Human β-Defensin 23 as a Carrier for In Vitro and In Vivo Delivery of mRNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of hBD23/mRNA Complex
2.3. Characterization of hBD23/mRNA Complex
2.4. Serum Nuclease Resistance
2.5. Cellular Uptake Study
2.6. Intracellular Toxicity and Immunogenicity Assay
2.7. Evaluation of hBD23/mRNA-Mediated Protein Expression
2.8. In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
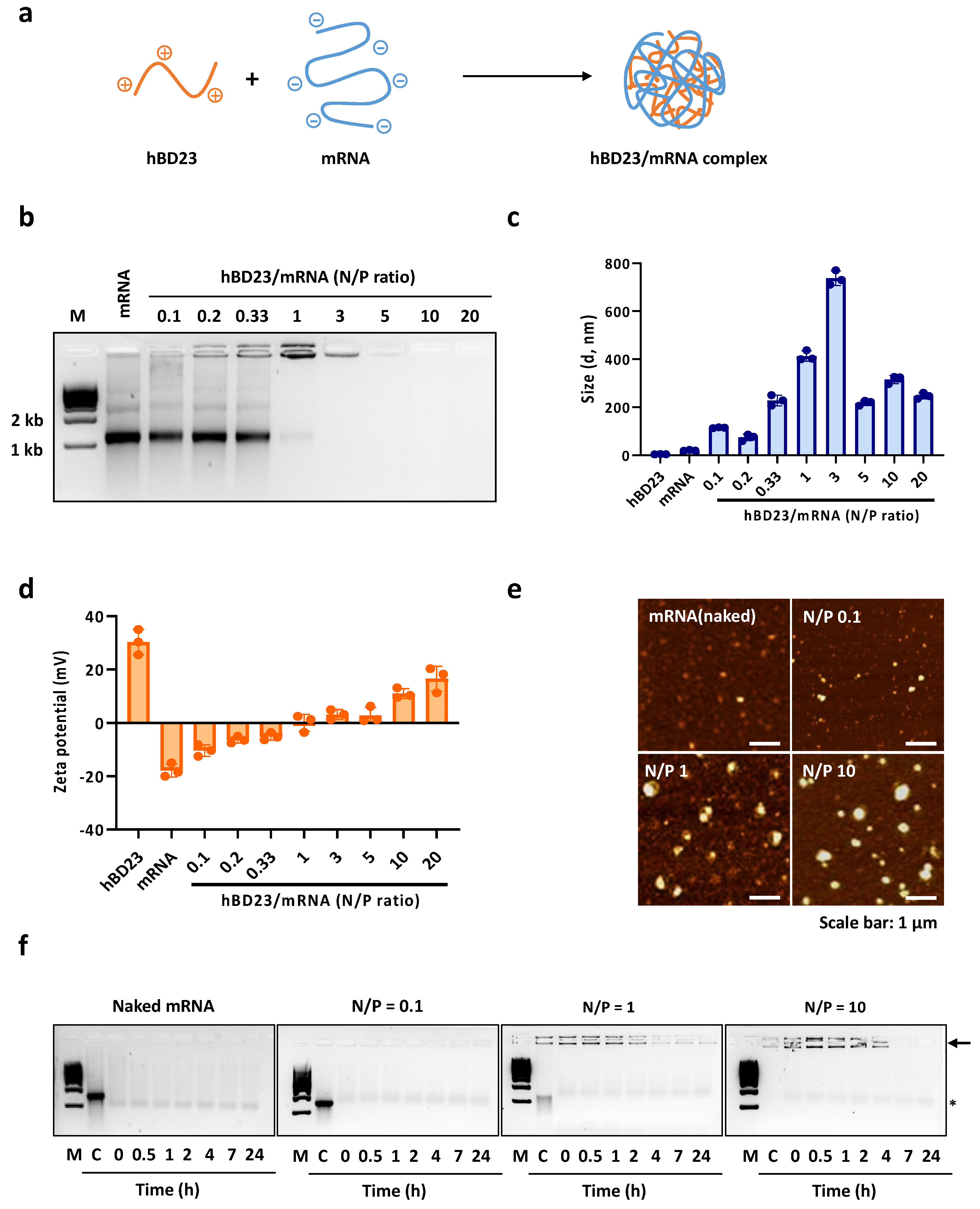
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of hBD23/mRNA Complexes
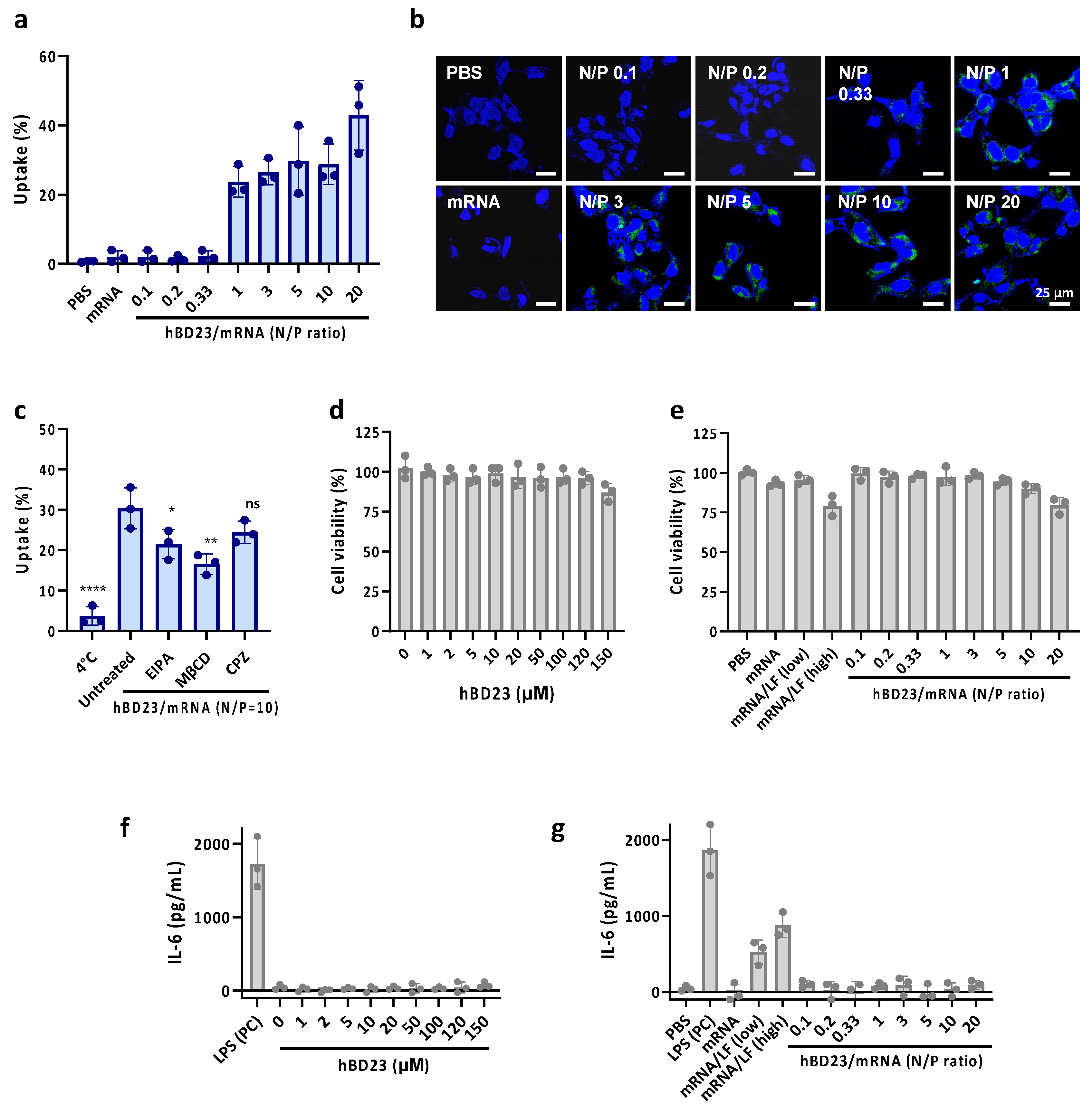
3.2. Cellular Uptake of hBD23/mRNA Complexes
3.3. Cytotoxicity of hBD23/mRNA Complexes
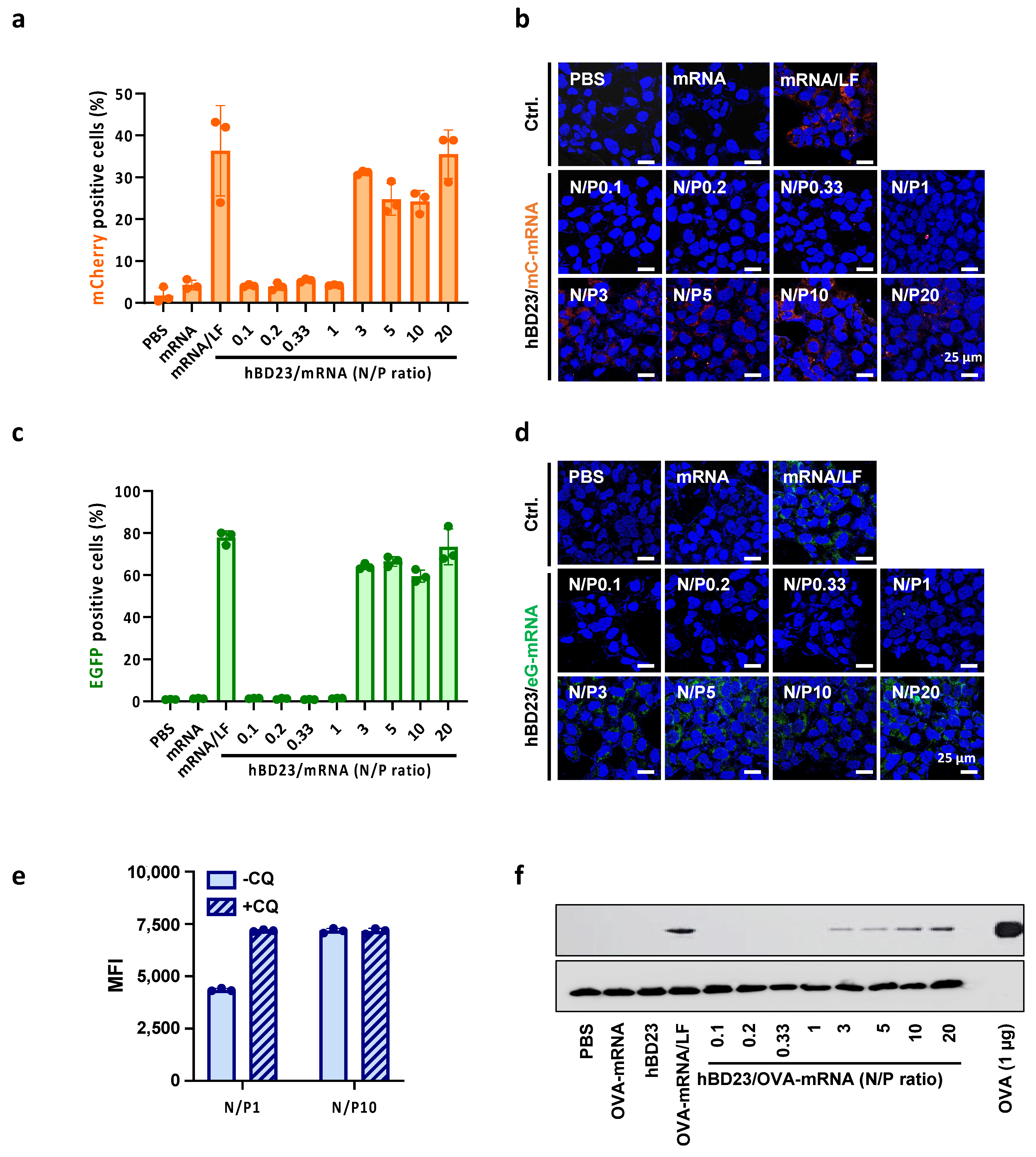
3.4. In Vitro Delivery of hBD23/mRNA Complexes for Protein Expression
3.5. In Vivo Delivery of hBD23/mRNA Complexes for Protein Expression
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohner, E.; Yang, R.; Foo, K.S.; Goedel, A.; Chien, K.R. Unlocking the promise of mRNA therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Wu, W.; Eshan, N.A.; Ma, Y.; Yu, C.; Fenton, O.S.; Song, H. Engineering nanoparticle toolkits for mRNA delivery. Adv. Drug Deli. Rev. 2023, 200, 115042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibba, M.L.; Ciccone, G.; Esposito, C.L.; Catuogno, S.; Giangrande, P.H. Advances in mRNA non-viral delivery approaches. Adv. Drug Deli. Rev. 2021, 177, 113930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, K.; Whitehead, K.A. Tools for translation: Non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Eygeris, Y.; Guptam, M.; Sahay, G. Self-assembled mRNA vaccines. Adv. Drug Deli. Rev. 2021, 170, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Jia, L.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Deng, J.; Zhu, A.; Ma, L.; Li, W.; et al. The nano delivery systems and applications of mRNA. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 227, 113910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Geetha, K.M.J. Lipid nanoparticles in the development of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Vaccines. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/covid-19-vaccines (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. mRNA-liphid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M. Allergic reactions and anaphylaxis to LNP-based COVID-19 vaccines. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copolovici, D.M.; Langel, K.; Eriste, E.; Langel, U. Cell-penetrating pepetides: Design, synthesis, and applications. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1972–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.H.; Park, J.; Koo, H. Recent advances in selective and targeted drug/gene delivery systems using cell-penetrating peptides. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2023, 46, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoo, H.; Oba, M.; Uchida, S. Cell-penetrating peptides: Emerging tools for mRNA delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettinger, T.; Carlisle, R.C.; Read, M.L.; Ogris, M.; Seymour, L.W. Peptide-mediated RNA delivery: A novel approach for enhanced transfection of primary and post-mitotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 3882–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliotou, A.N.; Pappas, I.S.; Spyroulias, G.; Vlachaki, E.; Tsiftsoglou, A.S.; Vizirianakis, I.S.; Papadopoulou, L.C. Development of a novel PTD-mediated IVT-mRNA delivery platform for potential protein replacement therapy of metabolic/genetic disorders. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udhayakumar, V.K.; Beuckelaer, A.; McCaffrey, J.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kirschman, J.L.; Vanover, D.; Hoecke, L.V.; Roose, K.; Deswarte, K.; Geest, B.G.; et al. Arginine-rich peptide-based mRNA nanocomplexes efficiently instigate cytotoxic T cell immunity dependent on the amphipathic organization of the peptide. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, D.; Gorris, M.; Asbeck, A.; Palmen, E.; Ebisch, I.; Dolstra, H.; Hällbrink, M.; Massuger, L.; Brock, R. Peptide-mediated delivery of therapeutic mRNA in ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Man, R.; Liao, Q.; Kung, K.; Chow, M.; Lam, J.K.W. Effective mRNA pulmonary delivery by dry powder formulation of PEGylated synthetic KL4 peptide. J. Control. Release 2019, 314, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porosk, L.; Hark, H.H.; Arukuusk, P.; Haljasorg, U.; Peterson, P.; Kurrikoff, K. The development of cell-penetrating peptides for efficient and selective in vivo expression of mRNA in spleen tissue. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Yum, S.Y.; Goo, J.; Ahn, D.-R. Discovery of a non-cationic cell penetrating peptide derived from membrane-interacting human proteins and its potential as a protein delivery carrier. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11719. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y.; Jang, J.E.; Ahn, D.-R. Dimeric human β-defensin 3 as a universal platform for intracellular delivery of nucleic acid cargos. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeon, S.; Kang, S.J.; Kim, K.-R.; Thai, H.B.D.T.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.-S.; Ahn, D.-R. Lung-targeted delivery of TGF-β antisense oligonucleotides to treat pulmonary fibrosis. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-R.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Ahn, D.-R. Human β-Defensin 23 as a Carrier for In Vitro and In Vivo Delivery of mRNA. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102477
Kim K-R, Kim J, Cho S, Ahn D-R. Human β-Defensin 23 as a Carrier for In Vitro and In Vivo Delivery of mRNA. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(10):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102477
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyoung-Ran, Junghyun Kim, Seunghye Cho, and Dae-Ro Ahn. 2023. "Human β-Defensin 23 as a Carrier for In Vitro and In Vivo Delivery of mRNA" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 10: 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102477
APA StyleKim, K.-R., Kim, J., Cho, S., & Ahn, D.-R. (2023). Human β-Defensin 23 as a Carrier for In Vitro and In Vivo Delivery of mRNA. Pharmaceutics, 15(10), 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102477





