Cellular Analysis and Chemotherapeutic Potential of a Bi-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotube
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
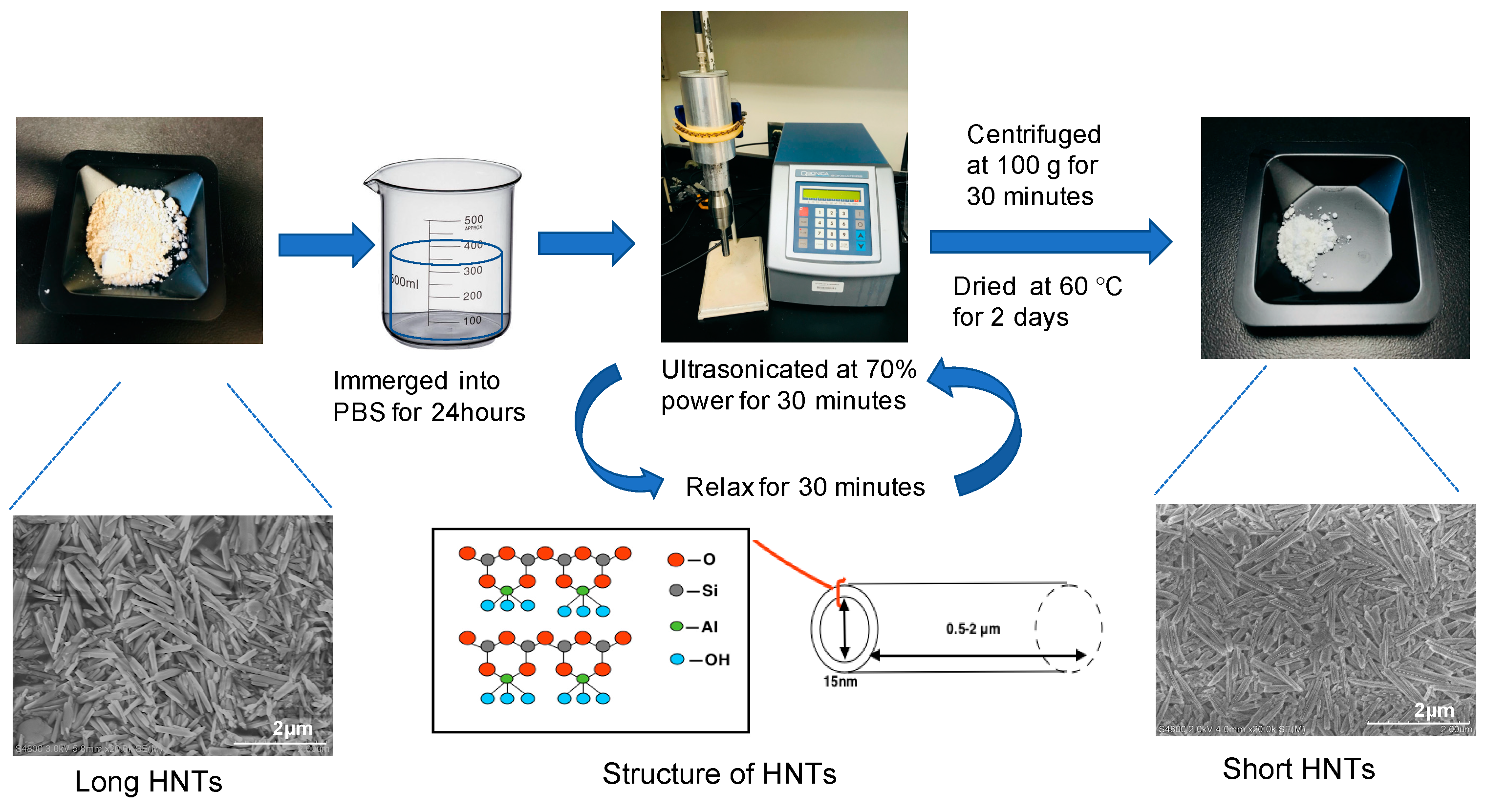
2.2. Production of Shortened HNTs
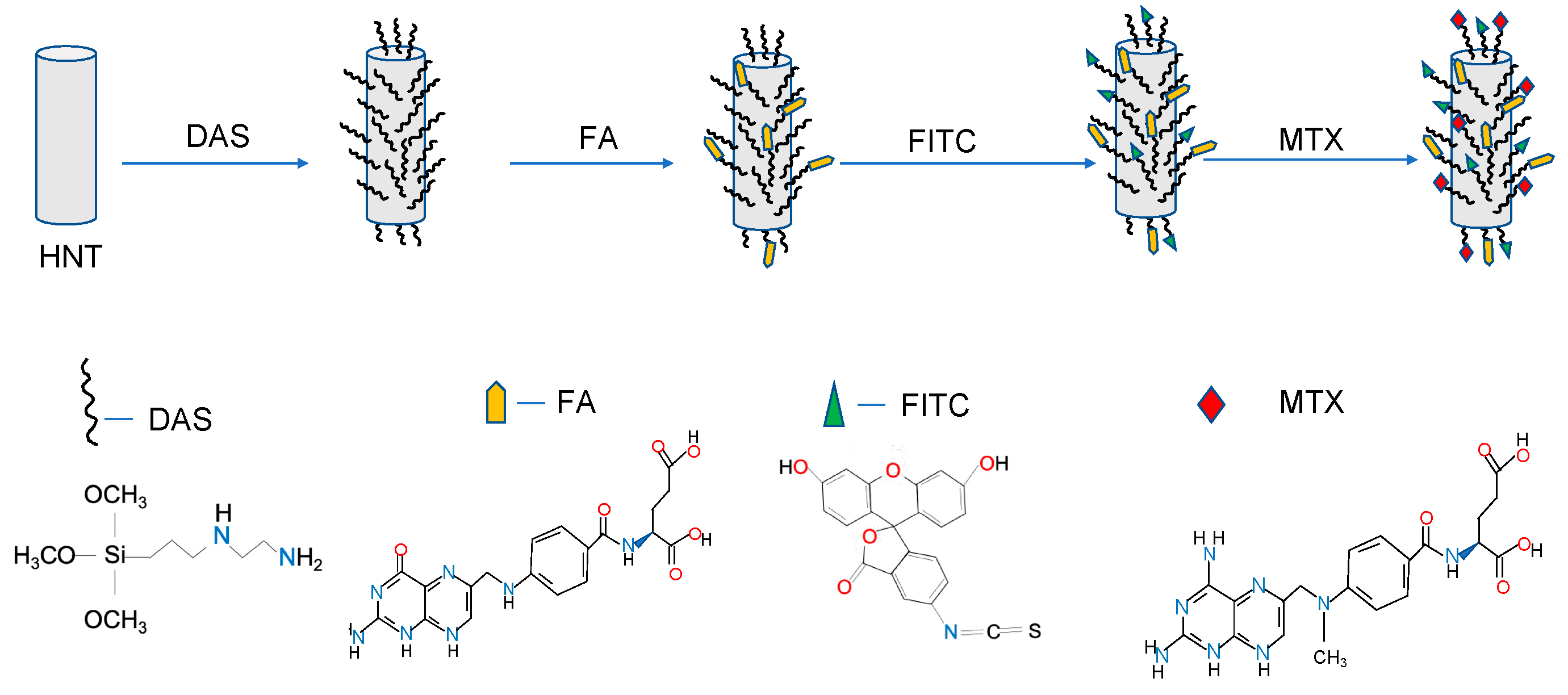
2.3. bi-HNTs Synthesis
2.4. bi-HNTs Characterization
2.4.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. MTS Assay
2.7. XTT Assay
2.8. Cell Uptake Efficiency
2.9. Cell Uptake Mechanism
2.10. Multi-Photon Imaging
2.11. Apoptosis and Necrosis
2.12. Drug Loading
2.13. Drug Loading Efficiency
2.14. Drug Release Profile
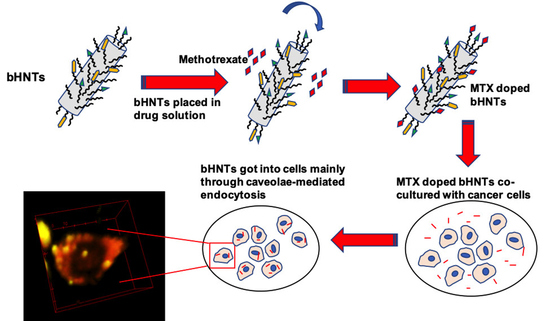
2.15. MTX-bi-HNTs Targeting
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
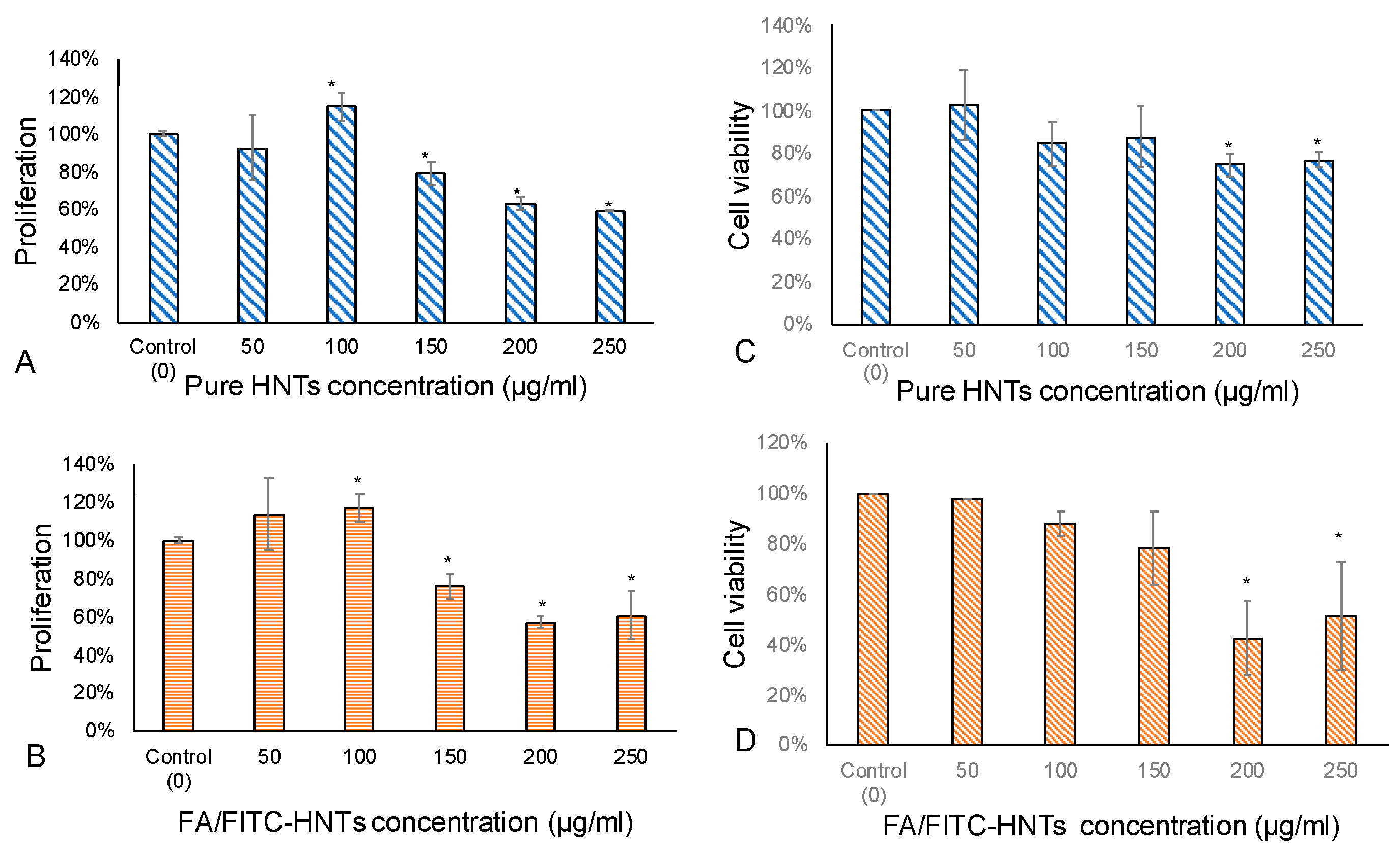
3.1. Optimal Dosage Determination
3.2. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size on the Interaction between bi-HNTs and Cells
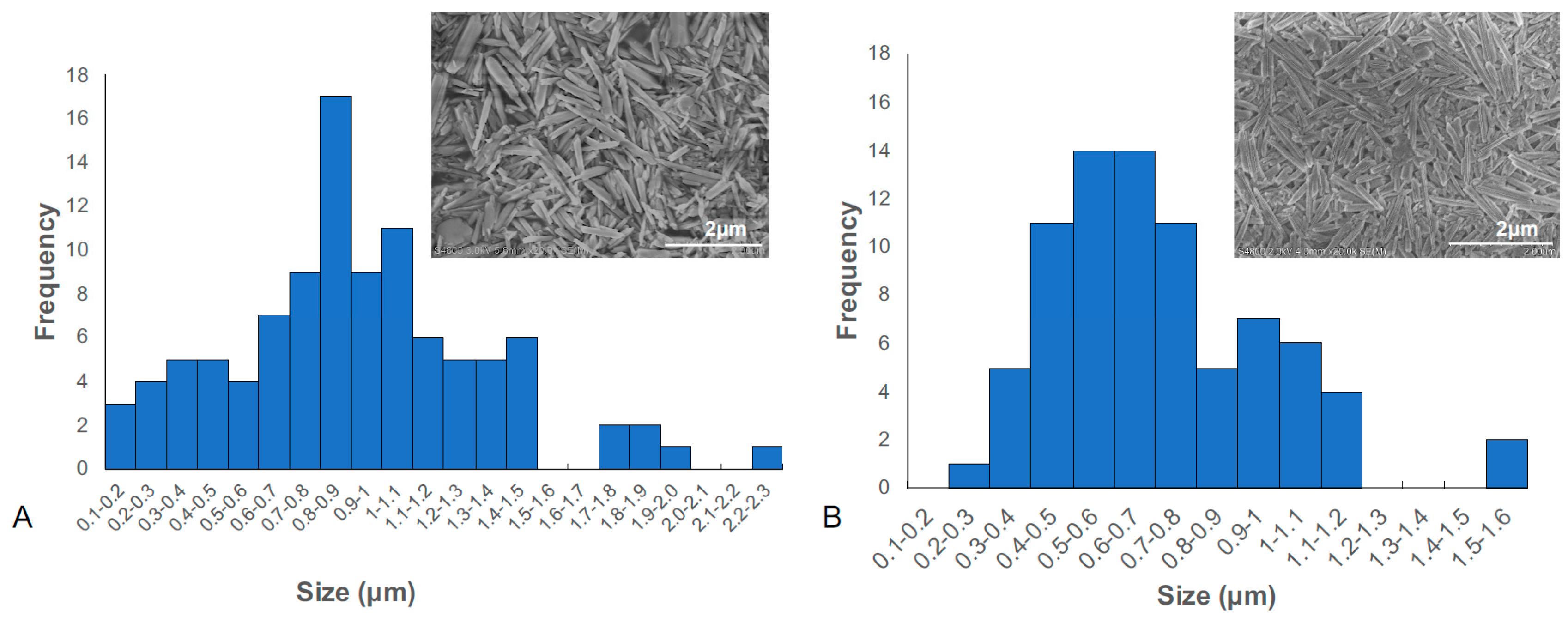
3.2.1. Nanoparticle Size Determination
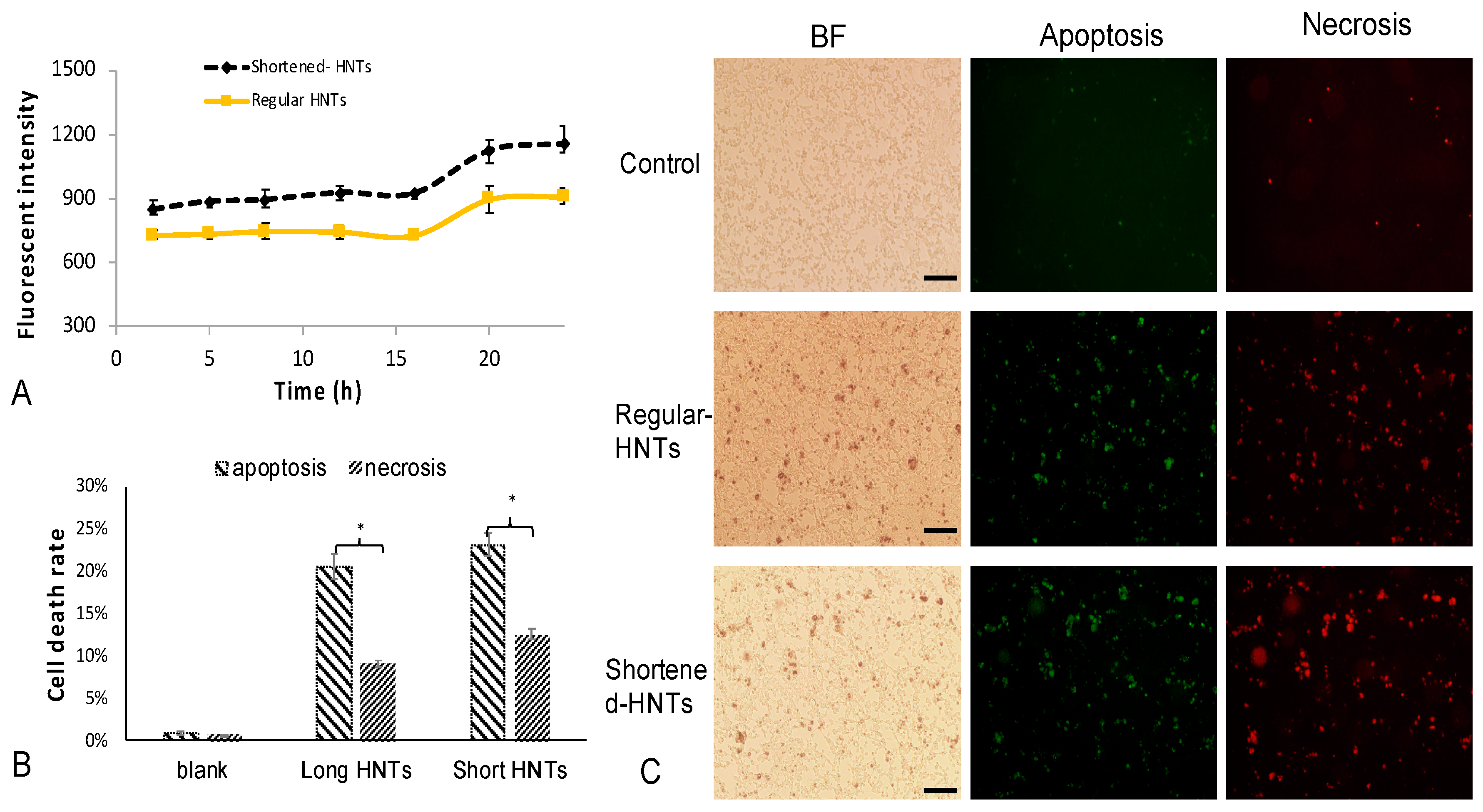
3.2.2. Cellular Interaction after Exposure to Long and Shortened HNTs
3.2.3. Apoptosis and Necrosis
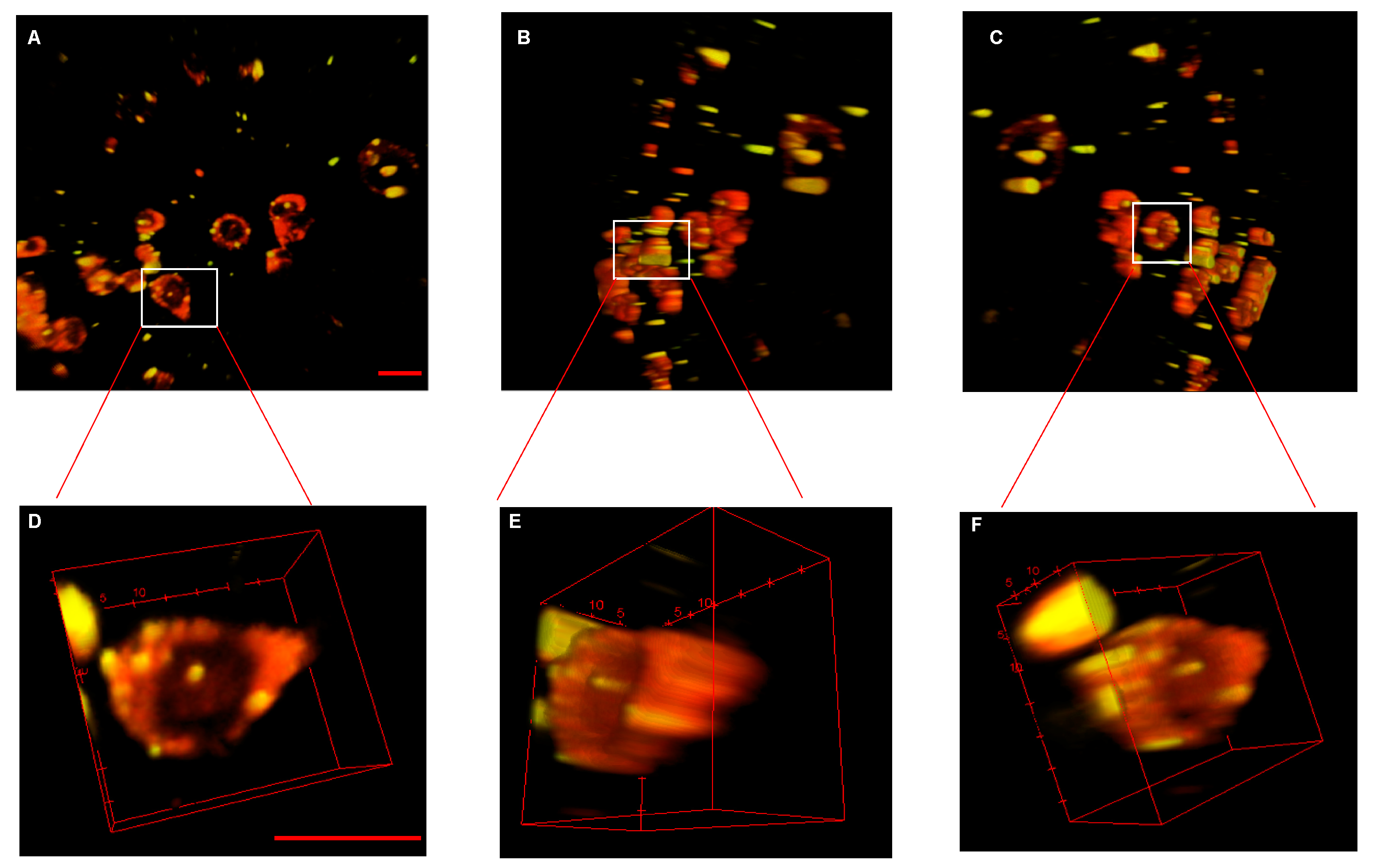
3.3. Intracellular Location of bi-HNTs
3.4. Targeted Drug Delivery
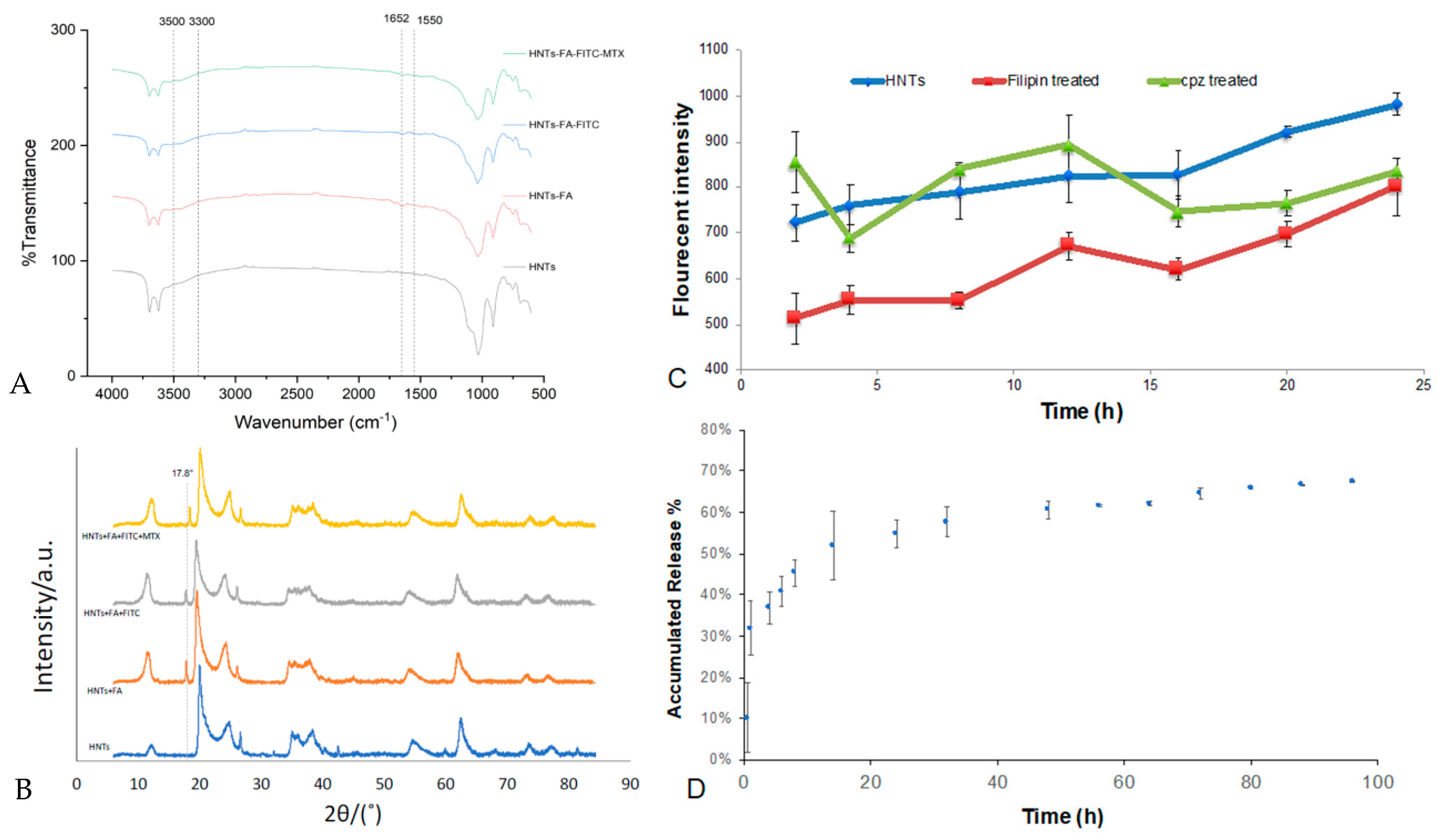
3.4.1. Folic Acid Coating and Drug Releasing
3.4.2. Cellular Uptake Mechanisms
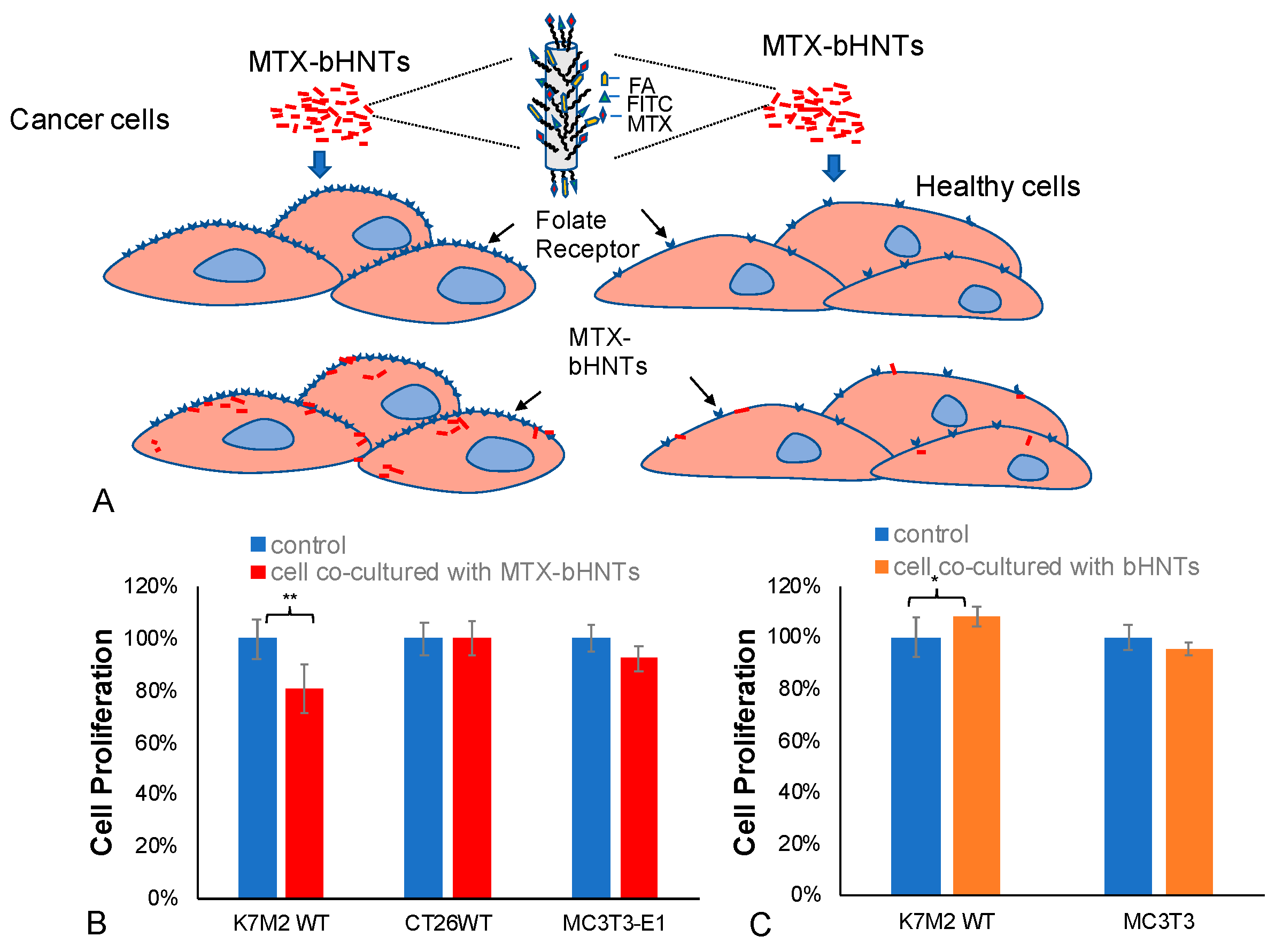
3.4.3. In Vitro Targeted Drug Release-Cellular Specificity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1749–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seigel, R.; Jemal, A. American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures 2015; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Caraglia, M.; De Rosa, G.; Abbruzzese, A.; Leonetti, C. Nanotechnologies: New Opportunities for Old Drugs. The Case of Aminobisphosphonates. J. Nanomed. Biother. Discov. 2011, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-A.; Choi, J.R.; Kim, J.-O.; Shin, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, J.-H. Influence of Reduced Folate Carrier and Dihydrofolate Reductase Genes on Methotrexate-Induced Cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 42, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lima, S.A.C.; Gaspar, A.; Reis, S.; Durães, L. Multifunctional nanospheres for co-delivery of methotrexate and mild hyperthermia to colon cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Polymeric Nanoparticles Containing Methotrexate to Improve Lymphatic Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harila-Saari, A.H.; Vainionpää, L.K.; Kovala, T.T.; Tolonen, E.U.; Marjatta Lanning, M.D.B. Nerve lesions after therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 1998, 82, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaïes, E.; Jebabli, N.; Trabelsi, S.; Salouage, I.; Charfi, R.; Klouz, M.L.A.A. Methotrexate Side Effects: Review Article. J. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 3, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrat, Y.; Naumenko, E.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Lvov, Y.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Tubular Nanocontainers for Drug Delivery. In Materials Nanoarchitectonics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar]
- Dionisi, C.; Hanafy, N.A.; Nobile, C.; De Giorgi, M.; Rinaldi, R.; Casciaro, S.; Lvov, Y.M.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes as Carriers for Curcumin: Characterization and Application. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2016, 15, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Zhong, S. Multifunctional halloysite nanotubes for targeted delivery and controlled release of doxorubicin in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 375101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, E.; Avgoustakis, K.; Pšenička, M.; Pospíšil, M.; Papoulis, D. Halloysite nanotubes as carriers for irinotecan: Synthesis and characterization by experimental and molecular simulation methods. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Lvov, Y.M.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Resveratrol Delivery to Cancer Cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, T.; Ruttala, H.B.; Gupta, B.; Poudel, B.K.; Choi, H.-G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Smart chemistry-based nanosized drug delivery systems for systemic applications: A comprehensive review. J. Control. Release 2017, 258, 226–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leamon, C. Folate-targeted chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, W.R.; Luo, Y.; McFarland, J.A.W.; Mills, D.K. Bi-Functionalized Clay Nanotubes for Anti-Cancer Therapy. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Holly, K.S.; Voziyanov, V.; Villalba, S.L.; Tong, R.; Grigsby, H.E.; Glasscock, E.; Szele, F.G.; Vlachos, I.; Murray, T.A. Gradient Index Microlens Implanted in Prefrontal Cortex of Mouse Does Not Affect Behavioral Test Performance over Time. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernici, C.D.; Kemp, B.S.; Murray, T.A. Time course images of cellular injury and recovery in murine brain with high-resolution GRIN lens system. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riela, S.; Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Bommarito, A.; Giordano, C.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Poma, P.; Lazzara, G. Development and characterization of co-loaded curcumin/triazole-halloysite systems and evaluation of their potential anticancer activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Wang, A.; Muhammad, F.; Qi, W.; Ren, H.; Guo, Y.-J.; Zhu, G. Halloysite Nanotubes, a Multifunctional Nanovehicle for Anticancer Drug Delivery. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikulina, A.; Voronin, D.; Fakhrullin, R.; Vinokurov, V.; Volodkin, D. Naturally derived nano- and micro-drug delivery vehicles: Halloysite, vaterite and nanocellulose. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 5638–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediako, E.G.; Nyankson, E.; Dodoo-Arhin, D.; Agyei-Tuffour, B.; Łukowiec, D.; Tomiczek, B.; Yaya, A.; Efavi, J.K. Modified halloysite nanoclay as a vehicle for sustained drug delivery. Heliyon 2018, 4, E00869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.-F.; He, R.-R.; Liu, M. Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Doxorubicin for Breast Cancer Using Chitosan Oligosaccharide-Modified Halloysite Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26578–26590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.-F.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.-B.; Jia, N.-Q. Functionalized halloysite nanotube-based carrier for intracellular delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, M.; Piana, S.; Colletti, C.G.; Noto, R.; Riela, S.; Baiamonte, C.; Giordano, C.; Pizzolanti, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; et al. Multicavity halloysite–amphiphilic cyclodextrin hybrids for co-delivery of natural drugs into thyroid cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4074–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.M.; Kumar, A.; Suneetha, M.; Han, S.S. pH and near-infrared active; chitosan-coated halloysite nanotubes loaded with curcumin-Au hybrid nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chang, Y.; Yang, J.; You, Y.; He, R.; Chen, T.; Zhou, C. Functionalized halloysite nanotube by chitosan grafting for drug delivery of curcumin to achieve enhanced anticancer efficacy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzamukova, M.R.; Naumenko, E.A.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Enzyme-activated intracellular drug delivery with tubule clay nanoformulation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.; Prajapati, N.; DeCoster, M.; Lvov, Y. Tagged halloysite nanotubes as a carrier for intercellular delivery in brain microvascular endothelium. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalieva, R.F.; Ishmukhametov, I.R.; Batasheva, S.N.; Rozhina, E.V.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Uptake of halloysite clay nanotubes by human cells: Colourimetric viability tests and microscopy study. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 15, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Boyer, C.; Grimes, R.; Mills, D. Drug Coated Clay Nanoparticles for Delivery of Chemotherapeutics. Curr. Nanosci. 2016, 12, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Shojaei, S.; Safa, K.D.; Ghasemi, Z.; Salehi, R.; Yousefi, B.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V. Biocompatible magnetic tris(2-aminoethyl)amine functionalized nanocrystalline cellulose as a novel nanocarrier for anticancer drug delivery of methotrexate. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Neoh, K.G.; Huang, C.; Shi, Z.; Kang, E.-T. Polyacrylamide hybrid nanogels for targeted cancer chemotherapy via co-delivery of gold nanoparticles and MTX. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 412, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Kim, S.-H.; Thambi, T.; Gil You, D.; Jeon, J.; Lee, J.O.; Chung, B.Y.; Jo, D.-G.; Park, J.H. A hyaluronic acid–methotrexate conjugate for targeted therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7632–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, N.; Turk, M.J.; Westrick, E.; Lewis, J.D.; Low, P.S.; Leamon, C.P. Folate receptor expression in carcinomas and normal tissues determined by a quantitative radioligand binding assay. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 338, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dramou, P.; Fizir, M.; Taleb, A.; Itatahine, A.; Dahiru, N.S.; Mehdi, Y.A.; Wei, L.; Zhang, J.; He, H. Folic acid-conjugated chitosan oligosaccharide-magnetic halloysite nanotubes as a delivery system for camptothecin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Lai, H.; Lu, C.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, X. Methotrexate-loaded PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo antitumoral activity. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-P.; Yang, J.; Gao, H.-Y.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.-F.; He, R.-R.; Liu, M. Folate-Conjugated Halloysite Nanotubes, an Efficient Drug Carrier, Deliver Doxorubicin for Targeted Therapy of Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Gao, R.-Y.; Liu, X.-C.; Du, H.-H.; Zhang, J.-L.; Ai, X.-C.; Zhang, J.-P.; Fu, L.-M.; Skibsted, L.H. Naturally occurring nanotube with surface modification as biocompatible, target-specific nanocarrier for cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials 2019, 190, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.-G.; Liu, S.-L.; Yao, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; Tian, W. Intracellular pathway of halloysite nanotubes: Potential application for antitumor drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Humayun, A.; Murray, T.A.; Kemp, B.S.; McFarland, A.; Liu, X.; Mills, D.K. Cellular Analysis and Chemotherapeutic Potential of a Bi-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotube. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100962
Luo Y, Humayun A, Murray TA, Kemp BS, McFarland A, Liu X, Mills DK. Cellular Analysis and Chemotherapeutic Potential of a Bi-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotube. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(10):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100962
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yangyang, Ahmed Humayun, Teresa A. Murray, Benjamin S. Kemp, Antwine McFarland, Xuan Liu, and David K. Mills. 2020. "Cellular Analysis and Chemotherapeutic Potential of a Bi-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotube" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 10: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100962
APA StyleLuo, Y., Humayun, A., Murray, T. A., Kemp, B. S., McFarland, A., Liu, X., & Mills, D. K. (2020). Cellular Analysis and Chemotherapeutic Potential of a Bi-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotube. Pharmaceutics, 12(10), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100962