Regulation of Apoptosis during Flavivirus Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
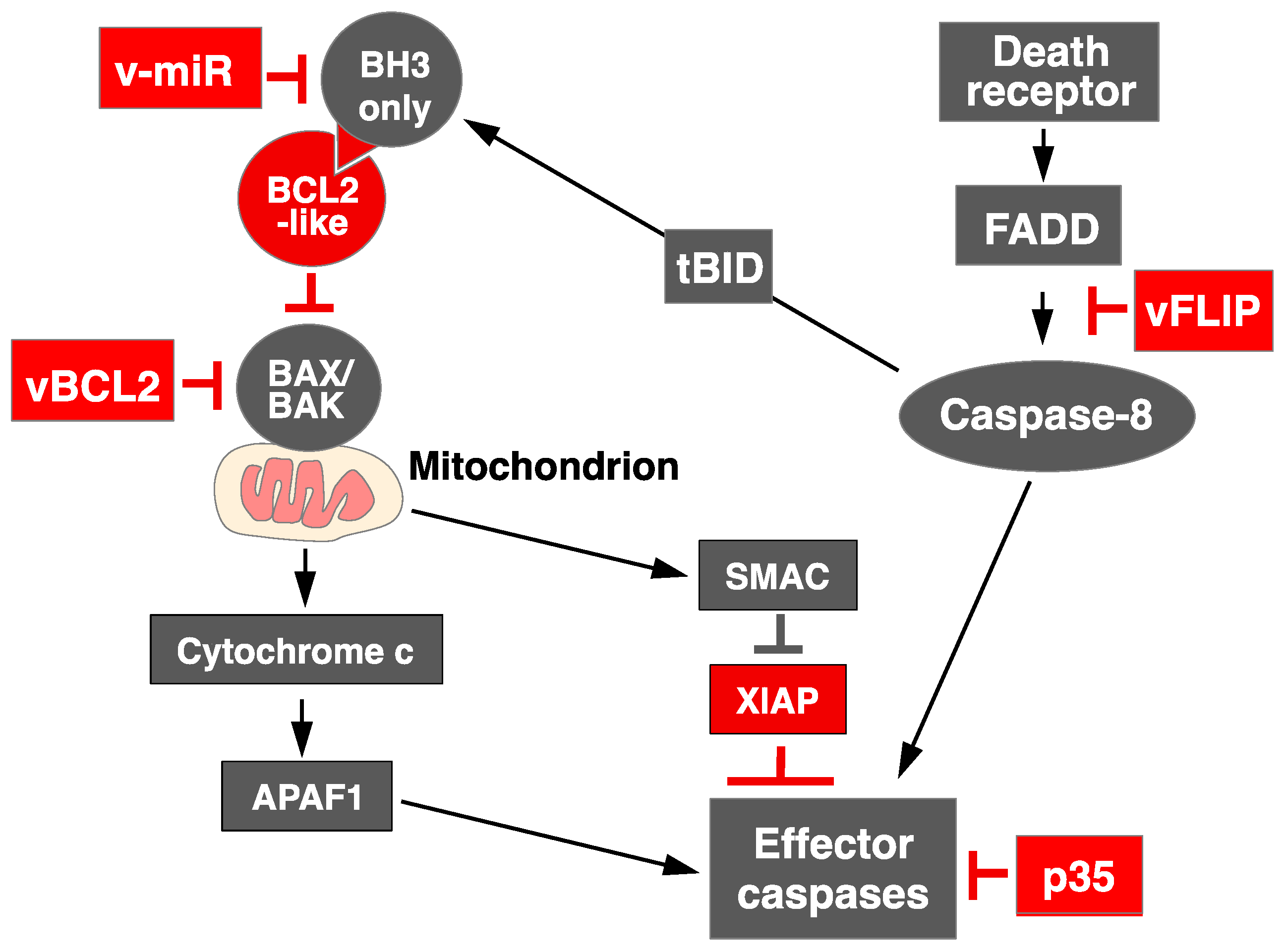
1.1. Overview of Apoptosis Signaling
1.2. Application of Mitochondria Mediated Apoptosis to Cancer Therapy
1.3. Apoptosis Regulation by RNA Virus: Lessons from DNA Virus
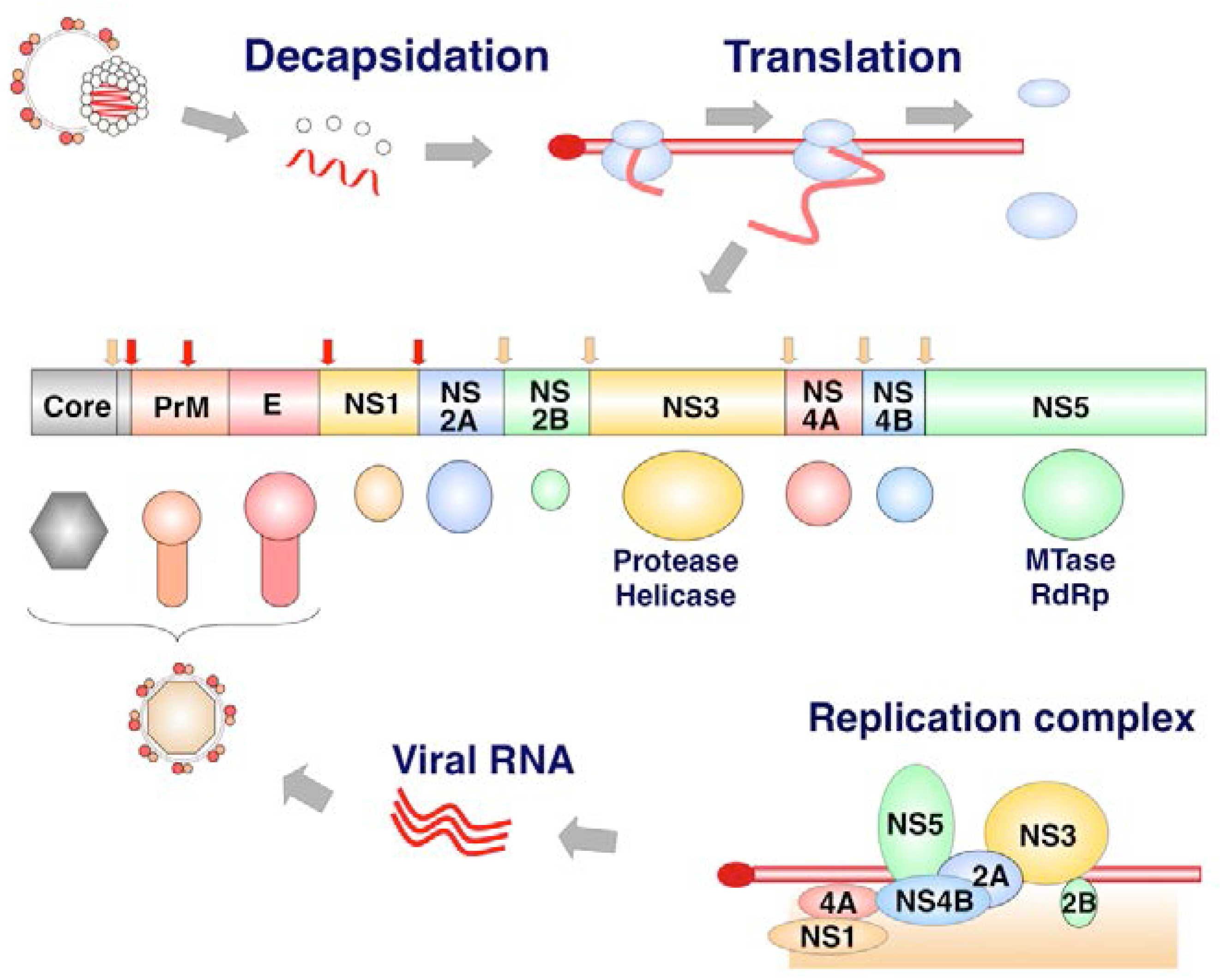
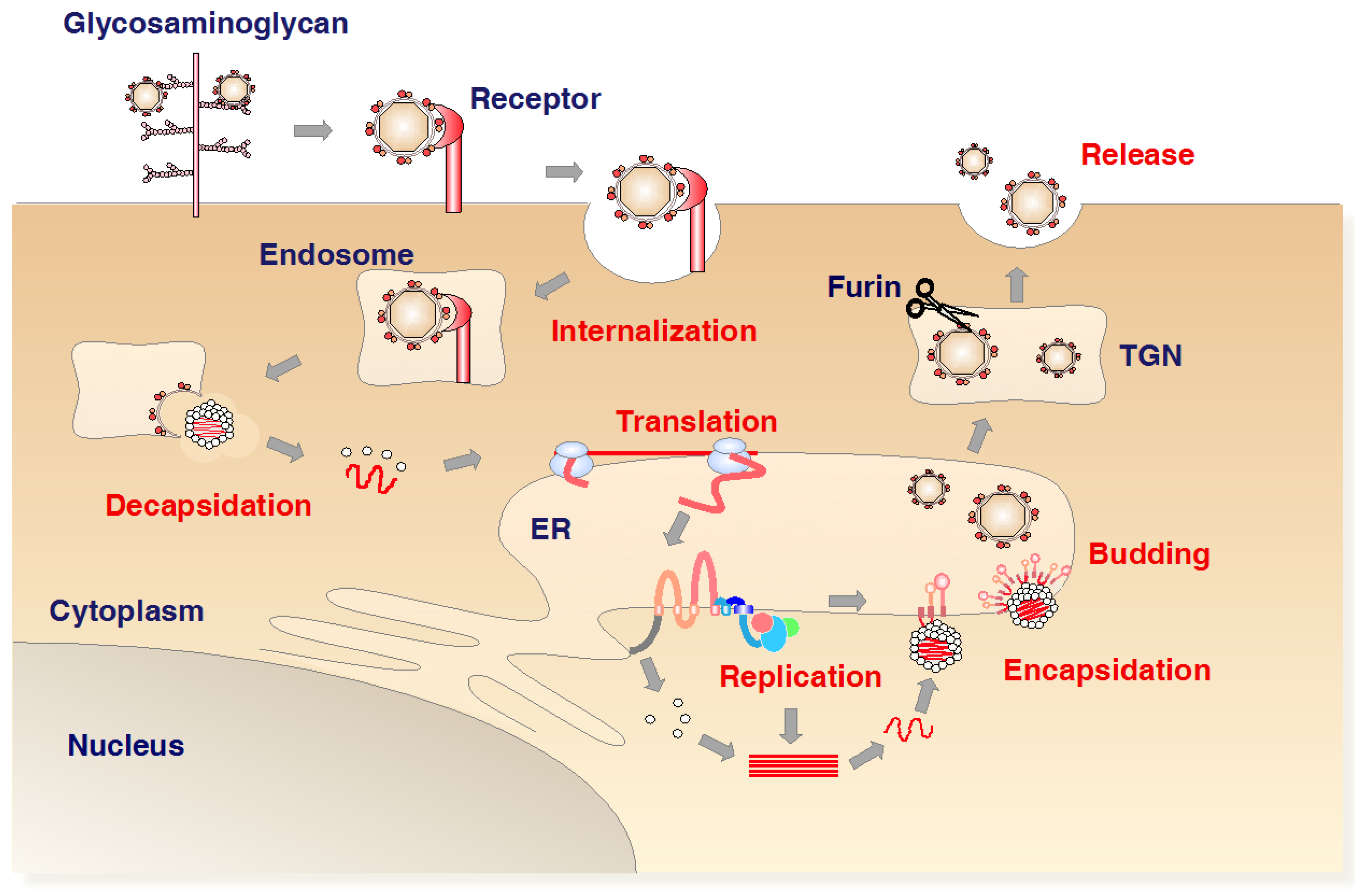
1.4. Life Cycle of Flavivirus Infection
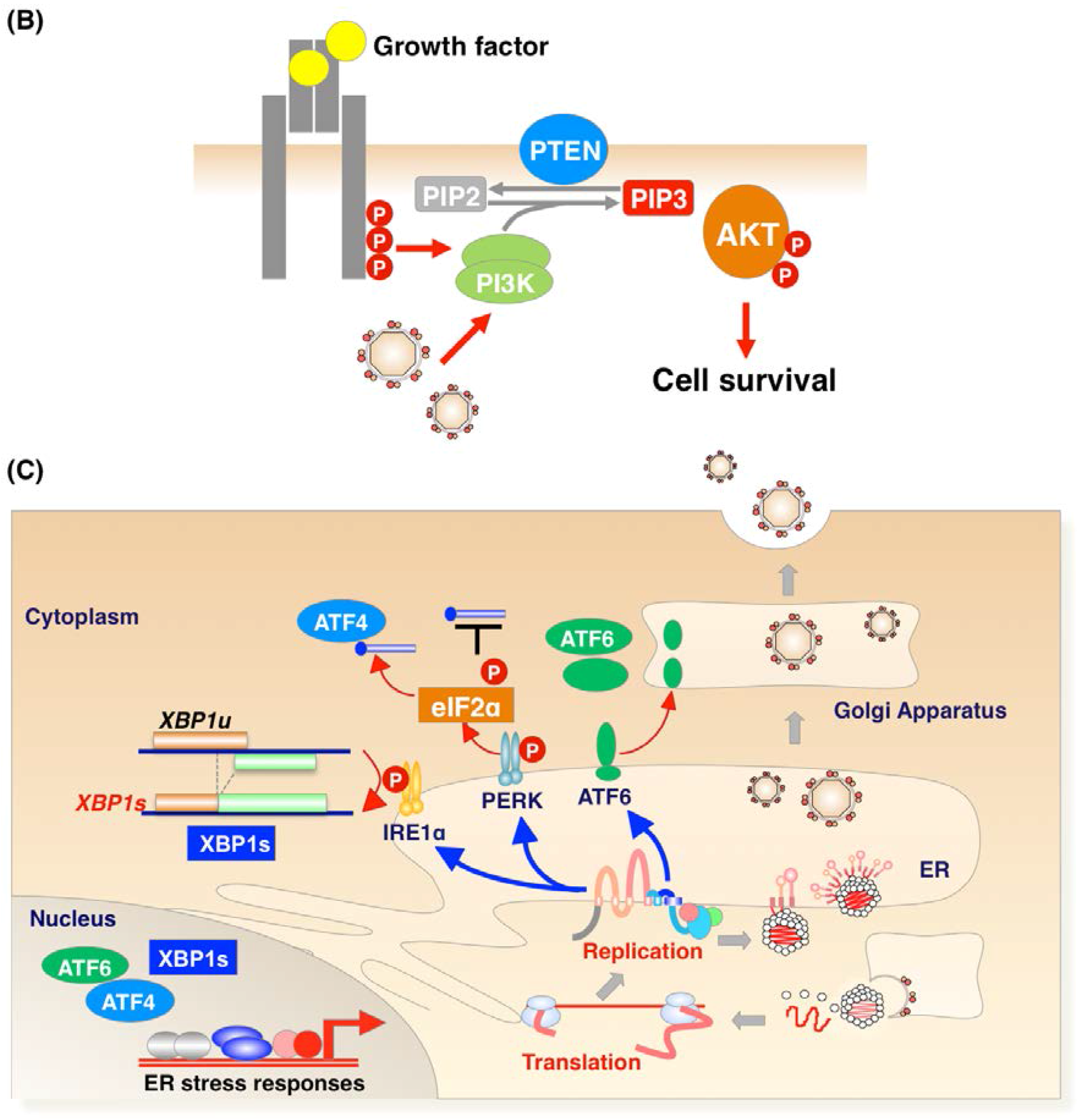
2. Apoptosis during Flavivirus-Infection
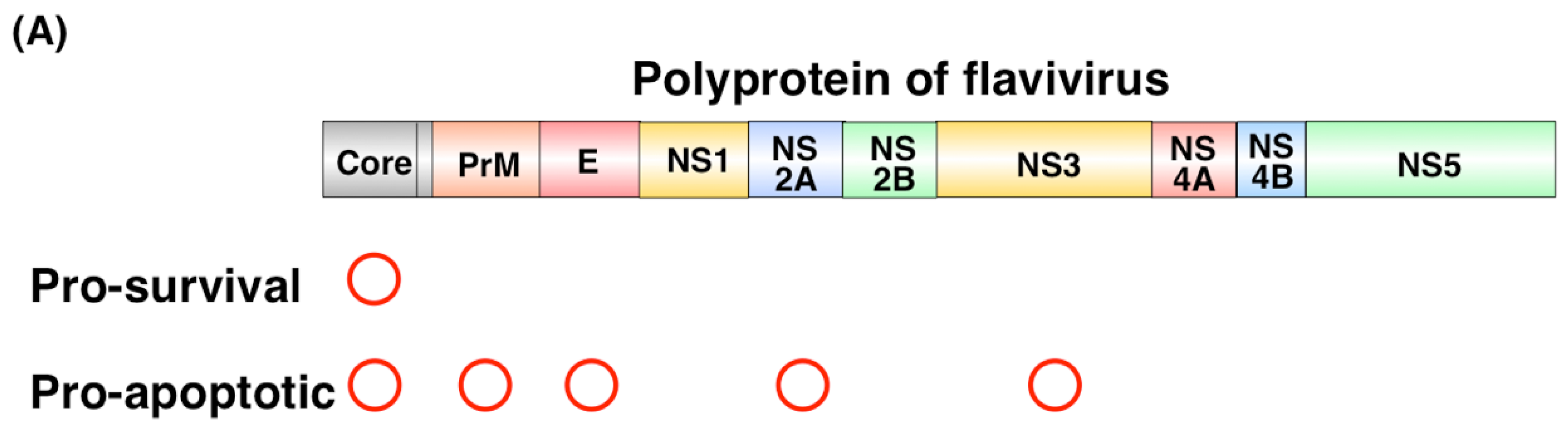
2.1. Pro-Survival and Pro Apoptotic Activity of Viral Proteins
2.2. Pro-Apoptotic or Pro-Survival Activity during Viral Infection
2.3. Physiological Significance of Apoptosis Signaling during Flavivirus Infection
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czabotar, P.E.; Lessene, G.; Strasser, A.; Adams, J.M. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2protein family: Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, S.W.G.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S.N.; Fletcher, J.I.; Kaufmann, T.; van Delft, M.F.; Chen, L.; Czabotar, P.E.; Ierino, H.; Lee, E.F.; Fairlie, W.D.; Bouillet, P.; et al. Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple BCL-2 homologs, not BAX or BAK. Science 2007, 315, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillet, P.; O’Reilly, L.A. CD95, BIM and T cell homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, T.; Schlipf, S.; Sanz, J.; Neubert, K.; Stein, R.; Borner, C. Characterization of the signal that directs BCL-x(L), but not BCL-2, to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütze, S.; Tchikov, V.; Schneider-Brachert, W. Regulation of TNFR1 and CD95 signaling by receptor compartmentalization. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltersdorf, T.; Elmore, S.W.; Shoemaker, A.R.; Armstrong, R.C.; Augeri, D.J.; Belli, B.A.; Bruncko, M.; Deckwerth, T.L.; Dinges, J.; Hajduk, P.J.; et al. An inhibitor of BCL-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005, 435, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Souers, A.J. From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souers, A.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Boghaert, E.R.; Ackler, S.L.; Catron, N.D.; Chen, J.; Dayton, B.D.; Ding, H.; Enschede, S.H.; Fairbrother, W.J.; et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leverson, J.D.; Phillips, D.C.; Mitten, M.J.; Boghaert, E.R.; Diaz, D.; Tahir, S.K.; Belmont, L.D.; Nimmer, P.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, X.M.; et al. Exploiting selective BCL-2 family inhibitors to dissect cell survival dependencies and define improved strategies for cancer therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 279ra40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.W.; Huang, D. Targeting BCL2 with BH3 mimetics: Basic science and clinical application of venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related B cell malignancies. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 101, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuconati, A. Viral homologs of BCL-2: Role of apoptosis in the regulation of virus infection. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2465–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campion, E.M.; Hakimjavadi, R.; Loughran, S.T.; Phelan, S.; Smith, S.M.; D’Souza, B.N.; Tierney, R.J.; Bell, A.I.; Cahill, P.A.; Walls, D. Repression of the proapoptotic cellular BIK/NBK gene by Epstein-Barr virus antagonizes transforming growth factor β1-induced B-cell apoptosis. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5001–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, J.; White, R.E.; Anderton, E.; Allday, M.J. Latent Epstein-Barr virus can inhibit apoptosis in B cells by blocking the induction of NOXA expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 28506–28515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Kunita, A.; Isogai, M.; Hibiya, T.; Ushiku, T.; Takada, K.; Fukayama, M. Profiling of virus-encoded microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma and their roles in gastric carcinogenesis. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5581–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.Y.-W.; Siu, K.-L.; Kok, K.-H.; Lung, R.W.-M.; Tsang, C.M.; To, K.-F.; Kwong, D.L.-W.; Tsao, S.W.; Jin, D.-Y. An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA targets PUMA to promote host cell survival. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kvansakul, M.; van Delft, M.F.; Lee, E.F.; Gulbis, J.M.; Fairlie, W.D.; Huang, D.C.S.; Colman, P.M. A structural viral mimic of prosurvival Bcl-2: A pivotal role for sequestering proapoptotic BAX and BAK. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Campbell, S.; Mehta, N.; Thibault, J.; Colman, P.M.; Barry, M.; Huang, D.C.S.; Kvansakul, M. Sheeppox virus SPPV14 encodes a BCL-2-like cell death inhibitor that counters a distinct set of mammalian proapoptotic proteins. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11501–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Krebs, J.F.; Snipas, S.J.; Price, A.; Alnemri, E.S.; Tomaselli, K.J.; Salvesen, G.S. Interaction of the baculovirus anti-apoptotic protein p35 with caspases. Specificity, kinetics, and characterization of the caspase/p35 complex. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 10757–10765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, J.; Armstrong, R.C.; Ottilie, S.; Martin, D.A.; Wang, Y.; Banks, S.; Wang, G.H.; Senkevich, T.G.; Alnemri, E.S.; Moss, B.; et al. Death effector domain-containing herpesvirus and poxvirus proteins inhibit both Fas- and TNFR1-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stürzl, M.; Hohenadl, C.; Zietz, C. Expression of K13/v-FLIP gene of human herpesvirus 8 and apoptosis in Kaposi’s sarcoma spindle cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thome, M.; Schneider, P.; Hofmann, K.; Fickenscher, H.; Meinl, E.; Neipel, F.; Mattmann, C.; Burns, K.; Bodmer, J.L.; Schröter, M.; et al. Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors. Nature 1997, 386, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Smith, C.A.; Pickup, D.J. Cowpox virus contains two copies of an early gene encoding a soluble secreted form of the type II TNF receptor. Virology 1994, 204, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, E.A.; Solomon, T. Pathogenic flaviviruses. Lancet 2008, 371, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Gubler, D.J.; Petersen, L.R. Emerging flaviviruses: The spread and resurgence of Japanese encephalitis, West Nile and dengue viruses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Garcia, M.-D.; Mazzon, M.; Jacobs, M.; Amara, A. Pathogenesis of flavivirus infections: Using and abusing the host cell. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netsawang, J.; Noisakran, S.; Puttikhunt, C.; Kasinrerk, W.; Wongwiwat, W.; Malasit, P.; Yenchitsomanus, P.-T.; Limjindaporn, T. Nuclear localization of dengue virus capsid protein is required for DAXX interaction and apoptosis. Virus Res. 2010, 147, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvanakantham, R.; Cheong, Y.K.; Ng, M.-L. West Nile virus capsid protein interaction with importin and HDM2 protein is regulated by protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanowski, M.D.; Hobman, T.C. The West Nile virus capsid protein blocks apoptosis through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent mechanism. J. Virol. 2012, 87, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catteau, A. Dengue virus M protein contains a proapoptotic sequence referred to as ApoptoM. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2781–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prikhod’ko, G.G.; Prikhod’ko, E.A.; Cohen, J.I.; Pletnev, A.G. Infection with Langat flavivirus or expression of the envelope protein induces apoptotic cell death. Virology 2001, 286, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.-L.; Chang, H.-H.; Lien, T.-S.; Chen, P.-K.; Chan, H.; Su, M.-T.; Liao, C.-Y.; Sun, D.-S. Suppressive effect of dengue virus envelope protein domain III on megakaryopoiesis. Virulence 2017, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Wang, X.J.; Clark, D.C.; Lobigs, M.; Hall, R.A.; Khromykh, A.A. A single amino acid substitution in the West Nile virus nonstructural protein NS2A disables its ability to inhibit α/β interferon induction and attenuates virus virulence in mice. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melian, E.B.; Edmonds, J.H.; Nagasaki, T.K.; Hinzman, E.; Floden, N.; Khromykh, A.A. West Nile virus NS2A protein facilitates virus-induced apoptosis independently of interferon response. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-C.; Shiu, S.-L.; Chuang, P.-H.; Lin, Y.-J.; Wan, L.; Lan, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-W. Japanese encephalitis virus NS2B-NS3 protease induces caspase 3 activation and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human medulloblastoma cells. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusan, A.E.; Kelley, P.G.; Pryor, M.J.; Whisstock, J.C.; Davidson, A.D.; Wright, P.J. Mutagenesis of the dengue virus type 2 NS3 proteinase and the production of growth-restricted virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafee, N. Dengue virus type 2 NS3 protease and NS2B-NS3 protease precursor induce apoptosis. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2191–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, M.P.; Chambers, J.A.; Pankhong, P.; Chattergoon, M.; Attatippaholkun, W.; Dang, K.; Shah, N.; Weiner, D.B. Host cell killing by the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 proteolytic complex: NS3 alone is sufficient to recruit caspase-8-based apoptotic pathway. Virology 2006, 345, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despres, P.; Flamand, M.; Ceccaldi, P.E.; Deubel, V. Human isolates of dengue type 1 virus induce apoptosis in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4090–4096. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gui, L. Coordinated regulation of autophagy and apoptosis determines endothelial cell fate during Dengue virus type 2 infection. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 397, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez Ochoa, M.; García Cordero, J.; Gutiérrez Castañeda, B.; Santos Argumedo, L.; Villegas Sepúlveda, N.; Cedillo Barrón, L. A clinical isolate of dengue virus and its proteins induce apoptosis in HMEC-1 cells: A possible implication in pathogenesis. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bacha, T.; Midlej, V.; Pereira da Silva, A.P.; Silva da Costa, L.; Benchimol, M.; Galina, A.; Da Poian, A.T. Mitochondrial and bioenergetic dysfunction in human hepatic cells infected with dengue 2 virus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) 2007, 1772, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thepparit, C.; Khakpoor, A.; Khongwichit, S.; Wikan, N.; Fongsaran, C.; Chingsuwanrote, P.; Panraksa, P.; Smith, D.R. Dengue 2 infection of HepG2 liver cells results in endoplasmic reticulum stress and induction of multiple pathways of cell death. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongtan, T.; Panyim, S.; Smith, D.R. Apoptosis in dengue virus infected liver cell lines HepG2 and Hep3B. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olagnier, D.; Peri, S.; Steel, C.; van Montfoort, N.; Chiang, C.; Beljanski, V.; Slifker, M.; He, Z.; Nichols, C.N.; Lin, R.; et al. Cellular oxidative stress response controls the antiviral and apoptotic programs in Dengue virus-infected dendritic cells. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, G.F.; Meyer, F.; Delfraro, A.; Mosimann, A.L.P.; Coluchi, N.; Vasquez, C.; Probst, C.M.; Bafica, A.; Bordignon, J.; Santos, C.N.D.D. Dengue virus type 3 isolated from a fatal case with visceral complications induces enhanced proinflammatory responses and apoptosis of human dendritic cells. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5374–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirudeen, A.M.A.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.X. Induction of p53-dependent and mitochondria-mediated cell death pathway by Dengue virus infection of human and animal cells. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parquet, M.D.; Kumatori, A.; Hasebe, F.; Morita, K.; Igarashi, A. West Nile virus-induced BAX-dependent apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2001, 500, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Gottlieb, D.; Diamond, M.S. Infection and injury of neurons by West Nile encephalitis virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13203–13213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, Y.L. Flavivirus activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling to block caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death at the early stage of virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8388–8399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medigeshi, G.R.; Lancaster, A.M.; Hirsch, A.J.; Briese, T.; Lipkin, W.I.; Defilippis, V.; Früh, K.; Mason, P.W.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Nelson, J.A. West Nile virus infection activates the unfolded protein response, leading to CHOP induction and apoptosis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10849–10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, J.; Harris, E. Dengue virus modulates the unfolded protein response in a time-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14226–14236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Xu, A.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, F.; Pan, Z.; Kong, L. Japanese encephalitis virus induces apoptosis by the IRE1/JNK pathway of ER stress response in BHK-21 cells. Arch. Virol. 2015, 161, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Sen, U.; Vrati, S. Regulated IRE1-dependent decay pathway is activated during Japanese encephalitis virus-induced unfolded protein response and benefits viral replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 95, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, R.L.; Mackenzie, J.M. ATF6 signaling is required for efficient West Nile virus replication by promoting cell survival and inhibition of innate immune responses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Grey, F.E.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Hirsch, A.J. Induction of the cellular microRNA, Hs_154, by West Nile virus contributes to virus-mediated apoptosis through repression of antiapoptotic factors. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5278–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.A.; Morrey, J.D.; Diamond, M.S. Caspase 3-dependent cell death of neurons contributes to the pathogenesis of West Nile virus encephalitis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.J.; McArthur, K.; Metcalf, D.; Lane, R.M.; Cambier, J.C.; Herold, M.J.; van Delft, M.F.; Bedoui, S.; Lessene, G.; Ritchie, M.E.; et al. Apoptotic caspases suppress mtDNA-induced STING-mediated type I IFN production. Cell 2014, 159, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rongvaux, A.; Jackson, R.; Harman, C.C.D.; Li, T.; West, A.P.; de Zoete, M.R.; Wu, Y.; Yordy, B.; Lakhani, S.A.; Kuan, C.-Y.; et al. Apoptotic caspases prevent the induction of type I interferons by mitochondrial DNA. Cell 2014, 159, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, B.; Diamond, M.S. Fas ligand interactions contribute to CD8+ T-cell-mediated control of West Nile virus infection in the central nervous system. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11749–11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, B.; Pinto, A.K.; Green, S.; Bosch, I.; Diamond, M.S. CD8+ T cells use TRAIL to restrict West Nile virus pathogenesis by controlling infection in neurons. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8937–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.A.; Deng, J.; Seymour, J.F.; Tam, C.; Kim, S.Y.; Fein, J.; Yu, L.; Brown, J.R.; Westerman, D.; Si, E.G.; et al. The BCL2 selective inhibitor venetoclax induces rapid onset apoptosis of CLL cells in patients via a TP53-independent mechanism. Blood 2016, 127, 3215–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.W.; Davids, M.S.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Puvvada, S.D.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Brown, J.R.; Gressick, L.; et al. Targeting BCL2 with venetoclax in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Viral Protein | Virus | Tested Cell Lines | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core | DENV | HepG2 | Pro-apoptotic | [30] |
| WNV | BHK | Pro-apoptotic | [31] | |
| A549, HEL/18 | Pro-survival | [32] | ||
| M | DENV, JEV, WNV, Yellow fever virus (YFV) | HeLa, HepG2, COS-7 | Pro-apoptotic | [33] |
| E | Langat virus | Vero, Neuro-2a | Pro-apoptotic | [34] |
| DENV | Progenitor cells of megakaryocytes | Pro-apoptotic | [35] | |
| NS2A | WNV | A549, L929, Vero | Pro-apoptotic | [36,37] |
| NS2B and NS3 | JEV, DENV, WNV | TE671, BHK | Pro-apoptotic | [38] |
| Virus | Tested Cell | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| DENV | Neuro 2a | Pro-apoptotic | [42] |
| DENV | HUVEC EA.hy926 | Pro-apoptotic | [43] |
| DENV | HMEC-1 | Pro-apoptotic | [44] |
| DENV | HepG2 | Pro-apoptotic | [45,46,47] |
| DENV | Hep3B | Pro-apoptotic | [47] |
| DENV | Monocyte derived dendritic cells (Mo-DC) | Pro-apoptotic | [48,49] |
| DENV | Huh7, BHK, Vero | Pro-apoptotic | [50] |
| WNV | Neuro 2a, K562 | Pro-apoptotic | [51] |
| WNV | ES cells derived neuron | Pro-apoptotic | [52] |
| JEV, DENV | N18, A549, BHK | Pro-survival | [53] |
| WNV | SK-N-MC, MEF, HEK293T Primary rat hippocampal neuron | Pro-apoptotic | [55] |
| DENV | 2fTGH, MEF | Pro-apoptotic | [56] |
| JEV | BHK | Pro-apoptotic | [57] |
| JEV | Neuro 2a | Pro-apoptotic | [58] |
| WNV | MEF | Pro-apoptotic | [59] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okamoto, T.; Suzuki, T.; Kusakabe, S.; Tokunaga, M.; Hirano, J.; Miyata, Y.; Matsuura, Y. Regulation of Apoptosis during Flavivirus Infection. Viruses 2017, 9, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090243
Okamoto T, Suzuki T, Kusakabe S, Tokunaga M, Hirano J, Miyata Y, Matsuura Y. Regulation of Apoptosis during Flavivirus Infection. Viruses. 2017; 9(9):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090243
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkamoto, Toru, Tatsuya Suzuki, Shinji Kusakabe, Makoto Tokunaga, Junki Hirano, Yuka Miyata, and Yoshiharu Matsuura. 2017. "Regulation of Apoptosis during Flavivirus Infection" Viruses 9, no. 9: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090243
APA StyleOkamoto, T., Suzuki, T., Kusakabe, S., Tokunaga, M., Hirano, J., Miyata, Y., & Matsuura, Y. (2017). Regulation of Apoptosis during Flavivirus Infection. Viruses, 9(9), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090243





