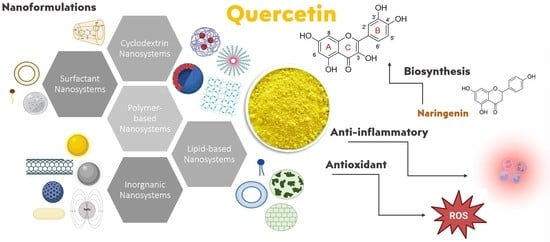
Recent Advances in Nanoformulations for Quercetin Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Origin, Physicochemical Characteristics, Biosynthesis, and Main Pharmacological Activities of QUE
3.1. Origin, Physicochemical Characteristics, Pharmacokinetics, and Metabolism
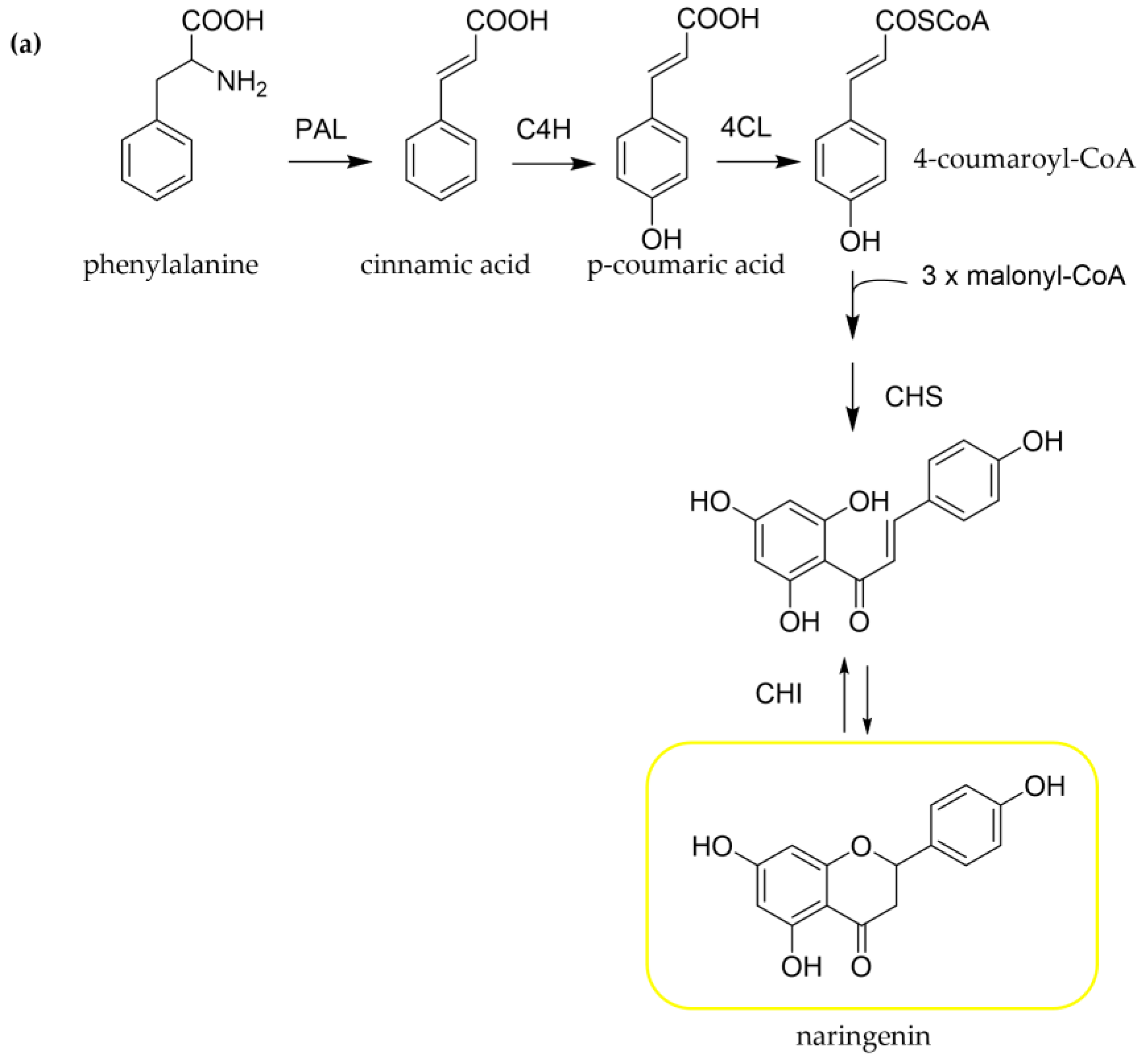
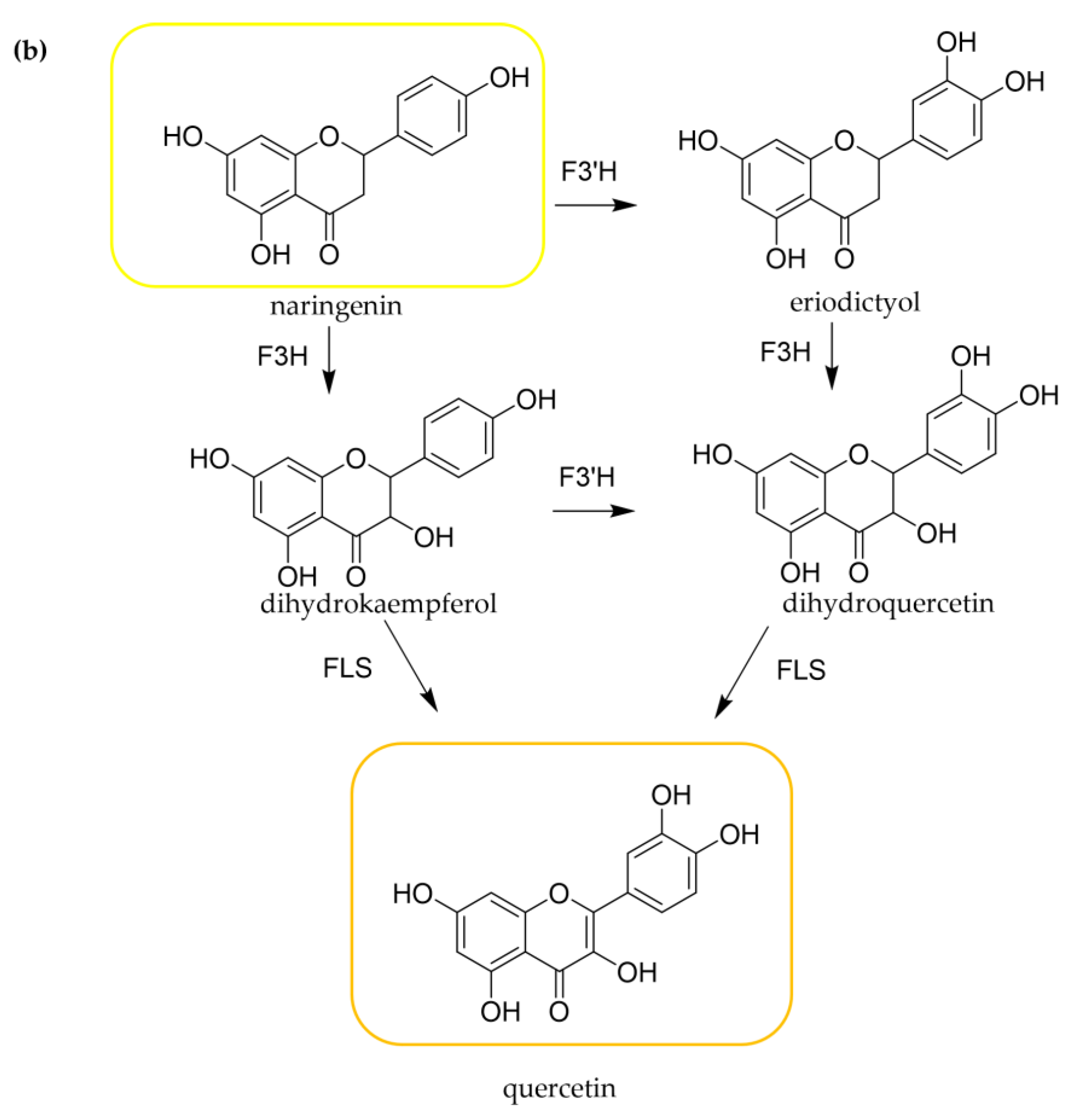
3.2. Biosynthesis
3.3. Main Pharmacological Properties: Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
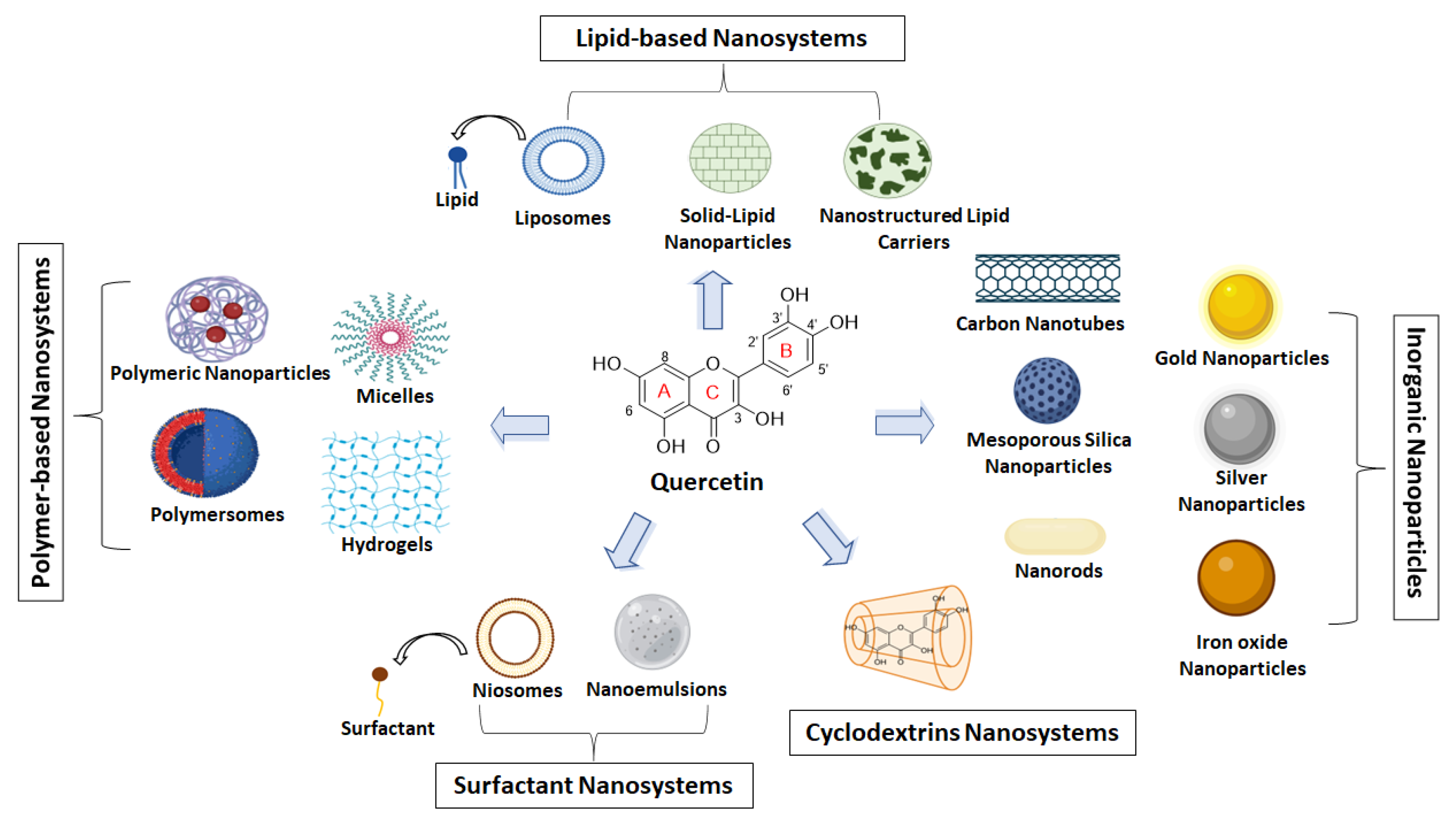
4. QUE Nanosystems
4.1. Polymer-Based Nanosystems
4.1.1. Polymeric Micelles
4.1.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles
4.1.3. Hydrogels
4.1.4. Polymersomes
4.2. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles
4.2.1. Liposomes and Liposome-Based Nanoparticles
4.2.2. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)
4.3. Surfactant-Based Nanoparticles
4.3.1. Niosomes
4.3.2. Nanoemulsions
4.4. Cyclodextrin-Based Nanoparticles
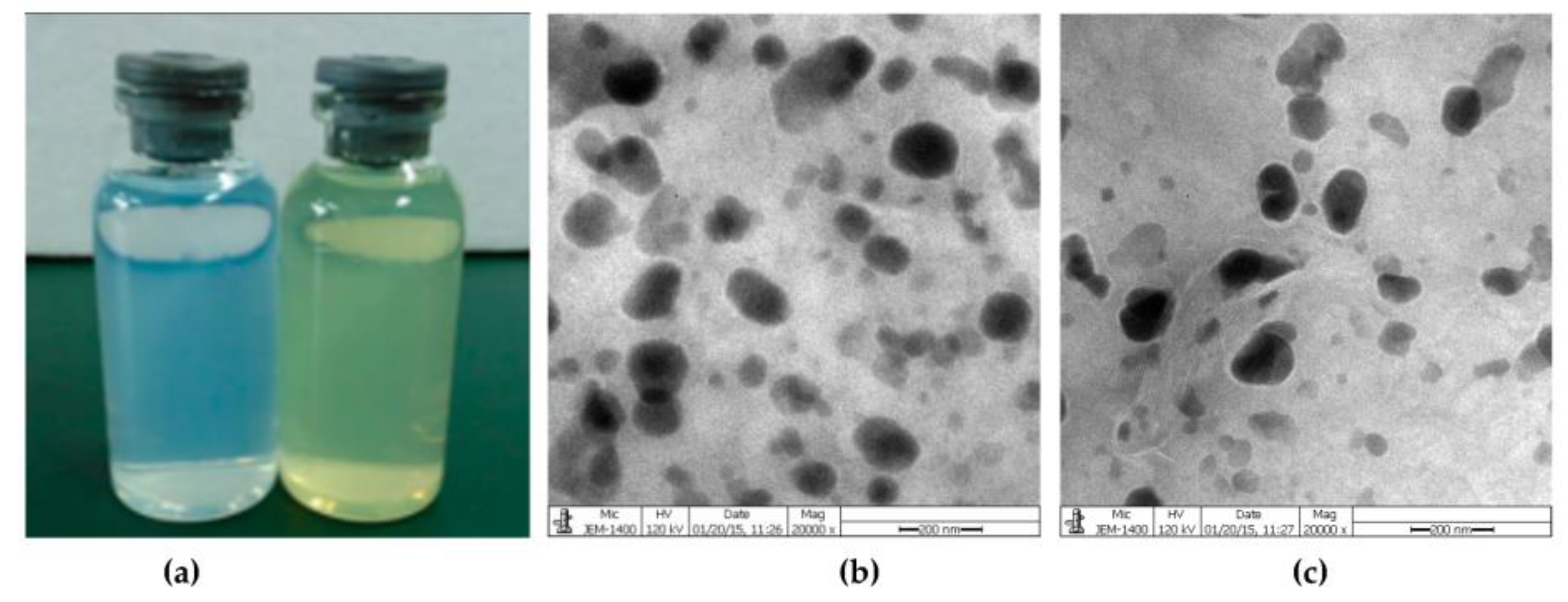
4.5. Inorganic Nanoparticles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azeem, M.; Hanif, M.; Mahmood, K.; Ameer, N.; Chughtai, F.R.S.; Abid, U. An insight into anticancer, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin: A review. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, R.; Huang, H. Anti-Allergic Effects of Quercetin and Quercetin Liposomes in RBL-2H3 Cells. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2022, 23, 692–701. [Google Scholar]
- Dian, L.; Yu, E.; Chen, X.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Wu, C. Enhancing oral bioavailability of quercetin using novel soluplus polymeric micelles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A.; Ronchi, M.; Petrangolini, G.; Bosisio, S.; Allegrini, P. Improved Oral Absorption of Quercetin from Quercetin Phytosome®, a New Delivery System Based on Food Grade Lecithin. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharm. 2019, 44, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantis, D.; Ramesova, S.; Chatzigiannis, C.; Degano, I.; Gerogianni, P.; Karadima, C.; Perikleous, S.; Rekkas, D.; Gerothanassis, I.; Galaris, D.; et al. Exploring the oxidation and iron binding profile of a cyclodextrin encapsulated quercetin complex unveiled a controlled complex dissociation through a chemical stimulus. BBA-Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, M.; Ghasemi-Kasman, M.; Ghasemi, S.; Akbari, A.; Moalem-Banhangi, M.; Zare, L.; Ahmadian, S.R. Fabrication and evaluation of novel quercetin-conjugated Fe3O4-β-cyclodextrin nanoparticles for potential use in epilepsy disorder. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6481–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpour, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Dehghanian, F.; Beheshti, S. Effects of quercetin-conjugated with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on learning and memory improvement through targeting microRNAs/NF-κB pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffleur, F.; Keckeis, V. Advances in drug delivery systems: Work in progress still needed? Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.H.; Park, K. Advanced drug delivery 2020 and beyond: Perspectives on the future. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 158, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Choi, D.K. Current application of phytocompound-based nanocosmeceuticals for beauty and skin therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1987–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffleur, F.; Bauer, B. Progress in nasal drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Drechsler, M.; Puglia, C.; Cortesi, R. New Strategies for the Delivery of Some Natural Anti-oxidants with Therapeutic Properties. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, G. Quercetin: A flavonol with multifaceted therapeutic applications? Fitoterapia 2015, 106, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S.R.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A. Quercetin derivatives: Drug design, development, and biological activities, a review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 229, 114068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Ikram, M.; Mulla, Z.S.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Taha, A.E.; Algammal, A.M.; Elewa, Y.H.A. The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Materska, M. Quercetin and Its Derivatives: Chemical Structure and Bioactivity—A Review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2008, 58, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, M.; Danielewska-Nikiel, B.; Borzelleca, J.F.; Flamm, G.W.; Williams, G.M.; Lines, T.C. A critical review of the data related to the safety of quercetin and lack of evidence of in vivo toxicity, including lack of genotoxic/carcinogenic properties. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2179–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganthy, N.; Devi, K.P.; Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Bioactive Effects of Quercetin in the Central Nervous System: Focusing on the Mechanisms of Actions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 892–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.J.; Wang, L.; DiCenzo, R.; Morris, M.E. Quercetin pharmacokinetics in humans. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2008, 29, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Fang, Z.; Dou, J.; Yu, A.; Zhai, G. Bioavailability of quercetin: Problems and promises. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2572–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ma, X.; Qi, X.; Xiao, J.; Xue, W.; Luo, Y.; Yue, T. Advance on the absorption, metabolism, and efficacy exertion of quercetin and its important derivatives. Food Front. 2020, 1, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yin, O.Q.; Zuo, Z.; Chow, M.S. Pharmacokinetics and modeling of quercetin and metabolites. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Woude, H.; Bersma, M.G.; Vervoort, J.; Rietjens, I.M. Identification of 14 quercetin phase II mono- and mixed conjugates and their formation by rat and human phase II in vitro model systems. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.L.; Tsai, Y.J.; Huang, C.M.; Tsai, T.H. Lymphatic absorption of quercetin and rutin in rat and their pharmacokinetics in systemic plasma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neamtu, A.A.; Maghiar, T.A.; Alaya, A.; Olah, N.K.; Turcus, V.; Pelea, D.; Totolici, B.D.; Neamtu, C.; Maghiar, A.M.; Mathe, E. A Comprehensive View on the Quercetin Impact on Colorectal Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yin, H. The Flavonoid Biosynthesis Network in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arif, Y.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. The role of quercetin in plants. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 166, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whinkel-Shirley, B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant. Physiol. 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewick, P. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. Health effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Qi, W.; Xiong, D.; Long, M. Quercetin: Its Antioxidant Mechanism, Antibacterial Properties and Potential Application in Prevention and Control of Toxipathy. Molecules 2022, 27, 6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Hu, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Cui, Y.-L. Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application. Molecules 2019, 24, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teskey, G.; Abrahem, R.; Cao, R.; Gyurjian, K.; Islamoglu, H.; Lucero, M.; Martinez, A.; Paredes, E.; Salaiz, O.; Robinson, B.; et al. Glutathione as a Marker for Human Disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 87, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Rinna, A. Glutathione: Overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Chee, K.M.; Lee, B.H. Anti- and prooxidant effects of chronic quercetin administration in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 482, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, H.M.; Boersma, M.G.; Boeren, S.; van Bladeren, P.J.; Vervoort, J.; Rietjens, I.M. Structure-activity study on the quinone/quinone methide chemistry of flavonoids. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Pu, L.; Chen, M.; Wei, J.; Xin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Shi, T.; Guo, C. Glutathione homeostasis is significantly altered by quercetin via the Keap1/Nrf2 and MAPK signaling pathways in rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2018, 62, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, K.; Chee, K.M. Long-term combined administration of quercetin and daidzein inhibits quercetin-induced suppression of glutathione antioxidant defenses. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.T.; Ding, C.; Zhou, N.; Xu, C. Quercetin protects gastric epithelial cell from oxidative damage in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 754, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-F.; Chen, G.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Shen, C.-K.; Lu, D.-Y.; Yang, L.-Y.; Chen, J.-H.; Yeh, W.-L. Regulatory Effects of Quercetin on M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization and Oxidative/Antioxidative Balance. Nutrients 2022, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.H.; Chan, S.H.; Chu, P.M.; Tsai, K.L. Quercetin is a potent anti-atherosclerotic compound by activation of SIRT1 signaling under oxLDL stimulation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odbayar, T.O.; Kimura, T.; Tsushida, T.; Ide, T. Isoenzyme-specific up-regulation of glutathione transferase and aldo-keto reductase mRNA expression by dietary quercetin in rat liver. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 325, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.P.; Mani, I.; Iversen, L.; Ziboh, V.A. Effects of naturally-occurring flavonoids and biflavonoids on epidermal cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase from guinea-pigs. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 1998, 58, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.I.; Vicente-Sánchez, C.; Jerkic, M.; Santiago, J.M.; Sánchez-González, P.D.; Pérez-Barriocanal, F.; López-Novoa, J.M. Effect of quercetin on metallothionein, nitric oxide synthases and cyclooxygenase-2 expression on experimental chronic cadmium nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 210, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Flórez, S.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, B.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Quercetin attenuates nuclear factor-kappaB activation and nitric oxide production in interleukin-1beta-activated rat hepatocytes. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.C.; Lee, W.R.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, H.C.; Ko, C.H.; Yang, L.L.; Chen, Y.C. In vitro and in vivo inhibitory activities of rutin, wogonin, and quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E(2) production. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 446, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mediavilla, V.; Crespo, I.; Collado, P.S.; Esteller, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway in Chang Liver cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 557, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjeet, K.R.; Ghosh, B. Quercetin inhibits LPS-induced nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in murine macrophages. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1999, 21, 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau, G.; Longpré, F.; Martinoli, M.G. Resveratrol and quercetin, two natural polyphenols, reduce apoptotic neuronal cell death induced by neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Chi, H.; Liu, J.; Han, H. Protective effects of quercetin and taraxasterol against H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury in vitro. Exp. Med. 2015, 10, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chroni, A.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Pispas, S. Biocompatible PEO-b-PCL Nanosized Micelles as Drug Carriers: Structure and Drug-Polymer Interactions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippa, N.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Polymer Self-Assembled Nanostructures as Innovative Drug Nanocarrier Platforms. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 2788–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.S.; Shaikh, S.J.; Ray, D.; Aswal, V.K.; Vaidya, F.; Pathak, C.; Sharma, R.K. Formulation, Solubilization, and In Vitro Characterization of Quercetin-Incorporated Mixed Micelles of PEO-PPO-PEO Block Copolymers. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Gao, C.; Yin, C.; Fan, J.; Wu, X.; Di, G.; Wang, J.; Guo, C. Development of quercetin-loaded PVCL-PVA-PEG micelles and application in inhibiting tumor angiogenesis through the PI3K/Akt/VEGF pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 437, 115889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranthaman, S.; Uthaiah, C.A.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Hani, U.; Ghazwani, M.; Alamri, A.H.; Fatease, A.A.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Gowda, D.V. Anti-Proliferative Potential of Quercetin Loaded Polymeric Mixed Micelles on Rat C6 and Human U87MG Glioma Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabahy, M.; Wooley, K.L. Design of polymeric nanoparticles for biomedical delivery applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2545–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, Q.; Peng, F.; Liu, L.; Gong, C. Strategies of polymeric nanoparticles for enhanced internalization in cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoqrot, S.; Abujamous, L. pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticles of quercetin as a potential colon cancer-targeted nanomedicine. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagad, M.; Khan, Z.A. Poly(n-butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles for oral delivery of quercetin: Preparation, characterization, and pharmacokinetics and biodistribution studies in Wistar rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3921–3935. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.T.; Wu, C.T.; Chang, Y.; Ho, F.M.; Chiang, C.K.; Liu, S.H. Therapeutic effect of quercetin polymeric nanoparticles on ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 608, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Xue, G.; Yu, S.; Yuan, C.; Huang, M.; Jiang, L. Improved therapeutic efficacy of quercetin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles on triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting uPA. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 34517–34526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doosti, M.; Seyed Dorraji, M.S.; Mousavi, S.N.; Rasoulifard, M.H.; Hosseini, S.H. Enhancing quercetin bioavailability by super paramagnetic starch-based hydrogel grafted with fumaric acid: An in vitro and in vivo study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippa, N.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Recent advances in micellar-like polyelectrolyte/protein complexes. In Design and Development of New Nanocarriers; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 57–88. ISBN 978-0-12-813627-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, S.; Teo, Y.Y.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K. Synthesis and characterization of karaya gum-g- poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels and in vitro release of hydrophobic quercetin. Polymer 2018, 147, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.; Barbosa, A.I.; Moniz, T.; Costa Lima, S.; Costa, P.; Celia, C.; Reis, S. Design and Characterization of Sodium Alginate and Poly(vinyl) Alcohol Hydrogels for Enhanced Skin Delivery of Quercetin. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, S.W.; Fu, S.C.; Cheuk, Y.C.; Chu, I.M.; Chan, K.M.; Qin, L.; Yung, S.H.; Kevin Ho, K.W. Intra-Articular Delivery of Quercetin Using Thermosensitive Hydrogel Attenuate Cartilage Degradation in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Cartilage 2020, 11, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safar Sajadi, S.M.; Khoee, S. The simultaneous role of porphyrins’ H- and J- aggregates and host-guest chemistry on the fabrication of reversible Dextran-PMMA polymersome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.P.; Dias, R.C.S.; Costa, M.R.P.F.N. Design of RAFT synthesized amphiphilic and stimuli-responsive block copolymers for encapsulation of polyphenols in polymersomes. CHEMPOR 2018, P-IM02, 579–580. [Google Scholar]
- Chavda, V.P.; Vihol, D.; Mehta, B.; Shah, D.; Patel, M.; Vora, L.K.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Phytochemical-loaded liposomes for anticancer therapy: An updated review. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xue, J.X.; Li, X.; Ao, R.; Lu, Y. Quercetin liposomes protect against radiation-induced pulmonary injury in a murine model. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, K.T.; Youn, Y.S.; Lee, E.S. pH-Sensitive Twin Liposomes Containing Quercetin and Laccase for Tumor Therapy. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 3688–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Xu, Y.; Wei, B. Quercetin liposomes ameliorate streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in diabetic rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yang, D.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Nie, H.; Liu, H. Quercetin loaded liposomes modified with galactosylated chitosan prevent LPS/D-GalN induced acute liver injury. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 131, 112527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, D.; Wu, W.; Chen, X.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Shao, Z.; Pu, F. Quercetin encapsulated in folic acid-modified liposomes is therapeutic against osteosarcoma by non-covalent binding to the JH2 domain of JAK2 via the JAK2-STAT3-PDL1. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caddeo, C.; Gabriele, M.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Valenti, D.; Fadda, A.M.; Pucci, L.; Manconi, M. Antioxidant activity of quercetin in Eudragit-coated liposomes for intestinal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonechi, C.; Donati, A.; Tamasi, G.; Leone, G.; Consumi, M.; Rossi, C.; Lamponi, S.; Magnani, A. Protective effect of quercetin and rutin encapsulated liposomes on induced oxidative stress. Biophys. Chem. 2018, 233, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mureşan, M.; Olteanu, D.; Filip, G.A.; Clichici, S.; Baldea, I.; Jurca, T.; Pallag, A.; Marian, E.; Frum, A.; Gligor, F.G.; et al. Comparative Study of the Pharmacological Properties and Biological Effects of Polygonum aviculare L. herba Extract-Entrapped Liposomes versus Quercetin-Entrapped Liposomes on Doxorubicin-Induced Toxicity on HUVECs. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.A.; Tarahovsky, Y.S.; Yagolnik, E.A.; Kuznetsova, S.M.; Muzafarov, E.N. Integration of Quercetin-Iron Complexes into Phosphatidylcholine or Phosphatidylethanolamine Liposomes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munot, N.; Kandekar, U.; Giram, P.S.; Khot, K.; Patil, A.; Cavalu, S. A Comparative Study of Quercetin-Loaded Nanocochleates and Liposomes: Formulation, Characterization, Assessment of Degradation and In Vitro Anticancer Potential. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Aguirre, M.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Cruz-Alcantar, P.; Aguilar-Elguézabal, A.; Saavedra-Leos, M.Z. Comparison of Polysaccharides as Coatings for Quercetin-Loaded Liposomes (QLL) and Their Effect as Antioxidants on Radical Scavenging Activity. Polymers 2020, 12, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Silva, M.; Faria-Silva, C.; Carvalheiro, M.C.; Simões, S.; Marinho, H.S.; Marcelino, P.; Campos, M.C.; Metselaar, J.M.; Fernandes, E.; Baptista, P.V.; et al. Quercetin Liposomal Nanoformulation for Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatahet, T.; Morille, M.; Hommoss, A.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Müller, R.H.; Bégu, S. Liposomes, lipid nanocapsules and smartCrystals®: A comparative study for an effective quercetin delivery to the skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 542, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castangia, I.; Manconi, M.; Allaw, M.; Perra, M.; Orrù, G.; Fais, S.; Scano, A.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Ghavam, M.; Rezvani, M.; et al. Mouthwash Formulation Co-Delivering Quercetin and Mint Oil in Liposomes Improved with Glycol and Ethanol and Tailored for Protecting and Tackling Oral Cavity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.S.; Yun, M.E.; Park, S.N. Surfactant-stable and pH-sensitive liposomes coated with N-succinyl-chitosan and chitooligosaccharide for delivery of quercetin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.T.J.; Anantha, M.; Leung, A.W.Y.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Militao, G.G.C.; Wehbe, M.; Sutherland, B.; Cullis, P.R.; Bally, M.B. Characterization of a liposomal copper(II)-quercetin formulation suitable for parenteral use. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, F.; Benedusi, M.; Sguizzato, M.; Cortesi, R.; Baldisserotto, A.; Buzzi, R.; Valacchi, G.; Esposito, E. Ethosomes and Transethosomes as Cutaneous Delivery Systems for Quercetin: A Preliminary Study on Melanoma Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mageed, H.M.; Abd El Aziz, A.E.; Mohamed, S.A.; AbuelEzz, N.Z. The tiny big world of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: An updated review. J. Microencapsul. 2022, 39, 72–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, J.; Saeedi, M.; Ahmadi, F.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Babaei, A.; Yaddollahi, S.; Rostamkalaei, S.S.; Asare-Addo, K.; Nokhodchi, A. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: A review of the methods of manufacture and routes of administration. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2022, 27, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, E.; Abouelfetouh, M.M.; Pan, Y.; Chen, D.; Xie, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles for enhanced oral absorption: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2020, 196, 111305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, L.; Consumi, M.; Leone, G.; Tamasi, G.; Magnani, A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Produced via a Coacervation Method as Promising Carriers for Controlled Release of Quercetin. Molecules 2021, 26, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, S.; Makled, S.; Awaad, A.; Boraie, N. Quercetin Loaded Cationic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in a Mucoadhesive In Situ Gel-A Novel Intravesical Therapy Tackling Bladder Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerapol, Y.; Manmuan, S.; Chaothanaphat, N.; Limmatvapirat, S.; Sirirak, J.; Tamdee, P.; Tubtimsri, S. New Approach for Preparing Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Volatile Oil-Loaded Quercetin Using the Phase-Inversion Temperature Method. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, R.G.R.; Granja, A.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C.; Pinheiro, M.; Neves, A.R.; Reis, S. Quercetin lipid nanoparticles functionalized with transferrin for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 148, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, R.G.R.; Granja, A.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C.; Pinheiro, M.; Neves, A.R.; Reis, S. RVG29-Functionalized Lipid Nanoparticles for Quercetin Brain Delivery and Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Baskaran, R.; Jang, Y.S.; Oh, S.H.; Yoo, B.K. Quercetin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Dispersion with Improved Physicochemical Properties and Cellular Uptake. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, G.; Li, L.; Lou, H. Enhancement of gastrointestinal absorption of quercetin by solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2009, 133, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganthala, P.D.; Alavala, S.; Chella, N.; Andugulapati, S.B.; Bathini, N.B.; Sistla, R. Co-encapsulated nanoparticles of Erlotinib and Quercetin for targeting lung cancer through nuclear EGFR and PI3K/AKT inhibition. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 211, 112305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, D.P.C.; Santos, R.; Reed, P.; Fonseca, L.P.; Oliva, A. Design of Quercetin-Loaded Natural Oil-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for the Treatment of Bacterial Skin Infections. Molecules 2022, 27, 8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, V.S.; Gawali, B.; Saha, P.; Naidu, V.G.M.; Murty, U.S.; Banerjee, S. Quercetin and piperine enriched nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) to improve apoptosis in oral squamous cellular carcinoma (FaDu cells) with improved biodistribution profile. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 909, 174400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Nie, S.; Pan, X.; Zhang, R.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S. Quercetin-nanostructured lipid carriers: Characteristics and anti-breast cancer activities in vitro. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, E.; Eftekhari, A.; Kavetskyy, T.; Khosroushahi, A.Y.; Turksoy, V.A.; Khalilov, R. Effects of quercetin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers on the paraquat-induced toxicity in human lymphocytes. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 167, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Xiong, T.; Li, J.; Du, M.; Gong, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Characterization and biodistribution in vivo of quercetin-loaded cationic nanostructured lipid carriers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 115, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, V.S.; Murty, U.S.; Banerjee, S. Nanostructured lipid carriers as a strategy for encapsulation of active plant constituents: Formulation and in vitro physicochemical characterizations. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 235, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Meng, Q. Combined and targeted drugs delivery system for colorectal cancer treatment: Conatumumab decorated, reactive oxygen species sensitive irinotecan prodrug and quercetin co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Fernandez, S.; Matos, J.K.R.; Scheunemann, G.S.; Salata, G.C.; Chorilli, M.; Watanabe, I.S.; de Araujo, G.L.B.; Santos, M.F.; Ishida, K.; Lopes, L.B. Nanostructured lipid carriers containing chitosan or sodium alginate for co-encapsulation of antioxidants and an antimicrobial agent for potential application in wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izza, N.; Watanabe, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Wibisono, Y.; Umakoshi, H. Characterization of entrapment behavior of polyphenols in nanostructured lipid carriers and its effect on their antioxidative activity. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 134, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Iqubal, M.K.; Imtiyaz, K.; Saleem, S.; Mittal, S.; Rizvi, M.M.A.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Topical nanostructured lipid carrier gel of quercetin and resveratrol: Formulation, optimization, in vitro and ex vivo study for the treatment of skin cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, K.M.; Mandal, A.S.; Biswas, N.; Guha, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Behera, M.; Kuotsu, K. Niosome: A future of targeted drug delivery systems. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 374–380. [Google Scholar]
- Gharbavi, M.; Amani, J.; Kheiri-Manjili, H.; Danafar, H.; Sharafi, A. Niosome: A Promising Nanocarrier for Natural Drug Delivery through Blood-Brain Barrier. Adv. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 2018, 6847971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ag Seleci, D.; Seleci, M.; Walter, J.-G.; Stahl, F.; Scheper, T. Niosomes as Nanoparticular Drug Carriers: Fundamentals and Recent Applications. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 7372306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoee, S.; Yaghoobian, M. Niosomes: A novel approach in modern drug delivery systems. In Nanostructures for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 207–237. [Google Scholar]
- Kauslya, A.; Borawake, P.D.; Shinde, J.V.; Chavan, R.S. Niosomes: A Novel Carrier Drug Delivery System. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2021, 11, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Ghadi, Z.; Ebrahimnejad, P.; Talebpour Amiri, F.; Nokhodchi, A. Improved oral delivery of quercetin with hyaluronic acid containing niosomes as a promising formulation. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavano, L.; Mauro, L.; Naimo, G.D.; Bruno, L.; Picci, N.; Andò, S.; Muzzalupo, R. Further Evolution of Multifunctional Niosomes Based on Pluronic Surfactant: Dual Active Targeting and Drug Combination Properties. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8926–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyad, N.; Maji, R.; Omolo, C.A.; Ganai, A.M.; Ibrahim, U.H.; Pathan, T.K.; Devnarain, N.; Karpoormath, R.; Dhawan, S.; Obakachi, V.A.; et al. Development of niosomes for encapsulating captopril-quercetin prodrug to combat hypertension. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmowafy, E.; El-Derany, M.O.; Biondo, F.; Tiboni, M.; Casettari, L.; Soliman, M.E. Quercetin Loaded Monolaurate Sugar Esters-Based Niosomes: Sustained Release and Mutual Antioxidant-Hepatoprotective Interplay. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ye, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Long, X. Niosomal Nanocarriers for Enhanced Skin Delivery of Quercetin with Functions of Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant. Molecules 2019, 24, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javani, R.; Hashemi, F.S.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Quercetin-loaded niosomal nanoparticles prepared by the thin-layer hydration method: Formulation development, colloidal stability, and structural properties. LWT 2021, 141, 110865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.; Dudhe, R.; Sharma, P.K. Nanoemulsion: An advanced mode of drug delivery system. 3 Biotech 2014, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, H.H.; Sainsbury, F. Nanoemulsions in drug delivery: Formulation to medical application. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2507–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.J.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhao, C.-X. Nanoemulsions for drug delivery. Particuology 2021, 64, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaolu, T.J. Nanoemulsions for health, food, and cosmetics: A review. Env. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3381–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutradhar, K.B.; Amin, M.L. Nanoemulsions: Increasing possibilities in drug delivery. Eur. J. Nanomed. 2013, 5, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Wu, M.T.; Wang, C.C.; Wu, Y.T. Nanoemulsion as a strategy for improving the oral bioavailability and anti-inflammatory activity of andrographolide. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.L.; Stanslas, J.; Basri, M.; Abedi Karjiban, R.A.; Kirby, B.P.; Sani, D.; Basri, H.B. Nanoemulsion-based Parenteral Drug Delivery System of Carbamazepine: Preparation, Characterization, Stability Evaluation and Blood-Brain Pharmacokinetics. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörmann, K.; Zimmer, A. Drug delivery and drug targeting with parenteral lipid nanoemulsions—A review. J. Control. Release 2016, 223, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi Oskooei, F.; Mehrzad, J.; Asoodeh, A.; Motavalizadehkakhky, A. Olive oil-based quercetin nanoemulsion (QuNE)’s interactions with human serum proteins (HSA and HTF) and its anticancer activity. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Pourmadadi, M.; Yazdian, F.; Rashedi, H.; Navaei-Nigjeh, M.; Eufrasio-da-Silva, T. Ameliorating quercetin constraints in cancer therapy with pH-responsive agarose-polyvinylpyrrolidone -hydroxyapatite nanocomposite encapsulated in double nanoemulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Mittal, V.; Wahab, S.; Alsayari, A.; Bin Muhsinah, A.; Almaghaslah, D. Intravenous Nanocarrier for Improved Efficacy of Quercetin and Curcumin against Breast Cancer Cells: Development and Comparison of Single and Dual Drug-Loaded Formulations Using Hemolysis, Cytotoxicity and Cellular Uptake Studies. Membranes 2022, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbain, N.H.; Basri, M.; Salim, N.; Wui, W.T.; Abdul Rahman, M.B. Development and Characterization of Aerosol Nanoemulsion System Encapsulating Low Water Soluble Quercetin for Lung Cancer Treatment. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, S137–S142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbain, N.H.; Salim, N.; Masoumi, H.R.F.; Wong, T.W.; Basri, M.; Abdul Rahman, M.B. In vitro evaluation of the inhalable quercetin loaded nanoemulsion for pulmonary delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, M.; Kazemi, S.; Shirafkan, F.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Barary, M.; Sio, T.T.; Hosseini, S.M.; Moghadamnia, A.A. The protective effects of quercetin nano-emulsion on intestinal mucositis induced by 5-fluorouracil in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 585, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceramella, J.; Groo, A.-C.; Iacopetta, D.; Séguy, L.; Mariconda, A.; Puoci, F.; Saturnino, C.; Leroy, F.; Since, M.; Longo, P.; et al. A winning strategy to improve the anticancer properties of Cisplatin and quercetin based on the nanoemulsions formulation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Velidakis, N.; Khattab, E.; Valsami, G.; Korakianitis, I.; Kadoglou, N.P. Potential Pharmaceutical Applications of Quercetin in Cardiovascular Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadev, M.; Nandini, H.S.; Ramu, R.; Gowda, D.V.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Al-Ghorbani, M.; Mabkhot, Y.N. Fabrication and Evaluation of Quercetin Nanoemulsion: A Delivery System with Improved Bioavailability and Therapeutic Efficacy in Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.Y.; Lee, M.S.; Chang, E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kang, B.; Ko, H.; Kim, I.H.; Zhong, Q.; Jo, Y.H.; Kim, C.T.; et al. Formulation and Characterization of Quercetin-loaded Oil in Water Nanoemulsion and Evaluation of Hypocholesterolemic Activity in Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, J.; El-Naggar, M.E. Synthesis of an environmentally quercetin nanoemulsion to ameliorate diabetic-induced cardiotoxicity. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33, 101983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangeni, R.; Kang, S.-W.; Oak, M.; Park, E.Y.; Park, J.W. Oral delivery of quercetin in oil-in-water nanoemulsion: In vitro characterization and in vivo anti-obesity efficacy in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Cano, A.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Zielińska, A.; Silva, A.M. Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions in Skin Drug Delivery. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, Κ.; Kadian, V.; Puri, V.; Yogeshvar Bhardwaj, B.; Sharma, A.; Pahwa, R.; Rao, R.; Gupta, M.; Singh, I. New insights into quercetin nanoformulations for topical delivery. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, D.; Kim, S. A transdermal delivery system to enhance quercetin nanoparticle permeability. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, K.M.; Al Nahyah, K.S.; Alhakamy, N.A. Self-Nanoemulsion Loaded with a Combination of Isotretinoin, an Anti-Acne Drug, and Quercetin: Preparation, Optimization, and In Vivo Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanzadeh, E.; Esmaeili, A.; Rahgozar, S.; Nourbakhshnia, M. Application of quercetin in neurological disorders: From nutrition to nanomedicine. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Aschner, M.; Cheang, W.S.; Akkol, E.K. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lin, W.; Deng, X.; Ba, X.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Tu, S. Potential Implications of Quercetin in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Zeng, Y.; Peng, W.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.; Ji, B.; Li, F. Pharmacological Aspects of Natural Quercetin in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaqeel, N.K.; AlSheikh, M.H.; Al-Hariri, M.T. Quercetin Nanoemulsion Ameliorates Neuronal Dysfunction in Experimental Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokhale, J.P.; Mahajan, H.S.; Surana, S.S. Quercetin loaded nanoemulsion-based gel for rheumatoid arthritis: In vivo and in vitro studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadade, D.D.; Pekamwar, S.S. Cyclodextrin Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Theranostics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiassa, V.; Garnero, C.; Longhi, M.R.; Zoppi, A. Cyclodextrin Multicomponent Complexes: Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, H.; Babu, R.J. Role of Cyclodextrins in Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafelehbashi, R.; Yaraki, M.T.; Saremi, L.H.; Lajevardi, A.; Haratian, M.; Astinchap, B.; Rashidi, A.M.; Moradian, R. A pH-responsive citric-acid/α-cyclodextrin-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a nanocarrier for quercetin: An experimental and DFT study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 109, 110597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Karim, A.; Chee, P.L.; Chan, M.F.; Loh, X.J. Micellized α-Cyclodextrin-Based Supramolecular Hydrogel Exhibiting pH-Responsive Sustained Release and Corresponding Oscillatory Shear Behavior Analysis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh Nguyen, H.; Goycoolea, F.M. Chitosan/Cyclodextrin/TPP Nanoparticles Loaded with Quercetin as Novel Bacterial Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Molecules 2017, 22, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zou, Y.; Song, L.; Han, S.; Yang, H.; Chu, D.; Dai, Y.; Ma, J.; O’Driscoll, C.M.; Yu, Z.; et al. A cyclodextrin-based nanoformulation achieves co-delivery of ginsenoside Rg3 and quercetin for chemo-immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 12, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñalva, R.; Esparza, I.; Morales-Gracia, J.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Irache, J.M. Casein nanoparticles in combination with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin improves the oral bioavailability of quercetin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirzadeh, K.; Nazarian, S.; Hayat, S.M.G. Inorganic nanomaterials: A brief overview of the applications and developments in sensing and drug delivery. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 3, 395–402. [Google Scholar]
- Asad, S.; Jacobsen, A.C.; Teleki, A. Inorganic nanoparticles for oral drug delivery: Opportunities, barriers, and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechsupa, N.; Kosintarajit, P.; Kamkan, K.; Khanjina, T.; Sirikul, C.; Innuan, P.; Suwan, A.; Anukul, N.; Kantapan, J. Iron(III)-Quercetin Complexes’ Safety for MRI Cell Tracking in Cell Therapy Applications: Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Assessment. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, A.M.; Ilyas, S.; Schlößer, H.A.; Szymura, A.; Roitsch, S.; Wennhold, K.; Langmuir, S.M. Receptor-Mediated In Vivo Targeting of Breast Cancer Cells with 17α-Ethynylestradiol-Conjugated Silica-Coated Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14819–14828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoonfal, M.; Aminianfar, A.; Asemi, Z.; Yousefi, B. Application of nanoparticles for efficient delivery of quercetin in cancer cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, S.; Zakeri, M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Dehghanian, F.; Esmaeili, A. Quercetin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modulate glucose metabolism-related genes and miR-29 family in the hippocampus of diabetic rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayda, S.; Hadla, M.; Palazzolo, S.; Riello, P.; Corona, G.; Toffoli, G.; Rizzolio, F. Inorganic Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: A Transition from Lab to Clinic. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 4269–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Das, S.; Bhat, F.A.; Raja Singh, P.; Patra, C.R.; Arunakaran, J. Gold nanoparticles-conjugated quercetin induces apoptosis via inhibition of EGFR/PI3K/Akt-mediated pathway in breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Cell. Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhukhan, P.; Kundu, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, N.; Manna, P.; Das, J.; Sil, P.C. Targeted delivery of quercetin via pH-responsive zinc oxide nanoparticles for breast cancer therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 100, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.M.; Sherif, N.M.; Hassan, N.S.; Althobaiti, F.; Hanafy, N.A.N.; Sahyon, H.A. Novel quercetin encapsulated chitosan functionalized copper oxide nanoparticles as anti-breast cancer agent via regulating p53 in rat model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, V.; Muthukumar Sathya, P.; Srivalli, T.; Mohan, H. Synthesis of quercetin functionalized wurtzite type zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential to regulate intrinsic apoptosis signaling pathway in human metastatic ovarian cancer. Life Sci. 2022, 309, 121022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wei, X.; Li, Y. Inorganic Nanomaterial for Biomedical Imaging of Brain Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. Neuronanomedicine: An Up-to-Date Overview. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpour, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Beheshti, S. Effect of quercetin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on diabetes-induced learning and memory impairment in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6311–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanzadeh, E.; Esmaeili, A.; Abadi, R.E.N.; Kazemipour, N.; Pahlevanneshan, Z.; Beheshti, S. Quercetin conjugated with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles improves learning and memory better than free quercetin via interacting with proteins involved in LTP. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardestani, A.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Esmaeili, A. Quercetin attenuates neurotoxicity induced by iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yin, T.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, J. Quercetin-modified gold-palladium nanoparticles as a potential autophagy inducer for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenders, V.; Koutsoumpou, X.; Sargsian, A.; Manshian, B.B. Biomedical nanomaterials for immunological applications: Ongoing research and clinical trials. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Nakara, A.; Shanmugam, V.K. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized using plant extracts: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2561–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemzadeh, E.; Karamian, M.; Abedi, F.; Hanafi-Bojd, M.Y. Topical treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis lesions using quercetin/ Artemisia-capped silver nanoparticles ointment: Modulation of inflammatory response. Acta Trop. 2022, 228, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumawat, M.; Madhyastha, H.; Singh, M.; Revaprasadu, N.; Srinivas, S.P.; Daima, H.K. Double functionalized haemocompatible silver nanoparticles control cell inflammatory homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhyastha, H.; Halder, S.; Queen Intan, N.; Madhyastha, R.; Mohanapriya, A.; Sudhakaran, R.; Sajitha, L.S.; Banerjee, K.; Bethasiwi, P.; Daima, H.; et al. Surface refined AuQuercetin nanoconjugate stimulates dermal cell migration: Possible implication in wound healing. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37683–37694. [Google Scholar]
- Badhwar, R.; Mangla, B.; Neupane, Y.R.; Khanna, K.; Popli, H. Quercetin loaded silver nanoparticles in hydrogel matrices for diabetic wound healing. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 505102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarjanli, Z.; Ghaedi, K.; Esmaeili, A.; Zarrabi, A.; Rahgozar, S. The antitoxic effects of quercetin and quercetin-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles (QNPs) against H2O2-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6813–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Polymer-Based Nanosystems | Lipid-Based Nanosystems | Surfactant-Based Nanosystems | Cyclodextrin-Based Nanoparticles | Inorganic Nanoparticles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric Micelles | Polymeric Nanoparticles | Hydrogels | Polymersomes | Liposomes | SLN-NLC | Niosomes | Nanoemulsions | |||
| Advantages | ||||||||||
| Biocompatibility | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | + |
| Biodegradability | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + |
| High Loading efficiency | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| Chemical versatility | +++ | +++ | + | +++ | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Physicochemical stability | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| Controlled release properties | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Administration by different routes | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Stimuli responsiveness | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | +++ |
| Improve of ADME(T) profile | +++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + |
| Targeting | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | +++ |
| Imaging | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | +++ |
| Theragnostic | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | +++ |
| Precision medicine | + | + | + | + | +++ | + | + | + | + | ++ |
| Disadvantages | ||||||||||
| Nanotoxicity | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | +++ |
| High cost | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | +++ |
| Limitations in scale-up | + | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Immunogenicity | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | +++ |
| Lack in regulatory framework | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + | +++ | ++ |
| Polymer-Based Nanosystems | Lipid-Based Nanosystems | Surfactant-Based Nanosystems | Cyclodextrin-Based Nanoparticles | Inorganic Nanoparticles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Properties of QUE | Polymeric Micelles | Polymeric Nanoparticles | Hydrogels | Polymersomes | Liposomes | SLN-NLC | Niosomes | Nanoemulsions | ||
| Improved solubility | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Improved EE | x | x | x | |||||||
| Co-loading with other APIs | x | x | x | x | ||||||
| Increased bioavailability | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Sustained release | x | x | ||||||||
| Controlled release | x | x | x | x | ||||||
| pH-responsive release | x | |||||||||
| Increased stability | x | x | ||||||||
| Targeting to tumors | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Targeting to brain | x | |||||||||
| Transdermal administration | x | x | ||||||||
| Facilitation of the uptake into cells | x | x | x | |||||||
| Improved anti-inflammatory properties | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Enhanced antioxidant activity | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomou, E.-M.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Saitani, E.-M.; Valsami, G.; Pippa, N.; Skaltsa, H. Recent Advances in Nanoformulations for Quercetin Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061656
Tomou E-M, Papakyriakopoulou P, Saitani E-M, Valsami G, Pippa N, Skaltsa H. Recent Advances in Nanoformulations for Quercetin Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061656
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomou, Ekaterina-Michaela, Paraskevi Papakyriakopoulou, Elmina-Marina Saitani, Georgia Valsami, Natassa Pippa, and Helen Skaltsa. 2023. "Recent Advances in Nanoformulations for Quercetin Delivery" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061656
APA StyleTomou, E.-M., Papakyriakopoulou, P., Saitani, E.-M., Valsami, G., Pippa, N., & Skaltsa, H. (2023). Recent Advances in Nanoformulations for Quercetin Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061656