Encapsulation of ε-Viniferin into Multi-Lamellar Liposomes: Development of a Rapid, Easy and Cost-Efficient Separation Method to Determine the Encapsulation Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Onion-Type MLLs
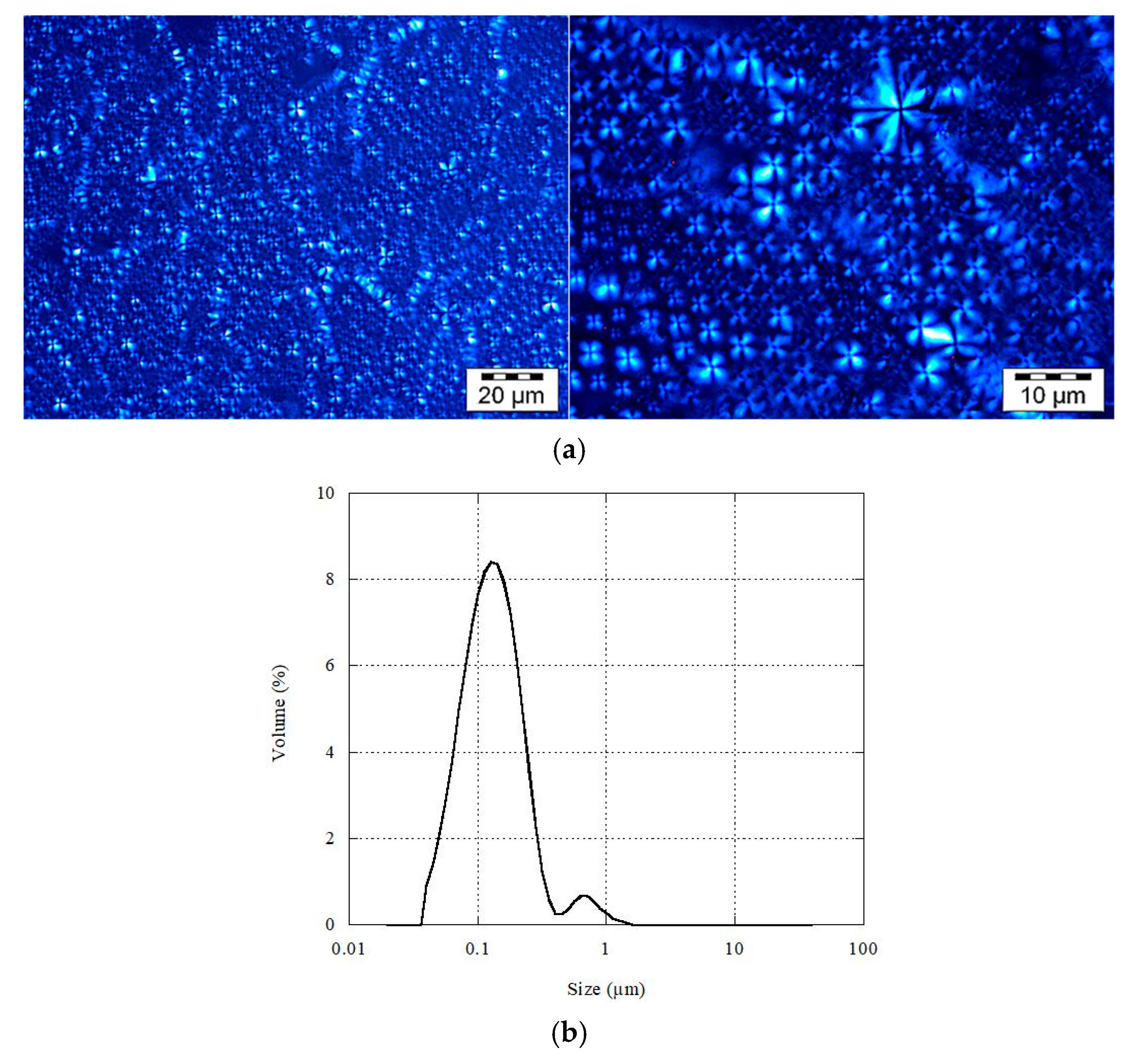
2.3. Determination of MLLs Size
2.4. Determination of MLLs Charge
2.5. Phosphorus Assay
2.6. UHPLC Analysis
2.7. Spectrophotometric Analysis
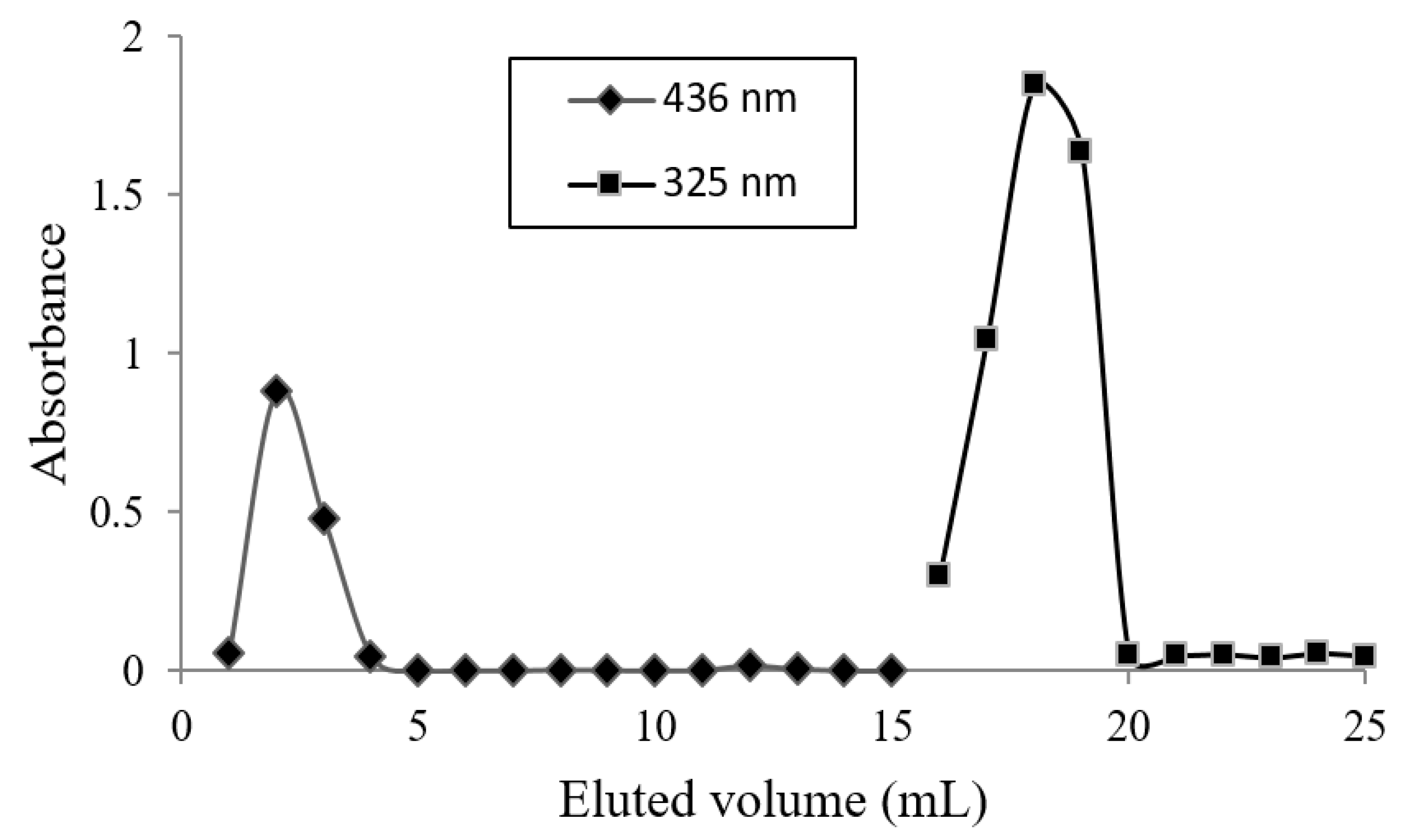
2.8. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
2.9. Ultracentrifugation
2.10. Retention Percentage of εVin by Filters
3. Results
3.1. Multilamellar Liposomes Characterization
3.2. The Adsorption Filtration Method
3.2.1. Description of the Method
3.2.2. Establishment of EE Equation using UV-VIS Spectrophotometry
3.3. Determination of εVin EE by Adsorption Filtration
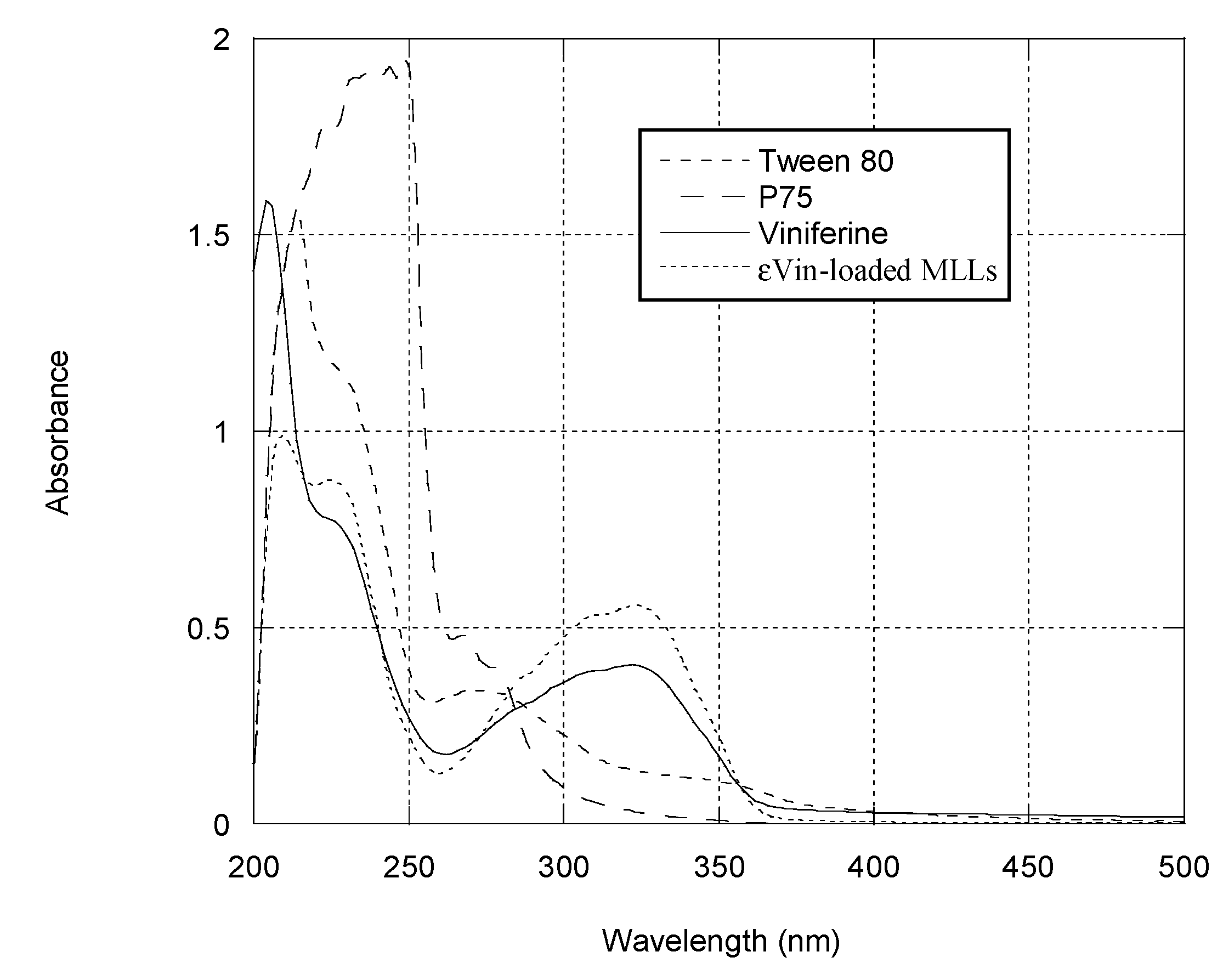
3.3.1. Spectral Analysis of MLLs Components, and εVin
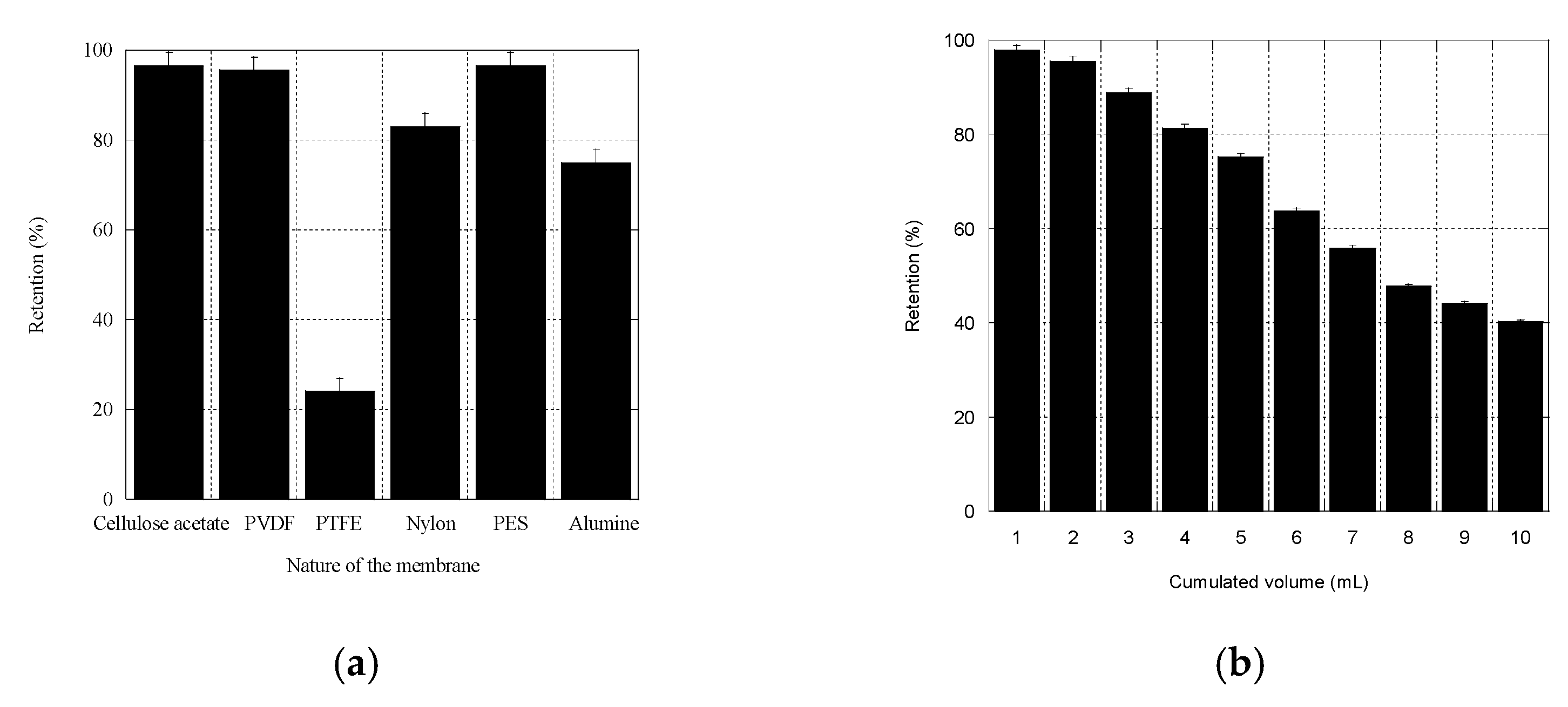
3.3.2. Choice of the Nature of the Syringe Filter Membrane
3.3.3. Liposomes Retention by 5 µm Pore-Sized PVDF Filters
3.3.4. Calculation of the Encapsulation Efficiency
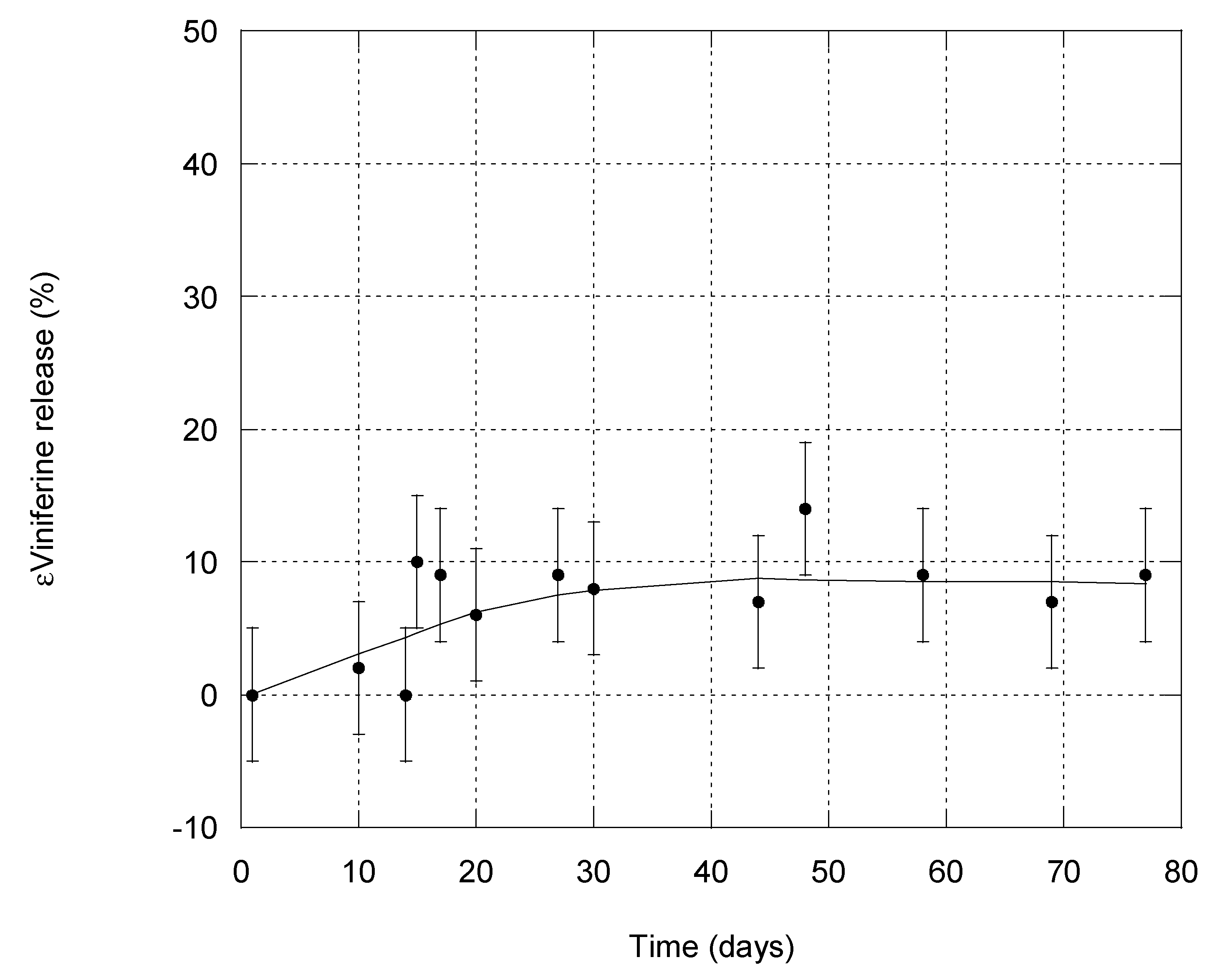
3.4. Stability of εVin-Loaded MLLs
3.5. Determination of εVin EE by Classical Techniques
4. Discussion
4.1. εVin Encapsulation Efficiency and Payload
4.2. Comparison of Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibbs, B.F.; Kermasha, S.; Alli, I.; Mulligan, C.N. Encapsulation in the Food Industry: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1999, 50, 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Barroso, L.; Viegas, C.; Vieira, J.; Ferreira-Pêgo, C.; Costa, J.; Fonte, P. Lipid-Based Carriers for Food Ingredients Delivery. J. Food Eng. 2021, 295, 110451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Saha, S.; Malhotra, M.; Kahouli, I.; Prakash, S. Microencapsulation for the Therapeutic Delivery of Drugs, Live Mammalians and Bacterial Cells, and Other Biopharmaceutics: Current Status and Future Directions. J. Pharm. 2013, 2013, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.N.; Hemant, K.S.Y.; Ram, M.; Shivakumar, H.G. Microencapsulation: A Promising Technique for Controlled Drug Delivery. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Pantschwa, J.M.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E.; Marimuthu, D.; Pillay, P. Nanodrug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemmer, M.; Patel, A.V. Review of Encapsulation Methods Suitable for Microbial Biological Control Agents. Biol. Control 2013, 67, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Srivastava, S.; Ghosh, S.; Khare, S.K. Phytochemical Delivery through Nanocarriers: A Review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-K. Liposomes for Enhanced Bioavailability of Water-Insoluble Drugs: In Vivo Evidence and Recent Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritim, S.; Boulas, P.; Lin, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of Liposome Formulation Parameters and Their Influence on Encapsulation, Stability and Drug Release in Glibenclamide Liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.-P.; Song, R.-X.; Wang, T.; Sun, M.-J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.-G. Inducing Sustained Release and Improving Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin via Chitosan Derivatives-Coated Liposomes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, A.; Garcia, M.; Krisa, S.; Atgié, C.; Sauvant, P.; Richard, T.; Faure, C. Encapsulation of Viniferin in Onion-Type Multi-Lamellar Liposomes Increases Its Solubility, Its Photo-Stability and Decreases Its Cytotoxicity on Caco-2 Intestinal Cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivière, C.; Pawlus, A.D.; Mérillon, J.-M. Natural Stibenoids: Distribution in the Plant Kingdom and Chemotaxonomic Interest in Vitacea. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 1317–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khawand, T.; Courtois, A.; Valls, J.; Richard, T.; Krisa, S. A Review of Dietary Stilbenes: Sources and Bioavailability. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 1007–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privat, C.; Telo, J.P.; Bernardes-Genisson, V.; Vieira, A.; Souchard, J.-P.; Nepveu, F. Antioxidant Properties of Trans-ε-Viniferin As Compared to Stilbene Derivatives in Aqueous and Nonaqueous Media. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassra, M.; Krisa, S.; Papastamoulis, Y.; Kapche, G.D.; Bisson, J.; André, C.; Konsman, J.P.; Schmitter, J.-M.; Mérillon, J.-M.; Waffo-Téguo, P. Inhibitory Activity of Plant Stilbenoids against Nitric Oxide Production by Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Microglia. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, C.; Izard, J.-C.; Roman, V.; Kern, C.; Mathiot, C.; Mentz, F.; Kolb, J.-P. Comparative Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Effects of Resveratrol, ϵ-Viniferin and Vine-Shots Derived Polyphenols (Vineatrols) on Chronic B Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells and Normal Human Lymphocytes. Leuk. Lymphoma 2002, 43, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillaud, M.; Guillard, J.; Richard, D.; Milin, S.; Chassaing, D.; Paccalin, M.; Page, G.; Rioux Bilan, A. Trans ε Viniferin Decreases Amyloid Deposits and Inflammation in a Mouse Transgenic Alzheimer Model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vion, E.; Page, G.; Bourdeaud, E.; Paccalin, M.; Guillard, J.; Rioux Bilan, A. Trans ε-Viniferin Is an Amyloid-β Disaggregating and Anti-Inflammatory Drug in a Mouse Primary Cellular Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 88, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, K.; Kusano, K.; Kitao, S.; Yanai, T.; Takata, R.; Kanauchi, O. ε-Viniferin, a Resveratrol Dimer, Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, A.; Atgié, C.; Marchal, A.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Lapèze, C.; Faure, C.; Richard, T.; Krisa, S. Tissular Distribution and Metabolism of Trans-ε-Viniferin after Intraperitoneal Injection in Rat. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Min, J.S.; Kim, D.; Zheng, Y.F.; Mailar, K.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, C.; Bae, S.K. A Simple and Sensitive Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Trans-ε-Viniferin Quantification in Mouse Plasma and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 134, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, S.J.; Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Boyd, B.J. Drug Release from Nanomedicines: Selection of Appropriate Encapsulation and Release Methodology. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2012, 2, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Vorauer-Uhl, K.; Katinger, H. Liposomes Produced in a Pilot Scale: Production, Purification and Efficiency Aspects. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 54, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, P.; Ray, T. Improving Liposome Integrity and Easing Bottlenecks to Production. Pharm. Technol. Eur. 2009, 22, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Omari-Siaw, E.; Sun, C.; Wei, Q.; Deng, W.; Yu, J.; et al. Galangin-Loaded, Liver Targeting Liposomes: Optimization and Hepatoprotective Efficacy. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Gomez, A.; Saifuddin, S.; Marshall, K.; Hosseinidoust, Z. Liposomal Nanovesicles for Efficient Encapsulation of Staphylococcal Antibiotics. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 10866–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magenheim, B.; Levy, M.Y.; Benita, S. A New in Vitro Rechnique for the Evaluation of Drug Release Profile from Colloidal Carriers—Ultrafiltration Technique at Low Pressure. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 94, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, W.R.; Minchey, S.R.; Ahl, P.L.; Janoff, A.S. The Determination of Liposome Captured Volume. Chem. Physcis Lipids 1993, 64, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruysschaert, T.; Marque, A.; Duteyrat, J.L.; Lesieur, S.; Winterhalter, M.; Fournier, D. Liposome Retention in Size Exclusion Chromatography. BMC Biotechnol. 2005, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Shim, W.G.; Moon, H. Biofilter in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biais, B.; Krisa, S.; Cluzet, S.; Da Costa, G.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Mérillon, J.-M.; Richard, T. Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Activities of Grapevine Stilbenes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4952–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crauste-Manciet, S.; Larquet, E.; Khawand, K.; Bessodes, M.; Chabot, G.G.; Brossard, D.; Mignet, N. Lipidic Spherulites: Formulation Optimisation by Paired Optical and Cryoelectron Microscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diat, O.; Roux, D.; Nallet, F. Effect of Shear on a Lyotropic Lamellar Phase. J. Phys. II 1993, 3, 1427–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouser, G.; Fkeischer, S.; Yamamoto, A. Two Dimensional Thin Layer Chromatographic Separation of Polar Lipids and Determination of Phospholipids by Phosphorus Analysis of Spots. Lipids 1970, 5, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olea, D.; Faure, C. Quantitative Study of the Encapsulation of Glucose Oxidase into Multilamellar Vesicles and Its Effect on Enzyme Activity. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 6111–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touti, R.; Noun, M.; Guimberteau, F.; Lecomte, S.; Faure, C. What Is the Fate of Multi-Lamellar Liposomes of Controlled Size, Charge and Elasticity in Artificial and Animal Skin? Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 151, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isailović, B.D.; Kostić, I.T.; Zvonar, A.; Đorđević, V.B.; Gašperlin, M.; Nedović, V.A.; Bugarski, B.M. Resveratrol Loaded Liposomes Produced by Different Techniques. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, E.; Thakur, S.; Qu, Z.; Jambhrunkar, S.; Parekh, H.S.; Popat, A. Enhancing Delivery and Cytotoxicity of Resveratrol through a Dual Nanoencapsulation Approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 462, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrington, G.; Chmel, N.P.; Norton, S.R.; Wemyss, A.M.; Lloyd, K.; Amarasinghe, D.P.; Rodger, A. Light Scattering Corrections to Linear Dichroism Spectroscopy for Liposomes in Shear Flow Using Calcein Fluorescence and Modified Rayleigh-Gans-Debye-Mie Scattering Glen. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Murase, O.; Sugishita, K.; Yoneyama, S.; Akada, K.; Ueha, M.; Nakamura, A.; Kobayashi, S. Optical Characterization of Liposomes by Right Angle Light Scattering and Turbidity Measurement. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Khan, M.A.; Burgess, D.J. A Quality by Design (QbD) Case Study on Liposomes Containing Hydrophilic API: II. Screening of Critical Variables, and Establishment of Design Space at Laboratory Scale. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amri, A.; Chaumeil, J.C.; Sfar, S.; Charrueau, C. Administration of Resveratrol: What Formulation Solutions to Bioavailability Limitations? J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, M.J.; Bally, M.B.; Webb, G.; Cullis, P.R. Production of Large Unilamellar Vesicles by a Rapid Extrusion Procedure. Characterization of Size Distribution, Trapped Volume and Ability to Maintain a Membrane Potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 812, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
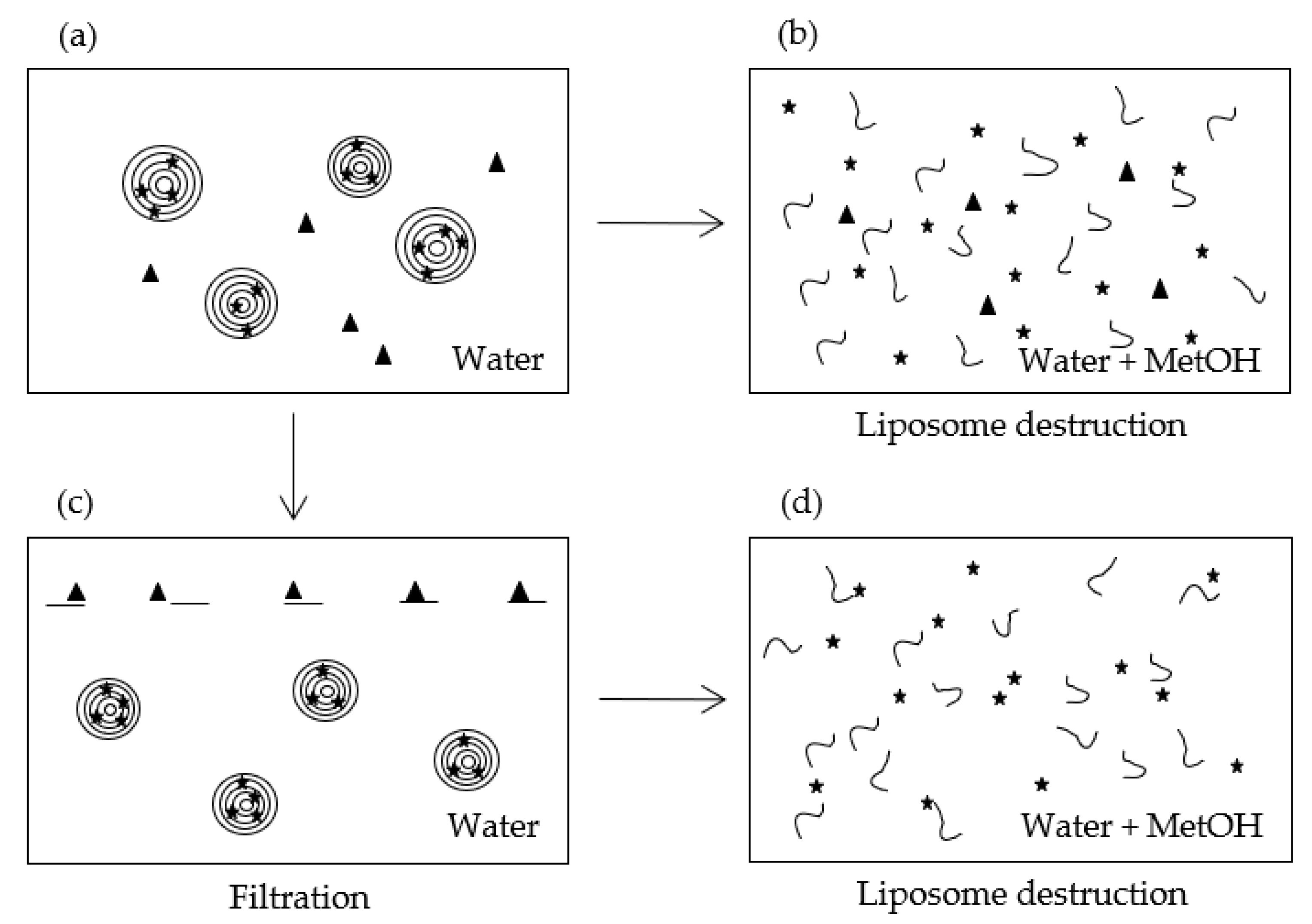
| Figure 2 | Dilution | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) εVin-MLLs whole aqueous dispersion | 1 | 0.221 | |
| (b) εVin-MLLs whole aqueous dispersion plus methanol (1:1) | 4 | 0.023 | 0.693 |
| (c) Filtered εVin-MLLs aqueous dispersion | 1 | 1.694 | |
| (d) Filtered εVin-MLLs aqueous dispersion plus methanol (1:1) | 4 | 0.016 | 0.578 |
| Value | Notation | Calculation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of retention of MLLs | 0% | %Rlip | Phosphorus assay |
| Theoretical A for εVin | 0.577 | Calibration curve | |
| Contribution of lipids and surfactant to the signal given at 325 nm in the whole dispersion | 0.116 ± 0.006 | Acomp. | Equation (1) |
| Contribution of εVin to the signal given at 325 nm by the filtrate | 0.462 ± 0.006 | [Act]fencεl | Equation (2) |
| Encapsulation efficiency | 80 ± 4% | EE | Equation (3) |
| Encapsulation efficiency corrected by %RVin | 79 ± 4% | EEc | Equation (4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beaumont, P.; Courtois, A.; Richard, T.; Krisa, S.; Faure, C. Encapsulation of ε-Viniferin into Multi-Lamellar Liposomes: Development of a Rapid, Easy and Cost-Efficient Separation Method to Determine the Encapsulation Efficiency. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040566
Beaumont P, Courtois A, Richard T, Krisa S, Faure C. Encapsulation of ε-Viniferin into Multi-Lamellar Liposomes: Development of a Rapid, Easy and Cost-Efficient Separation Method to Determine the Encapsulation Efficiency. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(4):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040566
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeaumont, Pauline, Arnaud Courtois, Tristan Richard, Stéphanie Krisa, and Chrystel Faure. 2021. "Encapsulation of ε-Viniferin into Multi-Lamellar Liposomes: Development of a Rapid, Easy and Cost-Efficient Separation Method to Determine the Encapsulation Efficiency" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 4: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040566
APA StyleBeaumont, P., Courtois, A., Richard, T., Krisa, S., & Faure, C. (2021). Encapsulation of ε-Viniferin into Multi-Lamellar Liposomes: Development of a Rapid, Easy and Cost-Efficient Separation Method to Determine the Encapsulation Efficiency. Pharmaceutics, 13(4), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040566







