Magnetofection In Vivo by Nanomagnetic Carriers Systemically Administered into the Bloodstream
Abstract
1. Introduction
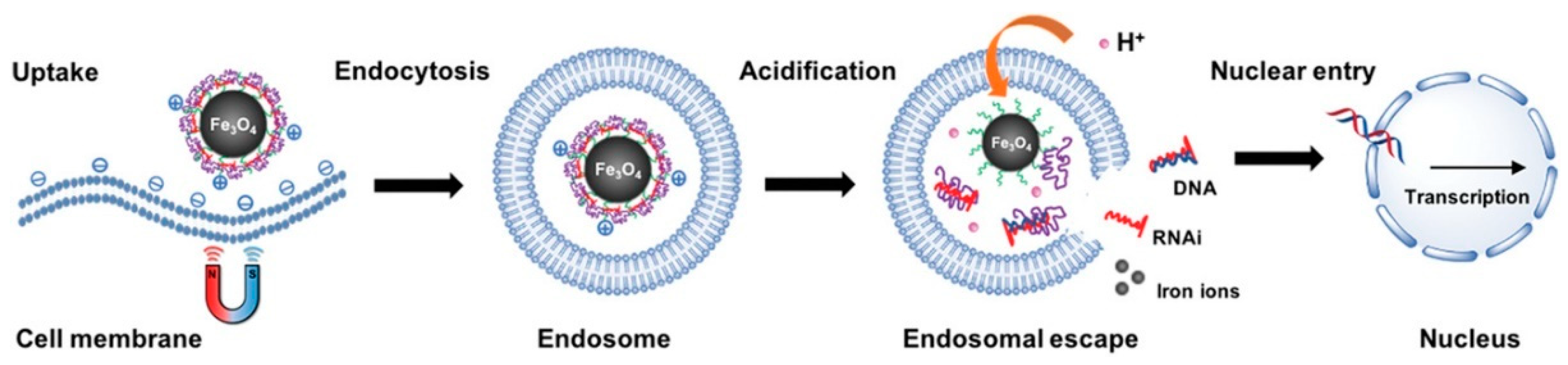
2. Applications of Nanoscale Carriers for Magnetofection In Vivo
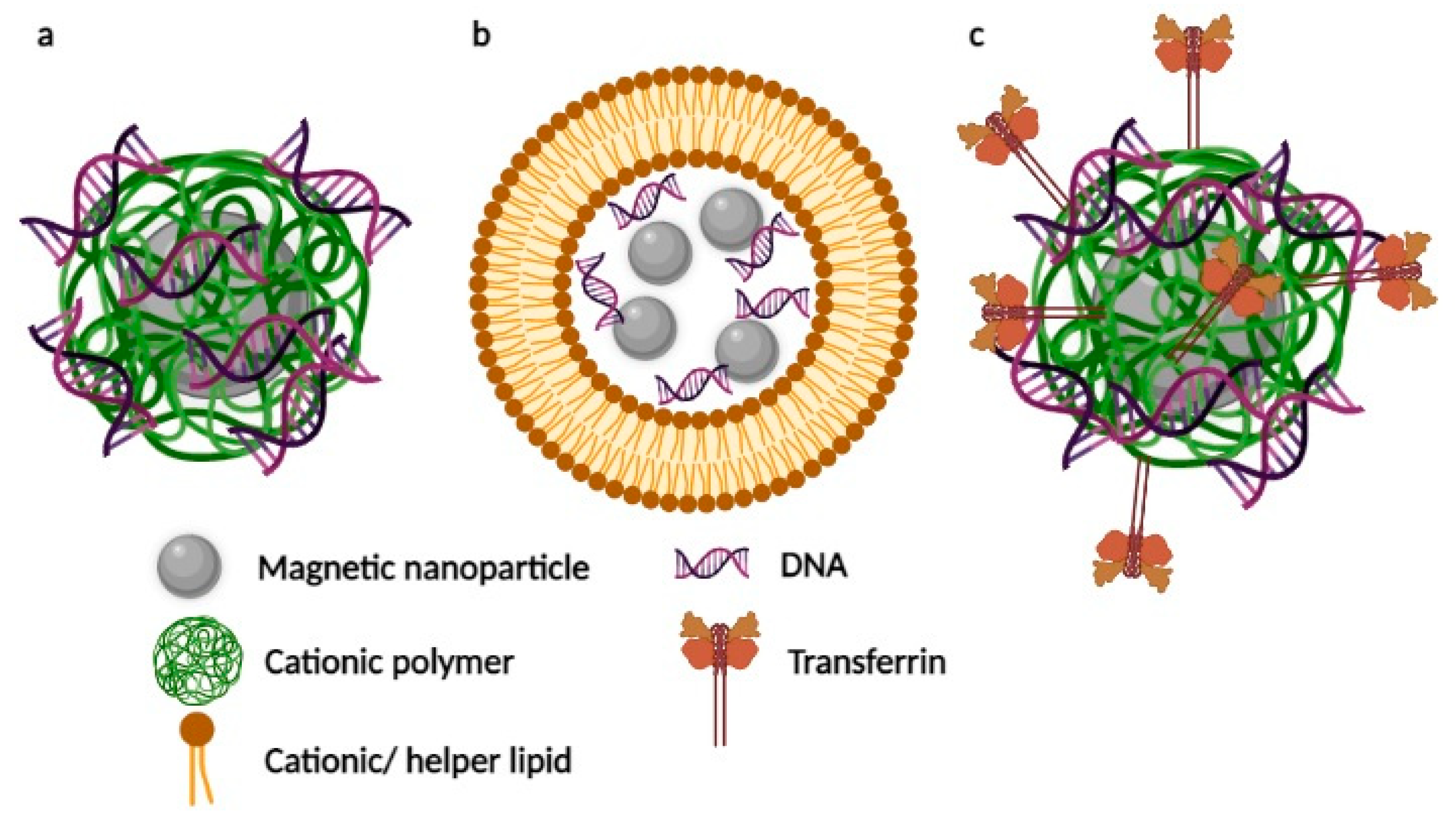
2.1. Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Cationic Polymers
2.2. Lipid-Coated Magnetic Nanostructures
2.3. Magnetic Nanosystems Possessing an Additional Active Targeting Modality
3. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plank, C.; Zelphati, O.; Mykhaylyk, O. Magnetically enhanced nucleic acid delivery. Ten years of magnetofection—Progress and prospects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1300–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Hashida, M. Nonviral approaches for targeted delivery of plasmid DNA and oligonucleotide. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Saltzman, W.M. Enhancement of transfection by physical concentration of DNA at the cell surface. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershina, A.G.; Sazonov, A.E.; Filimonov, V.D. Magnetic nanoparticles–DNA interactions: Design and applications of nanobiohybrid systems. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Acosta, J.R.; Iriarte-Mesa, C.; Ortega, G.A.; Díaz-García, A.M. DNA–Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Conjugates: Functional Magnetic Nanoplatforms in Biomedical Applications. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregubov, A.A.; Nikitin, P.I.; Nikitin, M.P. Advanced Smart Nanomaterials with Integrated Logic-Gating and Biocomputing: Dawn of Theranostic Nanorobots. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10294–10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, M.P.; Shipunova, V.; Deyev, S.; Nikitin, P.I. Biocomputing based on particle disassembly. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, M.P.; Zelepukin, I.; Shipunova, V.O.; Sokolov, I.L.; Deyev, S.M.; Nikitin, P.I. Enhancement of the blood-circulation time and performance of nanomedicines via the forced clearance of erythrocytes. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, V.N.; Kanev, I.L.; Mikheev, A.Y.; Shlyapnikova, E.A.; Shlyapnikov, Y.M.; Nikitin, M.P.; Nikitin, P.; Nwabueze, A.O.; van Hoek, M. Generation and delivery of nanoaerosols from biological and biologically active substances. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 69, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, Y.; Namiki, T.; Yoshida, H.; Ishii, Y.; Tsubota, A.; Koido, S.; Nariai, K.; Mitsunaga, M.; Yanagisawa, S.; Kashiwagi, H.; et al. A novel magnetic crystal–lipid nanostructure for magnetically guided in vivo gene delivery. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-S.; Yoon, T.-J.; Jang, E.-S.; Hong, K.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, O.R.; Park, C.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yi, G.-C.; Chang, K. Cetuximab-conjugated magneto-fluorescent silica nanoparticles for in vivo colon cancer targeting and imaging. Cancer Lett. 2010, 299, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregubov, A.; Sokolov, I.; Babenyshev, A.; Nikitin, P.; Cherkasov, V.; Nikitin, M. Magnetic hybrid magnetite/metal organic framework nanoparticles: Facile preparation, post-synthetic biofunctionalization and tracking in vivo with magnetic methods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 449, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiei, M.; Dreifuss, T.; Sadan, T.; Omer, N.; Blumenfeld-Katzir, T.; Fragogeorgi, E.; Loudos, G.; Popovtzer, R.; Ben-Eliezer, N. Trimodal Nanoparticle Contrast Agent for CT, MRI and SPECT Imaging: Synthesis and Characterization of Radiolabeled Core/Shell Iron Oxide@Gold Nanoparticles. Chem. Lett. 2019, 48, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeltier, E.; Rijo, P.; Rizzolio, F.; Popovtzer, R.; Petrikaite, V.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Passirani, C. Nanomedicine to target multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resist. Updat. 2020, 52, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medarova, Z.; Pham, W.; Farrar, C.; Petkova, V.; Moore, A.M. In vivo imaging of siRNA delivery and silencing in tumors. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Yigit, M.; Dai, G.; Moore, A.; Medarova, Z. Image-Guided Breast Tumor Therapy Using a Small Interfering RNA Nanodrug. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7553–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znoyko, S.L.; Orlov, A.; Pushkarev, A.V.; Mochalova, E.N.; Guteneva, N.V.; Lunin, A.; Nikitin, M.P.; Nikitin, P.I. Ultrasensitive quantitative detection of small molecules with rapid lateral-flow assay based on high-affinity bifunctional ligand and magnetic nanolabels. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1034, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guteneva, N.V.; Znoyko, S.L.; Orlov, A.V.; Nikitin, M.P.; Nikitin, P.I. Rapid lateral flow assays based on the quantification of magnetic nanoparticle labels for multiplexed immunodetection of small molecules: Application to the determination of drugs of abuse. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragina, V.A.; Orlov, A.V.; Znoyko, S.L.; Pushkarev, A.V.; Novichikhin, D.O.; Guteneva, N.V.; Nikitin, M.P.; Gorshkov, B.G.; Nikitin, P.I. Nanobiosensing based on optically selected antibodies and superparamagnetic labels for rapid and highly sensitive quantification of polyvalent hepatitis B surface antigen. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, M.P.; Vetoshko, P.M.; Brusentsov, N.A.; Nikitin, P.I. Highly sensitive room-temperature method of non-invasive in vivo detection of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, M.P.; Orlov, A.V.; Sokolov, I.L.; Minakov, A.A.; Nikitin, P.I.; Ding, J.; Bader, S.D.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Novosad, V. Ultrasensitive detection enabled by nonlinear magnetization of nanomagnetic labels. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11642–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarik, I.; Safarikova, M. BioMagnetic Research and Technology: A new online journal. Biomagn. Res. Technol. 2003, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haimov-Talmoud, E.; Harel, Y.; Schori, H.; Motiei, M.; Atkins, A.; Popovtzer, R.; Lellouche, J.-P.; Shefi, O. Magnetic Targeting of mTHPC To Improve the Selectivity and Efficiency of Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 45368–45380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.C.; Curtis, A.S.G. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R198–R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Love, K.T.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Lipidoid-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Efficient DNA and siRNA delivery. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Su, Z.; Li, J. Multifunctional fluorescent-magnetic polyethyleneimine functionalized Fe3O4–mesoporous silica yolk–shell nanocapsules for siRNA delivery. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8706–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhaylyk, O.; Antequera, Y.S.; Vlaskou, D.; Plank, C. Generation of magnetic nonviral gene transfer agents and magnetofection in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2391–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.; Anton, M.; Rudolph, C.; Rosenecker, J.; Krötz, F. Enhancing and targeting nucleic acid delivery by magnetic force. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2003, 3, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussif, O.; Lezoualc’H, F.; Zanta, M.A.; Mergny, M.D.; Scherman, D.; Demeneix, B.; Behr, J.P. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: Polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7297–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, A.; de Bruin, K.; Ruthardt, N.; Mykhaylyk, O.; Plank, C.; Bräuchle, C. Dynamics of magnetic lipoplexes studied by single particle tracking in living cells. J. Control. Release 2009, 137, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, K.; Ruthardt, N.; von Gersdorff, K.; Bausinger, R.; Wagner, E.; Ogris, M.; Bräuchle, C. Cellular Dynamics of EGF Receptor–Targeted Synthetic Viruses. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.P.; Yang, J.Y.; Lo, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, W.M.; Tang, X.S.; Xue, J.M.; Wang, S. Gene transfer using self-assembled ternary complexes of cationic magnetic nanoparticles, plasmid DNA and cell-penetrating Tat peptide. Biomaterials. 2010, 31, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.; Rosenecker, J. Magnetofection: The Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Nucleic Acid Delivery. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009, 2009, pdb-prot5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, S.; Orlando, C.; Carbone, A.; Di Gioia, S.; Conese, M. Magnetofection Enhances Lentiviral-Mediated Transduction of Airway Epithelial Cells through Extracellular and Cellular Barriers. Genes 2016, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.; Schillinger, U.; Scherer, F.; Bergemann, C.; Remy, J.-S.; Krötz, F.; Anton, M.; Lausier, J.; Rosenecker, J. The Magnetofection Method: Using Magnetic Force to Enhance Gene Delivery. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, U.; Brill, T.; Rudolph, C.; Huth, S.; Gersting, S.; Krötz, F.; Hirschberger, J.; Bergemann, C.; Plank, C. Advances in magnetofection—magnetically guided nucleic acid delivery. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdt, J.I.; Goya, G.F.; Calatayud, M.P.; Herenu, C.B.; Reggiani, P.C.; Goya, R.G. Magnetic field-assisted gene delivery: Achievements and therapeutic potential. Curr. Gene Ther. 2012, 12, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, N.; Sapet, C.; Le Gourrierec, L.; Bertosio, E.; Zelphati, O. Nucleic acid delivery using magnetic nanoparticles: The Magnetofection™ technology. Ther. Deliv. 2011, 2, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.M. Gene therapy progress and prospects: Magnetic nanoparticle-based gene delivery. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, F.; Sapet, C.; Laurent, N.; Bertosio, E.; Bertuzzi, M.; Zelphati, O. Magnetofection of Minicircle DNA Vectors. In Minicircle and Miniplasmid DNA Vectors; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kami, D.; Takeda, S.; Itakura, Y.; Gojo, S.; Watanabe, M.; Toyoda, M. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles to Gene Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3705–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizikov, A.; Kharlamova, M.; Nikitin, M.; Nikitin, P.; Kolychev, E. Nonviral Locally Injected Magnetic Vectors for In Vivo Gene Delivery: A Review of Studies on Magnetofection. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, Q.; Huang, T.; Ling, D.; Gao, J. New Insights into Biocompatible Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: A Potential Booster of Gene Delivery to Stem Cells. Small 2020, 16, 2001588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, C.; Kong, M.; Dong, A.; Qian, J.; Jiang, D.; Shen, Z. Tumor-targeting magnetic lipoplex delivery of short hairpin RNA suppresses IGF-1R overexpression of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 410, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Dong, A.; Duan, Q.; Shen, Z.; Ding, C. Tissue distribution and cancer growth inhibition of magnetic lipoplex-delivered type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor shRNA in nude mice. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Kong, M.; Jiang, D.; Dong, A.; Shen, Z.; Duan, Q. Cardiac-targeting magnetic lipoplex delivery of SH-IGF1R plasmid attenuate norepinephrine-induced cardiac hypertrophy in murine heart. Biosci. Rep. 2014, 34, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, Q.; He, Y.; Nie, Y.; Yue, D.; Gu, Z. Insight into the efficient transfection activity of a designed low aggregated magnetic polyethyleneimine/DNA complex in serum-containing medium and the application in vivo. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, N.; Ong, L.-L.; Kaminski, A.; Skrabal, C.; Ugurlucan, M.; Lorenz, P.; Gatzen, H.-H.; Lützow, K.; Lendlein, A.; et al. Enhanced thoracic gene delivery by magnetic nanobead-mediated vector. J. Gene Med. 2008, 10, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krötz, F.; de Wit, C.; Sohn, H.-Y.; Zahler, S.; Gloe, T.; Pohl, U.; Plank, C. Magnetofection—A highly efficient tool for antisense oligonucleotide delivery in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, J.; Deng, L.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, J. Preparation and characterization of magnetic cationic liposome in gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.-L.; Chou, H.-L.; Liao, Z.-X.; Huang, S.-J.; Ke, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-S.; Chiu, C.-C.; Wang, L.-F. Chondroitin sulfate-polyethylenimine copolymer-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as an efficient magneto-gene carrier for microRNA-encoding plasmid DNA delivery. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8554–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-Z.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, R.-Q.; Wang, B.W.-W.; Cui, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, B.-L.; Mei, Q.-B.; Zhou, S.-Y. The enhancement of siPLK1 penetration across BBB and its anti glioblastoma activity in vivo by magnet and transferrin co-modified nanoparticle. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.-Y.; Xu, T.-T.; Liu, Z.-L.; Shu-Zhong, G.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Guo, S.-Z.; Wang, B. Targeting of angiopoietin 2-small interfering RNA plasmid/chitosan magnetic nanoparticles in a mouse model of malignant melanoma in vivo. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2320–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, Z.; Lu, M.; Shao, D.; Yue, J.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Li, M.; He, K.; Zhang, M.; et al. Shape-controlled magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for magnetically-mediated suicide gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomaterials 2018, 154, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.-J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, F.; Guo, Y.-B.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Wang, Z.-W.; Yang, Y.-M.; Mao, Q.-S. Asialoglycoprotein receptor-magnetic dual targeting nanoparticles for delivery of RASSF1A to hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Shang, R.; Yang, X.; Lu, P.; Xia, C.; Wang, L.; Dou, K. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with polyethylenimine and galactose for siRNA targeted delivery in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Nesselmann, C.; Zhou, Z.; Ong, L.-L.; Öri, F.; Tang, G.; Kaminski, A.; Lützow, K.; Lendlein, A.; Liebold, A.; et al. Gene delivery to the heart by magnetic nanobeads. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, C.; Fang, E.; Lu, X.; Wang, G.; Tong, Q. Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and SATB1 shRNA by Thermosensitive Magnetic Cationic Liposomes for Gastric Cancer Therapy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannell, H.; Pircher, J.; Fochler, F.; Stampnik, Y.; Räthel, T.; Gleich, B.; Plank, C.; Mykhaylyk, O.; Dahmani, C.; Wörnle, M.; et al. Site directed vascular gene delivery in vivo by ultrasonic destruction of magnetic nanoparticle coated microbubbles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, W.; Nie, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Lan, F.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z. Low aggregation magnetic polyethyleneimine complexes with different saturation magnetization for efficient gene transfection in vitro and in vivo. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 23571–23581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Dai, J.; Song, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, W. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/SiO2 composite nanoparticles from primary silica particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Hu, Y.; Biasini, M.; Dong, C.; Guo, J.; Beyermann, W.P.; Yin, Y. One-Step Synthesis of Highly Water-Soluble Magnetite Colloidal Nanocrystals. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 7153–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A New Concept for Macromolecular Therapeutics in Cancer Chemotherapy: Mechanism of Tumoritropic Accumulation of Proteins and the Antitumor Agent Smancs. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.-D.; Guo, L.; Fang, H.-H.; Li, X.-B.; Song, J.-F.; Huang, X.-R.; Sun, H.-B. Band-Gap-Controllable Photonic Crystals Consisting of Magnetic Nanocrystal Clusters in a Solidified Polymer Matrix. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18542–18545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.-F.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, X.-A.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; et al. Facile Synthesis of Core-shell Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for pH-sensitive Anticancer Drug Delivery. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Dong, W.-F.; Song, J.-F.; Huo, Q.-S.; Sun, H.-B. Magnetic-mesoporous Janus nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1225–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, X.; Qiao, P.; Li, J.; Dong, W.-F.; Chen, L. Janus Silver-Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers for SERS Traceable and pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4303–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.-S.; Chang, Z.-M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.-M.; Zheng, X.; Li, M.; Shao, D.; Li, J.; et al. Berberine-loaded Janus nanocarriers for magnetic field-enhanced therapy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 89, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Zeng, Q.; Fan, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, O.; Chen, L.; Kong, X.; Zhang, H. Monitoring HSV-TK/ganciclovir cancer suicide gene therapy using CdTe/CdS core/shell quantum dots. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4336–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, M.; Pan, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Real-Time Visualizing and Tracing of HSV-TK/GCV Suicide Gene Therapy by Near-Infrared Fluorescent Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11082–11090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.; Guo, R.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Deng, N. Barriers and Strategies of Cationic Liposomes for Cancer Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 18, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán-Gracia, E.; López-Camacho, A.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Velázquez-Fernández, J.B.; Vallejo-Cardona, A.A. Nanomedicine review: Clinical developments in liposomal applications. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbake, U.; Doppalapudi, S.; Kommineni, N.; Khan, W. Liposomal Formulations in Clinical Use: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzbach, T.; Vlaskou, D.; Neshkova, I.; Konerding, M.A.; Wörtler, K.; Mykhaylyk, O.; Gänsbacher, B.; Machens, H.; Plank, C.; Giunta, R.E. Non-viral VEGF165 gene therapy—Magnetofection of acoustically active magnetic lipospheres (‘magnetobubbles’) increases tissue survival in an oversized skin flap model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, R.R.; Charloteaux-Wauters, M. Iron transport and storage. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 164, 485–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Zhang, K.; Qiao, C.; Jin, X.; Zheng, C.; Yang, B.; Sun, H. Antitumor effect of human TRAIL on adenoid cystic carcinoma using magnetic nanoparticle–mediated gene expression. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Takagi, M.; Shimamoto, A.; Kawakami, S.; Hashida, M. Small interfering RNA delivery to the liver by intravenous administration of galactosylated cationic liposomes in mice. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, G.; Wang, S.; Cheng, C.; Gao, J.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Qian, W.; Hou, S.; Zhang, D.; Dai, J.; et al. Development of SM5-1-conjugated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for hepatoma detection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, L.; Diao, Y.; Wu, H.; Speakman, S.A.; Hatton, T.A. Chromium(III) Terephthalate Metal Organic Framework (MIL-101): HF-Free Synthesis, Structure, Polyoxometalate Composites, and Catalytic Properties. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Furge, K.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Woude, G.F.V. Met receptor tyrosine kinase: Enhanced signaling through adapter proteins. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5582–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirfazli, A. Magnetic nanoparticles hit the target. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, N.M.; Le Roy, D.; Marelli-Mathevon, H.; Shaw, G.; Dias, A.; Kramer, R.B.G.; Cuong, L.V.; Kustov, M.; Zanini, L.F.; Villard, C.; et al. Micro-magnetic imprinting of high field gradient magnetic flux sources. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 262401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ling, J.; Tian, A.; Sun, N. Silencing Bag-1 gene via magnetic gold nanoparticle-delivered siRNA plasmid for colorectal cancer therapy in vivo and in vitro. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 10365–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, B.; Fishbein, I.; Chorny, M.; Alferiev, I.; Williams, D.; Yellen, B.; Friedman, G.; Levy, R.J. High field gradient targeting of magnetic nanoparticle-loaded endothelial cells to the surfaces of steel stents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pislaru, S.V.; Harbuzariu, A.; Gulati, R.; Witt, T.; Sandhu, N.P.; Simari, R.D.; Sandhu, G.S. Magnetically Targeted Endothelial Cell Localization in Stented Vessels. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorny, M.; Fishbein, I.; Yellen, B.B.; Alferiev, I.S.; Bakay, M.; Ganta, S.; Adamo, R.; Amiji, M.; Friedman, G.; Levy, R.J. Targeting stents with local delivery of paclitaxel-loaded magnetic nanoparticles using uniform fields. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8346–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räthel, T.; Mannell, H.; Pircher, J.; Gleich, B.; Pohl, U.; Krötz, F. Magnetic Stents Retain Nanoparticle-Bound Antirestenotic Drugs Transported by Lipid Microbubbles. Pharm. Res. 2011, 29, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babincová, M.; Babinec, P.; Bergemann, C. High-Gradient Magnetic Capture of Ferrofluids: Implications for Drug Targeting and Tumor Embolization. Zeitschrift Naturforschung C 2001, 56, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellen, B.B.; Forbes, Z.G.; Halverson, D.S.; Fridman, G.; Barbee, K.A.; Chorny, M.; Levy, R.; Friedman, G. Targeted drug delivery to magnetic implants for therapeutic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, C.; Diehl, D.; Henninger, P.; Iro, H.; Rockelein, R.; Schmidt, W.; Weber, H. A High Field Gradient Magnet for Magnetic Drug Targeting. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2006, 16, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBain, S.C.; Griesenbach, U.; Xenariou, S.; Keramane, A.; Batich, C.D.; Alton, E.W.F.W.; Dobson, J. Magnetic nanoparticles as gene delivery agents: Enhanced transfection in the presence of oscillating magnet arrays. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 405102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamau, S.W. Enhancement of the efficiency of non-viral gene delivery by application of pulsed magnetic field. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, M.; Chari, D. Enhancement of magnetic nanoparticle-mediated gene transfer to astrocytes by ‘magnetofection’: Effects of static and oscillating fields. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümler, P. Magnetic Guiding with Permanent Magnets: Concept, Realization and Applications to Nanoparticles and Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, B.; Kulkarni, S.; Nacev, A.; Muro, S.; Stepanov, P.Y.; Weinberg, I.N. Open challenges in magnetic drug targeting. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, D.; Shang, P.; Yin, D.-C. A review of magnet systems for targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 302, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilapong, C.; Sitthichai, S.; Thongtem, S.; Thongtem, T. Smart magnetic nanoparticle-aptamer probe for targeted imaging and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeart, D.; Hatem, S.; Heimburger, M.; Le Roux, A.; Michel, J.-B.; Mercadier, J.-J. How to Optimize In Vivo Gene Transfer to Cardiac Myocytes: Mechanical or Pharmacological Procedures? Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorevic, P.; Blankinship, M.J.; Allen, J.M.; Crawford, R.W.; Meuse, L.; Miller, D.; Russell, D.W.; Chamberlain, J. Systemic delivery of genes to striated muscles using adeno-associated viral vectors. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, J.K.; Kikkawa, K.; Thomas, A.D.; Marban, E.; Lawrence, J.H. Acceleration of widespread adenoviral gene transfer to intact rabbit hearts by coronary perfusion with low calcium and serotonin. Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissleder, R.; Bogdanov, A.; Neuwelt, E.A.; Papisov, M. Long-circulating iron oxides for MR imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 16, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkasymov, A.B.; Zelepukin, I.V.; Nikitin, P.I.; Nikitin, M.P.; Deyev, S.M. In vivo blockade of mononuclear phagocyte system with solid nanoparticles: Efficiency and affecting factors. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelepukin, I.V.; Yaremenko, A.V.; Yuryev, M.V.; Mirkasymov, A.B.; Sokolov, I.L.; Deyev, S.M.; Nikitin, P.I.; Nikitin, M.P. Fast processes of nanoparticle blood clearance: Comprehensive study. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelepukin, I.V.; Yaremenko, A.V.; Ivanov, I.N.; Yuryev, M.V.; Cherkasov, V.R.; Deyev, S.M.; Nikitin, P.I.; Nikitin, M.P. Long-Term Fate of Magnetic Particles in Mice: A Comprehensive Study. ACS Nano 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Waters, A.K.; Kalyan, P.; Achrol, A.S.; Kesari, S.; Yenugonda, V.M. Lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a next-generation drug delivery platform: State of the art, emerging technologies, and perspectives. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, ume 14, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelepukin, I.V.; Yaremenko, A.V.; Shipunova, V.O.; Babenyshev, A.V.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Nikitin, P.I.; Deyev, S.M.; Nikitin, M.P. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery via RBC-hitchhiking for the inhibition of lung metastases growth. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringaci, A.; Yaremenko, A.; Shevchenko, K.; Zvereva, S.; Nikitin, M. Metal-organic frameworks for simultaneous gene and small molecule delivery in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunin, A.V.; Korenkov, E.S.; Mochalova, E.N.; Nikitin, M.P. Green Synthesis of Size-Controlled in Vivo Biocompatible Immunoglobulin-Based Nanoparticles by a Swift Thermal Formation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13128–13134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morachis, J.M.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Almutairi, A. Physical and Chemical Strategies for Therapeutic Delivery by Using Polymeric Nanoparticles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkasov, V.R.; Mochalova, E.N.; Babenyshev, A.V.; Vasilyeva, A.V.; Nikitin, P.I.; Nikitin, M.P. Nanoparticle Beacons: Supersensitive Smart Materials with On/Off-Switchable Affinity to Biomedical Targets. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, B.; Friedman, G. Magnetic targeting for site-specific drug delivery: Applications and clinical potential. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlov, A.; Nikitin, M.P.; Bragina, V.A.; Znoyko, S.L.; Zaikina, M.N.; Ksenevich, T.; Gorshkov, B.G.; Nikitin, P. A new real-time method for investigation of affinity properties and binding kinetics of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorny, M.; Polyak, B.; Alferiev, I.S.; Walsh, K.; Friedman, G.; Levy, R.J. Magnetically driven plasmid DNA delivery with biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, K.G.; Cherkasov, V.R.; Tregubov, A.A.; Nikitin, P.I.; Nikitin, M.P. Surface plasmon resonance as a tool for investigation of non-covalent nanoparticle interactions in heterogeneous self-assembly & disassembly systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Shang, F.; Chen, D.; Cao, T.; Wang, X.; Jiao, J.; He, S.; Liang, X. Protein liposomes-mediated targeted acetylcholinesterase gene delivery for effective liver cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
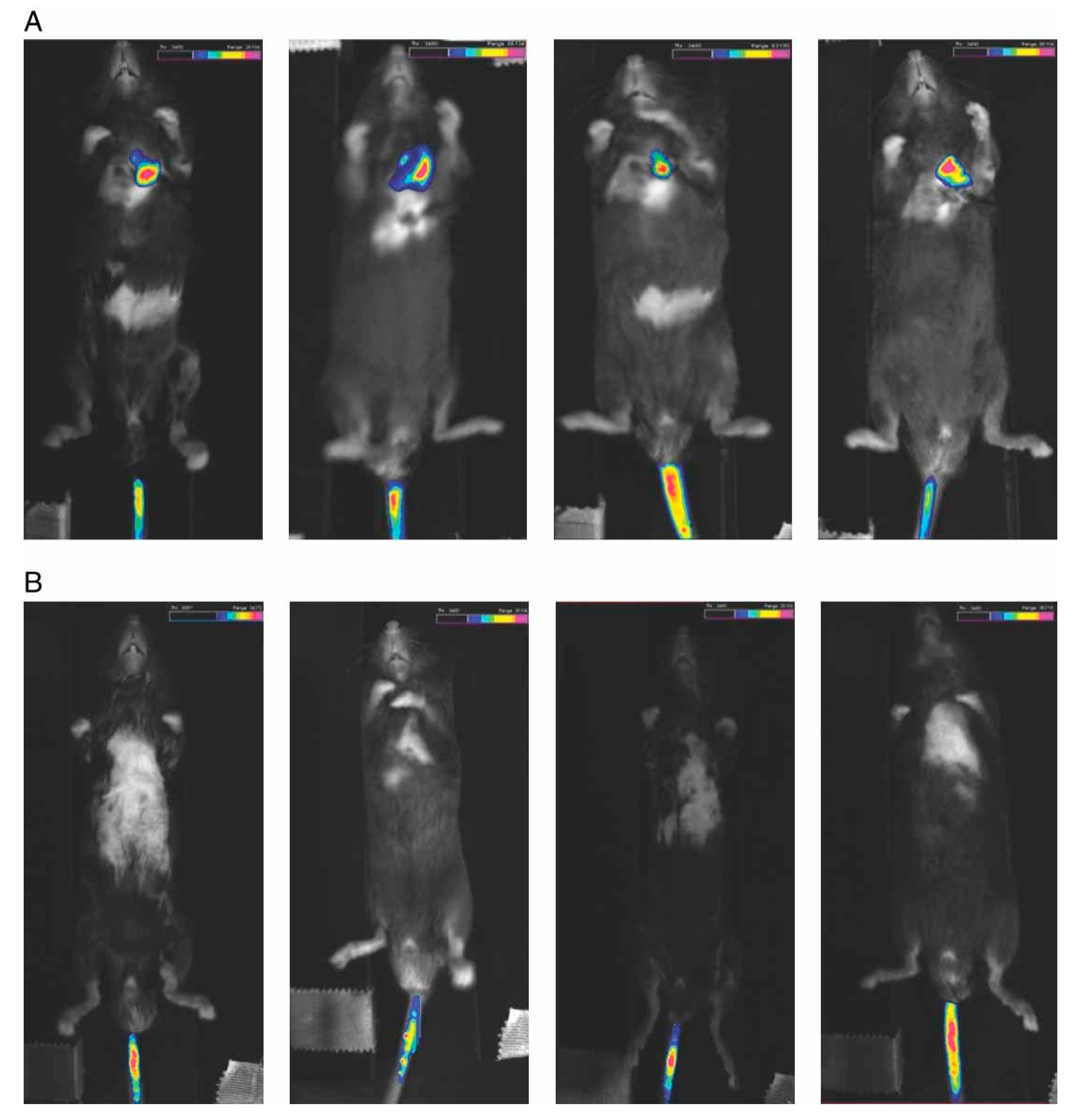


| Target (Tissue/Organ) | Animals | Nucleic Acid Type a | Magnetic Nanoparticle Composition b | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subcutaneous tumor/heart | Mouse | shRNA | combiMAG + Lp2000 | [44,45,46] |
| Subcutaneous tumor | Mouse | pDNA | Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH + PEI | [47] |
| Lungs/heart | Mouse | pDNA | MNBs (Miltenyi Biotec)-PEI | [48] |
| Right proximal region (subcutaneous tumor) | Mouse | siRNA | LipoMag | [10] |
| Right testis | Mouse | Antisense ODN | PolyMag | [49] |
| Liver | Rat | pDNA | MCL | [50] |
| Hind leg | Mouse | pDNA | PAAIO + CP | [51] |
| Striatum | Mouse | siRNA | Tf-PEG-PLL/MNP | [52] |
| Subcutaneous tumor/armpit | Mouse | siRNA | Fe3O4 + Chitosan | [53] |
| dorsal flank (subcutaneous tumor) | Mouse | pDNA | M-MSNs | [54] |
| Capsule of the liver lobe (transplanted tumor) | Mouse | pDNA | Gal-CMCS-Fe3O4-NPs | [55] |
| Left hepatic lobe | Mouse | siRNA | Gal-PEI-SPIO | [56] |
| Heart | Mouse | pDNA | MNB/PEI | [57] |
| Subcutaneous tumor | Mouse | pDNA | TSMCL | [58] |
| Vessels of the dorsal skin | Mouse | pDNA | MMB | [59] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sizikov, A.A.; Nikitin, P.I.; Nikitin, M.P. Magnetofection In Vivo by Nanomagnetic Carriers Systemically Administered into the Bloodstream. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111927
Sizikov AA, Nikitin PI, Nikitin MP. Magnetofection In Vivo by Nanomagnetic Carriers Systemically Administered into the Bloodstream. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(11):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111927
Chicago/Turabian StyleSizikov, Artem A., Petr I. Nikitin, and Maxim P. Nikitin. 2021. "Magnetofection In Vivo by Nanomagnetic Carriers Systemically Administered into the Bloodstream" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 11: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111927
APA StyleSizikov, A. A., Nikitin, P. I., & Nikitin, M. P. (2021). Magnetofection In Vivo by Nanomagnetic Carriers Systemically Administered into the Bloodstream. Pharmaceutics, 13(11), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111927






