Development and Characterization of Pullulan-Based Orodispersible Films of Iron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Microencapsulated Iron Particles
2.3. Characterization of the Iron Microparticles
2.3.1. Optical Microscopy
2.3.2. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy
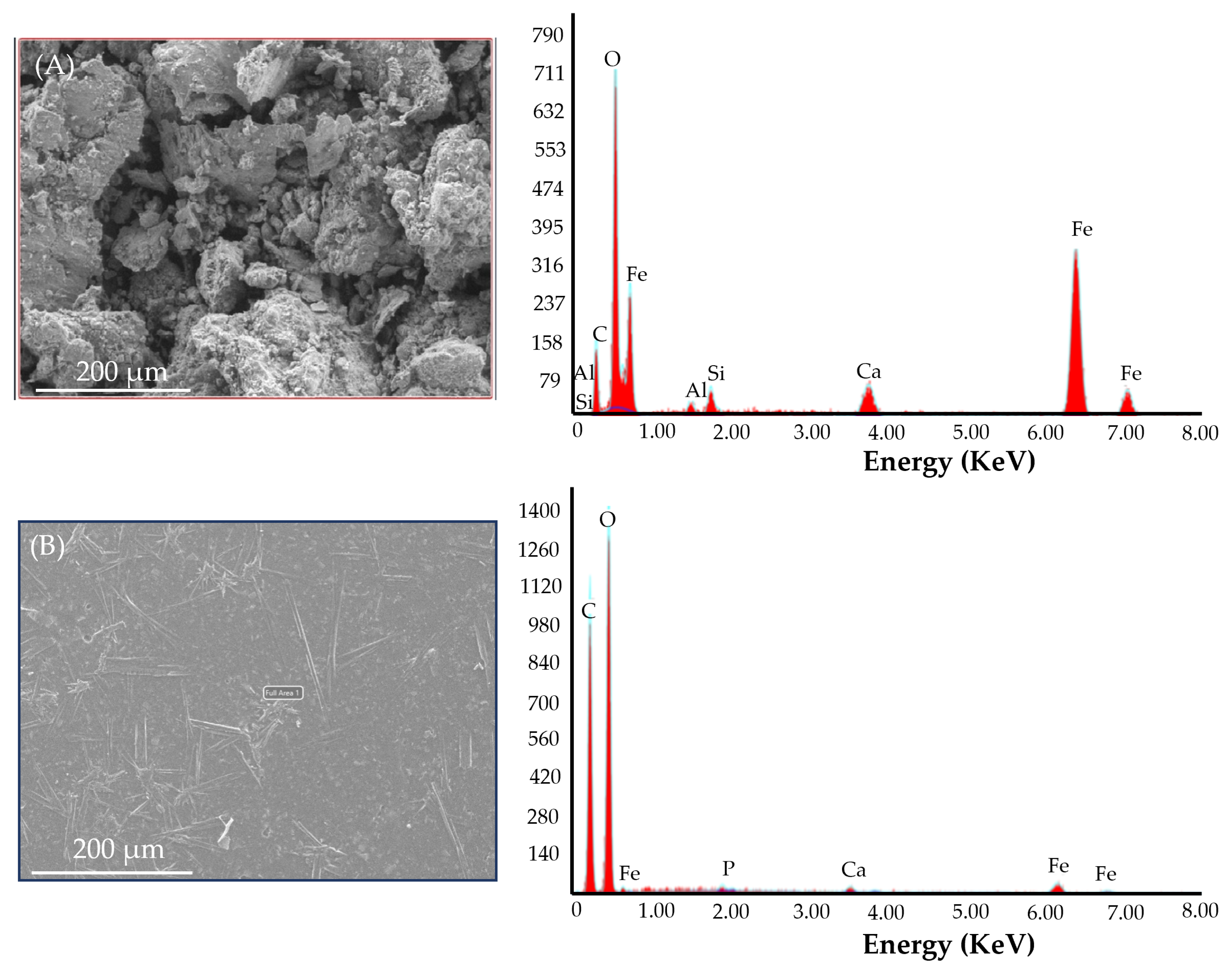
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with X-ray Energy Dispersion (EDS)
2.4. Fabrication of Pullulan-Based ODFs Loaded with Fe MPs
2.5. Characterization of the ODFs
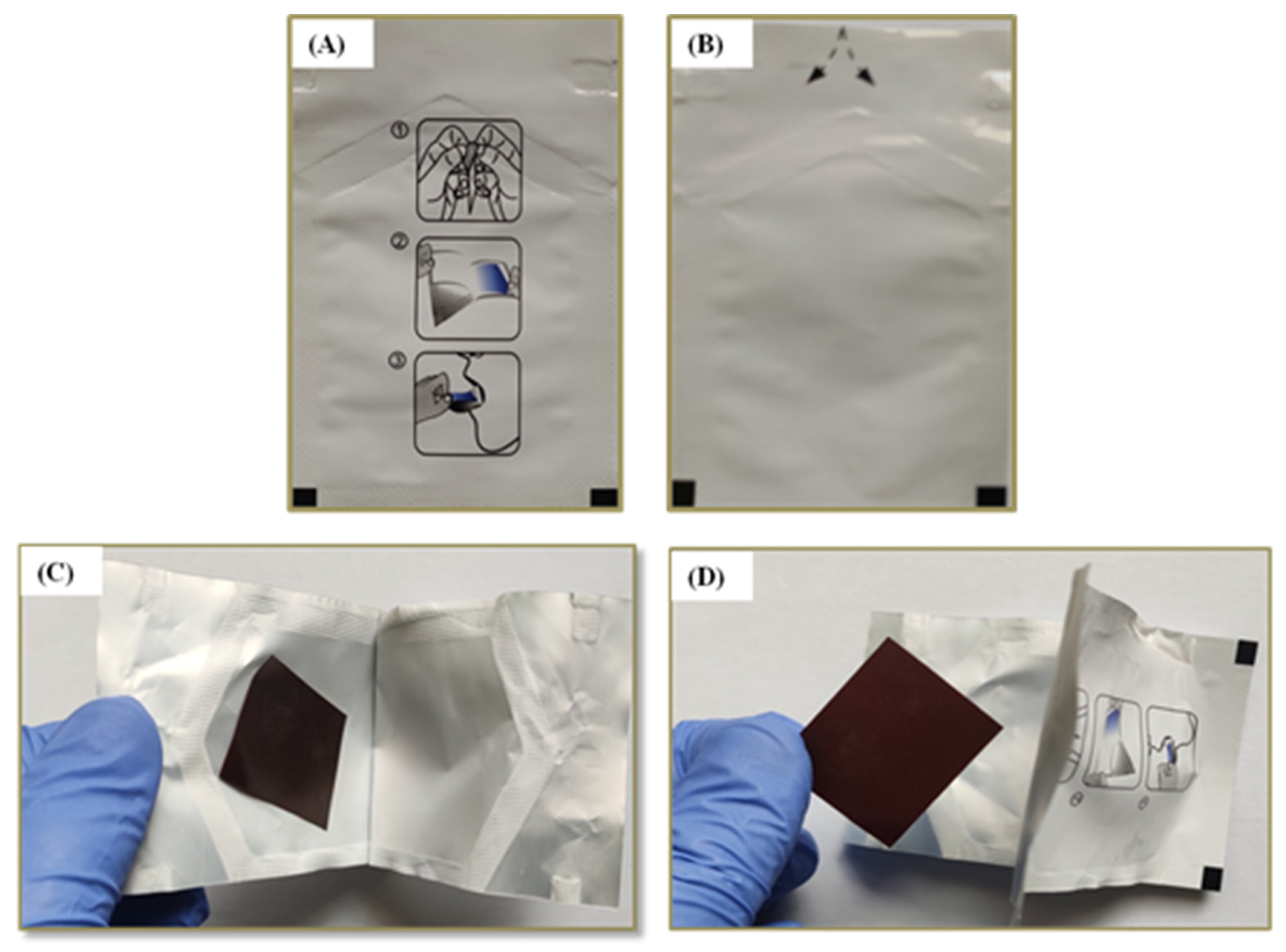
2.5.1. Physical Examination
2.5.2. Weight
2.5.3. Thickness
2.5.4. Drug Content
2.5.5. Disintegration Time
2.5.6. Folding Endurance
2.5.7. Tensile Strength
2.5.8. Surface pH
2.5.9. Karl–Fischer Titration (Water Content)
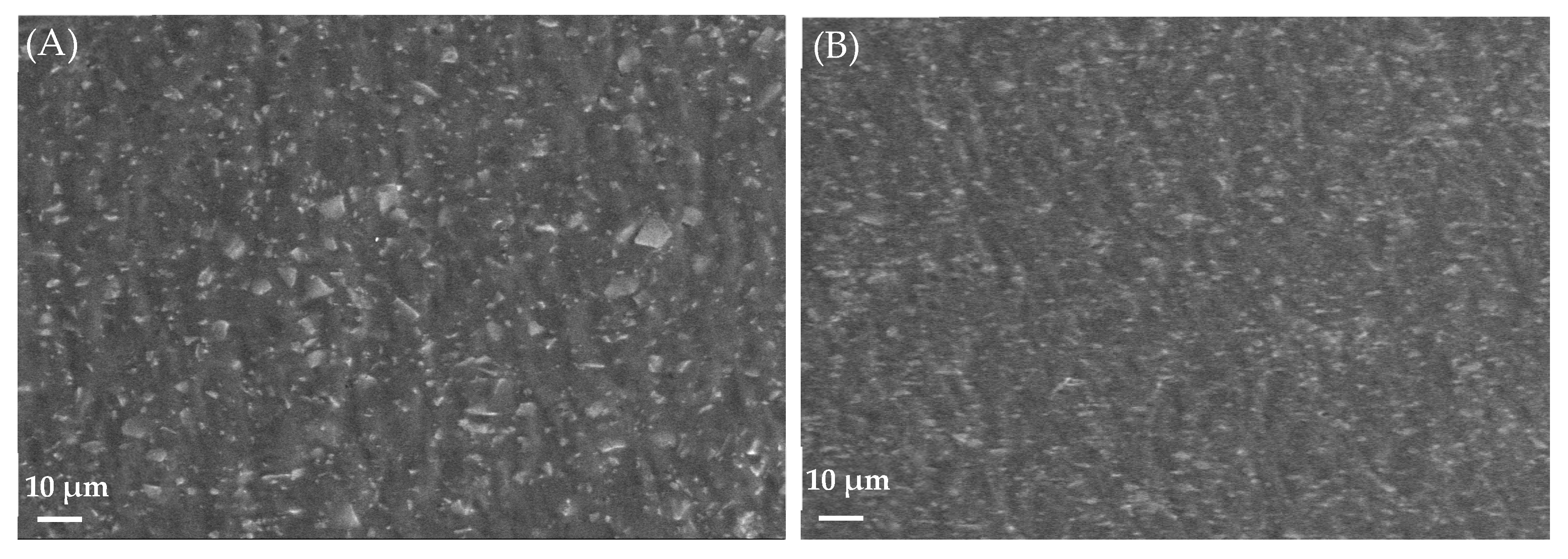
2.5.10. Morphology by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.5.12. Microbial Load
2.6. Dissolution Studies
2.7. Stability Studies
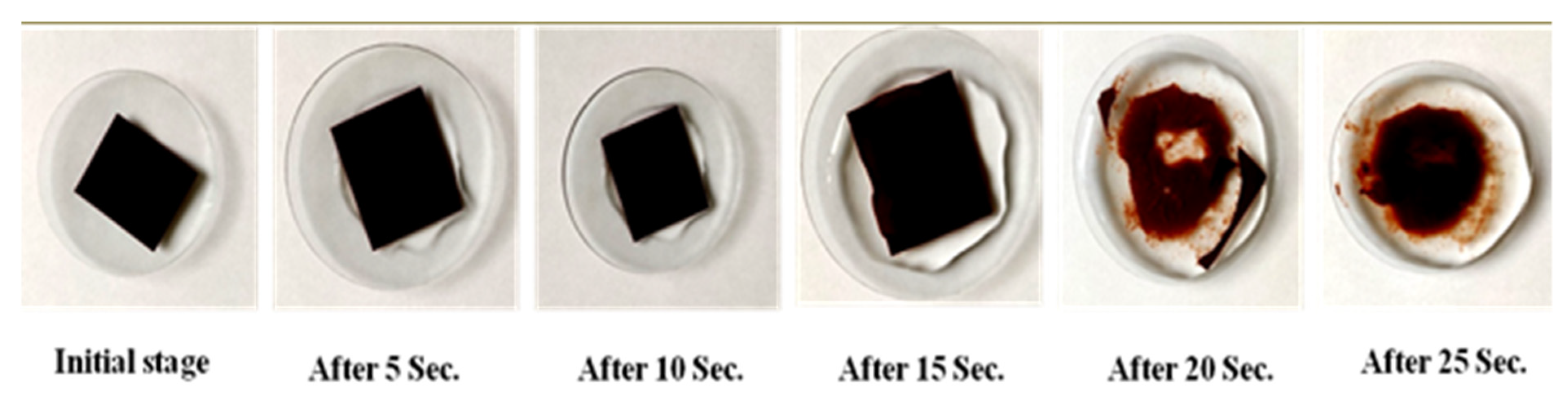
2.8. In Vivo Biocompatibility Study Using Hamster Cheek Pouch Model (Irritation Study)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microencapsulated Iron Particles and Their Characterization
3.2. Characterization of Iron Microparticles
3.3. Iron Orodispersible Films (i-ODFs)
Selection of Excipients
3.4. Characterization of the Pullulan-Based Iron-Loaded Orodispersible Films
3.4.1. Acceptability by the Subjects
3.4.2. Weight Variation
3.4.3. Thickness
3.4.4. Folding Endurance (FE)
3.4.5. Surface pH
3.4.6. Disintegration Time
3.4.7. Dissolution Profile
3.4.8. FTIR Spectrophotometric Method
3.4.9. Morphological Study Using SEM
3.4.10. Tensile Strength
3.4.11. Karl–Fischer Titration
3.4.12. Microbial Bioburden
3.4.13. Drug Content
3.5. Stability Studies
3.6. In Vivo Biocompatibility Study Using Hamster Cheek Pouch Model (Irritation Study)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petry, N.; Olofin, I.; Hurrell, R.F.; Boy, E.; Wirth, J.P.; Moursi, M.; Donahue Angel, M.; Rohner, F. The Proportion of Anemia Associated with Iron Deficiency in Low, Medium, and High Human Development Index Countries: A Systematic Analysis of National Surveys. Nutrients 2016, 8, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Hurrell, R.F. Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 2007, 370, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, K.; Kulnigg-Dabsch, S.; Gasche, C. Management of Iron Deficiency Anemia. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 11, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Guidelines on Food Fortification with Micronutrients; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; ISBN 92-4-159401-2. Available online: apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/43412/9241594012_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Da Silva Lopes, K.; Yamaji, N.; Rahman, M.O.; Suto, M.; Takemoto, Y.; Garcia-Casal, M.N.; Ota, E. Nutrition-specific interventions for preventing and controlling anaemia throughout the life cycle: An overview of systematic reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 9, CD013092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, K.B.; Tan, Y.T.F.; Peh, K.K. Characterization of oral disintegrating film containing donepezil for Alzheimer disease. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, R.M.; Alfadhel, M.; Seshadri, V.D.; Albagami, F.; Alrobaian, M.; Tawati, S.M.; Warsi, M.H.; Almurshedi, A.S. Fabrication and characterization of orodispersible films loaded with solid dispersion to enhance Rosuvastatin calcium bioavailability. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Gowda, D.V.; Rosenholm, J.M. Orodispersible films: Conception to quality by design. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, R.; Pawar, P.; Khanna, S.; Arora, S. Orally dissolving strips: A new approach to oral drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2013, 3, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkien, Z.; Stecher, L.; Mander, A.P.; Pereira, D.I.; Powell, J.J. Ferrous sulfate supplementation causes significant gastrointestinal side-effects in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Chassard, C.; Rohner, F.; N’Goran, E.K.; Nindjin, C.; Dostal, A.; Utzinger, J.; Ghattas, H.; Lacroix, C.; Hurrell, R.F. The effects of iron fortification on the gut microbiota in African children: A randomized controlled trial in Cote d’Ivoire. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortman, G.A.; Raffatellu, M.; Swinkels, D.W.; Tjalsma, H. Nutritional iron turned inside out: Intestinal stress from a gut microbial perspective. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 1202–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganini, D.; Zimmermann, M.B. The effects of iron fortification and supplementation on the gut microbiome and diarrhea in infants and children: A review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1688S–1693S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpf, V.J. Parenteral iron supplementation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 1996, 11, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Gómez-Ramírez, S.; Besser, M.; Pavía, J.; Gomollón, F.; Liumbruno, G.M.; Bhandari, S.; Cladellas, M.; Shander, A.; Auerbach, M. Current misconceptions in diagnosis and management of iron deficiency. Blood Transfus. 2017, 15, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, R.P.; Puthli, S.P. Oral strip technology: Overview and future potential. J. Control. Release 2009, 139, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, E.M.; Breitenbach, A.; Breitkreutz, J. Advances in orodispersible films for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Gowda, D.V. Orodispersible Thin Film: A new patient-centered innovation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunte, S.; Tandale, P. Fast dissolving strips: A novel approach for the delivery of verapamil. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Pharmaceutical evaluation and dynamic vapor sorption studies of fast dissolving intraoral films of Loratadine. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellanki, S.; Jagtap, S.; Masareddy, R. Dissofilm: A novel approach for delivery of phenobarbital; design and characterization. J. Young Pharm. 2011, 3, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Chaudhari, A.M.; Gandhi, A.K.; Maheriya, P. Pullulan based oral thin film formulation of zolmitriptan: Development and optimization using factorial design. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighatpanah, N.; Mirzaee, H.; Khodaiyan, F.; Kennedy, J.F.; Aghakhani, A.; Hosseini, S.S.; Jahanbin, K. Optimization and characterization of pullulan produced by a newly identified strain of Aureobasidium pullulans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Wei, G. Efficient pullulan production by Aureobasidium pullulans using cost-effective substrates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Said, I.A.; Aboelwafa, A.A.; ElGazayerly, O.N. Optimization of taste-masked dapoxetine oral thin films using factorial design: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.S.; Kaur, N.; Hassan, M.; Kennedy, J.F. Pullulan in biomedical research and development—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.A. Disorders of iron metabolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 342, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaji, J.A.; Isah, A.Y.; Agida, E.T.; Otu, T.; Abdullahi, H.I. Daily versus twice daily dose of ferrous sulphate supplementation in pregnant women: A randomized clinical trial. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.O. Iron supplementation: Overcoming technical and practical barriers. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 853S–855S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirve, S.; Bhave, S.; Bavdekar, A.; Naik, S.; Pandit, A.; Schauer, C.; Christofides, A.; Hyder, Z.; Zlotkin, S. Low dose ‘Sprinkles’—An innovative approach to treat iron deficiency anemia in infants and young children. Indian Pediatr. 2007, 44, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hyder, S.M.; Persson, L.A.; Chowdhury, A.M.; Ekström, E.C. Do side-effects reduce compliance to iron supplementation? A study of daily- and weekly-dose regimens in pregnancy. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2002, 20, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Reffitt, D.M.; Burden, T.J.; Seed, P.T.; Wood, J.; Thompson, R.P.; Powell, J.J. Assessment of iron absorption from ferric trimaltol. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2000, 37 Pt 4, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salnikow, K. Role of iron in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 76, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pein, M.; Preis, M.; Eckert, C.; Kiene, F.E. Taste-masking assessment of solid oral dosage forms--a critical review. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbari, A.; Fadaei, F.; Salehi, M.; Farahani, R.M.; Piryaei, A.; Heidari, M.H.; Nourozian, M.; Mansouri, V. A simple method for generating small calcium-alginate beads by syringe. J. Histotechnol. 2014, 37, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.H.; Lila, A.S.A.; Unissa, R.; Elsewedy, H.S.; Elghamry, H.A.; Soliman, M.S. Brucine-Loaded Ethosomal Gel: Design, Optimization, and Anti-inflammatory Activity. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.S.; Kumar, T.P. Characterization of Orodispersible Films: An Overview of Methods and Introduction to a New Disintegration Test Apparatus Using LDR—LED Sensors. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2925–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwa, B.; Moin, A.; Gowda, D.V.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Khafagy, E.S.; Allam, A.N. Pulmonary Targeting of Inhalable Moxifloxacin Microspheres for Effective Management of Tuberculosis. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgogna, M.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Paoletti, S.; Donati, I. On the initial binding of alginate by calcium ions. The tilted egg-box hypothesis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 7277–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brniak, W.; Maślak, E.; Jachowicz, R. Orodispersible films and tablets with prednisolone microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krampe, R.; Visser, J.C.; Frijlink, H.W.; Breitkreutz, J.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Preis, M. Oromucosal film preparations: Points to consider for patient centricity and manufacturing processes. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.F.; Silva, C.; Coelho, J.F.; Simões, S. Outlining critical quality attributes (CQAs) as guidance for the development of orodispersible films. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, J.C.; Dohmen, W.M.; Hinrichs, W.L.; Breitkreutz, J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Woerdenbag, H.J. Quality by design approach for optimizing the formulation and physical properties of extemporaneously prepared orodispersible films. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadra, I.; Obeid, M.A.; Dunn, C.; Watts, S.; Halbert, G.; Ford, S.; Mullen, A. Characterisation and optimisation of diclofenac sodium orodispersible thin film formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Batch No. | Ferric Saccharate (% w/v) | Sodium Alginate (% w/v) | Calcium Acetate (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 35 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| P2 | 35 | 3.0 | 1.0 |
| Ingredients | Composition% w/w | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | |
| Microencapsulated iron | 30.833 | 28.462 | 29.600 | 27.407 | 25.517 | 24.667 |
| Pullulan | 35.833 | 36.154 | 37.600 | 34.815 | 32.414 | 29.333 |
| Beta cyclodextrin | - | - | - | - | 13.793 | 13.333 |
| Zinc lactate | - | 3.846 | - | - | - | - |
| DCP (Dicalcium Phosphate) | 4.167 | 3.846 | - | - | - | - |
| Mannitol | 4.267 | 3.131 | 4.136 | 2.348 | 3.241 | 3.533 |
| Glucose | 4.167 | 3.846 | 4.000 | 3.704 | 3.448 | 3.333 |
| Fructose | 4.167 | 0.615 | 4.000 | 3.704 | 3.448 | 3.333 |
| Steviose 100 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.533 |
| Stevirome 5000 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.200 |
| Steviol glycosides | 0.667 | 3.846 | 0.640 | 0.593 | 0.828 | - |
| Calcium CMC | 4.167 | 0.769 | 4.000 | 3.704 | 3.448 | 3.333 |
| PEG 600 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.333 |
| Sorbitol 70% | - | - | - | - | - | 2.667 |
| Glycerol Triacetate | - | 0.769 | 0.800 | 0.741 | 1.379 | - |
| Tween 80 | 0.833 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lecithin | 1.500 | 0.769 | 1.440 | 1.333 | 1.379 | 2.667 |
| ascorbic acid | 0.125 | 0.769 | 0.080 | 0.074 | 0.069 | 0.067 |
| Malic acid | - | 3.077 | 3.200 | 2.963 | 2.759 | 2.667 |
| Glycerol | 4.167 | 3.846 | 4.000 | 3.704 | 2.759 | - |
| Glycerol oleate | 0.108 | 0.100 | 0.104 | 0.096 | - | - |
| Grape flavor | 5.000 | 6.154 | 6.400 | 5.926 | - | - |
| Kiwi flavor | - | - | - | 8.889 | 5.517 | 8.000 |
| Item | Batches | |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | |
| % Fe | 7.5 | 8.0 |
| % Ca | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| Name of the Element | Iron Microparticles (%) | Pullulan-Based Iron Orodispersible Film (%) |
|---|---|---|
| C | 11.5 | 39.5 |
| O | 19.1 | 53.2 |
| P | - | 0.5 |
| Ca | 6.8 | 1.0 |
| Fe | 60.2 | 5.8 |
| Al | 1.0 | - |
| Si | 1.4 | - |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| Parameter | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight variation (mg) | 145 ± 4.0 | 145 ± 5.0 | 140 ± 5.0 | 150 ± 4.0 | 150 ± 5.0 | 150 ± 3.0 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| Folding endurance | 100 ± 5.0 | 115 ± 5.0 | 110 ± 5.0 | 105 ± 5.0 | 100 ± 5.0 | 120 ± 5.0 |
| Surface pH | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 0.2 |
| Disintegration time (s) | 41 ± 3.0 | 41 ± 2.0 | 40 ± 5.0 | 40 ± 3.0 | 25 ± 1.0 | 23 ± 2.0 |
| Tensile strength (g/cm2) | 162 ± 0.31 | 160 ± 0.74 | 159 ± 0.11 | 167 ± 0.74 | 163 ± 0.16 | 165 ± 0.35 |
| Dissolution release profile | 86.50 ± 0.27 | 88.32 ± 0.53 | 90.25 ± 0.10 | 91.30 ± 0.17 | 95.17 ± 0.55 | 98.33 ± 0.35 |
| Parameter | Optimized Formulation (F6) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh | 30 Days | 60 Days | 90 Days | |
| Drug content | 99.4 ± 0.72 | 99.1 ± 0.54 | 98.7 ± 0.39 | 98.5 ± 0.45 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.1 5± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| Folding endurance | 120 ± 5.0 | 122 ± 3.0 | 124 ± 3.0 | 125 ± 2.0 |
| Surface pH | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 6.6± 0.1 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.4 ± 0.5 |
| Disintegration time (s) | 23 ± 2.0 | 23 ± 2.0 | 24 ± 1.0 | 24 ± 3.0 |
| Dissolution profile (%) | 98.3 ± 0.35 | 98.5 ± 0.23 | 98.4 ± 0.42 | 98.4 ± 0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, M.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Reddy, D.; Pathak, K.; Gowda, D.V.; Babu, A.V.N.; Aodah, A.H.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Alotaibi, H.F.; Abu Lila, A.S.; et al. Development and Characterization of Pullulan-Based Orodispersible Films of Iron. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031027
Gupta MS, Kumar TP, Reddy D, Pathak K, Gowda DV, Babu AVN, Aodah AH, Khafagy E-S, Alotaibi HF, Abu Lila AS, et al. Development and Characterization of Pullulan-Based Orodispersible Films of Iron. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031027
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Maram Suresh, Tegginamath Pramod Kumar, Dinesh Reddy, Kamla Pathak, Devegowda Vishakante Gowda, A. V. Naresh Babu, Alhussain H. Aodah, El-Sayed Khafagy, Hadil Faris Alotaibi, Amr Selim Abu Lila, and et al. 2023. "Development and Characterization of Pullulan-Based Orodispersible Films of Iron" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031027
APA StyleGupta, M. S., Kumar, T. P., Reddy, D., Pathak, K., Gowda, D. V., Babu, A. V. N., Aodah, A. H., Khafagy, E.-S., Alotaibi, H. F., Abu Lila, A. S., Moin, A., & Hussin, T. (2023). Development and Characterization of Pullulan-Based Orodispersible Films of Iron. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031027











