Vancomycin Loaded Glycerol Monooleate Liquid Crystalline Phases Modified with Surfactants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of the Bulk LCPs
2.2.2. Characterization of LCPs
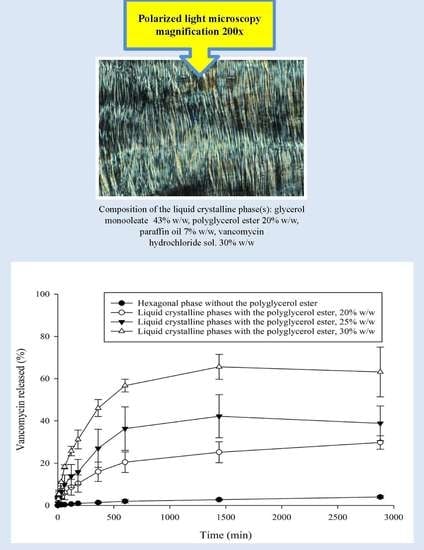
Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM)
Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
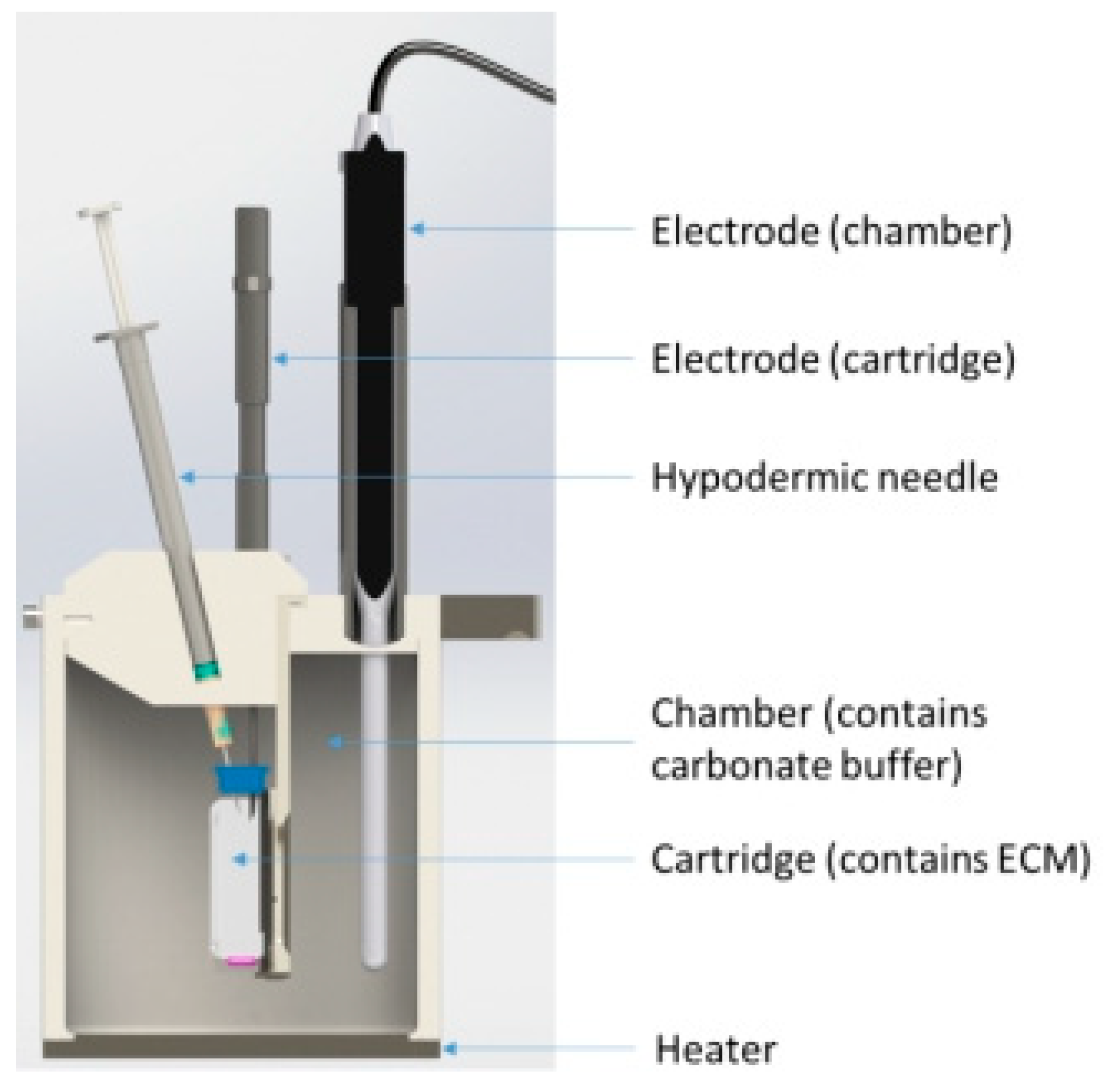
In Vitro VHCl Release Test I
In Vitro VHCl Release Test II
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis of VHCl
3. Results
3.1. PLM
3.2. SAXS
3.3. In Vitro VHCl Release Test I
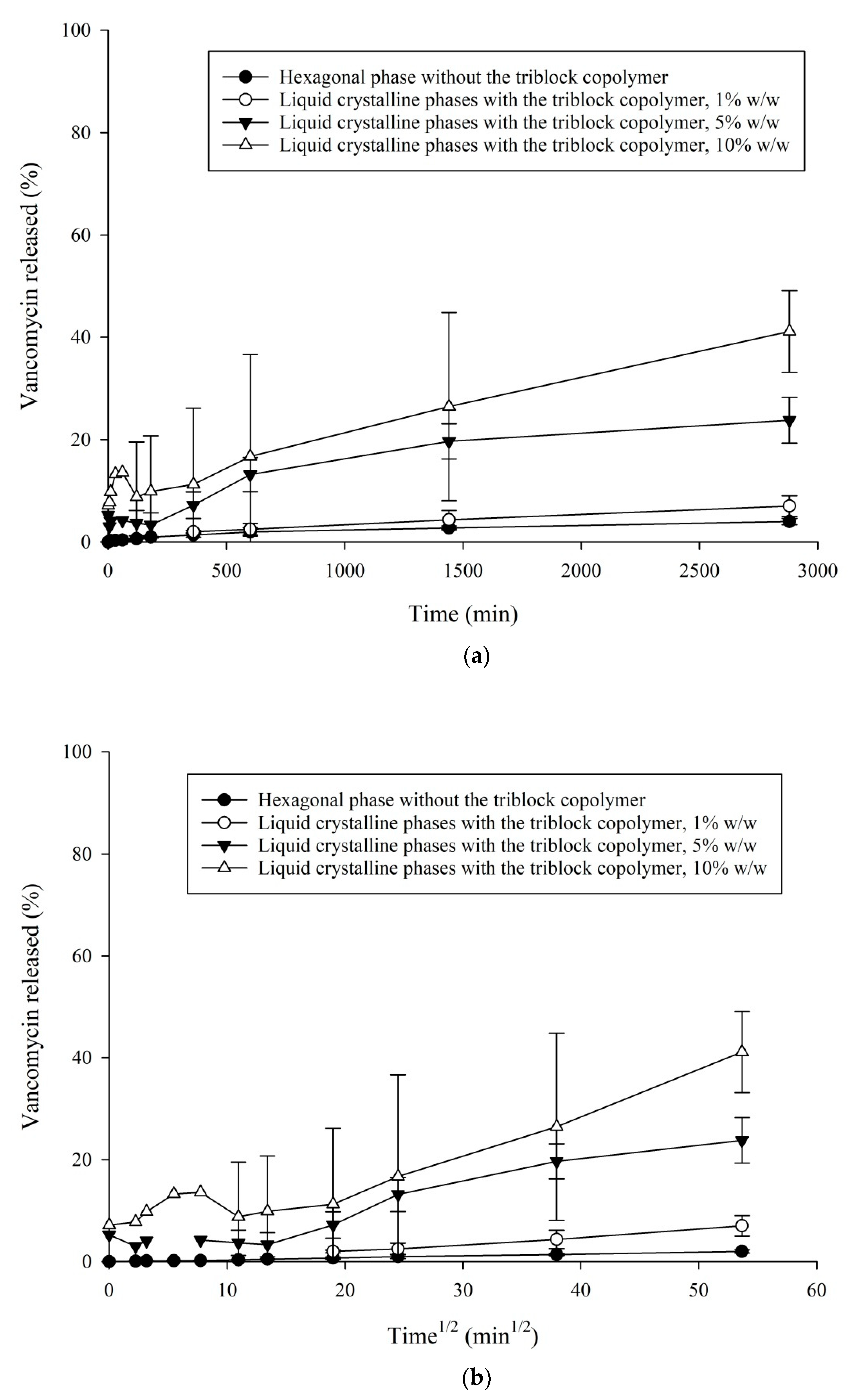
3.4. In Vitro VHCl Release Test II
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milak, S.; Zimmer, A. Glycerol monooleate liquid crystalline phases used in drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, S.; Fong, W.K.; Kirby, N.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J. Evaluating the link between self-assembled mesophase structure and drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.C.; Sadhale, Y.; Chilukuri, D.M. Cubic phase gels as drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clogston, J.; Caffrey, M. Controlling release from the lipidic cubic phase. Amino acids, peptides, proteins and nucleic acids. J. Control. Release 2005, 107, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J. Nanostructure of liquid crystalline matrix determines in vitro sustained release and in vivo oral absorption kinetics for hydrophilic model drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 365, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Caffrey, M. The phase diagram of the monoolein/water system: Metastability and equilibrium aspects. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, G.; Hardmeyer, A.; Widmer, C.; Chiu, M.L.; Nollert, P.; Locher, K.P.; Pedruzzi, L.; Landau, E.M.; Rosenbusch, J.P. Lipidic Cubic Phases: New Matrices for the Three-Dimensional Crystallization of Membrane Proteins. J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 121, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imberg, A.; Evertsson, H.; Stilbs, P.; Kriechbaum, M.; Engström, S. On the self-assembly of monoolein in mixtures of water and a polar aprotic solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagalowicz, L.; Mezzenga, R.; Leser, M.E. Investigating reversed liquid crystalline mesophases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, S.T. Identification of Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Mesophases. In Handbook of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 299–332. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, S.T. Bicontinuous structures in lyotropic liquid crystals and crystalline hyperbolic surfaces. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1996, 1, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabara, A.; Mezzenga, R. Controlling molecular transport and sustained drug release in lipid-based liquid crystalline mesophases. J. Control. Release 2014, 188, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, R.; Mezzenga, R. PH-responsive lyotropic liquid crystals for controlled drug delivery. Langmuir 2011, 27, 5296–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.M.; Bodmeier, R. Effect of dissolution media and additives on the drug release from cubic phase delivery systems. J. Control. Release 1997, 46, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentinig, S.; Sagalowicz, L.; Glatter, O. Self-assembled structures and pK a value of oleic acid in systems of biological levance. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11670–11679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.K.; Salentinig, S.; Prestidge, C.A.; Mezzenga, R.; Hawley, A.; Boyd, B.J. Generation of geometrically ordered lipid-based liquid-crystalline nanoparticles using biologically relevant enzymatic processing. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5373–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentinig, S.; Tangso, K.J.; Hawley, A.; Boyd, B.J. pH-driven colloidal transformations based on the vasoactive drug nicergoline. Langmuir 2014, 30, 14776–14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindell, K.; Engblom, J.; Jonströmer, M.; Carlsson, A.; Engström, S. Influence of a charged phospholipid on the release pattern of timolol maleate from cubic liquid crystalline phases. Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1998, 108, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Amar-Yuli, I.; Adamcik, J.; Blau, S.; Aserin, A.; Garti, N.; Mezzenga, R. Controlled embedment and release of DNA from lipidic reverse columnar hexagonal mesophases. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 8162–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, T.; Nakano, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Handa, T. Effects of an amphipathic α-helical peptide on lateral pressure and water penetration in phosphatidylcholine and monoolein mixed membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24987–24992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemelli, A.; Conde-Valentín, B.; Uhlig, F.; Glatter, O. Amino Acid Induced Modification of Self-Assembled Monoglyceride-Based Nanostructures. Langmuir 2015, 31, 10377–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clogston, J.; Craciun, G.; Hart, D.J.; Caffrey, M. Controlling release from the lipidic cubic phase by selective alkylation. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A.; Ollivon, M.; Bourgaux, C.; Campitelli, A. Diamond-type lipid cubic phase with large water channels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7188–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghmur, A.; De Campo, L.; Sagalowicz, L.; Leser, M.E.; Glatter, O. Control of the internal structure of MLO-based isasomes by the addition of diglycerol monooleate and soybean phosphatidylcholine. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9919–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, R.; Mezzenga, R. Diffusion, molecular separation, and drug delivery from lipid mesophases with tunable water channels. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16455–16462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga, H.M.G.; Tyler, A.I.I.; McCarthy, N.L.C.; Parsons, E.S.; Ces, O.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M.; Brooks, N.J. Temperature and pressure tuneable swollen bicontinuous cubic phases approaching nature’s length scales. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, S.; Lindahl, L.; Wallin, R.; Engblom, J. A study of polar lipid drug systems undergoing a thermoreversible lamellar-to-cubic phase transition. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 86, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.K.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J. Stimuli responsive liquid crystals provide “on-demand” drug delivery in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.K.; Hanley, T.L.; Thierry, B.; Kirby, N.; Boyd, B.J. Plasmonic nanorods provide reversible control over nanostructure of self-assembled drug delivery materials. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6136–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.K.; Hanley, T.L.; Thierry, B.; Kirby, N.; Waddington, L.J.; Boyd, B.J. Controlling the nanostructure of gold nanorod-lyotropic liquid-crystalline hybrid materials using near-infrared laser irradiation. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14450–14460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallooran, J.J.; Handschin, S.; Bolisetty, S.; Mezzenga, R. Twofold light and magnetic responsive behavior in nanoparticle-lyotropic liquid crystal systems. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5589–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.K.; Malic, N.; Evans, R.A.; Hawley, A.; Boyd, B.J.; Hanley, T.L. Alkylation of spiropyran moiety provides reversible photo-control over nanostructured soft materials. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangso, K.J.; Fong, W.K.; Darwish, T.; Kirby, N.; Boyd, B.J.; Hanley, T.L. Novel spiropyran amphiphiles and their application as light-responsive liquid crystalline components. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 10203–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghmur, A.; Paasonen, L.; Yliperttula, M.; Urtti, A.; Rappolt, M. Structural elucidation of light activated vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallooran, J.J.; Bolisetty, S.; Mezzenga, R. Macroscopic alignment of lyotropic liquid crystals using magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3932–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallooran, J.J.; Negrini, R.; Mezzenga, R. Controlling anisotropic drug diffusion in lipid-Fe3O4 nanoparticle hybrid mesophases by magnetic alignment. Langmuir 2013, 29, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milak, S.; Chemelli, A.; Glatter, O.; Zimmer, A. Vancomycin ocular delivery systems based on glycerol monooleate reversed hexagonal and reversed cubic liquid crystalline phases. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Goymann, C.C. Physicochemical characterization of colloidal drug delivery systems such as reverse micelles, vesicles, liquid crystals and nanoparticles for topical administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonjari, I.D.; Hosmani, A.H.; Karmarkar, A.B.; Godage, A.S.; Kadam, S.B.; Dhabale, P.N. Formulation and evaluation of in situ gelling thermoreversible mucoadhesive gel of fluconazole. Drug Discov. Ther. 2009, 3, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, W.I. Diffusional Models Useful in Biopharmaceutics. J. Pharm. Sci. 1967, 56, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.K.; Kim, J.C. Complex coacervation-controlled release from monoolein cubic phase containing silk fibroin and alginate. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.B.; Simonelli, A.P.; Higuchi, W.I. Drug Release from Wax Matrices, I. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 57, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libster, D.; Aserin, A.; Yariv, D.; Shoham, G.; Garti, N. Concentration- and temperature-induced effects of incorporated desmopressin on the properties of reverse hexagonal mesophase. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6336–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amar-Yuli, I.; Wachtel, E.; Shoshan, E.B.; Danino, D.; Aserin, A.; Garti, N. Hexosome and hexagonal phases mediated by hydration and polymeric stabilizer. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3637–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Dong, Y.; Larson, I.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J. Bulk and dispersed aqueous phase behavior of phytantriol: Effect of vitamin E acetate and F127 polymer on liquid crystal nanostructure. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9512–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisset, N.B.; Boyd, B.J.; Da Dong, Y. Tailoring liquid crystalline lipid nanomaterials for controlled release of macromolecules. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K.U.; Shin, W.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.D.; Kim, Y.C.; Tae, G.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J. Monoolein cubic phases containing hydrogen peroxide. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 36, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Bodmeier, R. Binding of drugs to monoglyceride-based drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 147, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, D.; Dorschel, D. A cubic-phase delivery system composed of glyceryl monooleate and water for sustained release of water-soluble drugs. Pharm. Technol. 1992, 16, 116–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.M.; Bodmeier, R. Low viscosity monoglyceride-based drug delivery systems transforming into a highly viscous cubic phase. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 173, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemelli, A.; Maurer, M.; Geier, R.; Glatter, O. Optimized loading and sustained release of hydrophilic proteins from internally nanostructured particles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16788–16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautou-Miranda, V.; Libert, F.; Grand-Boyer, A.; Gellis, C.; Chopineau, J. Impact of deep freezing on the stability of 25 mg/mL vancomycin ophthalmic solutions. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 234, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, H.; Sharma, V.K.; Contrerasrojas, L.R.; Yu, Y.; Alleman, C.; Sreedhara, A.; Fischer, S.; Khawli, L.A.; Yohe, S.; Bumbaca, D.; et al. A novel in vitro method to model the fate of subcutaneously administered biopharmaceuticals and associated formulation components. J. Control. Release 2015, 214, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnunen, H.M.; Mrsny, R.J. Improving the outcomes of biopharmaceutical delivery via the subcutaneous route by understanding the chemical, physical and physiological properties of the subcutaneous injection site. J. Control. Release 2014, 182, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianopoulos, T.; Poh, M.; Insin, N.; Bawendi, M.G.; Fukumura, D.; Munn, L.L.; Jain, R.K. Diffusion of particles in the extracellular matrix: The effect of repulsive electrostatic interactions. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencz, J.R.; Assia, E.I.; Diamantstein, L.; Rubinstein, E. Vancomycin concentration in the vitreous after intravenous and intravitreal administration for postoperative endophthalmitis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1999, 117, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Hexagonal Phase without Tuning Agent | % Glycerol Monooleate | Structure Parameter * (nm) | Radius of Water Channels in The Hexagonal Phase (Calculated) (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hexagonal Phase without tuning Agent [37] | HII | Lα | Ia3d | HII | |
| 63 | 6538 ± 0.02(37) | / | / | 3.70 | |
| LCP tuned with | structure parameter * (nm) | radius of water channels in the hexagonal phase (calculated) (nm) | |||
| PE% (w/w) | HII | Lα | Ia3d | HII | |
| 10 | 53 | 7.253 ± 0.06 | (4.965 ± 0.05) | 12.1387 ± 0.05 | 4.63 |
| 20 | 43 | 7.625 ± 0.07 | 4.887 ± 0.01 | ND | 5.36 |
| 25 | 38 | 7.996 ± 0.07 | 4.913 ± 0.01 | ND | 5.86 |
| 30 | 33 | 8.700 ± 0.20 | 5.009 ± 0.04 | ND | 6.63 |
| TC% (w/w) | HII | Lα | / | HII | |
| 1 | 63 | 6.732 ± 0.02 | ND ** | / | 3.81 |
| 5 | 63 | 6.379 ± 0.06 | ND ** | / | 3.61 |
| 10 | 63 | 6.061 ± 0.04 | ND ** | / | 3.43 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milak, S.; Chemelli, A.; Glatter, O.; Zimmer, A. Vancomycin Loaded Glycerol Monooleate Liquid Crystalline Phases Modified with Surfactants. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060521
Milak S, Chemelli A, Glatter O, Zimmer A. Vancomycin Loaded Glycerol Monooleate Liquid Crystalline Phases Modified with Surfactants. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060521
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilak, Spomenka, Angela Chemelli, Otto Glatter, and Andreas Zimmer. 2020. "Vancomycin Loaded Glycerol Monooleate Liquid Crystalline Phases Modified with Surfactants" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060521
APA StyleMilak, S., Chemelli, A., Glatter, O., & Zimmer, A. (2020). Vancomycin Loaded Glycerol Monooleate Liquid Crystalline Phases Modified with Surfactants. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060521