The Effect of the Particle Size Reduction on the Biorelevant Solubility and Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs with Different Acid-Base Character
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solubility Measurements
2.3. In situ Dissolution Measurements
2.4. Particle Size Analysis
2.5. PXRD
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Papaverine Hydrochloride
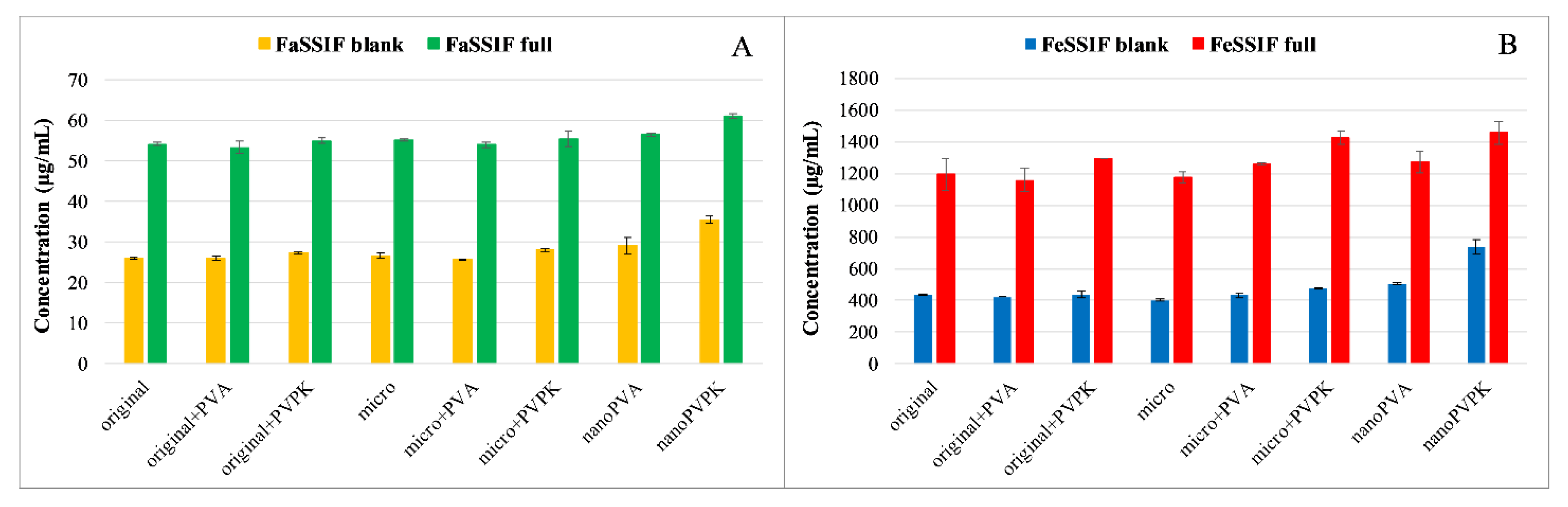
3.1.1. Solubility Measurements
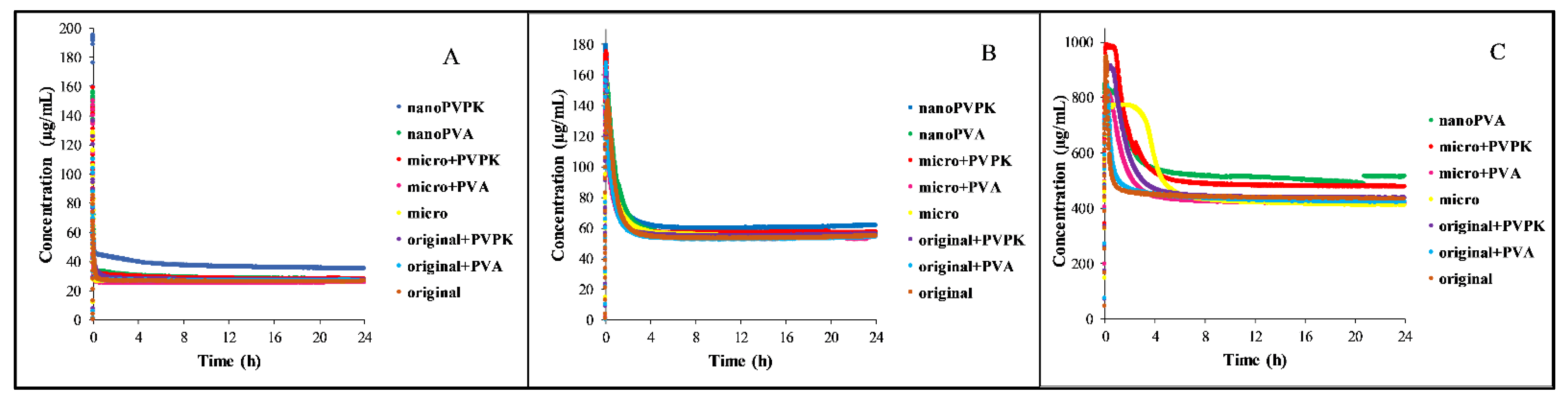
3.1.2. Dissolution Measurements
3.1.3. Particle Size Analysis
3.1.4. PXRD
3.2. Furosemide
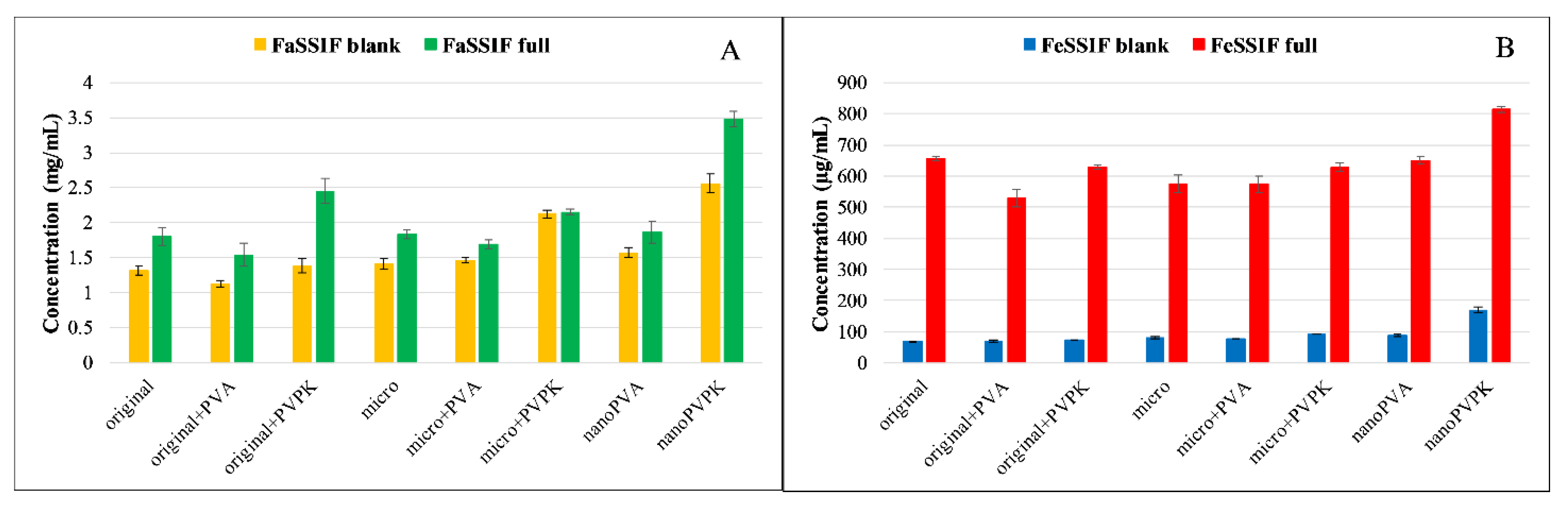
3.2.1. Solubility Measurements
3.2.2. Dissolution Measurements
3.2.3. Particle Size Analysis
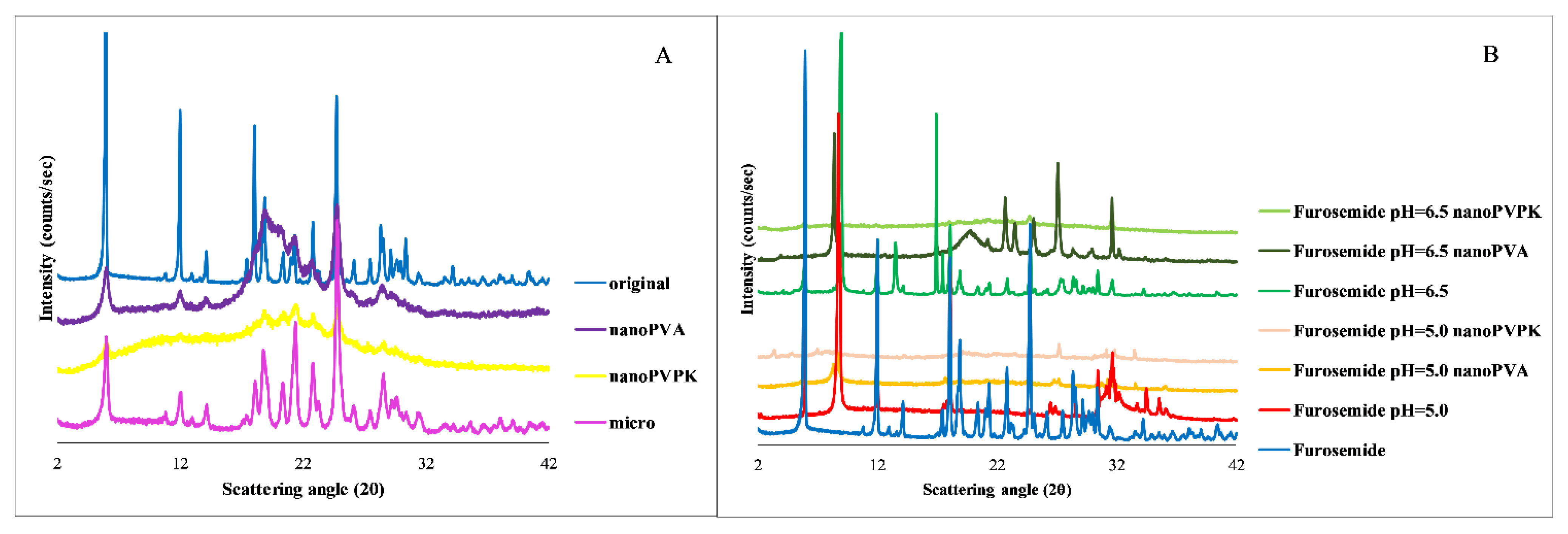
3.2.4. PXRD
3.3. Niflumic Acid
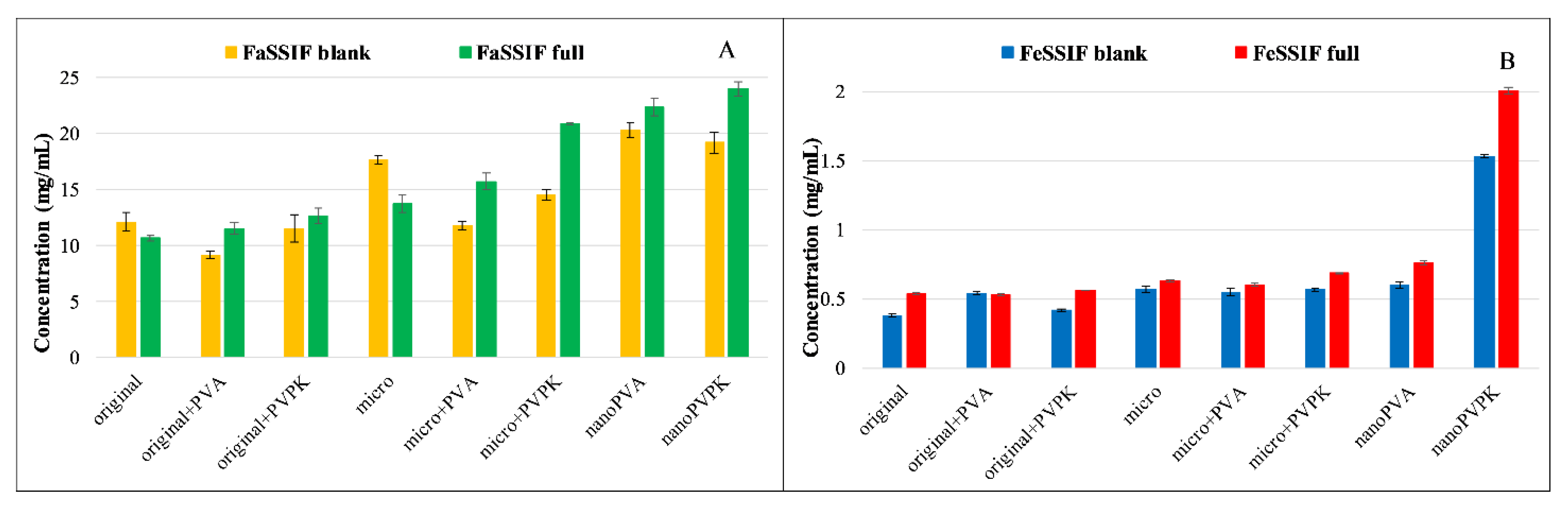
3.3.1. Solubility Measurements
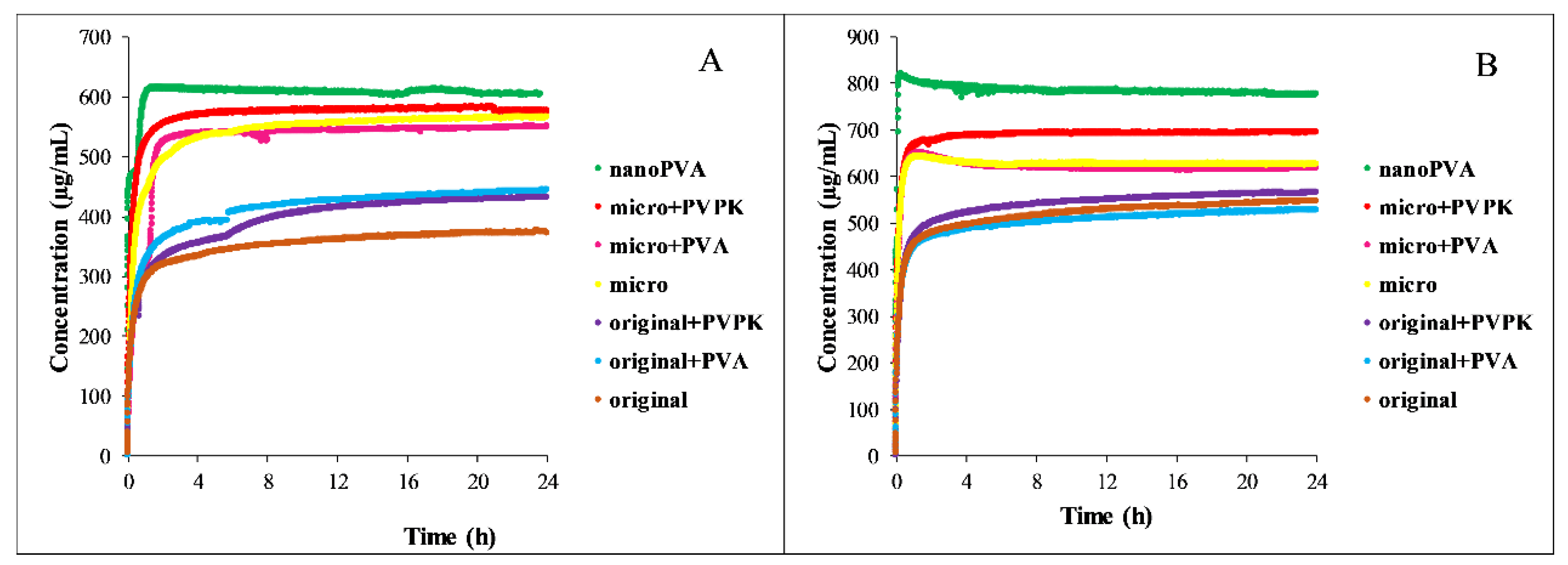
3.3.2. Dissolution Measurements
3.3.3. Particle Size Analysis
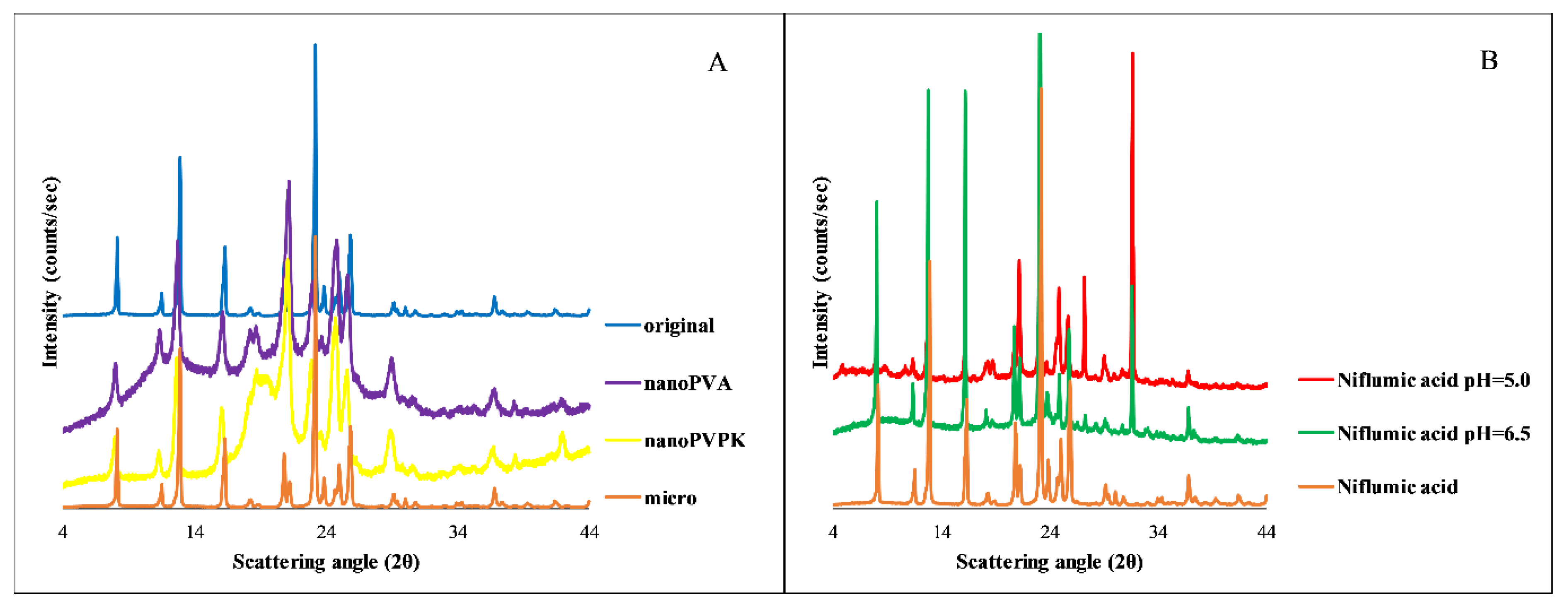
3.3.4. PXRD
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergström, C.A.S.; Box, K.; Holm, R.; Matthews, W.; McAllister, M.; Müllertz, A.; Rades, T.; Schäfer, K.J.; Teleki, A. Biorelevant intrinsic dissolution profiling in early drug development: Fundamental, methodological, and industrial aspects. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Patel, N.; Lin, S. Solubility and dissolution enhancement strategies: Current understanding and recent trends. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainurofiq, A.; Putro, D.S.; Ramadhani, D.A.; Putra, G.M.; Santo, L.D.D. A review on solubility enhancement methods for poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Rep. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 10, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, P.; Ro, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, I.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.M.; Yun, G.; Lee, J. Pharmaceutical particle technologies: An approach to improve drug solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szunyogh, T.; Ambrus, R.; Szabó-Révész, P. Nanonization of Niflumic Acid by Co-Grinding. Adv. Nanopart. 2013, 2, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeLeux, J.; Williams, R.O. Recent advancements in mechanical reduction methods: Particulate systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wais, U.; Jackson, A.W.; He, T.; Zhang, H. Nanoformulation and encapsulation approaches for poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 8, 1746–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, H.; Serajuddin, A.M. Development of Fully Redispersible Dried Nanocrystals by Using Sucrose Laurate as Stabilizer for Increasing Surface Area and Dissolution Rate of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csicsák, D.; Borbás, E.; Kádár, S.; Tőzsér, P.; Bagi, P.; Pataki, H.; Sinkó, B.; Takács-Novák, K.; Völgyi, G. Towards more accurate solubility measurements with real time monitoring: A carvedilol case study. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 11618–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeef, A.; Fuguet, E.; Llinàs, A.; Ràfols, C.; Bosch, E.; Völgyi, G.; Verbić, T.; Boldyreva, E.; Takács-Novák, K. Equilibrium solubility measurement of ionizable drugs—Consensus recommendations for improving data quality. ADMET DMPK 2016, 4, 117–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptay, G. On the size and shape dependence of the solubility of nano-particles in solutions. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 430, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarysse, S.; Brouwers, J.; Tack, J.; Annaert, P.; Augustijns, P. Intestinal drug solubility estimation based on simulated intestinal fluids: Comparison with solubility in human intestinal fluids. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantratid, E.; Janssen, N.; Reppas, C.; Dressman, J.B. Dissolution Media Simulating Conditions in the Proximal Human Gastrointestinal Tract: An Update. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, J.H.; Tsinman, O.; Sun, N.; Tsinman, K.; Avdeef, A.; Bergström, C.A.S. Dissolution Rate and Apparent Solubility of Poorly Soluble Drugs in Biorelevant Dissolution Media. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, E.; Comer, J.E.A.; Takács-Novák, K. Study of equilibrium solubility measurement by saturation shake-flask method using hydrochlorothiazide as model compound. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2008, 46, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Ho, C.; Yang, D.; Chen, J.; Orton, E. Measurement and Accurate Interpretation of the Solubility of Pharmaceutical Salts. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifee, M.; Inamda, N.; Dhamecha, D.L.; Rathi, A.A. Drug polymorphism: A review. Int. J. Health Res. 2009, 2, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács-Novák, K.; Szőke, V.; Völgyi, G.; Horváth, P.; Ambrus, R.; Szabó-Révész, P. Biorelevant solubility of poorly soluble drugs: Rivaroxaban, furosemide, papaverine and niflumic acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2013, 83, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlani, V.; Yuonayel, D.; Katpally, S.; Chukwumezie, B.N.; Adeyeye, M.C. Monitoring ibuprofen release from multiparticulates: In situ fiber-optic technique versus the HPLC method: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, E9–E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bynum, K.; Roinestad, K.; Kassis, A.; Pocreva, J.; Gehrlein, L.; Cheng, F.; Palermo, P. Analytical Performance of a Fiber Optic Probe Dissolution System. Dissolution Technol. 2001, 8, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, V.A. Dissolution Testing Using Fiber Optics—A Regulatory Perspective. Dissolution Technol. 2003, 10, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völgyi, G.; Csicsák, D.; Takács-Novák, K. Right filter-selection for phase separation in equilibrium solubility measurement. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, M.; Rao, G.S.N.K. Pharmaceutical assessment of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): As excipient from conventional to controlled delivery systems with a spotlight on COVID-19 inhibition. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Avdeef, A. Biorelevant pKa (37 °C) predicted from the 2D structure of the molecule and its pKa at 25 °C. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2011, 56, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandavilli, U.B.R.; Gangavaram, S.; Goud, N.R.; Cherukuvada, S.; Raghavender, S.; Nangia, A.; Manjunatha, S.G.; Nambiar, S.; Pal, S. High solubility crystalline hydrates of Na and K furosemide salts. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 4842–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kádár, S.; Csicsák, D.; Tőzsér, P.; Farkas, A.; Pálla, T.; Mirzahosseini, A.; Tóth, B.; Tóth, G.; Fiser, B.; Horváth, P.; et al. Understanding the pH Dependence of Supersaturation State—A Case Study of Telmisartan. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Parks, M. What is the True Solubility Advantage for Amorphous Pharmaceuticals? Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács-Novák, K.; Avdeef, A.; Box, K.J.; Podányi, B.; Szász, G. Determination of protonation macro- and microconstants and octanol/water partition coefficient of the antiinflammatory drug niflumic acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. 1995, 12, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Composition of the Formulation | Nomination |
|---|---|
| commercially available substance without excipient | original |
| physical mixture of the commercially available substance and PVA in 1:1 mass ratio | original + PVA |
| physical mixture of the commercially available substance and PVPK-25 in 1:1 mass ratio | original + PVPK |
| micronized sample without excipient | micro |
| physical mixture of the micronized substance and PVA in 1:1 mass ratio | micro + PVA |
| physical mixture of the micronized substance and PVPK-25 in 1:1 mass ratio | micro + PVPK |
| nanonized sample with PVA excipient | nanoPVA |
| nanonized sample with PVPK-25 excipient | nanoPVPK |
| d = 0.1 (µm) | d = 0.5 (µm) | d = 0.9 (µm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAP | original | 153.97 | 488.62 | 887.93 |
| micro | 101.71 | 263.70 | 596.47 | |
| FUR | original | 7.36 | 62.46 | 294.13 |
| micro | 14.97 | 58.94 | 148.10 | |
| NIF | original | 71.45 | 183.25 | 579.83 |
| micro | 38.91 | 110.46 | 224.97 | |
| pH = 6.5 | pH = 5.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d = 0.1 (µm) | d = 0.5 (µm) | d = 0.9 (µm) | d = 0.1 (µm) | d = 0.5 (µm) | d = 0.9 (µm) | ||
| PAP | original | 7.96 | 33.39 | 98.40 | 4.60 | 49.42 | 189.96 |
| original + PVA | 6.75 | 23.57 | 85.95 | 5.40 | 34.02 | 126.18 | |
| original + PVPK | 10.92 | 28.29 | 57.42 | 21.55 | 53.25 | 98.98 | |
| micro | 13.22 | 38.17 | 76.99 | 8.22 | 66.08 | 129.94 | |
| micro + PVA | 7.14 | 21.37 | 46.42 | 8.35 | 40.53 | 91.06 | |
| mikro + PVPK | 10.43 | 27.87 | 57.36 | 18.90 | 47.35 | 88.34 | |
| nanoPVA | 12.56 | 55.80 | 143.53 | 23.90 | 80.71 | 160.25 | |
| nanoPVPK | 7.77 | 37.98 | 113.67 | 29.73 | 62.00 | 120.43 | |
| pH = 6.5 | pH = 5.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d = 0.1 (µm) | d = 0.5 (µm) | d = 0.9 (µm) | d = 0.1 (µm) | d = 0.5 (µm) | d = 0.9 (µm) | ||
| FUR | original | 4.72 | 14.63 | 35.04 | 16.24 | 51.23 | 110.56 |
| original + PVA | 8.46 | 35.98 | 97.24 | 8.40 | 31.78 | 83.27 | |
| original + PVPK | 6.04 | 34.83 | 94.75 | 9.53 | 35.88 | 88.28 | |
| micro | 3.05 | 10.16 | 25.98 | 1.90 | 7.36 | 24.69 | |
| micro + PVA | 1.91 | 5.10 | 11.12 | 3.41 | 14.05 | 91.50 | |
| micro + PVPK | 1.51 | 1.75 | 9.51 | 2.29 | 16.92 | 50.15 | |
| nanoPVA | 4.56 | 22.61 | 66.78 | 7.18 | 32.44 | 89.24 | |
| nanoPVPK | 0.34 | 0.78 | 2.16 | 1.45 | 75.81 | 305.43 | |
| pH = 6.5 | pH = 5.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d = 0.1 (µm) | d = 0.5 (µm) | d = 0.9 (µm) | d = 0.1 (µm) | d = 0.5 (µm) | d = 0.9 (µm) | ||
| NIF | original | 19.07 | 58.55 | 128.24 | 56.21 | 151.25 | 488.95 |
| original + PVA | 8.29 | 38.74 | 112.33 | 9.97 | 47.10 | 126.18 | |
| original + PVPK | 11.39 | 42.73 | 95.69 | 13.60 | 66.44 | 164.08 | |
| micro | 8.59 | 32.98 | 96.05 | 16.57 | 71.37 | 164.93 | |
| micro + PVA | 4.71 | 18.60 | 94.05 | 7.61 | 52.11 | 147.07 | |
| micro + PVPK | 1.94 | 3.53 | 11.09 | 2.73 | 15.18 | 64.21 | |
| nanoPVA | 10.52 | 47.76 | 121.88 | 10.71 | 50.03 | 137.71 | |
| nanoPVPK | 1.98 | 3.34 | 9.48 | 1.33 | 5.26 | 17.26 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Csicsák, D.; Szolláth, R.; Kádár, S.; Ambrus, R.; Bartos, C.; Balogh, E.; Antal, I.; Köteles, I.; Tőzsér, P.; Bárdos, V.; et al. The Effect of the Particle Size Reduction on the Biorelevant Solubility and Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs with Different Acid-Base Character. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010278
Csicsák D, Szolláth R, Kádár S, Ambrus R, Bartos C, Balogh E, Antal I, Köteles I, Tőzsér P, Bárdos V, et al. The Effect of the Particle Size Reduction on the Biorelevant Solubility and Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs with Different Acid-Base Character. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010278
Chicago/Turabian StyleCsicsák, Dóra, Rita Szolláth, Szabina Kádár, Rita Ambrus, Csilla Bartos, Emese Balogh, István Antal, István Köteles, Petra Tőzsér, Vivien Bárdos, and et al. 2023. "The Effect of the Particle Size Reduction on the Biorelevant Solubility and Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs with Different Acid-Base Character" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 1: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010278
APA StyleCsicsák, D., Szolláth, R., Kádár, S., Ambrus, R., Bartos, C., Balogh, E., Antal, I., Köteles, I., Tőzsér, P., Bárdos, V., Horváth, P., Borbás, E., Takács-Novák, K., Sinkó, B., & Völgyi, G. (2023). The Effect of the Particle Size Reduction on the Biorelevant Solubility and Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs with Different Acid-Base Character. Pharmaceutics, 15(1), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010278








