Identification of a Novel Inhibitor against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design, Expression and Purification of MERS-5HB
2.2. Binding Assay by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.2.1. Binding of MERS-5HB to Immobilized Peptide
2.2.2. Binding of Peptide to Coated MERS-5HB
2.3. Affinity Measurement by Biolayer Interferometry
2.4. Pseudovirus Preparation and Titration
2.5. Inhibition of Pseudotyped MERS-CoV Infection
2.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.7. Inhibition of MERS-CoV S Protein-Mediated Cell–Cell Fusion
2.8. Biophysical Characterization of MERS-5HB
2.8.1. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Analysis
2.8.2. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. Design of MERS-5HB
3.2. Interactions between MERS-5HB and MERS-HR2P
3.3. Inhibition of Pseudotyped MERS-CoV Infection
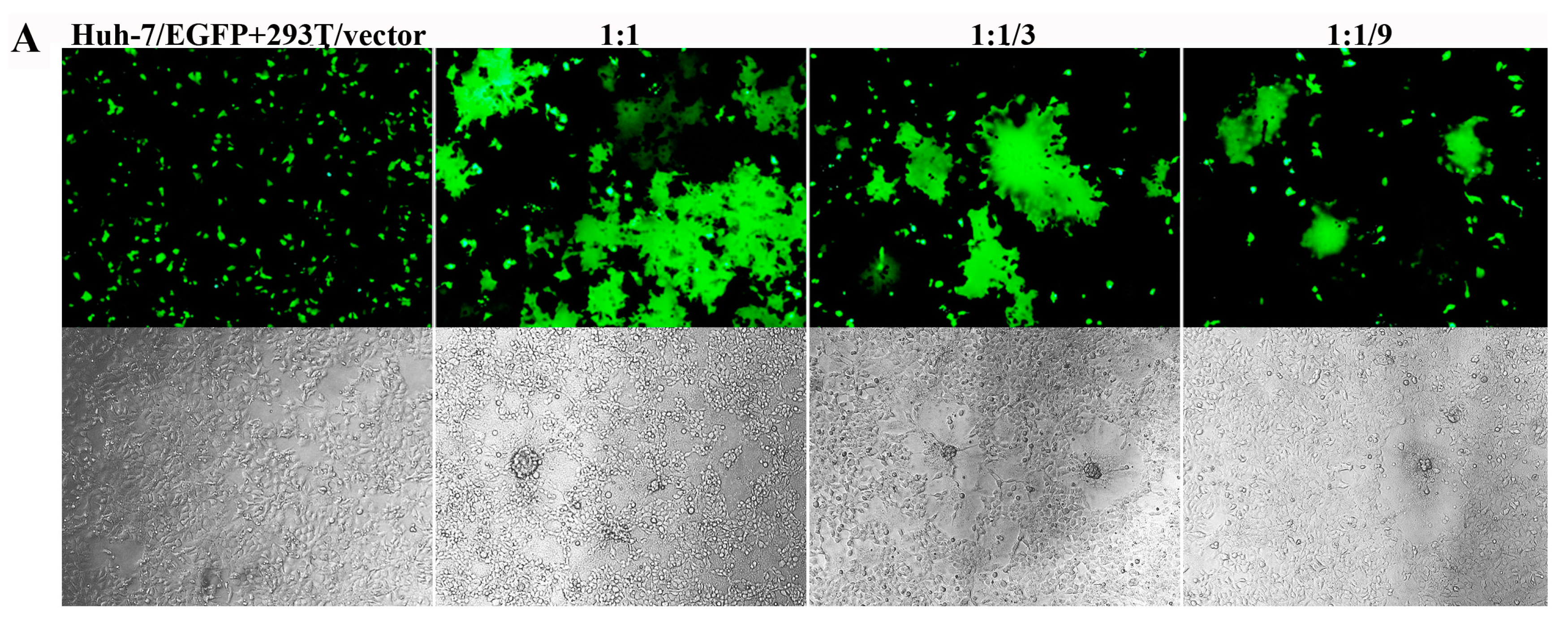
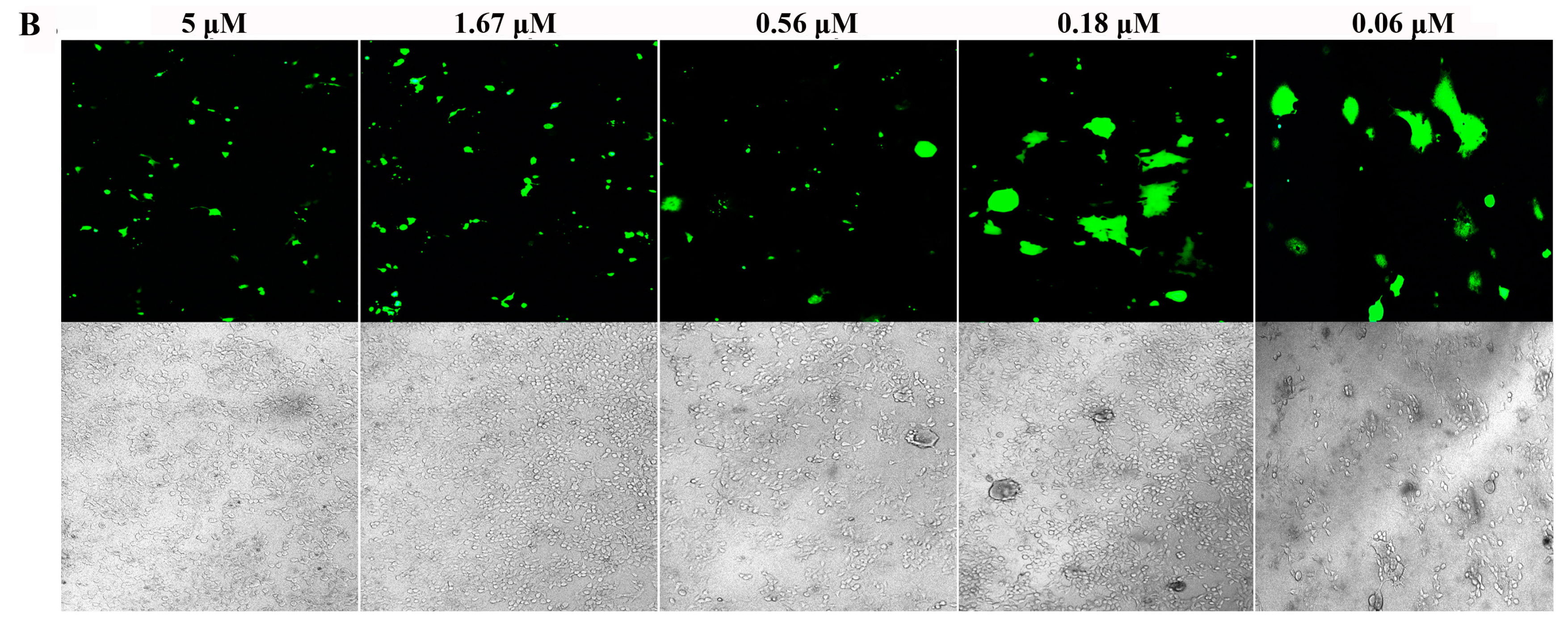
3.4. Inhibition of S Protein-Mediated Cell–Cell Fusion
3.5. Biophysical Characterization of MERS-5HB
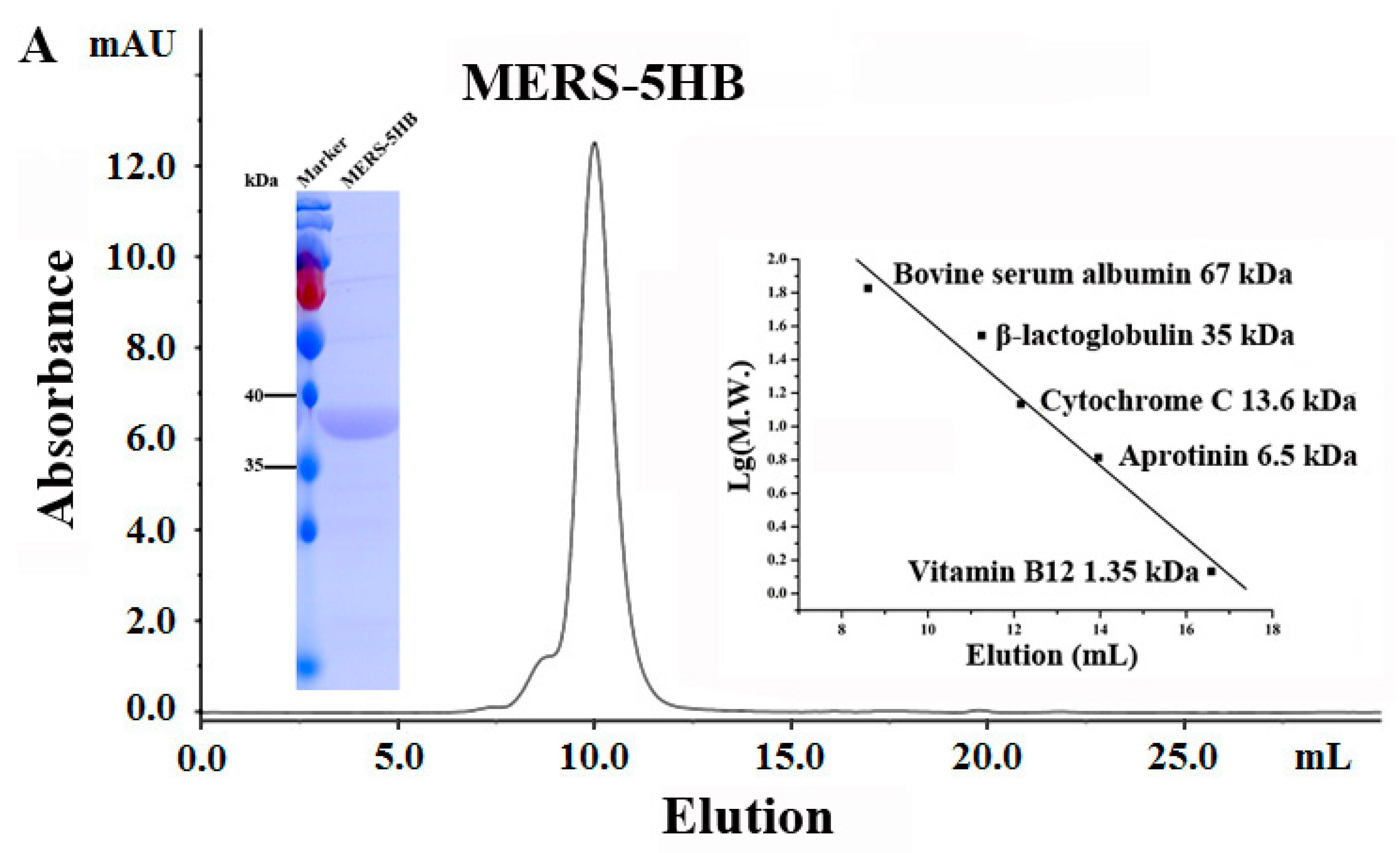
3.5.1. MERS-5HB Exists as a Monomer
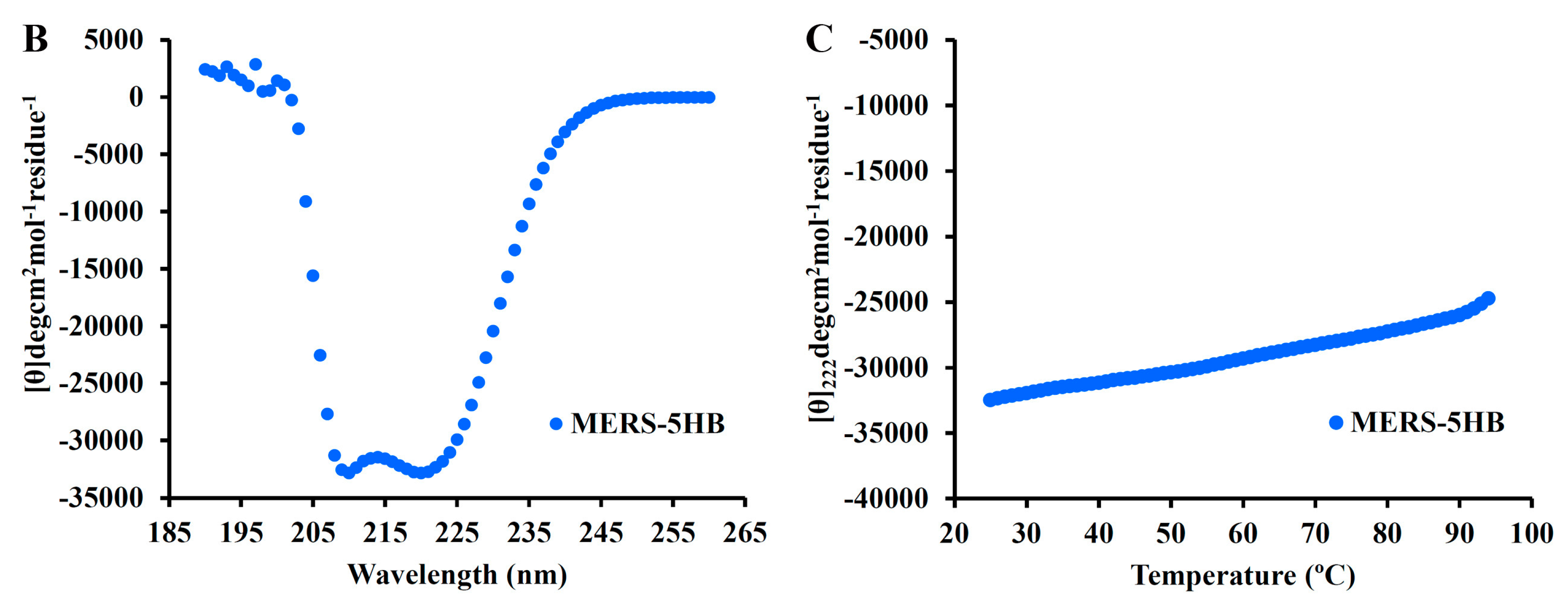
3.5.2. MERS-5HB Exhibits Thermo Stable α-Helical Conformation
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosten, C.; Gunther, S.; Preiser, W.; van der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.R.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris, J.S.; Lai, S.T.; Poon, L.L.; Guan, Y.; Yam, L.Y.; Lim, W.; Nicholls, J.; Yee, W.K.; Yan, W.W.; Cheung, M.T.; et al. Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet 2003, 361, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.S.; Zheng, B.J.; Li, Y.M.; Poon; Xie, Z.H.; Chan, K.H.; Li, P.H.; Tan, S.Y.; Chang, Q.; Xie, J.P.; et al. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet 2003, 362, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, A.; Chand, M.A.; Brown, C.S.; Aarons, E.; Tong, C.; Langrish, C.; Hoschler, K.; Brown, K.; Galiano, M.; Myers, R.; et al. Severe respiratory illness caused by a novel coronavirus, in a patient transferred to the United Kingdom from the Middle East, September 2012. Euro Surveill. 2012, 17, 20290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guery, B.; Poissy, J.; el Mansouf, L.; Sejourne, C.; Ettahar, N.; Lemaire, X.; Vuotto, F.; Goffard, A.; Behillil, S.; Enouf, V.; et al. Clinical features and viral diagnosis of two cases of infection with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus: A report of nosocomial transmission. Lancet 2013, 381, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Novel Coronavirus Infection-Update (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus). Available online: http://www.Who.Int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/ (accessed on 7 June 2017).
- Kupferschmidt, K. Emerging diseases. Soaring MERS cases in Saudi Arabia raise alarms. Science 2014, 344, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamati, P.; Razavi, S.M. Be vigilant: New MERS-CoV outbreaks can occur in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2015, 13, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Lu, G.; Qi, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Geng, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, H.; et al. Structure of the fusion core and inhibition of fusion by a heptad repeat peptide derived from the S protein of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13134–13140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chan, K.H.; Qin, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chan, J.F.; Du, L.; Yu, F.; et al. Structure-based discovery of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus fusion inhibitor. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Shin, J.S.; Shie, J.J.; Ku, K.B.; Kim, C.; Go, Y.Y.; Huang, K.F.; Kim, M.; Liang, P.H. Identification and evaluation of potent Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) 3CLPro inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, T.; Du, L.; Ju, T.W.; Prabakaran, P.; Lau, C.C.; Lu, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Exceptionally potent neutralization of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus by human monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7796–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J.; Lu, G.; Qi, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. A humanized neutralizing antibody against MERS-CoV targeting the receptor-binding domain of the spike protein. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, N.K.; Padron-Regalado, E.; Thompson, C.P.; Kupke, A.; Wells, D.; Sloan, M.A.; Grehan, K.; Temperton, N.; Lambe, T.; Warimwe, G.; et al. ChAdOx1 and MVA based vaccine candidates against MERS-CoV elicit neutralising antibodies and cellular immune responses in mice. Vaccine 2017, 35, 3780–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Kallies, R.; Philipps, H.; Gopner, G.; Muller, M.A.; Eckerle, I.; Brunink, S.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Characterization of a novel betacoronavirus related to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in European hedgehogs. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Shi, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Tong, P.; Guo, D.; Fu, L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Structure of MERS-CoV spike receptor-binding domain complexed with human receptor DPP4. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qi, J.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Bao, J.; et al. Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26. Nature 2013, 500, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhao, G.; Kou, Z.; Ma, C.; Sun, S.; Poon, V.K.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Debnath, A.K.; Zheng, B.J.; et al. Identification of a receptor-binding domain in the S protein of the novel human coronavirus Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus as an essential target for vaccine development. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9939–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Mou, H.; Smits, S.L.; Dekkers, D.H.; Muller, M.A.; Dijkman, R.; Muth, D.; Demmers, J.A.; Zaki, A.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013, 495, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xiao, G.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Niu, J.; Escalante, C.R.; Xiong, H.; Farmar, J.; Debnath, A.K.; Tien, P.; et al. Interaction between heptad repeat 1 and 2 regions in spike protein of SARS-associated coronavirus: Implications for virus fusogenic mechanism and identification of fusion inhibitors. Lancet 2004, 363, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Berger, B.; Kim, P.S. LearnCoil-VMF: Computational evidence for coiled-coil-like motifs in many viral membrane-fusion proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 290, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Kou, Z.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Jiang, S. Receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein induces highly potent neutralizing antibodies: Implication for developing subunit vaccine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Du, L.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Poon, V.K.; Wang, L.; Yu, F.; Zheng, B.J.; Jiang, S.; et al. A safe and convenient pseudovirus-based inhibition assay to detect neutralizing antibodies and screen for viral entry inhibitors against the novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, V.A.; Byington, R.E. Infectivity Assay (Virus Yield Assay); Stockton Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Gao, F.; Mascola, J.R.; Stamatatos, L.; Polonis, V.R.; Koutsoukos, M.; Voss, G.; Goepfert, P.; Gilbert, P.; Greene, K.M.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 ENV clones from acute and early subtype B infections for standardized assessments of vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10108–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Su, S.; Du, L.; Ying, T.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) entry inhibitors targeting spike protein. Virus Res. 2014, 194, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Feng, L.; Bao, J.K. The receptor binding domain of MERS-CoV: The dawn of vaccine and treatment development. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Tang, J.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S.; Du, L. Receptor-binding domain-based subunit vaccines against MERS-CoV. Virus Res. 2015, 202, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Tai, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, S.; Liu, C.; Tao, X.; Tseng, C.K.; Perlman, S.; et al. Introduction of neutralizing immunogenicity index to the rational design of MERS coronavirus subunit vaccines. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockx, B.; Donaldson, E.; Frieman, M.; Sheahan, T.; Corti, D.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Baric, R.S. Escape from human monoclonal antibody neutralization affects in vitro and in vivo fitness of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Deming, M.; Rockx, B.; Liddington, R.C.; Zhu, Q.K.; Baric, R.S.; Marasco, W.A. Effects of human anti-spike protein receptor binding domain antibodies on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus neutralization escape and fitness. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13769–13780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Lin, K.; Strick, N.; Neurath, A.R. HIV-1 inhibition by a peptide. Nature 1993, 365, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, C.T.; Shugars, D.C.; Greenwell, T.K.; McDanal, C.B.; Matthews, T.J. Peptides corresponding to a predictive alpha-helical domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 are potent inhibitors of virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9770–9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilby, J.M.; Hopkins, S.; Venetta, T.M.; DiMassimo, B.; Cloud, G.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Alldredge, L.; Hunter, E.; Lambert, D.; Bolognesi, D.; et al. Potent suppression of HIV-1 replication in humans by T-20, a peptide inhibitor of gp41-mediated virus entry. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, M.J.; Kay, M.S.; Kim, P.S. Protein design of an HIV-1 entry inhibitor. Science 2001, 291, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, M.J.; Hamer, D.H. Targeting therapeutics to an exposed and conserved binding element of the HIV-1 fusion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5016–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, R. Identification of a Novel Inhibitor against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. Viruses 2017, 9, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090255
Sun Y, Zhang H, Shi J, Zhang Z, Gong R. Identification of a Novel Inhibitor against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. Viruses. 2017; 9(9):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090255
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yaping, Huaidong Zhang, Jian Shi, Zhe Zhang, and Rui Gong. 2017. "Identification of a Novel Inhibitor against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus" Viruses 9, no. 9: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090255




