Abstract
A crucial challenge to face in the treatment of biofilm-associated infection is the ability of bacteria to develop resistance to traditional antimicrobial therapies based on the administration of antibiotics alone. This study aims to apply magnetic hyperthermia together with controlled antibiotic delivery from a unique magnetic-responsive nanocarrier for a combination therapy against biofilm. The design of the nanosystem is based on antibiotic-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) externally functionalized with a thermo-responsive polymer capping layer, and decorated in the outermost surface with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs). The SPIONs are able to generate heat upon application of an alternating magnetic field (AMF), reaching the temperature needed to induce a change in the polymer conformation from linear to globular, therefore triggering pore uncapping and the antibiotic cargo release. The microbiological assays indicated that exposure of E. coli biofilms to 200 µg/mL of the nanosystem and the application of an AMF (202 kHz, 30 mT) decreased the number of viable bacteria by 4 log10 units compared with the control. The results of the present study show that combined hyperthermia and antibiotic treatment is a promising approach for the effective management of biofilm-associated infections.
1. Introduction
Bacterial infections pose a serious threat to public health, becoming the second leading cause of death worldwide [1,2,3], with biofilms being the main cause of most resistant infections [1,4]. Biofilms are communities of microorganisms that are covered by a protective extracellular matrix. This self-produced matrix protects the bacteria from hostile environmental conditions, reduces the efficacy of antibiotics compared with the effect in their planktonic counterparts and is responsible for the increased resistance to antimicrobials [4,5]. It has been shown that bacteria in biofilms can tolerate antibiotics at concentrations up to 1000 times higher than bacteria in a planktonic state [6,7]. Both the prevalence of antibiotic resistance and the increase in biofilm-associated infections are driving the demand for new, advanced and more effective treatments for such infections [8,9,10]. In this regard, nanotechnology offers an innovative platform to address this challenge [11]. Nanocarriers able to load, protect and locally deliver antimicrobial agents become ideal candidates for developing new nanomedicines [12,13,14]. Among them, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) present attractive characteristics, such as their thermal/mechanical stability, adjustable pore size, high surface area, biocompatibility, low toxicity, ease of functionalization and capacity to host molecules inside their pores [15,16,17]. Furthermore, engineered and innovative recent formulations based in MSNs are envisioned as new nanoantibiotics for bacterial infection treatment [18]. For example, the combination of different antimicrobial elements within the same nanoplatform, such as the targeted co-delivery of antibiotics [19], or the combination of antibiotics plus multiactive metal ions [20] have been reported as advanced strategies in the fight against antimicrobial resistance. It is also feasible to functionalize MSNs with nanogates that can be opened to deliver antimicrobial cargo upon the application of an external or internal given stimuli, as has been widely reported [21,22,23]. External physical stimuli are gaining attention because they allow the control of antimicrobial release on demand. Thus, temperature [24,25], light [26] or alternating magnetic fields (AMF) [23] have been reported as promising release triggers.
Regarding the combination of different antimicrobial effects, it is well known that elevated temperatures, outside the optimal range of bacterial growth, inhibit bacterial proliferation and motility [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] by altering the structural integrity of biofilms [39,40], or reducing the rigidity of biofilms [40,41]. As a result, recent studies have focused on the use of hyperthermia as a physical method to make bacteria more sensitive to antimicrobial therapy [42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. Although to date, magnetic hyperthermia has been used mainly for the treatment of cancer [49,50,51,52], as a means to selectively ablate cancer cells without damaging the surrounding tissue [53,54], using hyperthermia to achieve an antibacterial effect is gaining increasing attention [55]. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) are one of the most effective heating materials for local hyperthermia when applying an AMF [56,57], as they absorb electromagnetic radiation when exposed to the high frequency field and convert it into localized heat [58,59]. The amount of heat generated by SPIONs not only depends on the size, shape, composition and aggregation state of the nanoparticles themselves, but also on the specific conditions (frequency and amplitude) of the applied AMF [60,61]. In this regard, different theoretical and experimental tests have revealed that, although the temperature generated on the surface of the SPIONs can reach up to the boiling point of the medium, it decays rapidly at a few nanometers from their surface [62,63,64]. Therefore, by tailoring such parameters it is feasible to optimize the local temperature induced in the surface of these SPIONs, affecting neither the surrounding media nor healthy tissues. Moreover, SPIONs in close contact with the biofilm would provoke the disruption of the polysaccharide matrix and biofilm removal through its rupture and detachment [65,66,67]. Due to their magnetic behavior, biocompatibility [68,69,70] and chemical stability, SPIONs are widely used in biomedical sciences, e.g., the management of Gram-negative bacterial infection, multimodal in vivo imaging, etc. [71,72,73,74]. However, the use of hyperthermia alone remains limited due to the potential thermal damage caused to the host tissue, as higher thermal doses are often required for the complete eradication of bacterial pathogens [75,76]. To help solve these problems, the use of hyperthermia as an adjuvant to antimicrobial treatment could facilitate the effective and rapid inactivation of the bacteria present in the biofilm, thereby reducing the duration of treatment and producing an improved effect by acting in a combined fashion [44].
Herein, we report on the design of a novel MSNs-based magnetic nanosystem to combine the AMF-triggered release of antibiotics and magnetic hyperthermia against bacterial biofilm. To this aim, MSNs were coated with a thermosensitive poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAM) polymer with the ability to undergo a hydrophilic-to-hydrophobic (linear-to-globular) phase transition at a temperature between 40–43 °C. The outermost surface of the polymer-coated nanosystem was decorated with magnetite (Fe3O4) SPIONs, which serve as hot spots causing the shrinkage of the polymeric network. When the nanosystem is loaded with levofloxacin, this effect triggers the release of the antibiotic cargo [62]. The clever design of the nanosystem, with SPIONs decorating the outermost surface, may allow the close contact of the magnetic elements with the target, i.e., the biofilm, improving the bactericidal effect because the heating is directly on the biofilm zone and is not shielded by the silica structure. In addition, the slight antimicrobial activity of the SPIONs themselves [77] may be enhanced by the developed nanosystem. This proof-of-concept based on the combination of magnetic-hyperthermia therapy and thermo-responsive antibiotic delivery throughout the smart assembly of different functional building blocks into a mesoporous silica-based nanoplatform paves the way towards the design of new nanomedicines for local antibiofilm therapies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Equipment
Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS), cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), levofloxacin (LEVO, L), sodium oleate 82%, FeCl3·6H2O 97%, oleic acid 90%, octadecene 90%, ammonium nitrate, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane 97% (APTES), 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate (MPS), phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), N,N’-methylenebis(acrylamide) (MBA), ammonium persulfate (APS), citric acid monohydrate ≥99.0%, N,N-diisopropylethylamine 99.5%, N-hydroxymethyl-acrylamide (NHMA, 48% wt. solution in water), piperidine ≥99.5%, fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl chloride (Fmoc-Cl), α-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)amino-27(ethyleneglycol)-omega-propionic acid (Fmoc-NH-(PEG)27-COOH) and Luria–Bertani broth (LB) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Madrid, Spain). All other chemicals (sodium carbonate monohydrate, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), absolute ethanol, acetone, hexane, etc.) were of the highest quality commercially available and used as received. Deionized water was further purified by passage through a Mili-Q Advantage A-10 purification system (Milipore Corporation, Burlington, MA, USA) to a final resistivity of 18.2 MΩ cm.
The analytical methods used to characterize the synthesized compounds were as follows: powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetry (TGA), Fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) and fluorescence spectroscopies, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), electrophoretic mobility measurements to calculate the values of zeta-potential (ζ), dynamic light scattering (DLS), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) and hyperthermia measurements. The equipment and conditions used are described in the Supplementary Materials.
2.2. Synthesis of Materials
2.2.1. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs)
Magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) were synthesized through a two-step procedure (Figure S1). The first synthetic step consisted of the thermal decomposition of an iron oleate complex in octadecene [78]. To prepare the iron precursor, 45 g of sodium oleate and 10.8 g of FeCl3·6H2O were added into a 500 mL single-mouth round bottom flask and mixed with 60 mL of distilled water, 80 mL of absolute ethanol and 140 mL of cyclohexane. The mixture was stirred for 4 h at 70 °C under reflux. After this time, the reaction was allowed to cool down to room temperature (RT) and the two distinguishable phases were separated by using a funnel. The organic phase containing the iron oleate was washed with an ethanol:water 50:50 (v/v) mixture (50 mL × 3 times) and the hexane was evaporated using a rotary evaporator, also removing ethanol and water residues from the washings. Hereinafter, the Fe3O4 NPs were prepared, using 4.5 g of the as prepared iron oleate and 0.71 g of oleic acid mixed with 50 mL of octadecene in a three-neck round bottom flask. A nitrogen flow and a refrigerant were connected to the flask and the mixture was stirred and heated up to 315 °C. At 50 °C, the stirring was stopped and at 100 °C the nitrogen flow was shut off. Once 315 °C was reached, the reaction was left for 1 h. Finally, the mixture was cooled and the sample was washed 4 times with ethanol by centrifugation (10,000 rpm during 5 min), and redispersed in toluene. In the second synthetic step, the nanoparticles suspended in the organic solvent were transferred to water via a ligand exchange method [79]. This process was performed using citric acid (0.05 g) in a DMF:chloroform solution 50:50 (v/v) (15 mL). Briefly, 15 mg of the synthesized NPs were placed in contact with the citric acid solution and kept overnight at 30 °C under stirring. The obtained product was then washed once with DMF to remove excess citric acid and then three times with ethanol, and left to dry at RT. In this way, we obtained the magnetic nanoparticles denoted as Fe3O4 NPs (Figure S1).
2.2.2. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNs)
The synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles was carried out following the modified Stöber method [80]. For this purpose, 1 g of CTAB (2.74 mmol) was dissolved in 480 mL of water and 3.75 mL of NaOH 2 M and heated to 80 °C. Then, a solution containing 5 mL of TEOS (22.4 mmol) was added to the previous solution under vigorous stirring using a syringe dispenser at a constant rate of 0.26 mL/min. The stirring and temperature were maintained for 2 h, and then the suspension was cooled to RT. The solid particles were isolated and washed by centrifugation (10,000 rpm during 5 min) several times with water and EtOH and finally dried. The nanoparticles still containing the surfactant (CTAB) inside the mesopores were denoted as MSN*. The surfactant-free MSNs were obtained by removing the organic template through an ion exchange method by suspending 180 mg of MSN* into 60 mL of an extracting solution composed of NH4NO3 (10 mg/mL), EtOH (95%, v/v) and water (5%). The mixture was heated to 75 °C and stirred overnight. Then, the nanoparticles were washed with water (once) and ethanol (three times). The extraction process was repeated two more times and the obtained solid was dried.
2.2.3. Grafting of Polyethyleneglycol to MSNs (MSNf-PEG)
The external surface of MSNs* was functionalized with amino and methacrylate groups using APTES and MPS, respectively, as reagents. For this purpose, 0.1 g of MSN* was dispersed in a solution of APTES (33.3 µL) and MPS (50 µL) (relation 2:3, v/v) in absolute ethanol (15 mL). The mixture was left under magnetic stirring at 45 °C for 24 h, and the nanoparticles were recovered by centrifugation and washed with ethanol. The solid (MSNf*) was dried at 37 °C for 24 h. Later, the surfactant was removed from the interior of the pores following the procedure described in Section 2.2.2 to obtain MSNf. Subsequently, the PEG-derivative, Fmoc-NH-(PEG)27-COOH (M.W. 1544.8 g/mol), was grafted to the surface of MSNf via reaction with the amino groups in the external surface of surfactant-free functionalized nanoparticles (MSNf). The number of accessible amino groups on MSNf was quantified by using Fmoc-Cl as described elsewhere [81] to calculate the amount of Fmoc-NH-(PEG)27-COOH to be added. Thus, 2 mL of a suspension of MSNf in DMF (4 mg/mL) was reacted with 68.8 mg Fmoc-Cl (overnight, RT and magnetic stirring). Subsequently, the excess of unreacted Fmoc-Cl was removed with DMF (4 × 10 min). Later, the amino groups were deprotected (NH-Fmoc). For this, the nanoparticles are placed in contact with a solution of DMF (20% piperidine) for 3 h under magnetic stirring in such a way that the starting nanoparticles with free amino groups were recovered by centrifugation, whereas 9-methylene-9H-fluorene (Fmoc) remained in the supernatant. The absorbance of the latter measured at 301 nm was then interpolated in a previously recorded calibration curve to determine the amount of Fmoc-Cl. Since there was an equimolar Fmoc-Cl:NH2 ratio, the number of amino groups on the surface of MSNf was also known, which allowed the determination of the amount of PEG derivative to be added. Briefly, a mixture of 1 eq of MSNf, 1.2 eq Fmoc-NH-(PEG)27-COOH, 1.5 eq EDC and 3 eq DIPEA in DMF as solvent was kept at RT overnight under magnetic stirring. Then, the nanoparticles were washed with DMF (twice) and ethanol (twice) and left to dry in an oven at 37 °C. In this way, we obtained the MSNf-PEG sample.
2.2.4. Polymerization of N-Isopropylacrylamide (MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM)
The radical polymerization was carried out using a 90:10 NIPAM to NHMA monomers ratio to obtain a polymer which undergoes a polymer transition from linear to globular in the 41–43 °C temperature range, as reported by Guisasola et al. [62]. Briefly, in a 100 mL three-neck round bottom flask, NIPAM (150.9 mg, 1.33 mmol), MBA (12 mg, 0.078 mmol), NHMA (49.4 µL, 0.148 mmol), CTAB (3.6 mg) and Na2CO3 (5 mg) were added to 45 mL of water. The solution was stirred under nitrogen bubbling at 70 °C for 30 min to remove all oxygen. Then, 50 mg of MSNf-PEG redispersed in 5 mL of absolute EtOH was added under the N2 stream and the solution was maintained for another 15 min. To initiate the polymerization of the monomer, 0.2 mL of a 35 mg/mL APS solution in previously deoxygenated water was added to the reaction mixture. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was allowed to cool and stirred overnight at RT. The mixture was centrifuged and washed 3 times with water to remove any unreacted monomers and finally allowed to dry, obtaining MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM♦. Afterwards, the Fmoc from the PEG derivative grafted to the nanoparticles was deprotected. For this purpose, MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM♦ sample (50 mg) was put in contact with 20 mL of a piperidine solution in DMF (20% vol.) for 3 h. Subsequently, the nanoparticles were washed to remove residual piperidine with DMF (×1) and ethanol (×3). In this way, the resulting nanosystem (MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM) exhibited free amino groups available for the subsequent incorporation of the Fe3O4 NPs.
2.2.5. Grafting of Fe3O4 NPs to MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM (mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM)
Of the MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM nanosystem, 30 mg was added to 15 mg of the Fe3O4 nanocrystals dispersed in ethanol and the mixture was kept overnight at 30 °C under stirring. Subsequently, the nanoparticles were retrieved by centrifugation and washed with ethanol (×3) to remove free Fe3O4 NPs, obtaining a mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM sample.
2.3. Levofloxacin Loading and Triggered Release
2.3.1. Loading of Levofloxacin (mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L)
Of the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM material, 15 mg was soaked in 5 mL of a 0.008 M solution of levofloxacin (LEVO) in EtOH and the suspension was shaken under orbital stirring for 16 h in dark at 50 °C to bring the polymer into globular conformation and allow the antibiotic to enter the pores. The sample was then cooled to favor the polymer adopting the expanded conformation to close the pore entrances and prevent cargo release, then centrifuged, washed with EtOH and dried to obtain the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L sample.
2.3.2. In Vial Triggered Levofloxacin Release Assays
Temperature as release trigger: The kinetic studies of LEVO release were performed in PBS 1× at different temperatures (20, 37 and 50 °C) and physiological pH 7.4. A double-chamber cuvette with two distinct compartments for sample and analysis was used for the experiments. The compartments were separated by a dialysis membrane (0.4 µm) that only allowed the diffusion of LEVO molecules. For this purpose, 0.68 mL of a suspension of the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L material in PBS (2.5 mg/mL) was placed in the sample compartment and 3.1 mL of fresh PBS in the analysis compartment. The volume of PBS placed in the analysis compartment was renewed at each measurement time. The amount of antibiotic released was measured by fluorescence spectroscopy using a Biotek Powerwave XS spectrofluorimeter (Gen5 software version 1.00.14). For the analysis of the released LEVO, λex = 292 nm and λem = 494 nm were used and the calibration curve was recorded in a concentration range of 0.002 to 20 mg/mL. The experiment was carried out on three different release plates in independent incubators for each of the assayed temperatures 50, 37 and 20 °C.
Magnetic field as release trigger: A second release experiment was performed by exposing the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L nanosystem to an AMF (202 kHz, 30 mT). For this purpose, 0.5 mL of a suspension of LEVO-loaded nanosystem in PBS (1.96 mg/mL) and 4 mL of PBS were added to a well. The application of the magnetic field was performed at 30 min intervals, until reaching a final time of 240 min. After each 30 min time interval, the amount of LEVO released from the nanosystem at 37 °C without AMF and with AMF application was measured.
2.4. Microbiological Assays
2.4.1. Bacterial Culture
Escherichia coli (Laboratory strain E. coli ATCC 25922) was used as a Gram-negative bacterial model for the assays. The E. coli bacteria were cultured by inoculation in Luria–Bertani (LB) broth and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C with orbital shaking at 100 rpm. After this time, 10 µL of the previous solution was inoculated in fresh LB medium and left to grow for 2 h. After that time, the bacteria were centrifuged for 10 min at 3500× g at 22 °C. The supernatant was discarded and the pellet was washed with PBS 3 times. The bacteria were then suspended and diluted in PBS to obtain a concentration of 2 × 109 bacteria/mL and then diluted with the corresponding broth to obtain 2 × 106 bacteria/mL. The concentration of bacteria was determined using a visible spectrophotometer (Photoanalizer D-105, Dinko instruments, Barcelona, Spain).
2.4.2. Biofilm Growth
E. coli biofilms were grown prior to assays on 55 × 14 mm-size Petri dishes and by adding 2 mL of a bacterial suspension of 106 bacteria per mL. The plate was maintained for 48 h at 37 °C, adding 0.5 mL of fresh medium after the first 24 h. After 48 h, each plate was thoroughly washed twice with 2 mL of PBS 1× buffer solution under sterile conditions to remove medium and non-biofilm-forming bacteria. The antimicrobial activity of the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L nanosystem against E. coli bacterial biofilms was quantitatively evaluated by determining the reduction in log10 (CFU/mL) (CFU = colony-forming units) to assess the viability of the biofilm.
2.4.3. Biofilm Viability Assay
E. coli biofilms were preformed during 48 h as described above and then 1 mL of a mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L suspension in LB at a concentration of 200 µg/mL was added. For comparative purposes, the performance of the LEVO-free nanosystem (mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM) was also tested. A neodymium magnet was placed under the test Petri dish for 30 min prior to the application of the AMF. Exposure of the preformed E. coli biofilms to LEVO-containing and LEVO-free nanosystems was performed for one hour at 37 °C with application of the AMF. After incubation, the medium was removed from the Petri dishes, which were washed once with 2 mL of sterile PBS 1× and another 2 mL of fresh PBS 1×. Subsequently, mechanical disruption of the biofilm was performed with a sterile wooden tongue depressor and sonication was applied for 5 min in a low-power ultrasonic bath to break up and disperse the biofilm in a total volume of 2 mL of PBS 1×. The presence or not of bacteria, as well as their quantification, was determined by counting CFUs per mL using the droplet plate method on LB agar plates. The dilutions used were 1:100, 1:1000 and 1:10,000 in PBS 1× of the bacteria exposed to the nanosystems were made and five drops (5 × 10 µL) of each solution were inoculated in LB agar plates divided into three sectors, which were incubated for 16 h at 37 °C. The procedure described in reference [82] was followed for the mean count of the five drops of each dilution and the average counting for all dilutions was calculated. Log10(CFUs/mL) compared with bacteria without treatment after 16 h as control was determined. All assays were performed in triplicate with respective controls.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization of the Nanosystem
The hybrid nanosystem designed in this research work was prepared through different synthetic steps, independently obtaining the polymer-functionalized MSNs and the SPIONs, to proceed with the incorporation of magnetic nanoparticles on the surface of the nanosystem at the end (Figure 1).
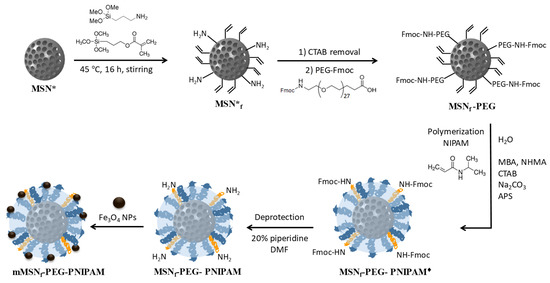
Figure 1.
Synthetic steps carried out to obtain the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM nanosystem: MSNs with the surfactant inside the mesopores were used as starting materials (MSN*); surface modification of MSN* with methacrylate and aminopropyl groups by using MPS and APTES, respectively (MSNf*); surfactant removal followed by grafting of Fmoc-NH-(PEG)27-COOH (MSNf-PEG); polymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide (MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM♦); deprotection of Fmoc to leave amino groups available (MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM); and grafting of Fe3O4 NPs to MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM (mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM).
The synthetic procedure to obtain Fe3O4 NPs involved a two-step process consisting of a thermal decomposition of the Fe(oleate)3 precursor followed by ligand exchange using citric acid (Figure S1) [78,79]. The iron oleate complex was first prepared by reacting FeCl3.6H2O and sodium oleate. Freshly prepared Fe(oleate)3 was mixed with oleic acid and 1-octadecene and the mixture was submitted to thermal decomposition, to obtain oleic acid-stabilized F3O4 NPs (OA-Fe3O4 NPs) as a colloidally stable suspension in toluene. OA-Fe3O4 NPs were analyzed by TEM, revealing the presence of nanocrystals with a relatively uniform spherical morphology (Figure 2A). The statistical treatment of NP sizes from several TEM images revealed a narrow size distribution of particle diameter centered at 12 ± 2 nm, assuming a log-normal distribution to make the fit in the histogram (Figure S2A). The XRD pattern of these NPs pointed to a pure crystalline magnetite (Fe3O4) structure (Figure S2B), and by using the Scherrer´s equation [83], the crystal size was estimated (10 nm). To evaluate the magnetic behavior of these OA-Fe3O4 NPs, they were characterized under a direct current (DC) magnetic field. The DC experiments showed loops with coercive fields close to zero and saturation magnetization values of 97.4 emu/gFe close to the bulk value for magnetite (~100 emu/gFe), demonstrating the superparamagnetic-like behavior of the synthetized OA-Fe3O4 NPs at RT (Figure S2C) [84].
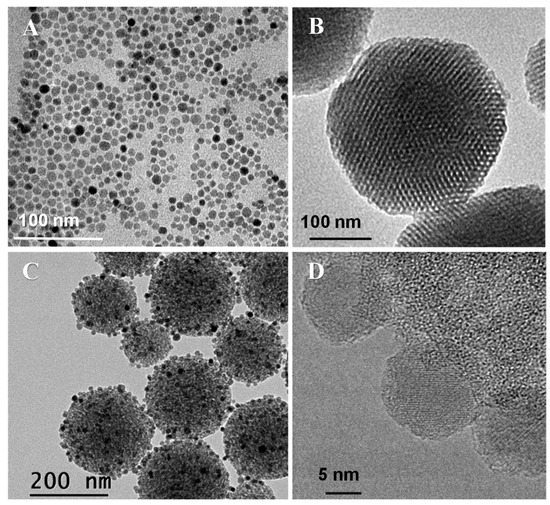
Figure 2.
TEM images of OA-Fe3O4 NPs (A), bare MSNs (B), mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM nanosystem (C) and HRTEM image of mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM (D).
The hydrophobic character of the synthesized OA-Fe3O4 NPs required a transfer step to aqueous medium for their subsequent anchoring to the mesoporous silica nanoparticles (Figure S1) [79]. For this purpose, the hydrophobic ligand (oleic acid) present in the OA-Fe3O4 NPs was exchanged with hydrophilic ligands bearing carboxylic groups that present affinity towards the magnetite surface. Herein, citric acid was used as the phase transfer agent, which may be adsorbed on the surface of magnetite nanoparticles through coordinating via one or two of the carboxylate groups depending on steric hindrance and also on the curvature of the surface [85]. This preserves at least one carboxylic acid group exposed to the aqueous medium, providing a surface of magnetite of hydrophilic character and giving rise to stable suspensions in water. The resulting samples were denoted as Fe3O4 NPs.
The second part of the synthesis of the hybrid nanosystem deals with the assembly of the different building blocks in the mesoporous silica nanoplatform (Figure 1). Firstly, the mesoporous silica nanoparticles still containing the surfactant inside the mesopores (MSN*) were employed as starting material for the subsequent grafting of APTES and MPS to promote the preferential functionalization of the external surface of nanoparticles.
On the one hand, APTES provided the nanosystem of –NH2 groups onto the surface of the MSNs for the successive PEGylation of MSNf by condensation reaction with the –COOH groups from the polyethyleneglycol derivative (Fmoc-NH-(PEG)27-COOH) via carbodiimide chemistry [86]. The grafting of PEG into the nanoparticles provides several advantages, such as maintaining the nanoparticles’ dispersibility, improving their long-term colloidal stability in different biological media and increasing their circulation times [87]. Of foremost significance is the fact that PEG serves as a flexible extender spacer arm for the subsequent anchorage of the Fe3O4 NPs, so they preferentially locate in the outermost periphery of the nanosystem to be more accessible for direct contact with the targeted biofilm. In addition, the chosen PEG derivative contains a Fmoc-protected amine terminal group, which also serves as an anchoring point for the Fe3O4 NPs grafting after deprotection.
On the other hand, the polymerizable methacrylate groups of MPS present on the surface of MSNf-PEG allowed the growth of the thermosensitive polymer (PNIPAM) onto the outer surface of the nanosystem. The radical polymerization process was carried out by using different reactants: MBA, as the crosslinking agent to create a more branched polymeric network that hinders the premature cargo release from the mesopores; a monomers mixture in a 90:10 NIPAM to NHMA molar ratio; and APS as initiator. The amount of attached polymer was 4.9% as determined by TGA. Thermosensitive polymers based on PNIPAM are widely used for drug delivery applications because they are able to undergo a transition from linear (swelling state) to globular (collapsed) conformation when heated above their lower critical solution temperature (LCST) and they exhibit good biocompatibility. The use of NHMA, as a hydrophilic co-monomer, allows the polymer transition temperature to be increased up to 42–45 °C, as it increases the polymer–water interactions necessary for the conformational change [62].
Finally, once the PNIPAM-based polymer was grown into the mesoporous silica nanosystem, the PEG-Fmoc was deprotected with a piperidine solution which allowed the amino groups to be free for the subsequent incorporation of the iron oxide nanoparticles, endowed with carboxylic groups. To reach this goal, the Fe3O4 NPs were incubated overnight at 37 °C in ethanol with the MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM nanosystem, to obtain mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM. The immobilization of Fe3O4 NPs on the surface of MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM can be probably ascribed to the combination of two main types of interactions. On the one hand, to the possible formation of hydrogen bonds taking place between the unbounded carboxylic acid groups (-COOH) of citric acid moieties onto the surface of Fe3O4 NPs and the amine and/or amide groups in the polymeric shell of the nanosystem. On the other hand, to hydrophobic interactions between the residual alkyl chains of the oleic acid units remaining on the surface of Fe3O4 NPs and the hydrocarbon chains of the PNIPAM polymer onto the mesoporous nanoparticles (see FTIR discussion below).
The bare MSNs are uniform in size with a mean diameter of 160 nm, confirmed by DLS (Table 1). The well-ordered mesoporous structure of MSNs is clearly observed in the TEM images (Figure 2B). After the successive functionalization steps, subsequent polymer growth and immobilization of the 12 nm Fe3O4 NPs, hardly any alteration of the morphology was observed. In addition, it is observed that the hydrodynamic nanosystem size increases up to 255 nm compared with the bare MSN (Table 1). Moreover, no fusion of nanoparticles is observed in the TEM images (Figure 2C). The amount of iron incorporated into the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM nanosystem was estimated by EDS (Figure S3). The atomic percentages of Fe and Si obtained were 7.2 ± 0.6 and 92.8 ± 0.4, respectively, resulting in a Fe/Si molar ratio of 0.0776.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the different MSNs synthesized in this work obtained by DLS and ζ-potential (data are mean ± SD of the five measurements).
A deep characterization of the different nanoparticles derived from the successive functionalization steps conducted in this research work (see Figure 1) was carried out by FTIR spectroscopy (Figure 3) and ζ-potential measurements (Table 1). As reference, the surfactant-free MSN material was added to the study. Figure 3 shows FTIR spectra of the different samples. As can be observed, all spectra display a broad band in the 3000–3600 cm−1 region, which can be attributed to the overlapping of the O-H stretching bands of hydrogen-bonded water molecules (H-O-H) and surface silanol groups (SiO-H) [88]. Si-O in-plane stretching vibrations of the silanol Si-OH groups appear at 953 cm−1. The intense Si-O covalent bond vibrations appear predominantly in the 1200–1000 cm−1 range, evidencing the existence of a dense silica network, where oxygen atoms serve as bridges between two silicon sites. Likewise, the symmetric stretching vibrations of Si-O-Si appear at ca. 800 cm−1 and its bending mode is observed at 470 cm−1. Finally, the low-intensity band at 590 cm−1 is assigned to Si-O stretching of the silica network defects [88].
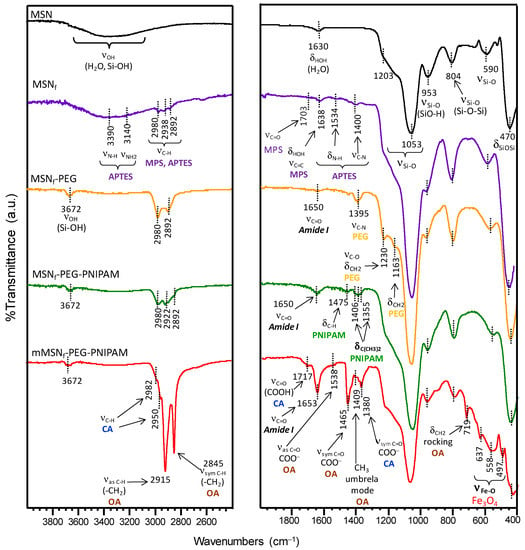
Figure 3.
FTIR characterization of the different functionalization stages performed to obtain the final nanosystem mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM.
The spectrum of the surfactant-free APTES and MPS functionalized material (MSNf) displays several bands in the 2892–2980 cm−1 range, assigned to C-H asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of the alkyl chains of the organosilane precursors. Additional vibration bands at 3390 cm−1 (NH2 stretching), 3140 cm−1 (N-H stretching), 1534 cm−1 (NH deformation) and 1400 cm−1 (C-N stretching) confirm the presence of aminopropyl groups from APTES. On the other hand, the bands at 1703 cm−1, (C=O stretching) and 1638 cm−1 (C=C stretching) account for the successful incorporation of MPS [89].
ζ-potential measurements in water support this finding, since there is a severe change from negative (−22 mV) in bare MSN to +47 mV in MSNf (Table 1). These values are due to the deprotonation of silanol groups in the MSN surface (Equation (1)) and protonation of primary amine groups in APTES after functionalization (Equation (2)), taking into account that the methacrylate groups do not virtually modify the surface charge [90,91].
R-Si-OH + H2O ⇌ R-Si-O− + H3O+ pKa ≈ 6.8
–NH2 + H2O ⇌ –NH3+ + OH− pKa ≈ 10.4
The success of the PEGylation procedure by the condensation reaction of –NH2 groups on the surface of MSNf and carboxylic acid groups from the PEG derivative (Fmoc-NH-(PEG)27-COOH) via carbodiimide chemistry was also confirmed by FTIR and ζ-potential measurements. Thus, the FTIR spectrum of MSNf-PEG (Figure 3) displays new bands at 1650 cm−1 (C=O asymmetric stretching of amide group), 1163 cm−1 (C–O stretching and CH2 rocking) and 1230 cm−1 (CH2 twisting) [92].
The appearance of such new bands is accompanied by a noticeable increase in the intensity of vibration bands at ca. 1400 cm−1 (C-N stretching) and those in the 2892–2980 cm−1 range (C-H stretching) compared with those present in MSNf. Moreover, the partial consumption of the surface –NH2 groups present in MSNf by reaction with the –COOH groups of the PEG-derivative explains the slight decrease in the obtained ζ-potential value to +34 mV for MSNf-PEG (Table 1).
The successful growth of the PNIPAM derivative by the radical polymerization of the above-mentioned monomers with the methacrylate groups from MPS onto the surface of MSNf-PEG was confirmed by FTIR. Figure 3 shows an increase in the intensity of the characteristic asymmetric stretching amide band at 1650 cm−1 and the appearance of new bands at 1475 cm−1 (C-H bending) and the doublet at 1406 and 1355 cm−1 attributed to the deformation of the isopropyl group (C(CH3)2) [62,93].
The ζ-potential value for this nanosystem would be expected to increase due to the presence of terminal –NH2 groups of PEG chains after the deprotection process. Nonetheless, the ζ-potential value for this sample decreases to 9 mV after the radical polymerization process, which can probably be ascribed to the partial masking of –NH2 groups by the globular PNIPAM polymeric chains grown onto the nanosystem surface.
In the final step of the process, Fe3O4 NPs were incorporated into MSNf-PEG-PNIPAM to obtain the final nanosystem, denoted as mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM. In the FTIR spectrum of this nanosystem, the appearance of well-defined characteristic vibration bands confirms the successful incorporation of the magnetic nanoparticles (Figure 3). The different vibration bands appearing at 637 and 558 cm−1 can be attributed to the lattice stretching vibration modes of Fe-O bonds in tetrahedral and octahedral sites, whereas the band at 497 cm−1 could correspond to the vibration band of Fe-O of bulk magnetite [94]. Moreover, the FTIR spectrum of mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM shows different vibration bands that are assigned to both citric acid (CA) and oleic acid (OA), which accounts for a partial ligand exchange of OA moieties by CA in Fe3O4 NPs (see Figure S1, Supporting Information). Among the different bands, noteworthy are those appearing at 1538 and 1465 cm−1, corresponding, respectively, to the asymmetric and symmetric C=O stretching of –COO− groups, which revealed that OA was chemically adsorbed onto the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles through chemical interaction between their –COO− groups and Fe atoms [95]. In addition, the band at 1717 cm−1, ascribed to the C=O stretching of –COOH, and the band at 1380 cm−1 assigned to the symmetric C=O stretching of –COO− groups of CA, points to the bond of a unique carboxylate group to iron, as previously reported [88,96]. The presence of unbounded –COOH groups in the Fe3O4 NPs able to interact with amide groups by hydrogen bond interactions would account for their immobilization into the PNIPAM and PEG polymeric branches. This fact is supported by FTIR, where the significant increase in the intensity of the vibration band (C=O stretching) of the amide group at 1653 cm−1 points to the existence of OcarboxylH···Oamide hydrogen bonds [97].
The negative ζ-potential value of −6 mV measured for the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM is also in good agreement with the presence of –COOH in the surface of the immobilized Fe3O4 NPs, which can undergo deprotonation in aqueous medium via the equilibrium shown in (Equation (3)).
−COOH + H2O ⇌ −COO− + H3O+ pKa ≈ 4.8
Finally, the presence of the alkyl chains of the oleic acid present in Fe3O4 NPs confers them a certain hydrophobic character, which would also contribute to their retention into the full nanosystem even though the polymer undergoes the hydrophilic-to-hydrophobic transition.
To investigate the stimulus-responsive behavior of this material and its bactericidal effect, the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM sample was loaded with a high-spectrum antibiotic such as levofloxacin (LEVO), generally used in the treatment of Gram-negative E. coli bacteria. The temperature chosen for the loading process was 50 °C to ensure the polymer to be in the globular conformation, allowing the antibiotic to enter the pores of the mesoporous silica. The loading process and stimuli-responsive release from the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L nanosystem is depicted in Figure 4.
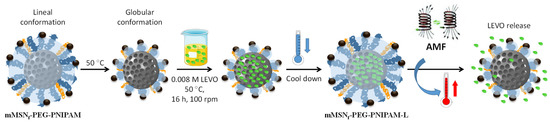
Figure 4.
Schematic depiction of the experimental procedures carried out for the loading and release of LEVO from the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM nanosystem. Briefly, the nanosystem was soaked into a LEVO solution in EtOH at 50 °C to bring the polymer into globular conformation and allow LEVO loading into the mesopores. Then, the cool down favors the polymer adopting the expanded conformation to close the pores and prevent antibiotic release. Finally, the application of an AMF produces an increase in the local temperature that provokes a conformational change in the polymer from linear to globular, which triggers pore uncapping and LEVO release.
3.2. In Vial Triggered Levofloxacin Release Assays
3.2.1. Temperature as Release Trigger
To evaluate the release behavior of the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L nanosystem under physiological conditions (PBS 1×, pH 7.4), antibiotic release experiments were carried out in vial at different temperatures (20, 37 and 50 °C). Figure 5A shows the release profiles of LEVO for the different temperatures up to 6 h. All release profiles are characteristic of the typical diffusion model of MSN materials. Thus, the release profiles were fitted to the first-origin kinetics according to (Equation (4)) [98]:
where “Y” is the amount of LEVO released (µg LEVO/mg material) at time “t”, “A” the maximum amount of LEVO released (µg LEVO/mg material) and “k” the release rate constant. The parameters resulting from kinetics fitting are shown in Table S1.
Y = A (1−e−k t)
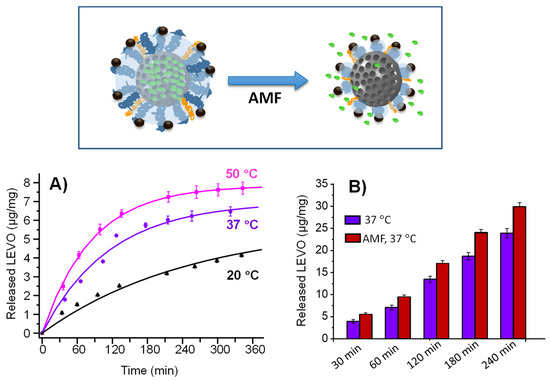
Figure 5.
(A) LEVO release profile at different temperatures: 20, 37 and 50 °C. (B) Total LEVO release at different times at 37 °C (blue bars) and same conditions plus magnetic field exposition (red bars). Data are mean ± SD of the three replicas. The different conditions used during both experiments are detailed in Section 2.3.2.
The amounts of antibiotic released in the first hours were higher at 50 °C than at 20 and 37 °C (Figure 5A). Especially at 20 °C, the release was greatly hampered. At a time of 80 min, the antibiotic dose released at 50 °C was 1.4 times higher than that released at 37 °C and 3.1 times higher than that at 20 °C. This fact indicates that the thermosensitive polymer coating maintains its linear polymeric behavior at temperatures of 20 and 37 °C, being able to retain its charge at physiological temperature and releases it once the LCST value is reached. These differences are reflected in the release rate “k” values of 0.0118, 0.0087 and 0.0039 for 50, 37 and 20 °C, respectively.
Therefore, although a partial premature cargo release was not avoided at the physiological conditions in the absence of external stimuli (1.53 µg/mg material after 80 min of assay for 20 °C and 3.5 µg/mg material for 37 °C), the application of the AMF significantly increased the amount of antibiotic released to the delivery medium (4.8 µg/mg material after 80 min of assay). This fact would contribute to enhance the antimicrobial effect of the nanosystem, as was observed during the microbiological studies discussed in Section 3.3.
3.2.2. Magnetic Field as Release Trigger
LEVO release experiments were also carried out by placing the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L nanosystem (1.96 mg/mL) in the hyperthermia device at 37 °C and applying an AMF (202 kHz and 30 mT). As a control, the same experiment in the absence of an AMF was also conducted. (Figure 5B). Frequencies that cause reasonable heating in hyperthermia are limited within the range 50 kHz < f < 1 MHz. Above 1 MHz, negative physiological damage may occur. On the other hand, the field amplitude is restricted to less than H0 < 15 kA/m [99]. Although the amplitude used in our case is higher, the f × H0 results (6 × 107 Oe Hz) fall within the fitness range (<6.25 × 107 Oe Hz) used in applications in small regions of the body of patients [70]. Therefore, the frequency and magnetic field conditions employed fall within the estimated safety range.
The sample subjected to an AMF presented a significantly higher released antibiotic dose than the sample without exposure in the same period of time (Figure 5B). At a time of 30 min, the percentage of levofloxacin released under magnetic field application to the study nanosystem was 43% higher compared with the nanosystem without magnetic field application. This different drug release behavior was also observed in different magnetic-field responsive MSNs-based drug delivery nanosystems incorporating SPIONs as hot spots [64], and may be due to the following factors: (i) the polymer transition temperature is reached faster in the particle environment when the field is applied; (ii) the vibrations of SPIONs when subjected to magnetic field can induce a higher release compared with incubator heating; and (iii) the localized temperature in the vicinity of the particle is higher than the global temperature [58,100], leading to greater diffusion of the antibiotic once the pore is opened. These mechanisms could act in concert, resulting in a higher release of LEVO in the presence of the AMF.
On the other hand, the values are very similar when comparing the amount of LEVO released (9.44 µg/mg material) at a time of 60 min under magnetic field application (Figure 5B) with the amount of total antibiotic released (7.87 µg/mg material) at 50 °C (Figure 5A), revealing that it is possible to cause the polymer transition under a magnetic field in a much shorter time. This fact would by supported by a recent study reported by Ovejero et al., who developed an innovative strategy, based on the linkage of fluorescent proteins as local thermal probes, to determine the specific local temperature in the surface of different sets of SPIONs using different AMF settings [61]. In the case of SPIONs obtained by thermal decomposition method exposed to a low-frequency AMF (100 kHz to 50 mT), a small increment in local temperature was produced. However, when SPIONs were submitted to more favorable AMF conditions (388 kHz and 15 mT), higher local temperatures up to ca. 70 °C were reached. In agreement with such studies, the AMF conditions used in the present work (202 kHz and 30 mT) could produce local temperatures above 50 °C in the surface of Fe3O4 NPs incorporated in the full nanosystem, which prompt the change in the polymer conformation and trigger faster LEVO release.
3.3. Microbiological Assays
The bactericidal effect of the mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L nanosystem on biofilms was studied to evaluate the combined effect of the antibiotic and the magnetic field on the same nanoplatform. For this purpose, pre-formed E. coli biofilms were exposed to a nanosystem concentration of 200 µg/mL. Prior to the application of the magnetic field, a neodymium magnet was placed underneath the Petri dish once the nanoparticles were added. This strategy aims at increasing the close contact between the magnetic nanocarrier and the biofilm surface and could even promote its penetration since, as previously reported, magnetic nanosystems can be guided to favor biofilm penetration in targeted antimicrobial therapies [8,101]. Once the magnetic field is applied, the antibiotic-free nanosystem (mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM) produced a reduction in biofilm of two units in the log10 CFU/mL with respect to the bacterial control (Figure 6). This positive antibiofilm effect agrees with previously published reports on the ability of pure iron oxide NPs to generate heat by means of an AMF as a powerful tool in terms of inactivating antimicrobial cells [56]. With respect to the nanosystem loaded with the antibiotic mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L and under the application of the alternating magnetic field, a large reduction in biofilm is observed, which is translated into four units of log10 CFU/mL (Figure 6).
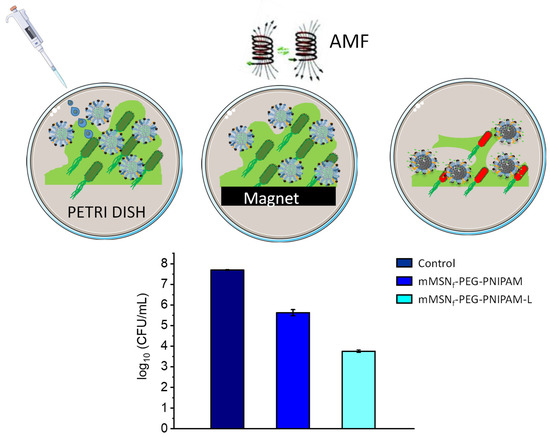
Figure 6.
Bactericidal effect of mMSNf-PEG-PNIPAM-L nanosystem on E. coli biofilm. The graph shows log10 (CFUs per mL) after biofilm exposure to 200 µg/mL of the nanosystems for 16 h, compared with biofilm without nanoparticles as control (first bar). Data are mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
Therefore, we have investigated the antibacterial efficacy of a new multicomponent nanosystem, noticing the enhanced effect produced by the combination of hyperthermia with the administration of antibiotics. The results obtained show relevant data in terms of bactericidal efficacy, being reflected in a viability reduction of almost four units in the log10 CFU/mL with respect to the control. It is worth noting that this remarkable antibiofilm effect is obtained at relatively small doses, envisaging this system as a promising nanoantibiotic. In addition, the versatility of this nanosystem relies on the possibility to load and release antibiotic cargoes of different families, which would allow the design of custom-made therapies depending on the characteristics of the infection to be treated. In this sense, this proof of concept allows us to bet on the performance obtained with this multicomponent nanosystem.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we report a new smart multicomponent nanodevice that combines the AMF-triggered delivery of a broad-spectrum antibiotic with magnetic hyperthermia for the local treatment of biofilm-associated bacterial infections as a proof of concept. This multicomponent nanosystem consists of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs), loaded with the broad-spectrum antibiotic levofloxacin, coated with a thermosensitive poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAM)-based polymer and externally decorated with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs). The enhanced effect produced by the combination of magnetic hyperthermia and the controlled administration of the antibiotic leads to bacterial death and a significant bacterial biofilm reduction. The obtained results open future possibilities, and current studies are focused on increasing the dose of the nanosystem to improve the bactericidal efficacy, testing the nanodevice on other bacterial species and loading other molecules inside the pores to demonstrate the versatility of the nanosystem. Hence, a novel infection treatment is envisioned through an advanced nanosystem that can be locally administrated at the infection site, disrupting and eradicating the biofilm in the presence of an AMF. It is anticipated that this new biofilm eradication strategy could lead to a decrease in antibiotic use and thus a decrease in antibiotic resistance in the clinical setting.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010163/s1, Equipment; Figure S1: Scheme of synthesis of OA-Fe3O4 NPs and subsequent ligand exchange with citric acid to afford Fe3O4 NPs; Figure S2: NPs size distribution obtained by TEM images, XRD pattern and magnetization curve of OA-Fe3O4 NPs; Figure S3: EDS spectrum and atomic percentage of iron content in mesoporous silica nanosystem; Table S1: Kinetic parameters of LEVO release at different temperatures (20, 37 and 50 °C).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.G., M.d.P.M., M.C., I.I.-B. and M.V.-R.; methodology, E.Á., M.E., A.G.-C., B.G., R.R.C., M.d.P.M., M.C. and I.I.-B.; validation, E.Á., M.E., A.G.-C., B.G., R.R.C., M.d.P.M., M.C. and I.I.-B.; formal analysis: E.Á., M.E., A.G.-C., B.G., R.R.C., M.d.P.M., M.C. and I.I.-B.; investigation: E.Á., M.E., A.G.-C., B.G., R.R.C., M.d.P.M., M.C. and I.I.-B.; resources, I.I.-B. and M.V.-R.; writing—original draft preparation: E.Á., M.E. and A.G.-C.; writing—review and editing, B.G., M.d.P.M., M.C., I.I.-B. and M.V.-R.; visualization, B.G., M.d.P.M., M.C., I.I.-B. and M.V.-R.; supervision, B.G., M.d.P.M., M.C., I.I.-B. and M.V.-R.; project administration: B.G., M.C., I.I.-B. and M.V.-R.; funding acquisition: I.I.-B. and M.V.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 814410 (GIOTTO), the European Research Council under ERC-2015-AdG Proposal No. 694160 (VERDI) and the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación grant number PID2020-117091RB-I00. E.Á. thanks the financial support by FPI fellowship No. BES-2016-078767 from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taubes, G. The bacteria fight back. Science 2008, 321, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The Top 10 Causes of Death. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death” (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Davey, M.E.; O’toole, G.A. Microbial Biofilms: From Ecology to Molecular Genetics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.F. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 276–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S. Antimicrobial Tolerance in Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, eLocator: 3.3.07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durmus, N.G.; Webster, T.J. Eradicating Antibiotic-Resistant Biofilms with Silver-Conjugated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, N.; Sauer-Durand, A.M.; Hartel, M.; Kuratli, J.; Vaupel, P.; Scherr, N.; Pluschke, G. wIRA: Hyperthermia as a treatment option for intracellular bacteria, with special focus on Chlamydiae and Mycobacteria. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pijls, B.G.; Sanders, I.M.J.G.; Kuijper, E.J.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H. Synergy between induction heating, antibiotics, and N-acetylcysteine eradicates Staphylococcus aureus from biofilm. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; González, B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Nanomaterials as promising alternative in the infection treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle-based local antimicrobial drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, A.J.; Kwon, Y.J. “Nanoantibiotics”: A new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassegoda, A.; Ivanova, K.; Ramon, E.; Tzanov, T. Strategies to prevent the occurrence of resistance against antibiotics by using advanced materials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; González, B.; Manzano, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery: An update. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Current insights. Molecules 2018, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Álvarez, E.; González, B.; Lozano, D.; Doadrio, A.L.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Nanoantibiotics Based in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: New Formulations for Bacterial Infection Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Mediero, A.; Carias-Cálix, R.A.; Jiménez-Jiménez, C.; Esteban, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Arabic gum plus colistin coated moxifloxacin-loaded nanoparticles for the treatment of bone infection caused by Escherichia coli. Acta Biomater. 2021, 137, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, E.; Estévez, M.; Jiménez-Jiménez, C.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; González, B.; Vallet-Regí, M. A versatile multicomponent mesoporous silica nanosystem with dual antimicrobial and osteogenic effects. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica materials as drug delivery: “The nightmare” of bacterial infection. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardos, A.; Piacenza, E.; Sancenón, F.; Hamidi, M.; Maleki, A.; Turner, R.J.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials with Bactericidal Properties. Small 2019, 15, e1900669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Targeted stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bacterial infection treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Galiana, I.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Stroeve, P.; Marcos, M.D.; Aznar, E.; Sancenón, F.; Murguía, J.R.; Amorós, P. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-gated Fe3O4/SiO2 core shell nanoparticles with expanded mesoporous structures for the temperature triggered release of lysozyme. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Deng, T.; Lin, F.-C.; Zhang, B.; Zink, J.I. Supramolecular Assemblies of Heterogeneous Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to Co-deliver Antimicrobial Peptides and Antibiotics for Synergistic Eradication of Pathogenic Biofilms. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5926–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, A.; González, B.; Harvey, C.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Effective reduction of biofilm through photothermal therapy by gold core@ shell based mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 328, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, R.A.N.; Frank, J.F. A predictive model for heat inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm on buna-N rubber. LWT -Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, A.; Ricker, E.B.; Nuxoll, E. Thermal mitigation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Biofouling 2015, 31, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgueiriño-Maceira, V.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Farle, M.; López-Quintela, A.; Sieradzki, K.; Diaz, R. Bifunctional gold-coated magnetic silica spheres. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2701–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Tsai, P.J.; Chen, Y.C. Multifunctional Fe3O4@Au nanoeggs as photothermal agents for selective killing of nosocomial and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Small 2009, 5, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlen, L.K.; Parker, A.; Walker, D.; Pasmore, M.; Sturman, P. Predictive modeling for hot water inactivation of planktonic and biofilm-associated Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis to support hot water sanitization programs. Biofouling 2016, 32, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.P.; Mercer, K.E.; Galitovskaya, E.N.; Smeltzer, M.S. Photothermal nanotherapeutics and nanodiagnostics for selective killing of bacteria targeted with gold nanoparticles. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Jiang, X. Small molecule-capped gold nanoparticles as potent antibacterial agents that target gram-negative bacteria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12349–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Tsai, P.J.; Chen, Y.C. Functional gold nanoparticles as photothermal agents for selective-killing of pathogenic bacteria. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, R.S.; Stone, J.W.; Gole, A.; Murphy, C.J.; Sabo-Attwood, T.L. Targeted photothermal lysis of the pathogenic bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with gold nanorods. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiotani, A.; Mori, T.; Niidome, T.; Niidome, Y.; Katayama, Y. Stable incorporation of gold nanorods into N-isopropylacrylamide hydrogels and their rapid shrinkage induced by near-infrared laser irradiation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4012–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.; Jang, J. A highly efficient palladium nanocatalyst anchored on a magnetically functionalized polymer-nanotube support. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7564–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.; Duong, H.T.T.; Selvanayagam, R.; Boyer, C.; Barraud, N. Iron oxide nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia stimulates dispersal in bacterial biofilms and enhances antibiotic efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavlovsky, L.; Sturtevant, R.A.; Younger, J.G.; Solomon, M.J. Effects of temperature on the morphological, polymeric, and mechanical properties of Staphylococcus epidermidis bacterial biofilms. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2036–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, I.P.; Sturtevant, R.; Heung, M.; Solomon, M.J.; Younger, J.G.; VanEpps, J.S. Hemodialysis catheter heat transfer for biofilm prevention and treatment. ASAIO J. 2016, 62, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Toledo, L.d.A.S.; Rosseto, H.C.; Bruschi, M.L. Iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles as antimicrobials for therapeutics. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Akakuru, O.U.; Zheng, J.; Wu, A. Applications of iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles in the diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Yamayoshi, I.; Mathew, S.; Lin, H.; Nayfach, J.; Simon, S.I. Magnetic nanoparticle targeted hyperthermia of cutaneous Staphylococcus aureus infection. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricker, E.B.; Nuxoll, E. Synergistic effects of heat and antibiotics on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Biofouling 2017, 33, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturtevant, R.A.; Sharma, P.; Pavlovsky, L.; Stewart, E.J.; Solomon, M.J.; Younger, J.G. Thermal augmentation of vancomycin against staphylococcal biofilms. Shock 2015, 44, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chopra, R.; Shaikh, S.; Chatzinoff, Y.; Munaweera, I.; Cheng, B.; Daly, S.M.; Xi, Y.; Bing, C.; Burns, D.; Greenberg, D.E. Employing high-frequency alternating magnetic fields for the non-invasive treatment of prosthetic joint infections. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazel, D.; Yilmaz, M. Are infectious diseases and microbiology new fields for thermal therapy research? Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falk, M.H.; Issels, R.D. Hyperthermia in oncology. Int. J. Hyperth. 2001, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wust, P.; Hildebrandt, B.; Sreenivasa, G.; Rau, B.; Gellermann, J.; Riess, H.; Felix, R.; Schlag, P. Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, G.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tiwari, S.; Shi, K.; et al. Comprehensive understanding of magnetic hyperthermia for improving antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3793–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Hauff, K.; Ulrich, F.; Nestler, D.; Niehoff, H.; Wust, P.; Thiesen, B.; Orawa, H.; Budach, V.; Jordan, A. Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 103, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colilla, M.; Balas, F.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Novel method to enlarge the surface area of SBA-15. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 3099–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, M.; Thiesen, B.; Wust, P.; Jordan, A. Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia for prostate cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2010, 26, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Bañobre-López, M.; Espiña, B.; Rivas, J.; Azeredo, J. Effect of magnetic hyperthermia on the structure of biofilm and cellular viability of a food spoilage bacterium. Biofouling 2013, 29, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, J.; Park, T.H. Inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01 biofilms by hyperthermia using superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 84, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Barick, K.C.; Bahadur, D. Inactivation of bacterial pathogens under magnetic hyperthermia using Fe3O4-ZnO nanocomposite. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchianò, V.; Salvador, M.; Moyano, A.; Gutiérrez, G.; Matos, M.; Yáñez-Vilar, S.; Piñeiro, Y.; Rivas, J.; Martínez-García, J.C.; Peddis, D.; et al. Electrodecoration and characterization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with bioactive synergistic nanocopper: Magnetic hyperthermia-induced ionic release for anti-biofilm action. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergt, R.; Dutz, S.; Röder, M. Effects of size distribution on hysteresis losses of magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 385214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périgo, E.A.; Hemery, G.; Sandre, O.; Ortega, D.; Garaio, E.; Plazaola, F.; Teran, F.J. Fundamentals and advances in magnetic hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ovejero, J.G.; Armenia, I.; Serantes, D.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Zeballos, N.; López-Gallego, F.; Grüttner, C.; Fuente, J.M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; del Puerto Morales, M.; et al. Selective Magnetic Nanoheating: Combining Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Multi-Hot-Spot Induction and Sequential Regulation. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 7213–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Talelli, M.; Arcos, D.; Moros, M.; De La Fuente, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic-responsive release controlled by hot spot effect. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12777–12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, H.; Salas, G.; Arias-Gonzalez, J.R. Heat generation in single magnetic nanoparticles under near-infrared irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 11, 2182–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetically triggered multidrug release by hybrid mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Du, C.; Liao, J.-Y.; Gu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Pei, J.; Gu, H.; Yin, D.; Gao, L.; Pan, Y. Synthesis of magnetite hybrid nanocomplexes to eliminate bacteria and enhance biofilm disruption. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2833–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Hu, B.; Xing, X. Microenvironment-responsive magnetic nanocomposites based on silver nanoparticles/gentamicin for enhanced biofilm disruption by magnetic field. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34905–34915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Reyes-Ortega, F.; Schneider-Futschik, E.K. Magnetic nanoparticle-based drug delivery approaches for preventing and treating biofilms in cystic fibrosis. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Wust, P.; Fähling, H.; Felix, R. Magnetic fluid hyperthermia (MFH): Cancer treatment with AC magnetic field induced excitation of biocompatible superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiergeist, R.; Andrä, W.; Buske, N.; Hergt, R.; Hilger, I.; Richter, U.; Kaiser, W. Application of magnetite ferrofluids for hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergt, R.; Hiergeist, R.; Hilger, I.; Kaiser, W.A.; Lapatnikov, Y.; Margel, S.; Richter, U. Maghemite nanoparticles with very high AC-losses for application in RF-magnetic hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 270, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Haron, M.J.; Namvar, F.; Nadi, B.; Rahman, M.Z.; Amin, J. Synthesis, surface modification and characterisation of biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 2013, 18, 7533–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barani, M.; Zeeshan, M.; Kalantar-Neyestanaki, D.; Farooq, M.A.; Rahdar, A.; Jha, N.K.; Sargazi, S.; Kumar Gupta, P.; Thakur, V.K. Nanomaterials in the Management of Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, H.; Xu, X.; Zou, J.; Lu, C. Biocompatible Superparamagnetic Europium-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Clusters as Multifunctional Nanoprobes for Multimodal In Vivo Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 33850–33861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, N.; Rizwan, M. Progress and prospects of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Artif. Organs. 2021, 45, 1272–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alumutairi, L.; Yu, B.; Filka, M.; Nayfach, J.; Kim, M.H. Mild magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia enhances the susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm to antibiotics. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Pan, J.; Zhao, J.; Tang, J.; Jiang, D.; Hu, P.; Jia, W.; Shi, J. Magneto-based synergetic therapy for implant-associated infections via biofilm disruption and innate immunity regulation. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakha, M.; Pal, S.; Samantarrai, D.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Mallick, B.C.; Pramanik, K.; Mallick, B.; Jha, S. Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salas, G.; Casado, C.; Teran, F.J.; Miranda, R.; Serna, C.J.; Morales, M.P. Controlled synthesis of uniform magnetite nanocrystals with high-quality properties for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21065–21075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, L.; De La Cueva, L.; Moros, M.; Mazarío, E.; De Bernardo, S.; De La Fuente, J.M.; Morales, M.P.; Salas, G. Aggregation effects on the magnetic properties of iron oxide colloids. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson Moye, H.; Boning, A.J. A versatile fluorogenic labelling reagent for primary and secondary amines: 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate. Anal. Lett. 1979, 12, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, A.J. Estimating the precision of serial dilutions and viable bacterial counts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 76, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 3rd ed.; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1978; ISBN 0201011743. [Google Scholar]
- Guardia, P.; Batlle-Brugal, B.; Roca, A.G.; Iglesias, O.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J.; Labarta, A.; Batlle, X. Surfactant effects in magnetite nanoparticles of controlled size. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 316, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahoo, Y.; Goodarzi, A.; Swihart, M.T.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Kaur, N.; Furlani, E.P.; Prasad, P.N. Aqueous ferrofluid of magnetite nanoparticles: Fluorescence labeling and magnetophoretic control. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3879–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Ibrahim, I.T. Carbodiimide chemistry: Recent advances. Chem. Rev. 1981, 81, 589–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Sánchez-Salcedo, S.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Hueso, J.L.; Vallet-Regí, M. Synthesis and characterization of zwitterionic SBA-15 nanostructured materials. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6459–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Time-delayed release of bioencapsulates: A novel controlled delivery concept for bone implant technologies. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4826–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.; Colilla, M.; Díez, J.; Pedraza, D.; Guembe, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles decorated with polycationic dendrimers for infection treatment. Acta Biomater. 2018, 68, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, A.; Colilla, M.; Balas, F.; Vallet-Regí, M. Surface electrochemistry of mesoporous silicas as a key factor in the design of tailored delivery devices. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5038–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, P.; Grunze, M.; Dahint, R.; Whitesides, G.M.; Laibinis, P.E. Molecular conformation in oligo(ethylene glycol)-terminated self-assembled monolayers on gold and silver surfaces determines their ability to resist protein adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futscher, M.H.; Philipp, M.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Schulte, A. The Role of Backbone Hydration of Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) Across the Volume Phase Transition Compared to its Monomer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyengar, S.J.; Joy, M.; Maity, T.; Chakraborty, J.; Kotnala, R.K.; Ghosh, S. Colloidal properties of water dispersible magnetite nanoparticles by photon correlation spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14393–14402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, S.I.C.J.; Marciello, M.; Carvalho, A.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; del Puerto Morales, M.; Roque, A.C.A. Effects of phase transfer ligands on monodisperse iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 437, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begin-Colin, S.; Felder-Flesch, D. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Fabrication to Clinical Applications; Thanh, N.T., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; p. 616. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, R.E.; Aguilera-Márquez, D.; Virués, C.; Inoue, M. Hydrogen bonding between carboxylic acids and amide-based macrocycles in their host-guest complexes. Supramol. Chem. 2008, 20, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, F.; Manzano, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. L-Trp adsorption into silica mesoporous materials to promote bone formation. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirou, S.V.; Basini, M.; Lascialfari, A.; Sangregorio, C.; Innocenti, C. Magnetic hyperthermia and radiation therapy: Radiobiological principles and current practice. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polo-Corrales, L.; Rinaldi, C. Monitoring iron oxide nanoparticle surface temperature in an alternating magnetic field using thermoresponsive fluorescent polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07B334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiahdoss, G.; Sharifi, S.; Grijpma, D.W.; Laurent, S.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Mahmoudi, M.; Busscher, H.J. Magnetic targeting of surface-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles yields antibacterial efficacy against biofilms of gentamicin-resistant staphylococci. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).