Perivascular and Perineural Pathways Involved in Brain Delivery and Distribution of Drugs after Intranasal Administration
Abstract
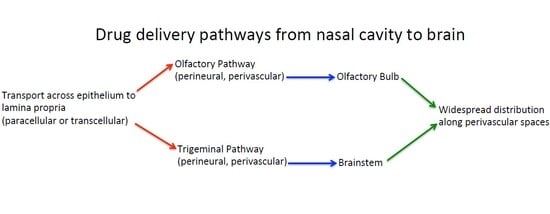
1. Introduction
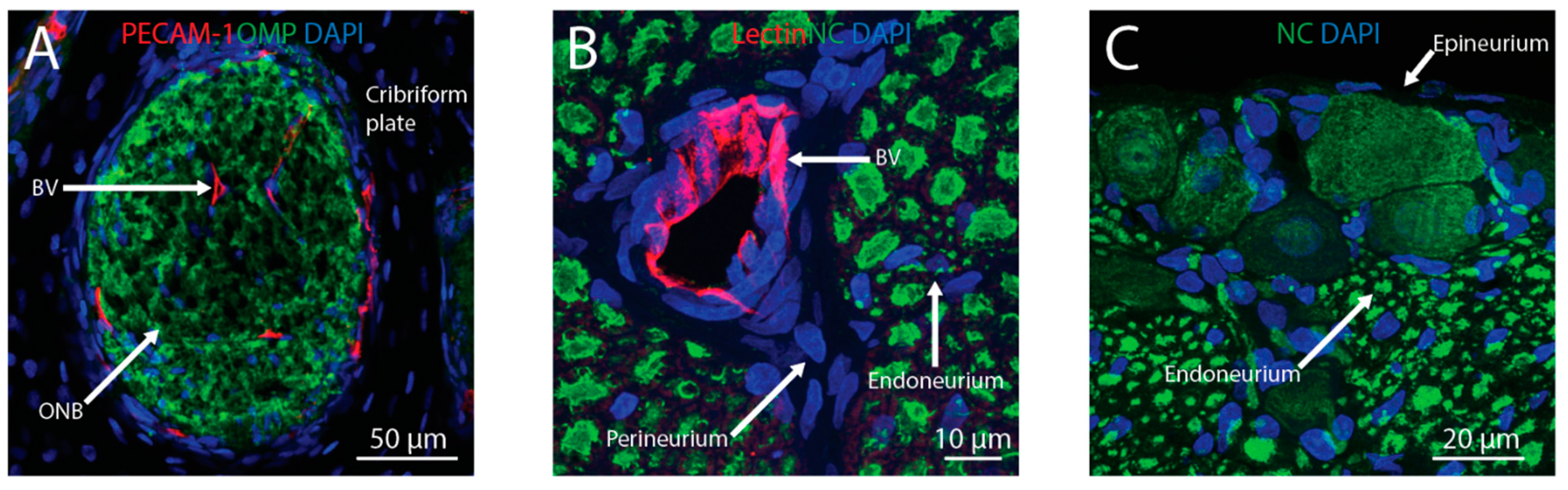
2. Transport across the Nasal Epithelium
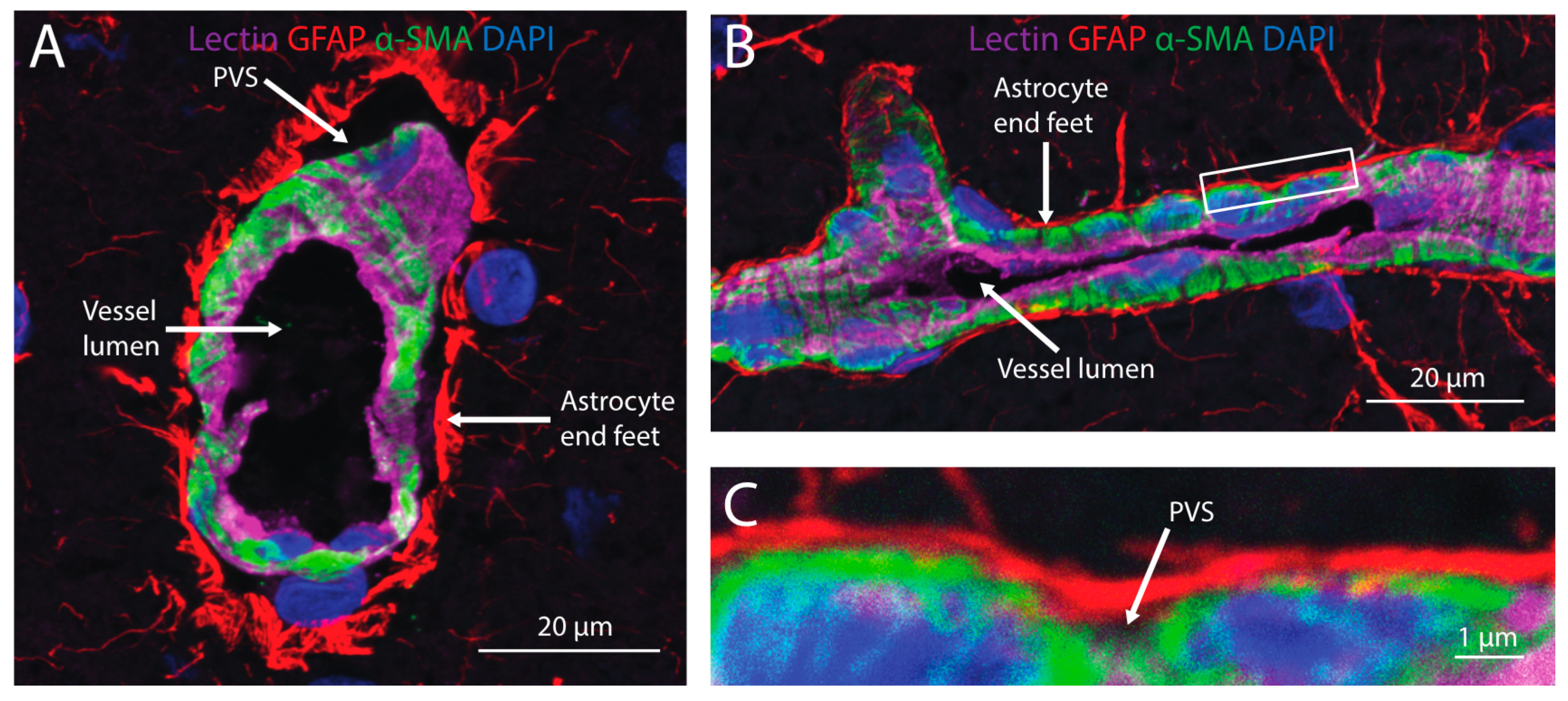
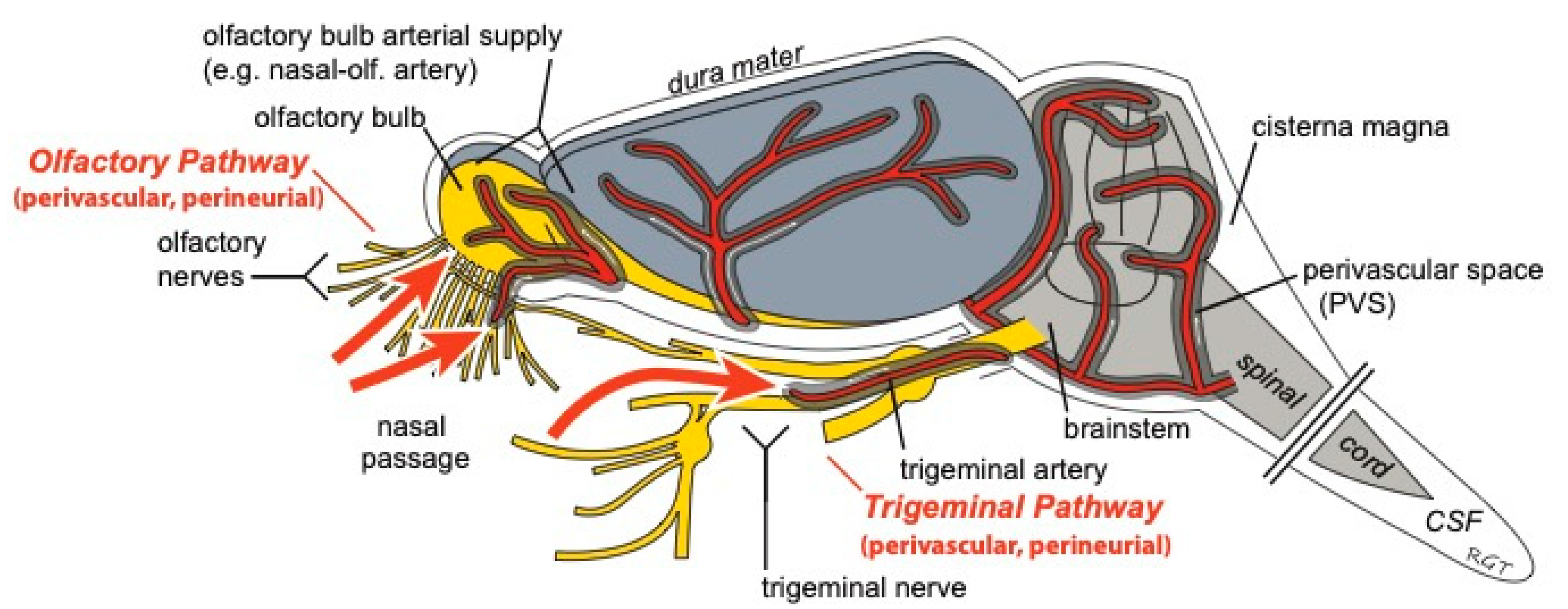
3. Transport into the Brain
4. Distribution within Brain
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butt, A.M.; Jones, H.C.; Abbott, N.J. Electrical resistance across the blood-brain barrier in anaesthetized rats: A developmental study. J. Physiol. 1990, 429, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, C.; Olesen, S.P. Electrical resistance of brain microvascular endothelium. Brain Res. 1982, 241, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, T.S.; Karnovsky, M.J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J. Cell Biol. 1967, 34, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. Hypoxic Stress and Inflammatory Pain Disrupt Blood-Brain Barrier Tight Junctions: Implications for Drug Delivery to the Central Nervous System. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieger, B.; Gao, B. Drug transporters in the central nervous system. Clin. Pharm. 2015, 54, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.S. Regulation of ABC transporters blood-brain barrier: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 125, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M. The blood-brain barrier: Bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, J.; Lange, T.; Kern, W.; McGregor, G.P.; Bickel, U.; Fehm, H.L. Sniffing neuropeptides: A transnasal approach to the human brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelcovych, M.T.; Gadiano, A.J.; Wu, Y.; Manning, A.A.; Thomas, A.G.; Khuder, S.S.; Yoo, S.W.; Xu, J.; McArthur, J.C.; Haughey, N.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Intranasal versus Subcutaneous Insulin in the Mouse. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.N.; Lochhead, J.J.; Pizzo, M.E.; Nehra, G.; Boroumand, S.; Greene, G.; Thorne, R.G. Delivery of immunoglobulin G antibodies to the rat nervous system following intranasal administration: Distribution, dose-response, and mechanisms of delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 286, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkema, J.R.; Carey, S.A.; Wagner, J.G. The nose revisited: A brief review of the comparative structure, function, and toxicologic pathology of the nasal epithelium. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 34, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, T.E.; St Jeor, V.L.; Kinnamon, J.C.; Silver, W.L. Ultrastructure of substance P- and CGRP-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the nasal epithelium of rodents. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990, 294, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuenke, M.; Schulte, E.; Schumacher, U. Head and Neuroanatomy; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Thorne, R.G. Intranasal drug delivery to the brain. In Drug Delivery to the Brain; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M., de Lange, E.C., Thorne, R.G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 401–431. [Google Scholar]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Thorne, R.G. Intranasal delivery of biologics to the central nervous system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, R.G.; Hanson, L.R.; Ross, T.M.; Tung, D.; Frey, W.H., II. Delivery of interferon-beta to the monkey nervous system following intranasal administration. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, R.G.; Pronk, G.J.; Padmanabhan, V.; Frey, W.H., II. Delivery of insulin-like growth factor-I to the rat brain and spinal cord along olfactory and trigeminal pathways following intranasal administration. Neuroscience 2004, 127, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinke, A.; Meier-Stiegen, S.; Drenckhahn, D.; Asan, E. Molecular composition of tight and adherens junctions in the rat olfactory epithelium and fila. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 130, 339–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolburg, H.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K.; Sam, H.; Horvat, S.; Deli, M.A.; Mack, A.F. Epithelial and endothelial barriers in the olfactory region of the nasal cavity of the rat. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 130, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Wolak, D.J.; Pizzo, M.E.; Thorne, R.G. Rapid transport within cerebral perivascular spaces underlies widespread tracer distribution in the brain after intranasal administration. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeano, C.; Qiu, Z.; Mishra, A.; Farnsworth, S.L.; Hemmi, J.J.; Moreira, A.; Edenhoffer, P.; Hornsby, P.J. The Route by Which Intranasally Delivered Stem Cells Enter the Central Nervous System. Cell Transpl. 2018, 27, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kincaid, A.E.; Ayers, J.I.; Bartz, J.C. Specificity, Size, and Frequency of Spaces that Characterize the Mechanism of Bulk Transepithelial Transport of Prions in the Nasal Cavities of Hamsters and Mice. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8293–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Ren, J.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, G.; Hou, D.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F. Lymphatic clearance is the main drainage route of lamotrigine-loaded micelles following delivery to the brain. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.P.; Liu, H.J.; Cheng, S.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, X.; Yu, H.X.; Liu, X.F. Direct transport of VEGF from the nasal cavity to brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 449, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekman, J.D.; Ho, R.J. Effects of localized hydrophilic mannitol and hydrophobic nelfinavir administration targeted to olfactory epithelium on brain distribution. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekman, J.D.; Ho, R.J. Enhanced analgesic responses after preferential delivery of morphine and fentanyl to the olfactory epithelium in rats. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, B.; Bjork, E. Visualization of in vivo olfactory uptake and transfer using fluorescein dextran. J. Drug Target. 2002, 10, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dando, S.J.; Mackay-Sim, A.; Norton, R.; Currie, B.J.; St John, J.A.; Ekberg, J.A.; Batzloff, M.; Ulett, G.C.; Beacham, I.R. Pathogens penetrating the central nervous system: Infection pathways and the cellular and molecular mechanisms of invasion. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 691–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L. The olfactory vector hypothesis of neurodegenerative disease: Is it viable? Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensson, K. Microbes’ roadmap to neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, R.G.; Emory, C.R.; Ala, T.A.; Frey, W.H., II. Quantitative analysis of the olfactory pathway for drug delivery to the brain. Brain Res. 1995, 692, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, F.; Peppel, P. Central projections of trigeminal primary afferents innervating the nasal mucosa: A horseradish peroxidase study in the rat. Neuroscience 1991, 41, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwood, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Card, D.; Craine, A.; Ryan, T.M.; Drew, P.J. Anatomical basis and physiological role of cerebrospinal fluid transport through the murine cribriform plate. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, P. Arterial patterns of the rat rhinencephalon and related structures. Exp. Neurol. 1975, 49, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bojsen-Moller, F. Demonstration of terminalis, olfactory, trigeminal and perivascular nerves in the rat nasal septum. J. Comp. Neurol. 1975, 159, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, M.L.; Bottger, B.; Silver, W.L.; Finger, T.E. Trigeminal collaterals in the nasal epithelium and olfactory bulb: A potential route for direct modulation of olfactory information by trigeminal stimuli. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 444, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspelund, A.; Antila, S.; Proulx, S.T.; Karlsen, T.V.; Karaman, S.; Detmar, M.; Wiig, H.; Alitalo, K. A dural lymphatic vascular system that drains brain interstitial fluid and macromolecules. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, M.W.B.; Cserr, H.F. Drainage of cerebral interstitial fluid and of cerebrospinal fluid into lymphatics. In Experimental Biology of the Lymphatic Circulation; Johnston, M.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 9, pp. 355–391. [Google Scholar]
- Erlich, S.S.; McComb, J.G.; Hyman, S.; Weiss, M.H. Ultrastructural morphology of the olfactory pathway for cerebrospinal fluid drainage in the rabbit. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 64, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Keyes, T.J.; Eccles, J.D.; Rouhani, S.J.; Peske, J.D.; Derecki, N.C.; Castle, D.; Mandell, J.W.; Lee, K.S.; et al. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature 2015, 523, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, B.A.; Valera, V.A.; Takahashi, S.; Ushiki, T. The olfactory route for cerebrospinal fluid drainage into the peripheral lymphatic system. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2006, 32, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Cho, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ham, J.S.; Park, I.; Suh, S.H.; Hong, S.P.; Song, J.H.; Hong, Y.K.; et al. Meningeal lymphatic vessels at the skull base drain cerebrospinal fluid. Nature 2019, 572, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Ries, M.; Decker, Y.; Muller, A.; Riner, C.; Bucker, A.; Fassbender, K.; Detmar, M.; Proulx, S.T. Rapid lymphatic efflux limits cerebrospinal fluid flow to the brain. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Ma, Y.; Yi, X.; Guo, R.; Zhu, W.; Fan, X.; Xu, G.; Frey, W.H., II; Liu, X. Intranasal delivery of transforming growth factor-beta1 in mice after stroke reduces infarct volume and increases neurogenesis in the subventricular zone. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, W.M. The nasal mucosa and the subarachnoid space. Am. J. Anat. 1937, 62, 121–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, D.B.; Svitak, A.L.; Gallus, N.J.; Ericson, M.E.; Frey, W.H., II; Hanson, L.R. Intranasal delivery of insulin via the olfactory nerve pathway. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Pizzo, M.E.; Preston, J.E.; Janigro, D.; Thorne, R.G. The role of brain barriers in fluid movement in the CNS: Is there a ‘glymphatic’ system? Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, E.N.; Bacskai, B.J.; Arbel-Ornath, M.; Aldea, R.; Bedussi, B.; Morris, A.W.; Weller, R.O.; Carare, R.O. Lymphatic Clearance of the Brain: Perivascular, Paravascular and Significance for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hladky, S.B.; Barrand, M.A. Elimination of substances from the brain parenchyma: Efflux via perivascular pathways and via the blood-brain barrier. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldmann, J.; Kwidzinski, E.; Brandt, C.; Mahlo, J.; Richter, D.; Bechmann, I. T cells traffic from brain to cervical lymph nodes via the cribroid plate and the nasal mucosa. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatterer, E.; Davoust, N.; Didier-Bazes, M.; Vuaillat, C.; Malcus, C.; Belin, M.F.; Nataf, S. How to drain without lymphatics? Dendritic cells migrate from the cerebrospinal fluid to the B-cell follicles of cervical lymph nodes. Blood 2006, 107, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, M.; Bechmann, I.; Pohland, M.; Kiwit, J.; Nitsch, R.; Glumm, J. Migration of monocytes after intracerebral injection at entorhinal cortex lesion site. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, M.; Shimoda, H.; Kajiwara, T.; Kato, S.; Yanagisawa, S. Topographic study on nerve-associated lymphatic vessels in the murine craniofacial region by immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. Biomed. Res. 2008, 29, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Kellohen, K.L.; Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. Distribution of insulin in trigeminal nerve and brain after intranasal administration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadaczek, P.; Yamashita, Y.; Mirek, H.; Tamas, L.; Bohn, M.C.; Noble, C.; Park, J.W.; Bankiewicz, K. The “perivascular pump” driven by arterial pulsation is a powerful mechanism for the distribution of therapeutic molecules within the brain. Mol. Ther. 2006, 14, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Zeppenfeld, D.M.; Venkataraman, A.; Plog, B.A.; Liao, Y.; Deane, R.; Nedergaard, M. Cerebral arterial pulsation drives paravascular CSF-interstitial fluid exchange in the murine brain. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18190–18199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre, H.; Tithof, J.; Du, T.; Song, W.; Peng, W.; Sweeney, A.M.; Olveda, G.; Thomas, J.H.; Nedergaard, M.; Kelley, D.H. Flow of cerebrospinal fluid is driven by arterial pulsations and is reduced in hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, T.; Fraser, P.A.; Cserr, H.F. Distribution of extracellular tracers in perivascular spaces of the rat brain. Brain Res. 1991, 545, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzo, M.E.; Wolak, D.J.; Kumar, N.N.; Brunette, E.; Brunnquell, C.L.; Hannocks, M.J.; Abbott, N.J.; Meyerand, M.E.; Sorokin, L.; Stanimirovic, D.B.; et al. Intrathecal antibody distribution in the rat brain: Surface diffusion, perivascular transport and osmotic enhancement of delivery. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 445–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennels, M.L.; Gregory, T.F.; Blaumanis, O.R.; Fujimoto, K.; Grady, P.A. Evidence for a ‘paravascular’ fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Res. 1985, 326, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.T.; Richards, H.K.; Kida, S.; Weller, R.O. Directional and compartmentalised drainage of interstitial fluid and cerebrospinal fluid from the rat brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1992, 83, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albargothy, N.J.; Johnston, D.A.; MacGregor-Sharp, M.; Weller, R.O.; Verma, A.; Hawkes, C.A.; Carare, R.O. Convective influx/glymphatic system: Tracers injected into the CSF enter and leave the brain along separate periarterial basement membrane pathways. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hladky, S.B.; Barrand, M.A. Mechanisms of fluid movement into, through and out of the brain: Evaluation of the evidence. Fluids Barriers CNS 2014, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, H.; Heerdt, P.M.; Fontes, M.; Rothman, D.L.; Volkow, N.D. Glymphatic System Function in Relation to Anesthesia and Sleep States. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 128, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, L.; Iliff, J.J.; Heys, J.J. Analysis of convective and diffusive transport in the brain interstitium. Fluids Barriers CNS 2019, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lochhead, J.J.; Davis, T.P. Perivascular and Perineural Pathways Involved in Brain Delivery and Distribution of Drugs after Intranasal Administration. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110598
Lochhead JJ, Davis TP. Perivascular and Perineural Pathways Involved in Brain Delivery and Distribution of Drugs after Intranasal Administration. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(11):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110598
Chicago/Turabian StyleLochhead, Jeffrey J., and Thomas P. Davis. 2019. "Perivascular and Perineural Pathways Involved in Brain Delivery and Distribution of Drugs after Intranasal Administration" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 11: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110598
APA StyleLochhead, J. J., & Davis, T. P. (2019). Perivascular and Perineural Pathways Involved in Brain Delivery and Distribution of Drugs after Intranasal Administration. Pharmaceutics, 11(11), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110598