D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Poly(ethylene Glycol 1000) Succinate-Coated Manganese-Zinc Ferrite Nanomaterials for a Dual-Mode Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent and Hyperthermia Treatments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Manganese Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles
2.3. Prepartation and Characterization of MZF@TPGS Formulatoin
2.4. Cell Cytotoxicity and Cellular Uptake of MZF@TPGS In Vitro
2.5. In Vivo MR Imaging
2.6. Antitumor Efficacy of MZF@TPGS Formulation-Mediated Hyperthermia
2.7. Histological Analysis
3. Results
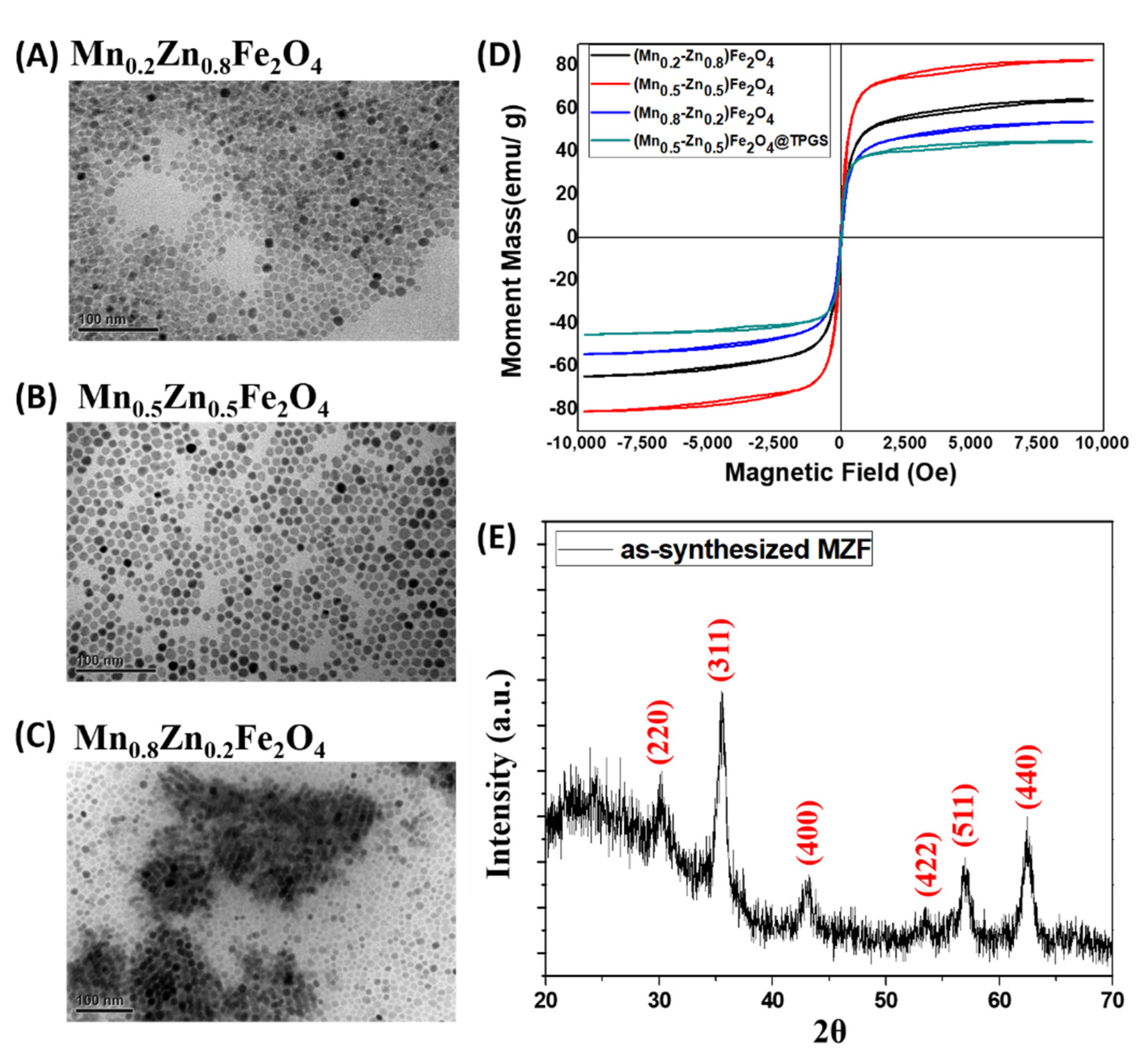
3.1. Characterization of MZF Nanoparticles and Their Formulations
3.2. Relaxivity, MR Imaging and Hyperthermia Tests of MZF@TPGS Formulations
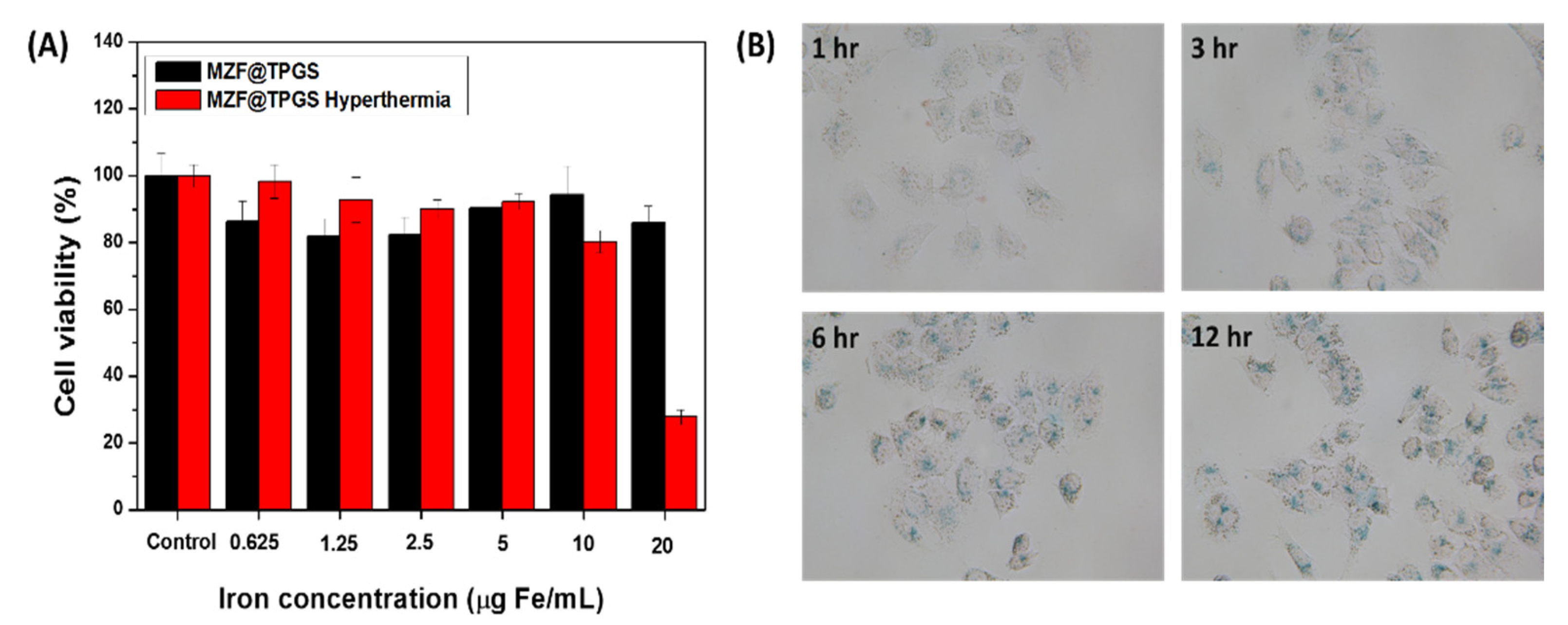
3.3. In Vitro Hyperthermia Efficacy of MZF@TPGs Formulation in KB Cells
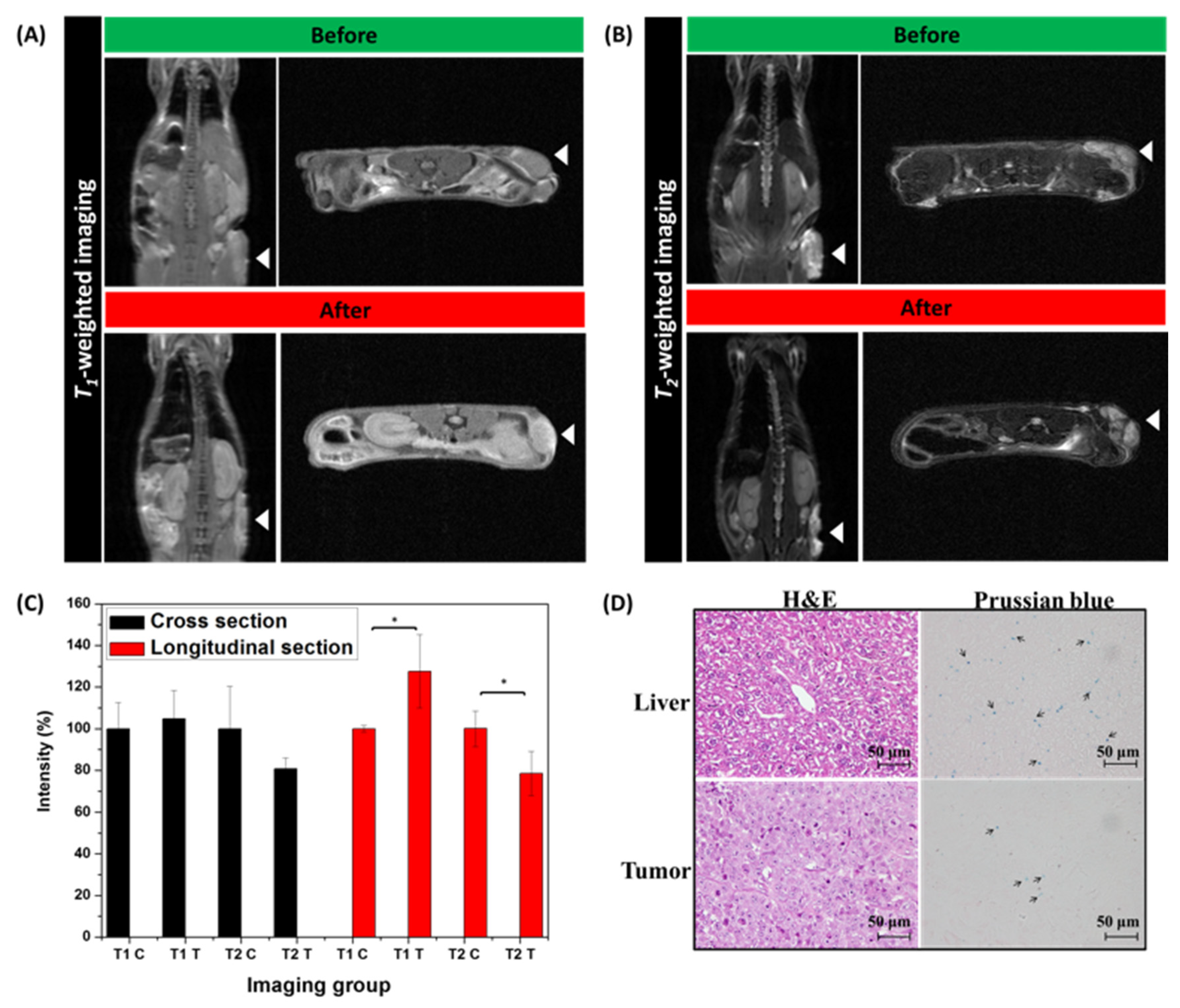
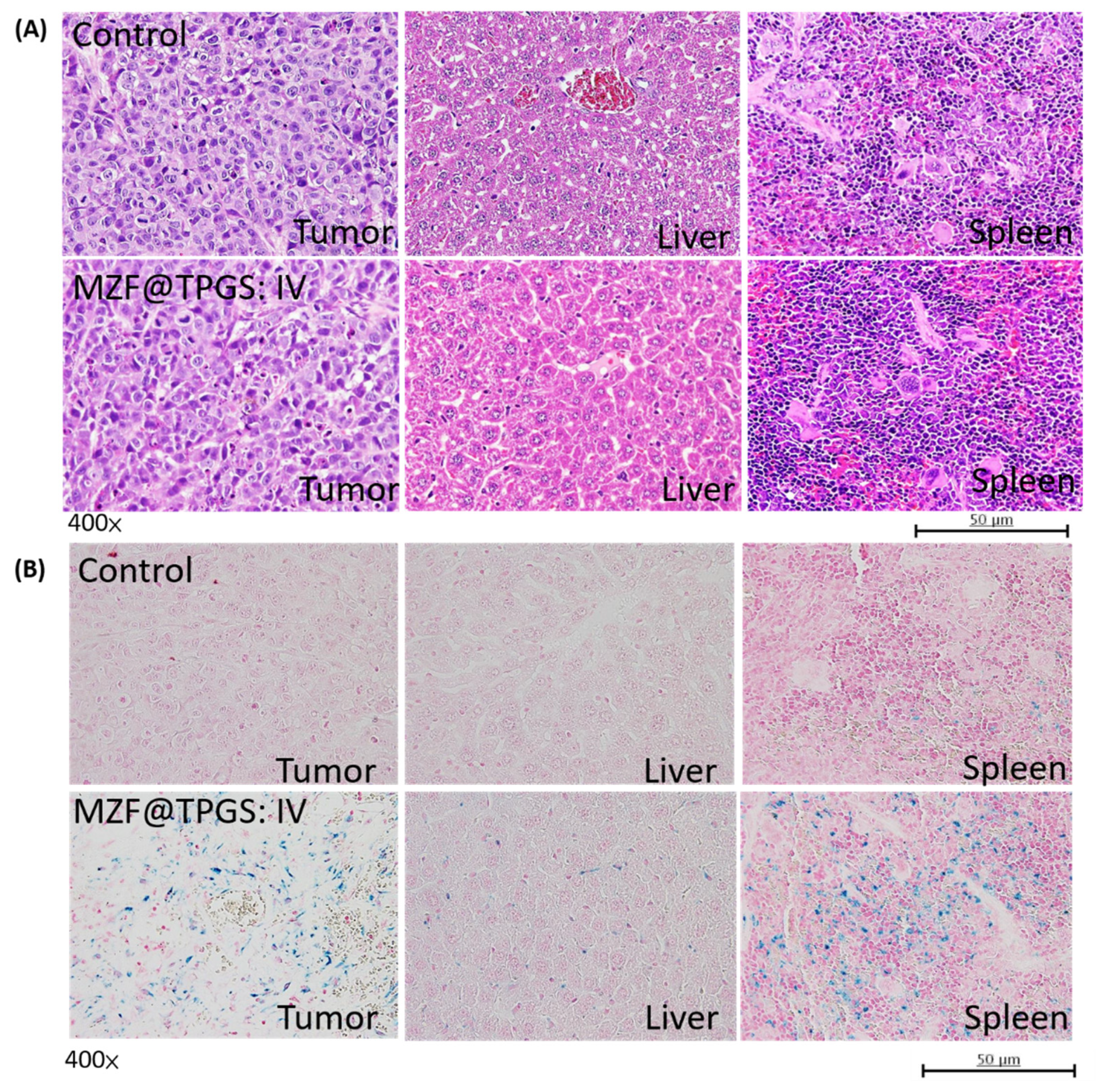
3.4. MZF@TPGS Formulation-Mediated MR Imaging and Hyperthermia In Vivo
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.J.; Yazan, L.S.; Abdullah, C.A.C. A Review on Current Nanomaterials and Their Drug Conjugate for Targeted Breast Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, D.; Lee, J.-H.; Shin, T.-H.; Cheon, J. Theranostic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubayev, V.I.; Pisanic, T.R.; Jin, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Theragnostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Islam, K.; Haque, M.; Kumar, A.; Hoq, A.; Hyder, F.; Hoque, S.M. Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles (MnFe2O4): Size Dependence for Hyperthermia and Negative/Positive Contrast Enhancement in MRI. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavu, L.M.; Rinaldi, R.; Di Corato, R. Application in Nanomedicine of Manganese-Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, S.K.; Padmanabhan, P.; Selvan, S.T. Multifunctional Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Diagnostics, Therapy and Macromolecule Delivery. Theranostics 2013, 3, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bietenbeck, M.; Florian, A.; Faber, C.; Sechtem, U.; Yilmaz, A. Remote Magnetic Targeting of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapeutic Drug Delivery: Where are We Now? Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3191–3203. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, S.H.; Kellar, K.E. Blood-Pool Contrast Agents for MRI: A Critical Evaluation. Acad. Radiol. 1998, 5, S200–S205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.Q.; Lu, Z.R. Integrin Targeted MR Imaging. Theranostics 2011, 1, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.P.; Xie, J. Development of Manganese-Based Nanoparticles as Contrast Probes for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Theranostics 2012, 2, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Bang, D.; Park, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.; Park, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, E.; Suh, J.S.; Huh, Y.M.; et al. Gadolinium-Enriched Polyaniline Particles (GPAPs) for Simultaneous Diagnostic Imaging and Localized Photothermal Therapy of Epithelial Cancer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, J.G.; Reilly, R.F., Jr. What Nephrologists Need to Know About Gadolinium. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2007, 3, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterbur, P.C. Image Formation by Induced Local Interactions Examples Employing Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Nature 1973, 242, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terreno, E.; Dastru, W.; Castelli, D.D.; Gianolio, E.; Crich, S.G.; Longo, D.; Aime, S. Advances in Metal-Based Probes for MR Molecular Imaging Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 3684–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letourneau, M.; Tremblay, M.; Faucher, L.; Rojas, D.; Chevallier, P.; Gossuin, Y.; Lagueux, J.; Fortin, M.-A. MnO-Labeled Cells: Positive Contrast Enhancement in MRI. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 13228–13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Urano, Y.; Nagano, T. Selective Sensing of Zinc Ions with a Novel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent. J. Chem. Soc. -Perkin Trans. 2001, 2, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Urano, Y.; Narazaki, M.; Yokawa, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nagano, T. Design and Synthesis of a Novel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent for Selective Sensing of Zinc Ion. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Major, J.L.; Parigi, G.; Luchinat, C.; Meade, T.J. The Synthesis and in vitro Testing of a Zinc-Activated MRI Contrast Agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13881–13886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stergar, J.; Jirák, Z.; Veverka, P.; Kubíčková, L.; Vrba, T.; Kuličková, J.; Knížek, K.; Porcher, F.; Kohout, J.; Kaman, O. Mn-Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles Coated with Mesoporous Silica as Core Material for Heat-Triggered Release of Therapeutic Agents. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Song, L.; Wen, S.; Zang, F.; Chen, G.; Ding, Q.; Yan, C.; Gu, N. High-Performance PEGylated Mn-Zn Ferrite Nanocrystals as a Passive-Targeted Agent for Magnetically Induced Cancer Theranostics. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9126–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Huang, J.; Sha, M. Recent Advances in Nanosized Mn-Zn Ferrite Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia for Cancer Treatment. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeun, M.; Jeoung, J.W.; Moon, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Paek, S.H.; Chung, K.-W.; Park, K.H.; Bae, S. Engineered Superparamagnetic Mn(0.5)Zn(0.5)Fe(2)O(4) Nanoparticles as a Heat Shock Protein Induction Agent for Ocular Neuroprotection in Glaucoma. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Neoh, K.G.; Wang, L.; Kang, E.-T.; Shuter, B. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Modulation of Macrophage Uptake by Controlled PEGylation of the Surface Coating. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8512–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, A.; Patel, R.; Arulmozhi, S.; Bothiraja, C. d-α-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol 1000 Succinate Conjugated Folic Acid Nanomicelles: Towards Enhanced Bioavailability, Stability, Safety, Prolonged Drug Release and Synergized Anticancer Effect of Plumbagin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 78106–78121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeun, M.; Moon, S.J.; Kobayashi, H.; Shin, H.Y.; Tomitaka, A.; Kim, Y.J.; Takemura, Y.; Paek, S.H.; Park, K.H.; Chung, K.-W.; et al. Effects of Mn Concentration on the AC Magnetically Induced Heating Characteristics of Superparamagnetic Mn(x)Zn(1-x)Fe(2)O(4) Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 202511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-M.; Hsiao, J.-K.; Yu, H.-P.; Lu, C.-W.; Huang, C.-C.; Shieh, M.-J.; Lai, P.-S. Polyethylene Glycol-Based Biocompatible and Highly Stable Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoclusters for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 15160–15167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival—Applicarion to Proliferation and Cyto-Toxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.A.; Miller, B.R.; Arbab, A.S.; Zywicke, H.A.; Jordan, E.K.; Lewis, B.K.; Bryant, L.H.; Bulte, J.W.M. Clinically Applicable Labeling of Mammalian and Stem Cells by Combining; Superparamagnetic Iron Oxides and Transfection Agents. Radiology 2003, 228, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.L.; Syu, W.J.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K.; Lai, P.S. Dendrimer Phthalocyanine-Encapsulated Polymeric Micelle-Mediated Photochemical Internalization Extends the Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy and Overcomes the Drug-Resistance in vivo. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, A.; Modest, J.; Geiler, A.L.; Gillette, S.; Chen, Y.; Geiler, M.; Hu, B.; Kim, S.; Stopher, K.; Vittoria, C.; et al. Structure, Morphology and Magnetic Properties of Mg(x)Zn(1-x)Fe2O4 Ferrites Prepared by Polyol and Aqueous Co-precipitation Methods: A Low-Toxicity Alternative to Ni(x)Zn(1-x)Fe2O4 ferrites. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 305708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadmanjiri, J. Preparation of Mn-Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles from Chemical Sol-Gel Combustion Method and the Magnetic Properties after Sintering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 4170–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jović Orsini, N.; Milić, M.M.; Torres, T.E. Zn- and (Mn, Zn)-Substituted Versus Unsubstituted Magnetite Nanoparticles: Structural, Magnetic and Hyperthermic Properties. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 225707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Taneja, S.; Sindhu, D.; Lüders, U.; Sharma, A.; Ravelo, B.; Thakur, A. Manganese Zinc Ferrites: A Short Review on Synthesis and Characterization. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2020, 33, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masthoff, I.C.; Gutsche, A.; Nirschl, H.; Garnweitner, G. Oriented Attachment of Ultra-Small Mn(1−x)ZnxFe2O4 Nanoparticles During the Non-Aqueous Sol–Gel Synthesis. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beji, Z.; Hanini, A.; Smiri, L.S.; Gavard, J.; Kacem, K.; Villain, F.; Greneche, J.M.; Chau, F.; Ammar, S. Magnetic Properties of Zn-Substituted MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized in Polyol as Potential Heating Agents for Hyperthermia. Evaluation of Their Toxicity on Endothelial Cells. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 5420–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Book Reviews. Announcements. Corros. Rev. 1997, 15, 533–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaiah, K.; Vijaya Babu, K. Structural, Magnetic and Electrical Properties of Nickel Doped Mn-Zn Spinel Ferrite Synthesized by Sol-Gel Method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 423, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-t.; Nah, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, M.G.; Cheon, J. Critical Enhancements of MRI Contrast and Hyperthermic Effects by Dopant-Controlled Magnetic Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H. Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Tran, H.-V.; Xu, S.; Lee, T.R. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Structures, Synthesis, Magnetic Properties, Surface Functionalization, and Emerging Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Sakamoto, W.; Yogo, T.; Miki, H.; Ozaki, S.; Abe, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Ishimura, K. Superparamagnetic Nanoparticle Clusters for Cancer Theranostics Combining Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Hyperthermia Treatment. Theranostics 2013, 3, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, P.H.; Jensen, C.; Charity, N.; Towner, R.; Mao, C.B. Oil Phase Evaporation-Induced Self-Assembly of Hydrophobic Nanoparticles into Spherical Clusters with Controlled Surface Chemistry in an Oil-in-Water Dispersion and Comparison of Behaviors of Individual and Clustered Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17724–17732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Liu, G.A.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, J.H.; Hong, R.Y. Preparation of Octahedral Shaped Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 Ferrites via Co-precipitation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 497, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.Y.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.H.; Ren, Y.M.; Fan, Z.J.; Zhang, M.L. Magnetic and High Rate Adsorption Properties of Porous Mn1-xZnxFe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) Adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 353, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejase, H.; Hayek, S.S.; Qadri, S.; Haik, Y. MnZnFe Nanoparticles for Self-Controlled Magnetic Hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3620–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, E.S.G.; Tang, X.S.; Sheng, Y.; Shuter, B.; Xue, J.M. Controlled Loading of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles in Fluorescent Nanogels as Effective T-2-Weighted MRI Contrast Agents. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.L.; Berret, J.F.; Fresnais, J.; Gossuin, Y.; Sandre, O. A Universal Scaling Law to Predict the Efficiency of Magnetic Nanoparticles as MRI T2-Contrast Agents. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, K.-W.; Hsu, S.-h. A Facile Method to Prepare Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide and Hydrophobic Drug-Encapsulated Biodegradable Polyurethane Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, F.; Jia, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, M. Facile Synthesis of Ultrasmall PEGylated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Dual-Contrast T1- and T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 245604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caro, C.; García-Martín, M.L.; Pernia Leal, M. Manganese-Based Nanogels as pH Switches for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herynek, V.; Turnovcová, K.; Gálisová, A.; Kaman, O.; Mareková, D.; Koktan, J.; Vosmanská, M.; Kosinová, L.; Jendelová, P. Manganese-Zinc Ferrites: Safe and Efficient Nanolabels for Cell Imaging and Tracking In Vivo. ChemistryOpen 2019, 8, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, C.; Xie, J.; Yan, D.; Hu, K.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Xiong, F. High-Performance Worm-like Mn–Zn Ferrite Theranostic Nanoagents and the Application on Tumor Theranostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 29536–29548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.; Krishnan, K.M. Synthesis of Magnetoliposomes with Monodisperse Iron Oxide Nanocrystal Cores for Hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekalo, K.; Baker, I.; Meyers, R.; Shyong, J. Magnetic Nanoparticles with High Specific Absorption Rate at Low Alternating Magnetic Field. Nano Life 2015, 5, 1550002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Wust, P.; Fähling, H.; Roland, F. Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia (MFH): Cancer Treatment with AC Magnetic Field Induced Excitation of Biocompatible Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, I.; Shokrollahi, H.; Amiri, S. Ferrite-Based Magnetic Nanofluids Used in Hyperthermia Applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-W.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Lai, S.-M.; Syu, W.-J.; Wang, T.-Y.; Lai, P.-S. Metal Nanobullets for Multidrug Resistant Bacteria and Biofilms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 78, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-F.; Zhang, L.-M.; Guan, H.-N.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Xu, S.-W. Effects of Oxidative Stress on Apoptosis in Manganese-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Cocks. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokel, R.A. Manganese Flux Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neuromolecular Med. 2009, 11, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Shi, X.; Hu, H.; Du, X.; Fang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, S. Water-Soluble Superparamagnetic Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3667–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ma, S.; Sun, J.; Xia, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gao, F.; Gong, Q.; Song, B.; et al. Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticle Micellar Nanocomposites as MRI Contrast Agent for Liver Imaging. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Tian, X.M.; Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Luo, N.Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.B.; Chen, D.H.; Wang, C.X.; Li, L.; et al. Ultrahigh Relaxivity and Safe Probes of Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles for in vivo Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Santra, C.R.; Ghosh, A.N.; Karmakar, P. Differential Toxicity of Rod and Spherical Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcena, C.; Sra, A.K.; Chaubey, G.S.; Khemtong, C.; Liu, J.P.; Gao, J. Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2224–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Chen, K. Facile Synthesis of Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles as Non-Lanthanide T-1 MRI Contrast Agents. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13500–13505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj Slimen, I.; Najar, T.; Ghram, A.; Dabbebi, H.; Ben Mrad, M.; Abdrabbah, M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Heat Stress and Oxidative-Induced Mitochondrial Damage. A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Hu, S.-H.; Hung, S.-Y.; Chiang, C.-S.; Liu, H.-L.; Chiu, T.-L.; Lai, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y. SPIO Nanoparticle-Stabilized PAA-F127 Thermosensitive Nanobubbles with MR/US Dual-Modality Imaging and HIFU-Triggered Drug Release for Magnetically Guided in vivo Tumor Therapy. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, P.; Di Corato, R.; Lartigue, L.; Wilhelm, C.; Espinosa, A.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; Gazeau, F.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. Water-Soluble Iron Oxide Nanocubes with High Values of Specific Absorption Rate for Cancer Cell Hyperthermia Treatment. Acs Nano 2012, 6, 3080–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, H.; Ou, Z.; Liu, J.; Duan, W.; Wang, H.; Ge, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, F.; et al. GPX4 and Vitamin E Cooperatively Protect Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells from Lipid Peroxidation and Ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Constantinou, C.; Papageorgis, P.; Constantinou, A.I. D-alpha-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol Succinate (TPGS) Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Selectively in Survivin-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 89, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beola, L.; Asín, L.; Roma-Rodrigues, C.; Fernández-Afonso, Y.; Fratila, R.M.; Serantes, D.; Ruta, S.; Chantrell, R.W.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V.; et al. The Intracellular Number of Magnetic Nanoparticles Modulates the Apoptotic Death Pathway after Magnetic Hyperthermia Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43474–43487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Hernández, M.; del Pino, P.; Mitchell, S.G.; Moros, M.; Stepien, G.; Pelaz, B.; Parak, W.J.; Gálvez, E.M.; Pardo, J.; de la Fuente, J.M. Dissecting the Molecular Mechanism of Apoptosis during Photothermal Therapy Using Gold Nanoprisms. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Lai, S.-M.; Li, C.-Z.; Yu, H.-P.; Venkatesan, P.; Lai, P.-S. D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Poly(ethylene Glycol 1000) Succinate-Coated Manganese-Zinc Ferrite Nanomaterials for a Dual-Mode Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent and Hyperthermia Treatments. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051000
Wang L, Lai S-M, Li C-Z, Yu H-P, Venkatesan P, Lai P-S. D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Poly(ethylene Glycol 1000) Succinate-Coated Manganese-Zinc Ferrite Nanomaterials for a Dual-Mode Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent and Hyperthermia Treatments. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(5):1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051000
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lin, Syu-Ming Lai, Cun-Zhao Li, Hsiu-Ping Yu, Parthiban Venkatesan, and Ping-Shan Lai. 2022. "D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Poly(ethylene Glycol 1000) Succinate-Coated Manganese-Zinc Ferrite Nanomaterials for a Dual-Mode Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent and Hyperthermia Treatments" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 5: 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051000
APA StyleWang, L., Lai, S.-M., Li, C.-Z., Yu, H.-P., Venkatesan, P., & Lai, P.-S. (2022). D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Poly(ethylene Glycol 1000) Succinate-Coated Manganese-Zinc Ferrite Nanomaterials for a Dual-Mode Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent and Hyperthermia Treatments. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051000





