Exploring the Metabolism of Loxoprofen in Liver Microsomes: The Role of Cytochrome P450 and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase in Its Biotransformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
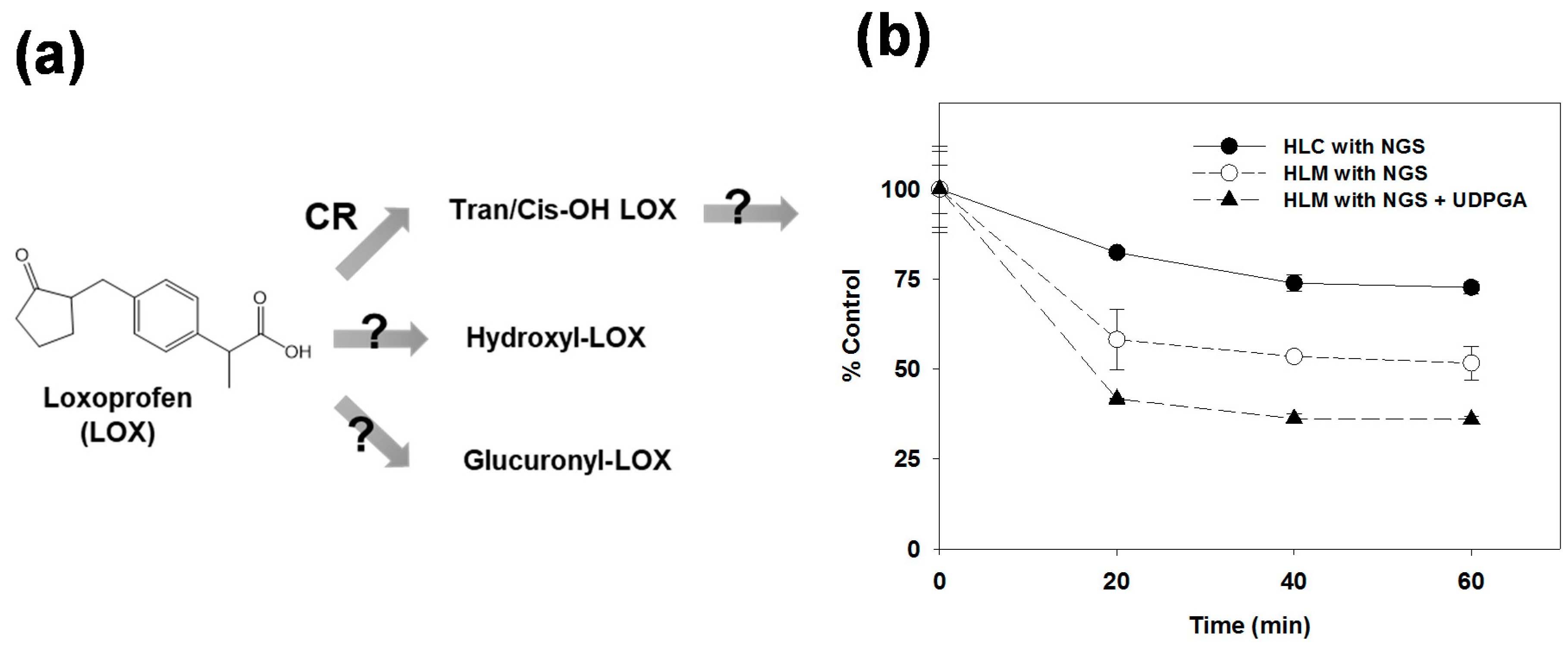
2.2. Metabolic Stabilities in Human Liver Microsomes and the Cytosols
2.3. Biotransformation of Loxoprofen in Microsomes and the Cytosols
2.4. Metabolism of Loxoprofen in Chemically-Induced Microsomes and CYP Enzyme Inhibitors
2.5. Recombinant cDNA-Expressed CYPs and UGTs Metabolism of Loxoprofen
2.6. Instrument
3. Results
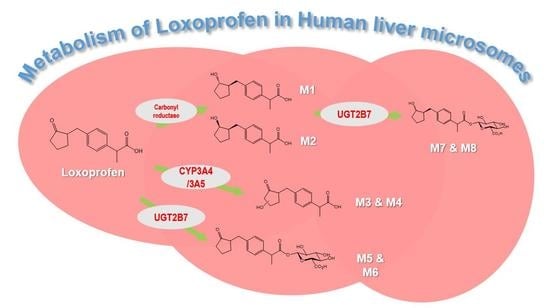
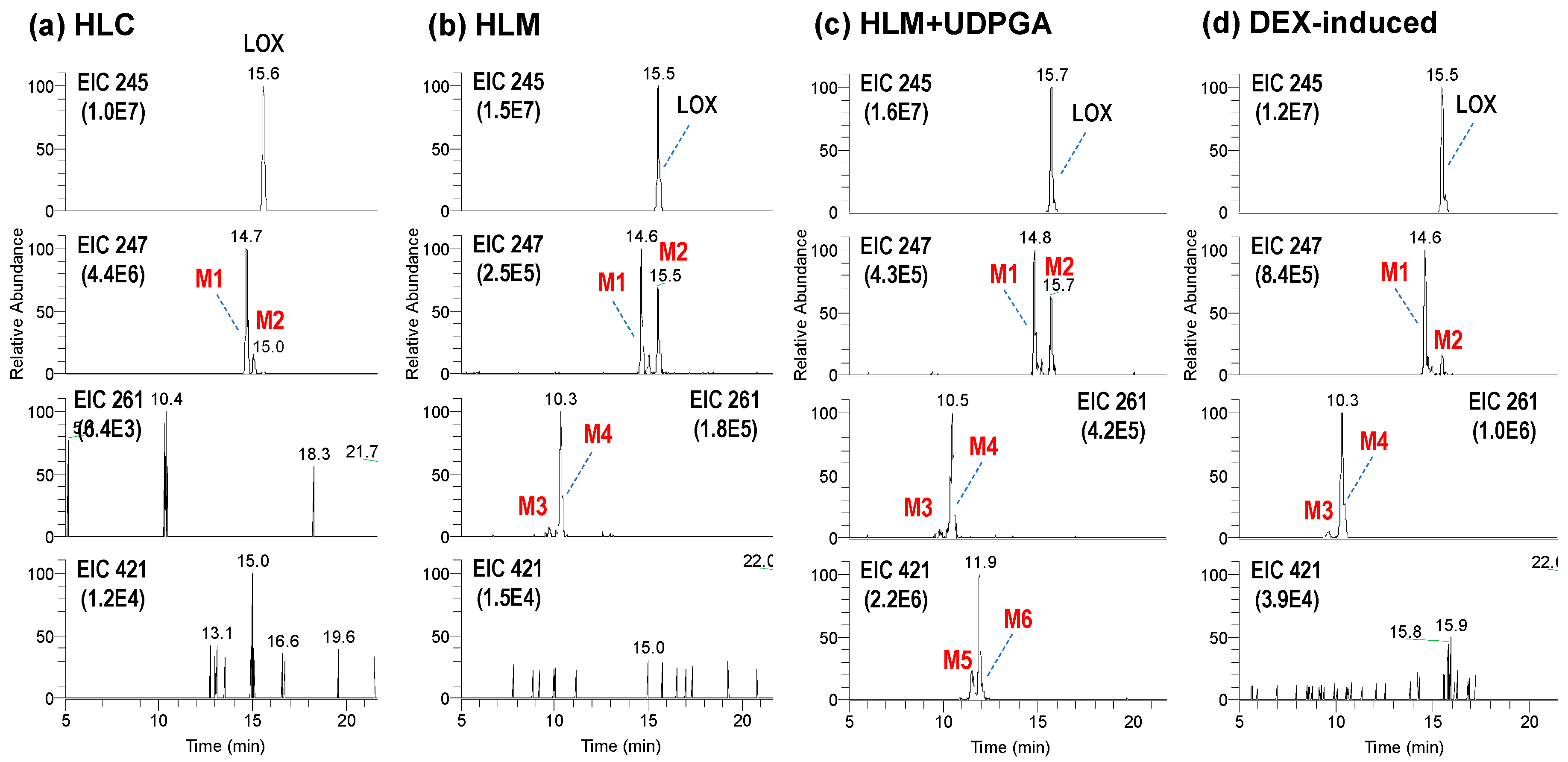
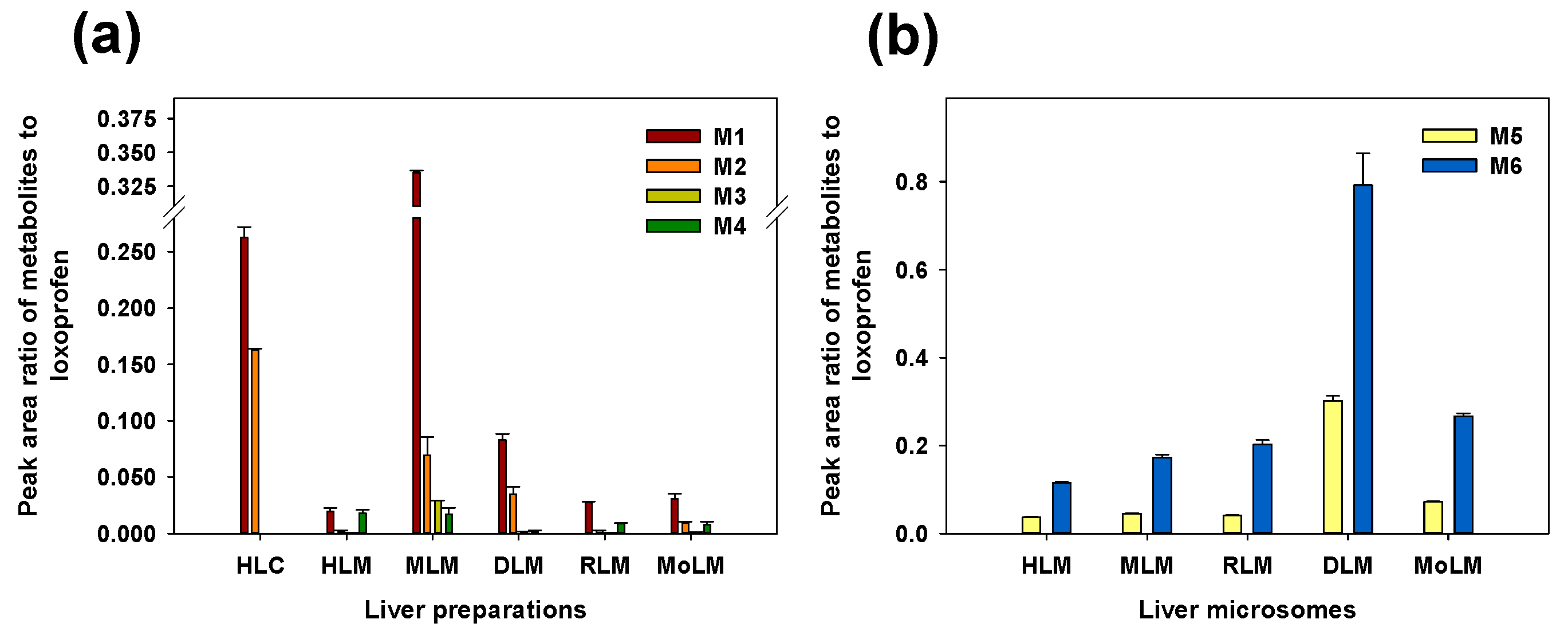
3.1. Microsomal Metabolism of Loxoprofen
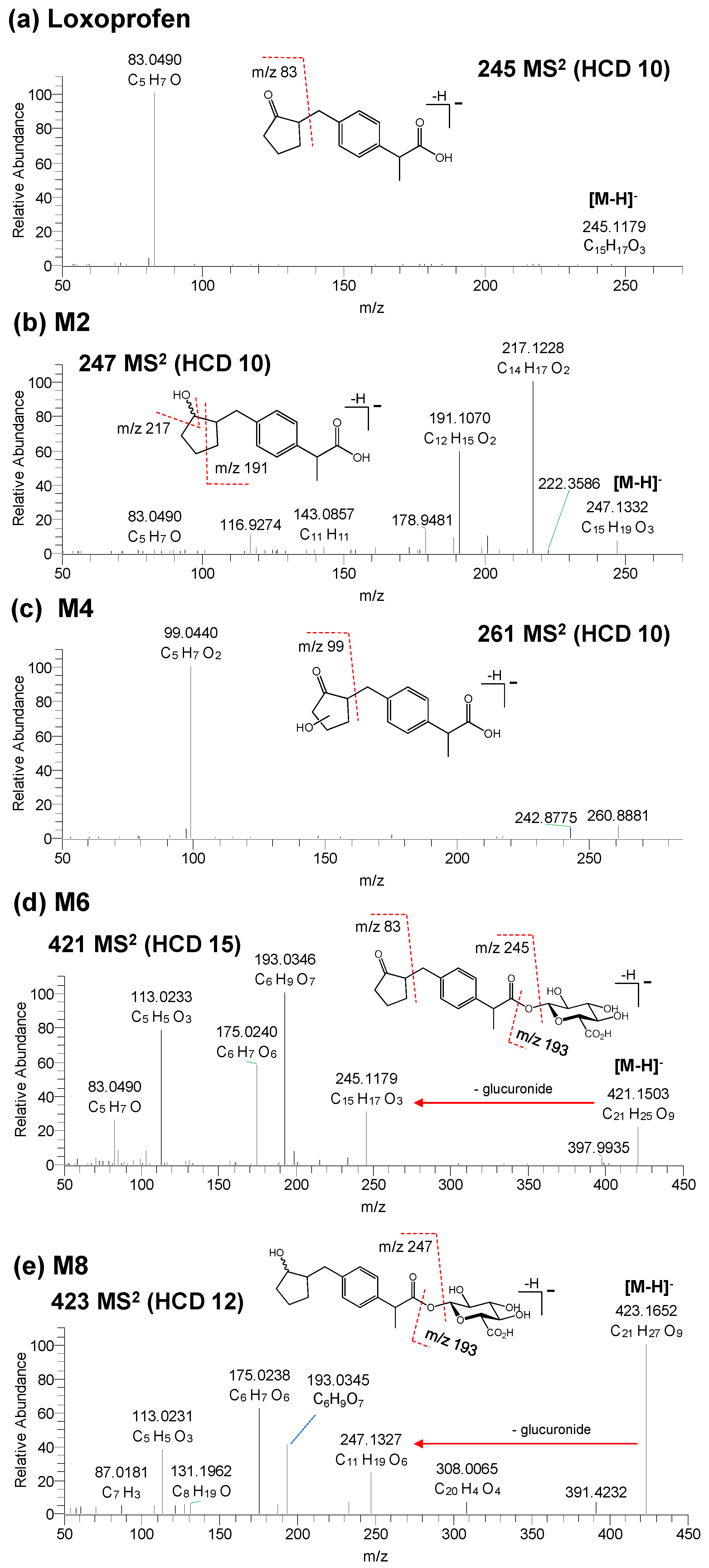
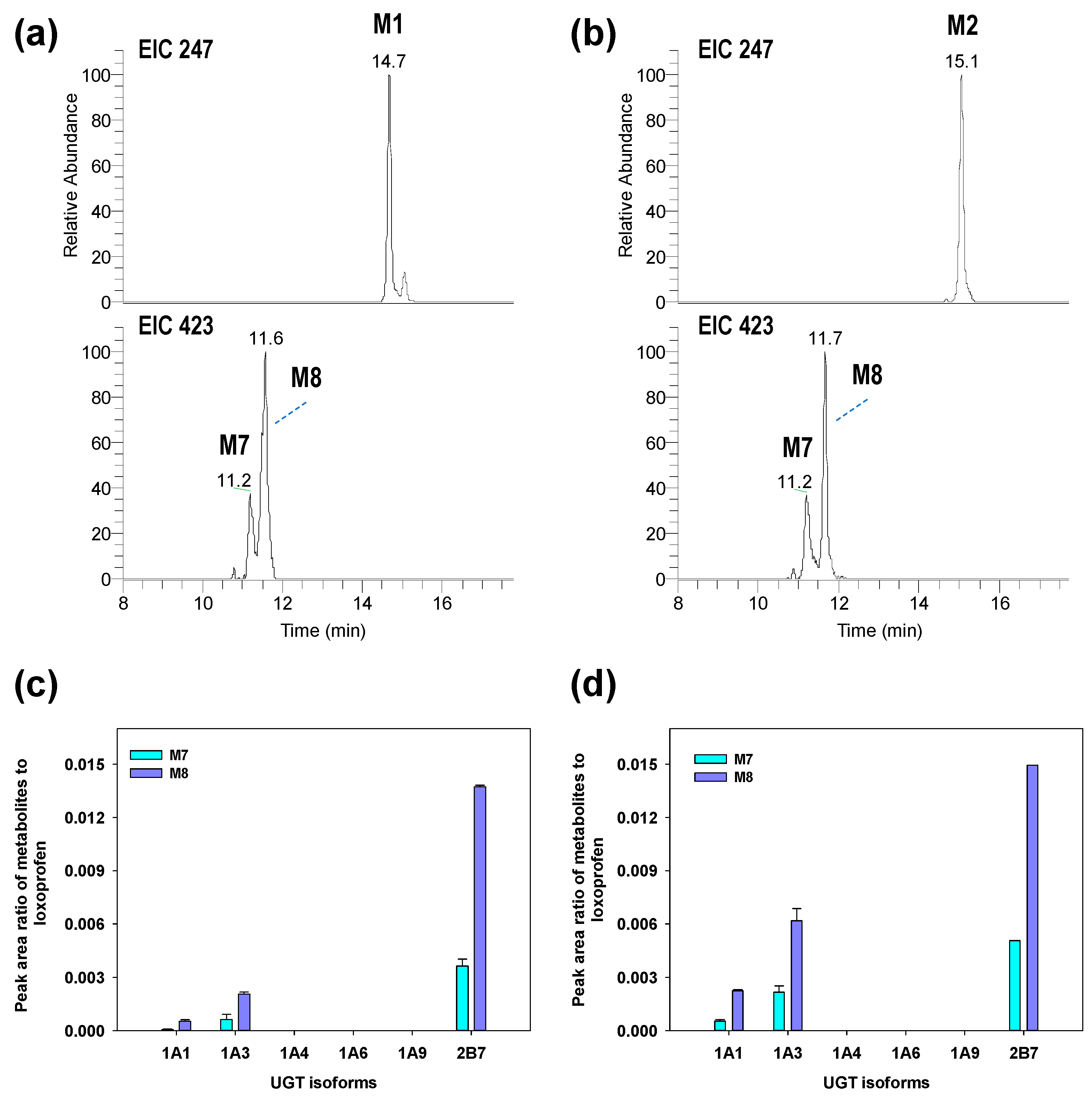
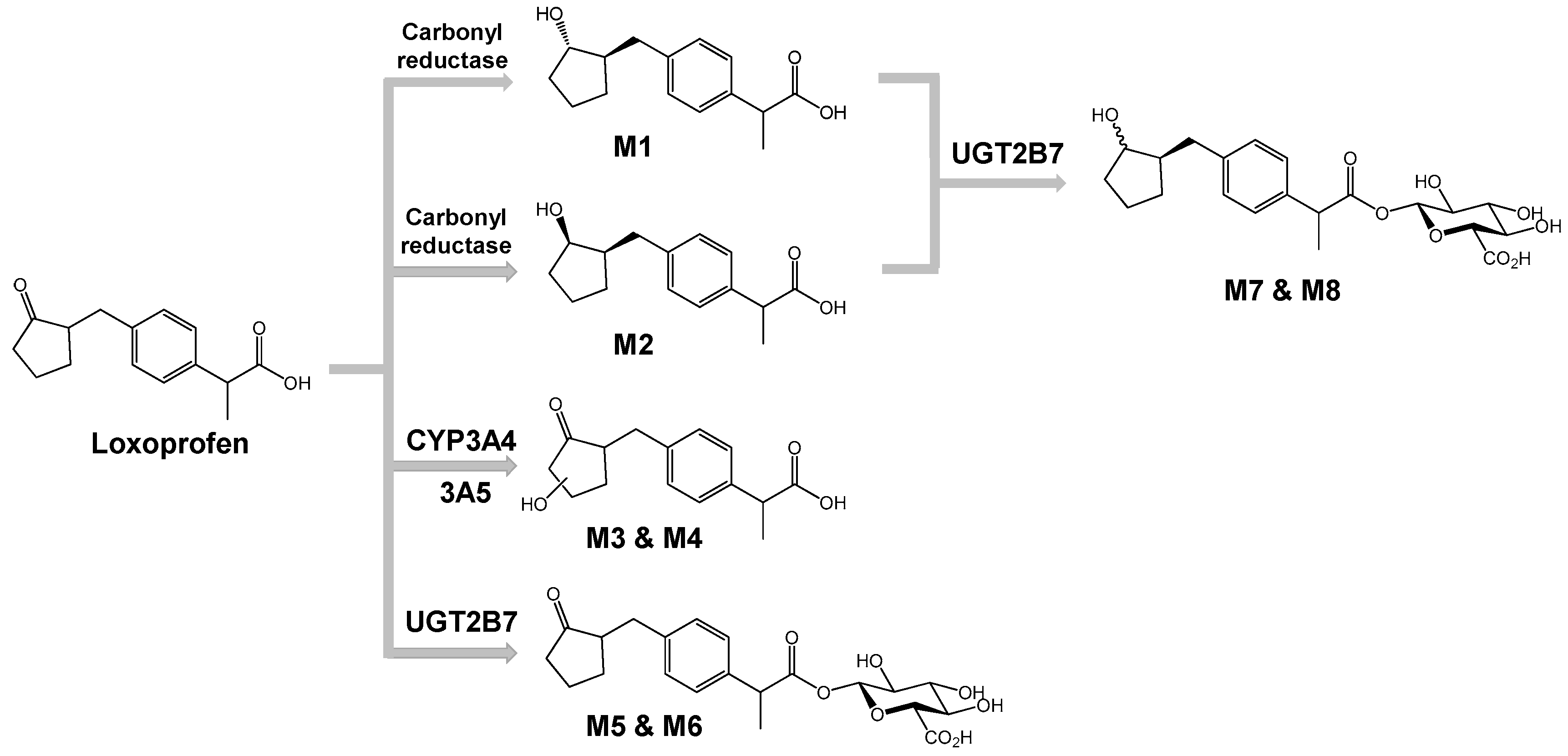
3.2. Structure Elucidation of Microsomal Metabolites In Vitro
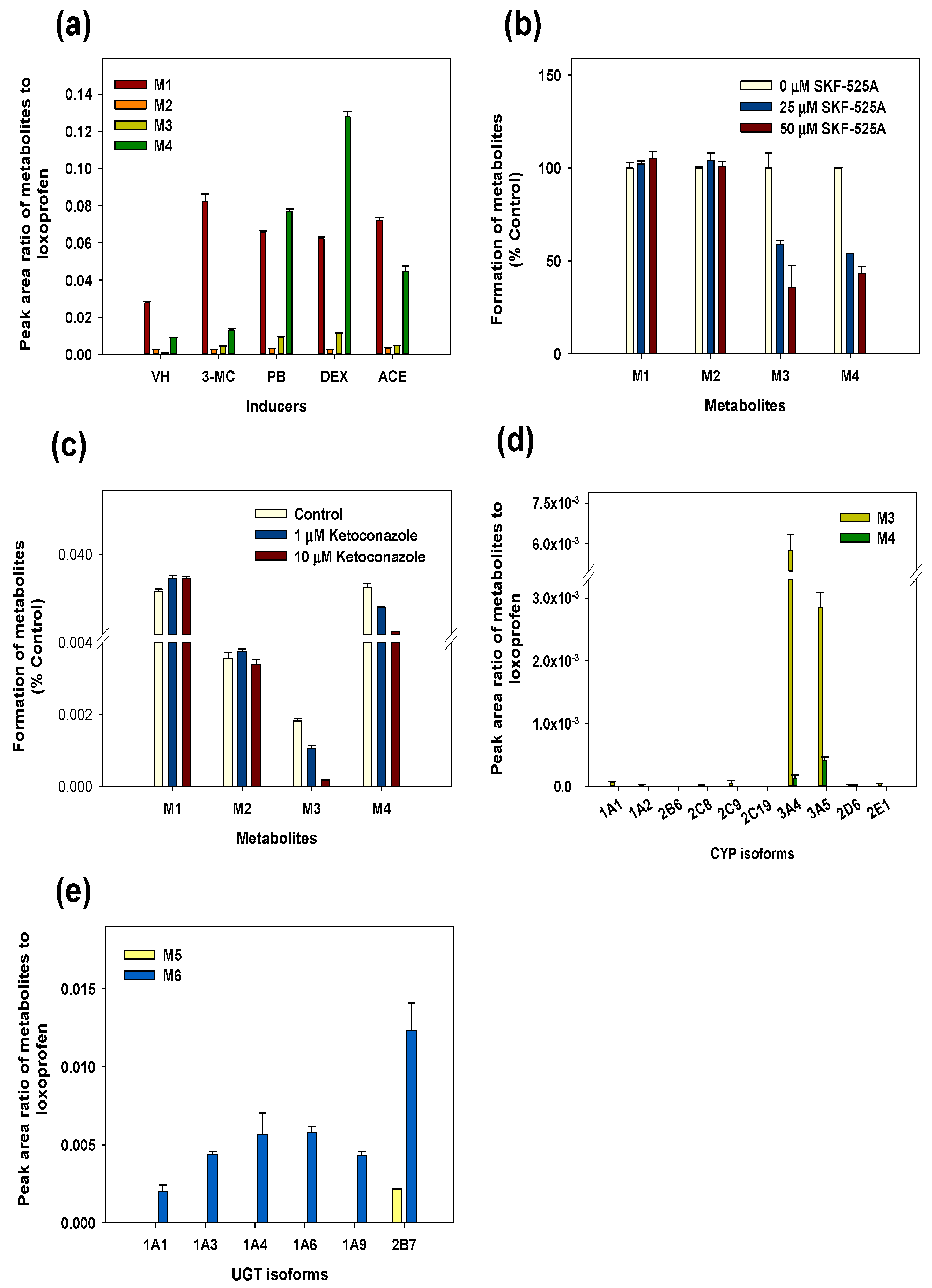
3.3. Reaction Phenotyping for Phase 1 and Phase 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Supplemental Methods
Animal Treatment and Preparation of Liver Microsomes
Instrument for Metabolic Stability
Appendix A.2. Supplemental Data
References
- Greig, S.L.; Garnock-Jones, K.P. Loxoprofen: A review in pain and inflammation. Clin. Drug. Investig. 2016, 36, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asami, T.; Yamanouchi, N.; Asami, A.; Tanaka, H.; Nogami, N. The effectiveness of patches containing loxoprofen sodium hydrate (lx-p) in the conservative therapy of muscular back pain—Clinical results using the japanese orthopaedic association back pain evaluation questionnaire (joabpeq). Jpn. J. Compr. Rehabil. Sci. 2013, 4, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Waikakul, S.; Soparat, K. Effectiveness and safety of loxoprofen compared with naproxen in nonsurgical low back pain. Clin. Drug. Investig. 1995, 10, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Hayashi, R.; Kawada, K. Optical inversion of (2R)-to (2S)-isomers of 2-[4-(2-administration oxocyclopentylmethyl)-phenyl] propionic acid (loxoprofen), a new anti-inflammatory agent, and its monohydroxy metabolites in the rat. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1984, 32, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.S.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, I.W.; Seo, S.Y.; Suh, Y.G.; Kim, D.D.; Shim, C.K.; Chung, S.J. Comparison of pharmacokinetics of loxoprofen and its active metabolites after an intravenous, intramuscular, and oral of loxoprofen in rats: Evidence for extrahepatic metabolism. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, C.; Kawai, T.; Nakamura, S.; Sugioka, T.; Tabira, J. Comparison of gastroduodenal ulcer incidence in healthy japanese subjects taking celecoxib or loxoprofen evaluated by endoscopy: A placebo-controlled, double-blind 2-week study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, H.; Inoue, G.; Nakazawa, T.; Imura, T.; Saito, W.; Uchida, K.; Miyagi, M.; Takahira, N.; Takaso, M. Loxoprofen sodium and celecoxib for postoperative pain in patients after spinal surgery: A randomized comparative study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2015, 20, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniwa, N.; Ueta, M.; Nakamura, R.; Okamoto-Uchida, Y.; Sugiyama, E.; Maekawa, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Furuya, H.; Yagami, A.; Matsukura, S. Drugs causing severe ocular surface involvements in japanese patients with stevensejohnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ueharaguchi, Y. Loxoprofen/piperacillin acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Reactions 2011, 1355, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.; Shi, J.; Jiang, P.; Sun, H. Acute kidney injury during concomitant use of valacyclovir and loxoprofen: Detecting drug–drug interactions in a spontaneous reporting system. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2014, 23, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Deguchi, Y.; Noda, K. Interaction between enoxacin, a new antimicrobial, and nimesulide, a new non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent in mice. Inflamm. Res. 1996, 45, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, K.; Akagi, Y.; Nozawa, N.; Shimomura, H.; Aoyama, T. Influence of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on aspirin’s antiplatelet effects and suggestion of the most suitable time for administration of both agents without resulting in interaction. J. Pharm. Health Care Sci. 2017, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, N.; Suemasu, S.; Watanabe, H.; Tahara, K.; Tanaka, K.-I.; Okamoto, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Maruyama, T.; Mizushima, T. Comparison of pharmacokinetics between loxoprofen and its derivative with lower ulcerogenic activity, fluoro-loxoprofen. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 28, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Ji, H.Y.; Sohn, D.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, Y.B.; Lee, H.S. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method of loxoprofen in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamura, R.; Kazui, M.; Kurihara, A.; Izumi, T. Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of loxoprofen after dermal application of loxoprofen gel to rats. Xenobiotica 2014, 44, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamura, R.; Sakurai, H.; Wada, N.; Nishiya, Y.; Honda, T.; Kazui, M.; Kurihara, A.; Shinagawa, A.; Izumi, T. Bioactivation of loxoprofen to a pharmacologically active metabolite and its disposition kinetics in human skin. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2015, 36, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhee, O.H.; Lee, M.H.; Shaw, L.M.; Lee, S.E.; Park, J.H.; Kang, J.S. Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence study of two brands of loxoprofen tablets in healthy volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung 2007, 57, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Park, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Direct and simultaneous analysis of loxoprofen and its diastereometric alcohol metabolites in human serum by on-line column switching liquid chromatography and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2006, 835, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, H.; Tsubayashi, A.; Nagata, Y.; Matsushima, Y.; Mori, C.; Kizu, J.; Higaki, M. Stereospecific analysis of loxoprofen in plasma by chiral column liquid chromatography with a circular dichroism-based detector. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 948, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-W.; Chung, S.-J.; Shim, C.-K. Altered metabolism of orally administered loxoprofen in human subjects after an oral administration of loxoprofen for three consecutive days followed by a seven-day washout. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nishikawa, Y.; Hayashi, R. Species differences in metabolism of sodium 2-[4-(2-oxocyclopentylmethyl)-phenyl] propionate dihydrate (loxoprofen sodium), a new anti-inflammatory agent. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 3656–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruto, S.; Terada, A. Synthesis of the 8 possible optically-active isomers of 2-[4-(2-hydroxycyclopentylmethyl) phenyl] propionic acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 4319–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.O.; Lee, S.K.; Jeon, T.W.; Jin, C.H.; Hyun, S.H.; Kim, E.J.; Moon, G.I.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, B.M.; et al. Role of metabolism in parathion-induced hepatotoxicity and immunotoxicity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2005, 68, 2187–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emoto, C.; Murase, S.; Sawada, Y.; Jones, B.C.; Iwasaki, K. In vitro inhibitory effect of 1-aminobenzotriazole on drug oxidations catalyzed by human cytochrome P450 enzymes: A comparison with SKF-525A and ketoconazole. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 18, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasanen, M. Species differences in CYP enzymes. Monografías de la Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia 2014, XIV, 63–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sharer, J.E.; Shipley, L.A.; Vandenbranden, M.R.; Binkley, S.N.; Wrighton, S.A. Comparisons of phase i and phase ii in vitro hepatic enzyme activities of human, dog, rhesus monkey, and cynomolgus monkey. Drug Metab. Dispos 1995, 23, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soars, M.G.; Riley, R.J.; Findlay, K.A.; Coffey, M.J.; Burchell, B. Evidence for significant differences in microsomal drug glucuronidation by canine and human liver and kidney. Drug Metab. Dispos 2001, 29, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.; Plant, N.; Swales, K.; Ayrton, A.; El-Sankary, W. Receptor-dependent transcriptional activation of cytochrome P4503A genes: Induction mechanisms, species differences and interindividual variation in man. Xenobiotica 2002, 32, 165–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honig, P.K.; Wortham, D.C.; Zamani, K.; Conner, D.P.; Mullin, J.C.; Cantilena, L.R. Terfenadine-ketoconazole interaction. JAMA 1993, 269, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.M.; Strong, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Reynolds, K.S.; Nallani, S.; Temple, R.; Abraham, S.; Habet, S.A.; Baweja, R.K.; Burckart, G.J. New era in drug interaction evaluation: Us food and drug administration update on CYP enzymes, transporters, and the guidance process. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 48, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, K.; Matsuda, H.; Nagase, K.; Shiraga, T.; Tokuma, Y.; Uchida, K. Effects of twenty-three drugs on the metabolism of FK506 by human liver microsomes. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol 1993, 82, 209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, C. Casarett & Doull’s Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Ma, X.; Krausz, K.W.; Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Rifampicin-activated human PXR and CYP3A4 induction enhance acetaminophen-induced toxicity. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, M.; Weidolf, L. Metabolism of xenobiotic carboxylic acids: Focus on coenzyme a conjugation, reactivity, and interference with lipid metabolism. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 1139–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassila, T.; Hokkanen, J.; Aatsinki, S.M.; Mattila, S.; Turpeinen, M.; Tolonen, A. Toxicity of carboxylic acid-containing drugs: The role of acyl migration and coa conjugation investigated. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 2292–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skonberg, C.; Olsen, J.; Madsen, K.G.; Hansen, S.H.; Grillo, M.P. Metabolic activation of carboxylic acids. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, H.K.; Klotz, U. Glucuronidation of drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 23, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, S.L.; Maggs, J.L.; Hammond, T.G.; Lambert, C.; Williams, D.P.; Park, B.K. Acyl glucuronides: The good, the bad and the ugly. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2010, 31, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehl, G.E.; Lampe, J.W.; Potter, J.D.; Bigler, J. Glucuronidation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Identifying the enzymes responsible in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinno, N.; Tagashira, M.; Tsurui, K.; Yamada, S. Contribution of cytochrome P450 and UDT-glucuronosyltransferase to the metabolism of drugs containing carboxylic acid groups: Risk assessment of acylglucuronides using human hepatocytes. Xenobiotica 2014, 44, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiang, T.K.; Ensom, M.H.; Chang, T.K. UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and clinical drug-drug interactions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 106, 97–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soars, M.G.; Petullo, D.M.; Eckstein, J.A.; Kasper, S.C.; Wrighton, S.A. An assessment of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase induction using primary human hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, R.; Cho, P.J.; Paudel, S.; Shrestha, A.; Kang, M.J.; Jeong, T.C.; Lee, E.-S.; Lee, S. Exploring the Metabolism of Loxoprofen in Liver Microsomes: The Role of Cytochrome P450 and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase in Its Biotransformation. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030112
Shrestha R, Cho PJ, Paudel S, Shrestha A, Kang MJ, Jeong TC, Lee E-S, Lee S. Exploring the Metabolism of Loxoprofen in Liver Microsomes: The Role of Cytochrome P450 and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase in Its Biotransformation. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030112
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Riya, Pil Joung Cho, Sanjita Paudel, Aarajana Shrestha, Mi Jeong Kang, Tae Cheon Jeong, Eung-Seok Lee, and Sangkyu Lee. 2018. "Exploring the Metabolism of Loxoprofen in Liver Microsomes: The Role of Cytochrome P450 and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase in Its Biotransformation" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030112
APA StyleShrestha, R., Cho, P. J., Paudel, S., Shrestha, A., Kang, M. J., Jeong, T. C., Lee, E.-S., & Lee, S. (2018). Exploring the Metabolism of Loxoprofen in Liver Microsomes: The Role of Cytochrome P450 and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase in Its Biotransformation. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030112