Product Validation and Stability Testing of Pharmacy Compounded Cholic Acid Capsules for Dutch Patients with Rare Bile Acid Synthesis Defects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cholic Acid Capsules
2.3. Pharmaceutical Quality Tests
2.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Refractive Index
2.5. Stability Study
2.6. In Vitro Dissolution Testing
3. Results
3.1. Productvalidation
3.2. Stability Study
3.2.1. Identification and Content Assay
3.2.2. Related Substances
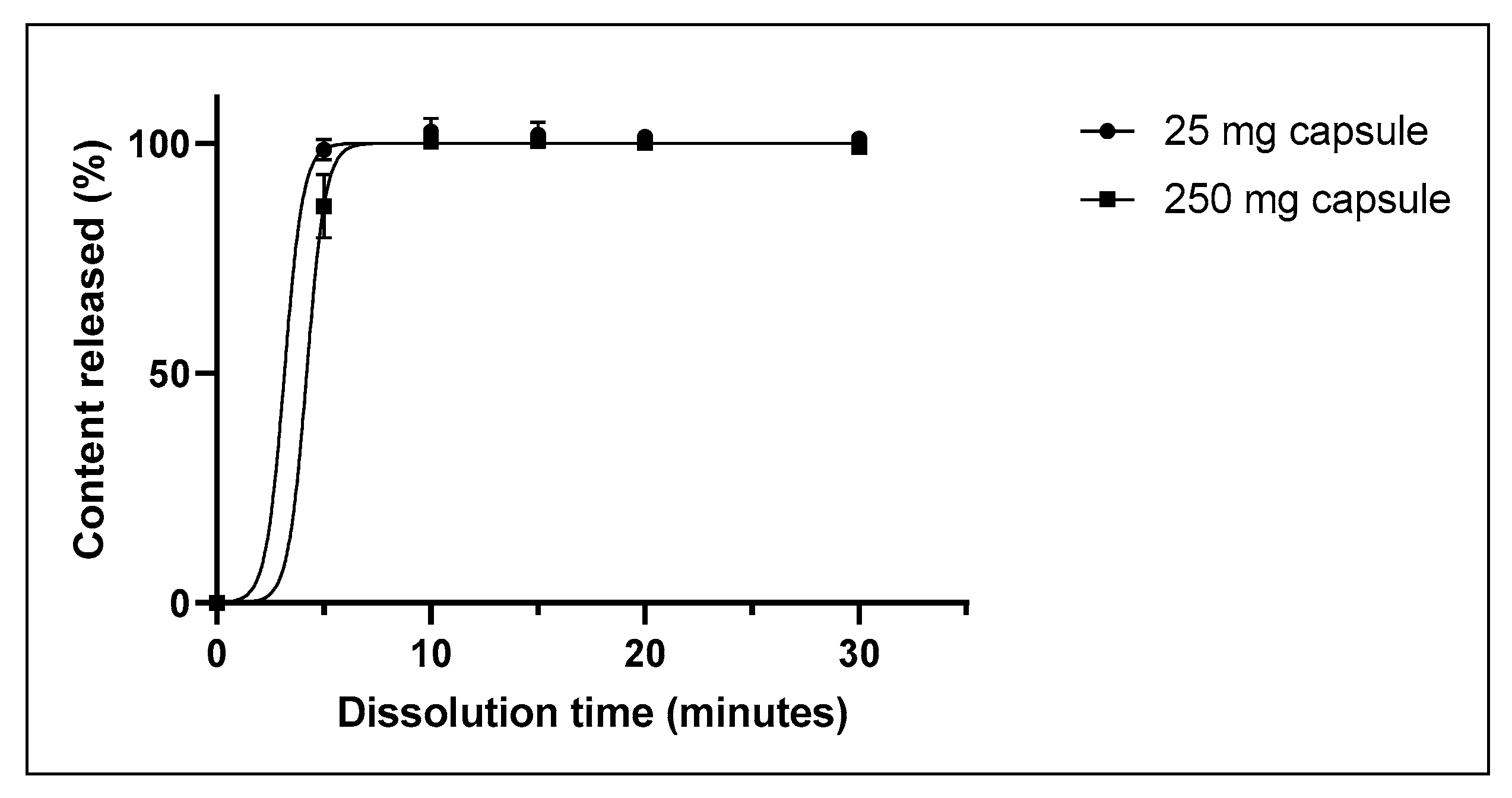
3.2.3. Dissolution and Disintegration of CA Capsules
3.3. Microbiology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heubi, J.E.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Bove, K.E. Inborn Errors of Bile Acid Metabolism. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bove, K.E.; Heubi, J.E.; Balistreri, W.F.; Setchell, K.D. Bile acid synthetic defects and liver disease: A comprehensive review. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2004, 7, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, P.T. Disorders of bile acid synthesis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahcevic, Z.R.; Goldman, M.; Schwartz, C.C.; Gustafsson, J.; Swell, L. Bile acid metabolism in cirrhosis. VII. Evidence for defective feedback control of bile acid synthesis. Hepatology 1981, 1, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, P.T. Inborn errors of bile acid metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1991, 14, 478–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, K.D.; Heubi, J.E. Defects in bile acid biosynthesis--diagnosis and treatment. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43 (Suppl. S1), S17–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, S.J.; Raymond, G.V.; Braverman, N.E.; Moser, A.B. Zellweger Spectrum Disorder. In GeneReviews(®); Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Faust, P.L.; Banka, D.; Siriratsivawong, R.; Ng, V.G.; Wikander, T.M. Peroxisome biogenesis disorders: The role of peroxisomes and metabolic dysfunction in developing brain. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinandusse, S.; Houten, S.M. Peroxisomes and bile acid biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, E.; Gerhardt, M.F.; Fabre, M.; Setchell, K.D.; Davit-Spraul, A.; Vincent, I.; Heubi, J.E.; Bernard, O.; Jacquemin, E. Oral cholic acid for hereditary defects of primary bile acid synthesis: A safe and effective long-term therapy. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1310–1320.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, E.; Matarazzo, L.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Dabadie, A.; Cohen, J.; Habes, D.; Hillaire, S.; Guettier, C.; Taburet, A.M.; Myara, A.; et al. Cholic acid for primary bile acid synthesis defects: A life-saving therapy allowing a favorable outcome in adulthood. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaini, A.A.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Al Saleem, B.; Heubi, J.E.; Lone, K.; Davit-Spraul, A.; Jacquemin, E. Bile Acid Synthesis Disorders in Arabs: A 10-year Screening Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubi, J.E.; Setchell, K.D.R. Open-label Phase 3 Continuation Study of Cholic Acid in Patients With Inborn Errors of Bile Acid Synthesis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubi, J.E.; Bishop, W.P. Long-Term Cholic Acid Treatment in a Patient with Zellweger Spectrum Disorder. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2018, 12, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubi, J.E.; Bove, K.E.; Setchell, K.D.R. Oral Cholic Acid Is Efficacious and Well Tolerated in Patients With Bile Acid Synthesis and Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, K.; Klouwer, F.C.; Koot, B.G.; Kemper, E.M.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Koelfat, K.V.; Lenicek, M.; Schaap, F.G.; Waterham, H.R.; Vaz, F.M.; et al. Cholic acid therapy in Zellweger spectrum disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouwer, F.C.C.; Koot, B.G.P.; Berendse, K.; Kemper, E.M.; Ferdinusse, S.; Koelfat, K.V.K.; Lenicek, M.; Vaz, F.M.; Engelen, M. The cholic acid extension study in Zellweger spectrum disorders: Results and implications for therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandia, D.; Chaussenot, A.; Besson, G.; Lamari, F.; Castelnovo, G.; Curot, J.; Duval, F.; Giral, P.; Lecerf, J.M.; Roland, D.; et al. Cholic acid as a treatment for cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in adults. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; von Bergmann, K.; Rotthauwe, H.W.; Leiss, O. Biliary lipid metabolism in children with chronic intrahepatic cholestasis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1984, 143, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.S.; Bove, K.E.; Lovell, M.A.; Sokol, R.J. Mechanisms of disease: Inborn errors of bile acid synthesis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 5, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboratoires CTRS. Summary of Product Characteristics Orphacol 50 mg and 250 mg Hard Capsules. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/orphacol-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- EMA. European Medicines Agency. Orphacol Public Assessment Report; EMEA/H/C/001250//0000. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/orphacol-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Travere Therapeutics, Inc. Cholbam Prescribing Information. Available online: https://cholbam.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/CHOLBAM-Prescribing-Information-2021-05.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Retrophin Europe Limited. Summary of Product Characteristics Kolbam 50 mg and 250 mg Hard Capsules. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/kolbam-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- EMA. European Medicines Agency. Public Statement Withdrawal Market Authorization Kolbam; EMA/282033/2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/public-statement/public-statement-kolbam-withdrawal-marketing-authorisation-european-union_en.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Polak, Y.; Jacobs, B.A.W.; Kemper, E.M. Pharmacy Compounded Medicines for Patients With Rare Diseases: Lessons Learned From Chenodeoxycholic Acid and Cholic Acid. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 758210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Pharmaceutical Preparations (2619), 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Capsules (0016), 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Uniformity of Dosage Units, 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Disintegration of Tablets and Capsules, 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Dissolution Test for Solid Dosage Forms, 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Microbiological Quality of Non-Sterile Pharmaceutical Preparations and Substances for Pharmaceutical Use, 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Absorption Spectrophotometry, Infrared, 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Chenodeoxycholic Acid (1189), 10th ed.; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ICH. Q2 (R1): Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2%28R1%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- ICH. Q1A (R2): Stability Testing of new Drug Substances and Products. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q1A%28R2%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Dissolution Methods Database. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/dissolution-methods-database (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Dissolution Methods. Cholic Acid. Available online: www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/dissolution (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Setchell, K.D.R.; Heubi, J.E.; Bove, K.E.; O’Connell, N.C.; Brewsaugh, T.; Steinberg, S.J.; Moser, A.; Squires, R.H., Jr. Liver disease caused by failure to racemize trihydroxycholestanoic acid: Gene mutation and effect of bile acid therapy. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, G.; Giordano, G.; Rispoli, G.A.; Maggiore, G.; Naturale, M.; Marchetti, D.; Iascone, M. Atypical clinical presentation and successful treatment with oral cholic acid of a child with defective bile acid synthesis due to a novel mutation in the HSD3B7 gene. Pediatr. Rep. 2017, 9, 7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. European Medicines Agency. Kolbam Public Assessment Report; EMA/689761/2015. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/kolbam-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Netherlands Trial Register. Long-Term Safety Study of Personalized Cholic Acid Treatment in Patients with Bile Acid Synthesis Defects. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=NL8630 (accessed on 8 September 2022).
| Test | Test Reference | Specification | Specification Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | In-house | White or almost white powder | In-house |
| Identification, IR, and HPLC | Ph.Eur. 2.2.24 (IR) In-house (HPLC) | Positive with reference standard | Cholic acid Ph.Eur. CRS |
| Content (% of labelled content) | In-house | 90.0–110.0 | In-house |
| Content uniformity | Ph.Eur. 2.9.40 | Ph.Eur. 2.9.40 | |
| Mass variation † (%) | ≤10.0 | ||
| Content uniformity * (AV) | ≤15.0 | ||
| Loss on drying (%) | Ph.Eur. 2.3.32 | ≤5.0 | In-house |
| Related substances (%) | In-house | In-house | |
| CDCA | ≤0.15 | ||
| DCA | ≤0.15 | ||
| MCA | ≤0.20 | ||
| Any unidentified substance | ≤0.10 | ||
| Total unidentified substances | ≤0.40 | ||
| Total Related Substances | ≤1.00 | ||
| Dissolution (minutes) ± | Ph.Eur. 2.9.3 and FDA [37] | <30 | In-house |
| Disintegration time (minutes) | Ph.Eur. 2.9.1 | <30 | In-house |
| Microbiology | Ph.Eur. 2.6.12 Ph.Eur. 2.6.13 | Ph.Eur. 5.1.4. | |
| TAMC (CFU/g) | <1000 | ||
| TYMC (CFU/g) | <100 | ||
| E. coli | Absent |
| Capsule Strength (mg) | Minimum (mg) | Maximum (mg) | Mean (mg) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | 196.3 | 220.2 | 209.9 | 0.0050 |
| 250 mg | 235.4 | 263.6 | 251.0 | 0.0068 |
| Batch Number | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Strength | 25 | 25 | 25 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| Batch size | 1300 | 1300 | 1300 | 1200 | 1200 | 1200 |
| Appearance | Complies | Complies | Complies | Complies | Complies | Complies |
| Identification | Complies | Complies | Complies | Complies | Complies | Complies |
| Content (% of labelled content) | 94.7 ¥ | 90.6 ¥ | 95.4 ¥ | 102.6 | 102.2 | 100.7 |
| Content uniformity | ||||||
| Mass variation † (%) | −2.1–3.6 | −4.1–2.8 | −3.2–2.4 | −3.3–4.3 | −6.2–5.07 | −5.5–3.8 |
| Content uniformity * (AV) | 7.3 | 8.2 | 14.7 | 5.8 | 10.8 | 6.4 |
| Loss on drying (%) | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Related substances (%) | ||||||
| CDCA | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| DCA | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| MCA | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.10 |
| Any unidentified substance | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Total unidentified substances | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Total Related Substances (%) | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.10 |
| Dissolution (minutes) ± | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Disintegration time (minutes) | 5 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| Microbiology | ||||||
| TAMC (CFU/g) | <5 | <5 | 10 | <5 | <5 | <5 |
| TYMC (CFU/g) | <5 | <5 | <5 | <5 | <5 | <5 |
| E. coli | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Strength | Time Stored (Months) | Storage Condition | CA Content | MCA Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) ± SD (n = 3) | Minimum (%) | Maximum (%) | Mean (%) ± SD (n = 3) | |||
| 25 mg | 0 | Long-term | NA ¥ | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| 3 | Long-term | NA ¥ | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | |
| 6 | Long-term | 100.03 ± 4.71 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | |
| 9 | Long-term | 93.40 ± 1.65 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | |
| 12 | Long-term | 94.43 ± 1.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | |
| 3 | Accelerated | NA ¥ | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | |
| 6 | Accelerated | 101.13 ± 0.83 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | |
| 250 mg | 0 | Long-term | 101.83 ± 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.12 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | Long-term | 99.63 ± 0.64 | 0.21 * | 0.27 * | 0.23 ± 0.03 | |
| 6 | Long-term | 100.67 ± 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | |
| 9 | Long-term | 97.13 ± 1.04 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | |
| 12 | Long-term | 96.90 ± 2.71 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | |
| 3 | Accelerated | 99.60 ± 0.69 | 0.21 * | 0.23 * | 0.22 ± 0.01 | |
| 6 | Accelerated | 99.87 ± 1.35 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polak, Y.; Jacobs, B.A.W.; Bouwhuis, N.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Kroon, M.A.G.M.; Kemper, E.M. Product Validation and Stability Testing of Pharmacy Compounded Cholic Acid Capsules for Dutch Patients with Rare Bile Acid Synthesis Defects. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030773
Polak Y, Jacobs BAW, Bouwhuis N, Hollak CEM, Kroon MAGM, Kemper EM. Product Validation and Stability Testing of Pharmacy Compounded Cholic Acid Capsules for Dutch Patients with Rare Bile Acid Synthesis Defects. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030773
Chicago/Turabian StylePolak, Yasmin, Bart A. W. Jacobs, Natalja Bouwhuis, Carla E. M. Hollak, Maurice A. G. M. Kroon, and Elles Marleen Kemper. 2023. "Product Validation and Stability Testing of Pharmacy Compounded Cholic Acid Capsules for Dutch Patients with Rare Bile Acid Synthesis Defects" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030773
APA StylePolak, Y., Jacobs, B. A. W., Bouwhuis, N., Hollak, C. E. M., Kroon, M. A. G. M., & Kemper, E. M. (2023). Product Validation and Stability Testing of Pharmacy Compounded Cholic Acid Capsules for Dutch Patients with Rare Bile Acid Synthesis Defects. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030773





