Development and Characterization of Eudragit®-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats and Their Formulation into Nanofiber Tablets for the Modified Release of Furosemide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Preparation of the Electrospinning Solutions and Fabrication of Micro-/Nanofibrous Mats
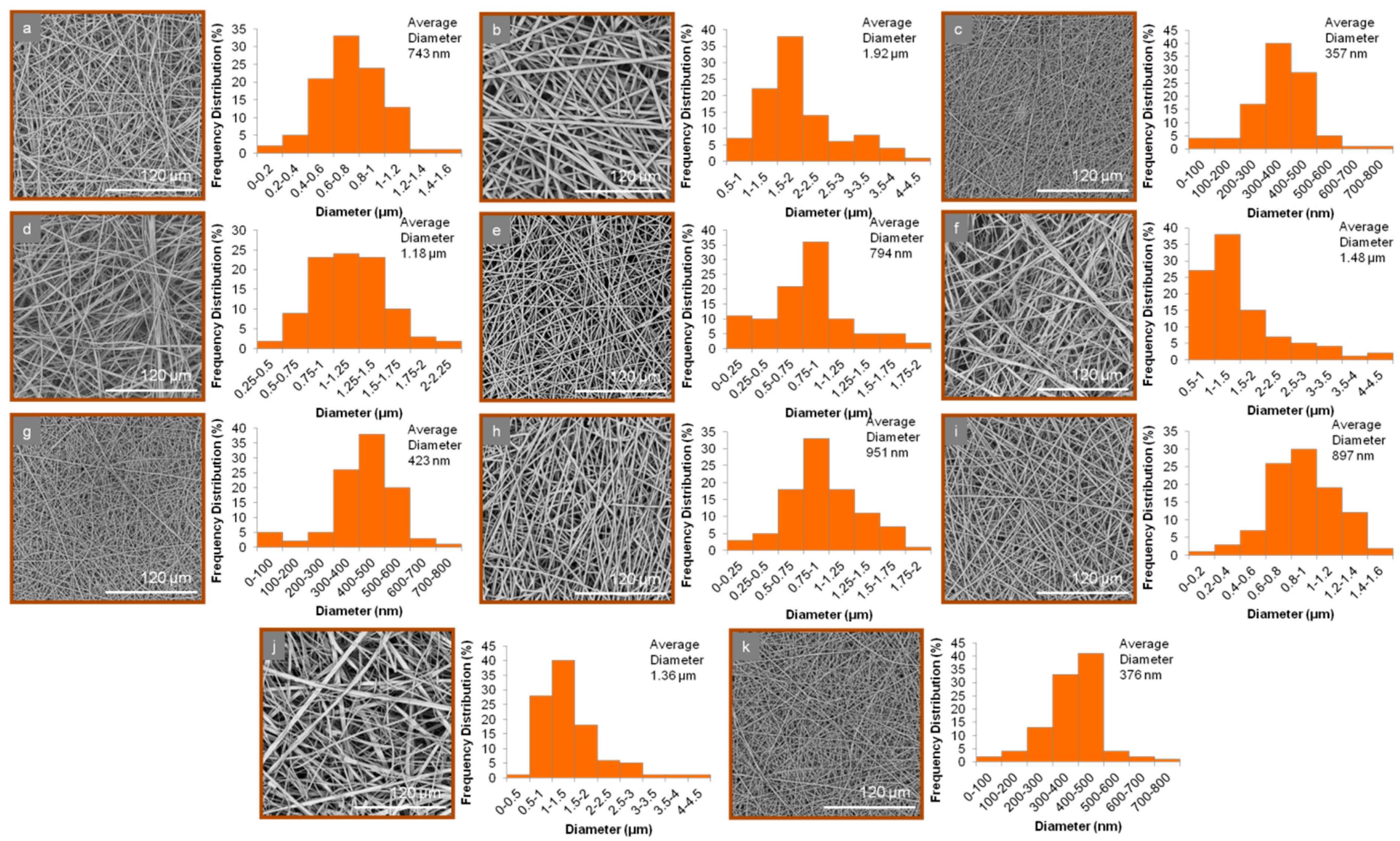
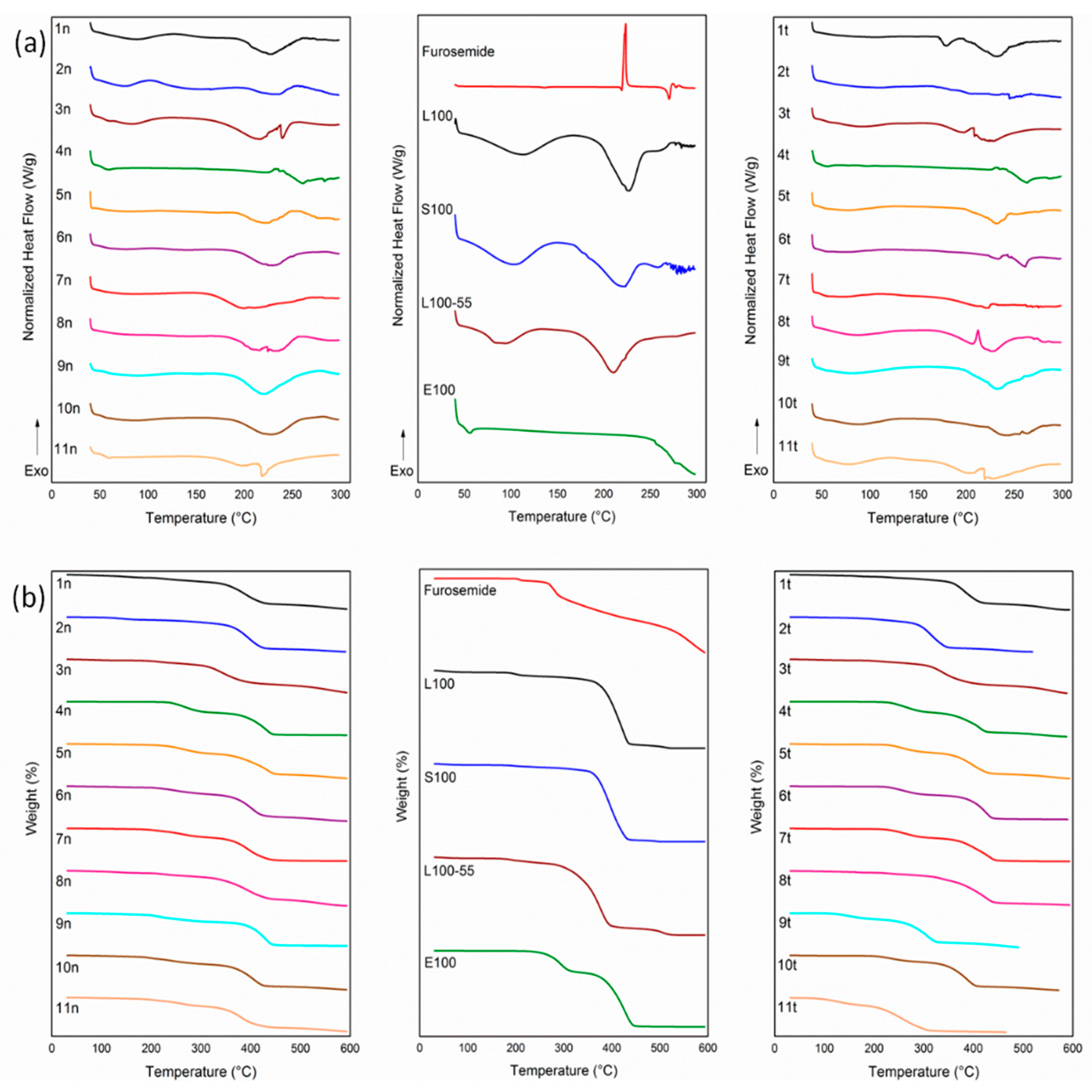
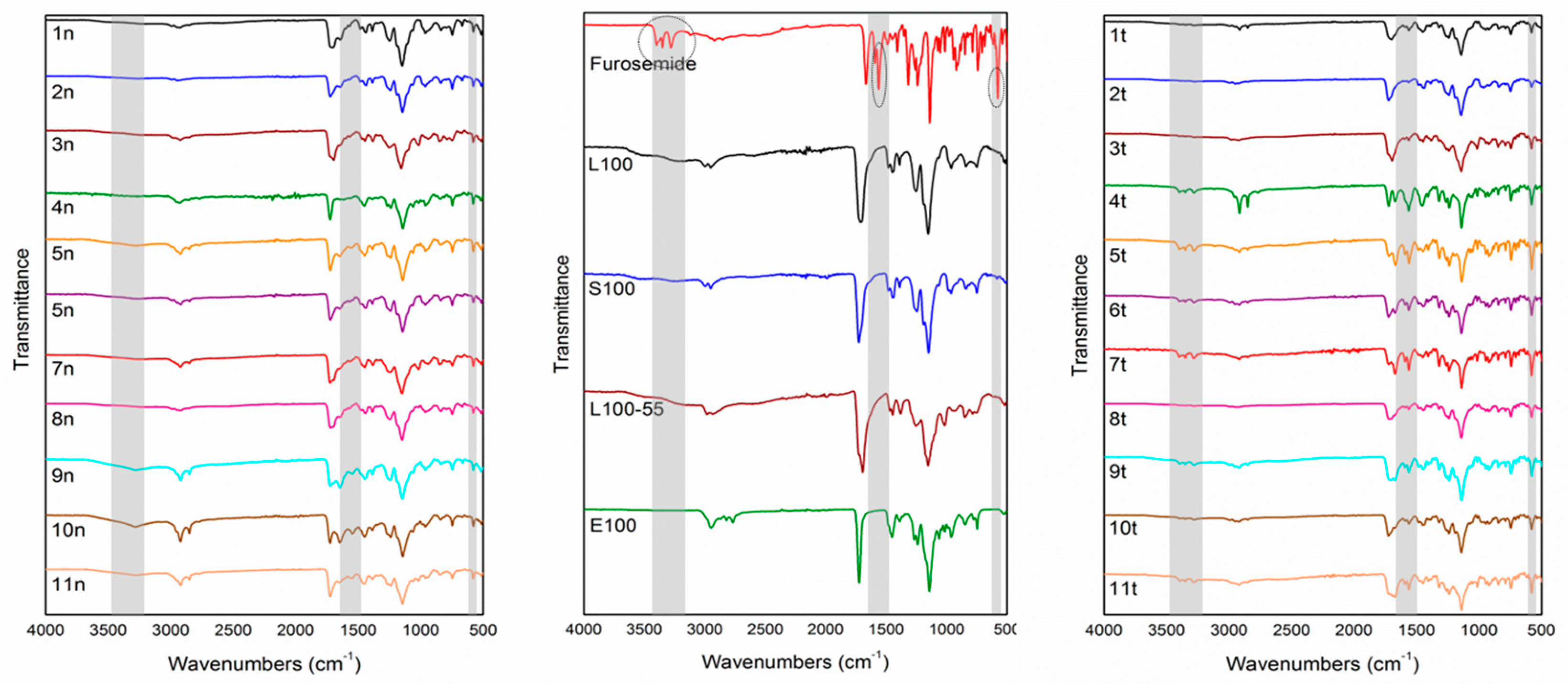
2.4. Characterization of Micro-/Nanofibrous Mats
2.5. Preparation of Nanofiber Tablets
2.6. Preparation of Matrix Tablets
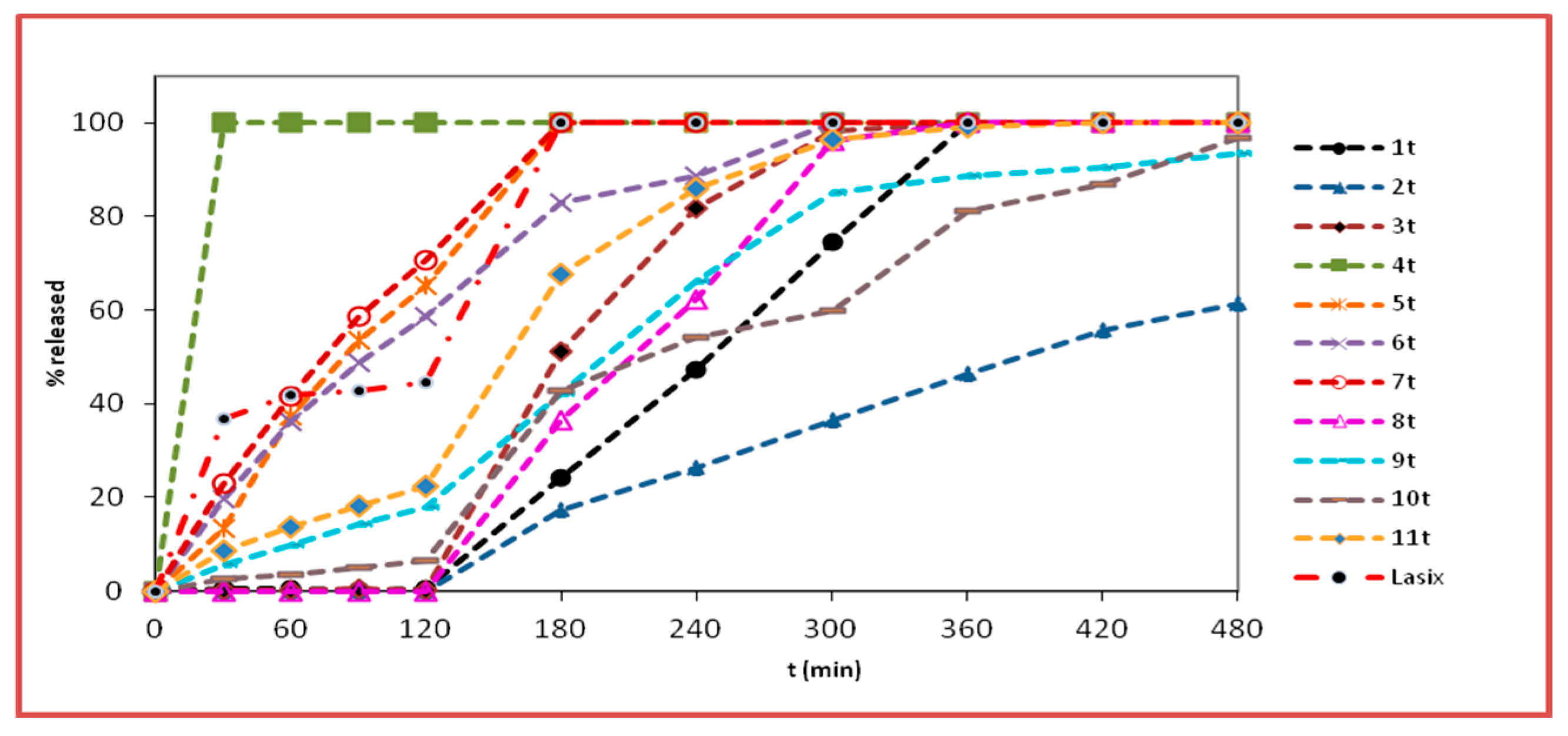
2.7. Dissolution Studies
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Provenza, N.; Calpena, A.C.; Mallandrich, M.; Sánchez, A.; Egea, M.A.; Clares, B. Permeation studies through porcine small intestine of furosemide solutions for personalised paediatric administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Kiriyama, A.; Nishimura, E.; Sakata, S.; Inoue, D.; Furubayashi, T.; Yutani, R.; Tanaka, A.; Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; et al. Novel strategy for the systemic delivery of furosemide based on a new drug transport mechanism. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banzett, R.B.; Schwartzstein, R.M.; Lansing, R.W.; O’Donnell, C.R. Aerosol furosemide for dyspnea: High-dose controlled delivery does not improve effectiveness. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2018, 247, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles Ponto, L.L.; Schoenwald, R.D. Furosemide (Frusemide): A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic review (Part I). Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 18, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, D.P.; de Villiers, M.M. All-atomistic molecular dynamics (AA-MD) studies and pharmacokinetic performance of PAMAM-dendrimer-furosemide delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyralides, G.G.; Dallas, P.P.; Rekkas, D.M. Development and in vitro evaluation of furosemide transdermal formulations using experimental design techniques. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 281, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perioli, L.; D’Alba, G.; Pagano, C. New oral solid dosage form for furosemide oral administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, L.Å.; Jogestrand, Τ.; Larsen, F.; Walldius, G.; Tedner, B. Effects of furosemide and slow-release furosemide on thoracic fluid volumes. Clin. Cardiol. 1986, 9, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efentakis, M.; Koutlis, A.; Vlachou, M. Development and evaluation of oral multiple-unit and single-unit hydrophilic controlled-release systems. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2010, 1, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Verma, S.; Shukla, S.B.; Jain, A.K.; Jain, P.; Yadav, P. Formulation and evaluation of gastroretentive tablets of furosemide (Evaluation based on drug release kinetics and factorial designs). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 935–978. [Google Scholar]
- Terao, T.; Matsuda, K.; Shouji, H. Improvement in site-specific intestinal absorption of furosemide by Eudragit® L100-55. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceves, J.M.; Cruz, R.; Hernandez, E. Preparation and characterization of furosemide-Eudragit® controlled release systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 195, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.; Siamidi, A.; Geraniou, E. Modified release of furosemide from Eudragits® and poly(ethylene oxide)-based matrices and dry-coated tablets. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.; Siamidi, A.; Kyriakou, S. Electrospinning and Drug Delivery. In Electrospinning and Electrospraying-Techniques and Applications; Haider, S., Haider, A., Eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, A.; Démuth, B.; Meskó, A.; Zelkó, R. Preformulation studies of furosemide-loaded electrospun nanofibrous systems for buccal administration. Polymers 2017, 9, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, D.G.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, X.K.; Deng, Y.C.; Zhao, M. Electrospun hypromellose-based hydrophilic composites for rapid dissolution of poorly water-soluble drug. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.H.; Bligh, S.W.; Williams, G.R. Nanofibers fabricated using triaxial electrospinning as zero order drug delivery systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18891–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-G.; Li, H.-P.; Yang, C.; Li, J.-J.; Wang, Q.; Williams, G.R. Double-pulsatile release core-shell fibers fabricated using modified tri-axial electrospinning. J. Control. Release 2017, 259, e24–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Yu, D.G.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Williams, G.R.; Bligh, S.W.A. Theranostic fibers for simultaneous imaging and drug delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, M.; Kikionis, S.; Siamidi, A.; Tragou, K.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V.; Tsotinis, A. Modified in vitro release of melatonin loaded in nanofibrous electrospun mats incorporated into mono-layered and three-layered tablets. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.A. The concept of dissolution efficiency. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1975, 27, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, W.R.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A simple equation for the description of solute release coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, G.; Singh, M. Review: In-vitro drug release characterization models. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ummadi, S.; Shravani, B.; Raghavendra Rao, N.G.; Reddy, S.; Sanjeev, B. Overview on controlled release dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 258–269. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, J.A.; Garnero, C.; Zoppi, A.; Sterren, V.; Ayala, A.P.; Longhi, M.R. Characterization of systems with amino-acids and oligosaccharides as modifiers of biopharmaceutical properties of furosemide. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Yu, Q.; Liu, X.; Hu, F.; Yuan, H. Preparation and characterization of a novel aqueous dispersion for enteric coating of pantoprazole sodium pellets. Acta Pharm. 2018, 68, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.I.; Štedul, H.P.; Kurjaković, N. A pH-dependent colon targeted oral drug delivery system using methacrylic acid copolymers. II. Manipulation of drug release using Eudragit® L100 and Eudragit® S100 combinations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.I.; Prebeg, Ž.; Kurjaković, N. A pH-dependent colon targeted oral drug delivery system using methacrylic acid copolymers: I. Manipulation of drug release using Eudragit® L100-55 and Eudragit® S100 combinations. J. Control. Release 1999, 58, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegiel, L.A.; Mauer, L.J.; Edgar, K.J.; Taylor, L.S. Mid-infrared spectroscopy as a polymer selection tool for formulating amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, K.; Li, H.; Abo-zeid, Y.; Williams, F.; Williams, G.R. The effect of molecular properties on active ingredient release from electrospun Eudragit® fibers. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.K.; Jagwani, Y. Mixed hydrotropy: Novel science of solubility enhancement. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 73, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, D.D.; Tang, J.F.; Chang, Y. The use of furosemide in critically ill trauma patients: A retrospective review. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock. 2014, 7, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredients | 1n | 2n | 3n | 4n | 5n | 6n | 7n | 8n | 9n | 10n | 11n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furosemide | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| L100 | 180 | 60 | 60 | 120 | |||||||
| S100 | 180 | 60 | 60 | 120 | |||||||
| L100-55 | 180 | 60 | 60 | 120 | |||||||
| E100 | 180 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 60 | ||||
| Total | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Ingredients | 1t | 2t | 3t | 4t | 5t | 6t | 7t | 8t | 9t | 10t | 11t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furosemide | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| L100 | 178 | 59 | 59 | 119 | |||||||
| S100 | 178 | 59 | 59 | 119 | |||||||
| L100-55 | 178 | 59 | 60 | 119 | |||||||
| E100 | 178 | 119 | 119 | 119 | 59 | 59 | 59 | ||||
| Mg stearate | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Fiber Mat | Average Diameter | Size Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1n | 743 ± 214 nm | 103 nm–1.41 μm |
| 2n | 1.92 ± 0.46 μm | 597 nm–4.13 μm |
| 3n | 357 ± 114 nm | 46 nm–738 nm |
| 4n | 1.18 ± 0.36 μm | 280 nm–2.40 μm |
| 5n | 794 ± 198 nm | 77 nm–1.83 μm |
| 6n | 1.48 ± 0.34 μm | 514 nm–4.07 μm |
| 7n | 423 ± 140 nm | 44 nm–779 nm |
| 8n | 951 ± 255 nm | 99 nm–1.98 μm |
| 9n | 897 ± 268 nm | 77 nm–1.83 μm |
| 10n | 1.36 ± 0.29 μm | 156 nm–4.32 μm |
| 11n | 376 ± 118 nm | 45 nm–658 nm |
| Formulations | t20% ± SD b | t50% ± SD b | t90% ± SD b | D.E.% a ± SD b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1t | 169.7 ± 2.5 | 245.7 ± 1.2 | 336.0 ± 2.6 | 49.6 ± 4.0 |
| 2t | 199.7 ± 0.9 | 384.0 ± 1.7 | - | 26.6 ± 0.1 |
| 3t | 144.0 ± 0.8 | 178.7 ± 0.6 | 269.8 ± 1.3 | 60.3 ± 3.8 |
| 4t | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 15.0 ± 0.6 | 27.3 ± 1.1 | 93.8 ± 0.6 |
| 5t | 39.0 ± 0.8 | 83.3 ± 1.5 | 163.3 ± 1.5 | 81.0 ± 2.3 |
| 6t | 31.0 ± 1.6 | 94.7 ± 1.2 | 247.7 ± 2.1 | 76.6 ± 2.5 |
| 7t | 27.3 ± 0.5 | 75.0 ± 1.0 | 159.0 ± 1.7 | 82.4 ± 1.8 |
| 8t | 153.0 ± 0.8 | 211.3 ± 0.6 | 289.0 ± 1.7 | 55.6 ± 0.6 |
| 9t | 126.3 ± 1.2 | 200.3 ± 1.5 | 404.0 ± 2.6 | 59.9 ± 2.4 |
| 10t | 141.7 ± 0.9 | 219.0 ± 1.7 | 438.0 ± 1.00 | 47.9 ± 0.4 |
| 11t | 104.0 ± 1.4 | 156.7 ± 0.6 | 262.7 ± 0.6 | 66.8 ± 2.9 |
| 1n | 167.3 ± 1.7 | 240.3 ± 2.5 | 368.2 ± 1.8 | 51.2 ± 3.9 |
| 2n | 162.3 ± 2.1 | 281.7 ± 2.1 | 380.7 ± 1.5 | 43.4 ± 0.6 |
| 3n | 140.7 ± 0.5 | 171.3 ± 2.3 | 232.0 ± 2.0 | 63.2 ± 1.4 |
| 4n | 6.3 ± 1.2 | 15.0 ± 1.0 | 27.7 ± 2.5 | 93.8 ± 0.6 |
| 5n | 13.3 ± 2.1 | 39.3 ± 0.6 | 103.7 ± 1.5 | 89.0 ± 3.0 |
| 6n | 21.0 ± 2.4 | 59.3 ± 1.2 | 180.7 ± 1.2 | 81.9 ± 1.4 |
| 7n | 12.7 ± 0.5 | 33.3 ± 3.1 | 95.8 ± 2.8 | 89.6 ± 1.1 |
| 8n | 154.0 ± 0.8 | 224.7 ± 3.5 | 343.3 ± 1.2 | 51.6 ± 0.8 |
| 9n | 36.7 ± 0.9 | 154.7 ± 1.5 | 286.3 ± 2.1 | 67.1 ± 1.7 |
| 10n | 52.0 ± 0.8 | 191.7 ± 2.1 | 424.7 ± 2.5 | 59.0 ± 0.9 |
| 11n | 24.7 ± 1.2 | 121.0 ± 3.6 | 236.2 ± 1.8 | 74.8 ± 2.4 |
| Lasix | 16.0 ± 0.0 | 126.0 ± 0.0 | 169.3 ± 0.6 | 79.4 ± 0.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlachou, M.; Kikionis, S.; Siamidi, A.; Kyriakou, S.; Tsotinis, A.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V. Development and Characterization of Eudragit®-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats and Their Formulation into Nanofiber Tablets for the Modified Release of Furosemide. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090480
Vlachou M, Kikionis S, Siamidi A, Kyriakou S, Tsotinis A, Ioannou E, Roussis V. Development and Characterization of Eudragit®-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats and Their Formulation into Nanofiber Tablets for the Modified Release of Furosemide. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(9):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090480
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlachou, Marilena, Stefanos Kikionis, Angeliki Siamidi, Sotiria Kyriakou, Andrew Tsotinis, Efstathia Ioannou, and Vassilios Roussis. 2019. "Development and Characterization of Eudragit®-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats and Their Formulation into Nanofiber Tablets for the Modified Release of Furosemide" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 9: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090480
APA StyleVlachou, M., Kikionis, S., Siamidi, A., Kyriakou, S., Tsotinis, A., Ioannou, E., & Roussis, V. (2019). Development and Characterization of Eudragit®-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats and Their Formulation into Nanofiber Tablets for the Modified Release of Furosemide. Pharmaceutics, 11(9), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090480










