Gold–Protein Composite Nanoparticles for Enhanced X-ray Interactions: A Potential Formulation for Triggered Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis
2.3. Zein Purification
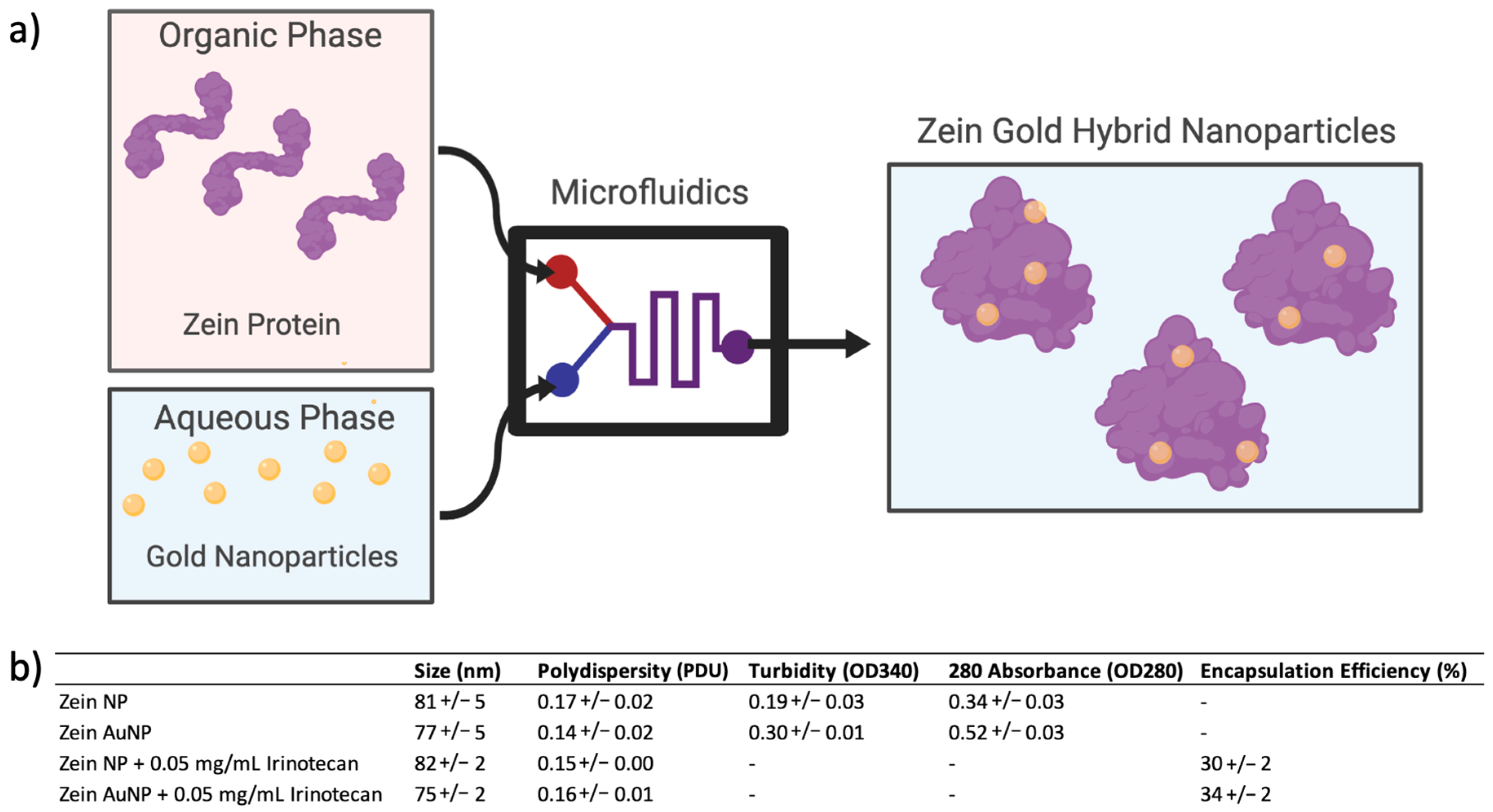
2.4. Zein Nanoparticle and Zein–Gold Hybrid Nanoparticle Synthesis and Characterization
2.5. Zein Nanoparticle and Zein–Gold Hybrid Nanoparticle Irradiation
2.6. SDS-PAGE
2.7. UV–Vis Aromaticity and Turbidity
2.8. Irinotecan Loading and Triggered Release
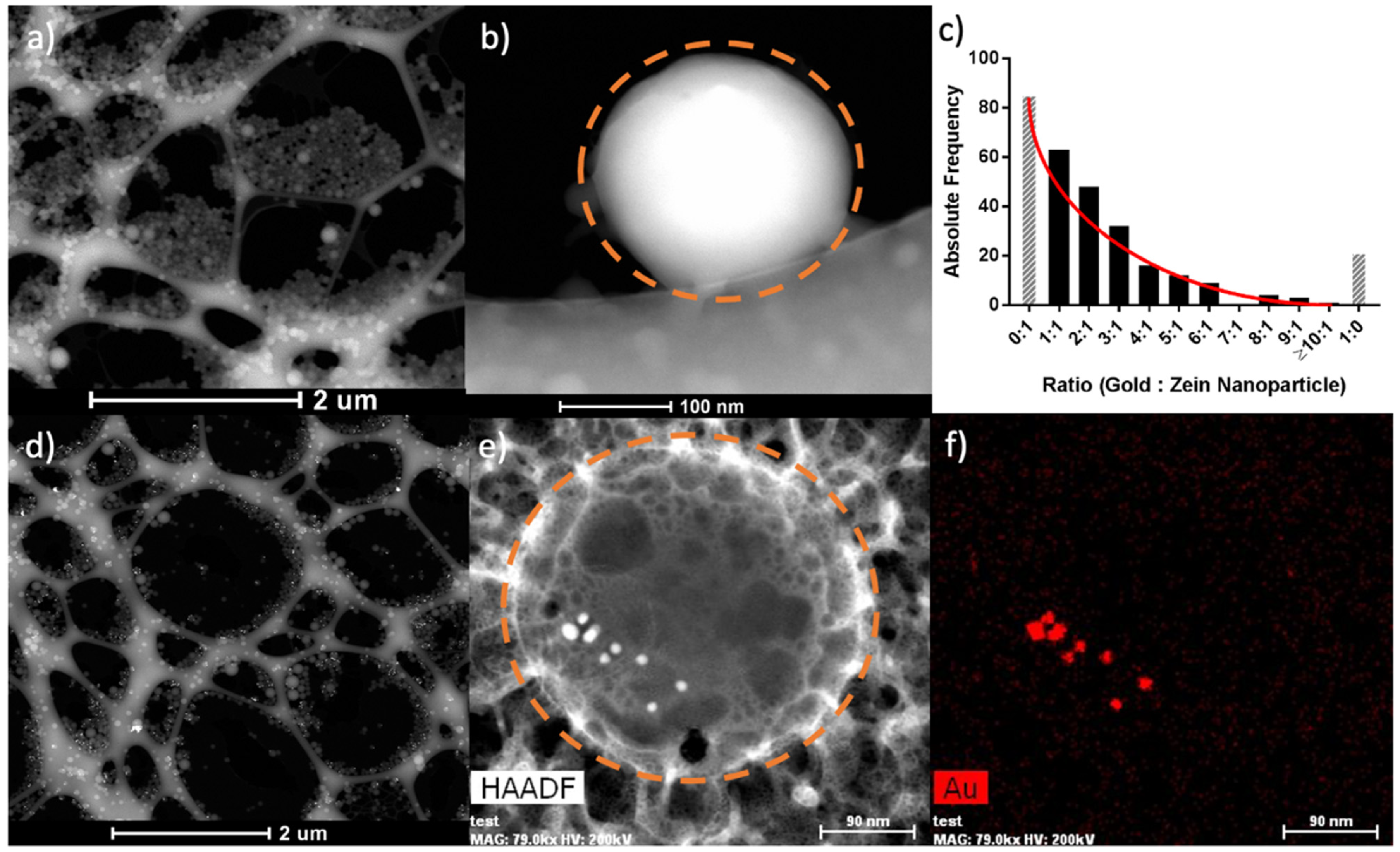
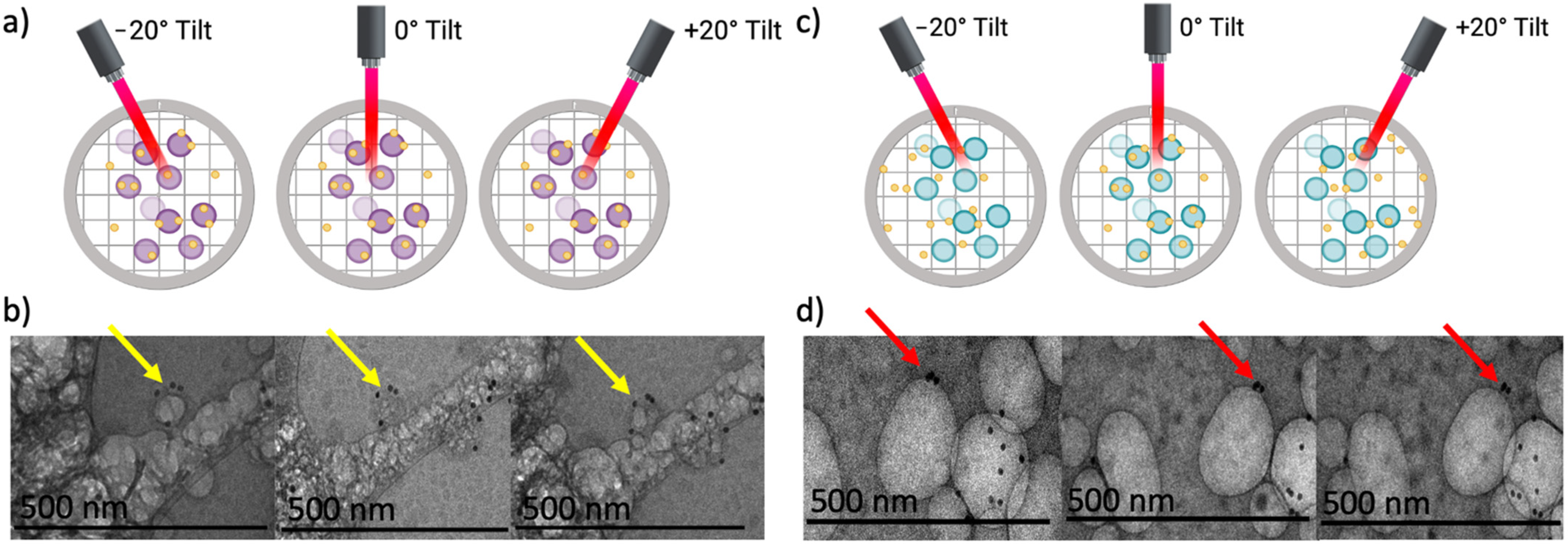
2.9. SEM, STEM, EDX, and Cryo-Electron Microscopy
2.10. Statistics and Image Processing
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Zein and Zein–Gold Hybrid Nanoparticles
3.1.1. Influence of X-rays on Zein and Zein–Gold Hybrid Particle Characteristics
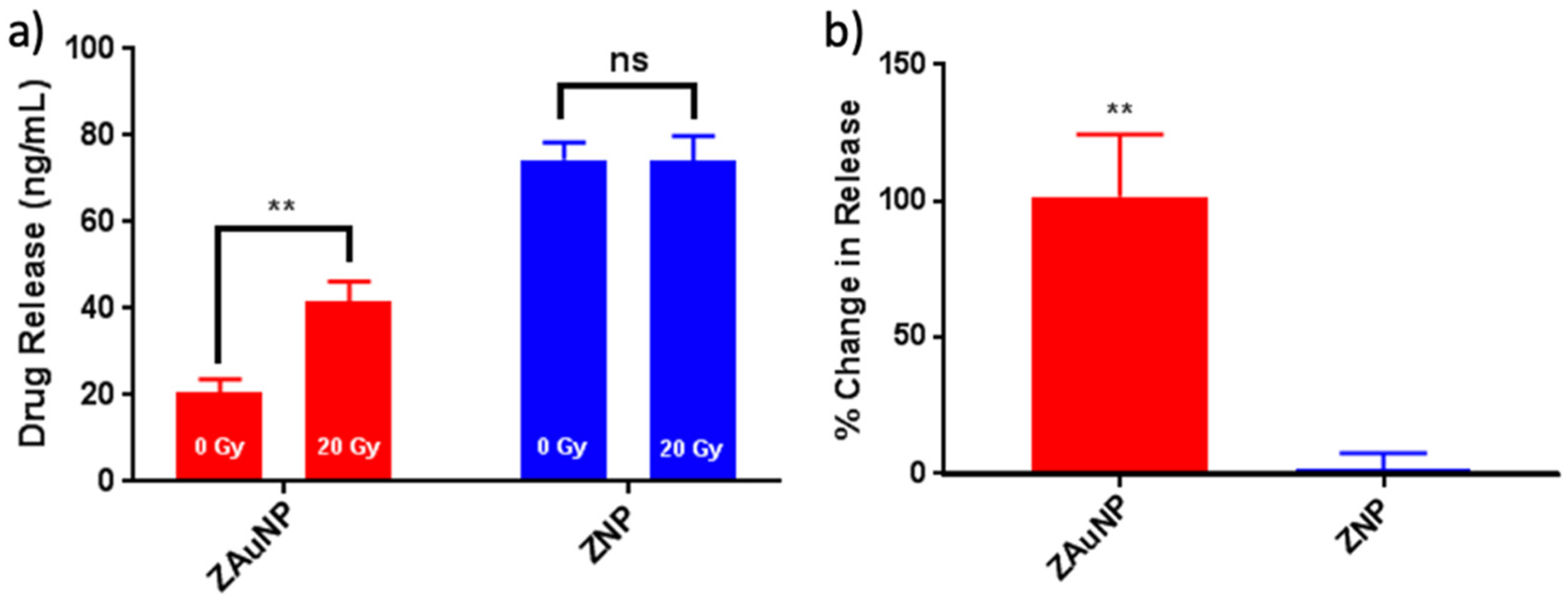
3.1.2. Triggered Release
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Analysis of Variance | (ANOVA) |
| Cisplatin | (CPT) |
| Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy | (Cryo-TEM) |
| Deionized | (DI) |
| Dynamic Light Scattering | (DLS) |
| Electron Microscopy | (EM) |
| Gold Nanoparticle | (AuNP) |
| Generally Recognized as Safe | (GRAS) |
| Head and Neck | (H&N) |
| Integrated Density | (ID) |
| Molecular Weight | (MW) |
| Near-Infrared Light | (NIR) |
| Optical Density | (OD) |
| Reactive Oxygen Species | (ROS) |
| Revolutions per Minute | (rpm) |
| Radiation Therapy | (RT) |
| Scanning Electron Microscopy | (SEM) |
| Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy | (STEM) |
| Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate | (SDS) |
| Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis | (SDS-PAGE) |
| Tetramethylethylenediamine | (TEMED) |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy | (TEM) |
| Ultraviolet Visible Spectroscopy | (UV–vis) |
| Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy | (VMAT) |
| Water Contact Angle | (WCA) |
| Water Vapor Permeability | (WVP) |
| Zein Nanoparticle | (ZNP) |
| Zein–Gold Hybrid Nanoparticle | (ZAuNP) |
References
- Nigro, C.L.; Denaro, N.; Merlotti, A.; Merlano, M. Head and neck cancer: Improving outcomes with a multidisciplinary approach. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlsson, L.; Bratman, S.V.; Siu, L.L.; Spreafico, A. The Cisplatin Total Dose and Concomitant Radiation in Locoregionally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer: Any Recent Evidence for Dose Efficacy? Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayette, J.; Molin, Y.; Lavergne, E.; Montbarbon, X.; Racadot, S.; Poupart, M.; Ramade, A.; Zrounba, P.; Céruse, P.; Pommier, P. Radiotherapy potentiation with weekly cisplatin compared to standard every 3 weeks cisplatin chemotherapy for locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 6203–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Ballegooie, C.; Man, A.; Win, M.; Yapp, D.T. Spatially specific liposomal cancer therapy triggered by clinical external sources of energy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, W.; Chen, W.; Clement, S.; Guller, A.; Zhao, Z.; Engel, A.; Goldys, E.M. Controlled gene and drug release from a liposomal delivery platform triggered by X-ray radiation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Bromma, K.; Sung, W.; Schuemann, J.; Chithrani, D. Determining the radiation enhancement effects of gold nanoparticles in cells in a combined treatment with cisplatin and radiation at therapeutic megavoltage energies. Cancers 2018, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savchenko, A.; Braun, G.B.; Molokanova, E. Nanostructured Antagonist of Extrasynaptic NMDA Receptors. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5495–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ballegooie, C.; Man, A.; Andreu, I.; Gates, B.D.; Yapp, D. Using a microfluidics system to reproducibly synthesize protein nanoparticles: Factors contributing to size, homogeneity, and stability. Processes 2019, 7, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larson, A.G.; Elnatan, D.; Keenen, M.M.; Trnka, M.J.; Johnston, J.B.; Burlingame, A.L.; Agard, D.A.; Redding, S.; Narlikar, G.J. Liquid droplet formation by HP1α suggests a role for phase separation in heterochromatin. Nature 2017, 547, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassucci, R.A.; Taylor, D.J.; Frank, J. Preparation of macromolecular complexes for cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 3239–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pant, M.P.; Mariam, J.; Joshi, A.; Dongre, P.M. UV radiation sensitivity of bovine serum albumin bound to silver nanoparticles. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Deng, Y.; Ye, L.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, Y. Enhancing hemocompatibility and the performance of Au@silica nanoparticles by coating with cRGD functionalized zein. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 125, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Sheng, J.; Shi, L.L.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Peng, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wan, J.; Yang, X. Non-covalent assembly of albumin nanoparticles by hydroxyl radical: A possible mechanism of the nab technology and a one-step green method to produce protein nanocarriers. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučković, M.; Radojčić, M.B.; Milosavljević, B.H. Gamma-radiation induced damage of proteins in the thick fraction of egg white. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2005, 70, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Wang, C.N.; Zhang, Y.C.; Liu, T.T.; Lv, J.P.; Shen, X.; Guo, M.R. Effects of gamma radiation on microbial, physicochemical, and structural properties of whey protein model system. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, S.; Gupta, O.P.; Mishra, C.B.; Thimmegowda, V.; Krishnan, V.; Singh, B.; Sachdev, A.; Dahuja, A. Gamma irradiation, an effective strategy to control the oxidative damage of soy proteins during storage and processing. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 177, 109134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron Es Dickman, S. Studies on the mechanism of action of ionizing radiations; inhibition. J. Gen. Physiol. 1949, 32, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durchschlag, H.; Fochler, C.; Feser, B.; Hausmann, S.; Seroneit, T.; Swientek, M.; Swoboda, E.; Winklmair, A.; Wlček, C.; Zipper, P. Effects of X- and UV-irradiation on proteins. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1996, 47, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Mafuné, F. Degradation of Protein in Nanoplasma Generated around Gold Nanoparticles in Solution by Laser Irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2393–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, M.D.; Hizkiahou, N.; Peled, S.; Gazit, E.; Segal, D. Total proteome turbidity assay for tracking global protein aggregation in the natural cellular environment. J. Biol. Methods 2017, 4, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Levine, R.L. Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, J.I.; Uranga, J.; Matxain, J.M. Computational study on the attack of.·oH radicals on aromatic amino acids. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6862–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J. Protein oxidation and peroxidation. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 805–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, R.T.; Fu, S.; Stocker, R.; Davies, M.J. Biochemistry and pathology of radical-mediated protein oxidation. Biochem. J. 1997, 324, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gianazza, E.; Viglienghi, V.; Righetti, P.G.; Salamini, F.; Soave, C. Amino acid composition of zein molecular components. Phytochemistry 1977, 16, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatham, A.S.; Field, J.M.; Morris, V.J.; I’Anson, K.J.; Cardle, L.; Dufton, M.; Shewry, P.R. Solution conformational analysis of the α-zein proteins of maize. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 26253–26259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, Y. Folate-conjugated zein/Fe3O4 nanocomplexes for the enhancement of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of gefitinib. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14907–14921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, Q. Facile encapsulation of hydroxycamptothecin nanocrystals into zein-based nanocomplexes for active targeting in drug delivery and cell imaging. Acta Biomater. 2017, 61, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicki, A.; Witzigmann, D.; Balasubramanian, V.; Huwyler, J. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: Challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J. Control. Release 2015, 200, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Zein-based micro- and nano-particles for drug and nutrient delivery: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, G. Overview on Zein Protein: A promising pharmaceutical excipient in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falappa, P.; Fassari, F.M.; Fanelli, A.; Genovese, E.; Ascani, E.; Crostelli, M.; Salsano, V.; Montanaro, A.; Di Lazzaro, A.; Serra, F. Aneurysmal bone cysts: Treatment with direct percutaneous ethibloc injection: Long-term results. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2002, 25, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emran, M.A.; Dubois, J.; Laberge, L.; Al-Jazaeri, A.; Bütter, A.; Yazbeck, S. Alcoholic solution of zein (Ethibloc) sclerotherapy for treatment of lymphangiomas in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamsbaum, C.; Kalifa, G.; Seringe, R.; Dubousset, J. Direct Ethibloc injection in benign bone cysts: Preliminary report on four patients. Skelet. Radiol. 1993, 22, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.; Garel, L.; Abela, A.; Laberge, L.; Yazbeck, S. Lymphangiomas in Children: Percutaneous Sclerotherapy with an Alcoholic Solution of Zein. Radiology 1997, 204, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, H.L.; Unnikrishnan, P.N.; Garg, N.K.; Sampath, J.S.; Bass, A.; Bruce, C.E. Long-term follow-up of Ethibloc injection in aneurysmal bone cysts. J. Pediatr Orthop. B 2009, 18, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.K.; Carty, H.; Walsh, H.P.J.; Dorgan, J.C.; Bruce, C.E. Percutaneous Ethibloc injection in aneurysmal bone cysts. Skelet. Radiol. 2000, 29, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsudaira, H.; Ueno, A.M.; Furuno, I. Iodine Contrast Medium Sensitizes Cultured Mammalian Cells to X Rays but Not to γ Rays. Radiat. Res. 1980, 84, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, R.S.; Callisen, H.; Winter, J.; Kagan, A.R.; Norman, A. Radiation dose enhancement in tumors with iodine. Med. Phys. 1983, 10, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, D.B.; Jelveh, S.; Jalali, F.; van Prooijen, M.; Allen, C.; Bristow, R.G.; Hill, R.P.; Jaffray, D. Gold Nanoparticles as Radiation Sensitizers in Cancer Therapy. Radiat. Res. 2010, 173, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard-Roselli, C.; Brun, E.; Gilles, M.; Baldacchino, G.; Kelsey, C.; McQuaid, H.; Polin, C.; Wardlow, N.; Currell, F. A new mechanism for hydroxyl radical production in irradiated nanoparticle solutions. Small 2014, 10, 3338–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuemann, J.; Berbeco, R.; Chithrani, D.B.; Cho, S.H.; Kumar, R.; McMahon, S.J.; Sridhar, S.; Krishnan, S. Roadmap to clinical use of gold nanoparticles for radiation sensitization. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misawa, M.; Takahashi, J. Generation of reactive oxygen species induced by gold nanoparticles under X-ray and UV Irradiations. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T. Physical, chemical and biological enhancement in X-ray nanochemistry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 15917–15931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Smilowitz, H.M.; O’Connor, M.J.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Slatkin, D.N. Gold nanoparticle imaging and radiotherapy of brain tumors in mice. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidson, R.A.; Guo, T. Average physical enhancement by nanomaterials under X-ray irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 30221–30228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, M.; Song, K.B. Effect of γ-irradiation on the Physicochemical Properties of Zein Films. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2003, 8, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.Y.; Lan, R.; Wang, J.Y. Quality Monitoring of Porous Zein Scaffolds: A Novel Biomaterial. Engineering 2017, 3, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.A.; Furuta, M. Influence of γ-irradiation on mechanical and water barrier properties of corn protein-based films. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.A.; Eldin, M.S.M.; Furuta, M. Biodegradable zein-based films: Influence of γ-irradiation on structural and functional properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, R.J.; van Leeuwen, Y.M.; Hendrix, Y.; Velikov, K.P.; Kegel, W.K.; Philipse, A.P. Morphology-controlled functional colloids by heterocoagulation of zein and nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 483, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Arunkumar, P.; Prasad, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Reddy, B.P.; De, A.; Srivastava, R. Facile synthesis of plasmonic zein nanoshells for imaging-guided photothermal cancer therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, P.; Vaseeharan, B.; Vijayakumar, S.; Balan, B.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Benelli, G. Biopolymer zein-coated gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial potential, toxicity and histopathological effects against the Zika virus vector Aedes aegypti. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 173, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, B.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Supramolecular design of coordination bonding architecture on zein nanoparticles for pH-responsive anticancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwland, M.; Papen-Bottenhuis, N.E.; Drost, W.C.; Slaghek, T.M.; Erich, B.S. Enzymatically triggered release of dye model compounds from zein particles. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 83, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapalli, P.K.; Labala, S.; Chawla, S.; Janupally, R.; Sriram, D.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Polymer-Gold nanoparticle composite films for topical application: Evaluation of physical properties and antibacterial activity. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazel, C.S.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from swellable polymers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 49, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Ballegooie, C.; Man, A.; Pallaoro, A.; Bally, M.; Gates, B.D.; Yapp, D.T. Gold–Protein Composite Nanoparticles for Enhanced X-ray Interactions: A Potential Formulation for Triggered Release. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091407
van Ballegooie C, Man A, Pallaoro A, Bally M, Gates BD, Yapp DT. Gold–Protein Composite Nanoparticles for Enhanced X-ray Interactions: A Potential Formulation for Triggered Release. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(9):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091407
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Ballegooie, Courtney, Alice Man, Alessia Pallaoro, Marcel Bally, Byron D. Gates, and Donald T. Yapp. 2021. "Gold–Protein Composite Nanoparticles for Enhanced X-ray Interactions: A Potential Formulation for Triggered Release" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 9: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091407
APA Stylevan Ballegooie, C., Man, A., Pallaoro, A., Bally, M., Gates, B. D., & Yapp, D. T. (2021). Gold–Protein Composite Nanoparticles for Enhanced X-ray Interactions: A Potential Formulation for Triggered Release. Pharmaceutics, 13(9), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091407






