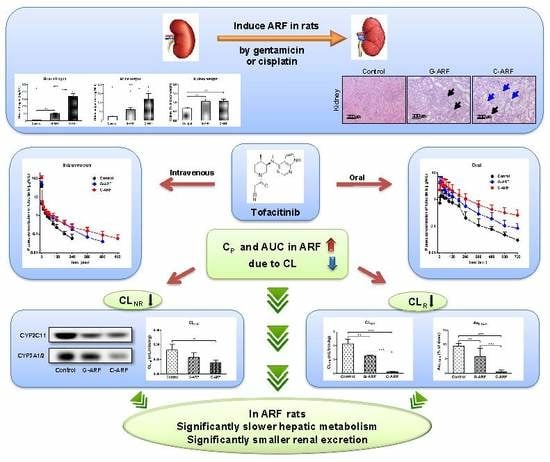
Slower Elimination of Tofacitinib in Acute Renal Failure Rat Models: Contribution of Hepatic Metabolism and Renal Excretion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Induction of Acute Renal Failure
2.4. Preliminary Study
2.5. Intravenous and Oral Administration of Tofacitinib
2.6. Measurement of Vmax, Km, and CLint
2.7. Immunoblot Analysis
2.8. HPLC Analysis
2.9. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Induction of Acute Renal Failure
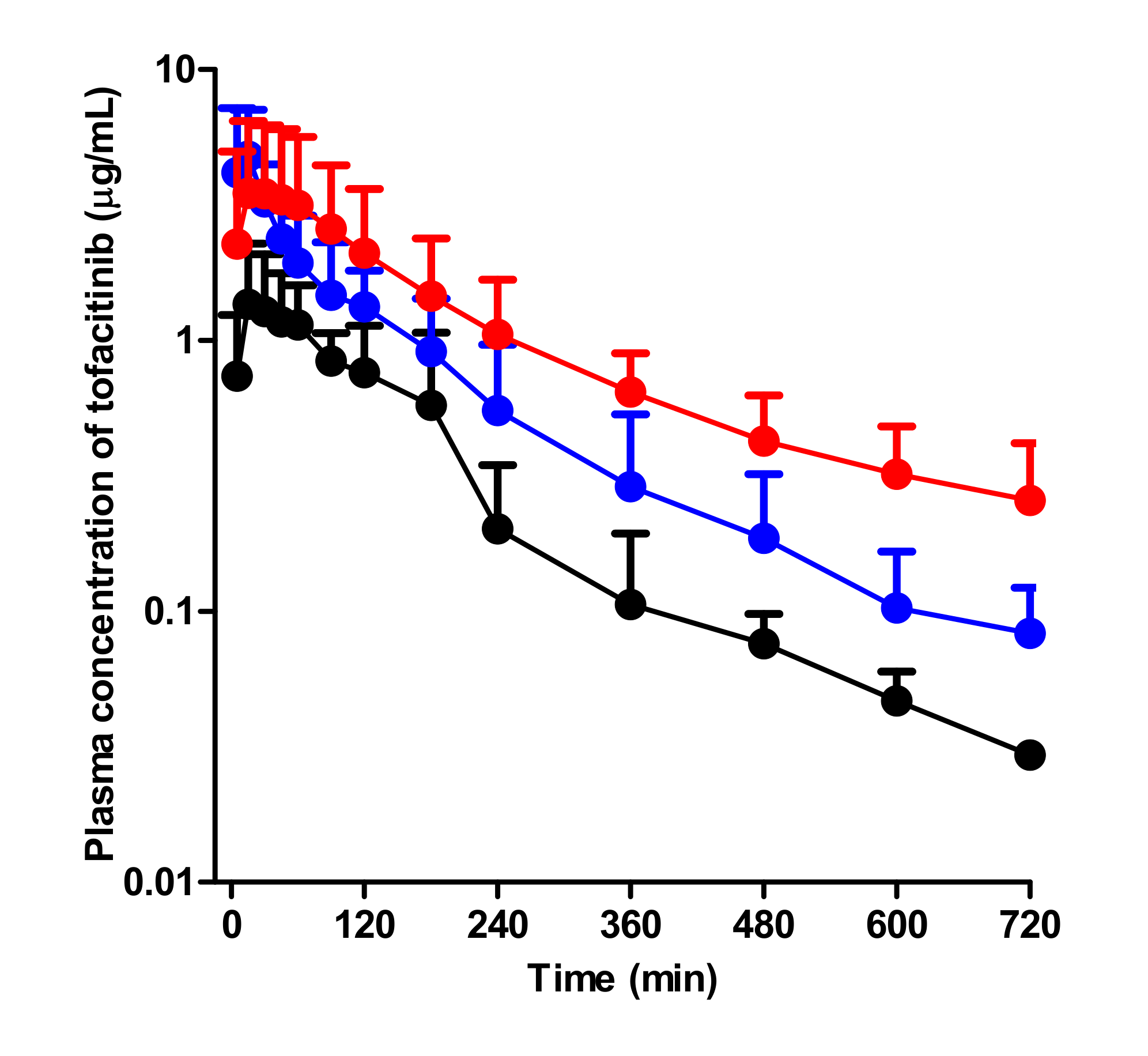
3.2. Pharmacokinetics of Tofacitinib After Intravenous Administration
3.3. Pharmacokinetics of Tofacitinib After Oral Administration
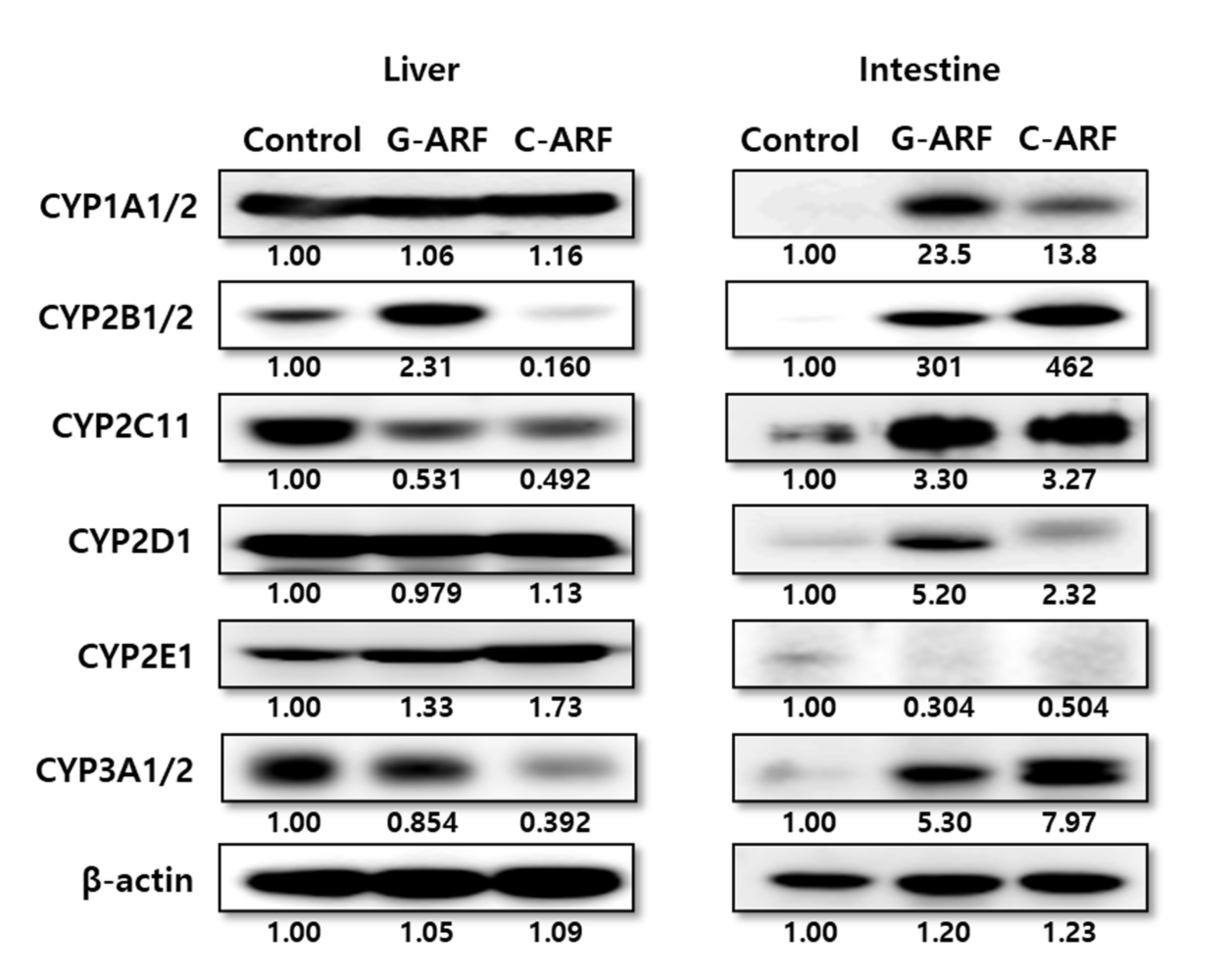
3.4. Effect of Acute Renal Failure on CYP Enzyme Expression
3.5. Measurement of Vmax, Km, and CLint of Tofacitinib in Hepatic Microsomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Claxton, L.; Taylor, M.; Soonasra, A.; Bourret, J.A.; Gerber, R.A. An economic evaluation of tofacitinib treatment in rheumatoid arthritis after methotrexate or after 1 or 2 TNF inhibitors from a U.S. payer perspective. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2018, 24, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Naganuma, M.; Kanai, T. Current new challenges in the management of ulcerative colitis. Intest. Res. 2019, 17, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonelli, E.; Villanacci, V.; Bassotti, G. Novel oral-targeted therapies for mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5322–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelez, H.; Van de Kerkhof, P.C.; Strohal, R.; Kubanov, A.; Valenzuela, F.; Lee, J.H.; Gupta, P. Tofacitinib versus etanercept or placebo in moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis: A phase 3 randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.A.; Menter, M.A.; Abe, M.; Elewski, B.; Feldman, S.R.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Langley, R.; Luger, T.; Thaci, D.; Buonanno, M.; et al. OPT Pivotal 1 and OPT Pivotal 2 investigators. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: Results from two randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy Crispin, M.; Ko, J.M.; Craiglow, B.G.; Li, S.; Shankar, G.; Urban, J.R.; Marinkovich, M.P. Safety and efficacy of the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib citrate in patients with alopecia areata. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e89776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, L.L.; Urban, J.; King, B.A. Treatment of recalcitrant atopic dematitis with the oral Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib citrate. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, H. Therapies in ankylosing spondylitis-from clinical trials to clinical practice. Rheumatology 2018, 57, vi23–vi28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowty, M.E.; Lin, J.; Ryder, T.F.; Wang, W.; Walker, G.S.; Vaz, A.; Prakash, C. The pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and clearancemechanisms of tofacitinib, a janus kinase inhibitor, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cada, D.J.; Demaris, K.; Levien, T.L.; Baker, D.E. Tofacitinib. Hosp. Pharm. 2013, 48, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, L.J. Tofacitinib: A review of its use in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 2013, 73, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.H. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib in rats: Influence of hepatic and intestinal first-pass metabolism. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koivuniemi, R.; Paimela, L.; Suomalainen, R.; Leirisalo-Repo, M. Amyloidosis as a cause of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.; Symmons, D.P.; Brewster, D.H.; Black, R.J.; Macfarlane, G.J. National study of cause-specific mortality in rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile chronic arthritis, and other rheumatic conditions: A 20 year followup study. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sihvonen, S.; Korpela, M.; Mustonen, J.; Laippala, P.; Pasternack, A. Renal disease as a predictor of increased mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2004, 96, c107–c114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karie, S.; Gandjbakhch, F.; Janus, N.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Rozenberg, S.; Mai Ba, C.U.; Bourgeois, P.; Deray, G. Kidney disease in RA patients: Prevalence and implication on RA-related drugs management: The MATRIX study. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karstila, K.; Korpela, M.; Sihvonen, S.; Mustonen, J. Prognosis of clinical renal disease and incidence of new renal findings in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Follow-up of a population-based study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswami, S.; Chow, V.; Boy, M.; Wang, C.; Chan, G. Pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, in patients with impaired renal function and end-stage renal disease. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 54, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, A.; Gündoğan, N.U.; Usubütün, A.; Kilinç, K.; Erdem, S.R.; Kara, A.; Bozkurt, A. The protective effect of taurine against gentamicin-induced acute tubular necrosis in rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Kader, M.; Taha, R.I. Comparative nephroprotective effects of curcumin and etoricoxib against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Acta. Histochem. 2020, 122, 151534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, K.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Lei, W. Sustained oxidative stress causes late acute renal failure via duplex regulation on p38 MAPK and Akt phosphorylation in severely burned rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Park, M.Y.; Kim, S.H. Simple determination and quantification of tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor, in rat plasma, urine and tissue homogenates by HPLC and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Lee, I.; Lee, M.G. Slower clearance of intravenous metformin in rats with acute renal failure induced by uranyl nitrate: Contribution of slower renal and non-renal clearance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, E.H.; Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, S.H. Effects of diabetes mellitus on the disposition of tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, in rats. Biomol. Ther. 2020, 28, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggleby, R.G. Analysis of enzyme progress curves by nonlinear regression. Methods Enzymol. 1995, 249, 61–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.Y.; Jung, Y.S.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, I.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, M.G. Faster clearance of omeprazole in rats with acute renal failure induced by uranyl nitrate: Contribution of increased expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A1 and intestinal CYP1A and 3A subfamilies. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibaldi, M.; Perrier, D. Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed.; Marcel-Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Chiou, W.L. Critical evaluation of the potential error in pharmacokinetic studies of using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level-time curve. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1978, 6, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.L. New calculation method of mean total body clearance of drugs and its application to dosage regimens. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatman, F.B.; Colburn, W.A.; Boxenbaum, H.G.; Posmanter, H.N.; Weinfeld, R.E.; Ronfeld, R.; Kaplan, S.A. Pharmacokinetics of diazepam following multiple-dose oral administration to healthy human subjects. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1977, 5, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.L. New calculation method for mean apparent drug volume of distribution and application to rational dosage regimens. J. Pharm. Sci. 1979, 68, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, J.S.; Dieterle, F.; Troth, S.; Perentes, E.; Cordier, A.; Verdes, P.; Staedtler, F.; Mahl, A.; Grenet, O.; Roth, D.R.; et al. A panel of urinary biomarkers to monitor reversibility of renal injury and a serum marker with improved potential to assess renal function. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddik, Z.H.; Newell, D.R.; Boxall, F.E.; Harrap, K.R. The comparative pharmacokinetics of carboplatin and cisplatin in mice and rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Salgado, C.; López-Hernández, F.J.; López-Novoa, J.M. Glomerular nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 223, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjumand, W.; Seth, A.; Sultana, S. Rutin attenuates cisplatin induced renal inflammation and apoptosis by reducing NFκB, TNF-α and caspase-3 expression in wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Suchal, K.; Bhatia, J.; Gamad, N.; Dinda, A.K.; Gupta, Y.K.; Arya, D.S. Molecular mechanisms underlying attenuation of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by epicatechin gallate. Lab. Invest. 2016, 96, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiou, W.L. A new simple approach to study the effect of changes in urine flow and/or urine pH on renal clearance and its applications. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 1986, 24, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, E.H.; Lee, J.; Ma, S.K.; Kim, I.J.; Frøkiaer, J.; Nielsen, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.W. Alpha-lipoic acid prevents cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2692–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, Y.J.; Lee, A.K.; Chung, H.C.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, D.C.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, M.G. Effects of acute renal failure on the pharmacokinetics of chlorzoxazone in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyrou, M.; Hanna, P.E.; Cribb, A.E. Cisplatin, gentamicin, and p-aminophenol induce markers of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the rat kidneys. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, G.R.; Shand, D.G. A physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1975, 18, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, H.; Hasunuma, M.; Hashimoto, Y. The hepatic and intestinal metabolic activities of P450 in rats with surgery- and drug-induced renal dysfunction. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velenosi, T.J.; Fu, A.Y.; Luo, S.; Wang, H.; Urquhart, B.L. Down-regulation of hepatic CYP3A and CYP2C mediated metabolism in rats with moderate chronic kidney disease. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dowling, T.C.; Briglia, A.E.; Fink, J.C.; Hanes, D.S.; Light, P.D.; Stackiewicz, L.; Karyekar, C.S.; Eddington, N.D.; Weir, M.R.; Henrich, W.L. Characterization of hepaticcytochrome P4503A activity in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 73, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Morimoto, J.; Hoshino, N.; Minouchi, T.; Yamaji, A. Factors that affect absorption behavior of cyclosporin a in gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Ren. Fail. 2000, 22, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Inui, K.I. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of tacrolimus in rats with experimental renal dysfunction. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Shim, H.J.; Lee, M.G. Pharmacokinetics of a new carbapenem, DA-1131, after intravenous administration to rats with uranyl nitrate-induced acute renal failure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.J.; Yoon, W.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, W.G.; Lee, M.G. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes of azosemide after intravenous and oral administration of azosemide to uranyl nitrate-induced acute renal failure rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1998, 19, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, M.G. Effects of acute renal failure on the pharmacokinetics of oltipraz in rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Han, K.S.; Chung, Y.K.; Chang, M.S.; Lee, M.G. Pharmacokinetic changes of a new proton pump inhibitor, YJA-20379-8, after intravenous and oral administration to rats with uranyl nitrate-induced acute renal failure. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1998, 102, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bruyère, A.; Declevès, X.; Bouzom, F.; Proust, L.; Martinet, M.; Walther, B.; Parmentier, Y. Development of an optimized procedure for the preparation of rat intestinal microsomes: Comparison of hepatic and intestinal microsomal cytochrome P450 enzyme activities in two rat strains. Xenobiotica 2009, 39, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

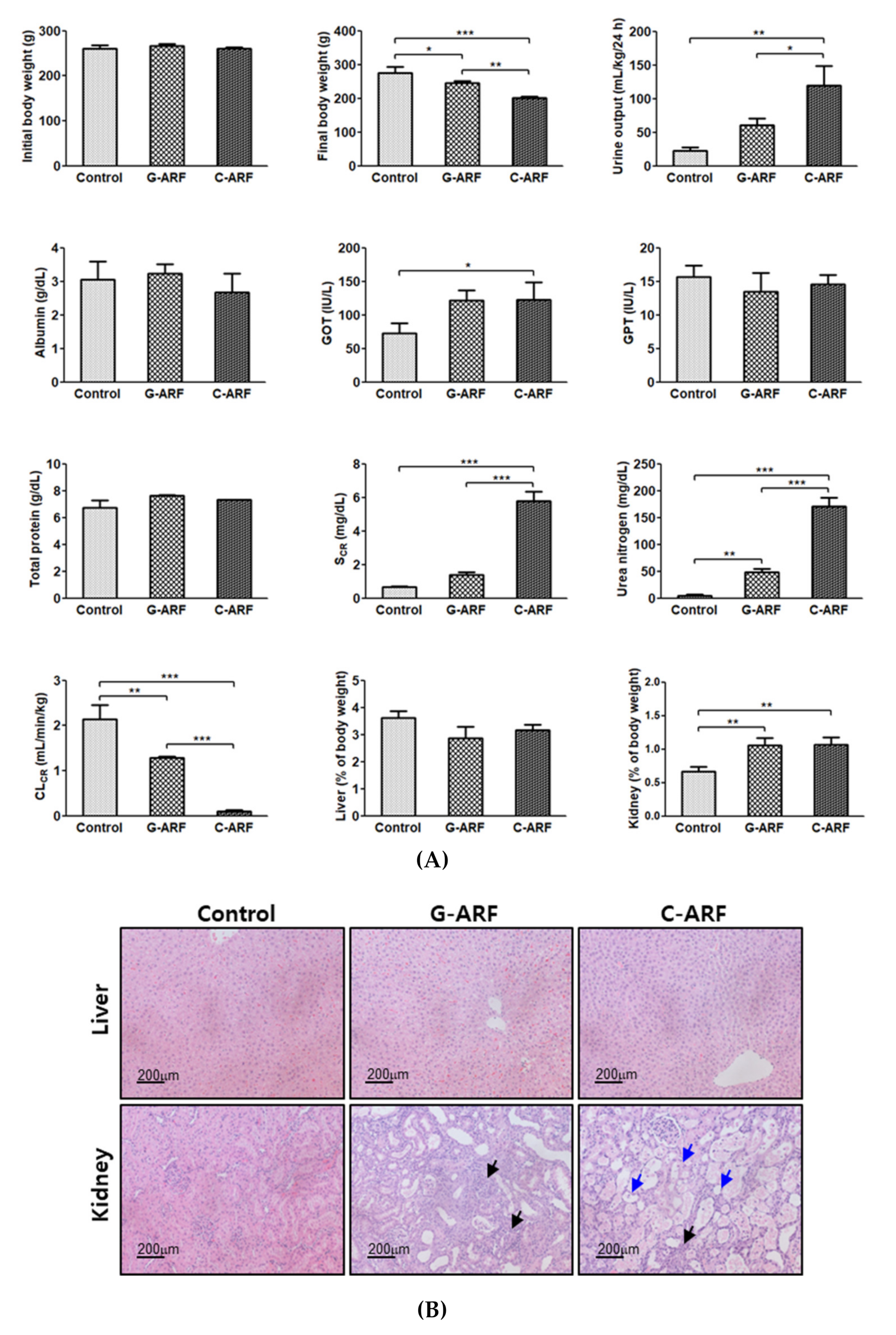


| Parameters | Control (n = 6) | G-ARF (n = 8) | C-ARF (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) a | 280 ± 19.0 | 251 ± 21.3 | 188 ± 10.2 |
| Terminal half-life (min) b | 39.4 ± 11.3 | 70.4 ± 29.6 | 134 ± 40.9 |
| AUC (μg∙min/mL) a | 264 ± 45.4 | 433 ± 90.0 | 693 ± 105 |
| MRT (min) c | 27.2 ± 10.4 | 53.5 ± 30.2 | 69.1 ± 39.6 |
| CL (mL/min/kg) d | 39.0 ± 7.97 | 24.3 ± 6.95 | 14.7 ± 2.29 |
| CLR (mL/min/kg) e | 4.75 ± 1.28 | 1.45 ± 1.54 | 0.0679 ± 0.0917 |
| CLNR (mL/min/kg) f | 34.3 ± 6.77 | 22.9 ± 5.54 | 14.6 ± 2.26 |
| Vss (mL/kg) | 1042 ± 402 | 1174 ± 519 | 1002 ± 558 |
| Ae0–24 h (% of dose) a | 9.51 ± 0.879 | 5.92 ± 2.76 | 0.458 ± 0.626 |
| GI24 h (% of dose) | 0.153 ± 0.306 | 0.00919 ± 0.0225 | 0.195 ± 0.157 |
| Parameters | Control (n = 8) | G-ARF (n = 6) | C-ARF (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) a | 264 ± 26.3 | 206 ± 14.9 | 174 ± 11.7 |
| AUC (μg∙min/mL) b | 217 ± 22.3 | 525 ± 178 | 752 ± 420 |
| Cmax (μg/mL) c | 1.74 ± 0.606 | 5.18 ± 2.59 | 4.20 ± 3.03 |
| Tmax (min) | 71.9 ± 64.7 | 30.8 ± 43.9 | 41.3 ± 36.5 |
| CLR (mL/min/kg) a | 5.66 ± 1.03 | 1.71 ± 0.871 | 0.300 ± 0.495 |
| Ae0–24 h (% of dose) d | 6.21 ± 1.12 | 4.82 ± 3.06 | 1.16 ± 1.37 |
| GI24 h (% of dose) | 0.231 ± 0.235 | 1.27 ± 1.72 | 0.505 ± 0.535 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, S.H.; Chang, S.-Y.; Kim, S.H. Slower Elimination of Tofacitinib in Acute Renal Failure Rat Models: Contribution of Hepatic Metabolism and Renal Excretion. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080714
Bae SH, Chang S-Y, Kim SH. Slower Elimination of Tofacitinib in Acute Renal Failure Rat Models: Contribution of Hepatic Metabolism and Renal Excretion. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(8):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080714
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Sung Hun, Sun-Young Chang, and So Hee Kim. 2020. "Slower Elimination of Tofacitinib in Acute Renal Failure Rat Models: Contribution of Hepatic Metabolism and Renal Excretion" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 8: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080714
APA StyleBae, S. H., Chang, S.-Y., & Kim, S. H. (2020). Slower Elimination of Tofacitinib in Acute Renal Failure Rat Models: Contribution of Hepatic Metabolism and Renal Excretion. Pharmaceutics, 12(8), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080714