Formulation of Dosage Forms with Proton Pump Inhibitors: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
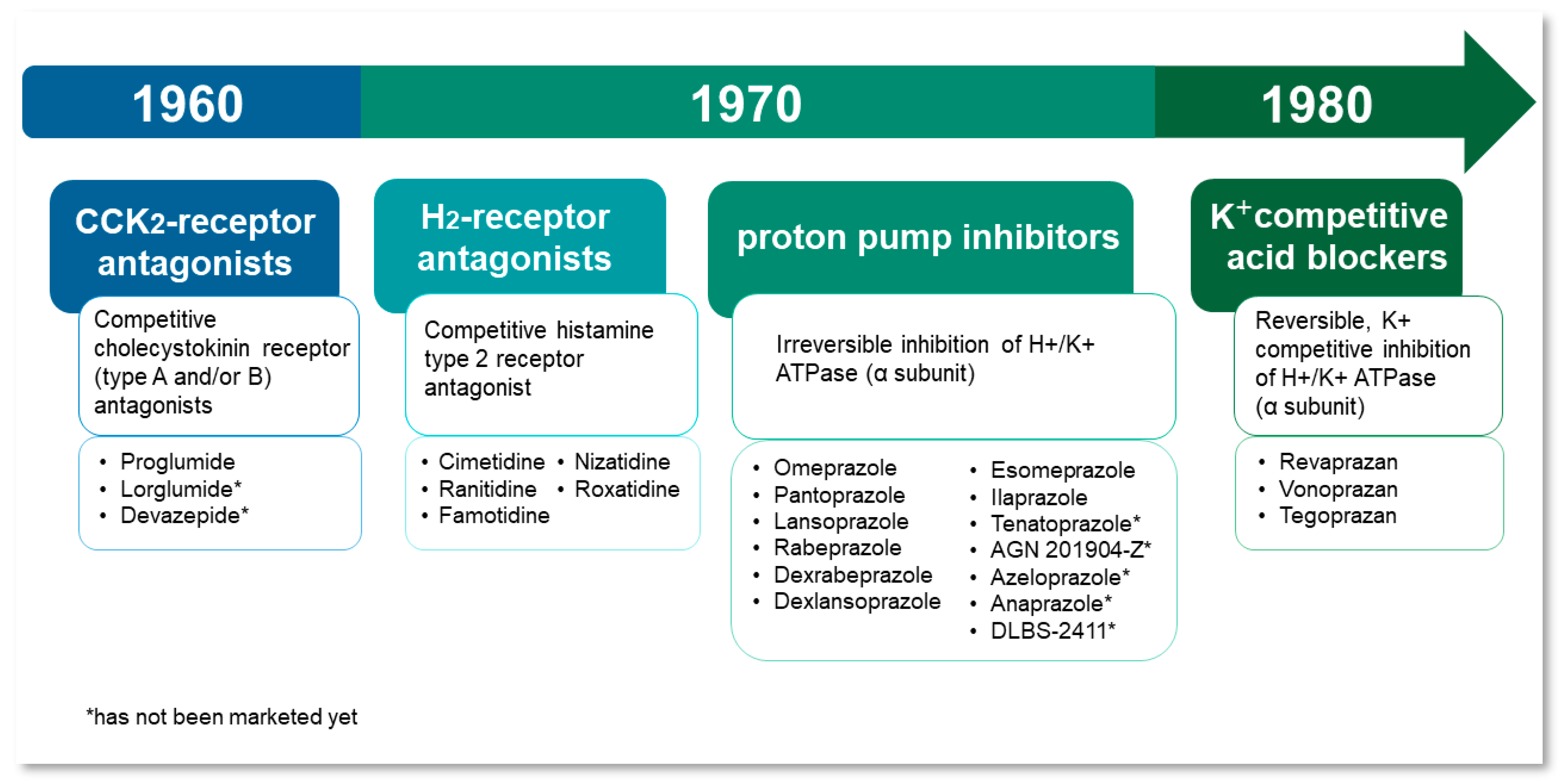
1.1. Historical Background
1.2. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
1.3. Medical Uses
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD),
- Functional dyspepsia,
- Erosive/Non-erosive Esophagitis,
- Gastric and duodenal ulcers,
- Helicobacter pylori infections (combination therapy),
- Hypersecretory syndromes (e.g., Zollinger-Ellison syndrome),
- and in the prevention of NSAID-induced gastroduodenal ulcers.
2. The Most Important Issues to Be Considered in the Formulation of Medicinal Products with PPIs
2.1. Physicochemical Properties of PPIs
2.2. Stability of Proton Pump Inhibitors
2.3. Stability in Solutions
2.4. Influence of Temperature
2.5. Influence of Salts
2.6. Influence of Light
2.7. Interaction of Enteric Polymers with PPIs and Its Effect on the Stability
2.8. Analytical Methods for PPIs Determination
| PPI | Analytical Method | Details | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| omeprazole | UV-Vis spectrophotometry | formation of colored species in reaction with 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone (MBTH) | [70] |
| UV-Vis spectrophotometry, 2nd derivative method | linearity in the range of 0.2–40.0 µg/mL | [71] | |
| differential pulse polarography | static mercury electrode; linearity in the range of 0.2–20 µmol/L | [72] | |
| RP-HPLC | UV-Vis detection at λ = 280 nm; mobile phase phosphate buffer (pH = 7.4):acetonitrile (70:30); linearity in the range of 10.0–30.0 µg/mL | [73] | |
| esomeprazole | RP-HPLC | UV-Vis detection at λ = 300 nm; mobile phase acetonitrile:methanol (50:50); linearity in the range of 5.0–25.0 µg/mL | [74] |
| lansoprazole | square-wave voltammetry | hanging mercury drop electrode (HMDE); pH of investigated solutions 2.0–11.0; linearity in the range of 1.0 × 10−9–5.0 × 10−8 M | [75] |
| RP-HPLC | UV-Vis detection at λ = 284 nm; mobile phase methanol:water (80:20); linearity in the range of 50.0–30.0 μg/mL | [76] | |
| LC-MS/MS | mobile phase water:acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid (60:40); IT-TOF detection; linearity in the range of 5.0–25.0 µg/mL | [77] | |
| pantoprazole | RP-HPLC | UV-Vis detection at λ = 289 nm; mobile phase potassium dihydrogen solution:acetonitrile (70:30); linearity in the range of 20.0–200.0 µg/mL | [78] |
| LC-ESI-MS/MS | LC mobile phase acetonitrile:water:methanol (57:25:18) with addition of 10 mmol/L acetic acid and 20 mmol/L ammonium acetate; transition m/z 383.8→199.6; linearity in the range of 5–5000 ng/mL | [79] | |
| Chiral LC-MS/MS | LC mobile phase 10 mM ammonium acetate solution containing 0.1% acetic acid:acetonitrile (28:72); transition m/z 384.1→200; linearity in the range of 5–10,000 ng/mL | [80] | |
| rabeprazole | LC-ESI-MS/MS | LC mobile phase methanol:water (50:50) with addition of 0.1% of formic acid in water; transition m/z 359.95→241.96; linearity in the range of 0.2–200 ng/mL | [81] |
| dexrabeprazole sodium | RP-UPLC | UV-Vis detection at λ = 284 nm; mobile phase A—phosphate buffer (pH = 7.0):acetonitrile (99:1) and mobile phase B—methanol:acetonitrile (95:5) (gradient elution) | [82] |
| ilaprazole | UPLC | UV-Vis detection at λ = 305 nm; mobile phase acetonitrile:methanol:ammonium acetate buffer (0.05 M; pH = 8.5) (gradient elution); linearity in the range of 0.05–0.60 µg/mL | [83] |
| LC-ESI-MS/MS | LC mobile phase 10 mmol/L ammonium formate:water-acetonitrile solution (50:50); transition m/z 367.2→184.0; linearity in the range of 0.23–2400 ng/mL | [84] | |
| tenatoprazole | RP-HPLC | UV-Vis detection at λ = 307 nm; mobile phase methanol:THF:acetate buffer (68:12:20); linearity in the range of 0.5–160.0 µg/mL | [85] |
| TLC | stationary phase—aluminium plates with silica gel; solvent system—toluene:ethyl acetate:methanol (6 + 4 + 1), Rf = 0.34; linearity in the range of 100.0–1500.0 ng/spot | [86] |
3. PPIs’ Pharmaceutical Formulations Available on the Market
3.1. Delayed-Release Tablets
3.2. Delayed-Release Capsules
3.3. Oral Suspensions
3.4. Powders for Injections or Infusions
| PPI | Dosage [mg] * | Drug Form | Brand Name (e.g.) | Additional Comments | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omeprazole | 10, 20, 40 | DR tablets | Omeprazole Dexcel Pharma |
| [90,91,92] |
| 20 | Orally disintegrating DR tablets | Omeprazole DR Orally Disintegrating tablets Dexcel Pharma |
| [122,123] | |
| 10, 20, 40 | Capsules with DR pellets | Losec |
| [132,133,134] | |
| Omeprazole Sandoz |
| [135] | |||
| 20, 40 | Oral Suspension, DR | Zegerid |
| [152] | |
| 2 mg/mL 4 mg/mL | Omeprazole, Powder for Oral Suspension |
| [153,154] | ||
| Omeprazole magnesium | 20 | DR tablets | Prilosec OTC |
| [93,94] |
| Losec Control | [95] | ||||
| 10, 20, 40 | Losec MUPS |
| [96,97,98,99] | ||
| Orally disintegrating DR tablets | Mezzopram |
| [124,125,126] | ||
| 20 | Capsules with DR pellets | Omeprazole Magnesium |
| [136] | |
| Omeprazole Magnesium DR mini-capsules |
| [147] | |||
| 2, 5, 10 | Oral suspension, DR | Prilosec |
| [150] | |
| Omeprazole sodium | 40 | Powder for solution for infusion | Omeprazole 40 mg Powder for Solution for Infusion |
| [167] |
| Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate | 20, 40 | DR tablets | Controloc (Pantoprazole sodium Takeda) Controloc Control 20 |
| [100,101,102] |
| Protonix | [148] | ||||
| 40 | Oral suspension DR | Protonix Pantoprazole SUN Pharma |
| [148,149] | |
| 40 | Powder for solution for injection | Protium I.V. Pantoprazole 40 mg Zentiva |
| [165,166] | |
| Protonix I.V. |
| [164] | |||
| Lansoprazole | 15, 30 | Orally disintegrating DR tablets | Zoton FasTab Lansoprazole Mylan |
| [127,128,129,130] |
| Prevacid |
| [131] | |||
| Capsules with DR pellets | Lansoprazole Accord |
| [137,138] | ||
| Lansoprazole Capsules Sandoz |
| [146] | |||
| Rabeprazole sodium | 10, 20 | DR tablets | Pariet Rabeprazole Accord |
| [103,104,105,106] |
| 20 | Aciphex Rabeprazole sodium Aurobindo |
| [107,108] | ||
| Esomeprazole magnesium | 20, 40 | DR tablets | Nexium Esomeprazole Accord |
| [109,110,111,114] |
| 20 | Nexium 24H Esomperazole Dr Reddy’s |
| [112,113] | ||
| 20, 40 | Capsules with DR pellets | Ventra |
| [139,140] | |
| Nexium |
| [141] | |||
| 2,5, 5, 10, 20, 40 | Oral suspension, DR | Nexium |
| [141,151] | |
| Esomeprazole sodium | 20, 40 | GR tablets | Esomeprazol Cinfa |
| [115,116] |
| 20, 40 | GR capsules | Esomperazol Cinfa |
| [142,143] | |
| 40 | Powder for solution for infusion/injection | Nexium IV |
| [162,163] | |
| Dexlansoprazole | 30, 60 | Capsules with DR pellets | Dexilant |
| [144,145] |
| Ilaprazole | 5, 10, 20 | DR tablets | Noltec Norutec | [117,118,119] |
3.5. Fixed-Dose Combinations
3.6. Administration of PPIs via a Feeding Tube
3.7. Pediatric Population
3.8. Storage and Packaging
4. Development of New Formulations with PPIs
4.1. Nanoparticles
4.2. Microparticles
4.3. Minitablets
4.4. Pellets
4.5. Tablets
4.6. Fixed-Dose Combination Products
4.7. Bilayer Tablets
4.8. Floating Tablets
4.9. Hydrogel Formulations
4.10. Mucoadhesive Tablets
4.11. Oral Liquid Suspensions
4.12. Transdermal Delivery
4.13. Suppositories
4.14. Intravenous Formulations
| Formulation | PPI | Development Stage | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticles | Omeprazole | In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [187] |
| In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [190] | ||
| Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [189] | |
| In vitro |
| [191] | ||
| Pantoprazole + Aceclofenac | In vitro In vivo (rats) |
| [193] | |
| Lansoprazole | In vitro |
| [188] | |
| In vitro |
| [192] | ||
| In vitro |
| [194] | ||
| In vitro |
| [196] | ||
| Lansoprazole + curcumin | In vitro |
| [197] | |
| Esomeprazole | In vitro Ex vivo permeability study In vivo PK and PD studies (rats) |
| [195] | |
| Microparticles | Omeprazole | In vitro In vivo PK study (rabbits) |
| [29] |
| In vitro |
| [224] | ||
| In vitro |
| [228] | ||
| In vitro |
| [233] | ||
| In vitro |
| [234] | ||
| Omeprazole + piperine | In vivo PK and bioavailability studies (rabbits) |
| [221] | |
| Omeprazole + clarithromycin | In vitro |
| [208] | |
| Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [51] | |
| In vitro |
| [52] | ||
| In vitro |
| [200] | ||
| In vitro |
| [202] | ||
| In vitro |
| [205] | ||
| In vitro |
| [206] | ||
| In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [209] | ||
| In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [210] | ||
| In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [211] | ||
| In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [215] | ||
| In vitro |
| [216] | ||
| In vitro |
| [218] | ||
| In vivo bioavailability study (dogs) |
| [219] | ||
| In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [222] | ||
| In vitro |
| [223] | ||
| Lansoprazole | In vitro In vivo PK and antiulcer activity studies (rats) |
| [199] | |
| In vitro |
| [204] | ||
| In vitro |
| [207] | ||
| In vitro |
| [212] | ||
| In vitro |
| [213] | ||
| In vitro |
| [217] | ||
| In vitro |
| [220] | ||
| In vitro |
| [227] | ||
| Rabeprazole | In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [198] | |
| In vitro |
| [201] | ||
| In vitro In vivo floating study (rabbits) |
| [235] | ||
| Rabeprazole + amoxicillin | In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity and radiographic study (rats) |
| [214] | |
| Esomeprazole | In vitro |
| [203] | |
| Minitablets | Omeprazole | In vitro |
| [236] |
| Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [237] | |
| Pellets | Omeprazole | In vitro In vivo PK and gastro-resistance studies (dogs/rats) |
| [239] |
| In vitro In vivo PK and bioequivalence studies (rabbits) |
| [242] | ||
| In vitro In silico (ANN, modelling tablet properties) |
| [248] | ||
| In vitro |
| [251] | ||
| In vitro |
| [252] | ||
| Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [241] | |
| Lansoprazole | In vitro |
| [31] | |
| In vitro |
| [238] | ||
| In vitro |
| [240] | ||
| In vitro In vivo PK study (dogs) |
| [243] | ||
| In vitro |
| [247] | ||
| In vitro In vivo bioavailability study (dogs) |
| [249] | ||
| Rabeprazole | In vitro |
| [245] | |
| In vitro |
| [246] | ||
| In vitro |
| [250] | ||
| Esomeprazole | In vitro In vivo PK study (rats) IVIVC |
| [30] | |
| In vitro In silico (ANN, coating process) |
| [244] | ||
| Tablets | Omeprazole | In vitro |
| [263] |
| In vitro |
| [264] | ||
| In vitro |
| [286] | ||
| Omeprazole + domperidone | In vitro |
| [287] | |
| Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [262] | |
| In vitro In vivo antiulcer activity (rats) |
| [269] | ||
| In vitro |
| [273] | ||
| In vitro |
| [274] | ||
| In vitro |
| [288] | ||
| Lansoprazole | In vitro |
| [257] | |
| In vitro |
| [266] | ||
| In vitro In vivo absorption studies (dogs), disintegration time in the mouth (human) |
| [276,277,278] | ||
| In vitro |
| [279] | ||
| In vivo (human) Clinical trials |
| [280,281] | ||
| In vivo (human) |
| [282] | ||
| In vivo bioequivalence studies (human) |
| [283] | ||
| In vitro In vivo (human) |
| [284] | ||
| In vitro |
| [285] | ||
| Rabeprazole | In vitro In vivo PK studies (beagle dogs) |
| [33] | |
| In vitro |
| [253] | ||
| In vitro |
| [258] | ||
| In vitro |
| [259] | ||
| In vitro |
| [270] | ||
| In vitro |
| [289] | ||
| Esomeprazole | In vitro |
| [256] | |
| In vitro |
| [260] | ||
| In vitro Ex vivo permeation studies (porcine mucosa) In vivo pharmacokinetics studies (rats) |
| [261] | ||
| In vitro |
| [267] | ||
| In vitro |
| [275] | ||
| Dexlansoprazole | In vitro |
| [272] | |
| Tenatoprazole | In vitro |
| [255] | |
| In vitro |
| [268] | ||
| Ilaprazole | In vitro |
| [254] | |
| In vitro |
| [271] | ||
| Fixed-dose combination products | Esomeprazole + naproxen | In vitro |
| [290] |
| Bilayer tablets | Lansoprazole + amoxycillin | In vitro |
| [293] |
| Esomeprazole + aceclofenac | In vitro |
| [294] | |
| Esomeprazole + clarithromycin | In vitro |
| [291] | |
| Esomeprazole + levosulpiride | In vitro |
| [292] | |
| Floating tablets | Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [295] |
| In vitro |
| [297] | ||
| Lansoprazole | In vitro |
| [296] | |
| In vitro |
| [299] | ||
| Rabeprazole | In vitro In vivo pharmacokinetic and antiulcer activity studies (rats) |
| [298] | |
| Hydrogel formulations | Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [301] |
| In vitro |
| [302] | ||
| In vitro In vivo studies on hydrogel gastro-retention (mice) |
| [303] | ||
| Rabeprazole | In vitro |
| [304] | |
| Mucoadhesive tablets | Omeprazole | In vitro |
| [305] |
| In vitro In vivo studies on absorption from the oral cavity and tablets adhesion to the oral mucosa (human) |
| [307] | ||
| In vitro In vivo pharmacokinetic studies (hamsters) |
| [308] | ||
| In vitro In vivo pharmacokinetic studies (hamster), mucoadhesive force measurement (human) |
| [309] | ||
| In vitro |
| [310] | ||
| Pantoprazole | In vitro |
| [306] | |
| Oral liquid suspensions | Omeprazole | In vitro |
| [311] |
| In vitro |
| [312] | ||
| In vitro In vivo preliminary toxicity and antiulcer activity studies (mice) |
| [313] | ||
| Transdermal delivery | Omeprazole | In vivo PK study (human) |
| [316] |
| Lansoprazole | Ex vivo penetration study (pigs) In vivo PK study (rats) |
| [315] | |
| Rabeprazole | Ex vivo penetration study (snake) |
| [314] | |
| Suppositories | Omeprazole | In vitro |
| [317] |
| Clinical trial (efficacy, PK) |
| [318] | ||
| Intravenous formulations | Omeprazole | In vitro |
| [319] |
| In vitro |
| [320] |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Nehra, A.K.; Alexander, J.A.; Loftus, C.G.; Nehra, V. Proton pump inhibitors: Review of emerging concerns. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welage, L.S. Pharmacologic properties of proton pump inhibitors. Pharmacotherapy 2003, 23, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herszényi, L.; Bakucz, T.; Barabás, L.; Tulassay, Z. Pharmacological approach to gastric acid suppression: Past, present, and future. Dig. Dis. 2020, 38, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-Q.; Hunt, R.H. Pharmacological and pharmacodynamic essentials of H2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors for the practising physician. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2001, 15, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignato, C.; Hunt, R.H. The potential role of potassium-competitive acid blockers in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 35, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Miwa, H. Potent potassium-competitive acid blockers: A new era for the treatment of acid-related diseases. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IQVIA. Medicine Spending and Affordability in the United States; IQVIA: Durham, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mikulic, M. Leading 10 Antisecretory Drugs and Mucosal Protectants Dispensed in England in 2021, by Number of Items. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/378256/top-ten-dispensed-antisecretory-drugs-by-item-in-england/ (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Olbe, L.; Carlsson, E.; Lindberg, P. A proton-pump inhibitor expedition: The case histories of omeprazole and esomeprazole. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2003, 2, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunack, W. What are the differences between the H2- receptor antagonists? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1987, 1, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Munson, K.; Vagin, O.; Sachs, G. The gastric HK-ATPase: Structure, function, and inhibition. Pflug. Arch.—Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 457, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, G.; Shin, J.M.; Vagin, O.; Lambrecht, N.; Yakubov, I.; Munson, K. The gastric H,K-ATPase as a drug target: Past, present, and future. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, S226–S242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, R. Cholecystokinin antagonists: Pharmacological and therapeutic potential. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 559–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, P.N.; Jensen, R.T.; Gardner, J.D. Cholecystokinin antagonists. Horm. Metabol. Res. 1986, 18, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Histamine type-2 receptor antagonists (H2 Blockers). In LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6.
- Daly, M.J.; Price, B.J. Ranitidine and other H2-receptor antagonists: Recent developments. Prog. Med. Chem. 1983, 20, 337–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knadler, M.P.; Bergstrom, R.F.; Callaghan, J.T.; Rubin, A. Nizatidine, an H2-Blocker. Its metabolism and disposition in man. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1986, 14, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, A.; Zwolińska-Wcisło, M.; Paśko, P. Effect of food and dosing regimen on safety and efficacy of proton pump inhibitors therapy—A literature review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Sachs, G. Pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2008, 10, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, D.S.; Kim, D.; Peura, D.A. 25 years of proton pump inhibitors: A comprehensive review. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.H.; Scarpignato, C. Potent acid suppression with PPIs and P-CABs: What’s new? Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 570–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignato, C.; Hunt, R.H. Proton pump inhibitors: The beginning of the end or the end of the beginning? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.H.; Armstrong, D.; Yaghoobi, M.; James, C.; Chen, Y.; Leonard, J.; Shin, J.M.; Lee, E.; Tang-Liu, D.; Sachs, G. Predictable prolonged suppression of gastric acidity with a novel proton pump inhibitor, AGN 201904-Z. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Homerin, M.; Domagala, F.; Ficheux, H.; Sachs, G. Characterization of the inhibitory activity of tenatoprazole on the gastric H+,K+-ATPase in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmiche, J.P.; Bruley Des Varannes, S.; Ducrotté, P.; Sacher-Huvelin, S.; Vavasseur, F.; Taccoen, A.; Fiorentini, P.; Homerin, M. Tenatoprazole, a novel proton pump inhibitor with a prolonged plasma half-life: Effects on intragastric pH and comparison with esomeprazole in healthy volunteers. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 19, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Kim, N. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the proton pump inhibitors. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.; Horn, J. Clinical pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors: What the practising physician needs to know. Drugs 2003, 63, 2739–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DrugBank Online. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/ (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Geng, L.; Han, L.; Huang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Qi, X. High anti-acid omeprazole lightweight capsule for gastro-enteric system acid-related disorders treatment. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. Treat. 2019, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, S.-L.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.-P.; Zhao, Y. Preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of esomeprazole magnesium-modified release pellets. Drug. Deliv. 2016, 23, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yang, M.; Fan, J.H.; Feng, C.X.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, J.X.; Guan, P.P.; Wu, W. Influences of sodium carbonate on physicochemical properties of lansoprazole in designed multiple coating pellets. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sun, L.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; Ren, C.; Ai, X.; Lian, H.; He, Z. Profiling biopharmaceutical deciding properties of absorption of lansoprazole enteric-coated tablets using gastrointestinal simulation technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-E. Quality by design applied development of immediate-release rabeprazole sodium dry-coated tablet. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, D.R.; Klein, S.; Zoller, T.; Vieria, N.R.; Barros, F.A.P.; Meurer, E.C.; Coelho, E.C.; Marchioretto, M.A.; Pedrazzoli, J. Evaluation of pantoprazole formulations in different dissolution apparatus using biorelevant medium. Arzneimittelforschung 2010, 60, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.M.; Sachs, G. Proton pump inhibitors. Encycl. Gastroenterol. 2004, 14, 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Maderuelo, C.; Lanao, J.M.; Zarzuelo, A. Enteric coating of oral solid dosage forms as a tool to improve drug bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brändström, A.; Bergman, N.-Å.; Grundevik, I.; Johansson, S.; Tekenbergs-Hjelte, L.; Ohlson, K. Chemical reactions of omeprazole and omeprazole analogues. III. Protolytic behaviour of compounds in the omeprazole system. Acta Chem. Scand. 1989, 43, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, V.F. The chemically elegant proton pump inhibitors. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2006, 70, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Schulman, S.G.; Zavala, P.J. Acid-base chemistry of omeprazole in aqueous solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 481, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, T.; Weidolf, L. Stereoselective disposition of proton pump inhibitors. Clin. Drug. Investig. 2008, 28, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancu, G.; Modroiu, A. Chiral Switch: Between therapeutical benefit and marketing strategy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.; das Gupta, V.; Bailey, R.E. Stability of omeprazole solutions at various pH values as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1995, 21, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaGreca, M.; Iesce, M.R.; Previtera, L.; Rubino, M.; Temussi, F.; Brigante, M. Degradation of lansoprazole and omeprazole in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.V.; Nudelman, N.S.; Steppe, M.; Schapoval, E.E.S. Structural elucidation of rabeprazole sodium photodegradation products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadik, M.; Bhusari, V.; Kulkarni, M.; Dhaneshwar, S. LC-UV and LC-MS evaluation of stress degradation behaviour of tenatoprazole. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroyer, A.; McGinity, J.W.; Leopold, C.S. Solid state interactions between the proton pump inhibitor omeprazole and various enteric coating polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quercia, R.A.; Fan, C.; Liu, X.; Chow, M.S.S. Stability of omeprazole in an extemporaneously prepared oral liquid. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 1997, 54, 1833–1836. [Google Scholar]
- El-Badry, M.; Taha, E.I.; Alanazi, F.K.; Alsarra, I.A. Study of omeprazole stability in aqueous solution: Influence of cyclodextrins. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpe, A.; Jacobsen, T. Effect of various salts on the stability of lansoprazole, omeprazole, and pantoprazole as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1999, 25, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin, R.P.; Colomé, L.M.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R. Validação de metodologia analítica por cromatografia líquida para doseamento e estudo da estabilidade de pantoprazol sódico. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhurke, R.; Kushwaha, I.; Desai, B.G. Improvement in photostability of pantoprazole sodium by microencapsulation. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin, R.P.; Colomé, L.M.; Schapoval, E.E.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Increasing sodium pantoprazole photostability by microencapsulation: Effect of the polymer and the preparation technique. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaghi, S.; Young, C.; Fegely, K.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.R. Delayed release film coating applications on oral solid dosage forms of proton pump inhibitors: Case studies delayed release solid dosage forms of proton pump inhibitors. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, A.; Leopold, C.S. Degradation of omeprazole induced by enteric polymer solutions and aqueous dispersions: HPLC investigations. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2005, 31, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, A.; Leopold, C.S. Quantification of omeprazole degradation by enteric coating polymers: An UV-VIS spectroscopy study. Pharmazie 2005, 60, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.A.; Nerkar, P.P. Determination of proton pump inhibitors by spectrophotometric, chromatographic and by hyphenated techniques: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, V.; López-Viota, M.; Sierra, J.; Ruiz, M.A. Spectrophotometric and chromatographic determination of omeprazole in pharmaceutical formulations. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 14, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahbi, A.-A.M.; Abdel-Razak, O.; Gazy, A.A.; Mahgoub, H.; Moneeb, M.S. Spectrophotometric determination of omeprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 30, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherif, Z.A.; Mohamed, A.O.; El-Bardicy, M.G.; El-Tarras, M.F. Reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of lansoprazole, omeprazole and pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate in presence of their acid-induced degradation products. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharathi, D.V.; Hotha, K.K.; Jagadeesh, B.; Chatki, P.K.; Thriveni, K.; Mullangi, R.; Naidu, A. Simultaneous estimation of four proton pump inhibitors—Lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole and rabeprazole: Development of a novel generic HPLC-UV method and its application to clinical pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkady, E.F.; Fouad, M.A.; Jaadan, B.M. LC–MS/MS bioassay of four proton pump inhibitors. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1076, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunduri, R.H.B.; Dannana, G.S. Development and validation of a high throughput UPLC–MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of esomeprazole, rabeprazole and levosulpiride in human plasma. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, R.; Narenderan, S.T.; Babu, B.; Meyyanathan, S.N.; George, A.J.; Kalaivani, M. Sensitive analytical liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopy method for the estimation of dexlansoprazole in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, M.-J.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.-L.; Xu, H.-J.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Zou, J.-J.; Fan, H.-W.; Zhou, X.-M. Quantification of pantoprazole in human plasma using LC-MS/MS for pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence study. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 35, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.; Kumar, R.S.; Shankar, M.B.; Danabal, P. Development and validation of a sensitive and high-throughput LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of esomeprazole and naproxen in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zaher, A.A.; El-Kady, E.F.; El-Messiry, H.M.; El-Ghwas, H.E.; El-Houssini, O.M. Synchronous LC-MS/MS determination of pantoprazole and amitriptyline in rabbit plasma: Application to comparative in vivo pharmacokinetic study of novel formulated effervescent granules with its marketed tablet dosage form. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, L.A.; Hancu, G.; Kelemen, H.; Tóth, G. Chiral separation in the class of proton pump inhibitors by chromatographic and electromigration techniques: An overview. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 1761–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.-N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Shen, Y.; Ying, Y.-W.; Su, Y.-W.; Zhang, X.-H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.-Q. Simultaneous enantioselective determination of omeprazole, rabeprazole, lansoprazole, and pantoprazole enantiomers in human plasma by chiral liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3183–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kommos, M.E.; Khashaba, P.Y.; Ali, H.R.H.; El-Wekil, M.M. Different chromatographic and electrophoretic methods for analysis of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): A review. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 1639–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, C.S.P.; Naidu, P.Y.; Murty, S.S.N. Spectrophotometric methods for the determination of omeprazole in bulk form and pharmaceutical formulations. Talanta 1997, 44, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özaltin, N.; Koçer, A. Determination of omeprazole in pharmaceuticals by derivative spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1997, 16, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özaltin, N.; Temizer, A. Differential pulse polarographic determination of omeprazole in pharmaceutical preparations. Electroanalysis 1994, 6, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, F.S.; Cruz, A.P.; Pereira, R.N.; Valente, B.R.; Silva, M.A.S. Development and validation of a RP-HPLC method to quantify omeprazole in delayed release tablets. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 30, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Shah, V.K.; Jain, P.K. HPLC method development and validation for the estimation of esomeprazole in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Radi, A. Adsorptive stripping square-wave voltammetric study of the degradation of lansoprazole in aqueous solutions. Microchem. J. 2002, 73, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, S.; Nisha, C.; Jyoti, R.; Inamullah; Surabhi, S.; Kumar, Y.A.; Hemendra, G.; Shashank, C.; Kumar, A.V. Validated RP-UPLC method development for estimation of lansoprazole in tablet dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 5, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.D.; Connor, J.D.; Smallwood, N.C.; Lugo, R.A. Quantification of lansoprazole in oral suspension by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography hybrid ion-trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 2011, 832414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaiah, K.; Kumar, U.R.A.; Tharapa, K. A New HPLC method for the quantification of pantoprazole in pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2008, 6, 579–586. [Google Scholar]
- Peres, O.; Oliveira, C.H.; Barrientos-Astigarraga, R.E.; Rezende, V.M.; Mendes, G.P.; de Nucci, G. Determination of pantoprazole in human plasma by LC-MS-MS using lansoprazole as internal standard. Arzneim. Forsch. Drug Res. 2004, 54, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Yu, L.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y. A chiral LC-MS/MS method for the enantioselective determination of R-(+)- and S-(-)-pantoprazole in human plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study of S -(-)-pantoprazole sodium injection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Rui, L.; Guo, Q. Development of a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry assay for the quantification of rabeprazole in human plasma. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2321–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadangale, S.T.; Dhalape, V.M.; Pinjari, R.V. Development and validation of rapid, sensitive RP-UPLC method for determination of related impurities in dexrabeprazole sodium. Orient. J. Chem. 2018, 34, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, B.; Ganesh, K.K.S.; Saravanan, D.; Ramakant, K.G.; Sivananthan, S. Simultaneous determination of ilaprazole and its related compounds in pharmaceutical dosage forms by UPLC. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2013, 36, 2968–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Tan, Z.-R.; Zhang, W.; Ou-Yang, D.-S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, D.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Fan, L.; Deng, H.-W. An improved LC-MS/MS method for quantitative determination of ilaprazole and its metabolites in human plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dhaneshwar, S.R.; Jagtap, V.N. Development and validation of stability indicating RP-HPLC-PDA method for tenatoprazole and its application for formulation analysis and dissolution study. Am. J. Analyt. Chem. 2011, 2, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dhaneshwar, S.R.; Bhusari, V.; Mahadik, M.V.; Santakumari, B. Application of a stability-indicating thin-layer chromatographic method to the determination of tenatoprazole in pharmaceutical dosage forms. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Article 57 Product Data EMA/518502/2018 Rev. 27. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/post-authorisation/data-medicines-iso-idmp-standards/public-data-article-57-database (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/ (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Omeprazole 10 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/662/smpc (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Omeprazole 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/663/smpc (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Omeprazole 40 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/664/smpc (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Prilosec OTC Official Label. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=35a79458-79f6-44d6-b74c-b4f4aaf0dde0&type=display (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- P&G. Prilosec OTC Product Monograph. Available online: https://prilosecotc.com/en-us/article/product-monograph (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Medicines.ie. SmPC Losec Control 20 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.ie/medicines/losec-control-32736/spc#tabs (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Bergstrand, P.J.A.; Lovgren, K.I. Multiple Unit Tableted Dosage Form of Omeprazole. U.S. Patent 58173381998, 6 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Losec MUPS Tablets 10 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1493/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Losec MUPS Tablets 20 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1514/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Losec MUPS Tablets 40 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1374/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Pantoprazole 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/483/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Pantoprazole 40 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/484/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). SmPC Controloc Control 20 mg. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/controloc-control (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Pariet 10 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/3804/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Pariet 20 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/7867/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Rabeprazole 10 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2842/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmpC Rabeprazole 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2843/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Medication Guide Aciphex Delayed-Release Tablets. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=020973 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Medication Guide Rabeprazole Sodium Tablet, Delayed Release. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d11c3211-b4d4-4893-8c1c-b8fb6d0a0b89 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Nexium 40 mg Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4658/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). Patient Leaflet: Esomeprazole 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2968/pil (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Esomeprazole 40 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/3002/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Nexium 24H Drug Label Info. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=61f67858-ba2f-449b-8b30-c15cdaf49222 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Esomeprazole Magnesium Tablet, Delayed Release—Drug Label Info. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=94e0d10a-4c72-4e58-abf7-cc00f7b90b23 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Nexium 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4657/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Medicine Online Information Center of AEMPS (CIMA). Leaflet Esomperazol Cinfa 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/pdfs/es/p/75071/P_75071.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Medicine Online Information Center of AEMPS (CIMA). Leaflet Esomeprazole Cinfa 40 mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/pdfs/es/p/75074/P_75074.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Actuamed. Norutec Tabletas, Vademecum Actuamed-Rx. Available online: https://www.medicamentos.com.mx/marca/713471 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Kim, S.K.; Bang, H.C.; Sohn, Y.T. Preformulation study of a proton pump inhibitor ilaprazole. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, F.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, J.; Zeng, S.; Wu, F.; Zhang, N.; Yu, L. Development of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of ilaprazole enantiomers in rat plasma and its pharmacokinetic application. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerome, A.; Mulder, C.J.J.; Schror, K.; Vavricka, S.R. Omeprazole MUPS®: An Advanced Formulation Offering Flexibility and Predictability for Self-Medication. Available online: https://selfcarejournal.com/article/omeprazole-mups-an-advanced-formulation-offering-flexibility-and-predictability-for-self-medication/ (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Abdul, S.; Chandewar, A.V.; Jaiswal, S.B. A flexible technology for modified-release drugs: Multiple-Unit Pellet System (MUPS). J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penhasi, A.; Gomberg, M.; Meisler, T.; Gauchman, J. Oral Dispersible Delayed Release Tablet Formulation. WO Patent 2011/111027 A2, 15 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. SUPPL-7 Label Container: Omeprazole Delayed-Release Orally Disintegrating Tablets 20 mg. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=209400 (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Mezzopram 10 mg Dispersible Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4585/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Mezzopram 20 mg Dispersible Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4584/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Mezzopram 40 mg Dispersible Gastro-Resistant Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4583/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Zoton Fas Tab 30 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1969/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Zoton FasTab 15 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1714/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Lansoprazole 15 mg Orodispersible Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4395/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Lansoprazole 30 mg Orodispersible Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4396/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Medication Guide Prevacid SoluTab and Prevacid Delayed-Release Capsules. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=021428 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Losec Capsules 10 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1495/smpc (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Losec Capsules 20 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1509/smpc (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Losec Capsules 40 mg. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1373/smpc (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Medication Guide Omeprazole Delayed-Release Capsules. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e4562da8-9d94-4417-9f80-c1ffd4247259 (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Omeprazole Magnesium Capsules, DR—Drug Label Info. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=0e8fde83-a55c-edaf-3c66-e1fc77d0bc11 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Lansoprazole 15 mg Gastro-Resistant Capsules. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4164/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Lansoprazole 30 mg Gastro-Resistant Capsules. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4761/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Ventra (Esomeprazole) 40 mg Gastro-Resistant Capsules, Hard. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4448/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Ventra (Esomeprazole) 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Capsules, Hard. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4447/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Medication Guide Nexium Delayed-Release Capsules, Delayed-Release Oral Suspension. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=021957 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Medicine Online Information Center of AEMPS (CIMA). Leaflet Esomeprazole Cinfa 20 mg Gastro-Resistant Capsules. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/pdfs/es/p/82921/P_82921.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Medicine Online Information Center of AEMPS (CIMA). Leaflet Esomeprazole Cinfa 40 mg Gastro-Resistant Capsules. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/pdfs/es/p/82922/P_82922.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Rejestr Produktów Leczniczych (RPL). ChPL Dexilant Kapsułki o Zmodyfikowanym Uwalnianiu, 30 mg, 60 mg. Available online: https://rejestrymedyczne.ezdrowie.gov.pl/api/rpl/medicinal-products/30689/characteristic (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Medication Guide Dexilant Delayed-Release Capsules. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=BasicSearch.process (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Medication Guide Lansoprazole Delayed-Release Capsules 15 mg, 30 mg. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=8a7a1fbf-652c-4c2a-8118-815341e8d2c1 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Perrigo Company PLC. Perrigo Announces U.S. FDA Approval for Omeprazole Magnesium Delayed-Release Mini Capsules. Available online: https://investor.perrigo.com/2022-05-26-PERRIGO-ANNOUNCES-U-S-FDA-APPROVAL-FOR-OMEPRAZOLE-MAGNESIUM-DELAYED-RELEASE-MINI-CAPSULES (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Medication Guide Protonix Delayed-Release Tablets, Delayed-Release Suspension. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=020987 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Sun Pharma. Medication Guide Pantoprazole Sodium for Delayed-Release Oral Suspension. Available online: https://www.sunpharma.com/usa/products (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Medication Guide Prilosec Oral Suspension. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/medguide.cfm?setid=b6761f84-53ac-4745-a8c8-1e5427d7e179 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Nexium 10 mg Gastro-Resistant Granules for Oral Suspension, Sachet. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/6674/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Medication Guide Zegerid Oral Suspension/Capsules. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=021636 (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Omeprazole 2 mg/mL, Powder for Oral Suspension. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/11031/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Omeprazole 4 mg/mL, Powder for Oral Suspension. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/11032/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Bladh, N.; Blychert, E.; Johansson, K.; Backlund, A.; Lundin, C.; Niazi, M.; Pettersson, G.; Fjellman, M. A new esomeprazole packet (sachet) formulation for suspension: In vitro characteristics and comparative pharmacokinetics versus intact capsules/tablets in healthy volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A.; Roach, A.C.; Carlsson, A.S.; Karlsson, A.A.S.; Behr, D.E. Stability of Esomeprazole Capsule Contents After In Vitro Suspension in Common Soft Foods and Beverages. Pharmacotherapy 2003, 23, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonini, H.C.; Silva, S.L.; Loures, S.; Almy, R.; Balland, A.; Brandão, M.A.F.; Ferreira, A.O. Compatibility of proton pump inhibitors in a preservative-free suspending vehicle. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2018, 25, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentinger, P.J.; Swenson, C.F.; Anaizi, N.H. Stability of pantoprazole in an extemporaneously compounded oral liquid. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2002, 59, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkoumov, A.; Soukrati, A.; Elkin, I.; Forest, J.M.; Hildgen, P.; Leclair, G. Quality evaluation of extemporaneous delayed-release liquid formulations of lansoprazole. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2011, 68, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferron, G.M.; Ku, S.; Abell, M.; Unruh, M.; Getsy, J.; Mayer, P.R.; Paul, J. Oral bioavailability of pantoprazole suspended in sodium bicarbonate solution. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2003, 60, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medicines Information Bank. Product Information: Omeprazol Sandoz Injectie 40, Powder and Solvent for Solution for Injection 40 mg. Available online: https://www.geneesmiddeleninformatiebank.nl/ords/f?p=111:3::SEARCH:::P0_DOMAIN,P0_LANG,P3_RVG1:H,EN,33289 (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- DailyMed. Nexium I.V. Drug Label Info. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c325bbfc-46f3-471e-7bbc-ed0d6965d13b (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Nexium I.V. 40 mg Powder for Solution for Injection/Infusion. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/43/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- DailyMed. Protonix I.V. Drug Label Info. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=f39b3e7d-39d2-4c8a-9974-4ab885241880 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Pantoprazole 40 mg Powder for Solution for Injection. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/11068/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Protium I.V. 40 Mg Powder for Solution for Injection. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2241/smpc (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC Omeprazole 40 mg Powder for Solution for Infusion. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4864/smpc (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Sjöstrand, S.E.; Olbe, L.; Fellenius, E.; Sachs, G.; Wallmark, B.; Huang, J.-Q.; Hunt, R.H.; Carlsson, E.; Havu, N.; Creutzfeldt, W.; et al. Proton Pump Inhibitors, 1st ed.; Olbe, L., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 161–172. ISBN 9783034897778. [Google Scholar]
- Leitner, A.; Zöllner, P. Visuelle Dokumentation der Stabilität der intravenösen Lösungen von Omeprazol (Losec®) und Pantoprazol (Pantoloc®). Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2002, 152, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupiec, T.C.; Aloumanis, V.; Ben, M.; Trissel, L.A.; Chan, P.; Patterson, J. Physical and chemical stability of esomeprazole sodium solutions. Ann. Pharmacother. 2008, 42, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, J.F.; McNulty, M.A.; Dusci, L.J.; Ilett, K.F. Stability of omeprazole sodium and pantoprazole sodium diluted for intravenous infusion. J. Pharm. Technol. 2006, 22, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.E. Stability of pantoprazole in 0.9% sodium chloride injection in polypropylene syringes. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2005, 62, 2410–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). SmPC VIMOVO 500 mg/20 mg Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5743 (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Drugs.com. Package Leaflet Diclofenac/Omeprazole Modified-Release Capsules, Hard, 75 mg/20 mg. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/uk/diclopram-75-mg-20-mg-modified-release-hard-capsules-leaflet.html (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Medicines Information Bank. Public Assessment Report Panclamox 40/500/1000 mg, Gastro-Resistant Tablet/ Film-Coated Tablet/Film-Coated Tablet. Available online: https://www.geneesmiddeleninformatiebank.nl/ords/f?p=111:3::SEARCH:::P0_DOMAIN,P0_LANG,P3_RVG1:H,EN,110766 (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Rejestr Produktów Leczniczych (RPL). ChPL DicloDuo Combi. Available online: https://rejestrymedyczne.ezdrowie.gov.pl/api/rpl/medicinal-products/34341/characteristic (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Finnish Medicines Agency (FIMEA). Leaflet: Information for the User Helipak A. Available online: http://spc.nam.fi/indox/english/humspc.jsp?letter=h (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Finnish Medicines Agency (FIMEA). Leaflet: Information for the User Helipak K. Available online: http://spc.nam.fi/indox/english/html/nam/humpil/5/23162835.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- AstraZeneca. Positive Agreement Received for Approval of VIMOVO in Europe. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2010/Positive-agreement-received-for-approval-of-VIMOVO-in-Europe-11102010.html#! (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Wensel, T.M. Administration of proton pump inhibitors in patients requiring enteral nutrition. P T 2009, 34, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- UpToDate. Drugs Demonstrated to be Effective for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/image?imageKey=PEDS%2F55435&topicKey=PEDS%2F5900&search=erge en niños&rank=2~150&source=see_link (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Ponrouch, M.P.; Sautou-Miranda, V.; Boyer, A.; Bourdeaux, D.; Montagner, A.; Chopineau, J. Proton pump inhibitor administration via nasogastric tube in pediatric practice: Comparative analysis with protocol optimization. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azurity Phamaceuticals. FIRST- Omperazole Rx, Product Information. Available online: https://firstkits.com/omeprazole/ (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Azurity Phamaceuticals. Lansoprazole 3 Mg/ML in FIRST®—PPI Suspension Compounding Kit Package Insert. Available online: https://firstkits.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Lansoprazole-Combined-PI_REV-04_PROOF.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Azurity Phamaceuticals. FIRST—Omeprazole Rx, Package Insert. Available online: https://firstkits.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Omeprazole-Package-Insert.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Davidson, A.G.; Mccallum, A. A Survey of the stability of omeprazole products from 13 countries. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1996, 22, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendas, E.R.; Abdelbary, A.A. Instantaneous enteric nano-encapsulation of omeprazole: Pharmaceutical and pharmacological evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 468, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alai, M.S.; Lin, W.J. A novel nanoparticulate system for sustained delivery of acid-labile lansoprazole. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasef, A.M.; Gardouh, A.R.; Ghorab, M.M. Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of pantoprazole loaded pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticles. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 3, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Safaran, R.; Minaiyan, M.; Mostafavi, A. Preparation and characterization of Eudragit L 100-55/chitosan enteric nanoparticles containing omeprazole using general factorial design: In vitro/ in vivo study. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, A.; Asati, S. Preparation, evaluation and optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles composed of pantoprazole. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2022, 12, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penjuri, S.C.B.; Ravouru, N.; Damineni, S.; Bns, S.; Poreddy, S.R. Formulation and evaluation of lansoprazole loaded nanosponges. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 13, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Guhathakarta, S.; Rajaram, R.; Korrapati, P.S. Electrospun zein/Eudragit nanofibers based dual drug delivery system for the simultaneous delivery of aceclofenac and pantoprazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 438, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, N.; Saini, V.; Bishnoi, V.K.; Garg, A.; Hisoria, M.; Sharma, J.; Nepali, K. Formulation and evaluation of lansoprazole niosome. Rasayan J. Chem. 2008, 1, 561–563. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, D.; Zafar, A.; Jafar, M.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Haque, M.A.; Gupta, J.K.; Bakshi, V.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshehri, S.; Jahangir, M.A.; et al. Development, in-vitro characterization and preclinical evaluation of esomeprazole-encapsulated proniosomal formulation for the enhancement of anti-ulcer activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.; Chaphalkar, R.; Deshmukh, K.; Gaud, R.S. Physicochemical investigation of engineered nanosuspensions containing model drug, lansoprazole. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshadidi, A.; Shahba, A.A.-W.; Sales, I.; Rashid, M.A.; Kazi, M. Combined curcumin and lansoprazole-loaded bioactive solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (Bio-SSNEDDS). Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Behera, U.A.; Beg, S.; Sruti, J.; Patro, C.N.; Dinda, S.C.; Rao, M.E.B. Design and characterization of enteric-coated controlled release mucoadhesive microcapsules of rabeprazole sodium. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alai, M.; Lin, W.J. A novel once daily microparticulate dosage form comprising lansoprazole to prevent nocturnal acid breakthrough in the case of gastro-esophageal reflux disease: Preparation, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoglu, T.; Gonul, N.; Dogan, A.; Basci, N. Development and in vitro evaluation of pantoprazole-loaded microspheres. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.S.; Kumar, S.S. Design and evaluation of floating microspheres of rabeprazole sodium. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 796–804. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, B.S.; Pancholi, J.; Samraj, P.I. Design and evaluation of floating microspheres of pantoprazole sodium. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2015, 3, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.K.; Tanwar, S.S.; Soni, P.; Jain, P. Formulation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of floating microspheres of esomeprazole. Int. J. Bioassays 2012, 1, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Haneesha, S.K.; Venkataramana, M.; Ramarao, N. Formulation and evaluation of lansoprazole loaded enteric coated microspheres. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.; Teja, N.B.; Ramakrishna, B.; Balagangadhar, B.; Kumar, B.V.; Reddy, V.G. Formulation and evaluation of double walled microspheres of loaded with pantoprazole. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Chem. 2011, 1, 770–779. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Shukla, T.; Jain, N.; Upmanyu, N.; Pandey, P.S.; Dhote, V. Formulation & Development pantoprazole loaded microsponges for management of GERD. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 4, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Vinod, K.R.; Sri, A.P.; Banji, D.; Anbazhagan, S.; Vasa, S.; Sandhya, S. Formulation and in vitro characterization of lansoprazole floating gastroretentive microspheres by modified non aqueous solvent evaporation method. Der Pharma Chem. 2010, 2, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, A.A.; Biyani, K.R.; Gawai, N.M.; Firdos, F.; Ingole, S.D. Formulation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive microspheres of clarithromycin and omeprazole. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2011, 4, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Raffin, R.P.; Colomé, L.M.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R. Enteric controlled-release pantoprazole-loaded microparticles prepared by using Eudragit S100 and Poly(ε-Caprolactone) blend. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2007, 12, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin, R.P.; Colomé, L.M.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Preparation, characterization, and in vivo anti-ulcer evaluation of pantoprazole-loaded microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Kumar, M.; Kaushik, D. Pantoprazole sodium loaded microballoons for the systemic approach: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Borkhataria, C.H.; Seth, N.R.; Patel, R.P.; Singh, S.; Parmar, G.R. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of lansoprazole micropellets. Int. J. Pharmtech. Res. 2009, 1, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy, K.; Govindarazan, G.; Ravi, T.K. Preparation and evaluation of lansoprazole floating micropellets. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 67, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, S.; Jain, A.; Amin, M.C.I.M.; Mishra, V.; Agrawal, G.P.; Kesharwani, P. Stomach specific polymeric low density microballoons as a vector for extended delivery of rabeprazole and amoxicillin for treatment of peptic ulcer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin, R.P.; Colomé, L.M.; Haas, S.E.; Jornada, D.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Development of HPMC and Eudragit S100® blended microparticles containing sodium pantoprazole. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin, R.P.; Colombo, P.; Sonvico, F.; Rossi, A.; Jornada, D.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Agglomerates containing pantoprazole microparticles: Modulating the drug release. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vora, C.; Patadia, R.; Mittal, K.; Mashru, R. Formulation, development, process optimization, and in vitro characterization of spray-dried lansoprazole enteric microparticles. Sci. Pharm. 2016, 84, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raffin, R.P.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Ré, M.I. Powder characteristics of pantoprazole delivery systems produced in different spray-dryer scales. Dry. Technol. 2006, 24, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin, R.P.; Colomé, L.M.; Hoffmeister, C.R.D.; Colombo, P.; Rossi, A.; Sonvico, F.; Colomé, L.M.; Natalini, C.C.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Costa, T.D.; et al. Pharmacokinetics evaluation of soft agglomerates for prompt delivery of enteric pantoprazole-loaded microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Z.; Lin, W.J.; Alai, M.S. Preparation of microparticles for acid-labile lansoprazole by solvent evaporation method combined with a spray drying process. J. Food Drug. Anal. 2012, 20, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddupalli, B.M.; Anisetti, R.N.; Ramani, R.; Malothu, N. Enhanced pharmacokinetics of omeprazole when formulated as gastroretentive microspheres along with piperine. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. Suppl. 2014, 4, S129–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomé, L.M.; Raffin, R.P.; Jornada, D.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Pantoprazole-loaded Eudragit blended microparticles: Preparation, characterization, in vitro gastro-resistance and in vivo anti-ulcer evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.T.; Nguyen, H.M.; Le, N.Q.; Trinh, T.T.L.; Tran, V.T. Formulation of enteric coated microspheres containing pantoprazole. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 63, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamsari, E.M.; Kermanshahi, R.K.; Erfan, M.; Ghadam, P. Microencapsulation of omeprazole by Lactobacillus Acidophilus ATCC 4356 surface layer protein and evaluation of its stability in acidic condition. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Valle, E.M.M. Cyclodextrins and their uses: A review. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Fridhriksdottir, H.; Olafsdottir, B.J.; Gudhmundsson, O. Solubilization and stabilization of drugs through cyclodextrin complexation. Acta Pharm. Nord. 1991, 3, 215–217. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Porcino, M.; Martineau-Corcos, C.; Guo, T.; Xiong, T.; Zhu, W.; Patriarche, G.; Péchoux, C.; Perronne, B.; Hassan, A.; et al. Efficient incorporation and protection of lansoprazole in cyclodextrin metal-organic frameworks. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.A.; Reyes, I.; Parera, A.; Gallardo, V. Adsorption of omeprazole on latex particles and characterization of the complex. Il Farm. 2000, 55, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.S. Enteric Coated Formulation of Benzimidazole Derivative and Method of Preparation Thereof. EP Patent 0998308 B1, 2 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thassu, D.; Hafey, P.; Magee, L.J., Jr. Acid Labile Drug Compositions. WO Patent 2004/060357 A1, 22 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cumming, K.I.; Clancy, M.J.; Codd, J.E.; Conaghey, O.M.; Templeton, L. Multiparticulate Oral Dosage Forms. WO Patent 00/40224 2000, 13 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.; Rehni, A.K.; Kalra, R.; Joshi, G.; Kumar, M.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Ion exchange resins: Drug delivery and therapeutic applications. Fabad J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- El-Badry, M.; Alanazi, F.K.; Mahrous, G.M.; Alsarra, I.A. Effects of Kollicoat IR® and Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin on the dissolution rate of omeprazole from its microparticles and enteric-coated capsules. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2010, 15, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Badry, M. Comparative study of preparation and characterization of enteric and enhanced release omeprazole microparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masareddy, R.S.; Rananaware, S.D.; Patil, B.R. Preparation and characterization of rabeprazole gastroretentive drug delivery system by ionotropic gelation technique. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2010, 3, 526–529. [Google Scholar]
- Filho, V.J.T.; Andreazza, I.F.; Sato, M.E.O.; Murakami, F.S. Development of a multiparticulate system containing enteric-release mini-tablets of omeprazole. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 50, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanska, M.; Sznitowska, M. Comparison of the coating process and in vitro dissolution of 3 mm gastro-resistant minitablets and 5 mm gastro-resistant tablets with pantoprazole. Pharmazie 2019, 74, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramu, S.; Reddy, P.C.G.; Rao, D.S.; Ramakrishna, G. Formulation and evaluation lansoprazole delayed release pellets. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2015, 5, 860–878. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Fan, L.-F.; Du, Q.; Xiang, B.; Li, C.-L.; Bai, M.; Chang, Y.-Z.; Cao, D.-Y. Design and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of multi-layer film coated pellets for omeprazole. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, S.S.; Nandgude, T.; Poddar, S. Formulation and optimization of lansoprazole pellets using factorial design prepared by extrusion-spheronization technique using carboxymethyl tamarind kernel powder. Recent. Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2017, 11, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yu, Q.; Liu, X.; Hu, F.; Yuan, H. Preparation and characterization of a novel aqueous dispersion for enteric coating of pantoprazole sodium pellets. Acta Pharm. 2018, 68, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Hay, Y.K.; Baie, S.H.; Bukhari, N.I.; Murtaza, G. Study of comparative bioavailability of omeprazole pellets. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2014, 71, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Tabata, T.; Makino, T.; Kikuta, J.; Hirai, S.; Kitamori, N. Manufacturing method of stable enteric granules of a new antiulcer drug (lansoprazole). Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1994, 20, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpalexis, P.; Grypioti, A. Development of a new esomeprazole delayed release gastro-resistant pellet formulation with improved storage stability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, K.L.; Muthukumaran, M.; Chenchuratnam, B. Formulation and evaluation of rabeprazole sodium enteric coated pellets. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2012, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Swathi, P. Formulation and evaluation of rabeprazole sodium and domperidone pellets. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 7, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Petchimuthu, S.; Narayanan, N.; Uthirapathy, S. Formulation and characterization of lansoprazole DR pellets by fluid bed coating technique. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 4, 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Türkoǧlu, M.; Varol, H.; Çelikok, M. Tableting and stability evaluation of enteric-coated omeprazole pellets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Cao, D. Eudragit L/HPMCAS blend enteric-coated lansoprazole pellets: Enhanced drug stability and oral bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tirpude, R.; Puranik, P. Rabeprazole sodium delayed-release multiparticulates: Effect of enteric coating layers on product performance. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Gaudio, P.; de Cicco, F.; Sansone, F.; Aquino, R.P.; Adami, R.; Ricci, M.; Giovagnoli, S. Alginate beads as a carrier for Omeprazole/SBA-15 inclusion compound: A step towards the development of personalized paediatric dosage forms. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.-F.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-M.; Ho, H.-O.; Sheu, M.-T. Formulation and process optimization of multiparticulate pulsatile system delivered by osmotic pressure-activated rupturable membrane. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 480, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, B.; Raju Talluri, S.; Rathnam, G. Formulation development and evaluation of enteric coated tablets of rabeprazole sodium. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2014, 9, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.B.S.; Sharma, A.; Garg, A.; Sisodiya, D.S. Formulation and evaluation of enteric coated tablet of ilaprazole. Int. Curr. Pharm. J. 2013, 2, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, N.B.; Velivela, S.; Mayasa, V.; Babu, B.R. Formulation and evaluation of delayed release enteric coated tablets of tenatoprazole, by optimizing the polymers. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.B.; Gupta, R.; Kumria, R.; Jacob, S.; Attimarad, M. Formulation and evaluation of enteric coated tablets of proton pump inhibitor. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2010, 1, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanthi, D.; Prashanti, S.; Meghana, G. Formulation and evaluation of press coated tablets of lansoprazole. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, G. Formulation and evaluation of rabeprazole sodium delayed release tablets. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2020, 10, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehetre, G.D.; Cheke, R.S.; Shrikhande, V.N. Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of enteric coated tablet incorporating rabeprazole. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2020, 10, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukari, T.; Ahire, G. Formulation and evaluation of esomeprazole delayed release tablets. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Benetti, C.; Flammini, L.; Vivo, V.; Colombo, P.; Colombo, G.; Elviri, L.; Scarpignato, C.; Buttini, F.; Bettini, R.; Barocelli, E.; et al. Esomeprazole immediate release tablets: Gastric mucosa ex vivo permeation, absorption and antisecretory activity in conscious rats. J. Control. Release 2016, 239, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, P.M.; Rathnanand, M.; Madhu Kumar, C. Stability enhancement of proton pump inhibitor in stomach: Formulation and in vitro evaluation of stabilized proton pump inhibitor. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migoha, C.O.; Ratansi, M.; Kaale, E.; Kagashe, G. Preformulation studies for generic omeprazole magnesium enteric coated tablets. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 307032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozdag, S.; Çalis, S.; Sumnu, M. Formulation and stability evaluation of enteric-coated omeprazole formulations. S.T.P. Pharma Sciences 1999, 9, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Das, D. Formulation, development and evaluation of buffer esomeprazole tablet in tablet preparation. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2014, 1, 7–35. [Google Scholar]
- Alsulays, B.B.; Kulkarni, V.; Alshehri, S.M.; Almutairy, B.K.; Ashour, E.A.; Morott, J.T.; Alshetaili, A.S.; Park, J.-B.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Preparation and evaluation of enteric coated tablets of hot-melt extruded lansoprazole. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmi, G.R.P.; Srikanth, G. Formulation and evaluation of colon specific drug delivery of press coated esomeprazole tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, B.; Sreekanth, J.; Satyavati, D. Formulation and evaluation of extended release matrix tablets of tenatoprazole sodium using synthetic polymers. J. Young Pharm. Suppl. 2020, 12, S39–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Babubhai, P.P.; Sajeev, M.S.; Jenita, J.L.; Priyadarshini, S.R.B. Sustained release enteric coated tablets of pantoprazole: Formulation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Acta Pharm. 2013, 63, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ashraf, M.S.; Afzal, M.; Kazmi, I.; Jahangir, M.; Singh, R.; Chandra, R.; Anwar, F. Formulation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablet of rabeprazole using wet granulation technique. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2014, 6, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, B.; Sreekanth, J.; Satyavati, D. Development of Extended Release Formulations of Ilaprazole Tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.S.; Bhutada, P.G. Formulation and evaluation of dexlansoprazole extended-release tablet. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 17, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, D.; Khurana, B.; Kaur, S. Development and evaluation of pulsatile drug delivery system of pantoprazole sodium for the management of nocturnal acid breakthrough. Pharmaspire 2019, 11, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sonar, G.S.; Rawat, S. Formulation and design of Multiunit Particulate System (MUPS) Tablet of pantoprazole by QbD: Effect of compression variables on the finished product. Int. J. Pharmtech. Res. 2015, 8, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zidan, R.N.; Majeed, S.M.; Al-Shaheen, M.K. Fabrication and evaluation of oral multi-particulate tablets of proton pump inhibitors: Esomeprazole as a model. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Nakano, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Tabata, T.; Hamaguchi, N.; Igari, Y. Formulation study for lansoprazole fast-disintegrating tablet. I. Effect of compression on dissolution behavior. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Kameoka, N.; Iki, H.; Tabata, T.; Hamaguchi, N.; Igari, Y. Formulation study for lansoprazole fast-disintegrating Tablet. II. Effect of triethyl citrate on the quality of the products. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Sugaya, M.; Nakano, Y.; Izutsu, D.; Mizukami, Y.; Okochi, K.; Tabata, T.; Hamaguchi, N.; Igari, Y. Formulation study for lansoprazole fast-disintegrating tablet. III. Design of rapidly disintegrating tablets. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choursiya, A.; Pandit, D. Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving tablets of lansoprazole by solubility enhancement technique. Curr. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 11, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, F.; Malfertheiner, P. Lansoprazole fast disintegrating tablet: A new formulation for an established proton pump inhibitor. Digestion 2003, 67, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, F. Lansoprazole oro-dispersible tablet: Pharmacokinetics and therapeutic use in acid-related disorders. Drugs 2005, 65, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, K.; Ito, Y.; Shibata, N.; Takada, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Takagi, N.; Irie, S.; Nakamura, K. Effect of water intake on pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole from fast disintegrating tablet in human subjects. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 19, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Shibata, N.; Takada, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Takagi, N.; Irie, S.; Nakamura, K. Evaluation of fast disintegrating lansoprazole tablet in human subjects. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 19, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chono, S.; Matsui, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kasai, R. Ingestibility and formulation quality of lansoprazole orally disintegrating tablets. J. Pharm. 2016, 2016, 6131608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chono, S.; Nakamura, K.; Matsui, M. Physical properties of lansoprazole orally disintegrating tablets. J. Generic Med. 2017, 13, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusban, F.; Perrie, Y.; Mohammed, A.R. Formulation of multiparticulate systems as lyophilised orally disintegrating tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Mishra, D.N.; Jassal, R.; Soni, P. Fast disintegrating combination tablets of omeprazole and domperidone. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2009, 2, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sai, C.C.H.; Swathi, N.; Chandi, R.P.; Nikitha, M.; Meghana, N.; Rama, R.N. Fabrication and characterization of pantoprazole sodium Ora-Solv tablets using different superdisintegrants. Asian J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 4, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamuralidhara, V.; Sreenivas, S.A.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Pramodkumar, T.M. Investigation on the effect of different disintegrants on the orodispersible tablets of rabeprazole. Asian J. Sci. Res. 2009, 2, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vynckier, A.K.; de Beer, M.; Monteyne, T.; Voorspoels, J.; de Beer, T.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Enteric protection of naproxen in a fixed-dose combination product produced by hot-melt co-extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israr, M.; Pugliese, N.; Farid, A.; Ghazanfar, S.; di Cerbo, A.; Muzammal, M.; Alamri, A.S.; Basheeruddin Asdaq, S.M.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, K.A. Preparation and characterization of controlled-release floating bilayer tablets of esomeprazole and clarithromycin. Molecules 2022, 27, 3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit, A.; Patel, M.K.; Manigauha, A. Formulation development and evaluation of bilayer tablet for effective treatment of gastric ulcer. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Pandey, D.; Jain, N.; Jain, S. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of bilayer tablets of lansoprazole and amoxycillin trihydrate for the treatment of peptic ulcer. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2021, 11, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhu, R.S.; Khatun, A.; Mannan, A. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of bilayer floating tablet of aceclofenac and esomeprazole by using natural and synthetic polymer. Nat. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 2, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, G.; Hanif, M. pH-sensitive pectin polymeric rafts for controlled-release delivery of pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, M.B.; Naga, M.M.; Banji, D.; Ravinder, N.A.; Arjun, G.; Ramalingam, R.; Sri, H.V. Formulation and evaluation of lansoprazole floating tablets. J. Pharm. Res. 2009, 8, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Manichandrika; Madhurima, K.; Fatima, N.; Aliya, A.; Siddiqui, K.; Begum, N. Formulation and evaluation of pantoprazole floating tablets. Int. J. Adv. Res. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Hanif, M.; Abbas, G.; Rasul, A.; Zaman, M.; ur Rehman, A.; Khan, H.U.; Maheen, S.; Ashfaq, M.; Iqbal, O. Prompt Drug Delivery of Rabeprazole through Raft Formation: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonam; Jain, N.; Banveer, J. Formulation, development and evaluation of gastroretentive sustained release tablets of lansoprazole using natural polymer. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2021, 11, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of Current Characterization and Evaluation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saruchi; Kaith, B.S.; Jindal, R.; Kapur, G.S. Synthesis of gum tragacanth and acrylic acid based hydrogel: Its evaluation for controlled release of antiulcerative drug pantoprazole sodium. J. Chin. Adv. Mater. Soc. 2014, 2, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.V.; Shivakumar, H.G. Preparation and characterization of superporous hydrogels as pH- sensitive drug delivery system for pantoprazole sodium. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, N.; Koland, M.; Sindhoor, S.M.; Prabhu, A. Formulation and evaluation of ion sensitive floating in situ gel of pantoprazole for gastro retentive delivery. Plant Arch. 2021, 21, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, B.K.; Kumar, A.; Padiyar, R.S. Hydrogel based colon targeted delivery of rabeprazole sodium. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Das, S.; Bahadur, S.; Saha, S.; Roy, A. Formulation and evaluation of omeprazole tablets for duodenal ulcer. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.S.; Jalajakshi, B. Formulation and evaluation sustained release mucoadhesive gastroretentive pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate tablets for anti–ulcer. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-G.; Kim, C.-K. Development of omeprazole buccal adhesive tablets with stability enhancement in human saliva. J. Control. Release 2000, 68, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-G.; Jung, J.-H.; Yong, C.S.; Rhee, C.-D.; Lee, M.-K.; Han, J.-H.; Park, K.-M.; Kim, C.-K. Formulation and in vivo evaluation of omeprazole buccal adhesive tablet. J. Control. Release 2000, 68, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.S.; Jung, J.-H.; Rhee, J.-D.; Kim, C.-K.; Choi, H.-G. Physicochemical characterization and evaluation of buccal adhesive tablets containing omeprazole. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2001, 27, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Boateng, J.S.; Mitchell, J.; Trivedi, V. Formulation, characterisation and stabilisation of buccal films for paediatric drug delivery of omeprazole. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo, O.; Perra, F.; Salvo, L.; Buontempo, F.; Lucangioli, S. Formulation and stability study of omeprazole oral liquid suspension for pediatric patients. Hosp. Pharm. 2020, 55, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, F.; Sereno, A.; Paide, M.; Sacré, P.; Guillaume, G.; Stéphenne, V.; Goole, J.; Amighi, K. Development and evaluation of an omeprazole-based delayed-release liquid oral dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diefenthaeler, H.S.; Bianchin, M.D.; Marques, M.S.; Nonnenmacher, J.L.; Bender, E.T.; Bender, J.G.; Nery, S.F.; Cichota, L.C.; Külkamp-Guerreiro, I.C. Omeprazole nanoparticles suspension: Development of a stable liquid formulation with a view to pediatric administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soral, M.; Nanjappa, S.H.; Alayadan, P. Formulation and evaluation of transdermal patch of rabeprazole sodium. J. Rep. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 10, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.J.; Duh, Y.S. Nanostructured lipid carriers for transdermal delivery of acid labile lansoprazole. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, C.E.; Lin, L.; Cloen, D.; Kufel, T.; Moon, R.; Frerichs, V. Omeprazole absorption from a compounded transdermal formulation in healthy volunteers. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2005, 45, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestebreurtje, P.; Roeleveld, N.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; van Sorge, A.A.; Plötz, F.B.; de Wildt, S.N. Development and stability study of an omeprazole suppository for infants. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 45, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestebreurtje, P.; de Koning, B.A.E.; Roeleveld, N.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; Tibboel, D.; van Groen, B.; van de Ven, C.P.; Plötz, F.B.; de Wildt, S.N. Rectal omeprazole in infants with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A randomized pilot trial. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 45, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvoet, C.; Heyden, Y.V.; Plaizier-Vercammen, J. Development of an omeprazole parenteral formulation with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2007, 12, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möschwitzer, J.; Achleitner, G.; Pomper, H.; Müller, R.H. Development of an intravenously injectable chemically stable aqueous omeprazole formulation using nanosuspension technology. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
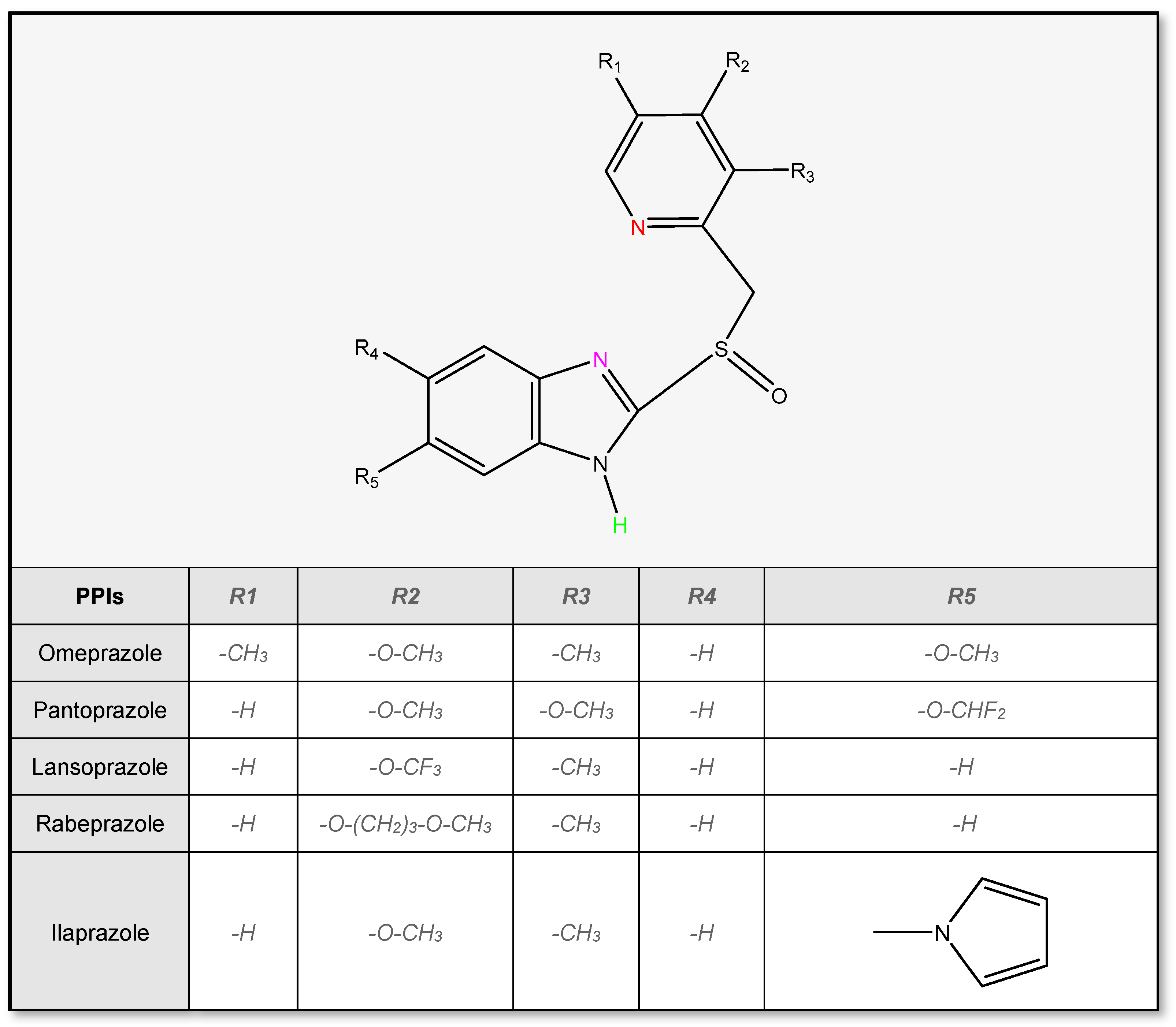
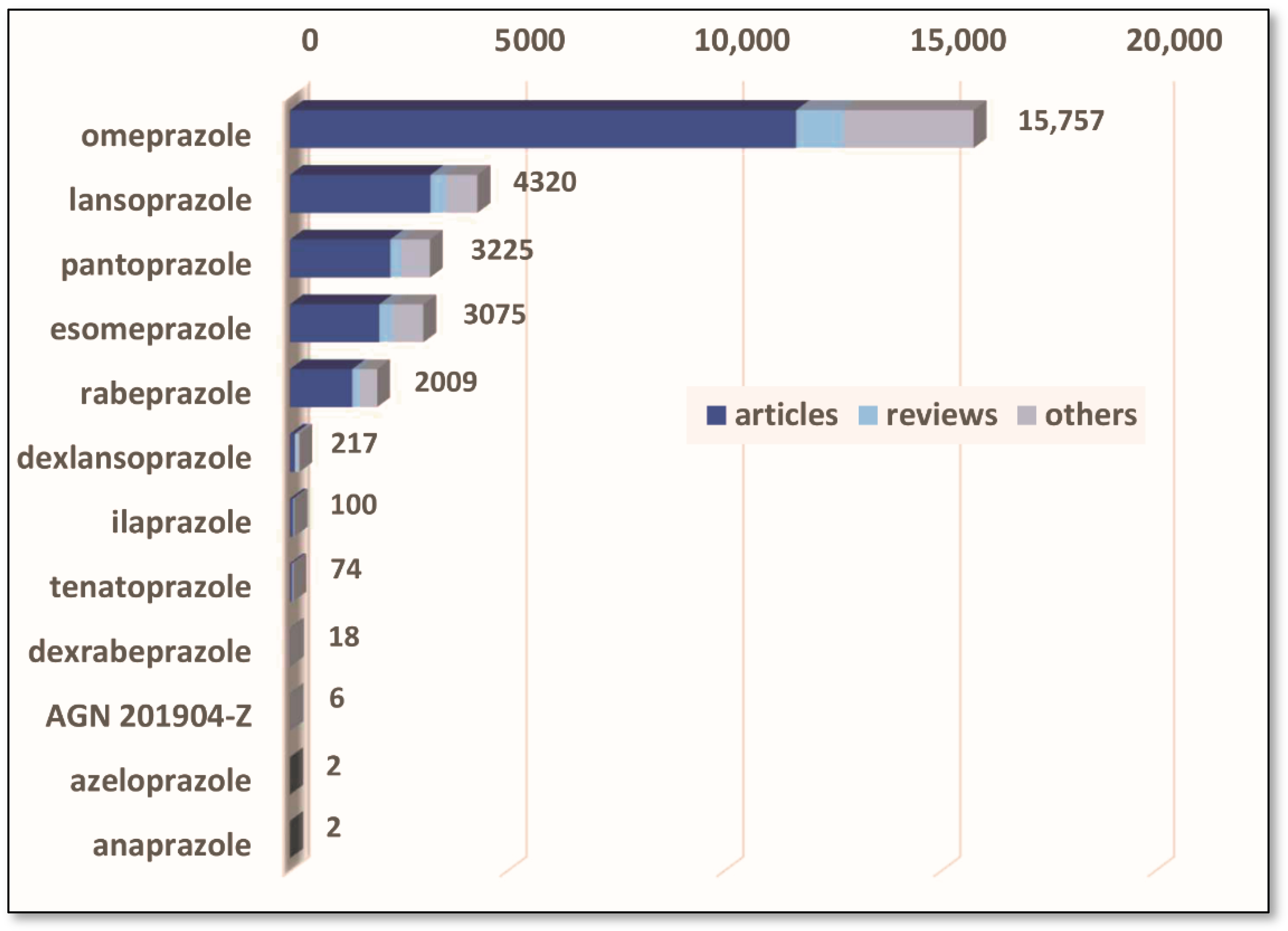
| PPIs | pKa | logP | Solubility [mg/mL] | BCS Classification | Half-Life [h] | tmax [h] | Cmax [μmol/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omeprazole | 4.77 9.29 | 1.66 | 0.359 | II | 0.5–1 | 0.5–3.5 | 0.23–23.2 (20 mg) |
| Pantoprazole | 3.55 9.15 | 2.11 | 0.495 | III | 1–1.9 | 2–3 | 2.87–8.61 (40 mg) |
| Lansoprazole | 4.16 9.35 | 2.84 | 0.250 | II | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.62–3.25 (30 mg) |
| Rabeprazole | 4.24 9.35 | 2.04 | 0.336 | III | 1–2 | 2–5 | 1.14 (20 mg) |
| Esomeprazole | 4.77 9.68 | 1.66 | 0.353 | II | 1–1.5 | 1.5 | 2.1–2.4 (20 mg) |
| Dexlansoprazole | 4.16 9.35 | 2.84 | 0.250 | II | 1–2 | 1–6 | 1.87 (30 mg) |
| Ilaprazole | 4.27 10.10 | 2.42 | 0.0934 | N/A | 3.0–3.4 | 0.75–1.0 | 4.2–5.1 (20 mg) |
| APIs | Dosage | Drug Formulation | Brand Name | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omeprazole + Diclofenac | 20 mg + 75 mg | Capsule with modified release pellets | DicloDuo Combi Diclopram | [88,174,176] |
| Omeprazole sodium + Macrogol 400 | 40 mg | Powder and solvent for solution for injection | Omeprazole Sandoz | [88,161] |
| Amoxicillin + Lansoprazole + Metronidazole | 500 mg + 30 mg + 400 mg | Combination pack (film coated tablet + GR capsule + tablet) | Helipak A | [88,177] |
| Amoxicillin Trihydrate + Clarithromycin + Omeprazole | 500 mg + 500 mg + 30 mg | Combination pack (film coated tablet + film coated tablet + GR capsule) | Helipak K | [88,178] |
| Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Pantoprazole | 1000 mg + 500 mg +40 mg | Combination pack (film coated tablet + film coated tablet + GR tablet) | Panclamox Zacpac | [88,175] |
| Omeprazole + Sodium bicarbonate | 20 mg + 1.68 g 40 mg + 1.68 g | Oral suspension | Zegerid | [87] |
| 20 mg + 1.1 g 40 mg + 1.1 g | Capsule | |||
| Omeprazole magnesium + Amoxicilin + Rifabutin | 10 mg + 250 mg + 12.5 mg | DR capsule | Talicia | |
| Lansoprazole + Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin | 30 mg + 500 mg + 500 mg | Combination pack (DR capsule + capsule + tablet) | Prevpac | |
| Esomeprazole magnesium + Naproxen | 20 mg + 375 mg | GR tablet | Vimovo | [87,173,179] |
| 20 mg + 500 mg |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srebro, J.; Brniak, W.; Mendyk, A. Formulation of Dosage Forms with Proton Pump Inhibitors: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102043
Srebro J, Brniak W, Mendyk A. Formulation of Dosage Forms with Proton Pump Inhibitors: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(10):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102043
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrebro, Justyna, Witold Brniak, and Aleksander Mendyk. 2022. "Formulation of Dosage Forms with Proton Pump Inhibitors: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10: 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102043
APA StyleSrebro, J., Brniak, W., & Mendyk, A. (2022). Formulation of Dosage Forms with Proton Pump Inhibitors: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics, 14(10), 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102043