Opposite Roles of RNase and Kinase Activities of Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1 (IRE1) on HSV-1 Replication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Cell Lines and Viruses
2.2. In Vitro Antiviral Assay
2.3. Western Blot and In-Cell Western
2.4. RNA Extraction and Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
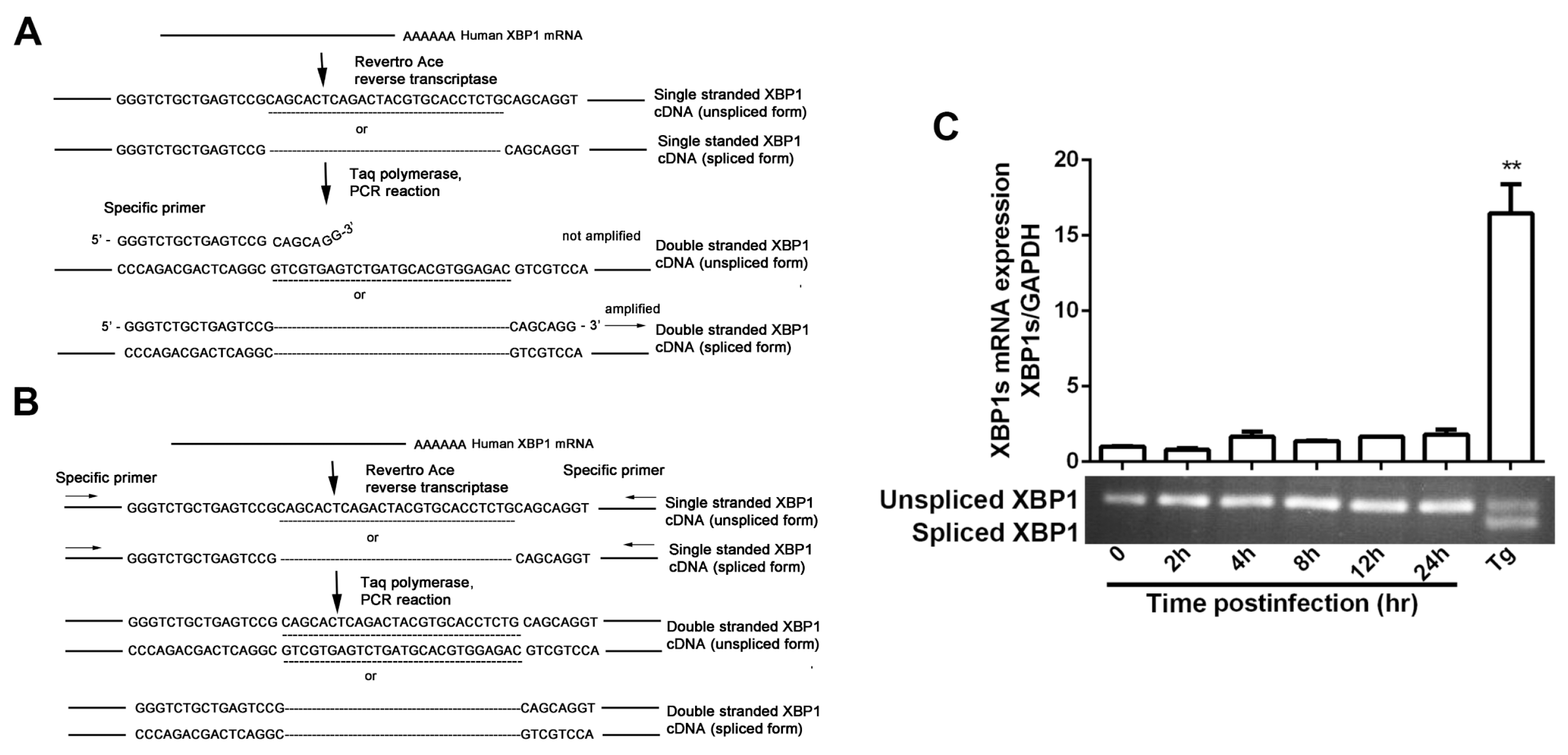
2.5. XBP1 mRNA Splicing Assay
2.6. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Analysis
2.7. Cell Transfection and HSV-1/Blue Assay
2.8. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
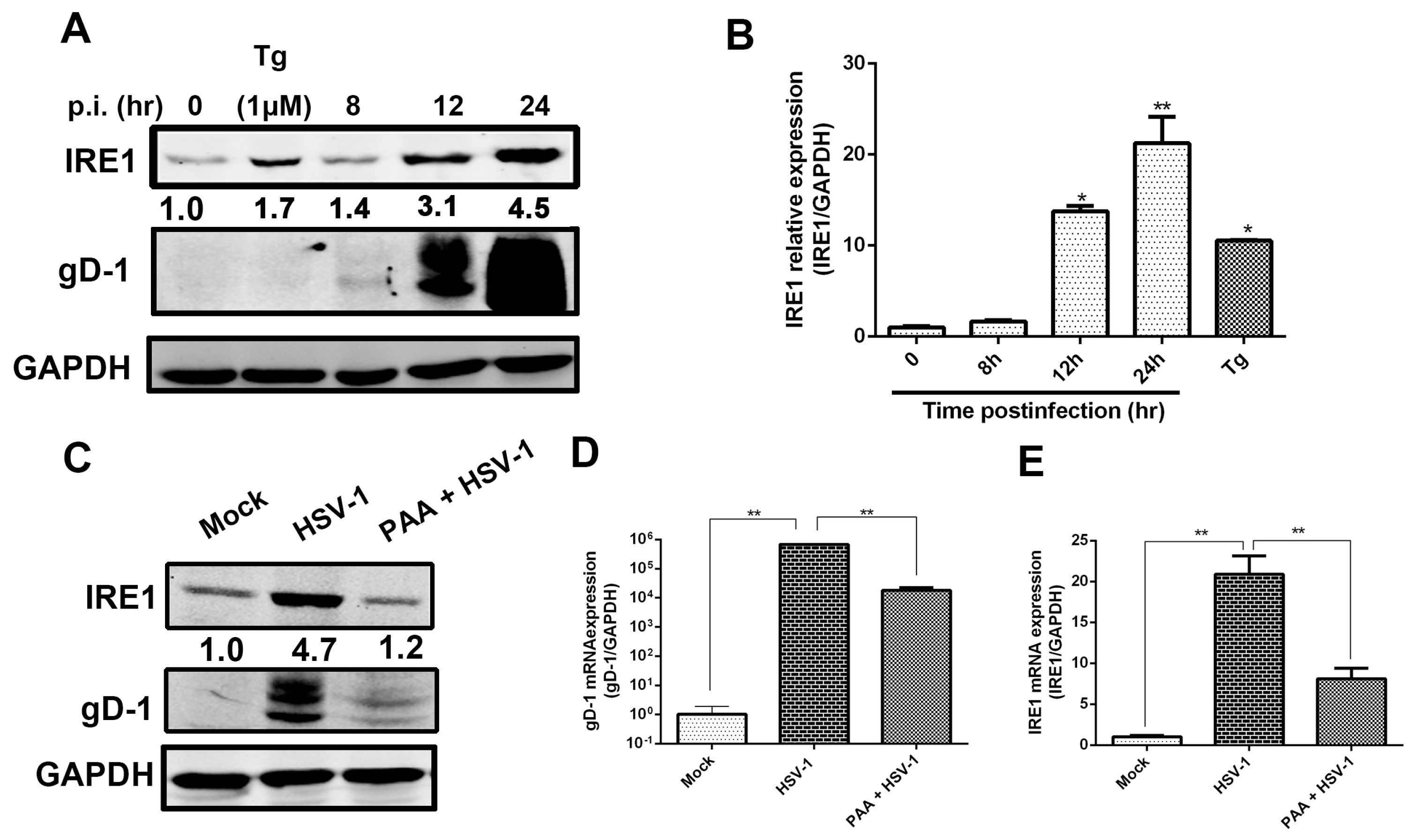
3.1. IRE1α Expression Was Up-Regulated during HSV-1 Infection
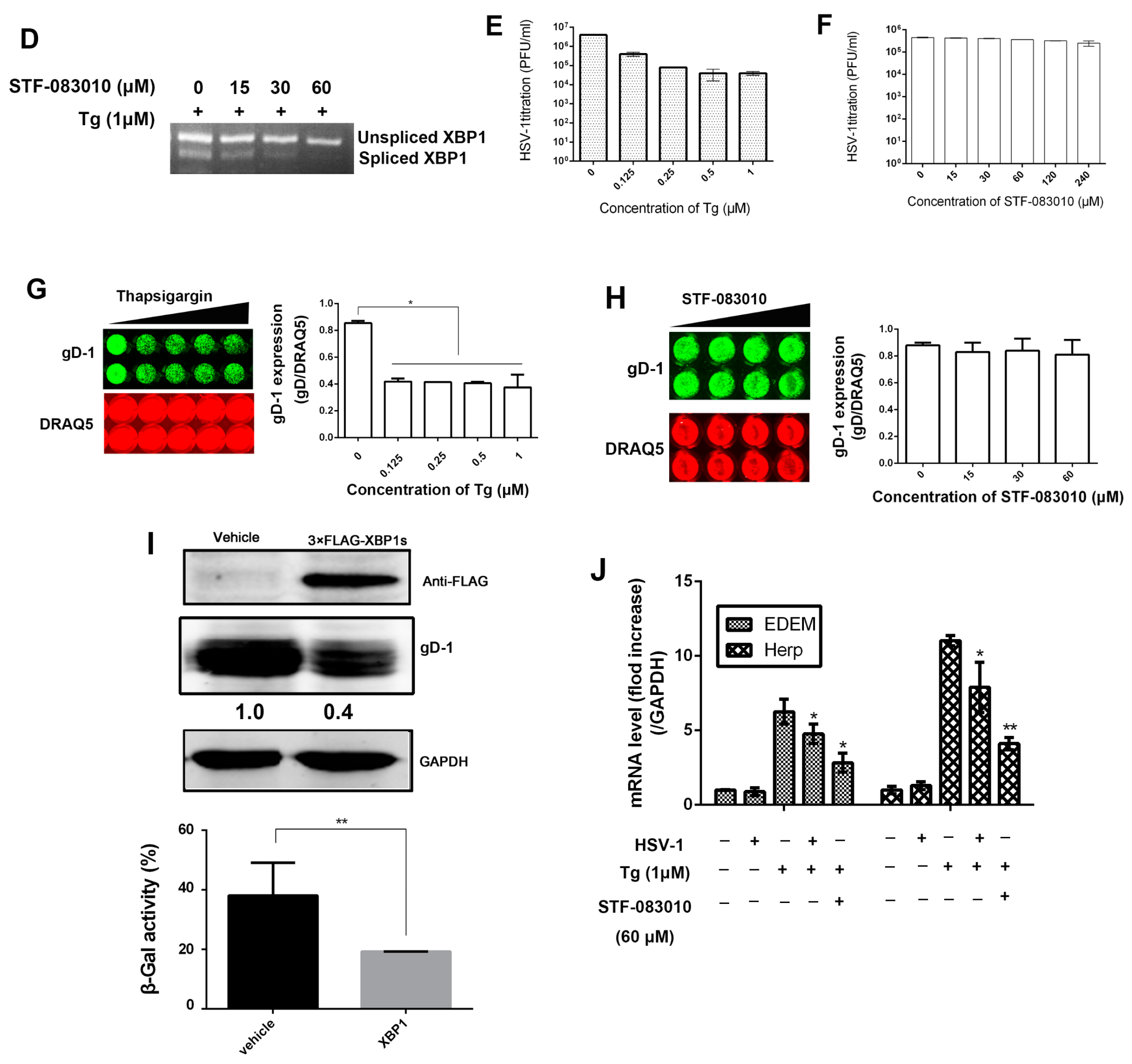
3.2. HSV-1 Replication Was Inhibited by the RNase Activity of IRE1α
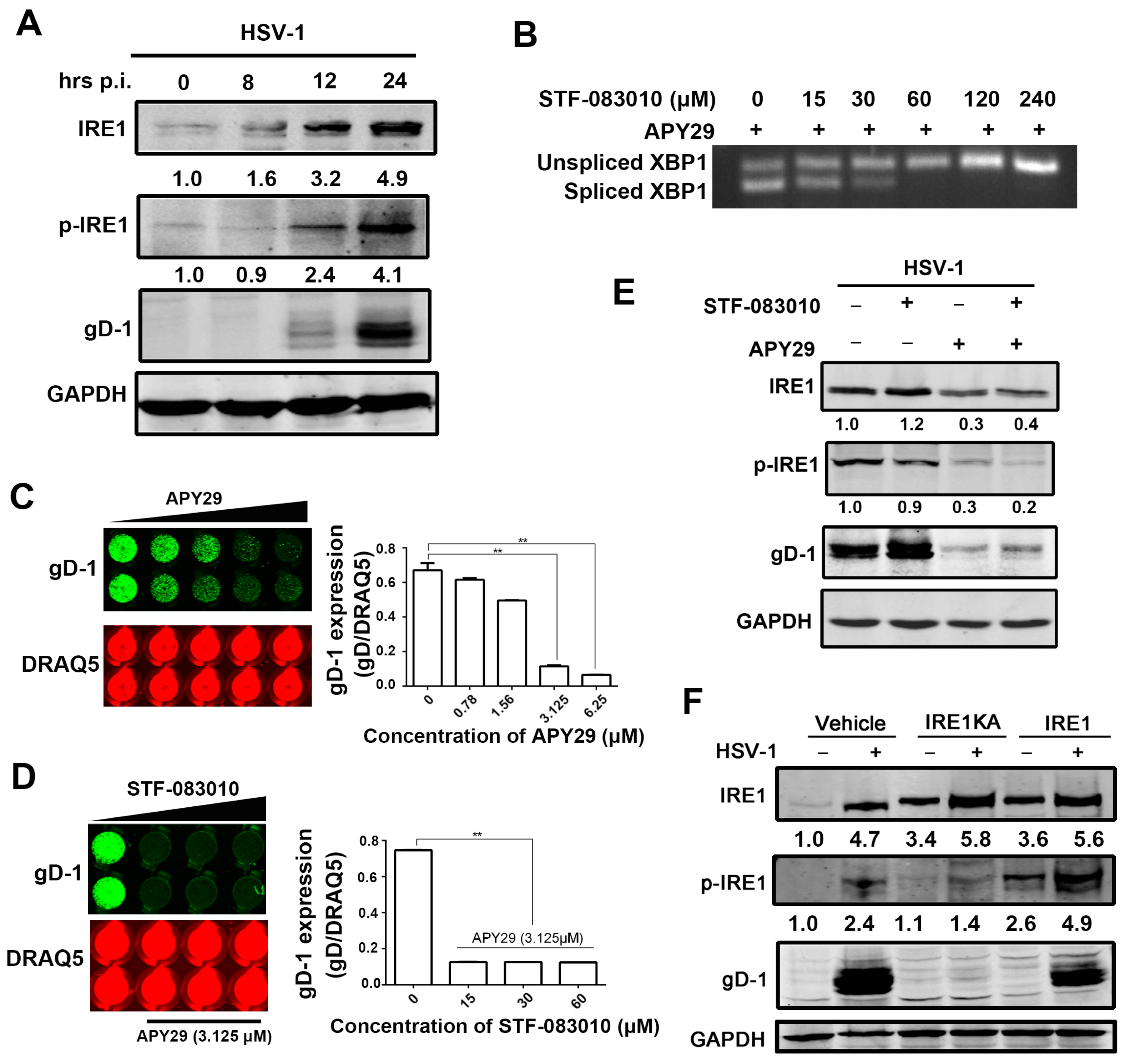
3.3. The Effect of IRE1α Kinase Activity on HSV-1 Replication
3.4. Kinase Activity of IRE1α Enhanced HSV-1 Replication via Activating JNK Signal Pathway
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, W.; Astor, T.L.; Liptak, L.M.; Cho, C.; Coen, D.M.; Schaffer, P.A. The herpes simplex virus type 1 regulatory protein ICP0 enhances virus replication during acute infection and reactivation from latency. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7501–7512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajcani, J.; Durmanova, V. Early expression of herpes simplex virus (HSV) proteins and reactivation of latent infection. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2000, 45, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkmann, A.; Zimmermann, H. HSV antivirals—Current and future treatment options. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 18, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, R.J. Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: Coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1211–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, U.; Cao, Q.; Yilmaz, E.; Lee, A.H.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Ozdelen, E.; Tuncman, G.; Gorgun, C.; Glimcher, L.H.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 2004, 306, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Huang, S.; Baltzis, D.; Rivas-Estilla, A.M.; Pluquet, O.; Hatzoglou, M.; Koumenis, C.; Taya, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Koromilas, A.E. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces p53 cytoplasmic localization and prevents p53-dependent apoptosis by a pathway involving glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Sen, U.; Vrati, S. Regulated IRE1-dependent decay pathway is activated during Japanese encephalitis virus-induced unfolded protein response and benefits viral replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B. Viruses, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and interferon responses. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.H.; Li, H.; Yasumura, D.; Cohen, H.R.; Zhang, C.; Panning, B.; Shokat, K.M.; Lavail, M.M.; Walter, P. IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science 2007, 318, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Liu, L.; Wen, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Teng, J. Cab45S inhibits the ER stress-induced IRE1-JNK pathway and apoptosis via GRP78/BiP. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardif, K.D.; Mori, K.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicons induce endoplasmic reticulum stress activating an intracellular signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 7453–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.L.; Liao, L.C.; Lin, Y.L. Japanese encephalitis virus infection initiates endoplasmic reticulum stress and an unfolded protein response. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4162–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Feng, Z.; He, B. Herpes simplex virus 1 infection activates the endoplasmic reticulum resident kinase PERK and mediates eIF-2alpha dephosphorylation by the gamma(1)34.5 protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirasophon, W.; Welihinda, A.A.; Kaufman, R.J. A stress response pathway from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus requires a novel bifunctional protein kinase/endoribonuclease (ire1p) in mammalian cells. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Z.; Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jolicoeur, E.M.; Kuroda, M.; Ron, D. Cloning of mammalian ire1 reveals diversity in the ER stress responses. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5708–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Credle, J.J.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Papa, F.R.; Stroud, R.M.; Walter, P. On the mechanism of sensing unfolded protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18773–18784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hendershot, L.M.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruegsegger, U.; Leber, J.H.; Walter, P. Block of HAC1 mRNA translation by long-range base pairing is released by cytoplasmic splicing upon induction of the unfolded protein response. Cell 2001, 107, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Glimcher, L.H. XBP-1 regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 7448–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollien, J.; Weissman, J. Decay of endoplasmic reticulum-localized mRNAs during the unfolded protein response. Science 2006, 313, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, D.S.; Domingos, P.M. Physiological roles of regulated ire1 dependent decay. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, F. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 2000, 287, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, I.H.; Zhang, M.S.; Powers, L.S.; Shao, J.Q.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Rutkowski, D.T.; Legge, K.; Monick, M.M. Influenza A viral replication is blocked by inhibition of the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) stress pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4679–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechill, J.; Chen, Z.; Brewer, J.W.; Baker, S.C. Coronavirus infection modulates the unfolded protein response and mediates sustained translational repression. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4492–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardif, K.D.; Mori, K.; Kaufman, R.J.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis C virus suppresses the IRE1-XBP1 pathway of the unfolded protein response. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17158–17164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isler, J.A.; Skalet, A.H.; Alwine, J.C. Human cytomegalovirus infection activates and regulates the unfolded protein response. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6890–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvey, M.; Arias, C.; Mohr, I. Maintenance of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells through the association of a viral glycoprotein with PERK, a cellular ER stress sensor. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Chen, J.; Gross, M.; Roizman, B. Association of a M(r) 90,000 phosphoprotein with protein kinase PKR in cells exhibiting enhanced phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF-2 alpha and premature shutoff of protein synthesis after infection with gamma (1)34.5-mutants of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10516–10520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnett, H.F.; Audas, T.E.; Liang, G.; Lu, R.R. Herpes simplex virus-1 disarms the unfolded protein response in the early stages of infection. Cell Stress Chaperones 2012, 17, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Su, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Sandri-Goldin, R.M. Herpes simplex virus 1 UL41 protein suppresses the IRE1/XBP1 signal pathway of the unfolded protein response via its RNase activity. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, T.I.; Bachenheimer, S.L. Activation of cJUN N-terminal kinase by herpes simplex virus type 1 enhances viral replication. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8415–8426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diao, L.; Zhang, B.; Xuan, C.; Sun, S.; Yang, K.; Tang, Y.; Qiao, W.; Chen, Q.; Geng, Y.; Wang, C. Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway by HSV-1 immediate early protein ICP0. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 308, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flexner, S. Contributions to the pathology of experimental virus encephalitis. IV. Recurring strains of herpes virus. J. Exp. Med. 1928, 47, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Y.; Song, S.; Yang, N.; Gao, J.; Wu, Z. Zinc ionophores pyrithione inhibits herpes simplex virus replication through interfering with proteasome function and NF-kappaB activation. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Chu, Y.; Song, H.Y.; Wu, Z.W. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 replication, and its activity may be mediated through dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8675–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Qiu, M.; Chu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Su, A.; Wu, Z. Downregulation of cellular c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase and NF-kappaB activation by berberine may result in inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5068–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, C.; Erturk, M.; Jennings, R.; Challanain, D.N.; Minson, A.; Duncan, I.; Boursnell, M.; Inglis, S. Protective vaccination against primary and recurrent disease caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 2 using a genetically disabled HSV-1. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, M.; Kitagaki, M.; Itagaki, H.; Aiba, S. Quantitative measurement of spliced XBP1 mRNA as an indicator of endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 31, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H. Unconventional splicing of XBP-1 mRNA in the unfolded protein response. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Ramirez, L.; Cao, H.B.; Nelson, D.; Hammond, E.; Lee, A.H.; Yoshida, H.; Mori, K.; Glimcher, L.H.; Denko, N.C.; Giaccia, A.J.; et al. XBP1 is essential for survival under hypoxic conditions and is required for tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5943–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, S.H.; Lee, K.; Vink, E.; Kaufman, R.J. Cytoplasmic IRE1alpha-mediated XBP1 mRNA splicing in the absence of nuclear processing and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18691–18706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijima, Y.; Ogunbunmi, E.; Fleischer, S. Drug action of thapsigargin on the Ca2+ pump protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 22912–22918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Yoshida, H.; Kokame, K.; Kaufman, R.J.; Mori, K. Differential contributions of ATF6 and XBP1 to the activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-responsive cis-acting elements ERSE, UPRE and ERSE-II. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 136, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, M.; Suzuki, R.; Watanabe, N.; Masaki, T.; Tomonaga, M.; Muhammad, A.; Kato, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Wakita, T.; et al. Role of the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway in degradation of hepatitis C virus envelope proteins and production of virus particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 37264–37273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papandreou, I.; Denko, N.C.; Olson, M.; Van Melckebeke, H.; Lust, S.; Tam, A.; Solow-Cordero, D.E.; Bouley, D.M.; Offner, F.; Niwa, M.; et al. Identification of an ire1alpha endonuclease specific inhibitor with cytotoxic activity against human multiple myeloma. Blood 2011, 117, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicker, I.B.; Seetharam, S. Herpes simplex type 1: LacZ recombinant viruses. I. Characterization and application to defining the mechanisms of action of known antiherpes agents. Antivir. Res. 1995, 28, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.C.; Wang, Y.; Peng, T. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) immediate-early (IE) promoter-directed reporter system for the screening of antiherpetics targeting the early stage of HSV infection. J. Biomol. Screen. 2010, 15, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, N.; Wada, I.; Hasegawa, K.; Yorihuzi, T.; Tremblay, L.O.; Herscovics, A.; Nagata, K. A novel ER alpha-mannosidase-like protein accelerates er-associated degradation. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Perera, B.G.; Hari, S.B.; Bhhatarai, B.; Backes, B.J.; Seeliger, M.A.; Schurer, S.C.; Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R.; Maly, D.J. Divergent allosteric control of the IRE1alpha endoribonuclease using kinase inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korennykh, A.V.; Egea, P.F.; Korostelev, A.A.; Finer-Moore, J.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.M.; Stroud, R.M.; Walter, P. The unfolded protein response signals through high-order assembly of IRE1. Nature 2009, 457, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, B.C.; Bond, P.J.; Sadowski, P.G.; Jha, B.K.; Zak, J.; Goodman, J.M.; Silverman, R.H.; Neubert, T.A.; Baxendale, I.R.; Ron, D.; et al. The molecular basis for selective inhibition of unconventional mRNA splicing by an IRE1-binding small molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E869–E878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Lerner, A.G.; Vande Walle, L.; Upton, J.P.; Xu, W.; Hagen, A.; Backes, B.J.; Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. IRE1alpha kinase activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to determine divergent cell fates. Cell 2009, 138, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipson, K.L.; Fonseca, S.G.; Ishigaki, S.; Nguyen, L.X.; Foss, E.; Bortell, R.; Rossini, A.A.; Urano, F. Regulation of insulin biosynthesis in pancreatic beta cells by an endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein kinase IRE1. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Su, A.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lv, X.; Xu, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Harmine blocks herpes simplex virus infection through downregulating cellular NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways induced by oxidative stress. Antivir. Res. 2015, 123, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.B.; Koong, A.C.; Niwa, M. IRE1 has distinct catalytic mechanisms for XBP1/HAC1 splicing and RIDD. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurel, M.; Chevet, E.; Tavernier, J.; Gerlo, S. Getting RIDD of RNA: IRE1 in cell fate regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Schmechel, S.C.; Raghavan, A.; Abelson, M.; Reilly, C.; Katze, M.G.; Kaufman, R.J.; Bohjanen, P.R.; Schiff, L.A. Reovirus induces and benefits from an integrated cellular stress response. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2019–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gao, B.; Ye, L.; Han, X.; Wang, W.; Kong, L.; Fang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; et al. Hepatitis B virus x protein (HBX) activates ATF6 and IRE1-XBP1 pathways of unfolded protein response. Virus Res. 2007, 124, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, Y.L. Flavivirus infection activates the XBP1 pathway of the unfolded protein response to cope with endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11868–11880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Sugden, B. The LMP1 oncogene of EBV activates PERK and the unfolded protein response to drive its own synthesis. Blood 2008, 111, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvey, M.; Arias, C.; Mohr, I. Resistance of mRNA translation to acute endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducing agents in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells requires multiple virus-encoded functions. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7354–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerveny, M.; Hessefort, S.; Yang, K.; Cheng, G.; Gross, M.; He, B. Amino acid substitutions in the effector domain of the gamma(1)34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus 1 have differential effects on viral response to interferon-α. Virology 2003, 307, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, I.; Hernáez, B.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.A.; Dalmau-Mena, I.; Alonso, C. The ATF6 branch of unfolded protein response and apoptosis are activated to promote african swine fever virus infection. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Ngoei, K.R.; Zhao, T.T.; Yeap, Y.Y.; Ng, D.C. c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling: Recent advances and challenges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, Y.; Armstrong, C.G.; Morrice, N.; Paterson, A.; Goedert, M.; Cohen, P. Synergistic activation of stress-activated protein kinase 1/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK1/JNK) isoforms by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4) and MKK7. Biochem. J. 2000, 352 Pt 1, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachos, G.; Clements, B.; Conner, J. Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection stimulates p38/c-Jun N-terminal mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and activates transcription factor AP-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5097–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargett, D.; McLean, T.; Bachenheimer, S.L. Herpes simplex virus ICP27 activation of stress kinases JNK and p38. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8348–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, A.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, Z. Opposite Roles of RNase and Kinase Activities of Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1 (IRE1) on HSV-1 Replication. Viruses 2017, 9, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090235
Su A, Wang H, Li Y, Wang X, Chen D, Wu Z. Opposite Roles of RNase and Kinase Activities of Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1 (IRE1) on HSV-1 Replication. Viruses. 2017; 9(9):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090235
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Airong, Huanru Wang, Yanlei Li, Xiaohui Wang, Deyan Chen, and Zhiwei Wu. 2017. "Opposite Roles of RNase and Kinase Activities of Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1 (IRE1) on HSV-1 Replication" Viruses 9, no. 9: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090235
APA StyleSu, A., Wang, H., Li, Y., Wang, X., Chen, D., & Wu, Z. (2017). Opposite Roles of RNase and Kinase Activities of Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1 (IRE1) on HSV-1 Replication. Viruses, 9(9), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090235





