Assessment of Mini-Tablets Coating Uniformity as a Function of Fluid Bed Coater Inlet Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Placebo Cores Preparation
2.2.2. Coating Procedure
2.2.3. Analysis of Coating Uniformity
2.2.4. Color Analysis of Mini-Tablets
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Placebo Mini-Tablets Development
3.2. Film Thickness Uniformity
3.3. Coated Mini-Tablets Color Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joshi, S.; Petereit, H.-U. Film coatings for taste masking and moisture protection. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanez, R.; Nitz, M.; Taranto, O.P. Enteric coating process of diclofenac sodium pellets in a fluid bed coater with a wurster insert: Influence of process variables on coating performance and release profile. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y.; Yang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, W.; Shan, L.; Gao, C. Novel ethylcellulose-coated pellets for controlled release of metoprolol succinate without lag phase: Characterization, optimization and in vivo evaluation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonar, G.; Rawat, S. Optimization of pantoprazole enteric pellets coating process by QbD: Effect of coating process variables on the intermediate quality of the product and scale up. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadi, S.S.; Toegel, S.; Viernstein, H. Innovations in coating technology. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2008, 2, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.C. Handbook of Fluidization and Fluid-Particle Systems; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 082470259X. [Google Scholar]
- Wurster, D.E.; Lindlof, J.A. Particle Coating Apparatus. U.S. Patent 3,241,520, 22 March 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Felton, L.A.; McGinity, J.W. Aqueous Polymeric Coatings for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780849387883. [Google Scholar]
- Savic, S.; Gregorka, M.; Dreu, R.; Srcic, S.; Sibanc, R.; Lustrik, M.; Zun, I. A Process Device for Coating Particles. WIPO Patent Application WO/2010/065000, 10 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dreu, R.; Lustrik, M.; Perpar, M.; Zun, I.; Srcic, S. Fluid-bed coater modifications and study of their influence on the coating process of pellets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luštrik, M.; Šibanc, R.; Srčič, S.; Perpar, M.; Žun, I.; Dreu, R. Characteristics of pellet fl ow in a Wurster coater draft tube utilizing piezoelectric probe. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luštrik, M.; Dreu, R.; Šibanc, R.; Srčič, S. Comparative study of the uniformity of coating thickness of pellets coated with a conventional Wurster chamber and a swirl generator-equipped Wurster chamber. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingmann, V.; Spomer, N.; Lerch, C.; Stoltenberg, I.; Frömke, C.; Bosse, H.M.; Breitkreutz, J.; Meissner, T. Favorable Acceptance of Mini-Tablets Compared with Syrup: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Infants and Preschool Children. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluk, A.; Sznitowska, M.; Brandt, A.; Sznurkowska, K.; Plata-Nazar, K.; Mysliwiec, M.; Kaminska, B.; Kotlowska, H. Can preschool-aged children swallow several minitablets at a time? Results from a clinical pilot study. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Chang, J.; Wu, S.; Wolfe, C.N.; Ternik, R.L.; Gunter, T.Z.; Victor, M.C. Feasibility of mini-tablets as a flexible drug delivery tool. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ghaffur, A.; Bains, J.; Hamdy, S. Acceptability of oral solid medicines in older adults with and without dysphagia: A nested pilot validation questionnaire based observational study. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Abe, K.; Hashizume, M.; Kawamura, M. A novel approach to sustained pseudoephedrine release: Differentially coated mini-tablets in HPMC capsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanska, M.; Sznitowska, M. Comparison of the coating process and in vitro dissolution of 3 mm gastro-resistant minitablets and 5 mm gastro-resistant tablets with pantoprazole. Pharmazie 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowska, M.; Kotlowska, H.; Madanecka, A.; Maja, S.; Doniza, D.; Sosnowicz, A.; Sznitowska, M. Prolonged-release minitablets with carbamazepine—Preliminary observations in vitro. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. PAT-tools for process control in pharmaceutical film coating applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Holmquist, B.; Lindquist, J.; Nilsson, O.; Wahlund, K.G. Analysis of film coating thickness and surface area of pharmaceutical pellets using fluorescence microscopy and image analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 22, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepańska, M.; Scanu, N.; Sznitowska, M. The effect of size of enteric-coated minitablets and type of the dispersing gel on the in vitro release of diclofenac. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2020, 77, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikowitz, K.; Folttmann, F.; Wirges, M.; Knop, K.; Pintye-Hódi, K.; Regdon, G.; Kleinebudde, P. Development of a Raman method to follow the evolution of coating thickness of pellets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hagrasy, A.S.; Chang, S.-Y.; Desai, D.; Kiang, S. Raman spectroscopy for the determination of coating uniformity of tablets: Assessment of product quality and coating pan mixing efficiency during scale-up. J. Pharm. Innov. 2006, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Seo, D.Y.; Lee, H.E.; Wang, I.C.; Kim, W.S.; Jeong, M.Y.; Choi, G.J. In line NIR quantification of film thickness on pharmaceutical pellets during a fluid bed coating process. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Römer, M.; Heinämäki, J.; Strachan, C.; Sandler, N.; Yliruusi, J. Prediction of Tablet Film-coating Thickness Using a Rotating Plate Coating System and NIR Spectroscopy. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haaser, M.; Gordon, K.C.; Strachan, C.J.; Rades, T. Terahertz pulsed imaging as an advanced characterisation tool for film coatings—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, D.; Zeitler, J.A.; Funke, A.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. A comparison of quality control methods for active coating processes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowska, M.; Sznitowska, M.; Kleinebudde, P. Determination of coating thickness of minitablets and pellets by dynamic image analysis. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zeitler, J.A.; Dong, Y.; Shen, Y.-C. Non-Destructive Evaluation of Polymer Coating Structures on Pharmaceutical Pellets Using Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, D.; Hannesschläger, G.; Sacher, S.; Leitner, M.; Buchsbaum, A.; Pescod, R.; Baele, T.; Khinast, J.G. In-Line Monitoring of a Pharmaceutical Pan Coating Process by Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, D.M.; Nafee, N.; Abdallah, O.Y. Mini-tablets versus pellets as promising multiparticulate modified release delivery systems for highly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksovski, A.; Dreu, R.; Gašperlin, M.; Planinšek, O. Mini-tablets: A contemporary system for oral drug delivery in targeted patient groups. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrekar, G.; Kitak, D.; Mehle, A.; Lavrič, Z.; Likar, B.; Tomaževič, D.; Dreu, R. In-Line Film Coating Thickness Estimation of Minitablets in a Fluid-Bed Coating Equipment. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 3440–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodea, M.; Napoca, C. Film coating preparation of metoprolol tartrate mini-tablets and in vitro drug release studies. Clujul Med. 2010, 83, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanska, M.; Paduszynski, P.; Kotlowska, H.; Sznitowska, M. Optimization of the coating process of minitablets in two different lab-scale fluid bed systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickley, R.G. Pediatric Oral Formulations: An Updated Review of Commercially Available Pediatric Oral Formulations Since 2007. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1335–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lura, A.; Tardy, G.; Kleinebudde, P.; Breitkreutz, J. Tableting of mini-tablets in comparison with conventionally sized tablets: A comparison of tableting properties and tablet dimensions. Int. J. Pharm. X 2020, 2, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleari, C. Standard Colorimetry: Definitions, Algorithms and Software; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781118894453. [Google Scholar]
- Šibanc, R.; Luštrik, M.; Dreu, R. Analysis of pellet coating uniformity using a computer scanner. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, R.W. Handbook of Biological Dyes and Stains; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780470586242. [Google Scholar]
- Oman Kadunc, N.; Šibanc, R.; Dreu, R.; Likar, B.; Tomaževič, D. In-line monitoring of pellet coating thickness growth by means of visual imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 470, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.X.; Turton, R. The Prediction of Variability Occurring in Fluidized Bed Coating Equipment. I. The Measurement of Particle Circulation Rates in a Bottom-Spray Fluidized Bed Coater. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2000, 5, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W.; Tang, E.S.K. Use of swirling airflow to enhance coating performance of bottom spray fluid bed coaters. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 327, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeleye, A.O.O.; Chui, C.-Y.; Nguyen, L.; Castrejón-Pita, A.A.; Ye, H.; Cui, Z. On the use of 3D-printed flow distributors to control particle movement in a fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 140, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

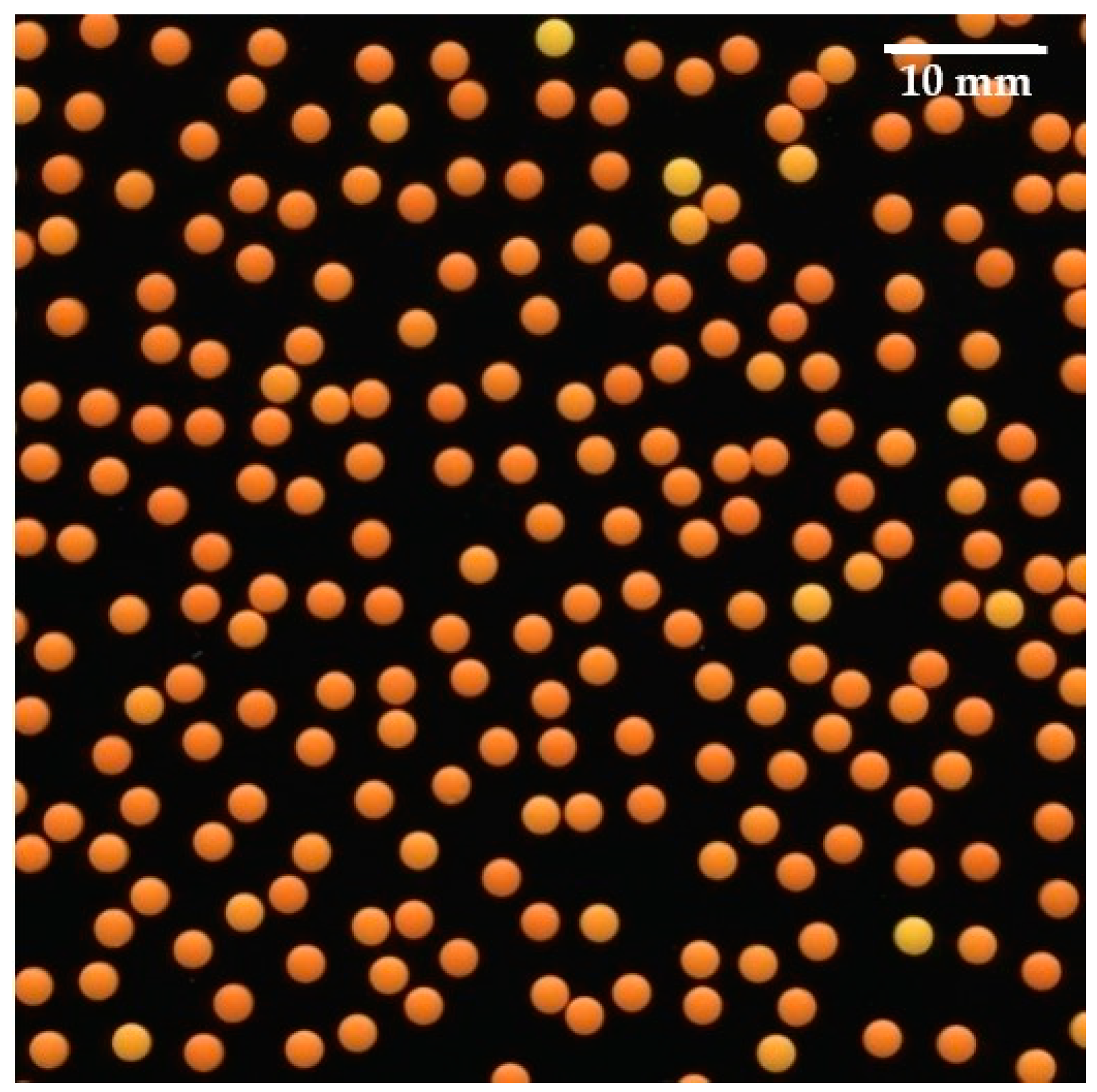


| Parameters | MT2.0 | MT2.5 | MT3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| Thickness (mm) ± RSD * | 2.02 (±0.85%) | 1.82 (±0.99%) | 2.21 (±0.54%) |
| Surface of a single unit (mm2) ± RSD * | 15.95 (±2.34%) | 18.84 (±2.45%) | 28.73 (±1.56%) |
| Mass (mg) ± RSD * | 7.97 (±1.34%) | 11.68 (±1.31%) | 19.96 (±0.75%) |
| Hardness (N) ± RSD * | 13.27 (±15.15%) | 22.12 (±12.32%) | 28.29 (±8.86%) |
| Friability (%) | 0.3 | 0.21 | 0.15 |
| Disintegration time (s) ± SD ** | 40 (±5 s) | 60 (±10 s) | 40 (±5 s) |
| Cores | MT2.0 | MT2.5 | MT3.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distributor | CW | CW | SW | CW | CW | SW | CW | CW | SW |
| Inlet airflow rate (m3/h) | 130 | 156 | 156 | 130 | 156 | 156 | 130 | 156 | 156 |
| Film thickness (µm) | 18.7 | 19.9 | 18.4 | 18.9 | 21.9 | 17.9 | 18.8 | 18.2 | 18.3 |
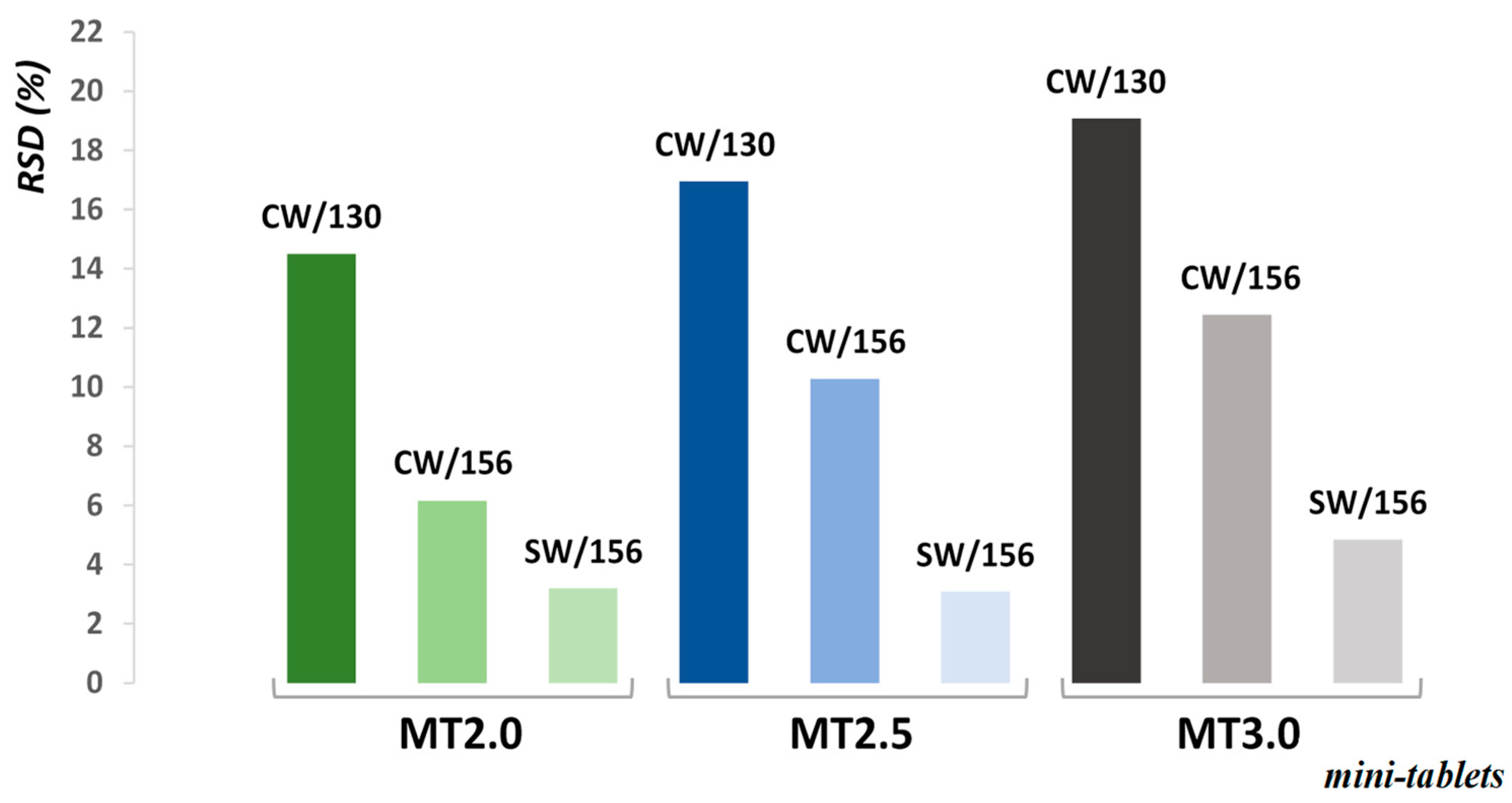
| Cores | Distributor/Air Rate (m3/h) | Average Hardness (N) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MT2.0 | CW/130 | 33.39 | 14.72 |
| CW/156 | 34.36 | 10.96 | |
| SW/156 | 33.70 | 9.00 | |
| MT2.5 | CW/130 | 43.58 | 14.72 |
| CW/156 | 42.68 | 10.20 | |
| SW/156 | 40.61 | 7.00 | |
| MT3.0 | CW/130 | 51.04 | 17.67 |
| CW/156 | 53.77 | 9.27 | |
| SW/156 | 51.57 | 8.10 |
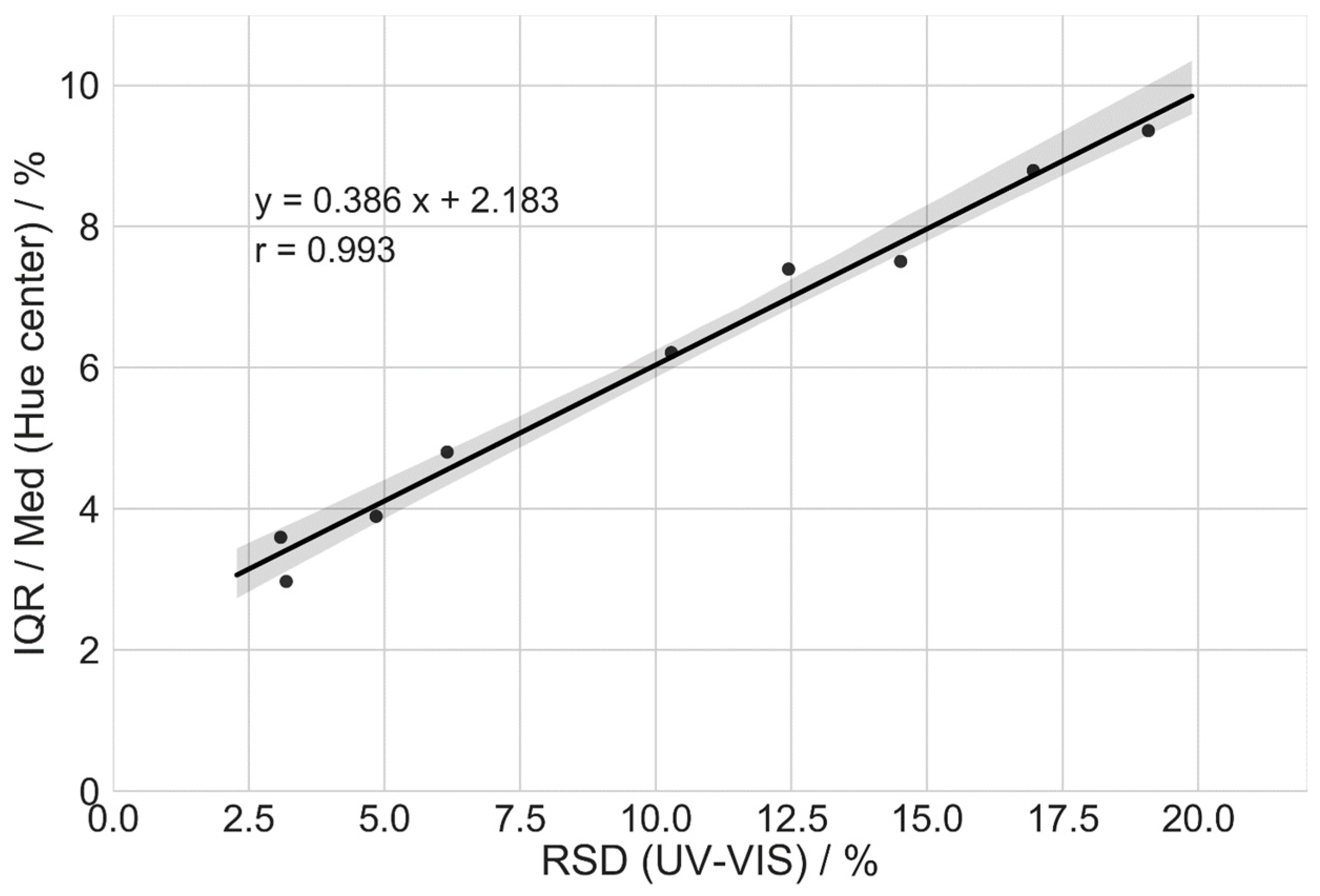
| Cores | Distributor/Airflow Rate (m3/h) | Coating Thickness RSD UV-VIS (%) | Center Hue RSD (%) | IQR/Median Hue Center (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT2.0 | CW/130 | 14.51 | 6.64 | 7.51 |
| CW/156 | 6.15 | 3.68 | 4.81 | |
| SW/156 | 3.19 | 2.18 | 2.97 | |
| MT2.5 | CW/130 | 16.95 | 10.66 | 8.79 |
| CW/156 | 10.28 | 5.07 | 6.22 | |
| SW/156 | 3.08 | 2.52 | 3.60 | |
| MT3.0 | CW/130 | 19.08 | 8.02 | 9.36 |
| CW/156 | 12.45 | 6.21 | 7.40 | |
| SW/156 | 4.84 | 3.21 | 3.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turk, M.; Šibanc, R.; Dreu, R.; Frankiewicz, M.; Sznitowska, M. Assessment of Mini-Tablets Coating Uniformity as a Function of Fluid Bed Coater Inlet Conditions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050746
Turk M, Šibanc R, Dreu R, Frankiewicz M, Sznitowska M. Assessment of Mini-Tablets Coating Uniformity as a Function of Fluid Bed Coater Inlet Conditions. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050746
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurk, Magdalena, Rok Šibanc, Rok Dreu, Maja Frankiewicz, and Małgorzata Sznitowska. 2021. "Assessment of Mini-Tablets Coating Uniformity as a Function of Fluid Bed Coater Inlet Conditions" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050746
APA StyleTurk, M., Šibanc, R., Dreu, R., Frankiewicz, M., & Sznitowska, M. (2021). Assessment of Mini-Tablets Coating Uniformity as a Function of Fluid Bed Coater Inlet Conditions. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050746






