Development and Evaluation of Multifunctional Poly(Lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Embedded in Carboxymethyl β-Glucan Porous Microcapsules as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Gefitinib
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
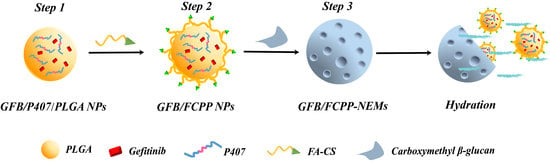
2.3. Fabrication of GFB/FCPP NPs
2.4. Fabrication of GFB/FCPP-NEMs
2.5. Characterization of the GFB/FCPP NPs and GFB/FCPP-NEMs
2.5.1. Morphological Analysis
2.5.2. Particle Size Distribution and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.5.3. Solid-State Test
2.5.4. FT-IR Spectroscopy Analysis
2.5.5. Drug Loading Amount Measurements
2.5.6. In Vitro Drug Release Test
2.6. Cellular Uptake Study
2.7. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of GFB/FCPP-NEMs
2.8. Physicochemical Stability
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of GFB/FCPP NPs and GFB/FCPP-NEMs
3.2. Solid-State Characterization
3.3. FT-IR Characterization
3.4. Drug Release Profiles
3.5. Cell Uptake and Intracellular Localization
3.6. Cytotoxicity
3.7. Physicochemical Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, J.; Hu, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, B. Development of PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor immune microenvironment and treatment for non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crino, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; Schiller, J.H.; Natale, R.B.; Miller, V.; Manegold, C.; Scagliotti, G.; Rosell, R.; Oliff, I.; Revves, A.J.; et al. Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase III trial—INTACT 2. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordella, R.; Bell, D.W.; Haber, D.A.; Settleman, J. Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science 2004, 305, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuurman, F.E.; Nuijen, B.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H. Oral anticancer drugs: Mechanisms of low bioavailability and strategies for improvement. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Saijo, Y.; Maemondo, M.; Gomi, K.; Tokue, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Ebina, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Moriya, T.; Nukiwa, T. Severe acute interstitial pneumonia and gefitinib. Lancet 2003, 361, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bajaj, N.; Xu, P.; Ohn, K.; Tsifansky, M.D.; Yeo, Y. Development of highly porous large PLGA microparticles for pulmonary drug delivery. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, S.; Haddadi, A.; Hung, R.W.; Lavasanifar, A. Targeting dendritic cells with nano-particulate PLGA cancer vaccine formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowerman, C.J.; Byrne, J.D.; Chu, K.S.; Schorzman, A.N.; Keeler, A.W.; Sherwood, C.A.; Perry, J.L.; Luft, J.C.; Darr, D.B.; Deal, A.M.; et al. Docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles improve efficacy in taxane-resistant triple-negative breast cancer. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Kuno, Y.; Sugimoto, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, Y. Surface-modified PLGA nanosphere with chitosan improved pulmonary delivery of calcitonin by mucoadhesion and opening of the intercellular tight junctions. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Han, L.; Qin, J.; Ru, G.; Li, R.; Wu, L.; Cui, D.; Yang, P.; He, Y.; Wang, J. N-trimethyl chitosan chloride-coated PLGA nanoparticles overcoming multiple barriers to oral insulin absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15430–15441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhas, N.L.; Ige, P.P.; Kudarha, R.R. Design, optimization and in-vitro study of folic acid conjugated-chitosan functionalized PLGA nanoparticle for delivery of bicalutamide in prostate cancer. Powder Technol. 2015, 283, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, R.; et al. Co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs with vitamin E TPGS by porous PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced chemotherapy against multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Nie, J.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; Mei, L.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. pH-Sensitive delivery vehicle based on folic acid-conjugated polydopamine- modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18462–18473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannon-Peppas, L.; Blanchette, J.O. Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Pluronic block copolymers: Evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiehzadeh, F.; Tafaghodi, M. Dry powder form of polymeric nanoparticles for pulmonary drug delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 2549–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesenak, M.; Urbancikova, I.; Banovcin, P. Respiratory tract infections and the role of biologically active polysaccharides in their management and prevention. Nutrients 2017, 9, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roudi, R.; Mohammadi, S.R.; Roudbary, M.; Mohsenzadegan, M. Lung cancer and beta-glucans: Review of potential therapeutic applications. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francioso, A.; Cossi, R.; Fanelli, S.; Mastromarino, P.; Mosca, L. Studies on trans-resveratrol/carboxymethylated (1,3/1,6)-beta-d-glucan association for aerosol pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Chia, H.H.; Chung, T.S. Effect of preparation temperature on the characteristics and release profiles of PLGA microspheres containing protein fabricated by double-emulsion solvent extraction/evaporation method. J. Control. Release 2000, 69, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depan, D.; Shah, J.; Misra, R.D.K. Controlled release of drug from folate-decorated and graphene mediated drug delivery system: Synthesis, loading efficiency, and drug release response. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 31, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakulska, M.M.; Donaghue, I.E.; Obermeyer, J.M.; Tuladhar, A.; McLaughlin, C.K.; Shendruk, T.N.; Shoichet, M.S. Encapsulation-free controlled release: Electrostaticadsorption eliminates the need for protein encapsulation in PLGA nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, K.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Diao, S. Three dimensional macroporous hydroxyapatite/chitosan foam-supported polymer micelles for enhanced oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 170, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Lin, Q.; Huang, Y.; Guan, G.; Jiang, Y. Tailoring the particle microstructures of gefitinib by supercritical CO2 anti-solvent process. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 20, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Saravanakumar, G.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Targeted delivery of low molecular drugs using chitosan and its derivatives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, M.; Qu, Q.; Ma, X.; Yu, S.H.; Zhao, Y. A preloaded amorphous calcium carbonate/doxorubicin@silica nanoreactor for pH-responsive delivery of an anticancer drug. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Cai, K. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles facilitated drug delivery via cascade pH stimuli in tumor microenvironment for tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannavà, C.; Tommasini, S.; Stancanelli, R.; Cardile, V.; Cilurzo, F.; Giannone, I.; Puglisi, G.; Ventura, C.A. Celecoxib-loaded PLGA/cyclodextrin microspheres: Characterization and evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity on human chondrocyte cultures. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 111, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford Versypt, A.N.; Pack, D.W.; Braatz, R.D. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery from autocatalytically degradable PLGA microspheres—A review. J. Control. Release 2013, 165, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.; Meena, J.; Katara, R.; Majumdar, D.K. Formulation and characterization of clozapine and risperidone co-entrapped spray-dried PLGA nanoparticles. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 21, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Roman, M. Synthesis and cellular uptake of folic acid-conjugated cellulose nanocrystals for cancer targeting. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosco, D.; Cilurzo, F.; Maiuolo, J.; Federico, C.; Di Martino, M.T.; Cristiano, M.C.; Tassone, P.; Fresta, M.; Paolino, D. Delivery of miR-34a by chitosan/PLGA nanoplexes for the anticancer treatment of multiple myeloma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Formulations | Particle Size (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential (mV) | 1 EE (%) | Drug Loading (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P407/PLGA NPs | 175.8 ± 11.2 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | −11.74 ± 1.24 | —— | —— |
| GFB/P407/PLGA NPs | 180.0 ± 12.3 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | −12.54 ± 2.30 | 90.42 ± 0.89 | 12.96 ± 0.41 |
| GFB/FCPP NPs | 255.4 ± 14.5 | 0.24 ± 0.09 | +3.75 ± 1.85 | 95.57 ± 1.33 | 7.68 ± 0.36 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Development and Evaluation of Multifunctional Poly(Lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Embedded in Carboxymethyl β-Glucan Porous Microcapsules as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Gefitinib. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090469
Li X, Wang J, Li S, Liu Z, Zheng Z, Zhang Y. Development and Evaluation of Multifunctional Poly(Lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Embedded in Carboxymethyl β-Glucan Porous Microcapsules as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Gefitinib. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(9):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090469
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaonan, Jinglei Wang, Shang Li, Zhaorong Liu, Zhiru Zheng, and Yanzhuo Zhang. 2019. "Development and Evaluation of Multifunctional Poly(Lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Embedded in Carboxymethyl β-Glucan Porous Microcapsules as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Gefitinib" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 9: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090469
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, J., Li, S., Liu, Z., Zheng, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Development and Evaluation of Multifunctional Poly(Lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Embedded in Carboxymethyl β-Glucan Porous Microcapsules as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Gefitinib. Pharmaceutics, 11(9), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090469