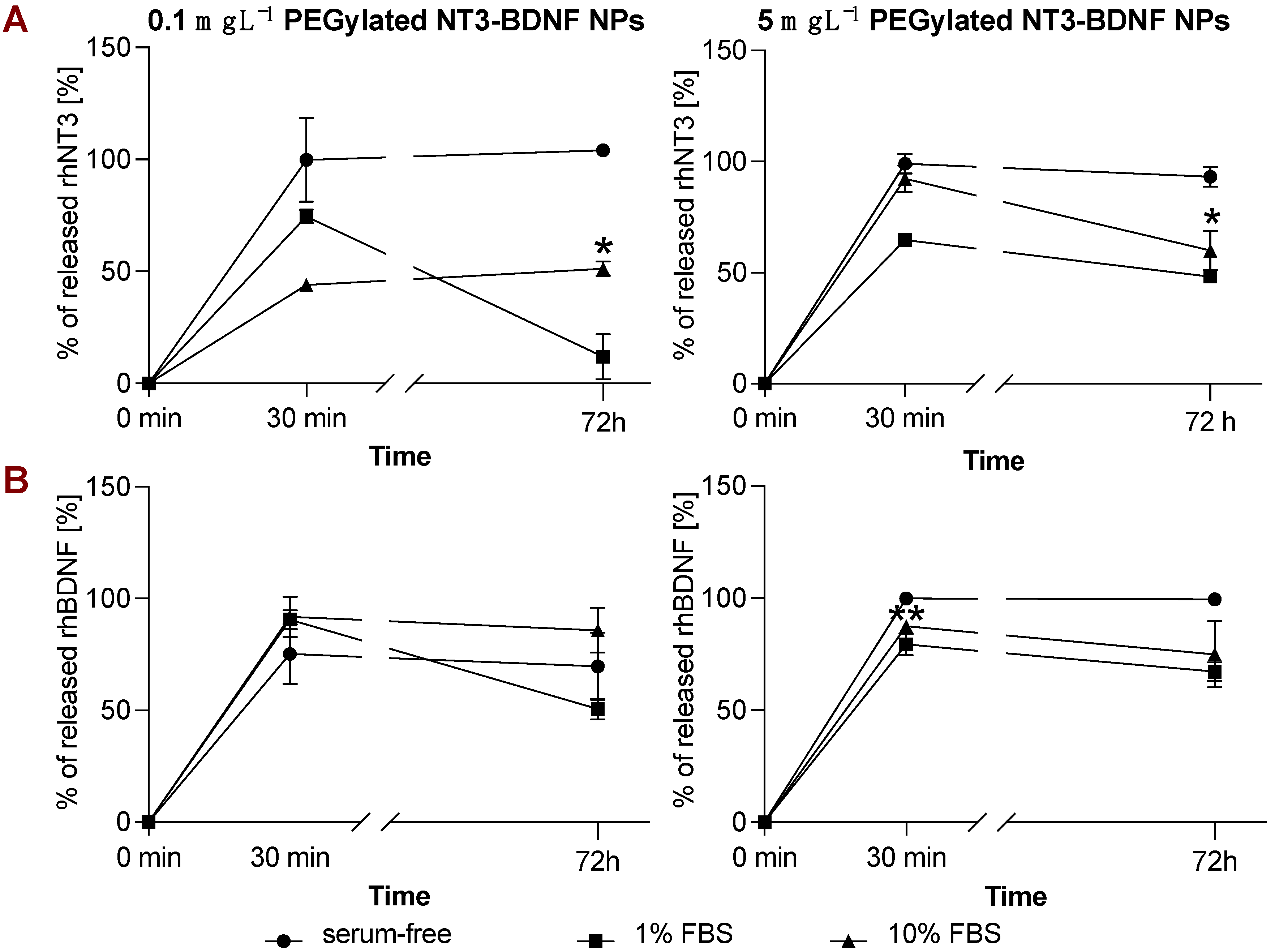
3.5. In Vitro NT3/BDNF Release Profile from PEGylated Nanoparticles in Different Media Conditions
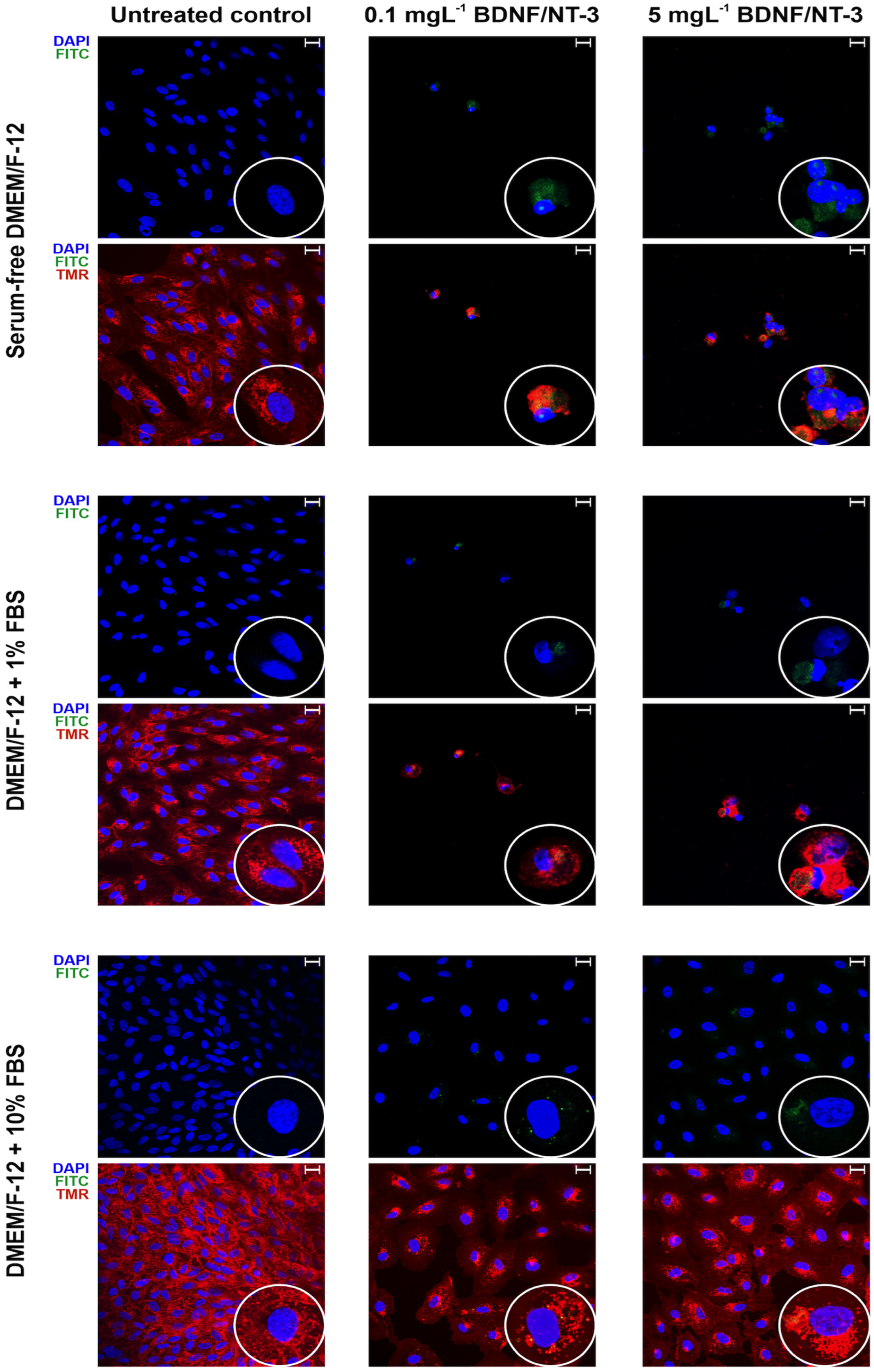
3.6. Confocal Microscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daly, C.; Ward, R.; Reynolds, A.L.; Galvin, O.; Collery, R.F.; Kennedy, B.N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as a Treatment Option for Retinal Degeneration. In Retinal Degenerative Diseases; Ash, J.D., Anderson, R.E., LaVail, M.M., Bowes Rickman, C., Hollyfield, J.G., Grimm, C., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1074, pp. 465–471. ISBN 978-3-319-75401-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, E.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.H. Role of HGF/c-Met in Serum-Starved ARPE-19 Cells. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.C.; Gies, V.; Jezierski, A.; Yang, L. Effects of Human Serum on the Stability and Cytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, N.; Hu, M.; Ju, Y.; Li, Q.; Caruso, F.; Hao, J.; Cui, J. Engineering Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Nanoparticles for Accelerated Blood Clearance Inhibition and Targeted Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18419–18428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Voigt, M.; Simon, J.; Danner, A.-K.; Frey, H.; Mailänder, V.; Helm, M.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Functionalization of Liposomes with Hydrophilic Polymers Results in Macrophage Uptake Independent of the Protein Corona. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2989–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.M.; Åberg, C.; Polo, E.; O’Connell, A.; Cookman, J.; Fallon, J.; Krpetić, Ž.; Dawson, K.A. Mapping Protein Binding Sites on the Biomolecular Corona of Nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, H.H.; Holt-Casper, D.; Grainger, D.W.; Ghandehari, H. Nanoparticle Uptake: The Phagocyte Problem. Nano Today 2015, 10, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle Interaction with Plasma Proteins as It Relates to Particle Biodistribution, Biocompatibility and Therapeutic Efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, M.M.; Bishop, P.N. Adult Vitreous Structure and Postnatal Changes. Eye 2008, 22, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.; Liew, G.; Gopinath, B.; Wong, T.Y. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Lancet 2018, 392, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and Zeta Potential—What They Are and What They Are Not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfo, R.; Tavakoli, S.; Junnuthula, V.; Williams, D.S.; Urtti, A.; van Hest, J.C.M. Exploring the Impact of Morphology on the Properties of Biodegradable Nanoparticles and Their Diffusion in Complex Biological Medium. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Hua, S.; et al. Size-Dependent Cytotoxicity and Reactive Oxygen Species of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelia Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5333–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazos, D.; Franzka, S.; Ulbricht, M. Size-Selective Protein Adsorption to Polystyrene Surfaces by Self-Assembled Grafted Poly(Ethylene Glycols) with Varied Chain Lengths. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8774–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowska, M.; Adamczyk, Z.; Oćwieja, M.; Nattich-Rak, M. Monolayers of Silver Nanoparticles on Positively Charged Polymer Microspheres. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 499, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbkowska, M.; Adamczyk, Z.; Cieśla, M.; Adamczak, M.; Bober, J. Lysozyme Monolayers at Polymer Microparticles: Electrokinetic Characteristics and Modeling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 17846–17855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Nattich, M.; Wasilewska, M.; Zaucha, M. Colloid Particle and Protein Deposition—Electrokinetic Studies. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 168, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelmagd, S.A.; Sun, B.; Chang, A.C.; Ku, Y.J.; Yeo, Y. Release Kinetics Study of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs from Nanoparticles: Are We Doing It Right? Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Cedervall, T.; Berggård, T.; Flanagan, M.B.; Lynch, I.; Elia, G.; Dawson, K. The Evolution of the Protein Corona around Nanoparticles: A Test Study. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7503–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, E.Á.; Turiák, L.; Visnovitz, T.; Cserép, C.; Mázló, A.; Sódar, B.W.; Försönits, A.I.; Petővári, G.; Sebestyén, A.; Komlósi, Z.; et al. Formation of a Protein Corona on the Surface of Extracellular Vesicles in Blood Plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Walczyk, D.; Campbell, A.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Dawson, K.A. Physical−Chemical Aspects of Protein Corona: Relevance to in Vitro and in Vivo Biological Impacts of Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Kuhn, G.; Fichter, M.; Gehring, S.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V. Unraveling the In Vivo Protein Corona. Cells 2021, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V. Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorents, A.; Maloverjan, M.; Padari, K.; Pooga, M. Internalisation and Biological Activity of Nucleic Acids Delivering Cell-Penetrating Peptide Nanoparticles Is Controlled by the Biomolecular Corona. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latreille, P.-L.; Le Goas, M.; Salimi, S.; Robert, J.; De Crescenzo, G.; Boffito, D.C.; Martinez, V.A.; Hildgen, P.; Banquy, X. Scratching the Surface of the Protein Corona: Challenging Measurements and Controversies. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1689–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meewan, J.; Somani, S.; Laskar, P.; Irving, C.; Mullin, M.; Woods, S.; Roberts, C.W.; Alzahrani, A.R.; Ferro, V.A.; McGill, S.; et al. Limited Impact of the Protein Corona on the Cellular Uptake of PEGylated Zein Micelles by Melanoma Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Negro, M.; González-Rubio, G.; Aicart, E.; Landfester, K.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Junquera, E. Insights into Colloidal Nanoparticle-Protein Corona Interactions for Nanomedicine Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 289, 102366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Burnum, K.E.; Luna, M.L.; Petritis, B.O.; Kim, J.-S.; Qian, W.-J.; Moore, R.J.; Heredia-Langner, A.; Webb-Robertson, B.-J.M.; Thrall, B.D.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Adsorbed Plasma Proteins Classifies Nanoparticles with Different Surface Properties and Size. Proteomics 2011, 11, 4569–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Kohno, H.; Ishihara, T.; Higaki, M.; Saito, S.; Matsushima, M.; Mizushima, Y.; Kitahara, K. Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Uveoretinitis with Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles Encapsulating Betamethasone Phosphate. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voet, A.R.; Tame, J.R. Protein-Templated Synthesis of Metal-Based Nanomaterials. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, S.; Spitler, R.; Erfanzadeh, M.; Alkilany, A.M.; Mahmoudi, M. Protein Corona: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 75, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segets, D.; Marczak, R.; Schäfer, S.; Paula, C.; Gnichwitz, J.-F.; Hirsch, A.; Peukert, W. Experimental and Theoretical Studies of the Colloidal Stability of Nanoparticles−A General Interpretation Based on Stability Maps. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4658–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvera Batista, C.A.; Larson, R.G.; Kotov, N.A. Nonadditivity of Nanoparticle Interactions. Science 2015, 350, 1242477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, E.; Chapman, R.G.; Holmlin, R.E.; Takayama, S.; Whitesides, G.M. A Survey of Structure−Property Relationships of Surfaces That Resist the Adsorption of Protein. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5605–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, S.J.; Premnath, V.; Merrill, E.W. Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Grafted to Silicon Surfaces: Grafting Density and Protein Adsorption. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 5059–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Fay, J.M.; Poon, C.; Vinod, N.; Zhao, Y.; Bullock, K.; Qin, S.; Manickam, D.S.; Yi, X.; Banks, W.A.; et al. Nanoformulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with Target Receptor-Triggered-Release in the Central Nervous System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratek-Skicki, A.; Żeliszewska, P.; Adamczyk, Z.; Cieśla, M. Human Fibrinogen Monolayers on Latex Particles: Role of Ionic Strength. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3700–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbkowska, M.; Adamczyk, Z. Human Serum Albumin Monolayers on Mica: Electrokinetic Characteristics. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15663–15673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbkowska, M.; Adamczak, M.; Barbasz, J.; Cieśla, M.; Machaliński, B. Adsorption/Desorption Transition of Recombinant Human Neurotrophin 4: Physicochemical Characterization. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9548–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbkowska, M.; Łuczkowska, K.; Rogińska, D.; Sobuś, A.; Wasilewska, M.; Ulańczyk, Z.; Machaliński, B. Novel Design of (PEG-Ylated)PAMAM-Based Nanoparticles for Sustained Delivery of BDNF to Neurotoxin-Injured Differentiated Neuroblastoma Cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.; Puig, J.; Martín, A.; Galisteo, F.; Gálvez, M.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. On the Adsorption of IgG onto Polystyrene Particles: Electrophoretic Mobility and Critical Coagulation Concentration. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1992, 270, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.L.; Reuter, K.G.; Kai, M.P.; Herlihy, K.P.; Jones, S.W.; Luft, J.C.; Napier, M.; Bear, J.E.; DeSimone, J.M. PEGylated PRINT Nanoparticles: The Impact of PEG Density on Protein Binding, Macrophage Association, Biodistribution, and Pharmacokinetics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5304–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Jones, S.W.; Parker, C.L.; Zamboni, W.C.; Bear, J.E.; Lai, S.K. Evading Immune Cell Uptake and Clearance Requires PEG Grafting at Densities Substantially Exceeding the Minimum for Brush Conformation. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Chow, S.F. In Vitro Release Study of the Polymeric Drug Nanoparticles: Development and Validation of a Novel Method. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Kuharev, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Fetz, V.; Hecht, R.; Schlenk, F.; Fischer, D.; Kiouptsi, K.; Reinhardt, C.; et al. Rapid Formation of Plasma Protein Corona Critically Affects Nanoparticle Pathophysiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Lee, B.-J. Protein Corona: A New Approach for Nanomedicine Design. IJN 2017, 12, 3137–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchetti, S.; Digiacomo, L.; Pozzi, D.; Peruzzi, G.; Micarelli, E.; Mahmoudi, M.; Caracciolo, G. Nanoparticles-Cell Association Predicted by Protein Corona Fingerprints. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12755–12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.-L.; Huang, Y.-J. Effects of Serum on Cytotoxicity of Nano- and Micro-Sized ZnO Particles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, M.S.; Friedman, A.E.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Oberdörster, G.; McGrath, J.L. The Influence of Protein Adsorption on Nanoparticle Association with Cultured Endothelial Cells. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Das, P.K. Probing Protein Adsorption on a Nanoparticle Surface Using Second Harmonic Light Scattering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 24325–24331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, C.; van Zadel, M.-J.; Bunn, A.; Bonn, M.; Gonella, G. In Situ Label-Free Study of Protein Adsorption on Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 9019–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vascon, F.; Gasparotto, M.; Giacomello, M.; Cendron, L.; Bergantino, E.; Filippini, F.; Righetto, I. Protein Electrostatics: From Computational and Structural Analysis to Discovery of Functional Fingerprints and Biotechnological Design. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1774–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.-X.; Pang, X. Electrostatic Interactions in Protein Structure, Folding, Binding, and Condensation. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1691–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.G.; Lannigan, K.; Shelton, W.A.; Meissner, J.; Bharti, B. Adsorption of Myoglobin and Corona Formation on Silica Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14157–14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdock, R.C.; Braydich-Stolle, L.; Schrand, A.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Hussain, S.M. Characterization of Nanomaterial Dispersion in Solution Prior to In Vitro Exposure Using Dynamic Light Scattering Technique. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesniak, A.; Salvati, A.; Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Radomski, M.W.; Dawson, K.A.; Åberg, C. Nanoparticle Adhesion to the Cell Membrane and Its Effect on Nanoparticle Uptake Efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Åberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular Coronas Provide the Biological Identity of Nanosized Materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Sakhtianchi, R.; Müller, B.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D.; Mahmoudi, M. Protein Corona Change the Drug Release Profile of Nanocarriers: The “Overlooked” Factor at the Nanobio Interface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytti, M.; Piippo, N.; Korhonen, E.; Honkakoski, P.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Fisetin and Luteolin Protect Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells from Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death and Regulate Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 17645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; Yip, X.; Glynn, F.; Shepherd, R.K.; Caruso, F. Nanoporous Peptide Particles for Encapsulating and Releasing Neurotrophic Factors in an Animal Model of Neurodegeneration. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3362–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chau, Y. Polymeric Nanoparticles Decorated with BDNF-Derived Peptide for Neuron-Targeted Delivery of PTEN Inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 124, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
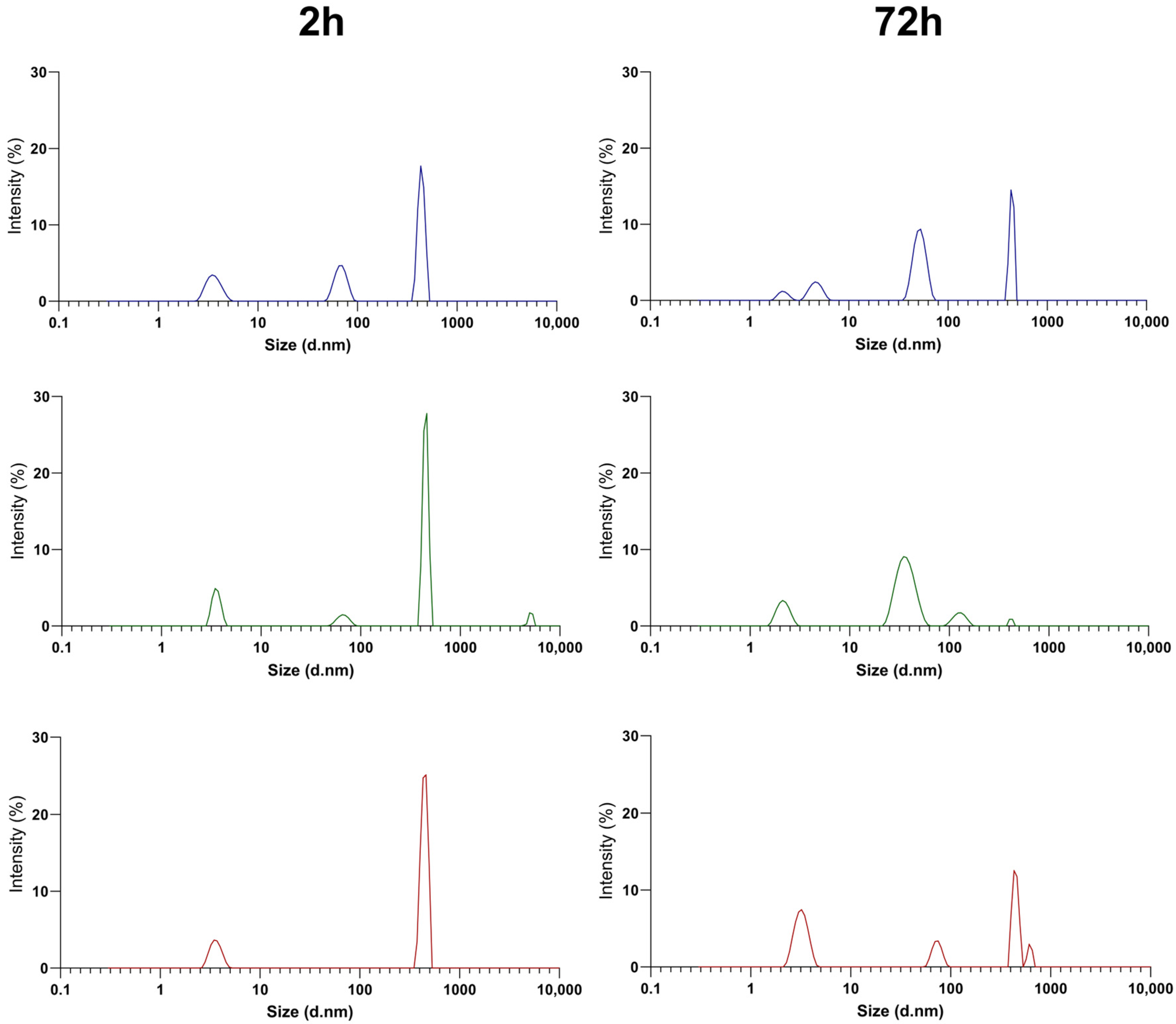
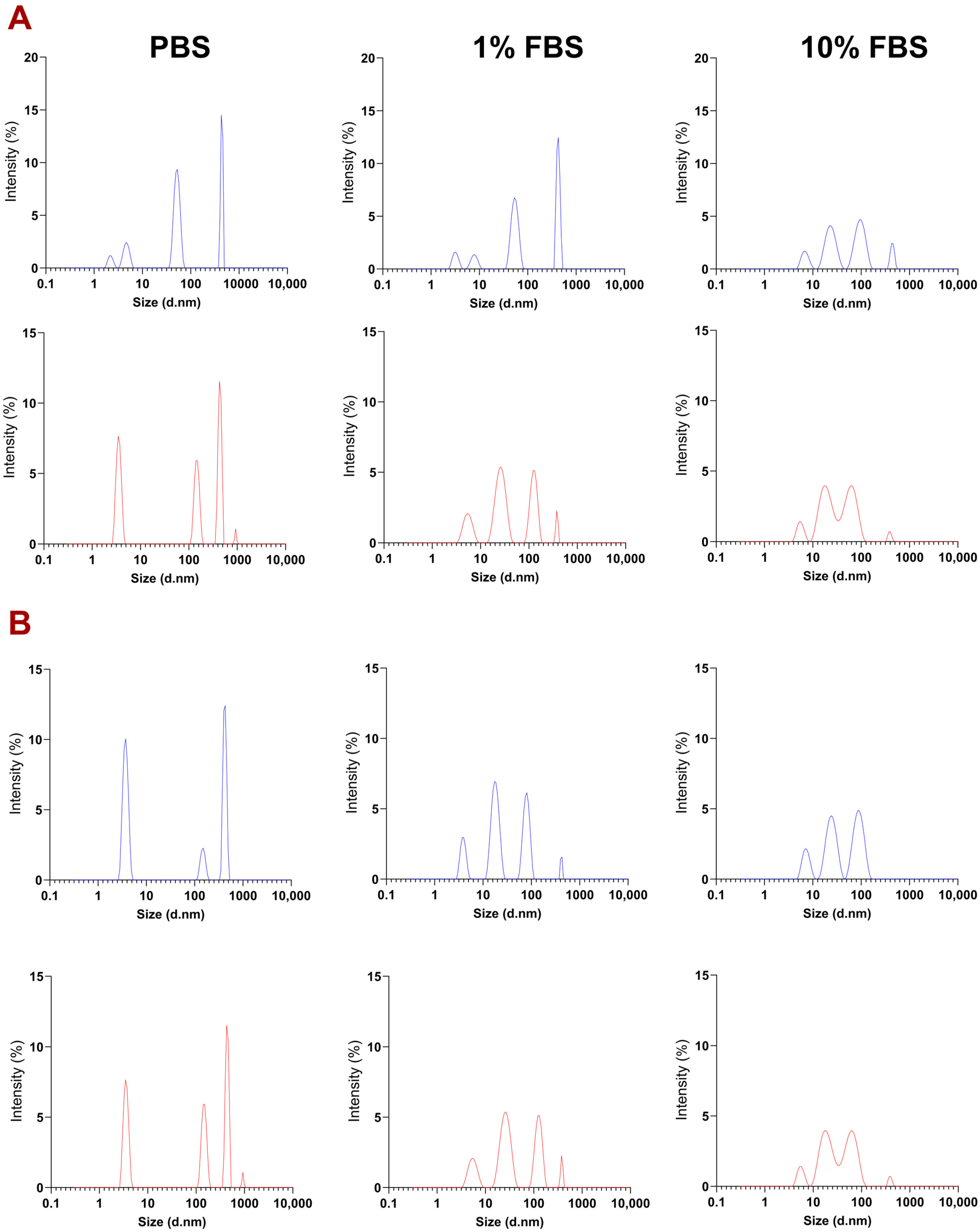
| ζ [mV] | 2 h | 24 h | 72 h | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | 1% FBS | 10% FBS | PBS | 1% FBS | 10% FBS | PBS | 1% FBS | 10% FBS | |
| PEGylated NT3/BDNF (0.1 mg L−1) | −8.7 ± 2.6 | −11.8 ± 4.30 | −5.99 ± 1.33 | −10.8 ± 2.52 | −7.6 ± 1.3 | −9.7 ± 2.2 | −5.4 ± 1.65 | −9.6 ± 2.1 | −9.7 ± 2.2 |
| PEGylated NT3/BDNF (1 mg L−1) | −14.1 ± 1.52 | −12.1 ± 2.7 | −6.4 ± 3.7 | −11.8 ± 3.1 | −12.3 ± 3.7 | −10.1 ± 2.4 | −3.36 ± 1.40 | −7.16 ± 2.51 | −8.42 ± 2.12 |
| PEGylated NT3/BDNF (5 mg L−1) | −13.9 ± 1.8 | −9.82 ± 3.9 | −7.1 ± 3.9 | −9.8 ± 0.5 | −10.2 ± 3.9 | −11.7 ± 1.06 | 1.9 ± 3.1 | −8.96 ± 1.27 | −11.46 ± 1.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dąbkowska, M.; Kosiorowska, A.; Machaliński, B. The Impact of Serum Protein Adsorption on PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles—Distribution, Protein Release, and Cytotoxicity in a Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cell Model. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092236
Dąbkowska M, Kosiorowska A, Machaliński B. The Impact of Serum Protein Adsorption on PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles—Distribution, Protein Release, and Cytotoxicity in a Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cell Model. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(9):2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092236
Chicago/Turabian StyleDąbkowska, Maria, Alicja Kosiorowska, and Bogusław Machaliński. 2023. "The Impact of Serum Protein Adsorption on PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles—Distribution, Protein Release, and Cytotoxicity in a Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cell Model" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 9: 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092236
APA StyleDąbkowska, M., Kosiorowska, A., & Machaliński, B. (2023). The Impact of Serum Protein Adsorption on PEGylated NT3–BDNF Nanoparticles—Distribution, Protein Release, and Cytotoxicity in a Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cell Model. Pharmaceutics, 15(9), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092236