Ultrasound-Responsive Nanobubbles for Combined siRNA-Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Delivery to Bone Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cerium Oxide Colloidal Solution and Fluorescent Labeling
2.3. Nanobubble Preparation and Characterization
2.4. Nanomaterial Characterization
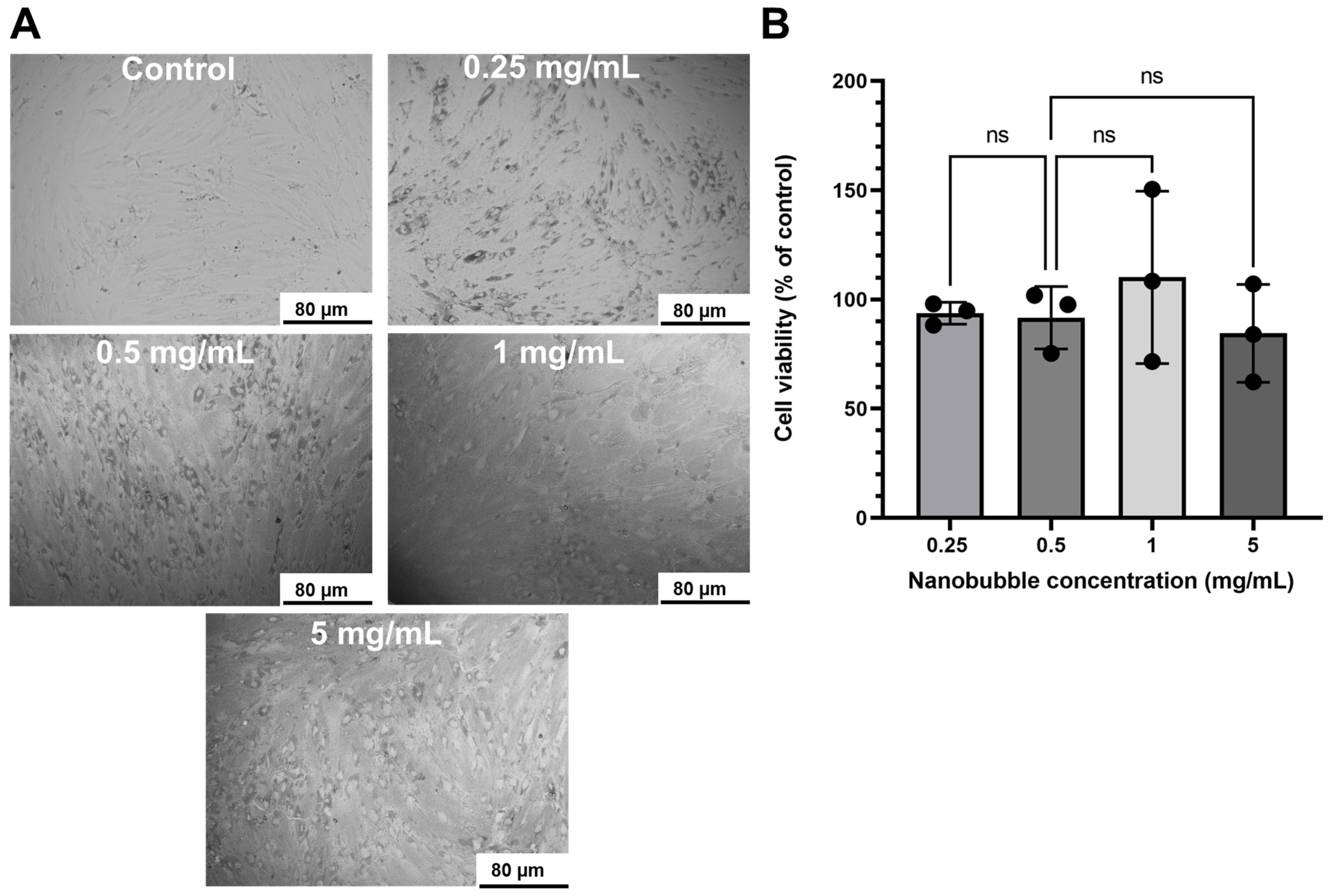
2.5. Cell Toxicity
2.6. In Vitro Mineralization
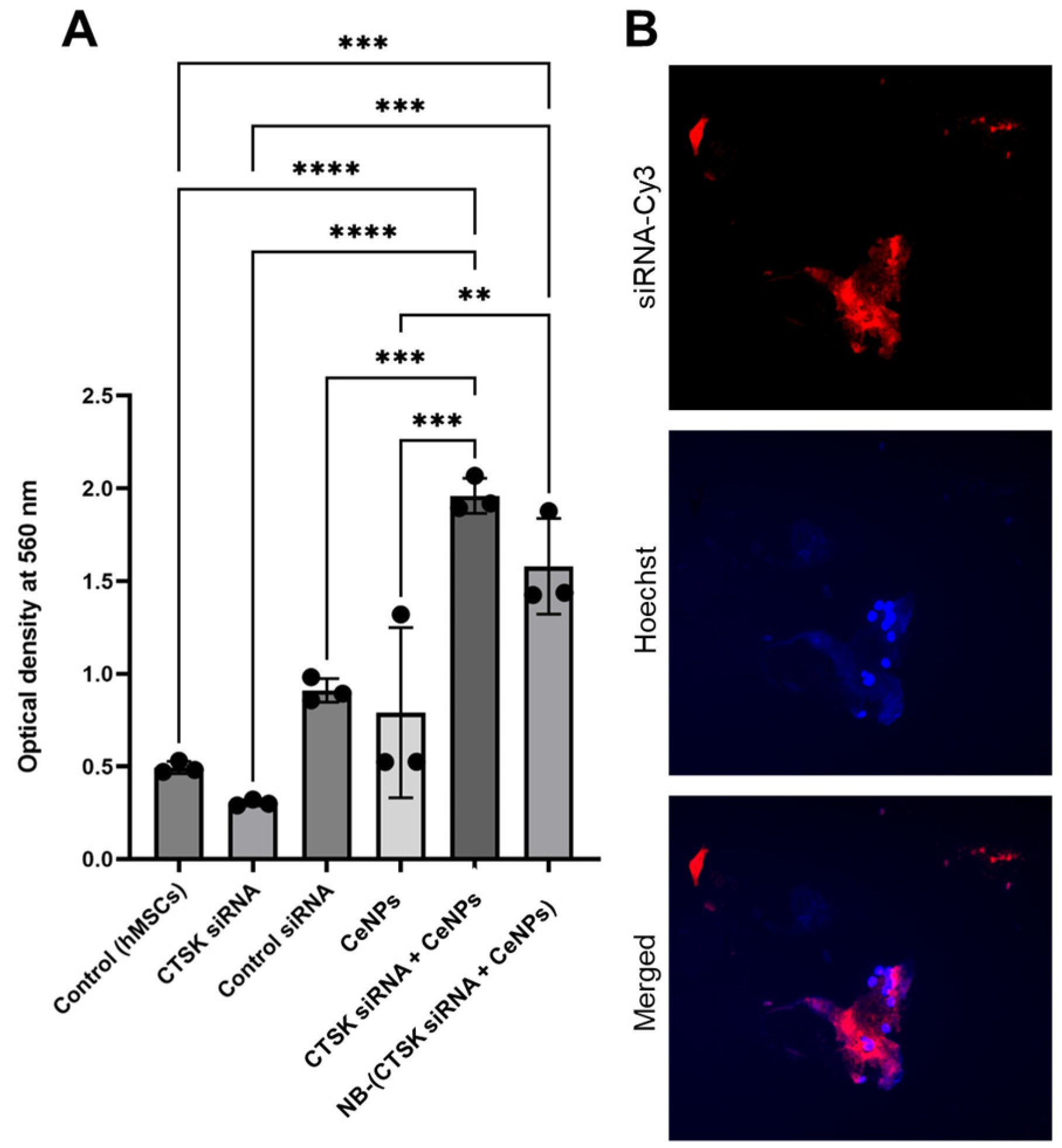
2.7. Cell Internalization
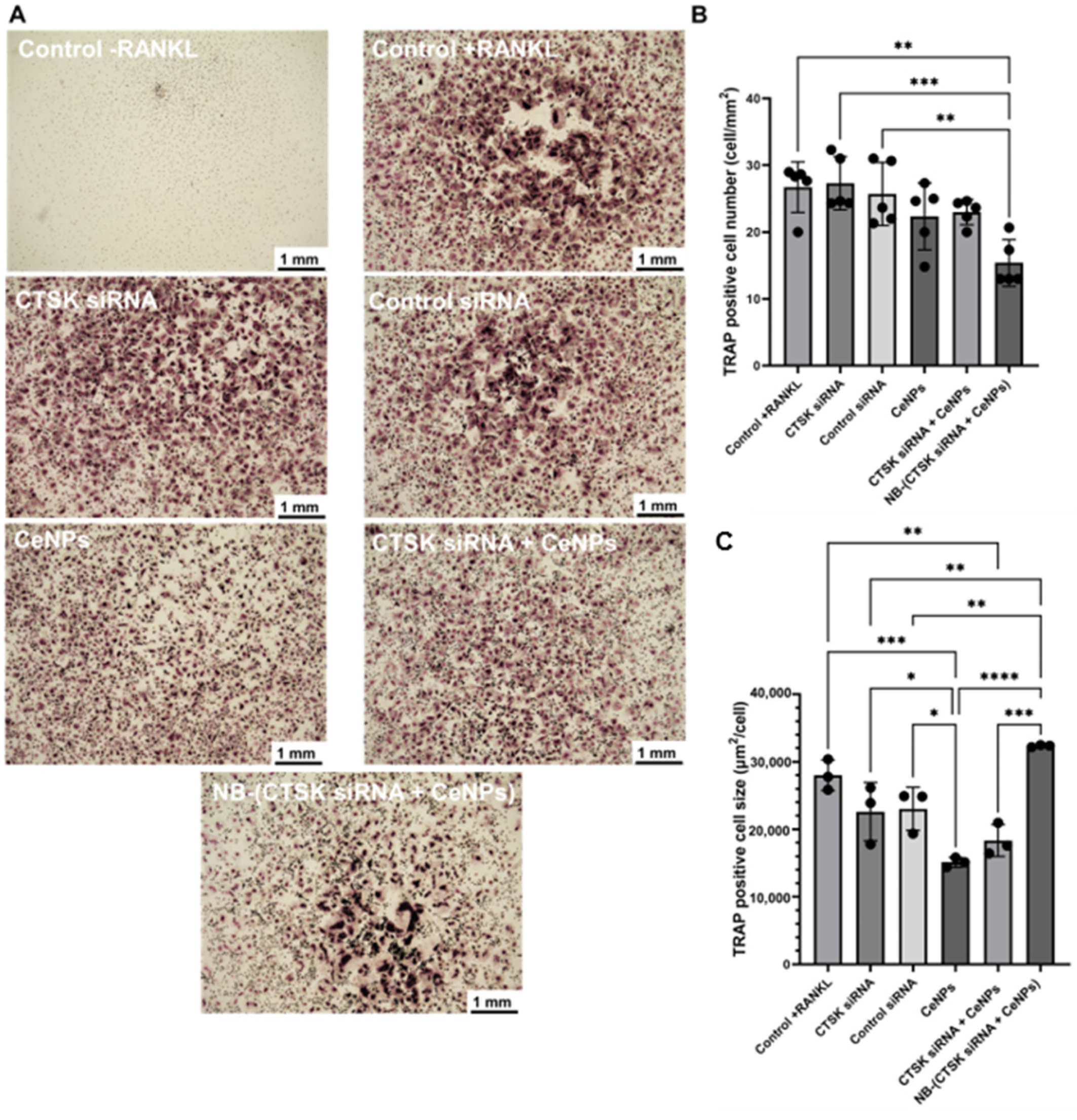
2.8. Osteoclastogenesis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
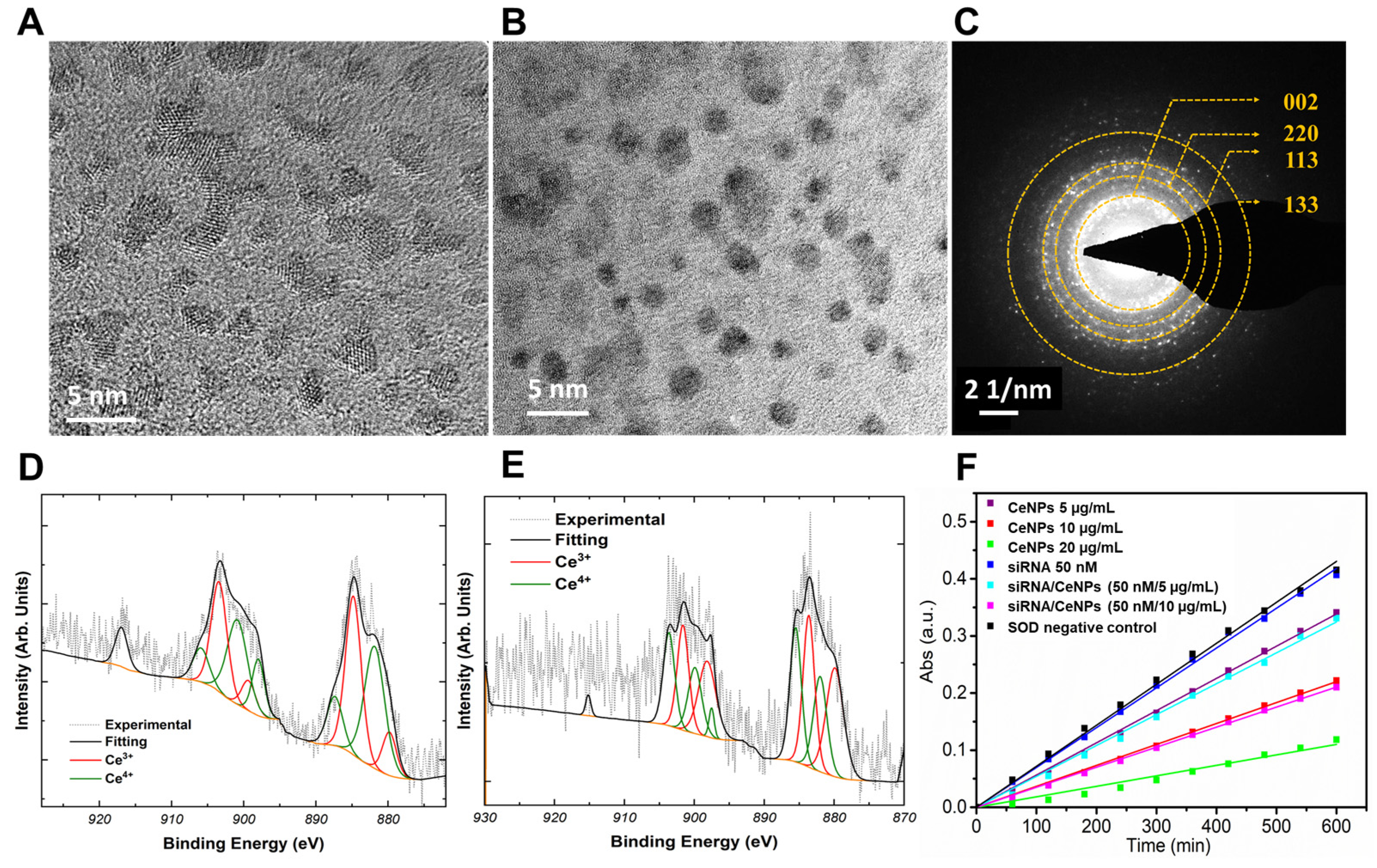
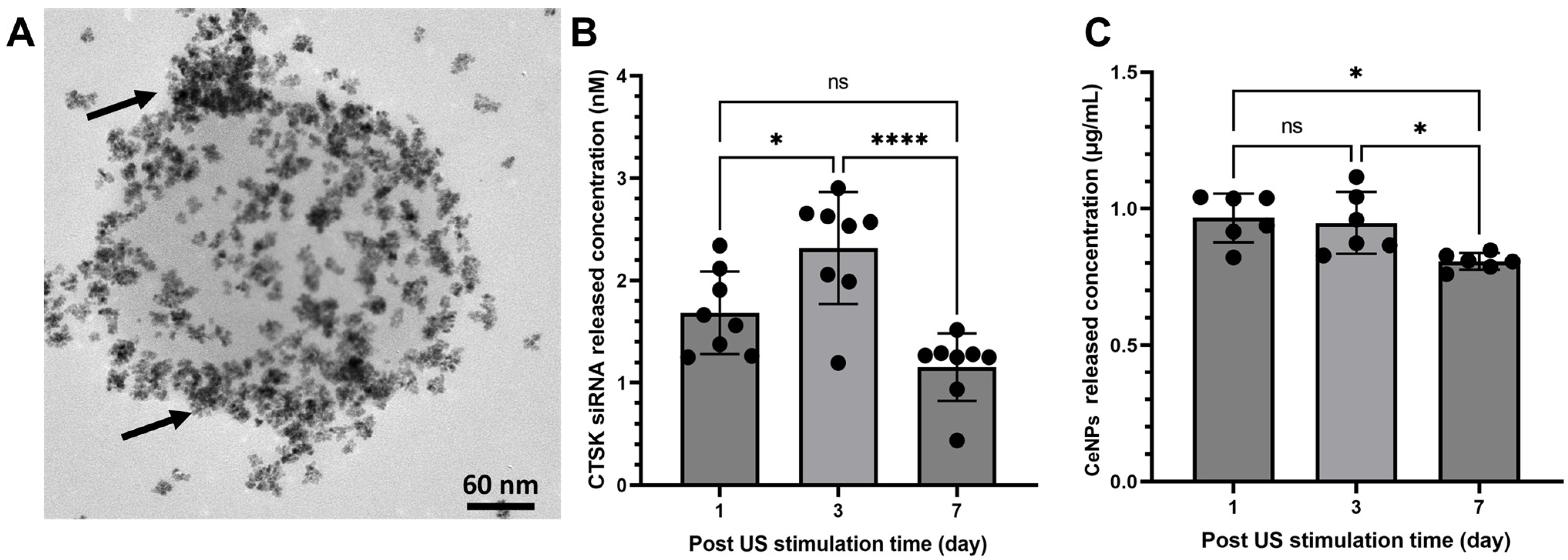
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Compston, J.E.; McClung, M.R.; Leslie, W.D. Osteoporosis. Lancet 2019, 393, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.G.; Xia, Z.; Dunford, J.E.; Oppermann, U.; Kwaasi, A.; Hulley, P.A.; Kavanagh, K.L.; Triffitt, J.T.; Lundy, M.W.; Phipps, R.J.; et al. Bisphosphonates: An update on mechanisms of action and how these relate to clinical efficacy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1117, 209–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.J. Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein, Its Regulation of Cartilage and Bone Development, and Role in Treating Bone Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 831–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.D.; Hattersley, G.; Riis, B.J.; Williams, G.C.; Lau, E.; Russo, L.A.; Alexandersen, P.; Zerbini, C.A.; Hu, M.Y.; Harris, A.G.; et al. Effect of Abaloparatide vs Placebo on New Vertebral Fractures in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuggle, N.R.; Cooper, C.; Harvey, N.C.; Al-Daghri, N.; Brandi, M.L.; Bruyere, O.; Cano, A.; Dennison, E.M.; Diez-Perez, A.; Kaufman, J.M.; et al. Assessment of Cardiovascular Safety of Anti-Osteoporosis Drugs. Drugs 2020, 80, 1537–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.G.; Cusano, N.E.; Silva, B.C.; Cremers, S.; Bilezikian, J.P. Cathepsin K: Its skeletal actions and role as a therapeutic target in osteoporosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statham, L.A.; Aspray, T.J. Odanacatib: The best osteoporosis treatment we never had? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 888–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelke, K.; Nagase, S.; Fuerst, T.; Small, M.; Kuwayama, T.; Deacon, S.; Eastell, R.; Genant, H.K. The effect of the cathepsin K inhibitor ONO-5334 on trabecular and cortical bone in postmenopausal osteoporosis: The OCEAN study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, E.; Rizoska, B.; Henderson, I.; Terelius, Y.; Jerling, M.; Edenius, C.; Grabowska, U. Nonclinical and clinical pharmacological characterization of the potent and selective cathepsin K inhibitor MIV-711. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClung, M.R.; O’Donoghue, M.L.; Papapoulos, S.E.; Bone, H.; Langdahl, B.; Saag, K.G.; Reid, I.R.; Kiel, D.P.; Cavallari, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; et al. Odanacatib for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: Results of the LOFT multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial and LOFT Extension study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; He, X.W.; Shi, Y.H.; Liu, Y.S.; Liu, F.D.; Hu, Y.; Zhuang, M.T.; Feng, X.Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, B.Q.; et al. Cathepsin K Knockout Exacerbates Haemorrhagic Transformation Induced by Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator After Focal Cerebral Ischaemia in Mice. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Grainger, D.W. Developing siRNA therapies to address osteoporosis. Ther. Deliv. 2013, 4, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Nanoparticles to Knockdown Osteoporosis-Related Gene and Promote Osteogenic Marker Expression for Osteoporosis Treatment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Siegwart, D.J.; Anderson, D.G. Strategies, design, and chemistry in siRNA delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zou, S.; Li, M.; Richardson, J.J.; Tardy, B.L.; Xie, L.; Komasa, S.; et al. Hierarchical assembly of nanostructured coating for siRNA-based dual therapy of bone regeneration and revascularization. Biomaterials 2020, 235, 119784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Singh, R.K.; Kang, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.W. Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis through siRNA delivery with tunable mesoporous bioactive nanocarriers. Acta Biomater. 2016, 29, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, L.A.; Trichet, V.; Escriou, V.; Rosset, P.; Amiaud, J.; Battaglia, S.; Charrier, C.; Berreur, M.; Brion, R.; Gouin, F.; et al. Inhibition of osteolysis and increase of bone formation after local administration of siRNA-targeting RANK in a polyethylene particle-induced osteolysis model. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Horie, S.; Funaki, Y.; Kikuchi, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Ishii, K.; Mori, S.; Vassaux, G.; Kodama, T. Delivery of Na/I symporter gene into skeletal muscle using nanobubbles and ultrasound: Visualization of gene expression by PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Kudo, N.; Nakamura, K.; Lim, S.Y.; Murakami, M.; Kumara, W.R.; Tamura, Y.; Ohta, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Takiguchi, M. Ultrasound image-guided therapy enhances antitumor effect of cisplatin. J. Med. Ultrason. (2001) 2014, 41, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Haar, G. Therapeutic applications of ultrasound. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2007, 93, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speed, C.A. Therapeutic ultrasound in soft tissue lesions. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardad, A.Z.; Choonara, Y.E.; Du Toit, L.C.; Kumar, P.; Mabrouk, M.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Pillay, V. A Review of Thermo- and Ultrasound-Responsive Polymeric Systems for Delivery of Chemotherapeutic Agents. Polymers 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crasto, G.J.; Kartner, N.; Reznik, N.; Spatafora, M.V.; Chen, H.; Williams, R.; Burns, P.N.; Clokie, C.; Manolson, M.F.; Peel, S.A. Controlled bone formation using ultrasound-triggered release of BMP-2 from liposomes. J. Control. Release 2016, 243, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; Sun, M.; Yang, B.; Xiao, J.; Du, J. Ultrasound-responsive polymersomes capable of endosomal escape for efficient cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, M.; Shi, X.; Li, J. Activatable Semiconducting Polymer Nanoinducers Amplify Oxidative Damage via Sono-Ferroptosis for Synergistic Therapy of Bone Metastasis. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 7699–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J. Stimuli-responsive nanocarrier delivery systems for Pt-based antitumor complexes: A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 16488–16511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Lee, H.; Fang, Z.; Velalopoulou, A.; Kim, J.; Thomas, M.B.; Liu, J.; Abramowitz, R.G.; Kim, Y.; Coskun, A.F.; et al. Single-cell analysis reveals effective siRNA delivery in brain tumors with microbubble-enhanced ultrasound and cationic nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. A hybrid nanoassembly for ultrasound-inducible cytosolic siRNA delivery and cancer sono-gene therapy. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Ren, X.; Yang, F.; Li, B.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Nie, F. Ultrasound-sensitive siRNA-loaded nanobubbles fabrication and antagonism in drug resistance for NSCLC. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenziano, M.; Bessone, F.; Dianzani, C.; Cucci, M.A.; Grattarola, M.; Pizzimenti, S.; Cavalli, R. Ultrasound-Responsive Nrf2-Targeting siRNA-Loaded Nanobubbles for Enhancing the Treatment of Melanoma. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shar, A.; Aboutalebianaraki, N.; Misiti, K.; Sip, Y.Y.L.; Zhai, L.; Razavi, M. A novel ultrasound-mediated nanodroplet-based gene delivery system for osteoporosis treatment. Nanomedicine 2022, 41, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agidigbi, T.S.; Kim, C. Reactive Oxygen Species in Osteoclast Differentiation and Possible Pharmaceutical Targets of ROS-Mediated Osteoclast Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domazetovic, V.; Marcucci, G.; Iantomasi, T.; Brandi, M.L.; Vincenzini, M.T. Oxidative stress in bone remodeling: Role of antioxidants. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2017, 14, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, X.; Shen, Q.; Guo, C.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, J. Hot Topics and Challenges of Regenerative Nanoceria in Application of Antioxidant Therapy. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 4857461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wang, W.; Gao, J.; Wei, H.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Cerium oxide nanoparticles protect primary osteoblasts against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative damage. Micro Nano Lett. 2014, 9, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Neal, C.J.; Sakthivel, T.S.; Seal, S.; Kean, T.; Razavi, M.; Coathup, M. Cerium oxide nanoparticles protect against irradiation-induced cellular damage while augmenting osteogenesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 126, 112145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Neal, C.J.; Sakthivel, T.S.; Fu, Y.; Omer, M.; Adhikary, A.; Ward, S.; Ta, K.M.; Moxon, S.; Molinari, M.; et al. A novel approach for the prevention of ionizing radiation-induced bone loss using a designer multifunctional cerium oxide nanozyme. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 21, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, P.; Pan, S.; Qi, Z.; Fu, C.; Yu, Z.; Kong, W.; Chang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; et al. The Advances of Ceria Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications in Orthopaedics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7199–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchibhatla, S.; Karakoti, A.S.; Vasdekis, A.E.; Windisch, C.F., Jr.; Seal, S.; Thevuthasan, S.; Baer, D.R. An unexpected phase transformation of ceria nanoparticles in aqueous media. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazici, H.; Alpaslan, E.; Webster, T.J. The Role of Dextran Coatings on the Cytotoxicity Properties of Ceria Nanoparticles Toward Bone Cancer Cells. JOM 2015, 67, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zou, L.; Xiao, M.; Huang, C.; Xie, Z.; He, H.; Guo, Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. Ceria nanoparticles promoted the cytotoxic activity of CD8(+) T cells by activating NF-kappaB signaling. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Shen, Q.; Xie, Y.; You, M.; Huang, L.; Zheng, X. Incorporation of Cerium Oxide into Hydroxyapatite Coating Protects Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Against H(2)O(2)-Induced Inhibition of Osteogenic Differentiation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 182, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Shen, Q.; Xie, Y.; You, M.; Huang, L.; Zheng, X. Incorporation of cerium oxide into hydroxyapatite coating regulates osteogenic activity of mesenchymal stem cell and macrophage polarization. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 31, 1062–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Zhu, D.Y.; Yin, J.H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.Q.; Ke, Q.F.; Gao, Y.S.; Guo, Y.P. Incorporation of cerium oxide in hollow mesoporous bioglass scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration by activating the ERK signaling pathway. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinna, A.; Torki Baghbaderani, M.; Vigil Hernandez, V.; Naruphontjirakul, P.; Li, S.; McFarlane, T.; Hachim, D.; Stevens, M.M.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Nanoceria provides antioxidant and osteogenic properties to mesoporous silica nanoparticles for osteoporosis treatment. Acta Biomater. 2021, 122, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.; Silva, M.; Maia-Filho, A.; Ferreira, D.; Figuerêdo-Silva, J.; Rovaris, K.; Fialho, A.C.; Leite-Oliveira, A.; Menezes de Oliveira, A.L.; da Fonseca, M.G.; et al. Effect of Cerium-Containing Hydroxyapatite in Bone Repair in Female Rats with Osteoporosis Induced by Ovariectomy. Minerals 2021, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.; Li, J.; He, J.; Luo, F.; Yu, T.; Dai, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, S. Bone-targeted pH-responsive cerium nanoparticles for anabolic therapy in osteoporosis. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4697–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, S.; Salinas, A.J.; Lusvardi, G.; Malavasi, G.; Menabue, L.; Vallet-Regi, M. Mesoporous bioactive scaffolds prepared with cerium-, gallium- and zinc-containing glasses. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4836–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane-Incorporated Gelatin Hydrogel Promotes Angiogenesis during Vascularized Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22410–22425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonavane, G.; Tomoda, K.; Makino, K. Biodistribution of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration: Effect of particle size. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, W.; Zhang, Y.N.; Ouyang, B.; Kingston, B.R.; Wu, J.L.Y.; Wilhelm, S.; Chan, W.C.W. Elimination Pathways of Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5785–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, L.M.; Mondragon, L.; Ramis, J.; Gusta, M.F.; Yudina, T.; Casals, E.; Bastus, N.G.; Fernandez-Varo, G.; Casals, G.; Jimenez, W.; et al. Exploring the Long-Term Tissue Accumulation and Excretion of 3 nm Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles after Single Dose Administration. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, F.M.; Pasut, G. PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.J.; Sakthivel, T.S.; Fu, Y.; Seal, S. Aging of Nanoscale Cerium Oxide in a Peroxide Environment: Its Influence on the Redox, Surface, and Dispersion Character. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 27323–27334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, T.N.; Jeyaram, A.; Patel, D.B.; Parajuli, B.; Livingston, N.K.; Arumugasaamy, N.; Schardt, J.S.; Jay, S.M. Oncogene Knockdown via Active Loading of Small RNAs into Extracellular Vesicles by Sonication. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2016, 9, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallbank, A.M.; Vaughn, A.E.; Niemiec, S.; Bilodeaux, J.; Lehmann, T.; Knudsen, L.; Kolanthai, E.; Seal, S.; Zgheib, C.; Nozik, E.; et al. CNP-miR146a improves outcomes in a two-hit acute- and ventilator-induced lung injury model. Nanomedicine 2023, 50, 102679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kolanthai, E.; Neal, C.J.; Kumar, U.; Zgheib, C.; Liechty, K.W.; Seal, S. Engineered Faceted Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles for Therapeutic miRNA Delivery. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghzaoui, C.; Neal, C.J.; Kolanthai, E.; Fu, Y.; Kumar, U.; Hu, J.; Zgheib, C.; Liechty, K.W.; Seal, S. Assessing the bio-stability of microRNA-146a conjugated nanoparticles via electroanalysis. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 5, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafun, J.D.; Kvashnina, K.O.; Casals, E.; Puntes, V.F.; Glatzel, P. Absence of Ce3+ sites in chemically active colloidal ceria nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10726–10732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plakhova, T.V.; Romanchuk, A.Y.; Butorin, S.M.; Konyukhova, A.D.; Egorov, A.V.; Shiryaev, A.A.; Baranchikov, A.E.; Dorovatovskii, P.V.; Huthwelker, T.; Gerber, E.; et al. Towards the surface hydroxyl species in CeO(2) nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18142–18149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, S.; Jeyaranjan, A.; Neal, C.J.; Kumar, U.; Sakthivel, T.S.; Sayle, D.C. Engineered defects in cerium oxides: Tuning chemical reactivity for biomedical, environmental, & energy applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6879–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasanthan, J.; Gurusamy, N.; Rajasingh, S.; Sigamani, V.; Kirankumar, S.; Thomas, E.L.; Rajasingh, J. Role of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Regenerative Therapy. Cells 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.B.; Yang, H.L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.K.; Yang, Y.L.; Yuan, L.J.; Zhang, L.; Duan, Y.Y. The Optimized Fabrication of Nanobubbles as Ultrasound Contrast Agents for Tumor Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis of nanobubbles for improved ultrasound tumor-imaging applications. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ge, K.; Ren, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. Effects of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on the Proliferation, Osteogenic Differentiation and Adipogenic Differentiation of Primary Mouse Bone Marrow Stromal Cells In Vitro. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 6444–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinger, C.I.; Day, C.J.; Morrison, N.A. Optimized transfection of diced siRNA into mature primary human osteoclasts: Inhibition of cathepsin K mediated bone resorption by siRNA. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 96, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guo, B.; Wu, H.; Tang, T.; Zhang, B.T.; Zheng, L.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Pan, X.; Chow, H.; et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic therapy. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, J.Y.; Chauret, N.; Cromlish, W.; Desmarais, S.; Duong, L.T.; Falgueyret, J.P.; Kimmel, D.B.; Lamontagne, S.; Leger, S.; LeRiche, T.; et al. The discovery of odanacatib (MK-0822), a selective inhibitor of cathepsin K. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Xie, J.; Chaugule, S.; Wang, D.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.; Tai, P.W.L.; Seo, S.K.; Gravallese, E.; Gao, G.; et al. Bone-Targeting AAV-Mediated Gene Silencing in Osteoclasts for Osteoporosis Therapy. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, J.S.; Johnson, J.P.; Carlson, D.A. Oxidative Stress and Osteoporosis. J. Bone Joint. Surg. Am. 2021, 103, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.H.; Yang, M.Y. The Role of Macrophage in the Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Xie, P.L.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.X.; Liu, J.H.; Yin, H.; Huang, J.; Tan, Y.J.; Luo, J.; et al. Omentin-1 prevents inflammation-induced osteoporosis by downregulating the pro-inflammatory cytokines. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.J.; Kolanthai, E.; Wei, F.; Coathup, M.; Seal, S. Surface Chemistry of Biologically-Active Reducible Oxide Nanozymes. Adv. Mater. 2023, e2211261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaldoss, M.J.N.; Mehmood, R.; Yang, J.L.; Koshy, P.; Kumar, N.; Unnikrishnan, A.; Sorrell, C.C. Anticancer therapeutic effect of cerium-based nanoparticles: Known and unknown molecular mechanisms. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 3671–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.; Li, K.; Xie, Y.; Huang, L.; Zheng, X. The Effects of Cerium Valence States at Cerium Oxide Coatings on the Responses of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Macrophages. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 179, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoti, A.S.; Tsigkou, O.; Yue, S.; Lee, P.D.; Stevens, M.M.; Jones, J.R.; Seal, S. Rare earth oxides as nanoadditives in 3-D nanocomposite scaffolds for bone regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8912–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, V.; Gambuzzi, E.; Malavasi, G.; Menabue, L.; Menziani, M.C.; Lusvardi, G.; Pedone, A.; Benedetti, F.; Luches, P.; D’Addato, S.; et al. Evidence of catalase mimetic activity in Ce(3+)/Ce(4+) doped bioactive glasses. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 4009–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, J.; Li, B.; Li, W.; Qiao, W.; Shen, J.; Jin, W.; Jiang, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Chu, P.K. Valence State Manipulation of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on a Titanium Surface for Modulating Cell Fate and Bone Formation. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Song, S.Y.; Go, S.H.; Sohn, H.S.; Baik, S.; Soh, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.C.; et al. Synergistic Oxygen Generation and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging by Manganese Ferrite/Ceria Co-decorated Nanoparticles for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 3206–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyadi, D.M.; Islam, N. Current Status of Alginate in Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 2020, 8886095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotoudeh Bagha, P.; Kolanthai, E.; Wei, F.; Neal, C.J.; Kumar, U.; Braun, G.; Coathup, M.; Seal, S.; Razavi, M. Ultrasound-Responsive Nanobubbles for Combined siRNA-Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Delivery to Bone Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102393
Sotoudeh Bagha P, Kolanthai E, Wei F, Neal CJ, Kumar U, Braun G, Coathup M, Seal S, Razavi M. Ultrasound-Responsive Nanobubbles for Combined siRNA-Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Delivery to Bone Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(10):2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102393
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotoudeh Bagha, Pedram, Elayaraja Kolanthai, Fei Wei, Craig J. Neal, Udit Kumar, Gillian Braun, Melanie Coathup, Sudipta Seal, and Mehdi Razavi. 2023. "Ultrasound-Responsive Nanobubbles for Combined siRNA-Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Delivery to Bone Cells" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 10: 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102393
APA StyleSotoudeh Bagha, P., Kolanthai, E., Wei, F., Neal, C. J., Kumar, U., Braun, G., Coathup, M., Seal, S., & Razavi, M. (2023). Ultrasound-Responsive Nanobubbles for Combined siRNA-Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Delivery to Bone Cells. Pharmaceutics, 15(10), 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102393






