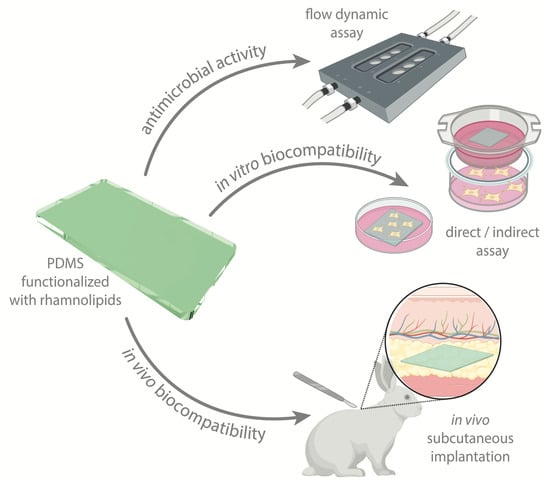
Assuring the Biofunctionalization of Silicone Covalently Bonded to Rhamnolipids: Antibiofilm Activity and Biocompatibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Solvents and Materials
2.2. Rhamnolipids Characterization
2.3. PDMS Surface Functionalization
Chemical Etching and RLs Functionalization
2.4. Surface Characterization
2.4.1. Wettability
2.4.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
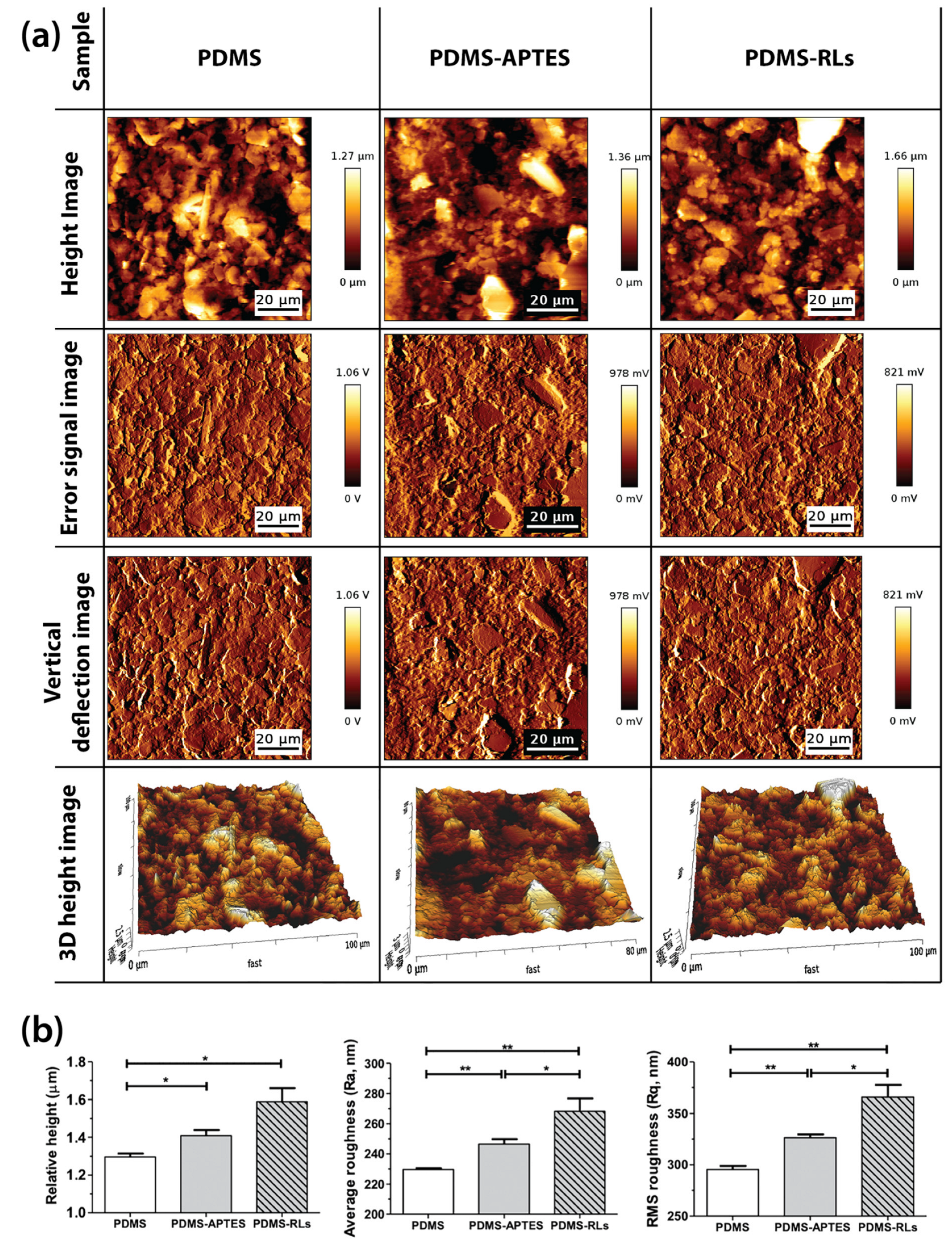
2.4.3. AFM
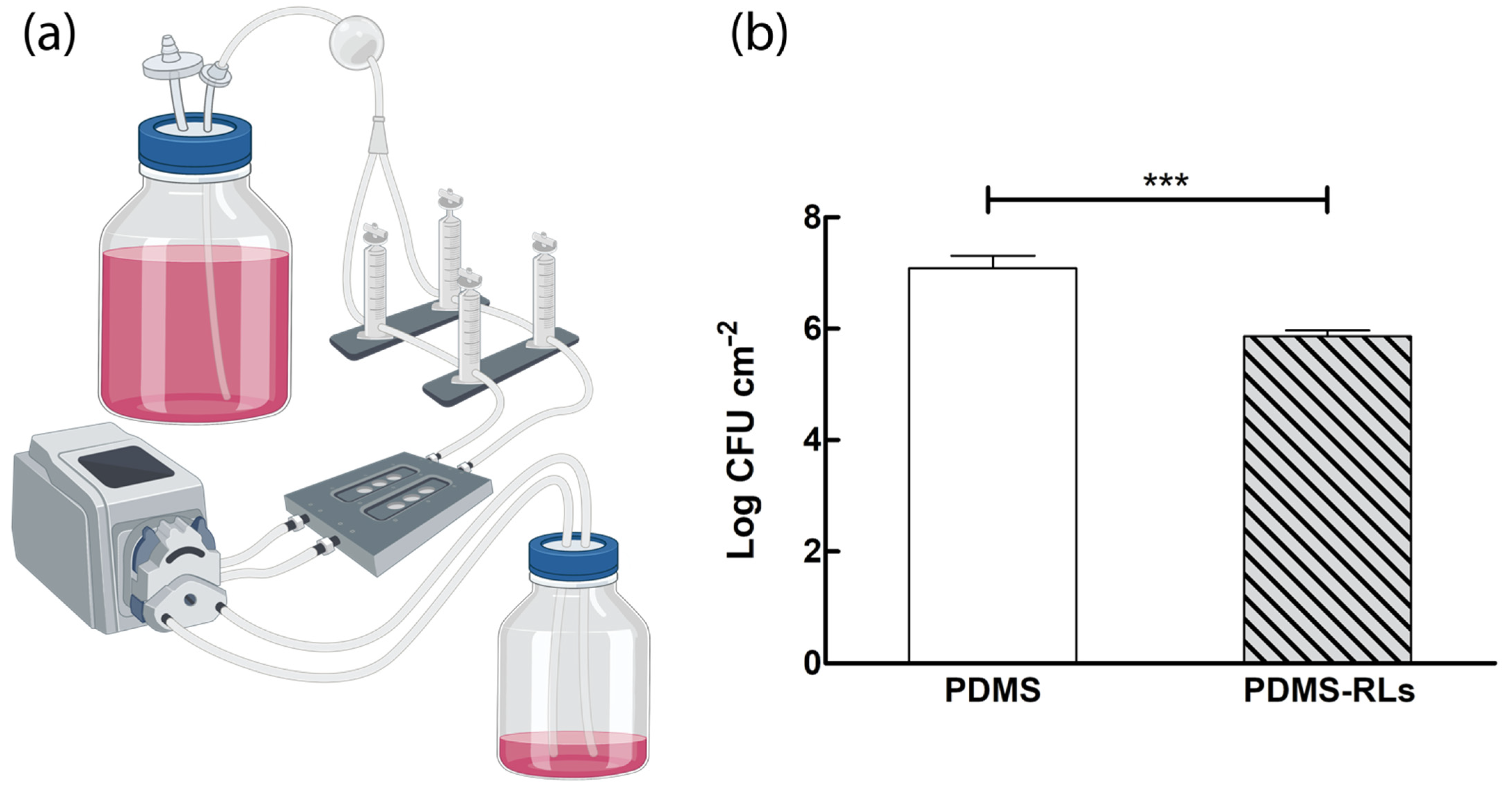
2.5. Antibiofilm Activity under Dynamic Conditions
2.5.1. Microorganisms
2.5.2. Flow Cell Assay
2.6. Biocompatibility
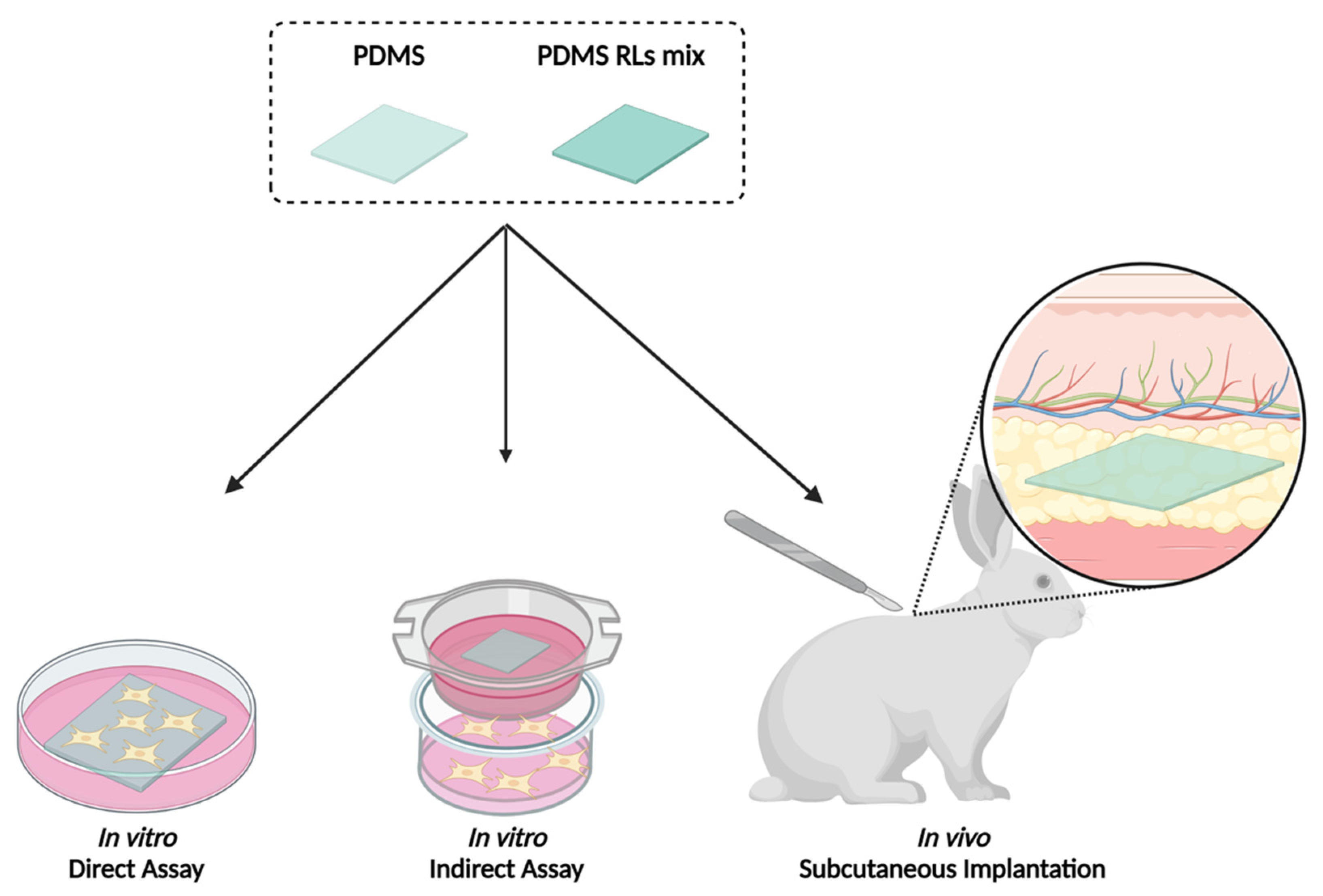
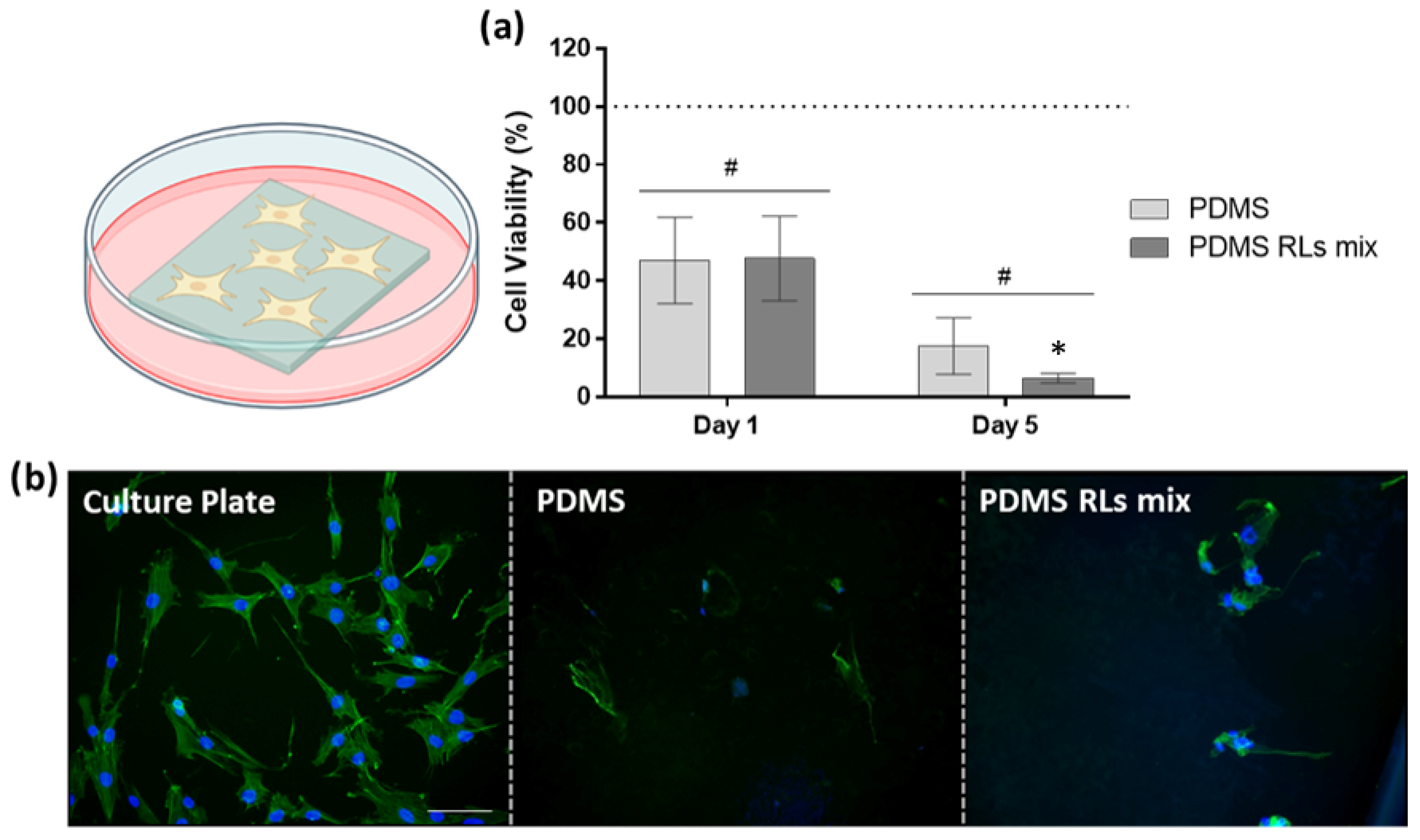
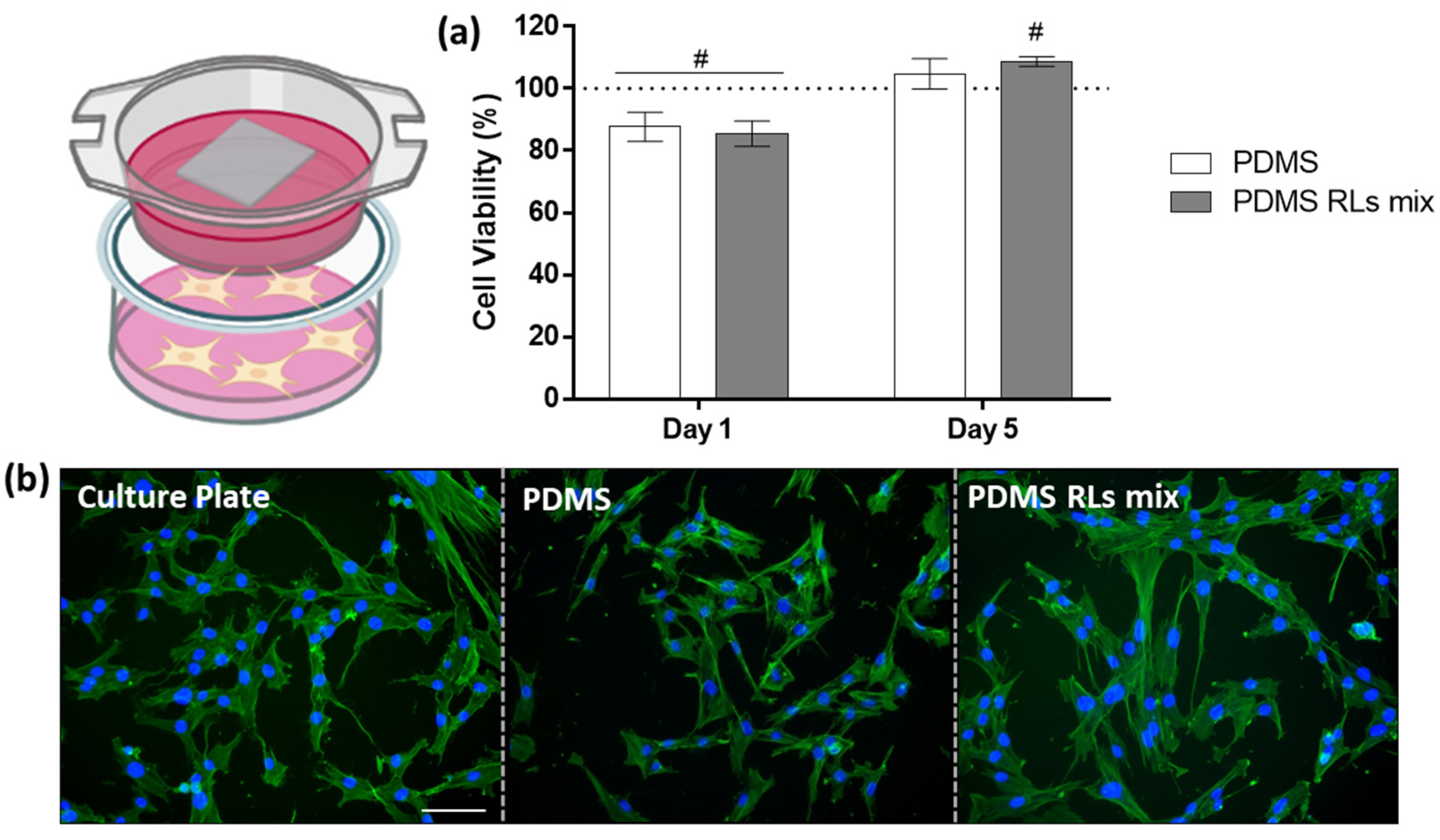
2.6.1. In Vitro Biocompatibility Assessment
Cell Viability/Metabolic Activity of the Culture
Cell Morphology
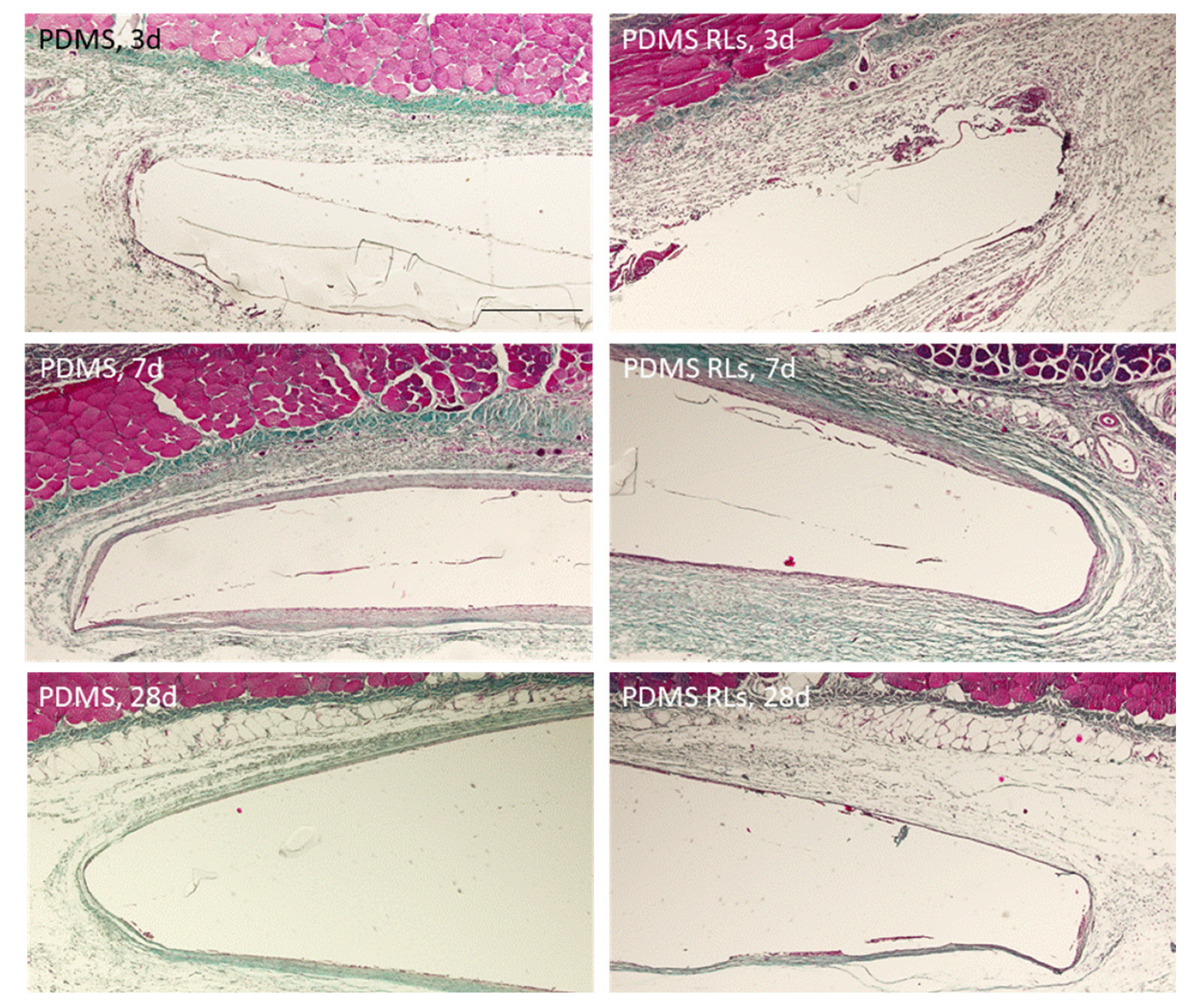
2.6.2. In Vivo Biocompatibility Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RLs Mixture Characterization
3.2. Functionalized Samples Characterization
3.3. Antibiofilm Activity under Dynamic Conditions
3.4. Biocompatibility
3.4.1. In Vitro Biological Evaluation
3.4.2. In Vivo Biological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zare, M.; Ghomi, E.R.; Venkatraman, P.D.; Ramakrishna, S. Silicone-based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications: Antimicrobial Strategies and 3D Printing Technologies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, C.M.C.; Lemos, S.M.C.; Monge, N.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. A Scope at Antifouling Strategies to Prevent Catheter-Associated Infections. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokhadzé, N.; Chennell, P.; Pereira, B.; Mailhot-Jensen, B.; Sautou, V. Critical Drug Loss Induced by Silicone and Polyurethane Implantable Catheters in a Simulated Infusion Setup with Three Model Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricardo, S.I.C.; Anjos, I.I.L.; Monge, N.; Faustino, C.M.C.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. A Glance at Antimicrobial Strategies to Prevent Catheter-Associated Medical Infections. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 3109–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffensen, S.L.; Vestergaard, M.H.; Groenning, M.; Alm, M.; Franzyk, H.; Nielsen, H.M. Sustained Prevention of Biofilm Formation on a Novel Silicone Matrix Suitable for Medical Devices. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, C.; Alves, M.; Santos, C.; Ribeiro, M.H.; Gonçalves, L.; Bettencourt, A.F.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Can Sophorolipids Prevent Biofilm Formation on Silicone Catheter Tubes? Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Pinto, S.N.; Aires-da-Silva, F.; Bettencourt, A.; Aguiar, S.I.; Gaspar, M.M. Liposomes as a Nanoplatform to Improve the Delivery of Antibiotics into Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.C.; Ribeiro, I.A.C.; Guedes, R.C.; Pinto, R.; Vaz, M.A.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Almeida, A.J.; Bettencourt, A.F. Key-Properties Outlook of a Levofloxacin-Loaded Acrylic Bone Cement with Improved Antibiotic Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chircov, C.; Ștefan, R.-E.; Dolete, G.; Andrei, A.; Holban, A.M.; Oprea, O.-C.; Vasile, B.S.; Neacșu, I.A.; Tihăuan, B. Dextran-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Curcumin for Antimicrobial Therapies. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, N.G.; Bettencourt, A.F.; Monge, N.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Novel Antibacterial Agents: An Emergent Need to Win the Battle Against Infections. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, S.A.; Naughton, P.J.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Microbial Biosurfactants in Cosmetic and Personal Skincare Pharmaceutical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardouri, M.; Bettencourt, A.; Martin, V.; Carvalho, F.A.; Santos, C.; Monge, N.; Santos, N.C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Gomes, P.S.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Using Plasma-Mediated Covalent Functionalization of Rhamnolipids on Polydimethylsiloxane towards the Antimicrobial Improvement of Catheter Surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 134, 112563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardouri, M.; Aljnadi, I.M.; Deuermeier, J.; Santos, C.; Costa, F.; Martin, V.; Fernandes, M.H.; Gonçalves, L.; Bettencourt, A.; Gomes, P.S.; et al. Bonding Antimicrobial Rhamnolipids onto Medical Grade PDMS: A Strategy to Overcome Multispecies Vascular Catheter-Related Infections. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramstedt, M.; Ribeiro, I.A.C.; Bujdakova, H.; Mergulhão, F.J.M.; Jordao, L.; Thomsen, P.; Alm, M.; Burmølle, M.; Vladkova, T.; Can, F.; et al. Evaluating Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Antifouling Materials for Urinary Tract Medical Devices: Challenges and Recommendations. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardouri, M.; Mendes, R.M.; Frenzel, J.; Costa, J.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Seeking Faster, Alternative Methods for Glycolipid Biosurfactant Characterization and Purification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 4311–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Rzhepishevska, O.; Grenho, L.; Malheiros, D.; Gonçalves, L.; Almeida, A.J.; Jordão, L.; Ribeiro, I.A.C.; Ramstedt, M.; Gomes, P.; et al. Levofloxacin-Loaded Bone Cement Delivery System: Highly Effective against Intracellular Bacteria and Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, L.L.; Edwards, J.L.; Shao, J.; Rabinak, C.; Entz, D.; Apicella, M.A. Biofilm Formation by Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.A.; de Melo, L.D.; da Silva, R.A.; Ferraz, M.P.; de Rodrigues Azeredo, J.C.; de Carvalho Pinheiro, V.M.; Colaço, B.J.; Fernandes, M.H.; de Sousa Gomes, P.; Monteiro, F.J. Encapsulated Bacteriophages in Alginate-Nanohydroxyapatite Hydrogel as a Novel Delivery System to Prevent Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infections. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 24, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, J.; Radzuan, M.; Winterburn, J. Infrared Spectroscopy for Studying Structure and Aging Effects in Rhamnolipid Biosurfactants. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Bassler, G.C.; Morrill, T.C. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ceresa, C.; Tessarolo, F.; Maniglio, D.; Tambone, E.; Carmagnola, I.; Fedeli, E.; Caola, I.; Nollo, G.; Chiono, V.; Allegrone, G.; et al. Medical-Grade Silicone Coated with Rhamnolipid R89 Is Effective against Staphylococcus Spp. Biofilms. Molecules 2019, 24, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, S.; Zapotoczna, M.; Stevens, N.T.; Humphreys, H.; O’Gara, J.P.; O’Neill, E. In Vitro Approach for Identification of the Most Effective Agents for Antimicrobial Lock Therapy in the Treatment of Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections Caused by Staphylococcus Aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.; Zapotoczna, M.; Stevens, N.T.; Humphreys, H.; O’Gara, J.P.; O’Neill, E. Eradication of Staphylococcus aureus Catheter-Related Biofilm Infections Using ML:8 and Citrox. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5968–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Krishnan, S.; Weinman, C.J.; Ober, C.K. Advances in Polymers for Anti-Biofouling Surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Yu, B.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, J.; Jeon, H.; Lee, D.Y.; Im, S.G.; Jon, S. Prevention of Bacterial Colonization on Catheters by a One-Step Coating Process Involving an Antibiofouling Polymer in Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19736–19745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidambi, S.; Udpa, N.; Schroeder, S.A.; Findlan, R.; Lee, I.; Chan, C. Cell Adhesion on Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Coated Polydimethylsiloxane Surfaces with Varying Topographies. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lutz, T.M.; Lang, N.; Lieleg, O. Bioinspired Dopamine/Mucin Coatings Provide Lubricity, Wear Protection, and Cell-Repellent Properties for Medical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2000831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achyuta, A.K.H.; Stephens, K.D.; Pryce Lewis, H.G.; Murthy, S.K. Mitigation of Reactive Human Cell Adhesion on Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) by Immobilized Trypsin. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.N.; Jiang, X.; Ryan, D.; Whitesides, G.M. Compatibility of Mammalian Cells on Surfaces of Poly(Dimethylsiloxane). Langmuir 2004, 20, 11684–11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenave, L.; Bareille, R.; Lefebvre, F.; Caix, J.; Baquey, C. Cytocompatibility Study of NHLBI Primary Reference Materials Using Human Endothelial Cells. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1992, 3, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, R.; Albrektsson, T.; Tengvall, P.; Wennerberg, A. Foreign Body Reaction to Biomaterials: On Mechanisms for Buildup and Breakdown of Osseointegration. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, E.; Lisignoli, G.; Borzì, R.M.; Pulsatelli, L. Biomaterials: Foreign Bodies or Tuners for the Immune Response? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, Q.; Shi, C.; Chen, M.; Ma, K.; Wan, J.; Liu, R. Dealing with the Foreign-Body Response to Implanted Biomaterials: Strategies and Applications of New Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, I.; Souza, A.; Sousa, P.; Ribeiro, J.; Castanheira, E.M.S.; Lima, R.; Minas, G. Properties and Applications of PDMS for Biomedical Engineering: A Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Assay | Designation | RLs Mixture (B1) | RLs Mixture (B2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UHPLC-MS | RhaRhaC10:0C8:0 | + | + |
| RhaC8:0C10:0 | + | + | |
| RhaRhaC8:0C12:0 | + | + | |
| RhaRhaC10:0C10:1 | + | + | |
| RhaRhaC10:C12:1 | + | + | |
| RhaRhaC10:0C12:0 | + | + | |
| RhaC10:0C12:1 | + | + | |
| RhaC10:0C10:1 | + | + | |
| RhaRhaC10:0C14:1 | + | + | |
| RhaC10:0C12:0 | + | + | |
| Contact angle (°) | PDMS | 85 ± 10 | 95 ± 4 |
| PDMS-RLs | 27 ± 4 | 17 ± 2 | |
| ATR-FTIR (cm−1) | RLs mixture | ||
| CH symmetrical stretch | 2960 * | 2960 * | |
| CH asymmetrical stretch | 2883 * | 2883 * | |
| C=O from ester */carboxylic | 1740 * | 1740 * | |
| CH2 deformation | 1408 | 1408 | |
| C-O-C in the rhamnose ring | 1078 | 1145 | |
| PDMS | |||
| C-H stretch of CH3 | 2965 * | 2965 * | |
| C-H of Si-(CH3)2 | 1263 * | 1263 * | |
| Si-O-Si stretch | 1014 * and 1087 * | 1014 * and 1087 * | |
| PDMS-RLs | |||
| C=O bond of the amide | 1668 | 1650 | |
| N-H bond of the amide | 1565 | 1565 | |
| C-N bond of the amide | - | 1450 | |
| Other bands present marked with * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dardouri, M.; Bettencourt, A.; Martin, V.; Carvalho, F.A.; Colaço, B.; Gama, A.; Ramstedt, M.; Santos, N.C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Gomes, P.S.; et al. Assuring the Biofunctionalization of Silicone Covalently Bonded to Rhamnolipids: Antibiofilm Activity and Biocompatibility. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091836
Dardouri M, Bettencourt A, Martin V, Carvalho FA, Colaço B, Gama A, Ramstedt M, Santos NC, Fernandes MH, Gomes PS, et al. Assuring the Biofunctionalization of Silicone Covalently Bonded to Rhamnolipids: Antibiofilm Activity and Biocompatibility. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091836
Chicago/Turabian StyleDardouri, Maïssa, Ana Bettencourt, Victor Martin, Filomena A. Carvalho, Bruno Colaço, Adelina Gama, Madeleine Ramstedt, Nuno C. Santos, Maria H. Fernandes, Pedro S. Gomes, and et al. 2022. "Assuring the Biofunctionalization of Silicone Covalently Bonded to Rhamnolipids: Antibiofilm Activity and Biocompatibility" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091836
APA StyleDardouri, M., Bettencourt, A., Martin, V., Carvalho, F. A., Colaço, B., Gama, A., Ramstedt, M., Santos, N. C., Fernandes, M. H., Gomes, P. S., & Ribeiro, I. A. C. (2022). Assuring the Biofunctionalization of Silicone Covalently Bonded to Rhamnolipids: Antibiofilm Activity and Biocompatibility. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091836