Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles in HPV Transmission and Carcinogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Extracellular Vesicles and Cancer
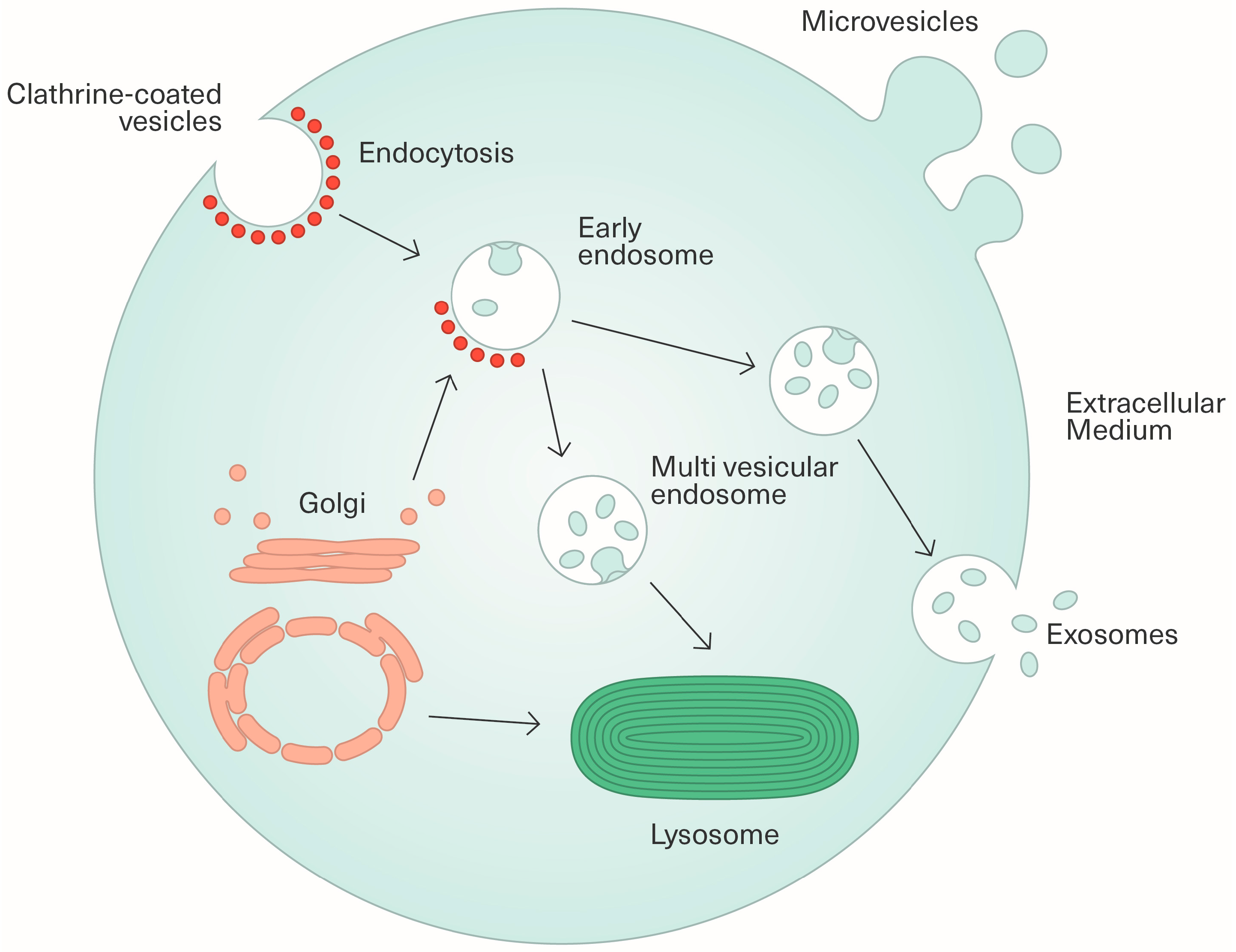
2.1. Biogenesis and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles
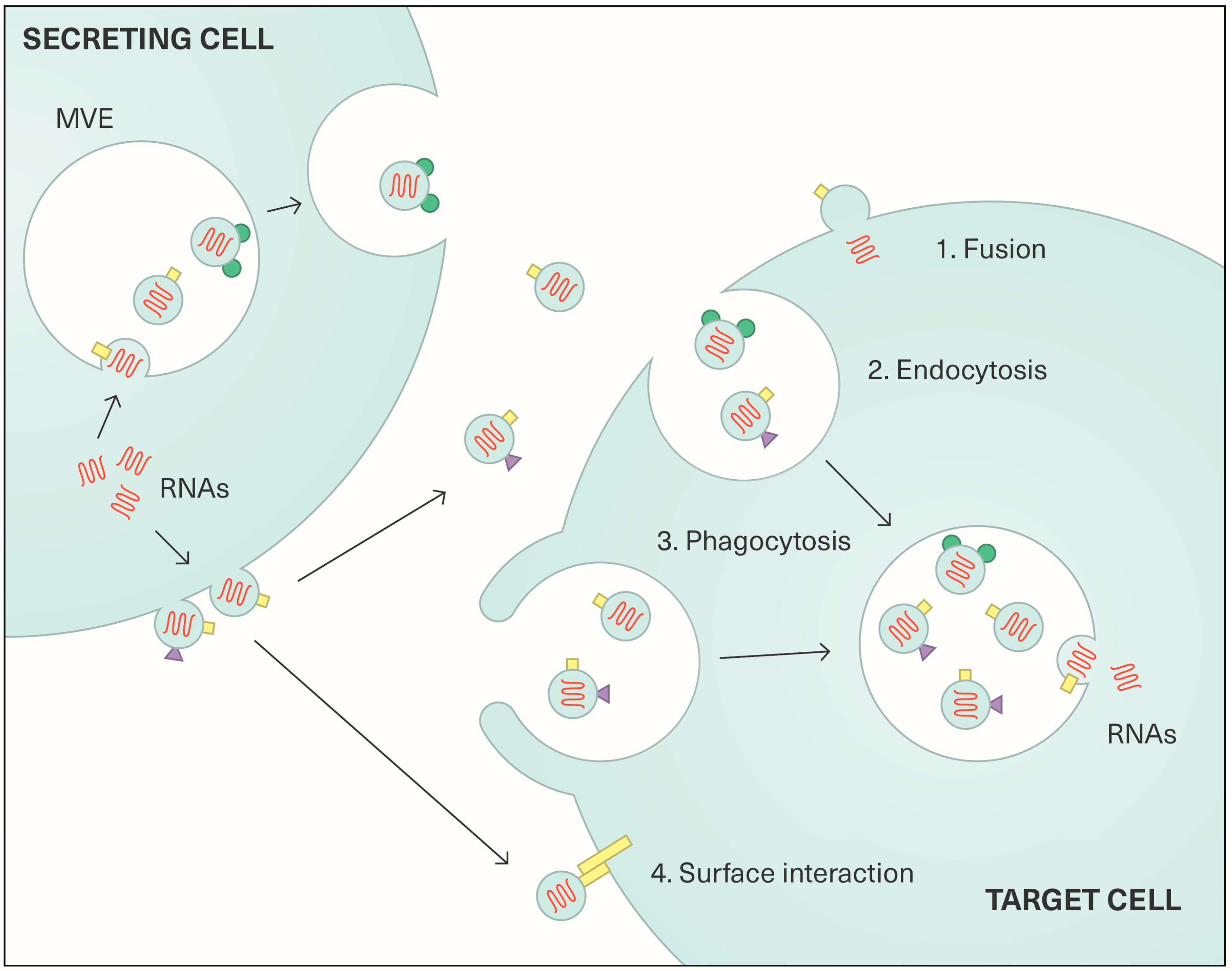
2.2. Content and Functions of Extracellular Vesicles
2.3. Pro-Tumorigenic Properties of Exosomes
2.4. Horizontal Oncogene Transfer by Apoptotic Bodies
3. Exosomes in Viral Transmission and Carcinogenesis Associated with Viruses Other than HPV
4. Extracellular Vesicles and HPV-Associated Carcinogenesis
4.1. E6/E7 and Anti-Apoptotic Exosomal Proteins
4.2. E6/E7 and miRNA Content of Exosomes
4.3. Exosome Release and Senescence Induction
4.4. Exosomes as Potential Biomarkers
4.5. HPV-Positive Apoptotic Bodies and Cell Transformation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopatina, T.; Gai, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Kholia, S.; Camussi, G. Cross Talk between Cancer and Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Extracellular Vesicles Carrying Nucleic Acids. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, J. Malignant messengers. Science 2016, 352, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, M.; Lam, T.K.; Hebert, E.; Divi, R.L. Extracellular vesicles: Potential applications in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and epidemiology. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2015, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, J.; Yeung, V.; Clayton, A. Extracellular vesicles as modulators of the cancer microenvironment. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. Tumor-Derived Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 74, 103–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zoller, M. Exosomes in Cancer Disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1381, 111–149. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. The potential of tumor-derived exosomes for noninvasive cancer monitoring. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1293–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr. Exosomal communication goes viral. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5200–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, C.V.; Heuser, J.E.; Stahl, P.D. Exosomes: Looking back three decades and into the future. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3.22.1–3.22.29. [Google Scholar]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Sormunen, R.; Cocquyt, V.; Vermaelen, K.; Vandesompele, J.; Bracke, M.; De Wever, O.; Hendrix, A. The impact of disparate isolation methods for extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranyai, T.; Herczeg, K.; Onodi, Z.; Voszka, I.; Modos, K.; Marton, N.; Nagy, G.; Mager, I.; Wood, M.J.; El Andaloussi, S.; et al. Isolation of Exosomes from Blood Plasma: Qualitative and Quantitative Comparison of Ultracentrifugation and Size Exclusion Chromatography Methods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, R.E.; Korbie, D.; Anderson, W.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Trau, M. Analysis of exosome purification methods using a model liposome system and tunable-resistive pulse sensing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Moller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, J.Z.; Lee, Y.; Vader, P.; Mager, I.; Johansson, H.J.; Heusermann, W.; Wiklander, O.P.; Hallbrink, M.; Seow, Y.; Bultema, J.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography for high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzas, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, C.; Di Vizio, D.; Sahoo, S.; Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Wauben, M.; Hill, A.F. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Results of a worldwide survey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 32945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.O.; Choi, D.Y.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, J.W.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Freeman, M.R.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of proteins isolated from microvesicles derived from human lung cancer pleural effusions. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Lucas, F.A.; Allenson, K.; Bernard, V.; Castillo, J.; Kim, D.U.; Ellis, K.; Ehli, E.A.; Davies, G.E.; Petersen, J.L.; Li, D.; et al. Minimally invasive genomic and transcriptomic profiling of visceral cancers by next-generation sequencing of circulating exosomes. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, A.; Rigas, J.R. Modulation of apoptosis signaling pathways and cell cycle regulation. Semin. Oncol. 1999, 26, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.C.; Cullen, S.P.; Martin, S.J. Apoptosis: Controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 9, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Carbon Ion-Irradiated Hepatoma Cells Exhibit Coupling Interplay between Apoptotic Signaling and Morphological and Mechanical Remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, E.; Nicco, C.; Lombard, B.; Veron, P.; Raposo, G.; Batteux, F.; Amigorena, S.; Thery, C. ICAM-1 on exosomes from mature dendritic cells is critical for efficient naive T-cell priming. Blood 2005, 106, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Schorey, J.S. Exosomes released from infected macrophages contain Mycobacterium avium glycopeptidolipids and are proinflammatory. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 25779–25789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.M.; Clos, J.; Horakova, E.; Wang, A.Y.; Wiesgigl, M.; Kelly, I.; Lynn, M.A.; McMaster, W.R.; Foster, L.J.; Levings, M.K.; et al. Leishmania exosomes modulate innate and adaptive immune responses through effects on monocytes and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5011–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateescu, B.; Kowal, E.J.; van Balkom, B.W.; Bartel, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Buzas, E.I.; Buck, A.H.; de Candia, P.; Chow, F.W.; Das, S.; et al. Obstacles and opportunities in the functional analysis of extracellular vesicle RNA—An ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1286095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaj, L.; Lessard, R.; Dai, L.; Cho, Y.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischhacker, M.; Schmidt, B. Circulating nucleic acids (CNAs) and cancer—A survey. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1775, 181–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Collino, F.; Vitillo, L.; Damasco, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5346–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, J.L.; San, R.S.; Wickline, S.A. Exosomes released by melanoma cells prepare sentinel lymph nodes for tumor metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3792–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runz, S.; Keller, S.; Rupp, C.; Stoeck, A.; Issa, Y.; Koensgen, D.; Mustea, A.; Sehouli, J.; Kristiansen, G.; Altevogt, P. Malignant ascites-derived exosomes of ovarian carcinoma patients contain CD24 and EpCAM. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 107, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiffe, E.; Pretet, J.L.; Launay, S.; Jacquin, E.; Saunier, M.; Hetzel, G.; Oudet, P.; Mougin, C. Apoptotic HPV positive cancer cells exhibit transforming properties. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermetet, F.; Jacquin, E.; Launay, S.; Gaiffe, E.; Couturier, M.; Hirchaud, F.; Sandoz, P.; Pretet, J.L.; Mougin, C. Efferocytosis of apoptotic human papillomavirus-positive cervical cancer cells by human primary fibroblasts. Biol. Cell 2016, 108, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiffe, E. Apoptotic Cells as Vectors of Viral Oncogenes: An Alternative Way of HPV-Associated Carcinogenesis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Franche-Comté, Besançon, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hermetet, F. Duality of Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Cells or Hidden Face of Janus: A Therapeutic Objective and An Implication in Horizontal Viral Oncogene Transfer. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Franche-Comté, Besançon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.F.; Searle, J. A mode of cell loss in malignant neoplasms. J. Pathol. 1972, 106, Pxi. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, S.W.; Lin, A.W. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Petit, P.; Zamzami, N.; Vayssiere, J.L.; Mignotte, B. The biochemistry of programmed cell death. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monks, J.; Rosner, D.; Geske, F.J.; Lehman, L.; Hanson, L.; Neville, M.C.; Fadok, V.A. Epithelial cells as phagocytes: Apoptotic epithelial cells are engulfed by mammary alveolar epithelial cells and repress inflammatory mediator release. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnaik, R.; Raff, M.C.; Scholes, J. Differences between the clearance of apoptotic cells by professional and non-professional phagocytes. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.A.; Lee, D.J.; Feng, L.; Antoni, A.; Lieberthal, W.; Schwartz, J.H.; Rauch, J.; Ucker, D.S.; Levine, J.S. Recognition of apoptotic cells by epithelial cells: Conserved versus tissue-specific signaling responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.E.; Savill, J.S.; Henson, P.M.; Haslett, C. Apoptotic neutrophils are phagocytosed by fibroblasts with participation of the fibroblast vitronectin receptor and involvement of a mannose/fucose-specific lectin. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 3218–3227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demory Beckler, M.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Franklin, J.L.; Ham, A.J.; Halvey, P.J.; Imasuen, I.E.; Whitwell, C.; Li, M.; Liebler, D.C.; Coffey, R.J. Proteomic analysis of exosomes from mutant KRAS colon cancer cells identifies intercellular transfer of mutant KRAS. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Micallef, J.; Lhotak, V.; May, L.; Guha, A.; Rak, J. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezu, T.; Tadokoro, H.; Azuma, K.; Yoshizawa, S.; Ohyashiki, K.; Ohyashiki, J.H. Exosomal miR-135b shed from hypoxic multiple myeloma cells enhances angiogenesis by targeting factor-inhibiting HIF-1. Blood 2014, 124, 3748–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, J.; Steadman, R.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z.; Clayton, A. Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9621–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, H.; Aleckovic, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; Garcia-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfers, J.; Lozier, A.; Raposo, G.; Regnault, A.; Thery, C.; Masurier, C.; Flament, C.; Pouzieux, S.; Faure, F.; Tursz, T.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreola, G.; Rivoltini, L.; Castelli, C.; Huber, V.; Perego, P.; Deho, P.; Squarcina, P.; Accornero, P.; Lozupone, F.; Lugini, L.; et al. Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, A.; Mitchell, J.P.; Court, J.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z. Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7458–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes and tumor-mediated immune suppression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battke, C.; Ruiss, R.; Welsch, U.; Wimberger, P.; Lang, S.; Jochum, S.; Zeidler, R. Tumour exosomes inhibit binding of tumour-reactive antibodies to tumour cells and reduce ADCC. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciravolo, V.; Huber, V.; Ghedini, G.C.; Venturelli, E.; Bianchi, F.; Campiglio, M.; Morelli, D.; Villa, A.; Della Mina, P.; Menard, S.; et al. Potential role of HER2-overexpressing exosomes in countering trastuzumab-based therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Taille, A.; Chen, M.W.; Burchardt, M.; Chopin, D.K.; Buttyan, R. Apoptotic conversion: Evidence for exchange of genetic information between prostate cancer cells mediated by apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5461–5463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, L.; Szeles, A.; Rajnavolgyi, E.; Folkman, J.; Klein, G.; Ernberg, I.; Falk, K.I. Horizontal transfer of DNA by the uptake of apoptotic bodies. Blood 1999, 93, 3956–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsmedh, A.; Szeles, A.; Henriksson, M.; Bratt, A.; Folkman, M.J.; Spetz, A.L.; Holmgren, L. Horizontal transfer of oncogenes by uptake of apoptotic bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6407–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsmedh, A.; Szeles, A.; Spetz, A.L.; Holmgren, L. Loss of the p21(Cip1/Waf1) cyclin kinase inhibitor results in propagation of horizontally transferred DNA. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bergsmedh, A.; Ehnfors, J.; Kawane, K.; Motoyama, N.; Nagata, S.; Holmgren, L. DNase II and the Chk2 DNA damage pathway form a genetic barrier blocking replication of horizontally transferred DNA. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehnfors, J.; Kost-Alimova, M.; Persson, N.L.; Bergsmedh, A.; Castro, J.; Levchenko-Tegnebratt, T.; Yang, L.; Panaretakis, T.; Holmgren, L. Horizontal transfer of tumor DNA to endothelial cells in vivo. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenquer, M.; Amorim, M.J. Exosome Biogenesis, Regulation, and Function in Viral Infection. Viruses 2015, 7, 5066–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnaiah, V.; Thumann, C.; Fofana, I.; Habersetzer, F.; Pan, Q.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Willemsen, R.; Demmers, J.A.; Stalin Raj, V.; Jenster, G.; et al. Exosome-mediated transmission of hepatitis C virus between human hepatoma Huh7.5 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13109–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr.; Gunawardena, H.P.; Dekroon, R.M.; Heaton, P.R.; Edwards, R.H.; Ozgur, S.; Griffith, J.D.; Damania, B.; Raab-Traub, N. Modulation of B-cell exosome proteins by gamma herpesvirus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2925–E2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, J.; Middeldorp, J.; Sculley, T. Localization of the Epstein-Barr virus protein LMP 1 to exosomes. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aga, M.; Bentz, G.L.; Raffa, S.; Torrisi, M.R.; Kondo, S.; Wakisaka, N.; Yoshizaki, T.; Pagano, J.S.; Shackelford, J. Exosomal HIF1α supports invasive potential of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-associated LMP1-positive exosomes. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4613–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzeit, C.; Nagy, N.; Gentile, M.; Lyberg, K.; Gumz, J.; Vallhov, H.; Puga, I.; Klein, E.; Gabrielsson, S.; Cerutti, A.; et al. Exosomes derived from Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines induce proliferation, differentiation, and class-switch recombination in B cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5852–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanbo, A.; Kawanishi, E.; Yoshida, R.; Yoshiyama, H. Exosomes derived from Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells are internalized via caveola-dependent endocytosis and promote phenotypic modulation in target cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10334–10347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautreau, A.; Poullet, P.; Louvard, D.; Arpin, M. Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7300–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, S.; Visco, V.; Raffa, S.; Wakisaka, N.; Pagano, J.S.; Torrisi, M.R. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 promotes concentration in multivesicular bodies of fibroblast growth factor 2 and its release through exosomes. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keryer-Bibens, C.; Pioche-Durieu, C.; Villemant, C.; Souquere, S.; Nishi, N.; Hirashima, M.; Middeldorp, J.; Busson, P. Exosomes released by EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells convey the viral latent membrane protein 1 and the immunomodulatory protein galectin 9. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibi, J.; Niki, T.; Riedel, A.; Pioche-Durieu, C.; Souquere, S.; Rubinstein, E.; Le Moulec, S.; Guigay, J.; Hirashima, M.; Guemira, F.; et al. Blood diffusion and Th1-suppressive effects of galectin-9-containing exosomes released by Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Blood 2009, 113, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walboomers, J.M.; Jacobs, M.V.; Manos, M.M.; Bosch, F.X.; Kummer, J.A.; Shah, K.V.; Snijders, P.J.; Peto, J.; Meijer, C.J.; Munoz, N. Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J. Pathol. 1999, 189, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Franceschi, S.; Howell-Jones, R.; Snijders, P.J.; Clifford, G.M. Human papillomavirus type distribution in 30,848 invasive cervical cancers worldwide: Variation by geographical region, histological type and year of publication. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses and cancer: From basic studies to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffner, M.; Werness, B.A.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Levine, A.J.; Howley, P.M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 1990, 63, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, D.V.; Yee, C.L.; Howley, P.M.; Munger, K. Efficiency of binding the retinoblastoma protein correlates with the transforming capacity of the E7 oncoproteins of the human papillomaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4442–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, E.C.; DiMaio, D. Repression of human papillomavirus oncogenes in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells causes the orderly reactivation of dormant tumor suppressor pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12513–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, E.C.; Yang, E.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, H.W.; DiMaio, D.; Hwang, E.S. Rapid induction of senescence in human cervical carcinoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10978–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Aspe, J.R.; Asumen, M.G.; Almaguel, F.; Odumosu, O.; Acevedo-Martinez, S.; De Leon, M.; Langridge, W.H.; Wall, N.R. Extracellular, cell-permeable survivin inhibits apoptosis while promoting proliferative and metastatic potential. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Jutzy, J.M.; Aspe, J.R.; McGregor, D.W.; Neidigh, J.W.; Wall, N.R. Survivin is released from cancer cells via exosomes. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, M.M.; Ferguson Bennit, H.R.; Gonda, A.; Diaz Osterman, C.J.; Hibma, A.; Khan, S.; Wall, N.R. Exosomes Secreted from Human Cancer Cell Lines Contain Inhibitors of Apoptosis (IAP). Cancer Microenviron. 2015, 8, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honegger, A.; Leitz, J.; Bulkescher, J.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Silencing of human papillomavirus (HPV) E6/E7 oncogene expression affects both the contents and the amounts of extracellular microvesicles released from HPV-positive cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honegger, A.; Schilling, D.; Bastian, S.; Sponagel, J.; Kuryshev, V.; Sultmann, H.; Scheffner, M.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Dependence of intracellular and exosomal microRNAs on viral E6/E7 oncogene expression in HPV-positive tumor cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuner, R.; Vogt, M.; Sultmann, H.; Buness, A.; Dymalla, S.; Bulkescher, J.; Fellmann, M.; Butz, K.; Poustka, A.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Identification of cellular targets for the human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncogenes by RNA interference and transcriptome analyses. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harden, M.E.; Munger, K. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 and E7 oncoprotein expression alters microRNA expression in extracellular vesicles. Virology 2017, 508, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiantore, M.V.; Mangino, G.; Iuliano, M.; Zangrillo, M.S.; De Lillis, I.; Vaccari, G.; Accardi, R.; Tommasino, M.; Columba Cabezas, S.; Federico, M.; et al. Human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins affect the expression of cancer-related microRNAs: Additional evidence in HPV-induced tumorigenesis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, J.; Wu, Y.; Xing, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, J. MicroRNA-222 promotes the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells. Clin. Investig. Med. 2014, 37, E131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.T.; Lin, H.H.; Lien, Y.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Hong, C.F.; Kao, Y.R.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Chen, S.J.; et al. EGFR promotes lung tumorigenesis by activating miR-7 through a Ras/ERK/Myc pathway that targets the Ets2 transcriptional repressor ERF. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8822–8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Lai, M.; Chen, M.; Xie, C.; Liao, R.; Kang, Y.J.; Xiao, C.; Hu, W.Y.; Han, J.; Sun, P. The miR-17-92 cluster of microRNAs confers tumorigenicity by inhibiting oncogene-induced senescence. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8547–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Mi, J.; Shu, X.; Liu, F.; Li, C. miR-92a family and their target genes in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 323, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Paine, M.S.; Brooks, A.M.; McCubrey, J.A.; Renegar, R.H.; Wang, R.; Terrian, D.M. Senescence-associated exosome release from human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7864–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lespagnol, A.; Duflaut, D.; Beekman, C.; Blanc, L.; Fiucci, G.; Marine, J.C.; Vidal, M.; Amson, R.; Telerman, A. Exosome secretion, including the DNA damage-induced p53-dependent secretory pathway, is severely compromised in TSAP6/Steap3-null mice. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The regulation of exosome secretion: A novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Riley, T.; Levine, A.J. The regulation of the endosomal compartment by p53 the tumor suppressor gene. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppe, J.P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Munoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 2853–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Mancera, P.A.; Young, A.R.; Narita, M. Inside and out: The activities of senescence in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Jutzy, J.M.; Valenzuela, M.M.; Turay, D.; Aspe, J.R.; Ashok, A.; Mirshahidi, S.; Mercola, D.; Lilly, M.B.; Wall, N.R. Plasma-derived exosomal survivin, a plausible biomarker for early detection of prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Gong, W. Increased exosomal microRNA-21 and microRNA-146a levels in the cervicovaginal lavage specimens of patients with cervical cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.C.; Luo, X.H.; Tao, G.X.; Guan, M.; Yuan, H.; Hu, D.K. Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs are Differentially Expressed in the Cervicovaginal Lavage Samples of Cervical Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 30, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campitelli, M.; Jeannot, E.; Peter, M.; Lappartient, E.; Saada, S.; de la Rochefordiere, A.; Fourchotte, V.; Alran, S.; Petrow, P.; Cottu, P.; et al. Human papillomavirus mutational insertion: Specific marker of circulating tumor DNA in cervical cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeannot, E.; Becette, V.; Campitelli, M.; Calmejane, M.A.; Lappartient, E.; Ruff, E.; Saada, S.; Holmes, A.; Bellet, D.; Sastre-Garau, X. Circulating human papillomavirus DNA detected using droplet digital PCR in the serum of patients diagnosed with early stage human papillomavirus-associated invasive carcinoma. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2016, 2, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.R.; Oguin, T.H.; Martinez, J. The clearance of dying cells: Table for two. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.; Sainson, R.C. Regulation of the anti-tumour immune response by cancer-associated fibroblasts. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 25, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, G.S.; Poutahidis, T.; Erdman, S.E.; Kirsch, R.; Riddell, R.H.; Diamandis, E.P. Cancer-associated fibroblasts drive the progression of metastasis through both paracrine and mechanical pressure on cancer tissue. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colburn, N.H.; Bruegge, W.F.; Bates, J.R.; Gray, R.H.; Rossen, J.D.; Kelsey, W.H.; Shimada, T. Correlation of anchorage-independent growth with tumorigenicity of chemically transformed mouse epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, H.; Lengauer, C. Aneuploidy and cancer. Nature 2004, 432, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giam, M.; Rancati, G. Aneuploidy and chromosomal instability in cancer: A jackpot to chaos. Cell Div. 2015, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trejo-Becerril, C.; Perez-Cardenas, E.; Taja-Chayeb, L.; Anker, P.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Medina-Velazquez, L.A.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A.; Perez-Montiel, D.; Chavez-Blanco, A.; Cruz-Velazquez, J.; et al. Cancer progression mediated by horizontal gene transfer in an in vivo model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahan, P.B.; Stroun, M. The virtosome-a novel cytosolic informative entity and intercellular messenger. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2010, 28, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, E.R.; Vernon, S.D.; Hewan-Lowe, K.O.; Lee, D.R.; Thoms, W.W.; Reeves, W.C. An unusual cervical carcinoma showing exception to epitheliotropism of human papillomavirus. Hum. Pathol. 1999, 30, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, F.; Favicchio, R.; Simon, T.; Alifrangis, C.; Stebbing, J.; Giamas, G. Extracellular vesicles swarm the cancer microenvironment: From tumor-stroma communication to drug intervention. Oncogene 2017, 36, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guenat, D.; Hermetet, F.; Prétet, J.-L.; Mougin, C. Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles in HPV Transmission and Carcinogenesis. Viruses 2017, 9, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9080211
Guenat D, Hermetet F, Prétet J-L, Mougin C. Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles in HPV Transmission and Carcinogenesis. Viruses. 2017; 9(8):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9080211
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuenat, David, François Hermetet, Jean-Luc Prétet, and Christiane Mougin. 2017. "Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles in HPV Transmission and Carcinogenesis" Viruses 9, no. 8: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9080211
APA StyleGuenat, D., Hermetet, F., Prétet, J.-L., & Mougin, C. (2017). Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles in HPV Transmission and Carcinogenesis. Viruses, 9(8), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9080211





