Solubility and Physical Stability Enhancement of Loratadine by Preparation of Co-Amorphous Solid Dispersion with Chlorpheniramine and Polyvinylpyrrolidone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Amorphous and Co-Amorphous Materials
2.3. Preparation of Solid Dispersions and Physical Mixtures
2.4. Solubility Studies
2.5. DSC Analysis
2.6. XRPD Analysis
2.7. FT-IR Analysis
2.8. Dissolution Studies
2.9. HPLC Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Outer Appearance of the Samples
3.2. Solubility of LRD
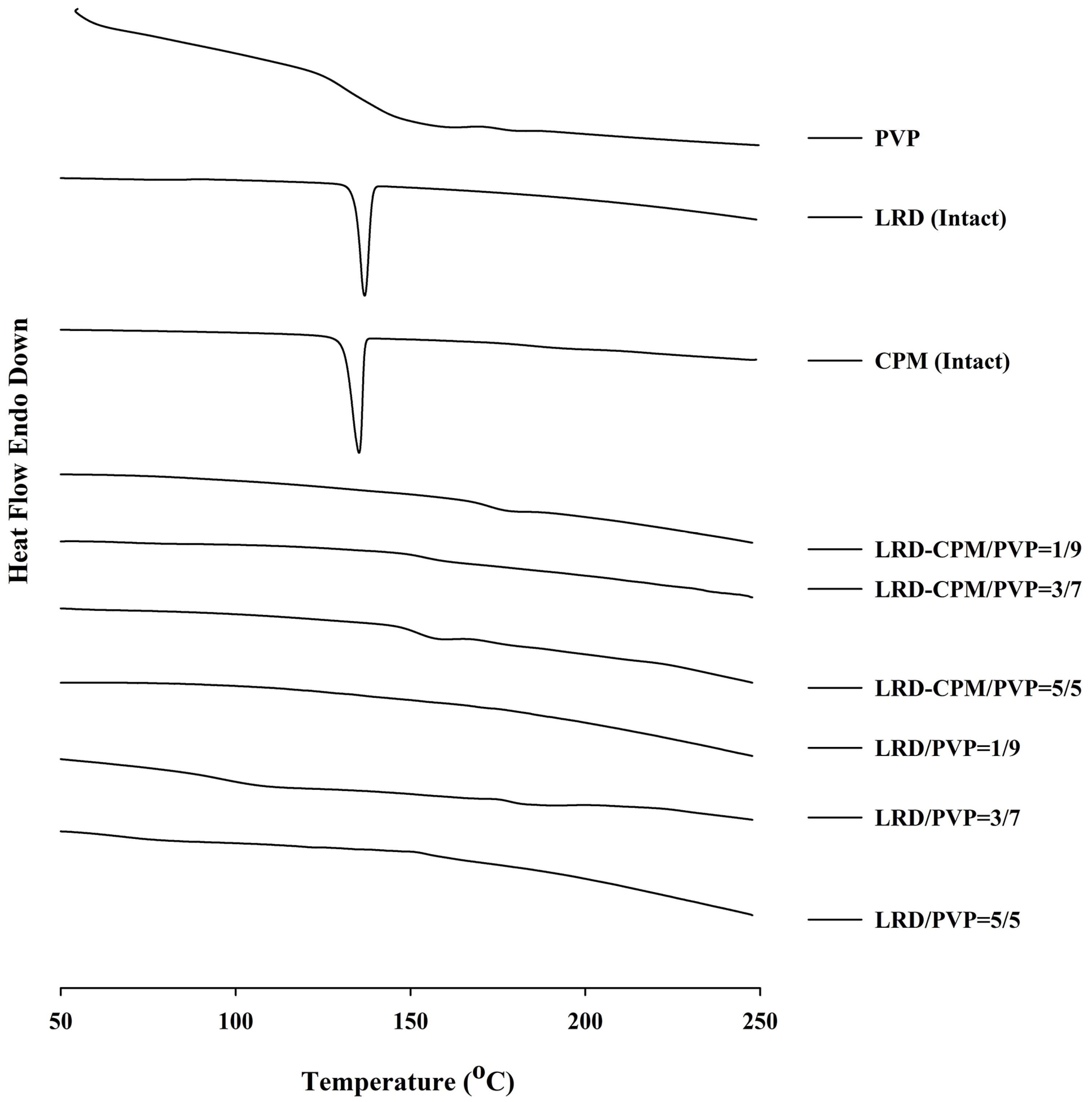
3.3. DSC Analysis
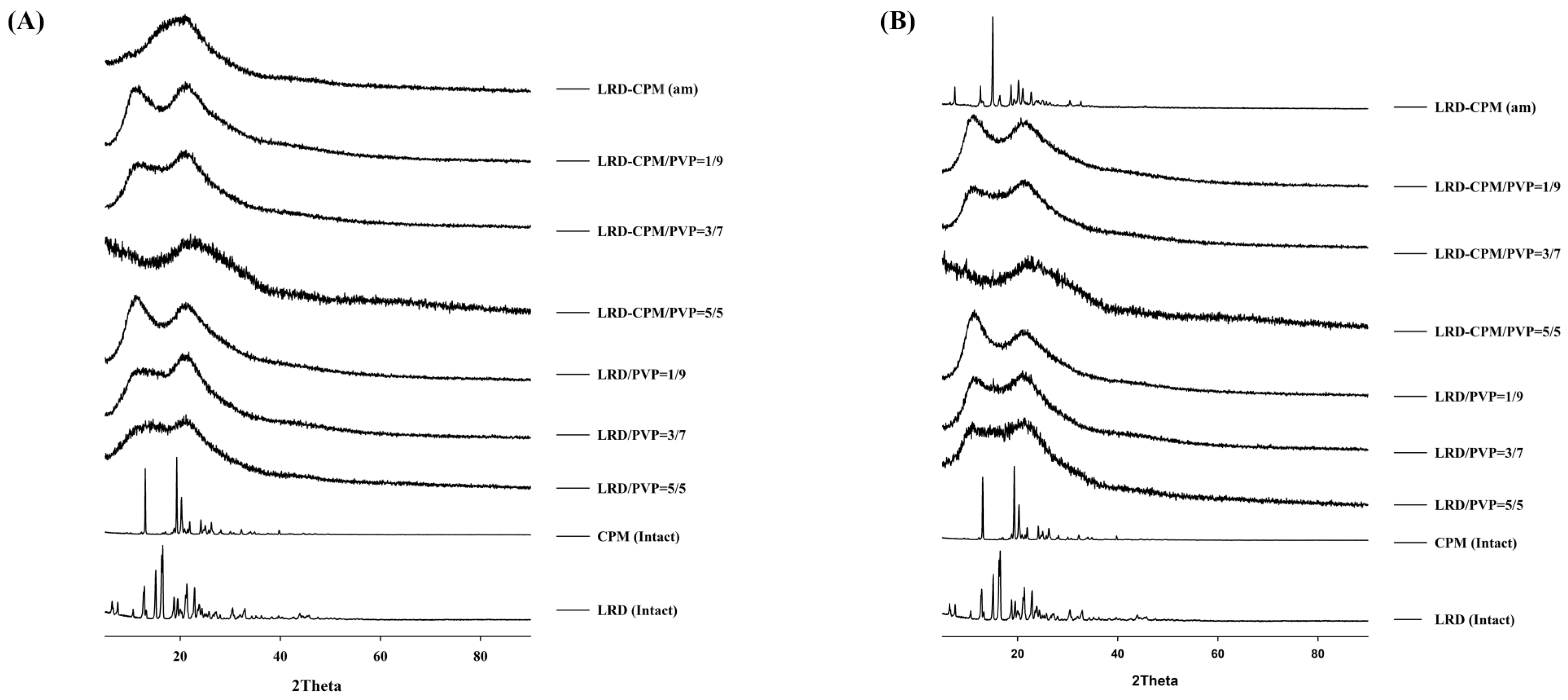
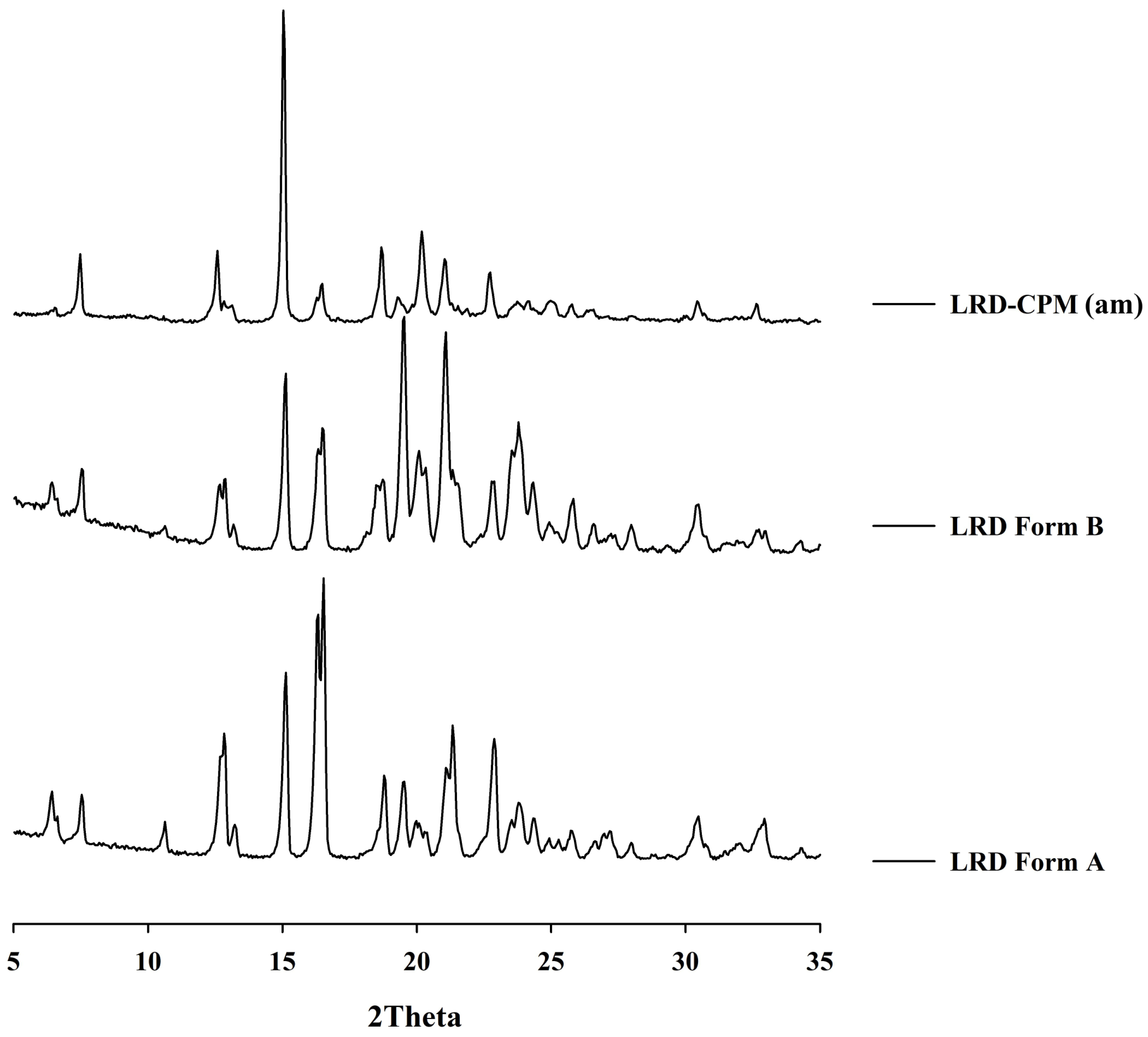
3.4. XRPD Analysis
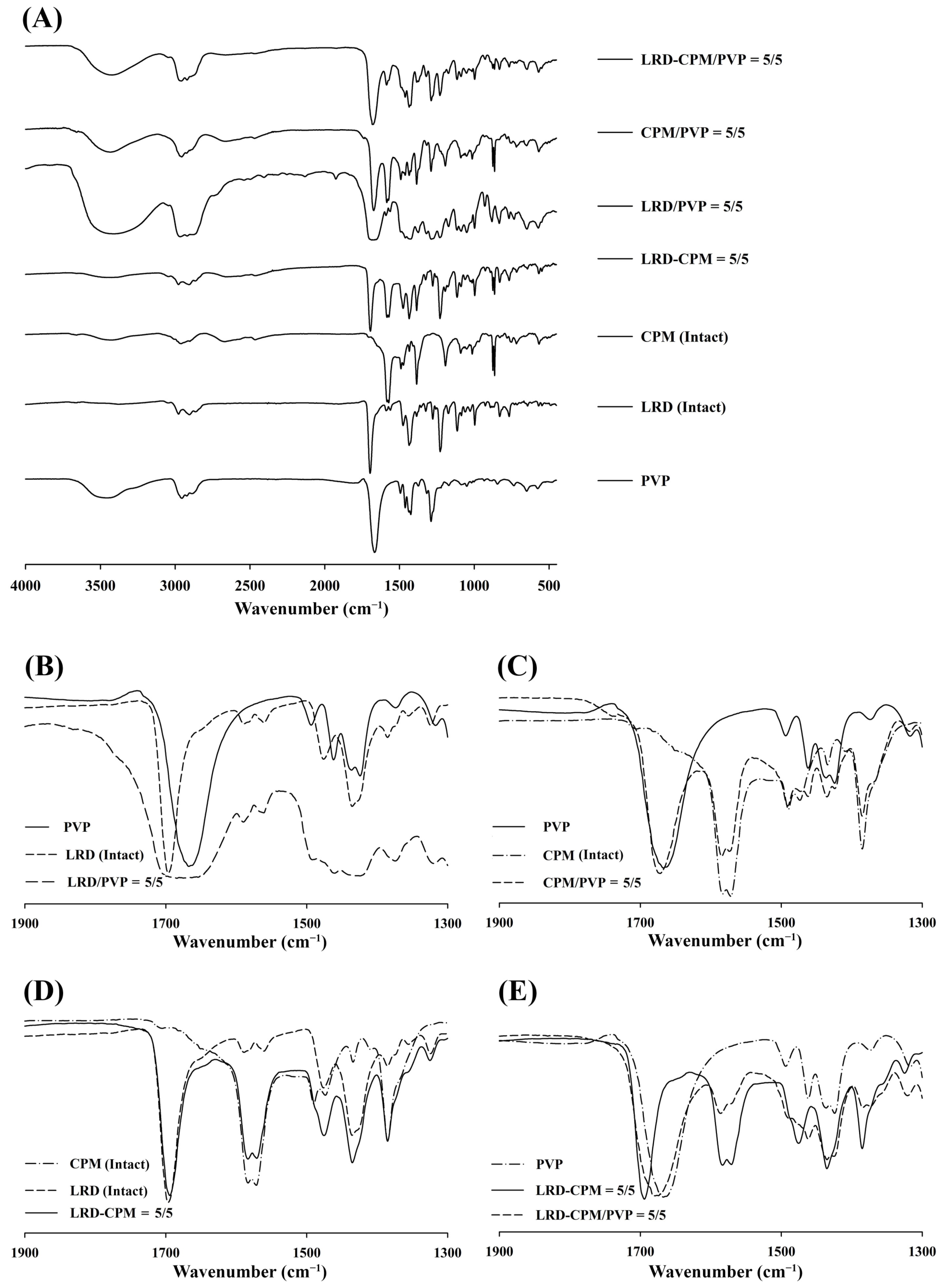
3.5. FT-IR Analysis
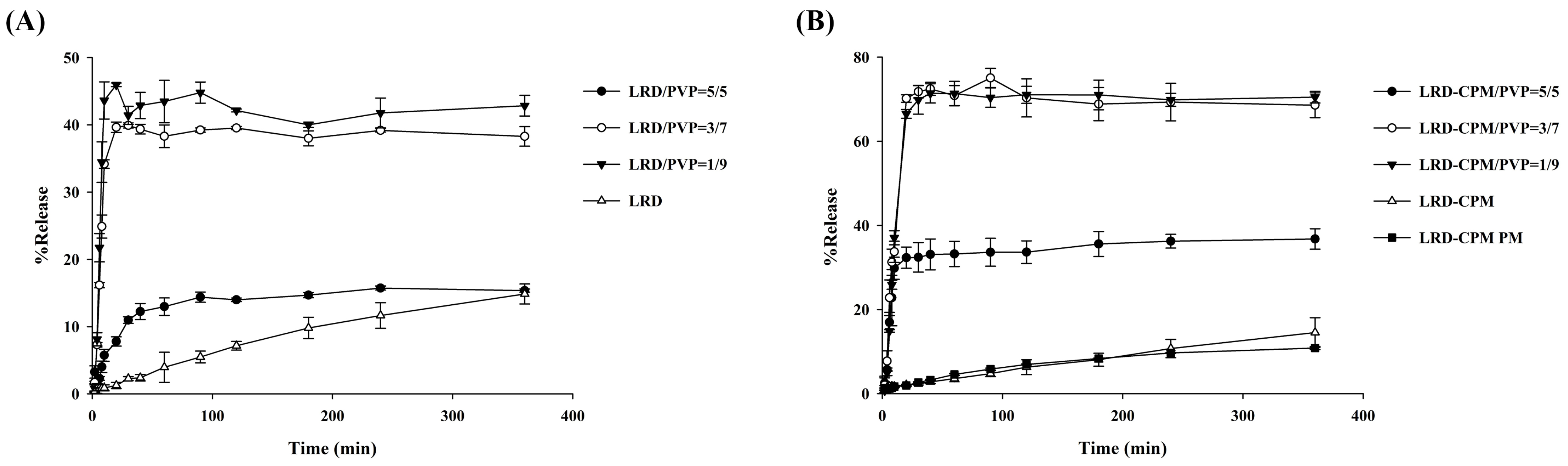
3.6. Dissolution Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sosnik, A.; Augustine, R. Challenges in oral drug delivery of antiretrovirals and the innovative strategies to overcome them. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 103, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benes, M.; Pekarek, T.; Beranek, J.; Havlicek, J.; Krejcik, L.; Simek, M.; Tkadlecova, M.; Dolezal, P. Methods for the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions—A comparative study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suknuntha, K.; Jones, D.S.; Tantishaiyakul, V. Properties of felodipine-poly(vinylpyrrolidone) solid dispersion films and the impact of solvents. Sci. Asia 2012, 38, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pandey, M.M.; Jaipal, A.; Charde, S.Y.; Goel, P.; Kumar, L. Dissolution enhancement of felodipine by amorphous nanodispersions using an amphiphilic polymer: Insight into the role of drug-polymer interactions on drug dissolution. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2016, 21, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.; Mohapatra, S.; Gopinath, T.; Vogt, F.G.; Suryanarayanan, R. Role of the strength of drug-polymer interactions on the molecular mobility and crystallization inhibition in ketoconazole solid dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3339–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khougaz, K.; Clas, S.D. Crystallization inhibition in solid dispersions of MK-0591 and poly(vinylpyrrolidone) polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H.; Atef, E. Amorphous stabilization and dissolution enhancement of amorphous ternary solid dispersions: Combination of polymers showing drug-polymer interaction for synergistic effects. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3511–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bley, H.; Fussnegger, B.; Bodmeier, R. Characterization and stability of solid dispersions based on PEG/polymer blends. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, S.; de Armas, H.N.; D’Autry, W.; Van Schepdael, A.; Van den Mooter, G. Characterization of ternary solid dispersions of Itraconazole in polyethylene glycol 6000/polyvidone-vinylacetate 64 blends. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.B.; Thipparaboina, R.; Kumar, D.; Shastri, N.R. Co amorphous systems: A product development perspective. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, K.; Mannava, M.K.C.; Nangia, A. A novel curcumin-artemisinin coamorphous solid: Physical properties and pharmacokinetic profile. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 58357–58361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobmann, K.; Strachan, C.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Korhonen, O.; Laitinen, R. Co-amorphous simvastatin and glipizide combinations show improved physical stability without evidence of intermolecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Grohganz, H.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T.; Gordon, K.C. A theoretical and spectroscopic study of co-amorphous naproxen and indomethacin. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, E.; Lobmann, K.; Rades, T.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. Hot melt extrusion and spray drying of co-amorphous indomethacin-arginine with polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengale, S.J.; Ranjan, O.P.; Hussen, S.S.; Krishna, B.S.M.; Musmade, P.B.; Shenoy, G.G.; Bhat, K. Preparation and characterization of co-amorphous Ritonavir-Indomethacin systems by solvent evaporation technique: Improved dissolution behavior and physical stability without evidence of intermolecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 62, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengale, S.J.; Hussen, S.S.; Krishna, B.S.M.; Musmade, P.B.; Shenoy, G.G.; Bhat, K. Fabrication, solid state characterization and bioavailability assessment of stable binary amorphous phases of Ritonavir with Quercetin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.W.; Zechnich, A.D.; Haxby, D.G. Second-generation antihistamines: A comparative review. Drugs 1999, 57, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Rausl, D.; Zanoski, R.; Zidar, S.; Mikulcic, J.H.; Krizmanic, L.; Eskinja, M.; Mildner, B.; Knezevic, Z. Classification of loratadine based on the biopharmaceutics drug classification concept and possible in vitro-in vivo correlation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizon, F.; Eloy, J.D.; Donaduzzi, C.M.; Mitsui, M.L.; Marchetti, J.M. Dissolution rate enhancement of loratadine in polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions by solvent methods. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.A.; Taylor, L.S. Evaluation and modeling of the eutectic composition of various drug-polyethylene glycol solid dispersions. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2011, 16, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, L.; El-Barghouthi, M.I.; Masoud, N.A.; Abdoh, A.A.; Al Omari, M.M.; Zughul, M.B.; Badwan, A.A. Inclusion complexation of loratadine with natural and modified cyclodextrins: Phase solubility and thermodynamic studies. J. Solut. Chem. 2007, 36, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandari, S.; Jadav, S.; Eedara, B.B.; Jukanti, R.; Veerareddy, P.R. Physicochemical characterization and dissolution enhancement of loratadine by solid dispersion technique. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haria, M.; Fitton, A.; Peters, D.H. Loratadine. A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in allergic disorders. Drugs 1994, 48, 617–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, M.; Hirsh, J.; Rariy, R. Antihistamine Combination 2008. U.S. Patent No 20080207593A1, 28 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. Loratadine USP35-NF30. In USP36-NF31 (The United States Pharmacopeial Convention); United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2013; pp. 4143–4144. ISBN 0195-7996. [Google Scholar]
- Gala, D.; DiBenedetto, D.J. Ethyl 4-(8-chloro-5,6-dihydro-11 H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-ylidene)-1-piperidene Carboxylate Polymorph. U.S. Patent No 6335347, 1 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Khunt, M.D.; Keshava, N.K.R.; Madduri, S.R.; Sripathi, S.S.; Valluri, S. Preparation of loratadine form i. U.S. Patent No 11/696391, 4 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, R.; Fu, Q.; Yu, P.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Du, W.; Chang, C.; Zeng, A. A new polymorphic form and polymorphic transformation of loratadine. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85063–85073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhart, C.G.; McCorkle, T. Chlorpheniramine maleate. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Florey, K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978; Volume 7, pp. 43–80. ISBN 0099-5428. [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dai, W.-G. Fundamental aspects of solid dispersion technology for poorly soluble drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, R.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y.; Chen, L.; Pan, H.; Yang, X.; Pan, W.; et al. Analysis of the literature and patents on solid dispersions from 1980 to 2015. Molecules 2018, 23, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T. Amino acids as co-amorphous stabilizers for poorly water soluble drugs—Part 1: Preparation, stability and dissolution enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.J.; Woo, M.R.; Choi, H.G.; Jin, S.G. Effects of polymers on the drug solubility and dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble rivaroxaban. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, G.P.; AbuDiak, O.A.; Jones, D.S. Physicochemical characterization of hot melt extruded bicalutamide–polyvinylpyrrolidone solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, K.; Berghmans, H.; Leuner, C.; Dressman, J.; Van Werde, K.; Mullens, J.; Benoist, L.; Thimon, M.; Meublat, L.; Verreck, G.; et al. Characterization of solid dispersions of itraconazole and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose prepared by melt extrusion, part II. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.T.; Larsen, F.H.; Löbmann, K.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Influence of variation in molar ratio on co-amorphous drug-amino acid systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 107, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuk, S.E.; Zubaidullina, L.S.; Ziganshin, M.A.; Mukhametzyanov, T.A.; Schick, C.; Gerasimov, A.V. Kinetic stability of amorphous solid dispersions with high content of the drug: A fast scanning calorimetry investigation. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria Ortiz, K.; Hernández Espinell, J.R.; Ortiz Torres, D.; López-Mejías, V.; Stelzer, T. Polymorphism in solid dispersions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 20, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Gajda, M.; Baranowski, P.; Szymczyk, P.; Karolewicz, B.; Nartowski, K.P. Stabilisation and growth of metastable form II of fluconazole in amorphous solid dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2019, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Amino acids as co-amorphous stabilizers for poorly water-soluble drugs—Part 2: Molecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinarong, P.; Kouwen, S.; Visser, M.R.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Frijlink, H.W. Effect of drug-carrier interaction on the dissolution behavior of solid dispersion tablets. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2010, 15, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterren, V.B.; Aiassa, V.; Garnero, C.; Linck, Y.G.; Chattah, A.K.; Monti, G.A.; Longhi, M.R.; Zoppi, A. Preparation of chloramphenicol/amino acid combinations exhibiting enhanced dissolution rates and reduced drug-induced oxidative stress. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2017, 18, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Samples | Solubility * (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Mixture | Solid Dispersion | |
| LRD/PVP = 5/5 | 4.30 ± 0.86 | 7.97 ± 0.33 |
| LRD/PVP = 3/7 | 4.95 ± 1.10 | 17.60 ± 5.24 |
| LRD/PVP = 1/9 | 13.84 ± 1.76 | 37.63 ± 7.41 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 5/5 | 5.71 ± 0.42 | 62.37 ± 16.96 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 3/7 | 13.87 ± 7.85 | 84.47 ± 12.21 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 1/9 | 12.34 ± 7.78 | 195.03 ± 13.44 |
| Samples | Tg * (°C) |
|---|---|
| LRD/PVP = 5/5 | 158.17 |
| LRD/PVP = 3/7 | 179.50 |
| LRD/PVP = 1/9 | 184.72 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 5/5 | 150.70 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 3/7 | 154.98 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 1/9 | 172.33 |
| Sample | First-Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | Hixson–Crowell | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | r2 | k | r2 | n | k | r2 | k | r2 | |
| LRD (intact) | 0.0007 | 0.808 | 0.464 | 0.734 | 0.62 | 0.241 | 0.763 | 0.0002 | 0.806 |
| CM (intact) | 0.0006 | 0.249 | 0.487 | 0.827 | 0.28 | 0.937 | 0.823 | 0.0002 | 0.244 |
| LRD/PVP = 5/5 | 0.0024 | 0.575 | 1.675 | 0.908 | 0.68 | 1.025 | 0.925 | 0.0008 | 0.555 |
| LRD/PVP = 3/7 | 0.0109 | 0.102 | 5.737 | 0.516 | 0.49 | 7.667 | 0.778 | 0.0031 | 0.242 |
| LRD/PVP = 1/9 | 0.0137 | 0.250 | 6.561 | 0.363 | 0.42 | 1.082 | 0.642 | 0.0038 | 0.420 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 5/5 | 0.0084 | 0.322 | 4.902 | 0.445 | 0.44 | 7.451 | 0.708 | 0.0025 | 0.439 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 3/7 | 0.0377 | 0.832 | 9.984 | 0.766 | 0.66 | 7.365 | 0.889 | 0.0111 | 0.763 |
| LRD-CPM/PVP = 1/9 | 0.0339 | 0.824 | 9.593 | 0.760 | 0.71 | 5.904 | 0.886 | 0.0100 | 0.756 |
| Physical mixture = 5/5 | 0.0008 | 0.775 | 0.558 | 0.924 | 0.44 | 0.606 | 0.805 | 0.0003 | 0.771 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suknuntha, K.; Khumpirapang, N.; Tantishaiyakul, V.; Okonogi, S. Solubility and Physical Stability Enhancement of Loratadine by Preparation of Co-Amorphous Solid Dispersion with Chlorpheniramine and Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112558
Suknuntha K, Khumpirapang N, Tantishaiyakul V, Okonogi S. Solubility and Physical Stability Enhancement of Loratadine by Preparation of Co-Amorphous Solid Dispersion with Chlorpheniramine and Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(11):2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112558
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuknuntha, Krit, Nattakanwadee Khumpirapang, Vimon Tantishaiyakul, and Siriporn Okonogi. 2023. "Solubility and Physical Stability Enhancement of Loratadine by Preparation of Co-Amorphous Solid Dispersion with Chlorpheniramine and Polyvinylpyrrolidone" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 11: 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112558
APA StyleSuknuntha, K., Khumpirapang, N., Tantishaiyakul, V., & Okonogi, S. (2023). Solubility and Physical Stability Enhancement of Loratadine by Preparation of Co-Amorphous Solid Dispersion with Chlorpheniramine and Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Pharmaceutics, 15(11), 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112558








