Mesoscale Simulations of pH-Responsive Amphiphilic Polymeric Micelles for Oral Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dissipative Particle Dynamics (DPD) Theory
2.2. The Coarse-Grained Model and Simulation Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Hydrophilic and Cationic PAEMA Block
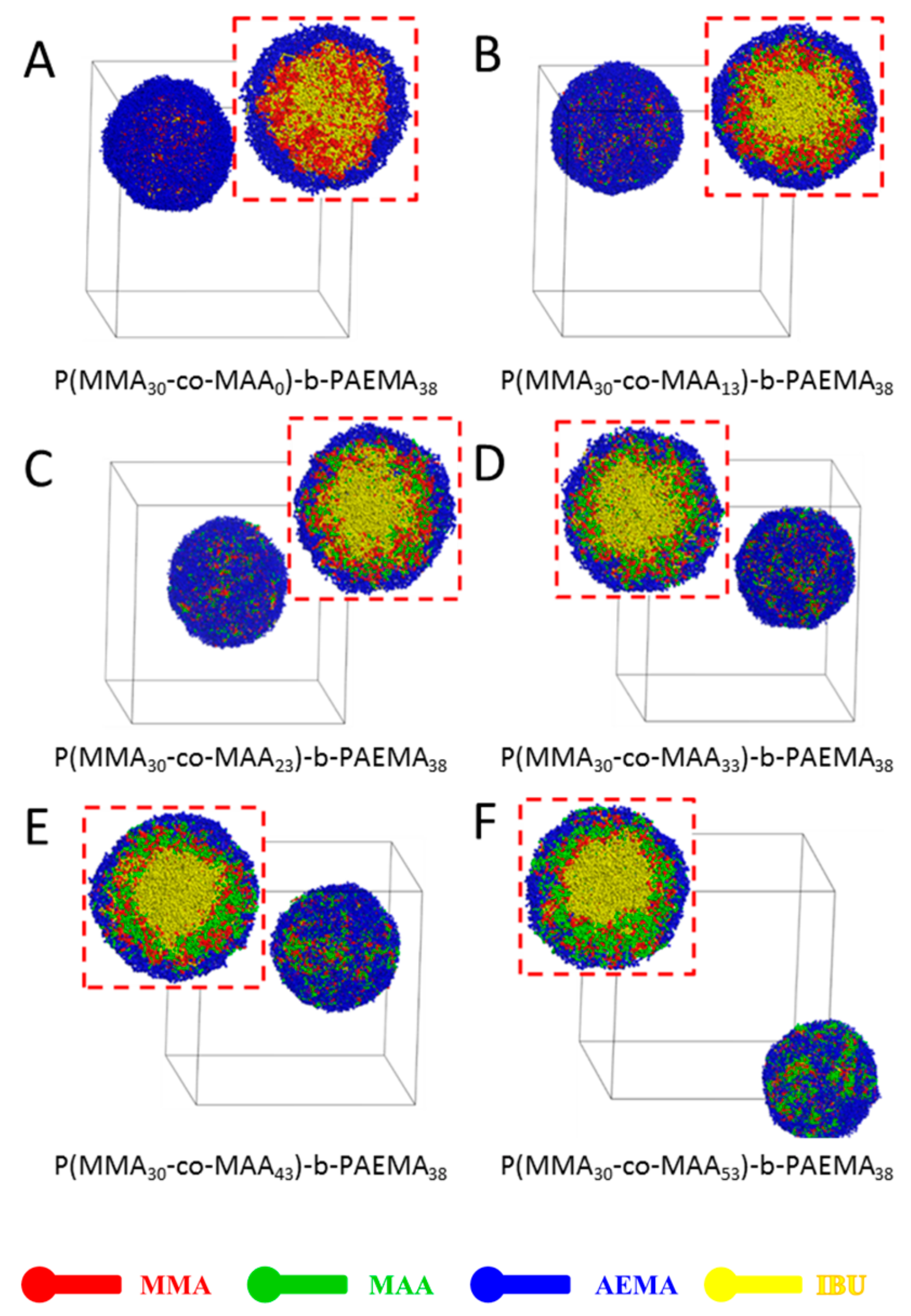
3.2. Effect of pH-Sensitive PMAA Block
3.3. Effect of Mole Fraction of Drug in Feed
3.4. Self-Assembly Ability
3.5. Effect of Topological Structure of Copolymer
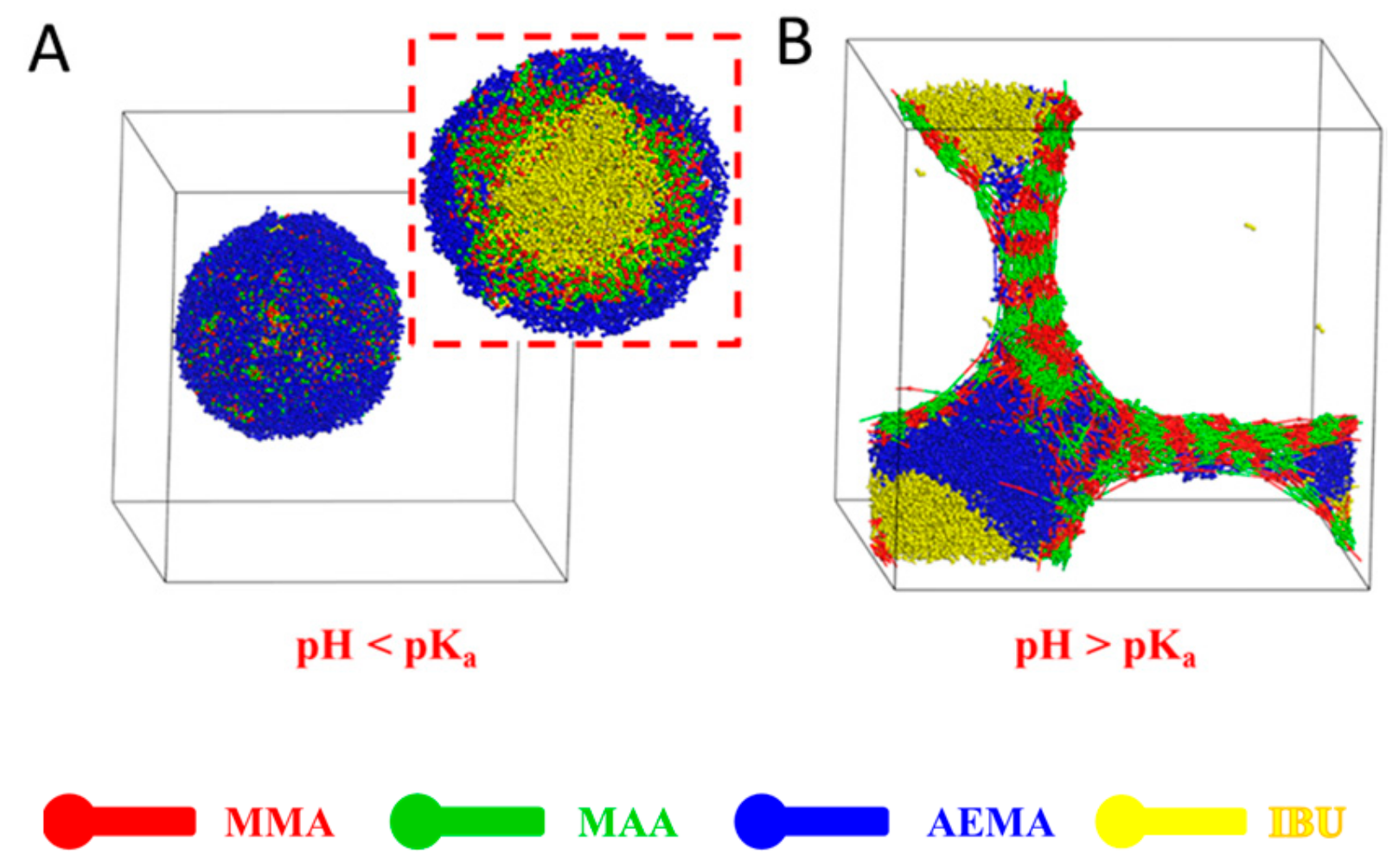
3.6. Effect of pH in Solution
4. Discussions and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, T.; Shirui, M. Amphiphilic polymeric micelles as the nanocarrier for peroral delivery of poorly soluble anticancer drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 687. [Google Scholar]
- Raveendran, R. Chapter 12—Polymeric micelles: Smart nanocarriers for anticancer drug delivery. In Drug Delivery Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications; Sharma, C.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 255–273. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, S.; Ge, L.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Translatable high drug loading drug delivery systems based on biocompatible polymer nanocarriers. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1732–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Patil, N.G.; Bhosle, G.S.; Ambade, A.V.; Gupta, S.S. Amphiphilic glycopolypeptide star copolymer-based cross-linked nanocarriers for targeted and dual-stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Gunatillake, P.A.; Hao, X. Brush-shaped RAFT polymer micelles as nanocarriers for a ruthenium (II) complex photodynamic anticancer drug. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 113, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Bai, R.; Shen, Z.; Deng, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. PEG-detachable polymeric micelles self-assembled from amphiphilic copolymers for tumor-acidity-triggered drug delivery and controlled release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5701–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Cao, F.; Peng, D.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C. Amphiphilic block copolymer poly(acrylic acid)-b-polycaprolactone as a novel pH-sensitive nanocarrier for anti-cancer drugs delivery: In-Vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Polymers 2019, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodzadeh, F.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Jannat, B.; Ghorbani, M. Fabrication and characterization of gold nanospheres-cored pH-sensitive thiol-ended triblock copolymer: A smart drug delivery system for cancer therapy. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1344–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattu, C.; Brachi, G.; Ciardelli, G. Smart polymeric nanoparticles. In Smart Nanoparticles for Biomedicine; Ciofani, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, X.; Tang, G. Mechanisms of drug release in pH-sensitive micelles for tumour targeted drug delivery system: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W. A smart pH-sensitive delivery system for enhanced anticancer efficacy via paclitaxel endosomal escape. Front. Pharmacol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bui, Q.N.; Duy, L.T.M.; Yang, H.Y.; Lee, D.S. One-Step preparation of pH-responsive polymeric nanogels as intelligent drug delivery systems for tumor therapy. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh-Holagh, S.; Hashemi-Najafabadi, S.; Shaki, H.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E. Self-assembled and pH-sensitive mixed micelles as an intracellular doxorubicin delivery system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 523, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, R.; Yang, S.T.; Zhou, Q.H.; Lin, J. Stepwise pH-sensitive and biodegradable polypeptide hybrid micelles for enhanced cellular internalization and efficient nuclear drug delivery. Colloid Surf. B 2019, 181, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Phi, P.Q.; Choi, S.T. Tribological Behavior of Grafted Nanoparticle on Polymer-Brushed Walls: A Dissipative Particle Dynamics Study. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 11988–11998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woitiskia, C.B.; Neufeld, R.J.; Veiga, F.; Carvalho, R.A.; Figueiredo, I.V. Pharmacological effect of orally delivered insulin facilitated by multilayered stable nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, D.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Goblet cell-targeting nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery and the influence of mucus on insulin transport. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Sonaje, K.; Lin, K.M.; Juang, J.H.; Mi, F.L.; Yang, H.W.; Sung, H.W. Multi-ion-crosslinked nanoparticles with pH-responsive characteristics for oral delivery of protein drugs. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, T.; Lee, B.H.; Fabien, N. Current status and new perspectives on chitin and chitosan as functional biopolymers. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2017, 181, 1314–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Xu, F.; Feng, Q.S.; Chen, Y.S.; Ma, C. Preparation and characterization of PMAA/MWCNTs nanohybrid hydrogels with improved mechanical properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92B, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroni, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A. Enteric coatings for colonic drug delivery: State of the art. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 1027–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, X.; Tian, K.; Liu, P. Independent temperature and pH dual-responsive PMAA/PNIPAM microgels as drug delivery system: Effect of swelling behavior of the core and shell materials in fabrication process. Colloid Surf. A 2017, 526, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yao, W.D.; Rao, Y.F.; Lu, X.Y.; Gao, J.Q. pH-Responsive carriers for oral drug delivery: Challenges and opportunities of current platforms. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.X.; Clegg, J.R.; Ander, E.W.; Peppas, N.A. Tunable poly(methacrylic acid)-co-acrylamide) nanoparticles through inverse emulsion polymerization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.C.R.; Cragg, S.M.; Barbu, E.; De Sousa, F.B. The potential of electrospun poly(methyl methacrylate)/polycaprolactone core–sheath fibers for drug delivery applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5712–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Solanki, P.; Mitra, S. Curcuminoid-loaded poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zou, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. Self-assembly and drug release control of dual-responsive copolymers based on oligo(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate and spiropyran. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, G.; Zaidi, M.G.H.; Biplab, K.C. In vivo acute cytotoxicity study of poly(2-amino ethyl methacrylate-co-methylene bis-acrylamide) magnetic composite synthesized in supercritical CO2. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.Y.; Wu, Z.M.; Yang, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.Y. Smart pH-responsive polymeric micelles for programmed oral delivery of insulin. Colloid. Surface. B 2019, 183, 110443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, X. Distortion and flow of nematics simulated by dissipative particle dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 184902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, K.; Lisal, M.; Colina, C.M. Adsorption behavior of model proteins on surfaces. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 2011, 302, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, D.; Lin, W.; Wen, L.; Zhang, L. Enhanced stability of crosslinked and charged unimolecular micelles from multigeometry triblock copolymers with short hydrophilic segments: Dissipative particle dynamics simulation. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Shamsara, J. Application of DPD in the design of polymeric nano-micelles as drug carriers. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2016, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.S.; Yi, P.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Hao, X.; Chen, Q. 4/6-Herto-arm and 4/6-mikto-arm star-shaped block polymeric drug-loaded micelles and their pH-responsive controlled release properties: A dissipative particle dynamics simulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 15222–15232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, S.; Hu, S. Self-assembly of DCPD-loaded cross-linked micelle from triblock copolymers and its pH-responsive behavior: A dissipative particle dynamics study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 195, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.L.; Bray, D.J.; Del Regno, A.; Seaton, M.A.; Ferrante, A.S.; Warren, P.B. Micelle formation in alkyl sulfate surfactants using dissipative particle dynamics. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Yang, C.; Xue, Z.; Huang, Y.; Luo, H.; Zu, X.; Zhang, L.; Yi, G. Controlled construction of gold nanoparticles in situ from β-cyclodextrin based unimolecular micelles for in vitro computed tomography imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 528, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Z.K.; Gao, J.; Li, C.; Sun, S.; Hu, S. Dissipative particle dynamics simulations reveal the pH-driven micellar transition pathway of monorhamnolipids. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2017, 506, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogerbrugge, P.J.; Koelman, J.M.V.A. Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 1992, 19, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelman, J.M.V.A.; Hoogerbrugge, P.J. Dynamic simulations of hard-sphere suspensions under steady shear. Europhys. Lett. 1993, 21, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Español, P.; Warren, P. Statistical mechanics of dissipative particle dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 1995, 30, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; Warren, P.B. Dissipative particle dynamics: Bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 4423–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagonabarraga, I.; Frenkel, D. Dissipative particle dynamics for interacting systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 5015–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, S.Y.; Nies, E.L.F.; Michels, M.A.J. Thermodynamic consistency in dissipative particle dynamics simulations of strongly nonideal liquids and liquid mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 9383–9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; Madden, T.J. Dynamic simulation of diblock copolymer microphase separation. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 8713–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; McGrother, S. Bead–bead interaction parameters in dissipative particle dynamics: Relation to bead-size, solubility parameter, and surface tension. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Ángeles, F.; Kwon, H.-K.; Sadman, K.; Wu, T.; Shull, K.R.; Olvera de la Cruz, M. Self-Assembly of charge-containing copolymers at the liquid–liquid interface. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.; Nagao, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Miura, Y. Self-Assembly of a double hydrophilic block glycopolymer and the investigation of its mechanism. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8591–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.V.K.J. Double hydrophilic block copolymer self-assembly in aqueous solution. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prego, C.; Torres, D.; Fernandez-Megia, E.; Novoa-Carballal, R.; Quiñoá, E.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan–PEG nanocapsules as new carriers for oral peptide delivery: Effect of chitosan pegylation degree. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchford, K.; Burt, H. A review of the formation and classification of amphiphilic block copolymer nanoparticulate structures: Micelles, nanospheres, nanocapsules and polymersomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tho, C.C.; Galaktionova, D.; Chen, X.; Kral, P.; Mirsaidov, U. Dynamics of amphiphilic block copolymers in an aqueous solution: Direct imaging of micelle formation and nanoparticle encapsulation. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Huang, T.X.; Zhao, B.; Guo, X.D.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, L.J. Self-assembled pH-responsive MPEG-b-(PLA-co-PAE) block copolymer micelles for anticancer drug delivery. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6273–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiner, U.; Krappe, U.; Jakob, T.; Abetz, V.; Stadler, R. Spheres on spheres—A novel spherical multiphase morphology in polystyrene-block-polybutadiene-block-poly(methyl methacrylate) triblock copolymers. Polym. Bull. 1998, 40, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Liu, B.; Xu, L.; Hu, F.-N.; Zhu, J.-J. Facile route to Zn-based II−VI semiconductor spheres, hollow spheres, and core/shell nanocrystals and their optical properties. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10286–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| aij | W | IBU1 | IBU2 | IBU3 | MMA | MAA | AE | MAA−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 25 | |||||||
| IBU1 | 144.17 | 25 | ||||||
| IBU2 | 97.50 | 30.85 | 25 | |||||
| IBU3 | 106.80 | 29.03 | 25.06 | 25 | ||||
| MMA | 116.88 | 28.97 | 25.12 | 25.01 | 25 | |||
| MAA | 71.41 | 43.82 | 30.13 | 30.48 | 31.40 | 25 | ||
| AE | 90.67 | 38.11 | 25.02 | 30.75 | 25.44 | 27.65 | 25 | |
| MAA−1 | 98.92 | 482.09 | 372.07 | 412.66 | 436.81 | 308.32 | 342.01 | 25 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Duan, M.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, C.Y. Mesoscale Simulations of pH-Responsive Amphiphilic Polymeric Micelles for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120620
Wu Z, Duan M, Xiong D, Zhang CY. Mesoscale Simulations of pH-Responsive Amphiphilic Polymeric Micelles for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(12):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120620
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhimin, Manzhen Duan, Di Xiong, and Can Yang Zhang. 2019. "Mesoscale Simulations of pH-Responsive Amphiphilic Polymeric Micelles for Oral Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 12: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120620
APA StyleWu, Z., Duan, M., Xiong, D., & Zhang, C. Y. (2019). Mesoscale Simulations of pH-Responsive Amphiphilic Polymeric Micelles for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 11(12), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120620






