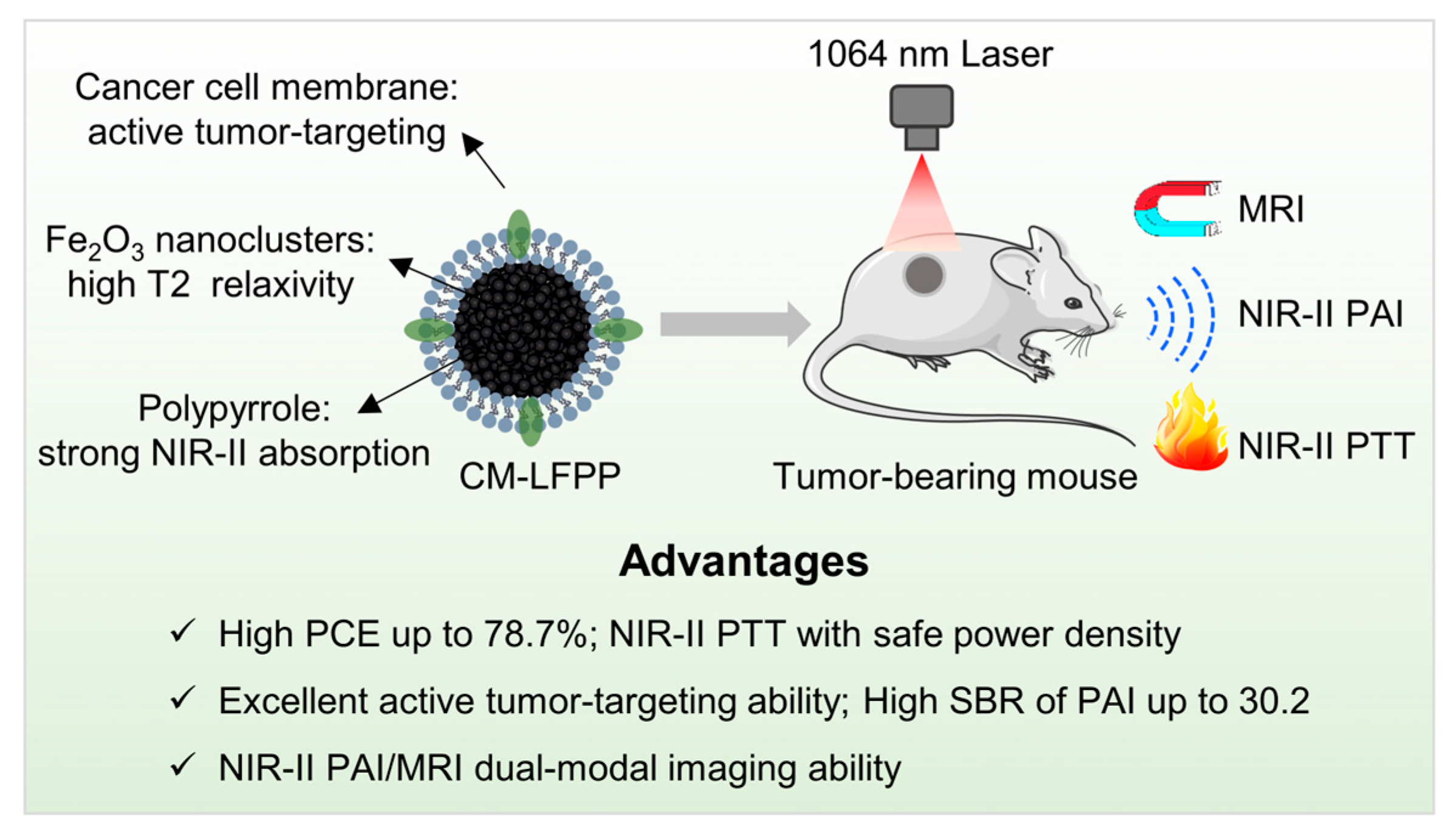
Biomimetic Theranostic Agents with Superior NIR-II Photoacoustic and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performance for Targeted Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CM-LFPP
2.3. Characterization of the CM-LFPP
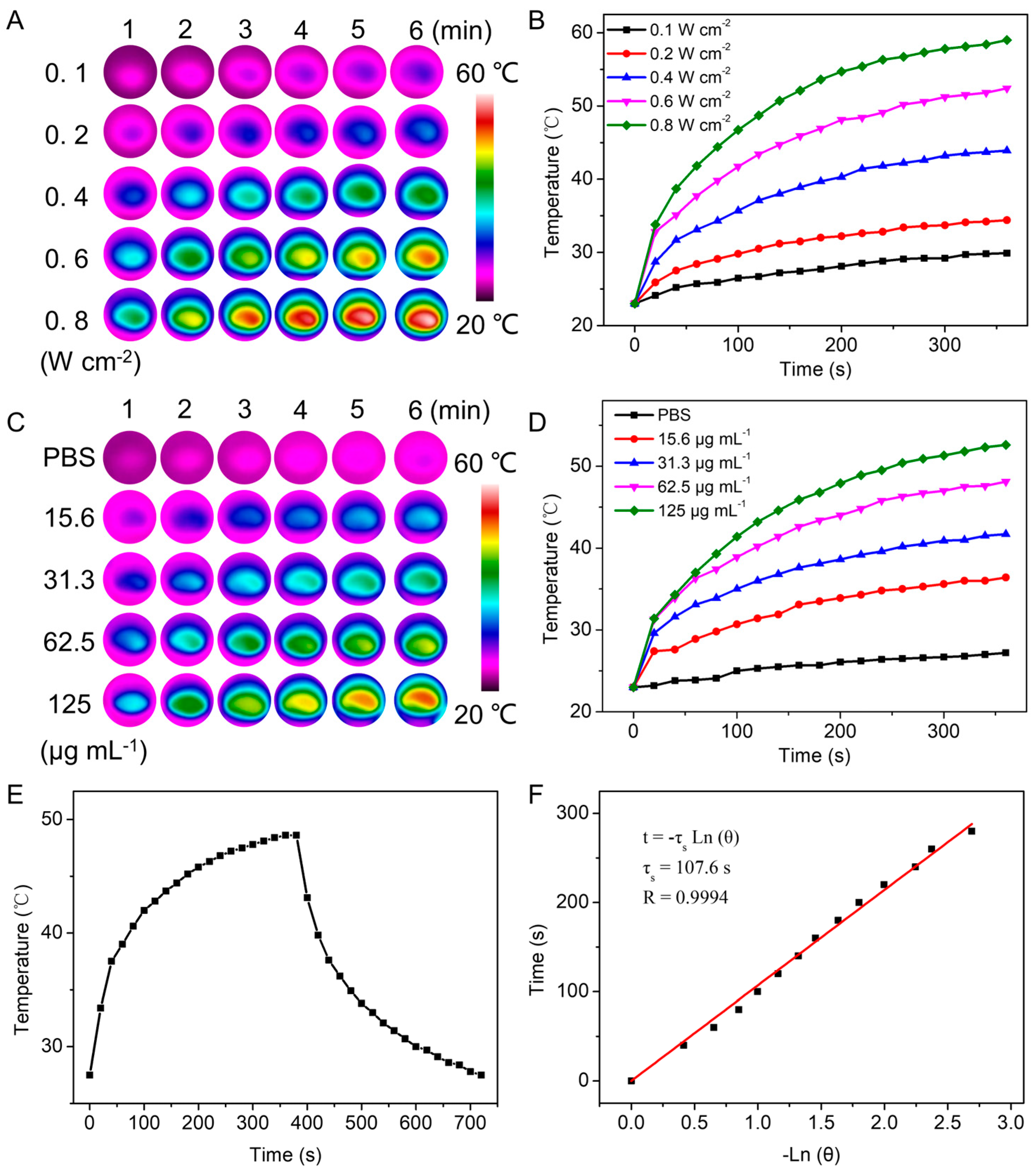
2.4. Photothermal Performance of the CM-LFPP
2.5. Photoacoustic Imaging Ability of the CM-LFPP
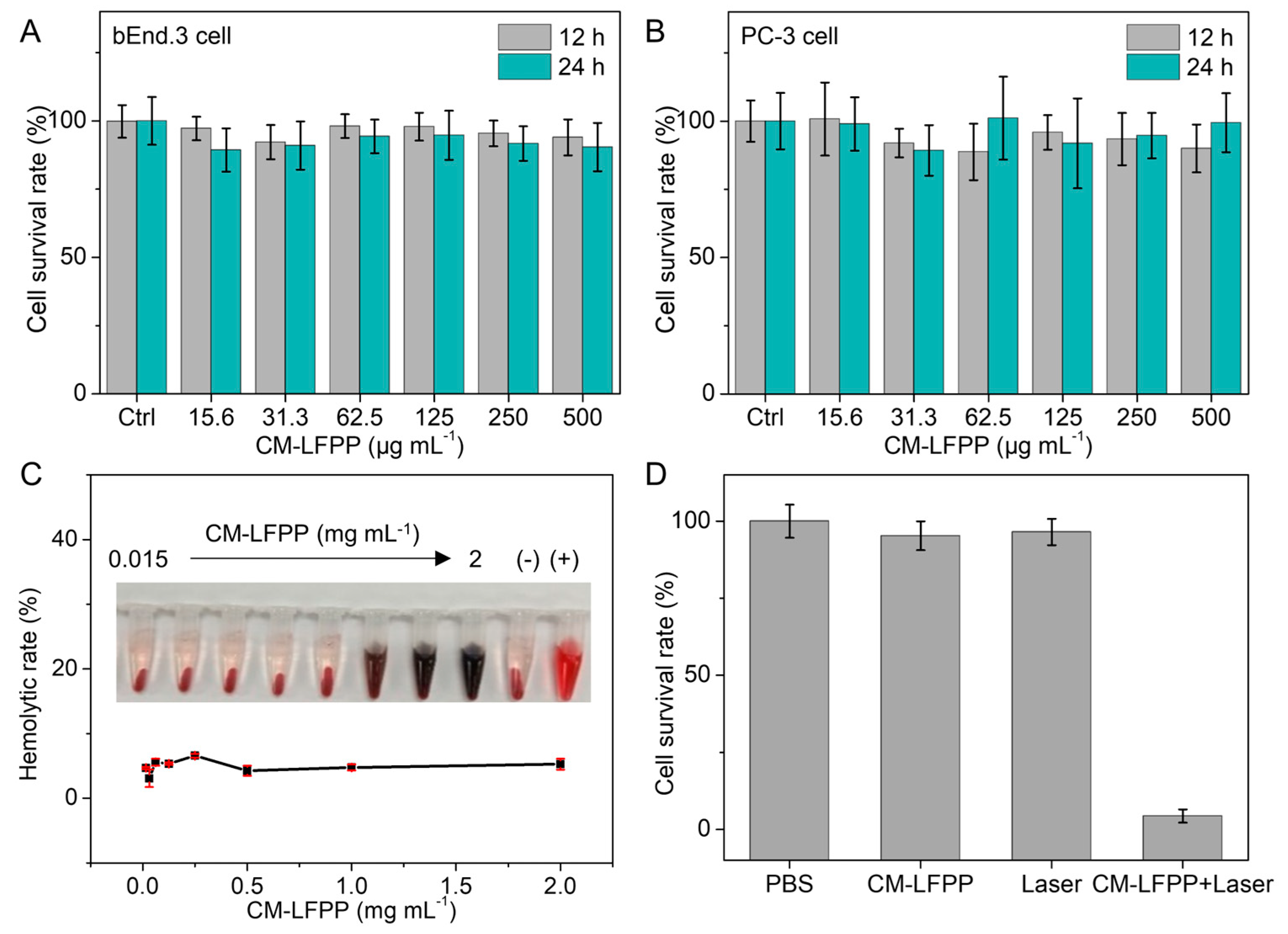
2.6. Cell Culture and Cell Cytotoxicity
2.7. MRI Capacity of the CM-LFPP
2.8. Animal Studies
2.9. Hemolysis Test
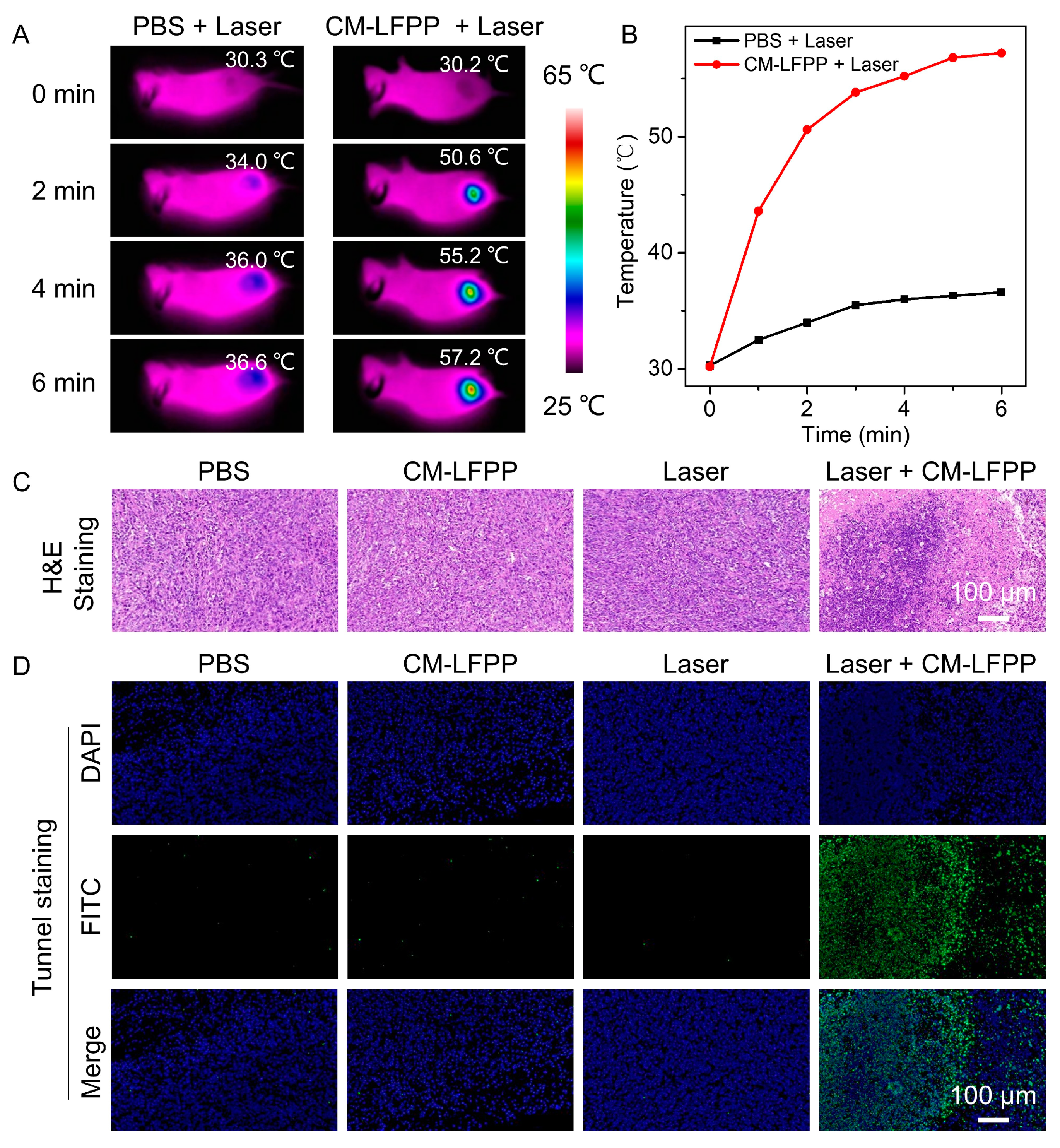
2.10. Histological and Blood Biochemistry Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the CM-LFPP
3.2. In Vitro Photothermal Performance of CM-LFPP
3.3. In Vitro PA/MRI Dual-Modal Imaging Ability of CM-LFPP
3.4. In Vitro Biocompatibility
3.5. In Vivo NIR-II PA Imaging
3.6. In Vivo MRI
3.7. In Vivo PTT
3.8. In Vivo Biosafety Evaluation of the CM-LFPP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culp, M.B.; Soerjomataram, I.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A. Recent Global Patterns in Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. Eau-Eanm-Estro-Esur-Siog Guidelines on Prostate Cancer—2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poppel, H.; Roobol, M.J.; Chapple, C.R.; Catto, J.W.F.; N’Dow, J.; Sønksen, J.; Stenzl, A.; Wirth, M. Prostate-Specific Antigen Testing as Part of a Risk-Adapted Early Detection Strategy for Prostate Cancer: European Association of Urology Position and Recommendations for 2021. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcean, A.; Curcean, S.; Rescigno, P.; Ap Dafydd, D.; Tree, A.; Reid, A.; Koh, D.M.; Sohaib, A.; Tunariu, N.; Shur, J. Imaging Features of the Evolving Patterns of Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2022, 77, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabile, A.; Giganti, F.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Taneja, S.S.; Villeirs, G.; Gill, I.S.; Allen, C.; Emberton, M.; Moore, C.M.; Kasivisvanathan, V. Multiparametric Mri for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Current Status and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 17, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, M.; Jäderling, F.; Discacciati, A.; Bergman, M.; Annerstedt, M.; Aly, M.; Glaessgen, A.; Carlsson, S.; Grönberg, H.; Nordström, T. Mri-Targeted or Standard Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmochowska, N.; Milanova, V.; Mukkamala, R.; Chow, K.K.; Pham, N.T.H.; Srinivasarao, M.; Ebert, L.M.; Stait-Gardner, T.; Le, H.; Shetty, A.; et al. Nanoparticles Targeted to Fibroblast Activation Protein Outperform PSMA for MRI Delineation of Primary Prostate Tumors. Small 2023, 2204956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Qian, J.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Z. Transition-Metal-Doped Hydrophilic Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Modulates Mri Contrast Performance for Accurate Diagnosis of Orthotopic Prostate Cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 9613–9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, D.; Yuan, C.N.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, J.; Basilion, J.P.; Meade, T.J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Psma-Positive Prostate Cancer by a Targeted and Activatable Gd(III) MR Contrast Agent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 17097–17108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.; Blasiak, B.; Tomanek, B.; Latta, P.; van Veggel, F. Target-Specific Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Human Prostate Adenocarcinoma Using Nadyf4-Nagdf4 Core Shell Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 24345–24355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadfar, S.M.; Roemhild, K.; Drude, N.I.; von Stillfried, S.; Knüchel, R.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Diagnostic, Therapeutic and Theranostic Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Zeng, J.; Huo, L.; Liu, K.; Wei, R.; Ni, K.; Gao, J. Recent Advances in Engineering Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 12, 214–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Guo, B. Recent Development of Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodal Imaging of Glioblastoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Yuan, Z. Photoacoustic-Based Multimodal Nanoprobes: From Constructing to Biological Applications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Park, B.; Choi, S.; Oh, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, C. Recent Advances in Contrast-Enhanced Photoacoustic Imaging: Overcoming the Physical and Practical Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J. Contrast Agents for Photoacoustic Imaging: A Review Focusing on the Wavelength Range. Biosensors 2022, 12, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Gao, D.; Hu, D.; Zhou, H.; Ma, T.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, P.; et al. Activatable NIR-II Photoacoustic Imaging and Photochemical Synergistic Therapy of MRSA Infections Using Miniature Au/Ag Nanorods. Biomaterials 2020, 251, 120092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Sui, J.; Jin, L.; Lin, L.; Fu, Q.; Lin, H.; Song, J. NIR-II Functional Materials for Photoacoustic Theranostics. Bioconjugate Chem. 2022, 33, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upputuri, P.K.; Pramanik, M. Photoacoustic Imaging in the Second near-Infrared Window: A Review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 040901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bhattarai, P.; Dai, Z.; Chen, X. Photothermal Therapy and Photoacoustic Imaging Via Nanotheranostics in Fighting Cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2053–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Sheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Yuan, Z. Protein-Modified CuS Nanotriangles: A Potential Multimodal Nanoplatform for in Vivo Tumor Photoacoustic/Magnetic Resonance Dual-Modal Imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. Non-Metallic T2-Mri Agents Based on Conjugated Polymers. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lu, F.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Gadolinium-Chelated Conjugated Polymer-Based Nanotheranostics for Photoacoustic/Magnetic Resonance/NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging-Guided Cancer Photothermal Therapy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4168–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, S.; Feng, L.; Liu, S.; Gai, S.; Dai, Y.; Xie, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Y. Renal-Clearable Nickel-Doped Carbon Dots with Boosted Photothermal Conversion Efficiency for Multimodal Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy in the Second near-Infrared Biowindow. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Lee, C.-S.; Shi, J.; et al. A Multifunctional Targeted Nanoprobe with High NIR-II PAI/MRI Performance for Precise Theranostics of Orthotopic Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 8779–8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Jiang, C.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, G.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Zhou, X.; Huang, P. Manganese-Dioxide-Coating-Instructed Plasmonic Modulation of Gold Nanorods for Activatable Duplex-Imaging-Guided NIR-II Photothermal-Chemodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.; Yang, W.; Xie, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.-L.; Lin, W.-W.; Huang, G.; Lu, C.-H.; Yang, H.-H. Copper Manganese Sulfide Nanoplates: A New Two-Dimensional Theranostic Nanoplatform for Mri/Msot Dual-Modal Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy in the Second near-Infrared Window. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4763–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Sui, M.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, L.; Liu, M.; Chen, S.; Zhou, X. Delicately Designed Cancer Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles for Targeted 19F MR/PA/FL Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57290–57301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Pan, C.; Shi, Y.; Zou, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, C.; et al. Biomimetic Yolk-Shell Nanocatalysts for Activatable Dual-Modal-Image-Guided Triple-Augmented Chemodynamic Therapy of Cancer. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19038–19052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Mao, Y.; Feng, S.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. Biomimetic smart mesoporous carbon nanozyme as a dual-GSH depletion agent and O2 generator for enhanced photodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 2022, 148, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Lo, W.S.; Chen, G.; Gu, Y.; Wong, W.T. Biomimetic Anti-PD-1 Peptide-Loaded 2D FePSe3 Nanosheets for Efficient Photothermal and Enhanced Immune Therapy with Multimodal MR/PA/Thermal Imaging. Adv. Sci. 2020, 8, 2003041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; She, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P. Highly Efficient GSH-Responsive “Off-On” NIR-II Fluorescent Fenton Nanocatalyst for Multimodal Imaging-Guided Photothermal/Chemodynamic Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 10470–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Pan, D.; Chen, S.; Martikainen, M.-V.; Kårlund, A.; Ke, J.; Pulkkinen, H.; Ruhanen, H.; Roponen, M.; Käkelä, R.; et al. Systematic Design of Cell Membrane Coating to Improve Tumor Targeting of Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhao, K.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Huang, C.; An, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wu, Q.; Cui, L.; et al. Fluid Nanoporous Microinterface Enables Multiscale-Enhanced Affinity Interaction for Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2213236119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.-G.; Noh, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, N.-M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-Large-Scale Syntheses of Monodisperse Nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, D.; Hu, D.; Lan, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yuan, Z.; Sheng, Z. Delivery of Biomimetic Liposomes Via Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels Route for Targeted Therapy of Parkinson. Research 2023, 6, 0030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, D.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z. Molecular Engineering of near-Infrared Light-Responsive Bodipy-Based Nanoparticles with Enhanced Photothermal and Photoacoustic Efficiencies for Cancer Theranostics. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5315–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; He, Y.; Tao, X.; Yao, Y.; Huang, X.; Ma, Y.; Peng, Z.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y. Subcutaneous Power Supply by Nir-Ii Light. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhen, X.; Xie, C.; Pu, K. Dual-Peak Absorbing Semiconducting Copolymer Nanoparticles for First and Second near-Infrared Window Photothermal Therapy: A Comparative Study. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhen, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jin, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Song, S.; Li, C.; et al. One-Dimensional Fe2P Acts as a Fenton Agent in Response to Nir II Light and Ultrasound for Deep Tumor Synergetic Theranostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Qu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Peng, X.; Zhang, R. Multifunctional Mno2/Ag3SbS3 Nanotheranostic Agent for Single-Laser-Triggered Tumor Synergistic Therapy in the Nir-Ii Biowindow. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4980–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, K.; Meng, X.; Dai, W.; Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Engineered Exosome-Mediated near-Infrared-Ii Region V2c Quantum Dot Delivery for Nucleus-Target Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Ye, J.; Li, Z.; Fu, F.; Lin, S.-L.; Chang, C.A.; Yang, H.; Song, J. Magnetic Targeted near-Infrared Ii Pa/Mr Imaging Guided Photothermal Therapy to Trigger Cancer Immunotherapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4997–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Zhu, D.; Duo, Y.; Li, Y.; Quan, H. Bimetallic Nanodots for Tri-Modal CT/MRI/PA Imaging and Hypoxia-Resistant Thermoradiotherapy in the NIR-II Biological Windows. Biomaterials 2020, 233, 119656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Ma, Y.-T. Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Verification of Anti-HER2 Indocyanine Green–Doxorubicin-Loaded Polyethyleneimine-Coated Perfluorocarbon Double Nanoemulsions for Targeted Photochemotherapy of Breast Cancer Cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Photothermal Agents | Photothermal Conversion Efficiency | Laser | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-CDs | 76.1% | 1064 nm | [26] |
| Fe2P NRs | 56.6% | 1064 nm | [42] |
| MnO2/Ag3SbS3 | 23.15% | 1064 nm | [43] |
| BSA-Boca-BODIPY NPs | 58.7% | 808 nm | [39] |
| V2C-TAT@Ex-RGD | 45.05% | 1064 nm | [44] |
| PFTQ-PEG-Gd NPs | 26% | 808 nm | [25] |
| TSIO nanoagents | 45.51% | 1064 nm | [45] |
| CM-LFPP | 78.7% | 1064 nm | This work |
| Items | 0 day | Day 1 | Day 4 | Day 7 | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (109/L) | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ± 0.7 | 4.4 ± 0.7 | 4.1 ± 1.1 | 0.8–6.8 |
| Lym # (109/L) | 3.9 ± 0.4 | 5.0 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 3.3 ± 0.9 | 0.7–5.7 |
| Mon # (109/L) | 0.1 ± 0.05 | 0.1 ± 0.04 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.06 | 0.0–0.3 |
| Gran # (109/L) | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.1–1.8 |
| Lym% | 81.0 ± 1.4 | 81.0 ± 3.3 | 81.2 ± 5.6 | 80.0 ± 4.1 | 55.8–90.6 |
| Mon% | 2.9 ± 0.08 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 2.8 ± 0.8 | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 1.8–6.0 |
| Gran% | 16.1 ± 1.4 | 16.3 ± 2.9 | 16.0 ± 4.9 | 17.0 ± 3.2 | 8.6–38.9 |
| RBC (1012/L) | 8.9 ± 0.4 | 8.8 ± 0.2 | 8.6 ± 0.4 | 8.8 ±0.3 | 6.4–9.4 |
| MCV (fL) | 52.0 ± 0.6 | 51.4 ± 0.5 | 52.0 ± 0.8 | 52.3 ± 1.3 | 48.2–58.3 |
| MCH (pg) | 16.1 ± 0.2 | 16.0 ± 0.1 | 16.2 ± 0.3 | 16.2 ± 0.2 | 15.8–19 |
| RDW% | 14.8 ± 0.1 | 14.2 ± 0.8 | 14.7 ± 0.6 | 14.4 ± 0.7 | 13–17 |
| PLT (109/L) | 870 ± 88.6 | 813 ± 189 | 774 ± 161 | 879 ± 86 | 450–1590 |
| MPV (fL) | 5.6 ± 0.4 | 5.8 ± 0.1 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 3.8–6.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Hu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Gao, D. Biomimetic Theranostic Agents with Superior NIR-II Photoacoustic and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performance for Targeted Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061617
Liu L, Yang S, Zheng Z, Li Q, Liu C, Hu D, Liu Z, Zhang X, Zhang R, Gao D. Biomimetic Theranostic Agents with Superior NIR-II Photoacoustic and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performance for Targeted Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061617
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ling, Shangpo Yang, Ziliang Zheng, Qingshuang Li, Chenchen Liu, Dehong Hu, Zhou Liu, Xiaoping Zhang, Ruiping Zhang, and Duyang Gao. 2023. "Biomimetic Theranostic Agents with Superior NIR-II Photoacoustic and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performance for Targeted Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061617
APA StyleLiu, L., Yang, S., Zheng, Z., Li, Q., Liu, C., Hu, D., Liu, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, R., & Gao, D. (2023). Biomimetic Theranostic Agents with Superior NIR-II Photoacoustic and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performance for Targeted Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061617




