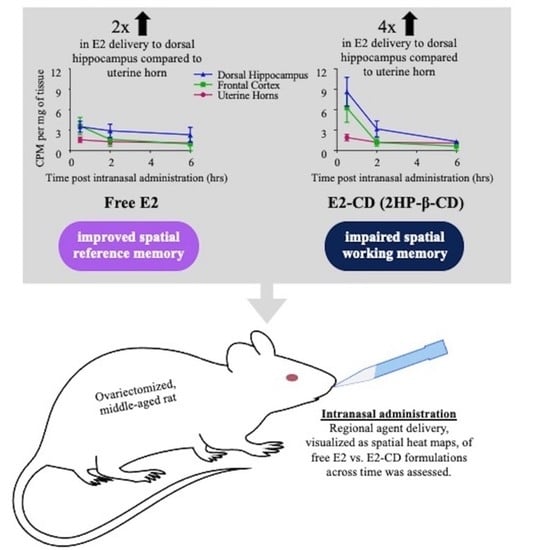
Intranasal 17β-Estradiol Modulates Spatial Learning and Memory in a Rat Model of Surgical Menopause
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Study 1: Brain-Distribution and Biodistribution of Intranasal Free E2 and E2-CD Complexes
2.3.1. Ovariectomy (Ovx)
2.3.2. Treatments
2.3.3. Tissue Collection
2.3.4. Tissue Processing
2.4. Study 2: Spatial Learning and Memory and Uterine Stimulation Following Daily Intranasal Free E2 and E2-CD Treatment
2.4.1. Ovariectomy (Ovx)
2.4.2. Treatment Administration
2.4.3. Water Radial-Arm Maze (WRAM)
2.4.4. Morris Water Maze (MWM)
2.4.5. Visible Platform
2.4.6. Open Field
2.4.7. Uterine Horn Weights
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study 1: Brain-Distribution and Biodistribution of Intranasal Free E2 and E2-CD Complexes
3.2. Study 2: Spatial Learning and Memory, and Uterine Stimulation, Following Daily Intranasal Free E2 and E2-CD Treatment
3.2.1. Body Weight
3.2.2. Water Radial-Arm Maze (WRAM)
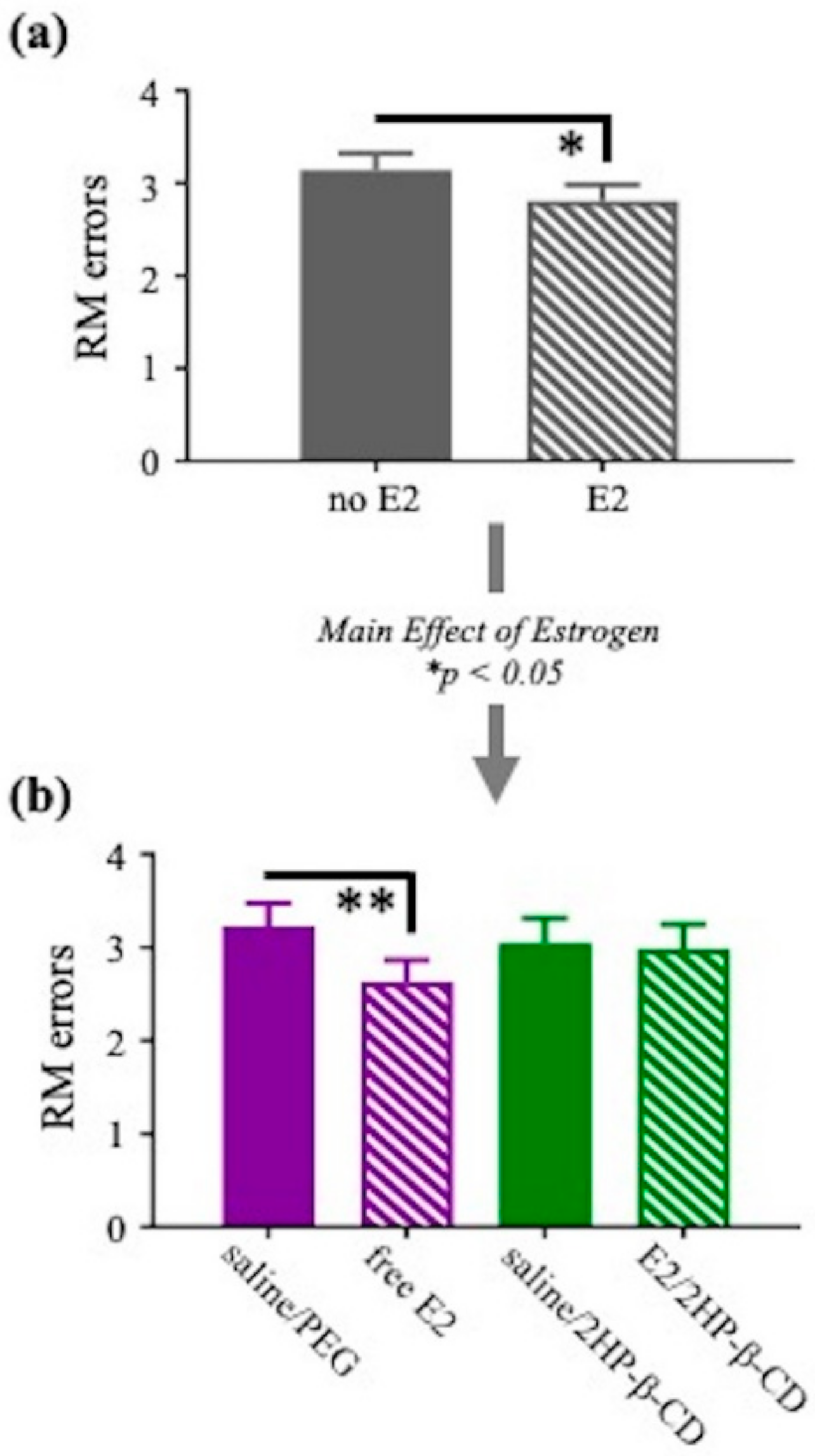
3.2.3. Morris Water Maze (MWM)
3.2.4. Visible Platform Task
3.2.5. Open Field
3.2.6. Uterine Horn Weight
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NAMS. Menopause Practice: A Clinician’s Guide, 5th ed.; The North American Menopause Society (NAMS): Mayfield Heights, OH, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Maki, P.M. Minireview: Effects of different HT formulations on cognition. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3564–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NAMS. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause J. N. Am. Menopause Soc. 2017, 24, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl, H. Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: Influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8, 3–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakapenka, A.V.; Pena, V.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Ovarian hormones, cognition, and reproductive aging: Applications and implications for translating preclinical endocrine brain research to the clinic. In Estrogens and Memory: Basic Research and Clinical Implications; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baksu, B.; Baksu, A.; Göker, N.; Citak, S. Do different delivery systems of hormone therapy have different effects on psychological symptoms in surgically menopausal women? A randomized controlled trial. Maturitas 2009, 62, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksu, B.; Davas, I.; Agar, E.; Akyol, A.; Uluocak, A. Do different delivery systems of estrogen therapy influence serum lipids differently in surgically menopausal women? J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2007, 33, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte-Nelson, H.A.; Francis, K.R.; Umphlet, C.D.; Granholm, A.C. Progesterone reverses the spatial memory enhancements initiated by tonic and cyclic oestrogen therapy in middle-aged ovariectomized female rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harburger, L.L.; Bennett, J.C.; Frick, K.M. Effects of estrogen and progesterone on spatial memory consolidation in aged females. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, N.C.; Pardon, L.P.; Yates, M.A.; Juraska, J.M. Effects of long-term treatment with 17 β-estradiol and medroxyprogesterone acetate on water maze performance in middle aged female rats. Horm. Behav. 2010, 58, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kurdoglu, M.; Yildirim, M.; Kurdoglu, Z.; Erdem, A.; Erdem, M.; Bilgihan, A.; Goktas, B. Cardiovascular risk assessment with oxidised LDL measurement in postmenopausal women receiving intranasal estrogen replacement therapy. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2011, 27, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakapenka, A.V.; Hiroi, R.; Quihuis, A.M.; Carson, C.; Patel, S.; Berns-Leone, C.; Fox, C.; Sirianni, R.W.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Contrasting effects of individual versus combined estrogen and progestogen regimens as working memory load increases in middle-aged ovariectomized rats: One plus one does not equal two. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 64, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.M.; Hulst, J.L.; Berbling, J.L. Estradiol replacement enhances working memory in middle-aged rats when initiated immediately after ovariectomy but not after a long-term period of ovarian hormone deprivation. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fortress, A.M.; Fan, L.; Orr, P.T.; Zhao, Z.; Frick, K.M. Estradiol-induced object recognition memory consolidation is dependent on activation of mTOR signaling in the dorsal hippocampus. Learn. Mem. 2013, 20, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Orr, P.T.; Chambers, C.H.; Lewis, M.C.; Frick, K.M. Estradiol-induced object memory consolidation in middle-aged female mice requires dorsal hippocampal extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4390–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Studd, J.; Pornel, B.; Marton, I.; Bringer, J.; Varin, C.; Tsouderos, Y.; Christiansen, C. Efficacy and acceptability of intranasal 17 β-oestradiol for menopausal symptoms: Randomised dose-response study. Lancet 1999, 353, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, N.; Farr, S.A.; Kageyama, H.; Shioda, S.; Banks, W.A. Delivery of galanin-like peptide to the brain: Targeting with intranasal delivery and cyclodextrins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Ghananeem, A.M.; Traboulsi, A.A.; Dittert, L.W.; Hussain, A.A. Targeted Brain Delivery of 17β-Estradiol Via Nasally Administered Water Soluble Prodrugs. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2002, 3, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, E.P.; Cotter, J.D.; Prakapenka, A.V.; Cook, R.L.; Diperna, D.M.; Sirianni, R.W. Targeting small molecule delivery to the brain and spinal cord via intranasal administration of rabies virus glycoprotein (RVG29)-modified PLGA nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procyshyn, T.L.; Lombardo, M.V.; Lai, M.-C.; Auyeung, B.; Crockford, S.K.; Deakin, J.; Soubramanian, S.; Sule, A.; Baron-Cohen, S.I.; Bethlehem, R.A. Effects of oxytocin administration on salivary sex hormone levels in autistic and neurotypical women. Mol. Autism 2020, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Merhi, Z. Safety data for the use of nasal human menopausal gonadotropins: A potential novel approach for fertility treatment. JBRA Assist. Reprod. 2019, 23, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogol, A.D.; Tkachenko, N.; Bryson, N. Natesto TM, a novel testosterone nasal gel, normalizes androgen levels in hypogonadal men. Andrology 2016, 4, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misra, A. Nasal route for delivery of emergency contraceptives. J. Pharm. Anal. Insights 2016, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Firat, Y.; Engin-Ustun, Y.; Kizilay, A.; Ustun, Y.; Akarcay, M.; Selimoglu, E.; Kafkasli, A. Effect of intranasal estrogen on vocal quality. J. Voice 2009, 23, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudard, A.M.I.; Silva De Souza, S.; Puga, M.E.; Marjoribanks, J.; da Silva, E.M.; Torloni, M.R. Bioidentical hormones for women with vasomotor symptoms. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, CD010407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dijck, J.A.A.M.; Otten, J.D.M.; Karssemeijer, N.; Kenemans, P.; Verbeek, A.L.M.; Van Der Mooren, M.J. Less mammographic density after nasal versus oral administration of postmenopausal hormone therapy. Climacteric 2011, 14, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelo-Branco, C.; Coloma, J.L. The role of intranasal estradiol spray in the management of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms in menopausal women. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2010, 26, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, G.; Spritzer, P.M. Effects of micronized progesterone added to non-oral estradiol on lipids and cardiovascular risk factors in early postmenopause: A clinical trial. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelissier, C.; De Kervasdoue, A.; Chuong, V.T.; Maugis, E.L.; De Mouillac, F.; Breil, M.H.; Moniot, G.; Zeitoun-Lepvrier, G.; Robin, M.; Rime, B. Clinical evaluation, dose-finding and acceptability of AERODIOL, the pulsed estrogen therapy for treatment of climacteric symptoms. Maturitas 2001, 37, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, M.M.; Scicchitano, P.; Gesualdo, M.; Fornarelli, F.; Pinto, V.; Farinola, G.; Lagioia, R.; Sassara, M.; Zito, A.; Federici, A.; et al. Systemic vascular hemodynamic changes due to 17-β-estradiol intranasal administration. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 18, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Kır, F.; Ahin, S.; Köken, G.; Köse, M.; Serhan Cevrioglu, A.; Kaya, E. Acute effect of intranasal estrogen on cerebral and cerebellar perfusion in postmenopausal women. Maturitas 2008, 59, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.M.; Lewis, M.C.; Pechenino, A.S.; Lauren, L.; Orr, P.T.; Gresack, J.E.; Schafe, G.E.; Frick, K.M. Estradiol-induced enhancement of object memory consolidation involves hippocampal Erk activation and membrane-bound estrogen receptors. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8660–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harburger, L.L.; Saadi, A.; Frick, K.M. Dose-dependent effects of post-training estradiol plus progesterone treatment on object memory consolidation and hippocampal extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in young ovariectomized mice. Neuroscience 2009, 160, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinopoli, K.J.; Floresco, S.B.; Galea, L.A.M. Systemic and local administration of estradiol into the prefrontal cortex or hippocampus differentially alters working memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2006, 86, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, N.; Farr, S.A.; Nakamachi, T.; Morley, J.E.; Nakamura, M.; Shioda, S.; Banks, W.A. Intranasal administration of PACAP: Uptake by brain and regional brain targeting with cyclodextrins. Peptides 2012, 36, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mennenga, S.E.; Koebele, S.V.; Mousa, A.A.; Alderete, T.J.; Tsang, C.W.S.; Acosta, J.I.; Camp, B.W.; Demers, L.M.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Pharmacological blockade of the aromatase enzyme, but not the androgen receptor, reverses androstenedione-induced cognitive impairments in young surgically menopausal rats. Steroids 2015, 99, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braden, B.B.; Andrews, M.G.; Acosta, J.I.; Mennenga, S.E.; Lavery, C.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. A comparison of progestins within three classes: Differential effects on learning and memory in the aging surgically menopausal rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 322, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Singh, A.; Madhav, N. Nasal cavity: A promising transmucosal platform for drug delivery and research approaches from nasal to brain targeting. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2012, 2, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, N.; Perfield, J.; Strissel, K.; Obin, M.; Greenberg, A. Reduced energy expenditure and increased inflammation are early events in the development of ovariectomy-induced obesity. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz-Chaves, Y.; Kwiatkowska-Naqvi, A.; Von Hülst, H.; Pernía, O.; Carrero, P.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Behavioral effects of estradiol therapy in ovariectomized rats depend on the age when the treatment is initiated. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, H.A.; Denenberg, V.H. Estradiol facilitates performance as working memory load increases. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1999, 24, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennenga, S.E.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. The importance of incorporating both sexes and embracing hormonal diversity when conducting rodent behavioral assays. In The Maze Book: Theories, Practice, and Protocols for Testing Rodent Cognition; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 299–321. [Google Scholar]
- Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. (Ed.) The water radial-arm maze: Four out of eight arms platformed protocol for rodents. In The Maze Book: Theories, Practice, and Protocols for Testing Rodent Cognition; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. (Ed.) The Morris maze protocol for rodents. In The Maze Book: Theories, Practice, and Protocols for Testing Rodent Cognition; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 441–449. [Google Scholar]
- Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. (Ed.) The visible platform task for rodents. In The Maze Book: Theories, Practice, and Protocols for Testing Rodent Cognition; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 451–454. [Google Scholar]
- Mennenga, S.E.; Gerson, J.E.; Dunckley, T.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Harmine treatment enhances short-term memory in old rats: Dissociation of cognition and the ability to perform the procedural requirements of maze testing. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 138, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mennenga, S.E.; Gerson, J.E.; Koebele, S.V.; Kingston, M.L.; Tsang, C.W.S.; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Baxter, L.C.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Understanding the cognitive impact of the contraceptive estrogen ethinyl estradiol: Tonic and cyclic administration impairs memory, and performance correlates with basal forebrain cholinergic system integrity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiroi, R.; Weyrich, G.; Koebele, S.V.; Mennenga, S.E.; Talboom, J.S.; Hewitt, L.T.; Lavery, C.N.; Mendoza, P.; Jordan, A.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Benefits of hormone therapy estrogens depend on estrogen type: 17β-estradiol and conjugated equine estrogens have differential effects on cognitive, anxiety-like, and depressive-like behaviors and increase tryptophan hydroxylase-2 mRNA levels in dorsal raphe nucleus subregions. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koebele, S.V.; Nishimura, K.J.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A.; Kemmou, S.; Ortiz, J.B.; Judd, J.M.; Conrad, C.D. A long-term cyclic plus tonic regimen of 17β-estradiol improves the ability to handle a high spatial working memory load in ovariectomized middle-aged female rats. Horm. Behav. 2020, 118, 104656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Talboom, J.S.; Braden, B.B.; Tsang, C.W.S.; Mennenga, S.; Andrews, M.; Demers, L.M.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Continuous estrone treatment impairs spatial memory and does not impact number of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in the surgically menopausal middle-aged rat. Horm. Behav. 2012, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerlind, K.C.; Gibson, K.J.; Malone, P.; Evans, G.L.; Turner, R.T. Differential effects of estrogen metabolites on bone and reproductive tissues of ovariectomized rats. J. Bone Min. Res. 1998, 13, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Green, R.; Luttge, W.G.; Whalen, R.E. Uptake and retention of tritiated estradiol in brain and peripheral tissues of male, female and neonatally androgenized female rats. Endocrinology 1969, 85, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.V. Comments on Dr. Pearlman’s paper; Comparison of androgens and estrogens as to their fate in target tissues. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 1963, 12, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Jehan, Q.; Srivasta, S.; Akhlaq, M.; Ahmad, A.; Setty, B.S. Kinetics of distribution and retention of 3H-oestradiol-17 beta in rat tissues: A comparative study with free oestradiol and after its incorporation into liposomes. Endocrinology 1982, 80, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Meyer, E.M.; Millard, W.J.; Simpkins, J.W. Ovarian steroid deprivation results in a reversible learning impairment and compromised cholinergic function in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain Res. 1994, 644, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bakri, N.K.; Islam, A.; Zhu, S.; Elhassan, A.; Mohammed, A.; Winblad, B.; Adem, A. Effects of estrogen and progesterone treatment on rat hippocampal NMDA receptors: Relationship to Morris water maze performance. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2004, 8, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Long-term effects of melatonin or 17β-estradiol on improving spatial memory performance in cognitively impaired, ovariectomized adult rats. J. Pineal Res 2004, 37, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, Á.; Delattre, A.M.; Pereira, S.I.R.; Carolino, R.G.; Szawka, R.E.; Anselmo-Franci, J.A.; Zanata, S.M.; Ferraz, A.C. 17β-Estradiol replacement in young, adult and middle-aged female ovariectomized rats promotes improvement of spatial reference memory and an antidepressant effect and alters monoamines and BDNF levels in memory- and depression-related brain areas. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, K.J.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A.; Neisewander, J.L.; Conrad, C.D. Assessment of estradiol influence on spatial tasks and hippocampal CA1 spines: Evidence that the duration of hormone deprivation after ovariectomy compromises 17β-estradiol effectiveness in altering CA1 spines. Horm. Behav. 2008, 54, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talboom, J.S.; Williams, B.J.; Baxley, E.R.; West, S.G.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Higher levels of estradiol replacement correlate with better spatial memory in surgically menopausal young and middle-aged rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 90, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayer, J.; Gläscher, J.; Finsterbusch, J.; Schulte, L.H.; Sommer, T. Linear and inverted U-shaped dose-response functions describe estrogen effects on hippocampal activity in young women. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barha, C.K.; Dalton, G.L.; Galea, L.A.M. Low doses of 17α-estradiol and 17β-estradiol facilitate, whereas higher doses of estrone and 17α- and 17β-estradiol impair, contextual fear conditioning in adult female rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iivonen, S.; Heikkinen, T.; Puoliväli, J.; Helisalmi, S.; Hiltunen, M.; Soininen, H.; Tanila, H. Effects of estradiol on spatial learning, hippocampal cytochrome P450 19, and estrogen alpha and beta mRNA levels in ovariectomized female mice. Neuroscience 2006, 137, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzum, G.; Bahcekapili, N.; Baltaci, A.K.; Mogulkoc, R.; Ziylan, Y.Z. Chronic (3-Weeks) Treatment of estrogen (17β-estradiol) enhances working and reference memory in ovariectomized rats: Role of acetylcholine. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, A.L. Protective effect of practice on cognition during aging: Implications for predictive characteristics of performance and efficacy of practice. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2002, 78, 294–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talboom, J.S.; West, S.G.; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Enders, C.K.; Crain, I.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Learning to remember: Cognitive training-induced attenuation of age-related memory decline depends on sex and cognitive demand, and can transfer to untrained cognitive domains. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2791–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koebele, S.V.; Mennenga, S.E.; Poisson, M.L.; Hewitt, L.T.; Patel, S.; Mayer, L.P.; Dyer, C.A.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A. Characterizing the effects of tonic 17β-estradiol administration on spatial learning and memory in the follicle-deplete middle-aged female rat. Horm. Behav. 2020, 126, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresack, J.E.; Frick, K.M. Post-training estrogen enhances spatial and object memory consolidation in female mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 84, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Nedungadi, T.P.; Zhu, L.; Sobhani, N.; Irani, B.G.; Davis, K.E.; Zhang, X.; Zou, F.; Gent, L.M.; Hahner, L.D.; et al. Distinct hypothalamic neurons mediate estrogenic effects on energy homeostasis and reproduction. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dooley, M.; Spencer, C.M.; Ormrod, D. Estradiol-intranasal: A review of its use in the management of menopause. Drugs 2001, 61, 2243–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chi, N.; Tang, X. Preparation of estradiol chitosan nanoparticles for improving nasal absorption and brain targeting. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachim, E.; Barakat, R.; Lew, B.; Kim, K.K.; Ko, C.M.; Choi, H. Single intranasal administration of 17β-estradiol loaded gelatin nanoparticles confers neuroprotection in the post-ischemic brain. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 29, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Treatment | Formulation | E2:CD Molar Ratio | Aqueous Medium | Rationale for CD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | free E2 | - | 20% PEG300 saline | - |
| B | E2/randomly methylated β-CD | 1:2 | Saline | CD derivative found in Aerodiol intranasal spray |
| C | E2/2HP-β-CD | 1:2 | Saline | CD derivative used in behavioral studies evaluating estrogen effects on the brain |
| D | E2/β-CD | 1:4 | Saline | Base CD for the derivatives used in treatments B and C |
| E | E2/γ-CD | 1:5 | Saline | CD with a larger inner cavity than β-CD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prakapenka, A.V.; Peña, V.L.; Strouse, I.; Northup-Smith, S.; Schrier, A.; Ahmed, K.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.A.; Sirianni, R.W. Intranasal 17β-Estradiol Modulates Spatial Learning and Memory in a Rat Model of Surgical Menopause. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121225
Prakapenka AV, Peña VL, Strouse I, Northup-Smith S, Schrier A, Ahmed K, Bimonte-Nelson HA, Sirianni RW. Intranasal 17β-Estradiol Modulates Spatial Learning and Memory in a Rat Model of Surgical Menopause. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(12):1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121225
Chicago/Turabian StylePrakapenka, Alesia V., Veronica L. Peña, Isabel Strouse, Steven Northup-Smith, Ally Schrier, Kinza Ahmed, Heather A. Bimonte-Nelson, and Rachael W. Sirianni. 2020. "Intranasal 17β-Estradiol Modulates Spatial Learning and Memory in a Rat Model of Surgical Menopause" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 12: 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121225
APA StylePrakapenka, A. V., Peña, V. L., Strouse, I., Northup-Smith, S., Schrier, A., Ahmed, K., Bimonte-Nelson, H. A., & Sirianni, R. W. (2020). Intranasal 17β-Estradiol Modulates Spatial Learning and Memory in a Rat Model of Surgical Menopause. Pharmaceutics, 12(12), 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121225