Optimization of Innovative Three-Dimensionally-Structured Hybrid Vesicles to Improve the Cutaneous Delivery of Clotrimazole for the Treatment of Topical Candidiasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Vesicle Preparation
2.3. Vesicle Characterization
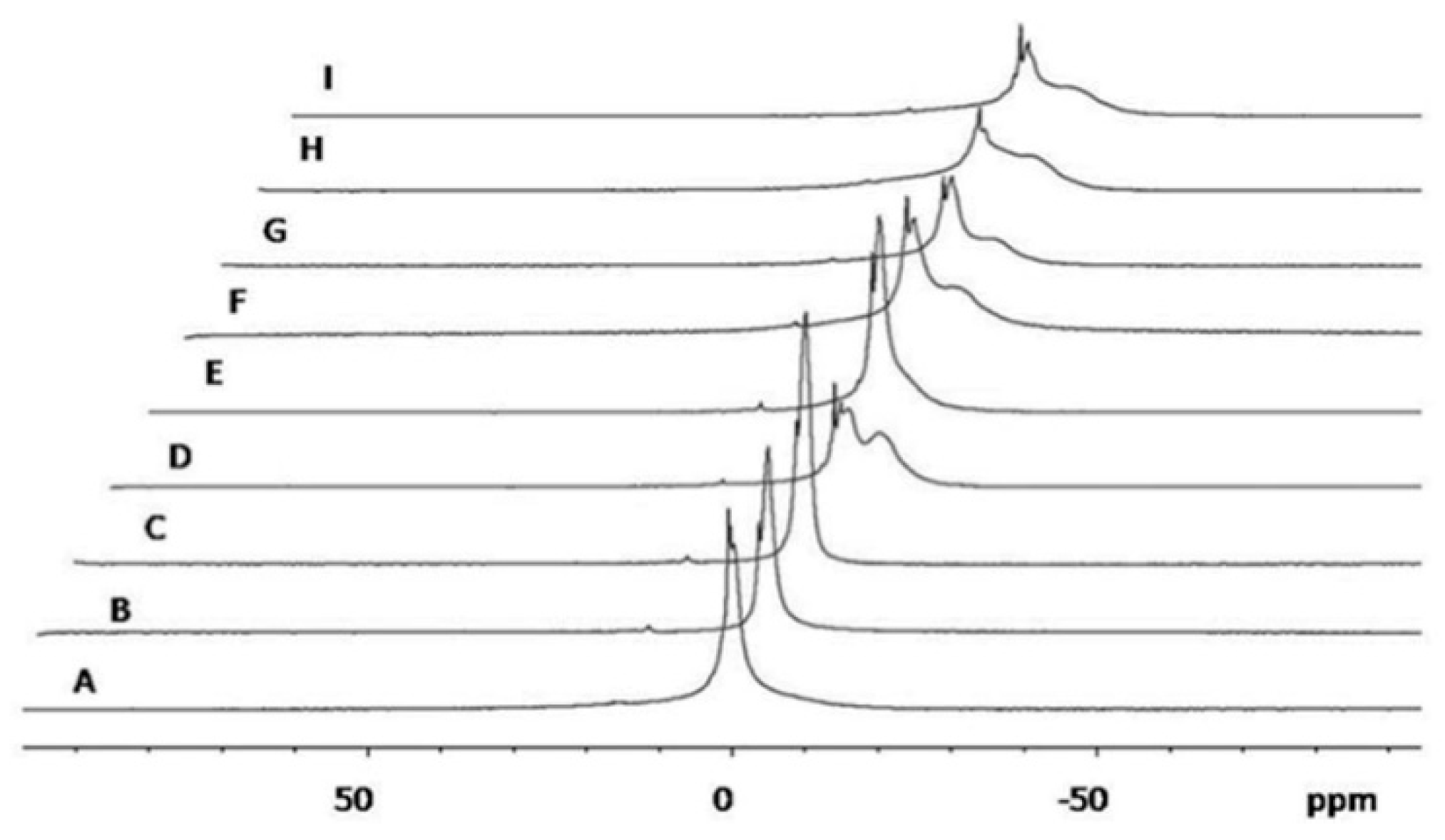
2.4. 31P-NMR Measurements
2.5. Small- and Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering
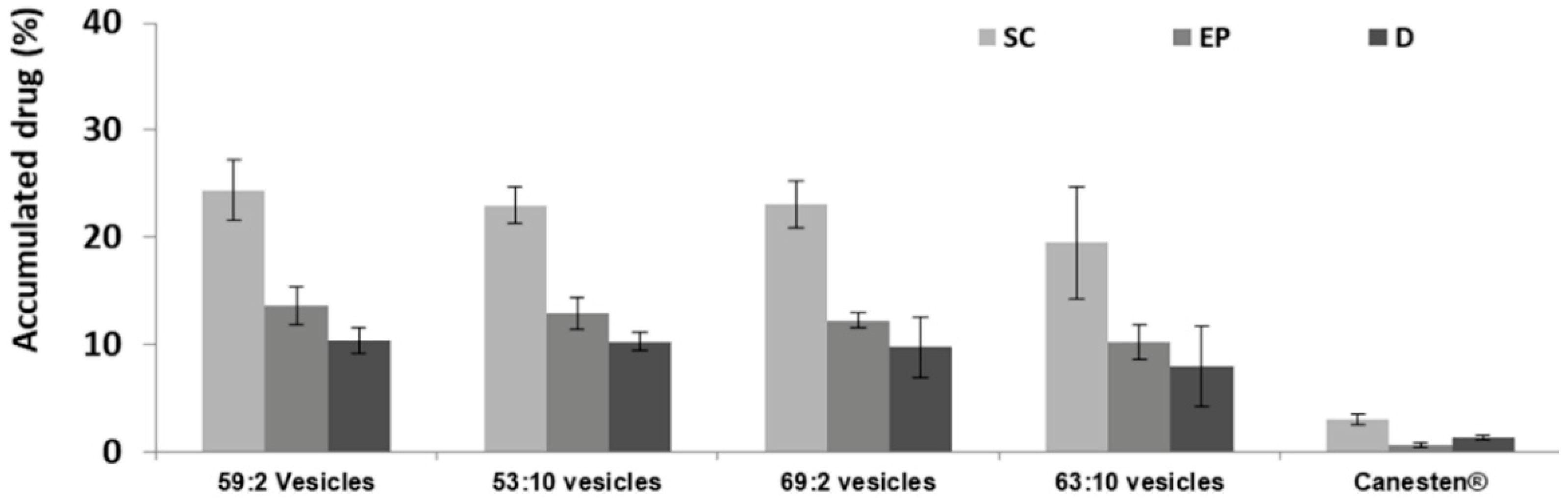
2.6. In Vitro Skin Delivery Studies
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. In Vitro Antifungal Activity
2.9. In Vivo Antifungal Activity
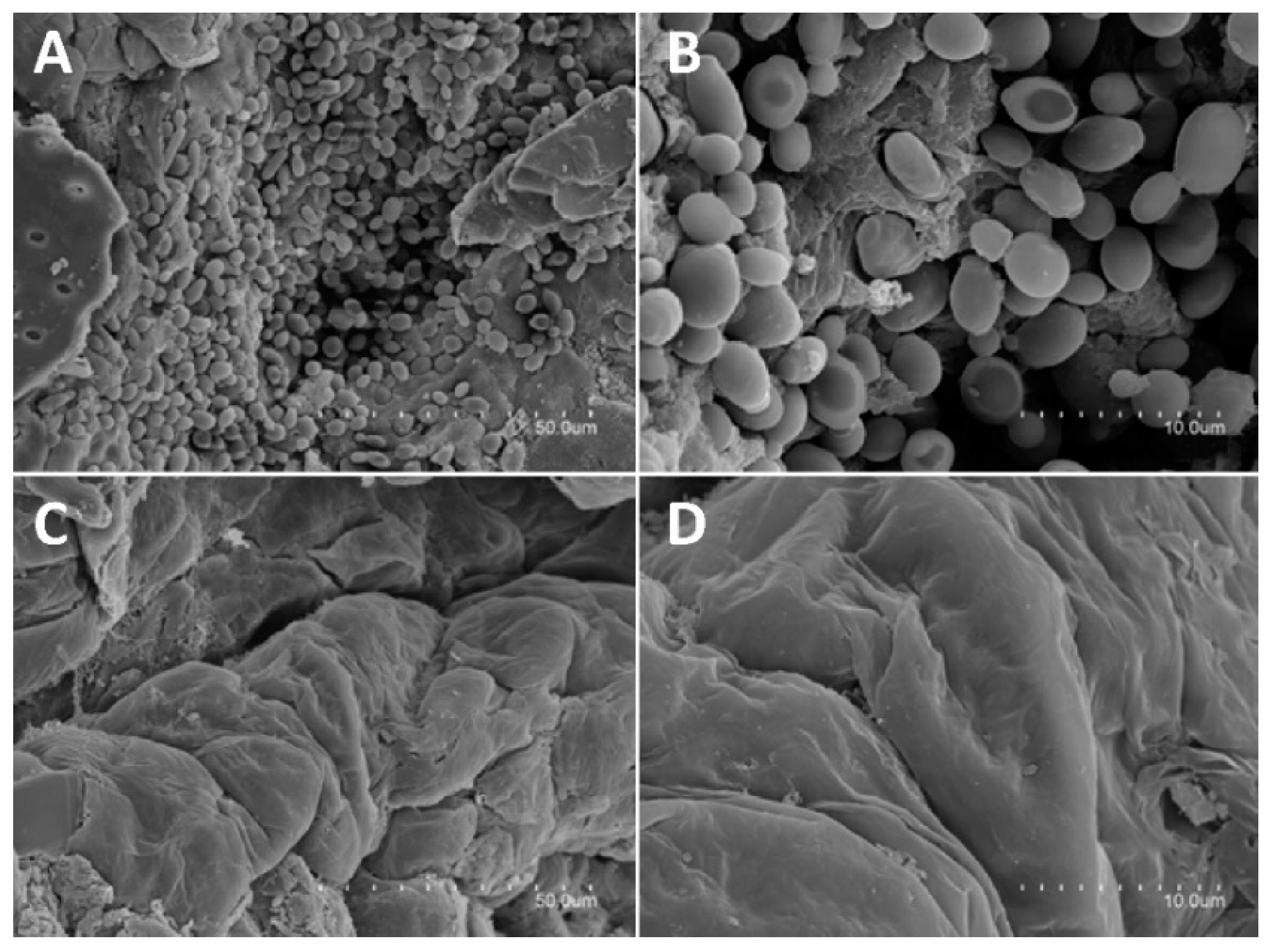
2.10. Microscopic Visualization of Skin Infected with C. albicans
2.11. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
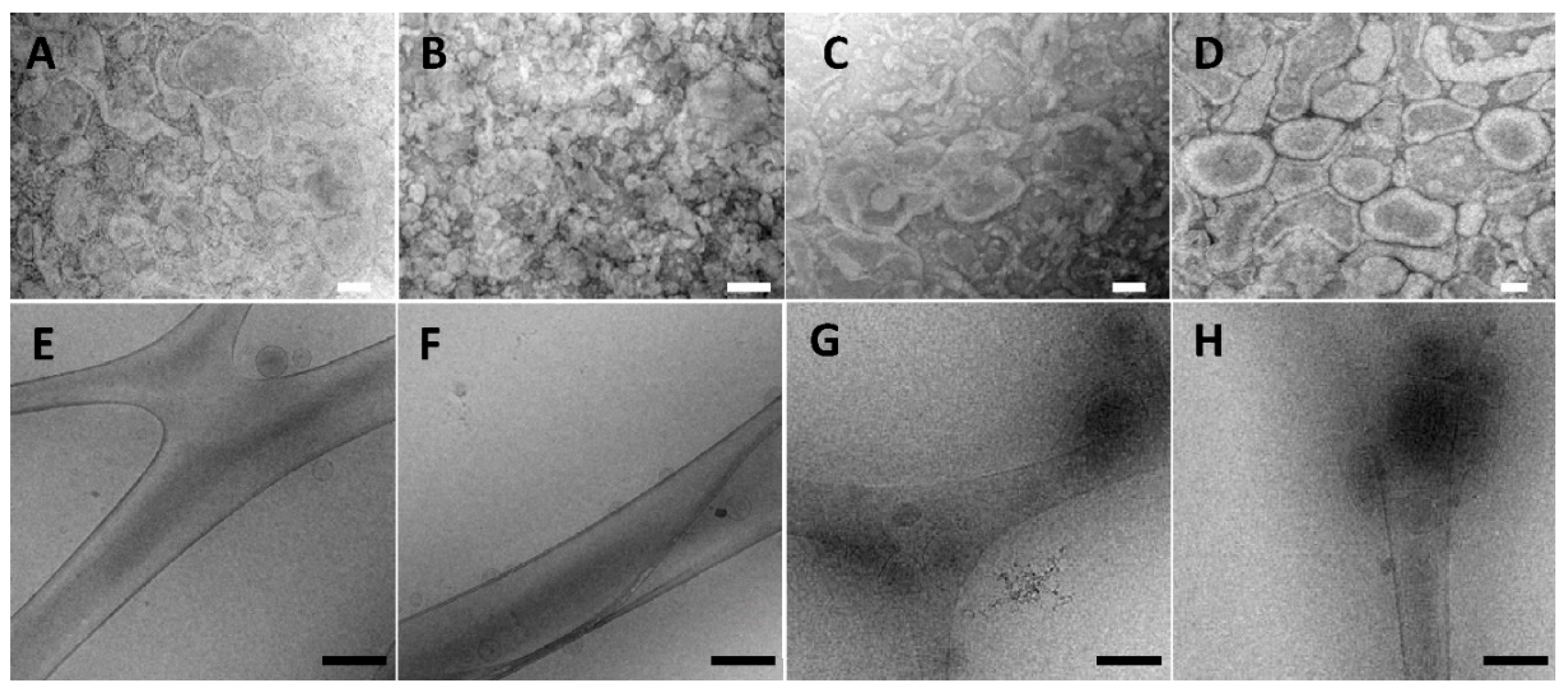
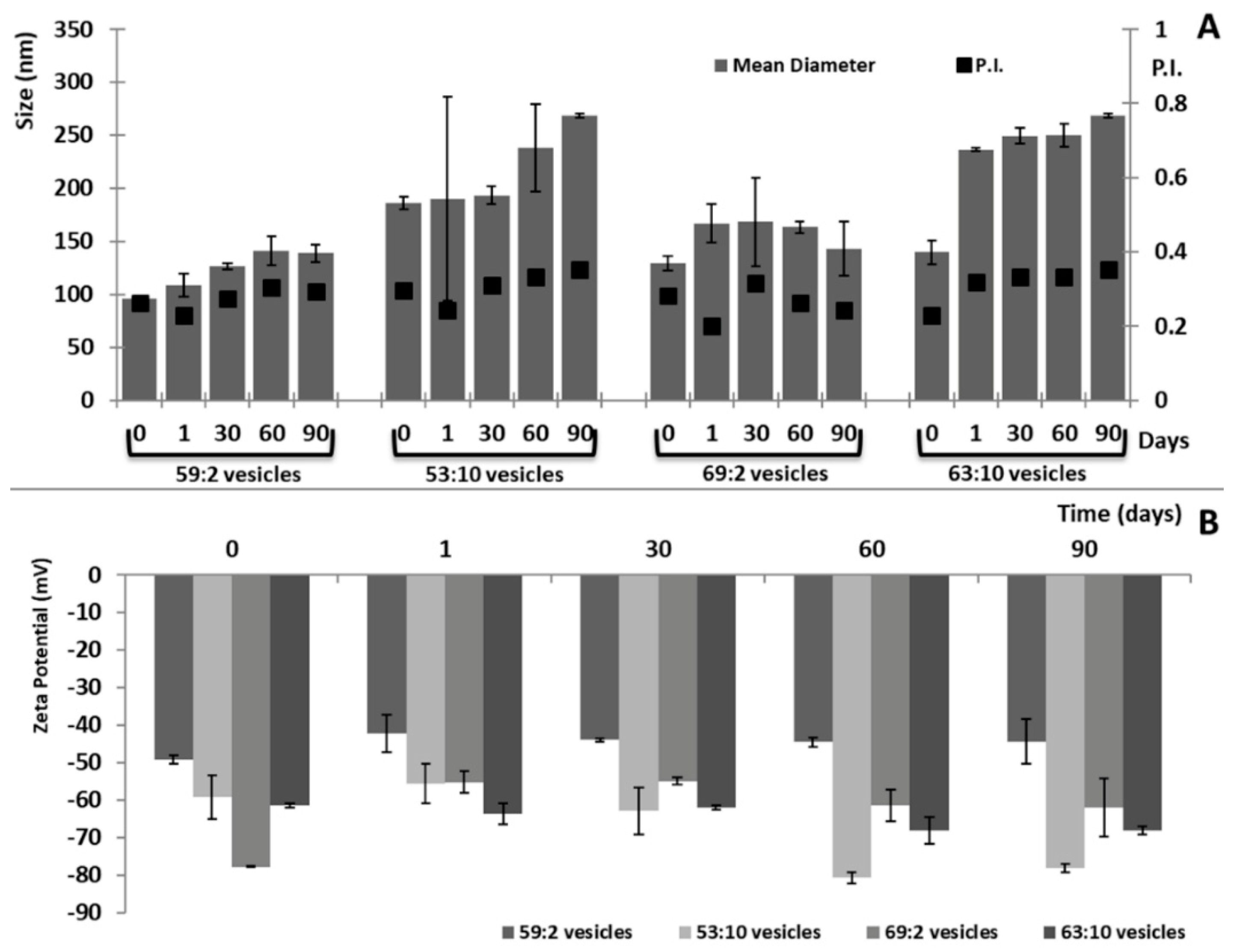
3.1. Characterization of Three-Dimensionally-Structured Hybrid Vesicles
3.2. 31P-NMR Measurements and Small- and Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS and WAXS)
3.3. In Vitro Skin Permeation Studies
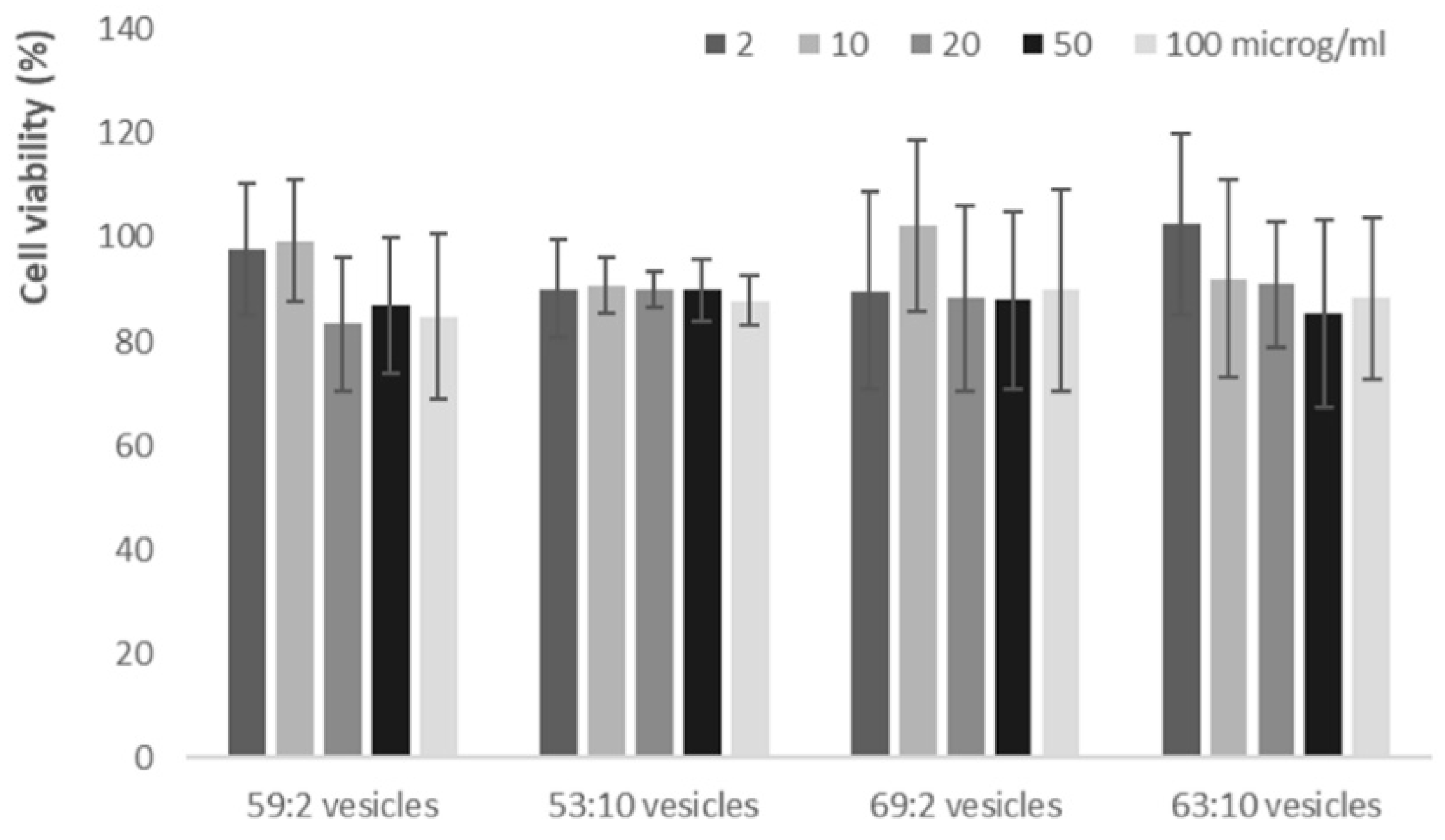
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Clotrimazole Loaded Hybrid Vesicles
3.5. In Vitro Antifungal Susceptibility Test
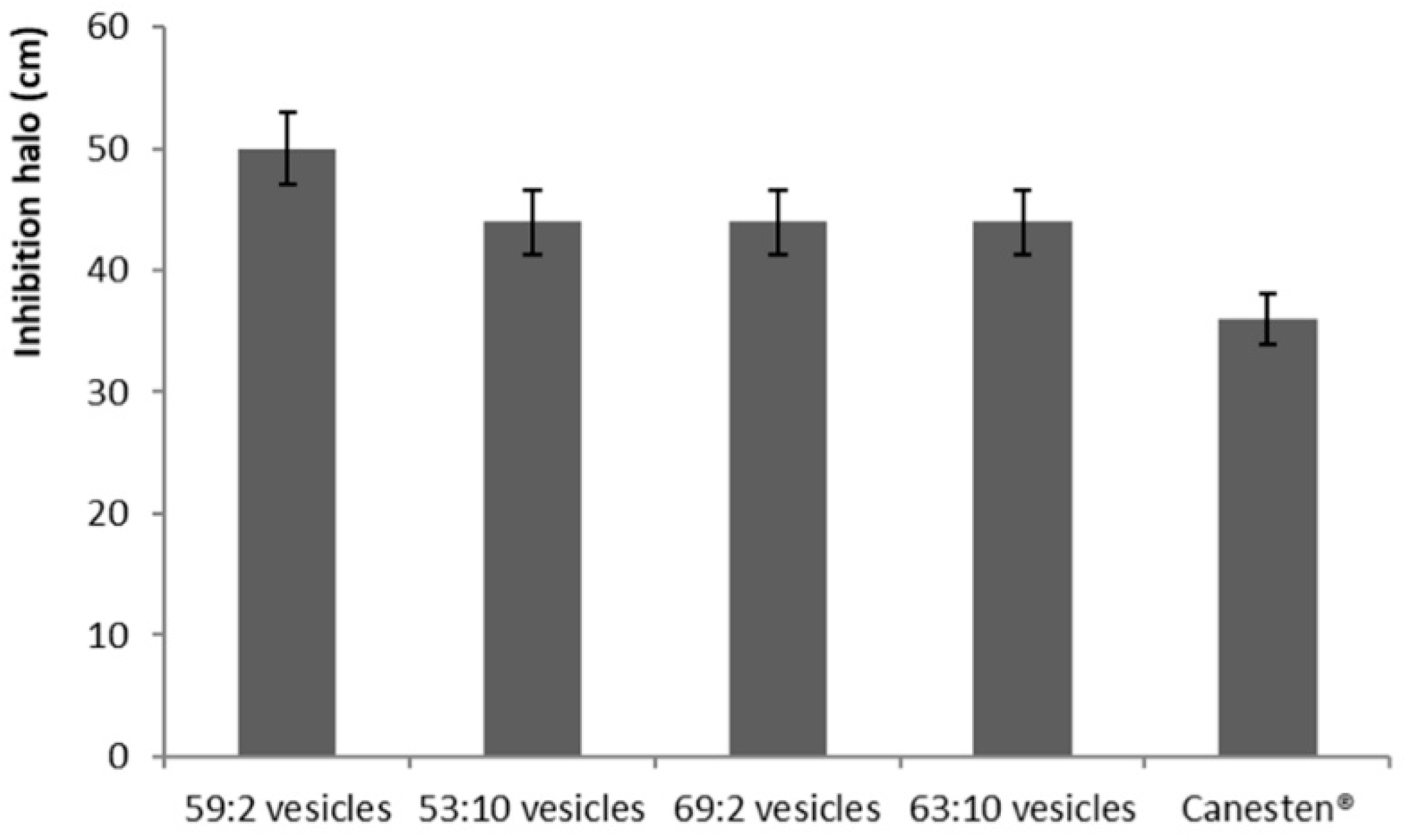
3.6. In Vivo Antifungal Activity Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dowd, F.J. Candida Albicans Infections. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Jim, E.R., Nancy, A.M.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 9780128012383. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, T.L.; Wuepper, K.D. Experimental Cutaneous Candidiasis In Rodents. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1976, 66, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, J.; Kuhn, D.M.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Hoyer, L.L.; McCormick, T.; Ghannoum, M.A. Biofilm formation by the fungal pathogen Candida albicans: Development, architecture, and drug resistance. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5385–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannoum, M.A.; Rice, L.B. Antifungal agents: Mode of action, mechanisms of resistance, and correlation of these mechanisms with bacterial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, Y.M.; Connor, B.L. Comparison of clotrimazole cream, Whitfield’s ointment and Nystatin ointment for the topical treatment of ringworm infections, pityriasis versicolor, erythrasma and candidiasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1973, 89, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, P.R.; Brogden, R.N.; Pinder, R.M.; Speight, T.M.; Avery, G.S. Clotrimazole. Drugs 1975, 9, 424–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Maibach, H.I. Deep Percutaneous Penetration into Muscles and Joints. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güngör, S.; Sedef Erdal, M.; Aksu, B. New Formulation Strategies in Topical Antifungal Therapy. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2013, 3, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.M.A.; Abdallah, O.Y.; Naggar, V.F.; Khalafallah, N.M. Lipid vesicles for skin delivery of drugs: Reviewing three decades of research. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 332, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, B.W. Novel Mechanisms and Devices to Enable Successful Trans Dermal Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeywell-Nguyen, P.L.; Bouwstra, J.A. Vesicles as a tool for transdermal and dermal delivery. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2005, 2, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, M.; Gulasekharam, V. Liposomes--a selective drug delivery system for the topical route of administration: Gel dosage form. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1982, 34, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevc, G.; Blume, G. New, highly efficient formulation of diclofenac for the topical, transdermal administration in ultradeformable drug carriers, Transfersomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2001, 1514, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Gebauer, D.; Stieber, J.; Schätzlein, A.; Blume, G. Ultraflexible vesicles, Transfersomes, have an extremely low pore penetration resistance and transport therapeutic amounts of insulin across the intact mammalian skin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1998, 1368, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir-Palomo, S.; Nácher, A.; Díez-Sales, O.; Vila Busó, O.M.A.; Caddeo, C.; Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Fadda, A.M.; Saurí, A.R. Inhibition of skin inflammation by baicalin ultradeformable vesicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touitou, E.; Dayan, N.; Bergelson, L.; Godin, B.; Eliaz, M. Ethosomes—novel vesicular carriers for enhanced delivery: Characterization and skin penetration properties. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, N.; Touitou, E. Carriers for skin delivery of trihexyphenidyl HCl: Ethosomes vs. liposomes. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainbinder, D.; Touitou, E. Testosterone Ethosomes for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery. Drug Deliv. 2005, 12, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, D.; Lucania, G.; Mardente, D.; Alhaique, F.; Fresta, M. Ethosomes for skin delivery of ammonium glycyrrhizinate: In vitro percutaneous permeation through human skin and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity on human volunteers. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, M.; Mura, S.; Sinico, C.; Fadda, A.M.; Vila, A.O.; Molina, F. Development and characterization of liposomes containing glycols as carriers for diclofenac. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 342, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Zaru, M.; Manconi, M.; Lai, F.; Valenti, D.; Sinico, C.; Fadda, A.M. Glycerosomes: A new tool for effective dermal and transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Castangia, I.; Caddeo, C.; Pando, D.; Escribano, E.; Valenti, D.; Lampis, S.; Zaru, M.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Improvement of quercetin protective effect against oxidative stress skin damages by incorporation in nanovesicles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, V.; Manca, M.L.; Bullita, E.; Tamburini, E.; Castangia, I.; Cardia, M.C.; Valenti, D.; Fadda, A.M.; Peris, J.E.; Manconi, M. Inhalable polymer-glycerosomes as safe and effective carriers for rifampicin delivery to the lungs. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, M.L.; Cencetti, C.; Matricardi, P.; Castangia, I.; Zaru, M.; Sales, O.D.; Nacher, A.; Valenti, D.; Maccioni, A.M.; Fadda, A.M.; et al. Glycerosomes: Use of hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine mixture and its effect on vesicle features and diclofenac skin penetration. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, M.L.; Castangia, I.; Zaru, M.; Nácher, A.; Valenti, D.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Development of curcumin loaded sodium hyaluronate immobilized vesicles (hyalurosomes) and their potential on skin inflammation and wound restoring. Biomaterials 2015, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castangia, I.; Caddeo, C.; Manca, M.L.; Casu, L.; Latorre, A.C.; Díez-Sales, O.; Ruiz-Saurí, A.; Bacchetta, G.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Delivery of liquorice extract by liposomes and hyalurosomes to protect the skin against oxidative stress injuries. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Zaru, M.; Castangia, I.; Cabras, A.; Cappai, N.; Fadda, A.M. Ialurosomi, Loro Uso in Composizioni Topiche Farmaceutiche o Cosmetiche e Relativo Procedimento di Preparazione. U.S. Patent ITRM20,140,687, 102,014,902,312,901, 27 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Fadda, A.M. Phospholipid Threedimensional Vesicular Aggregates Scattered in Alcoholic Mixtures with No or Low Water Content, Their Preparation and Use in Formulations for Topical Application. EU Patent Application n.EP18163201.9, 3 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Valenti, D.; Lai, F.; Loy, G.; Matricardi, P.; Fadda, A.M. Liposomes coated with chitosan-xanthan gum (chitosomes) as potential carriers for pulmonary delivery of rifampicin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 101, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, G.; Rappolt, M.; Amenitsch, H.; Laggner, P. Structural information from multilamellar liposomes at full hydration: Full q-range fitting with high quality x-ray data. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 4000–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, G.; Koschuch, R.; Pozo-Navas, B.; Rappolt, M.; Lohner, K.; Laggner, P. Structural analysis of weakly ordered membrane stacks. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Nacher, A.; Carbone, C.; Valenti, D.; Maccioni, A.M.; Sinico, C.; Fadda, A.M. Development of novel diolein-niosomes for cutaneous delivery of tretinoin: Influence of formulation and in vitro assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Peris, J.E.; Melis, V.; Valenti, D.; Cardia, M.C.; Lattuada, D.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Nanoincorporation of curcumin in polymer-glycerosomes and evaluation of their in vitro-in vivo suitability as pulmonary delivery systems. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105149–105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, M.; Marongiu, F.; Castangia, I.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Tuberoso, C.I.G.; D’hallewin, G.; Bacchetta, G.; Fadda, A.M. Polymer-associated liposomes for the oral delivery of grape pomace extract. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germano Orrrù, V.P.; Ciusa, M.L.; Taccori, F.; Pisano, M.B.; Caterina, M.; Cosentino, S.; Fadda, M.E.F. Azole Resistance and ERG11 464 Polymorphism in Oral Candida albicans Clinical Strains Isolated in Sardinia. Open Mycol. J. 2019, 2, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalyan, B.C.; Topaç, T.; Ağca, H.; Sağlam, S.; Efe, K.; Ener, B. Comparison of Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) and European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) broth microdilution methods for determining the susceptibilities of Candida isolates. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2018, 52, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pintus, A.; Aragoni, M.C.; Cinellu, M.A.; Maiore, L.; Isaia, F.; Lippolis, V.; Orrù, G.; Tuveri, E.; Zucca, A.; Arca, M. [Au(pyb-H)(mnt)]: A novel gold(III) 1,2-dithiolene cyclometalated complex with antimicrobial activity (pyb-H = C-deprotonated 2-benzylpyridine; mnt = 1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolate). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 170, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitonyte, J.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Valenti, D.; Peris, J.E.; Usach, I.; Nacher, A.; Matos, M.; Gutiérrez, G.; Orrù, G.; et al. Bifunctional viscous nanovesicles co-loaded with resveratrol and gallic acid for skin protection against microbial and oxidative injuries. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, G.; Demontis, C.; Mameli, A.; Tuveri, E.; Coni, P.; Pichiri, G.; Coghe, F.; Rosa, A.; Rossi, P.; D’hallewin, G. The Selective Interaction of Pistacia lentiscus Oil vs. Human Streptococci, an Old Functional Food Revisited with New Tools. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erriu, M.; Pili, F.M.G.; Tuveri, E.; Pigliacampo, D.; Scano, A.; Montaldo, C.; Piras, V.; Denotti, G.; Pilloni, A.; Garau, V.; et al. Oil Essential Mouthwashes Antibacterial Activity against Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: A Comparison between Antibiofilm and Antiplanktonic Effects. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 164267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Vyas, S.P. Development, characterization and in vivo assessment of effective lipidic nanoparticles for dermal delivery of fluconazole against cutaneous candidiasis. In Chemistry and Physics of Lipids; Richard, M.E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 165, pp. 454–461. [Google Scholar]
- Mellado, E.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Regadera, J.; González, M.; Díaz-Guerra, T.M.; Rodríguez-Tudela, J.L. Sustained gastrointestinal colonization and systemic dissemination by Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis and Candida parapsilosis in adult mice. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 38, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Falchi, A.M.; Castangia, I.; Valenti, D.; Lampis, S.; Fadda, A.M. Close-packed vesicles for diclofenac skin delivery and fibroblast targeting. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A. Review of the cosolvency models for predicting solubility of drugs in water-cosolvent mixtures. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 32–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traïkia, M.; Warschawski, D.E.; Recouvreur, M.; Cartaud, J.; Devaux, P.F. Formation of unilamellar vesicles by repetitive freeze-thaw cycles: Characterization by electron microscopy and 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance. Eur. Biophys. J. 2000, 29, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, M.L.; Matricardi, P.; Cencetti, C.; Peris, J.E.; Melis, V.; Carbone, C.; Escribano, E.; Zaru, M.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Combination of argan oil and phospholipids for the development of an effective liposome-like formulation able to improve skin hydration and allantoin dermal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 505, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çağdaş, M.; Sezer, A.D.; Bucak, S. Liposomes as Potential Drug Carrier Systems for Drug Delivery. In Application of Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery; Ali, D.S., Ed.; Scitus Academics Llc.: Cupertino, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, S.; Choi, J.S. Liposomes: Versatile and Biocompatible Nanovesicles for Efficient Biomolecules Delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, M.L.; Castangia, I.; Matricardi, P.; Lampis, S.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Molecular arrangements and interconnected bilayer formation induced by alcohol or polyalcohol in phospholipid vesicles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Ruiz, J.L.; Calpena-Capmany, A.C.; Cañadas-Enrich, C.; Bozal-de Febrer, N.; Suñer-Carbó, J.; Souto, E.B.; Clares-Naveros, B. Biopharmaceutical profile of a clotrimazole nanoemulsion: Evaluation on skin and mucosae as anticandidal agent. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, F.M.; Shaker, D.S.; Ghorab, M.K.; Nasr, M.; Ismail, A. Formulation, Characterization, and Clinical Evaluation of Microemulsion Containing Clotrimazole for Topical Delivery. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2011, 12, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Pathak, K. Cavamax W7 composite ethosomal gel of clotrimazole for improved topical delivery: Development and comparison with ethosomal gel. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2012, 13, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñigo, M.; Pemán, J.; Del Pozo, J.L. Antifungal Activity against Candida Biofilms. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2012, 35, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Lecithin (mg/mL) | Clotrimazole (mg/mL) | Glycerol (mL) | Ethanol (mL) | Water (mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59:2 vesicles | 90 | 10 | 0.59 | 0.39 | 0.02 |
| 53:10 vesicles | 90 | 10 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.10 |
| 69:2 vesicles | 90 | 10 | 0.69 | 0.29 | 0.02 |
| 63:10 vesicles | 90 | 10 | 0.63 | 0.27 | 0.10 |
| Mean Diameter (nm) | PI | Zeta Potential (mV) | EE (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empty 59:2 vesicles | 171 ± 2 | 0.38 | −55 ± 2 | - |
| Empty 53:10 vesicles | 244 ± 13 | 0.43 | −68 ± 3 | - |
| Empty 69:2 vesicles | 169 ± 2 | 0.30 | −65 ± 1 | - |
| Empty 63:10 vesicles | 221 ± 3 | 0.38 | −66 ± 3 | - |
| Clotrimazole 59:2 vesicles | 96 ± 2 | 0.26 | −64 ± 58 | 96 ± 5 |
| Clotrimazole 53:10 vesicles | 186 ± 6 | 0.29 | −59 ± 2 | 84 ± 5 |
| Clotrimazole 69:2 vesicles | 129 ± 7 | 0.28 | −77 ± 1 | 98 ± 8 |
| Clotrimazole 63:10 vesicles | 140 ± 11 | 0.23 | −61 ± 1 | 81 ± 7 |
| zH | σH | dB | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empty liposomes | 18.7 ± 0.1 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 51.0 ± 0.6 |
| Empty 59:2 vesicles | 16.9 ± 0.2 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 59.9 ± 0.8 |
| Empty 53:10 vesicles | 16.8 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 60.4 ± 0.8 |
| Empty 69:2 vesicles | 19.0 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 56.8 ± 1.0 |
| Empty 63:10 vesicles | 20.4 ± 0.1 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 60.0 ± 1.0 |
| Clotrimazole 59:2 vesicles | 17.7 ± 0.2 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 60.6 ± 1.2 |
| Clotrimazole 53:10 vesicles | 17.4 ± 0.2 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 62.0 ± 1.2 |
| Clotrimazole 69:2 vesicles | 18.5 ± 0.2 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 55.0 ± 1.2 |
| Clotrimazole 63:10 vesicles | 18.9 ± 0.1 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 54.2 ± 1.0 |
| MIC (µg/mL) | MBC (µg/mL) | MBIC (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clotrimazole 59:2 vesicles | 2.5 | 2.5 | <0.002 |
| Clotrimazole 53:10 vesicles | >5 | >5 | 5 |
| Clotrimazole 69:2 vesicles | >5 | >5 | 5 |
| Clotrimazole 63:10 vesicles | 1.25 | 1.25 | 0.004 |
| Canesten® | NE | NE | NE |
| Empty 59:2 vesicles | >5 | >5 | >5 |
| Empty 53:10 vesicles | >5 | >5 | >5 |
| Empty 69:2 vesicles | >5 | >5 | >5 |
| Empty 63:10 vesicles | >5 | >5 | >5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manca, M.L.; Usach, I.; Peris, J.E.; Ibba, A.; Orrù, G.; Valenti, D.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Gomez-Fernandez, J.C.; Aranda, F.J.; Fadda, A.M.; et al. Optimization of Innovative Three-Dimensionally-Structured Hybrid Vesicles to Improve the Cutaneous Delivery of Clotrimazole for the Treatment of Topical Candidiasis. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060263
Manca ML, Usach I, Peris JE, Ibba A, Orrù G, Valenti D, Escribano-Ferrer E, Gomez-Fernandez JC, Aranda FJ, Fadda AM, et al. Optimization of Innovative Three-Dimensionally-Structured Hybrid Vesicles to Improve the Cutaneous Delivery of Clotrimazole for the Treatment of Topical Candidiasis. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(6):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060263
Chicago/Turabian StyleManca, Maria Letizia, Iris Usach, José Esteban Peris, Antonella Ibba, Germano Orrù, Donatella Valenti, Elvira Escribano-Ferrer, Juan Carmelo Gomez-Fernandez, Francisco José Aranda, Anna Maria Fadda, and et al. 2019. "Optimization of Innovative Three-Dimensionally-Structured Hybrid Vesicles to Improve the Cutaneous Delivery of Clotrimazole for the Treatment of Topical Candidiasis" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 6: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060263
APA StyleManca, M. L., Usach, I., Peris, J. E., Ibba, A., Orrù, G., Valenti, D., Escribano-Ferrer, E., Gomez-Fernandez, J. C., Aranda, F. J., Fadda, A. M., & Manconi, M. (2019). Optimization of Innovative Three-Dimensionally-Structured Hybrid Vesicles to Improve the Cutaneous Delivery of Clotrimazole for the Treatment of Topical Candidiasis. Pharmaceutics, 11(6), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060263












