Site-Specific 111In-Radiolabeling of Dual-PEGylated Porous Silicon Nanoparticles and Their In Vivo Evaluation in Murine 4T1 Breast Cancer Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Methods
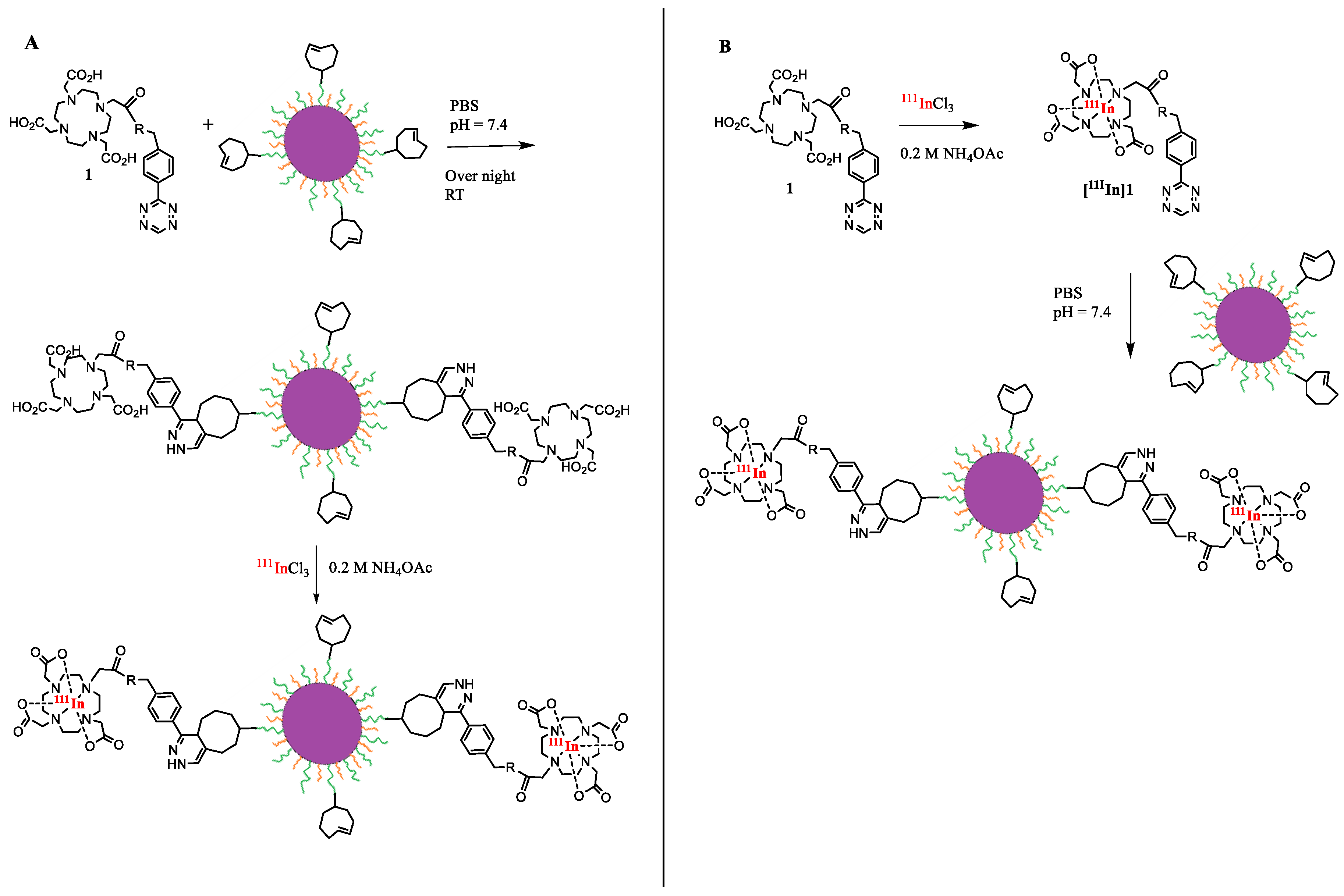
2.2.1. Preparation of BCN and TCO Conjugated Nanoparticles
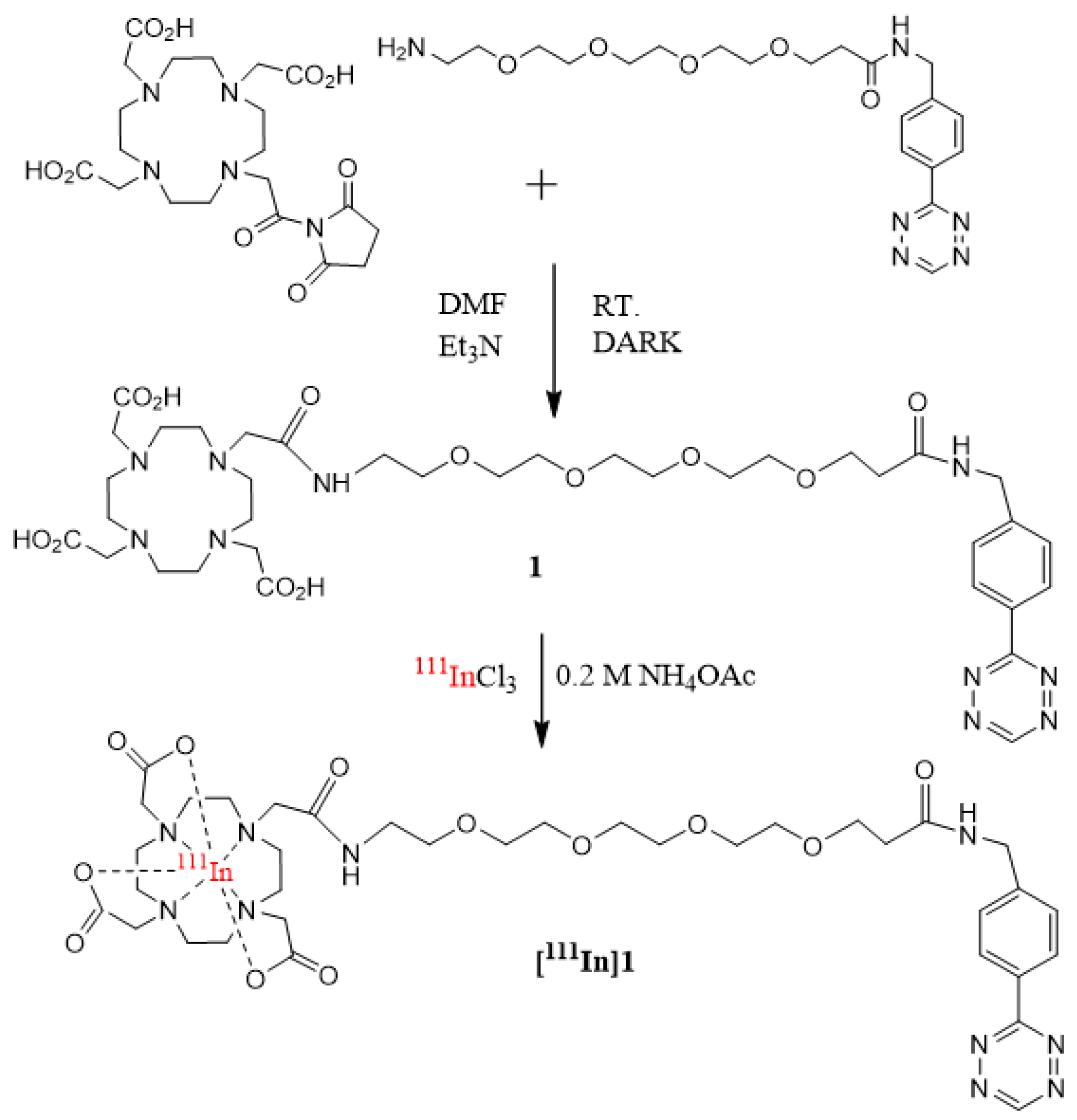
2.2.2. Synthesis of 2,2′,2″-(10-(18-((4-(1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl)amino)-2,18-dioxo-6,9,12,15-tetraoxa-3-azaoctadecyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triyl)triacetic acid (1, DOTA-PEG4-Tz)
2.2.3. Conjugation of 1 to BCN-DPEG-TOPSi
2.2.4. Conjugation of 1 to TCO-DPEG-TOPSi
2.2.5. 111In-radiolabeling of DPEG-TOPSi Particles
2.2.6. Particle Physicochemical Characterization
2.2.7. Cytotoxicity
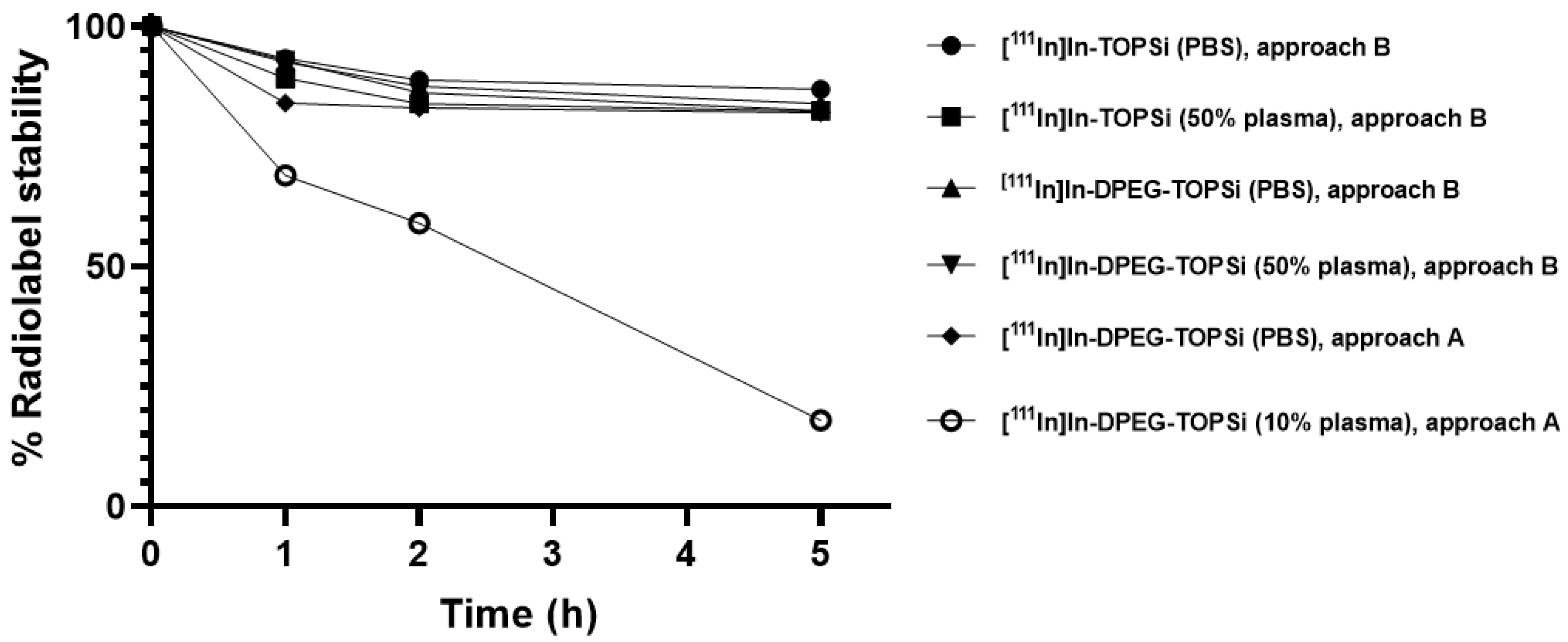
2.2.8. Radiochemical Stability of the 111In-Labeled Particles
2.2.9. Ex Vivo Biodistribution
2.2.10. In Vivo SPECT/CT Imaging
2.2.11. Autoradiography
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of the DPEG-TOPSi Nanoparticles
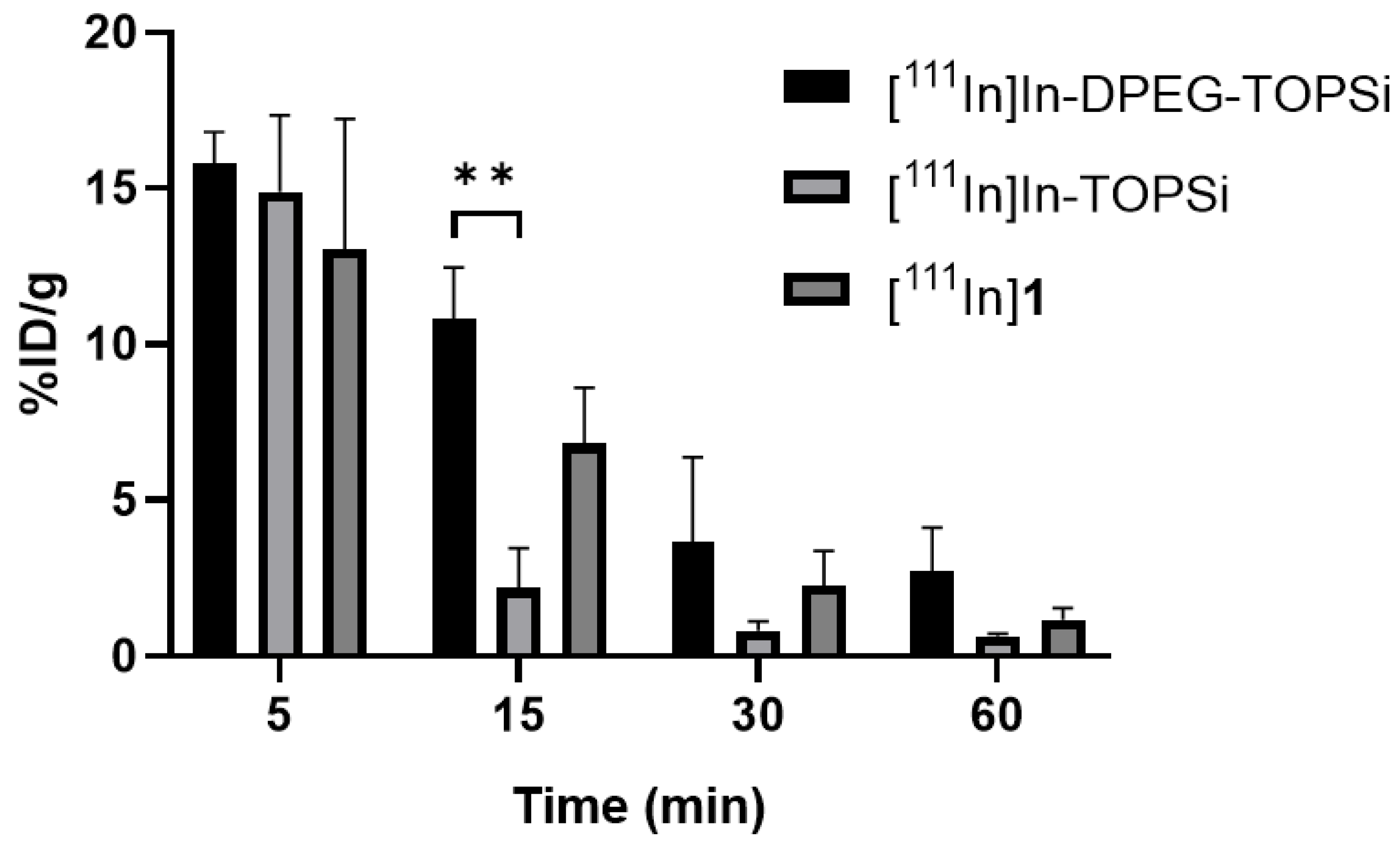
3.2. Radiolabeling of [111In]In-DPEG-TOPSi and [111In]In-TOPSi
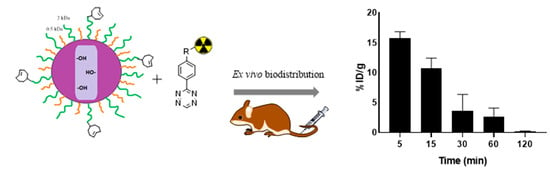
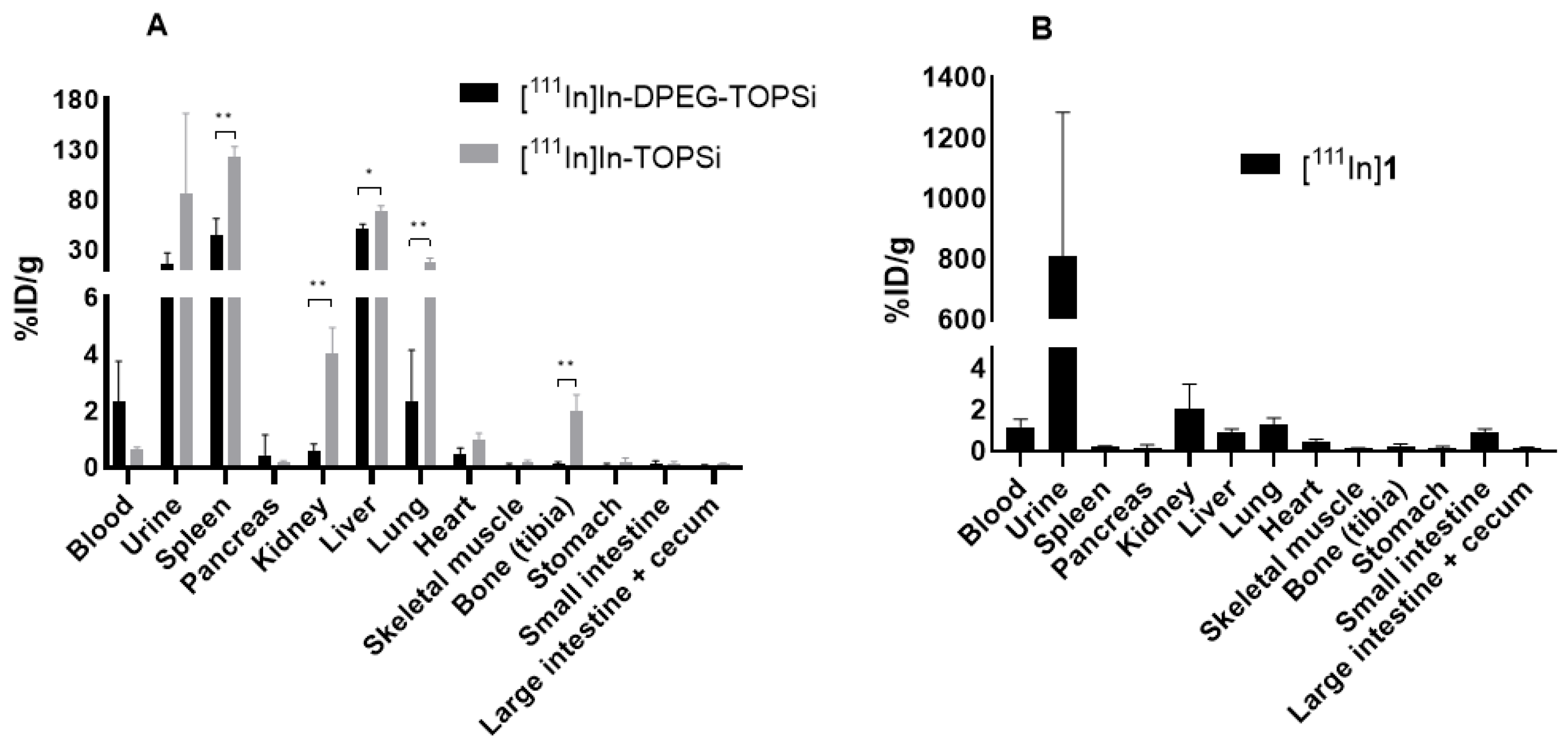
3.3. Ex Vivo Biodistribution
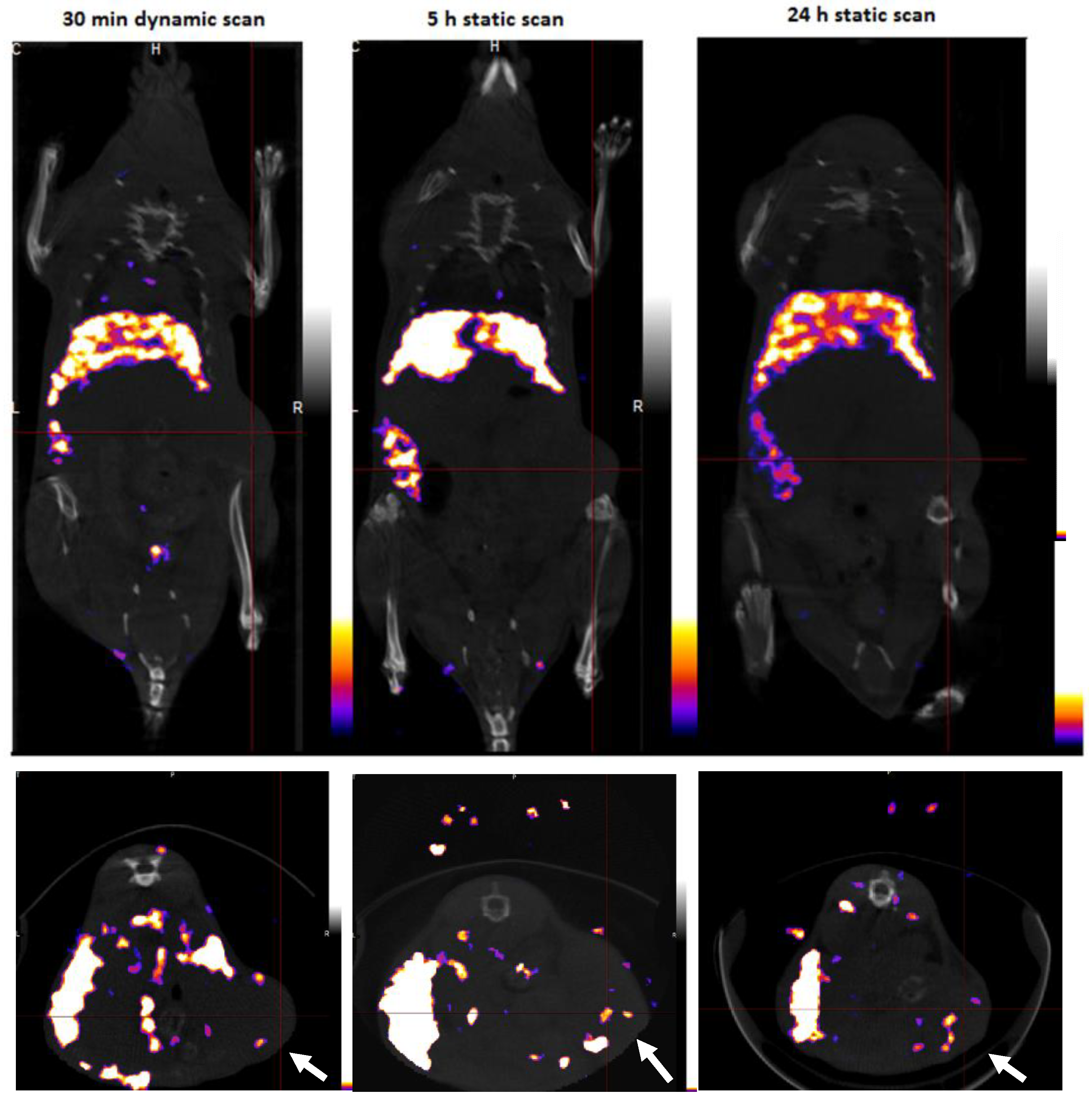
3.4. SPECT/CT Imaging
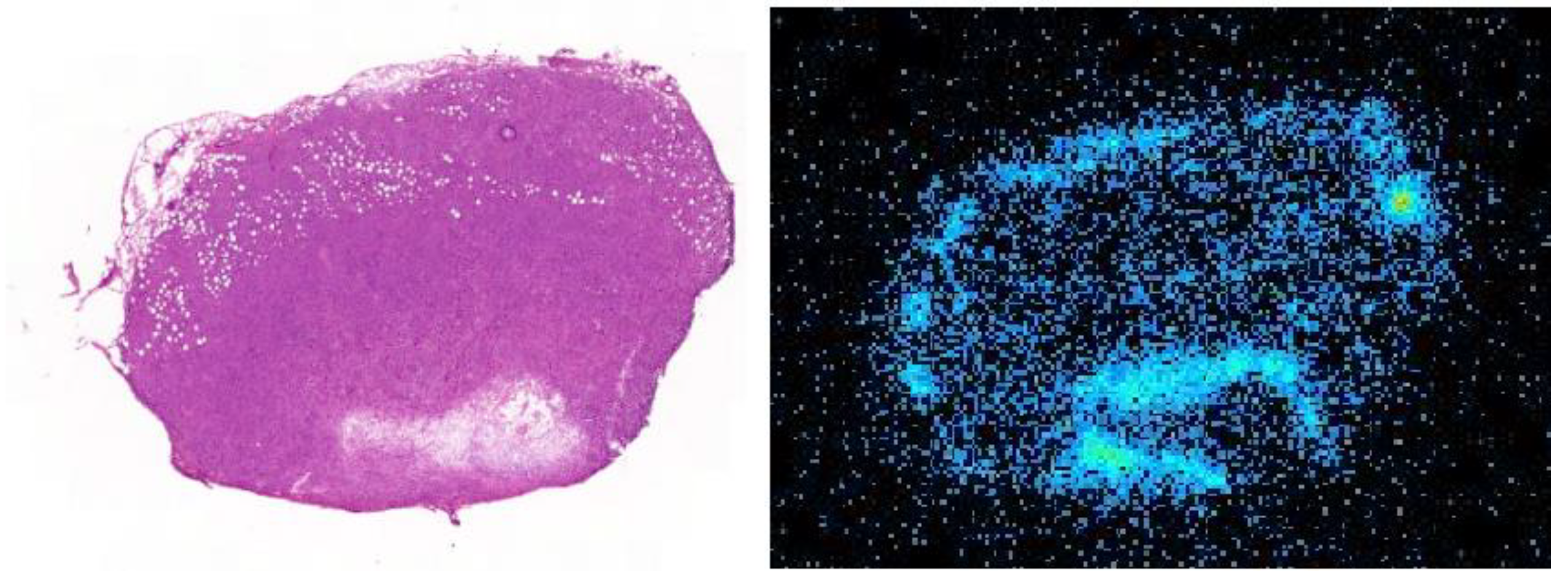
3.5. Tumor Autoradiography
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bae, K.H.; Chung, H.J.; Park, T.G. Nanomaterials for cancer therapy and imaging. Mol. Cells 2011, 31, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Thanou, M. Targeting nanoparticles to cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlerding, E.B.; Chen, F.; Cai, W. Biodegradable and Renal Clearable Inorganic Nanoparticles. Adv. Sci (Weinh) 2016, 3, 1500223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, P.; Adolphi, N.L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.-S.; Butler, K.S.; Durfee, P.N.; Croissant, J.G.; Noureddine, A.; Coker, E.N.; Bearer, E.L.; et al. Establishing the effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticle properties on in vivo disposition using imaging-based pharmacokinetics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, C.; Tasciotti, E.; Fakhoury, J.R.; Fine, D.; Pullan, L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Fu, L.; Liu, X.; Ferrari, M. Tailored Porous Silicon Microparticles: Fabrication and Properties. Chemphyschem 2010, 11, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasciotti, E.; Liu, X.; Bhavane, R.; Plant, K.; Leonard, A.D.; Price, B.K.; Cheng, M.M.-C.; Decuzzi, P.; Tour, J.M.; Robertson, F.; et al. Mesoporous silicon particles as a multistage delivery system for imaging and therapeutic applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 151. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nnano.2008.34#supplementary-information (accessed on 10 October 2019). [CrossRef]
- Salonen, J.; Kaukonen, A.M.; Hirvonen, J.; Lehto, V.-P. Mesoporous Silicon in Drug Delivery Applications. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 632–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.-A.; Hamidi, M.; Mäkilä, E.M.; Zhang, H.; Almeida, P.V.; Kaasalainen, M.; Salonen, J.J.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Santos, H.A. The mechanisms of surface chemistry effects of mesoporous silicon nanoparticles on immunotoxicity and biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7776–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Nanoparticles in targeted cancer therapy: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles entering preclinical development stage. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2012, 7, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zheng, J. Clearance Pathways and Tumor Targeting of Imaging Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6655–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, B.; Gu, J.; Serda, R.E.; Bhavane, R.; Tasciotti, E.; Chiappini, C.; Liu, X.; Tanaka, T.; Decuzzi, P.; Ferrari, M. Tailoring the degradation kinetics of mesoporous silicon structures through PEGylation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 94A, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalainen, M.; Kamakura, R.; Riikonen, J.; Finnilä, M.; Nissinen, T.; Rantanen, J.; Niemelä, M.; Perämäki, P.; Mäkinen, M.; Herzig, K.H.; et al. Biodegradation of inorganic drug delivery systems in subcutaneous conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 122, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, X.J.; Lee, T.-C.; Dou, Q.; Deen, G.R. Utilising inorganic nanocarriers for gene delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, D.J.; Liu, X.; Curley, S.A.; Ferrari, M.; Serda, R.E. Porous silicon advances in drug delivery and immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissinen, T.; Näkki, S.; Laakso, H.; Kučiauskas, D.; Kaupinis, A.; Kettunen, M.I.; Liimatainen, T.; Hyvönen, M.; Valius, M.; Gröhn, O.; et al. Tailored Dual PEGylation of Inorganic Porous Nanocarriers for Extremely Long Blood Circulation in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32723–32731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, X.; Wenyi, Z.; Jisen, S.; Shou-jun, X. Engineered Stealth Porous Silicon Nanoparticles via Surface Encapsulation of Bovine Serum Albumin for Prolonging Blood Circulation in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11718–11724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmire, M.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: Considerations and caveats. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2008, 3, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.P.A.; Ranjan, S.; Kinnunen, S.; Correia, A.; Talman, V.; Mäkilä, E.; Barrios-Lopez, B.; Kemell, M.; Balasubramanian, V.; Salonen, J.; et al. Drug-Loaded Multifunctional Nanoparticles Targeted to the Endocardial Layer of the Injured Heart Modulate Hypertrophic Signaling. Small 2017, 13, 1701276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gref, R.; Minamitake, Y.; Peracchia, M.; Trubetskoy, V.; Torchilin, V.; Langer, R. Biodegradable long-circulating polymeric nanospheres. Science 1994, 263, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gref, R.; Lück, M.; Quellec, P.; Marchand, M.; Dellacherie, E.; Harnisch, S.; Blunk, T.; Müller, R.H. ‘Stealth’ corona-core nanoparticles surface modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG): Influences of the corona (PEG chain length and surface density) and of the core composition on phagocytic uptake and plasma protein adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2000, 18, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, R.; Choyke, P.L. Improving conventional enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects; what is the appropriate target? Theranostics 2013, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, U.; Maeda, H.; Jain, R.K.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M.; Zamboni, W.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Barry, S.T.; Gabizon, A.; Grodzinski, P.; Blakey, D.C. Challenges and Key Considerations of the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect for Nanomedicine Drug Delivery in Oncology. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2412–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, J.E.; Moorhouse, A.D. The growing applications of click chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.-P.; Adumeau, P.; Lewis, J.S.; Zeglis, B.M. Click Chemistry and Radiochemistry: The First 10 Years. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 2791–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Sharpless, K.B. The growing impact of click chemistry on drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, T.; Zeglis, B.M. The inverse electron demand Diels–Alder click reaction in radiochemistry. J. Labelled Comp. Radiopharm. 2014, 57, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knall, A.-C.; Slugovc, C. Inverse electron demand Diels–Alder (iEDDA)-initiated conjugation: A (high) potential click chemistry scheme. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, L.R.; Aurell, M.J.; Pérez, P.; Contreras, R. Quantitative characterization of the global electrophilicity power of common diene/dienophile pairs in Diels–Alder reactions. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 4417–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liang, Y.; Houk, K.N. Theoretical Elucidation of the Origins of Substituent and Strain Effects on the Rates of Diels–Alder Reactions of 1,2,4,5-Tetrazines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11483–11493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, B.L.; Guo, Z.; Bernardes, G.J.L. Inverse electron demand Diels–Alder reactions in chemical biology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4895–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näkki, S.; Wang, J.T.W.; Wu, J.; Fan, L.; Rantanen, J.; Nissinen, T.; Kettunen, M.I.; Backholm, M.; Ras, R.H.A.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; et al. Designed inorganic porous nanovector with controlled release and MRI features for safe administration of doxorubicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näkki, S.; Rytkönen, J.; Nissinen, T.; Florea, C.; Riikonen, J.; Ek, P.; Zhang, H.; Santos, H.A.; Närvänen, A.; Xu, W.; et al. Improved stability and biocompatibility of nanostructured silicon drug carrier for intravenous administration. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tamarov, K.; Fan, L.; Granroth, S.; Rantanen, J.; Nissinen, T.; Peräniemi, S.; Uski, O.; Hirvonen, M.-R.; Lehto, V.-P. Scalable Synthesis of Biodegradable Black Mesoporous Silicon Nanoparticles for Highly Efficient Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 23529–23538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnard, J.; Berny, R.; Carduner, H.; Leray, P.; Morteau, E.; Provence, M.; Servagent, N.; Thers, D. The micro-pattern gas detector PIM: A multi-modality solution for novel investigations in functional imaging. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2009, 610, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarparanta, M.; Mäkilä, E.; Heikkilä, T.; Salonen, J.; Kukk, E.; Lehto, V.-P.; Santos, H.A.; Hirvonen, J.; Airaksinen, A.J. 18F-Labeled Modified Porous Silicon Particles for Investigation of Drug Delivery Carrier Distribution in Vivo with Positron Emission Tomography. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.D.; Li, C.-P.; Chiang, C.E.; Schuller, I.K.; Sailor, M.J. A Label-Free Porous Alumina Interferometric Immunosensor. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Sarparanta, M.P.; Mäkilä, E.M.; Hyvönen, M.L.K.; Laakkonen, P.M.; Salonen, J.J.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Airaksinen, A.J.; Santos, H.A. Multifunctional porous silicon nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Biomaterials 2015, 48, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.P.A.; Ranjan, S.; Correia, A.M.R.; Mäkilä, E.M.; Kinnunen, S.M.; Zhang, H.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Almeida, P.V.; Salonen, J.J.; Ruskoaho, H.J.; et al. In vitro and in vivo assessment of heart-homing porous silicon nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2016, 94, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha-Duong, N.T.; Hémadi, M.; Chikh, Z.; Chahine, J.M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of metal-loaded transferrins: Transferrin receptor 1 interactions. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, H.; Fitzsimmons, J.; Shelton, T.; Hoffman, T.J.; Cutler, C.S.; Lewis, M.R.; Athey, P.S.; Gulyas, G.; Kiefer, G.E.; Frank, R.K.; et al. Preparation and biological evaluation of 111In-, 177Lu- and 90Y-labeled DOTA analogues conjugated to B72.3. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2007, 34, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytkönen, J.; Miettinen, R.; Kaasalainen, M.; Lehto, V.-P.; Salonen, J.; Närvänen, A. Functionalization of mesoporous silicon nanoparticles for targeting and bioimaging purposes. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarparanta, M.; Bimbo, L.M.; Rytkönen, J.; Mäkilä, E.; Laaksonen, T.J.; Laaksonen, P.; Nyman, M.; Salonen, J.; Linder, M.B.; Hirvonen, J.; et al. Intravenous Delivery of Hydrophobin-Functionalized Porous Silicon Nanoparticles: Stability, Plasma Protein Adsorption and Biodistribution. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Frangioni, J.V. Nanoparticles for Biomedical Imaging: Fundamentals of Clinical Translation. Mol. Imaging 2010, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Measure | TOPSi | TCO-TOPSi | [111In]In-TOPSi | DPEG-TOPSi | DPEG-TOPSi-NH2 | TCO-DPEG-TOPSi | [111In]In-DPEG-TOPSi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (diameter, nm) | 176 ± 6 | 225 ± 10 | 198 ± 4 | 192 ± 1 | 196 ± 4 | 276 ± 4 | 226 ± 3 |
| PDI | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | ||||
| Zeta potential (mV) | −29.3 ± 0.9 | −7.2 ± 0.2 | 12.0 ± 0.8 | ||||
| BET surface area (m2/g) | 163 ± 20 | 60 ± 2 | 52 ± 9 | ||||
| BJH volume (m3/g) | 0.48 ± 0.04 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | ||||
| BJH pore size (nm) | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 8.8 ± 0.8 | 10.4 ± 1.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lumen, D.; Näkki, S.; Imlimthan, S.; Lambidis, E.; Sarparanta, M.; Xu, W.; Lehto, V.-P.; Airaksinen, A.J. Site-Specific 111In-Radiolabeling of Dual-PEGylated Porous Silicon Nanoparticles and Their In Vivo Evaluation in Murine 4T1 Breast Cancer Model. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120686
Lumen D, Näkki S, Imlimthan S, Lambidis E, Sarparanta M, Xu W, Lehto V-P, Airaksinen AJ. Site-Specific 111In-Radiolabeling of Dual-PEGylated Porous Silicon Nanoparticles and Their In Vivo Evaluation in Murine 4T1 Breast Cancer Model. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(12):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120686
Chicago/Turabian StyleLumen, Dave, Simo Näkki, Surachet Imlimthan, Elisavet Lambidis, Mirkka Sarparanta, Wujun Xu, Vesa-Pekka Lehto, and Anu J. Airaksinen. 2019. "Site-Specific 111In-Radiolabeling of Dual-PEGylated Porous Silicon Nanoparticles and Their In Vivo Evaluation in Murine 4T1 Breast Cancer Model" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 12: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120686
APA StyleLumen, D., Näkki, S., Imlimthan, S., Lambidis, E., Sarparanta, M., Xu, W., Lehto, V.-P., & Airaksinen, A. J. (2019). Site-Specific 111In-Radiolabeling of Dual-PEGylated Porous Silicon Nanoparticles and Their In Vivo Evaluation in Murine 4T1 Breast Cancer Model. Pharmaceutics, 11(12), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120686