Isolation and Characterization of a Shewanella Phage–Host System from the Gut of the Tunicate, Ciona intestinalis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation from the Gut of Ciona Intestinalis
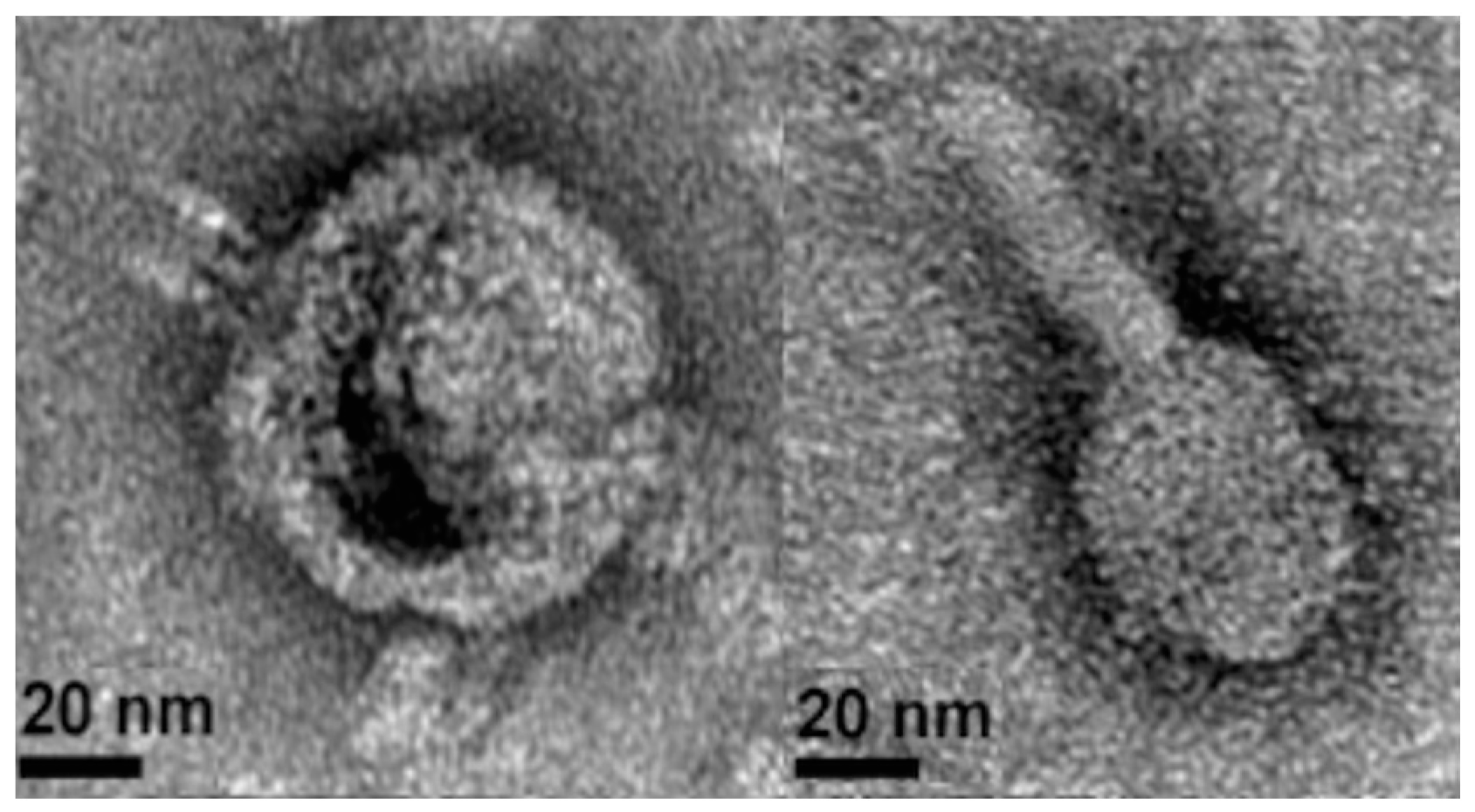
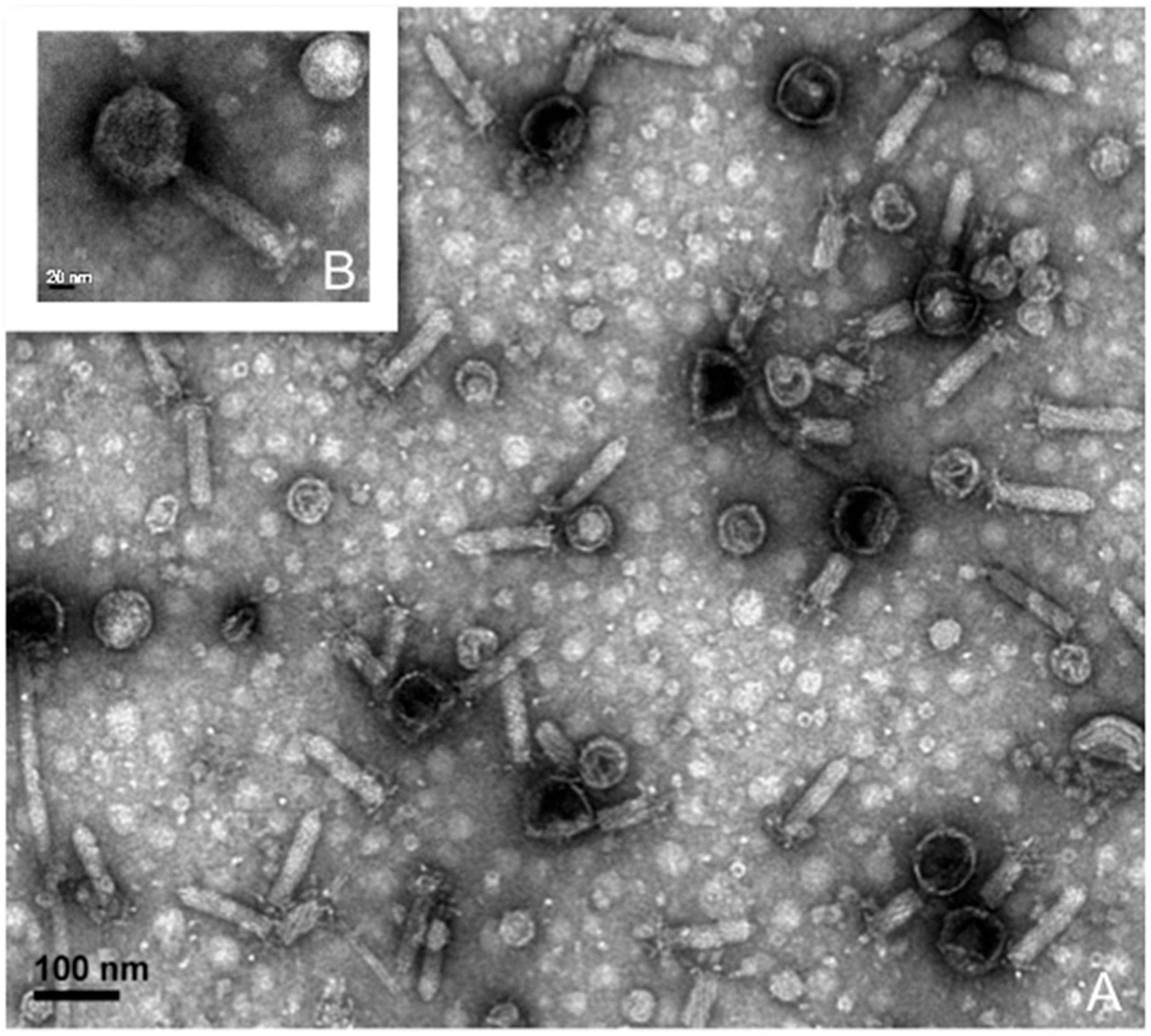
2.2. Phage Isolation, Propagation, and Purification for Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3. DNA Extraction, Sequencing and Analysis
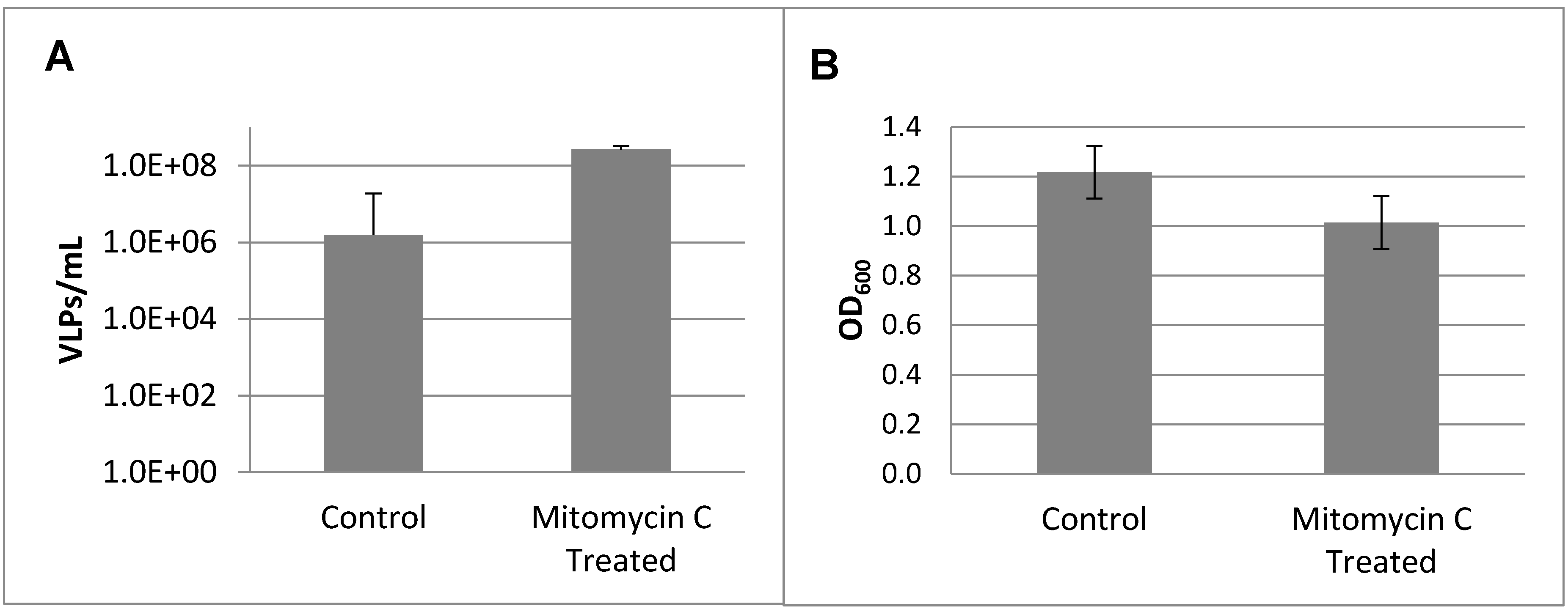
2.4. Prophage Induction and Identification
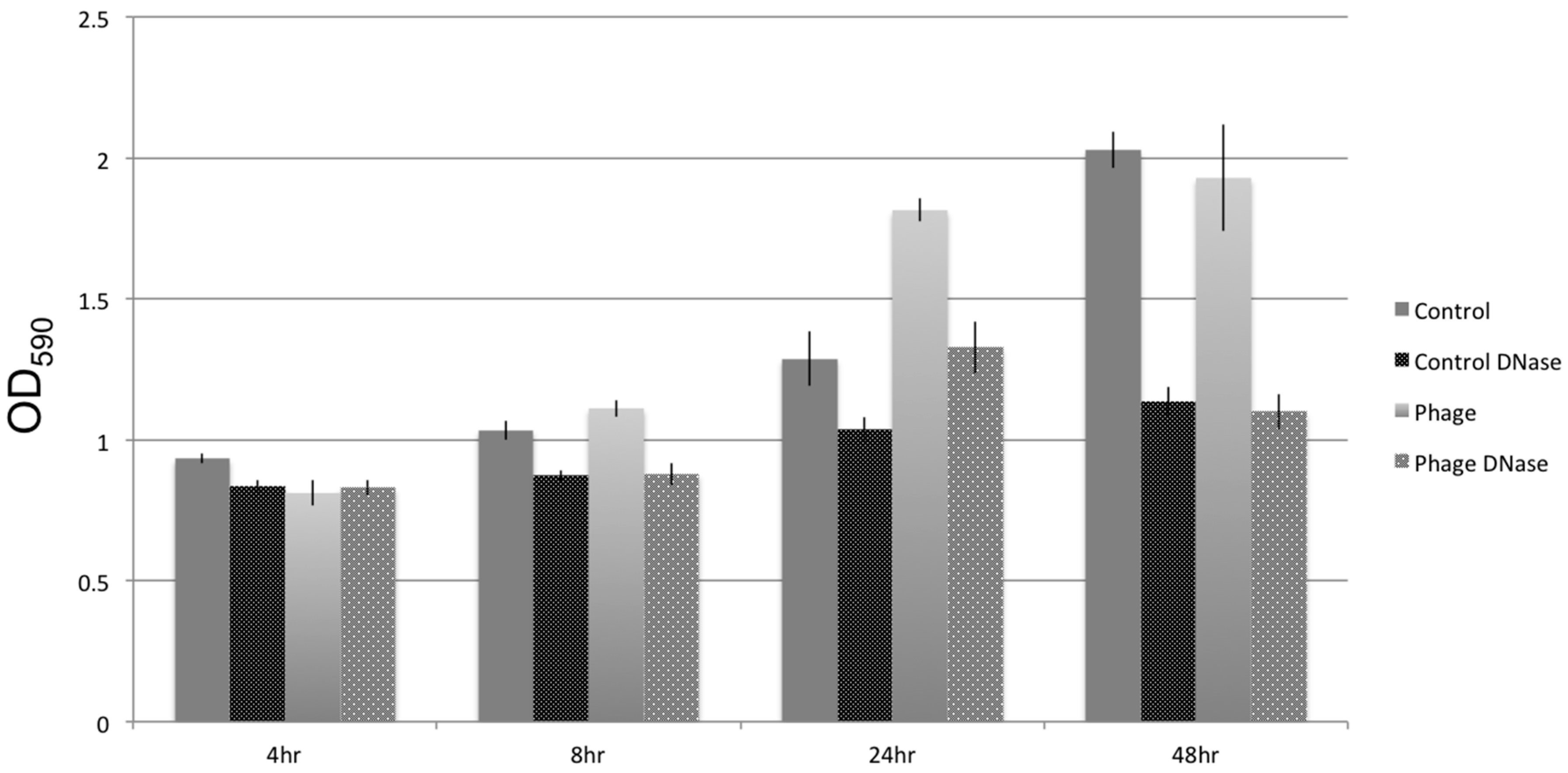
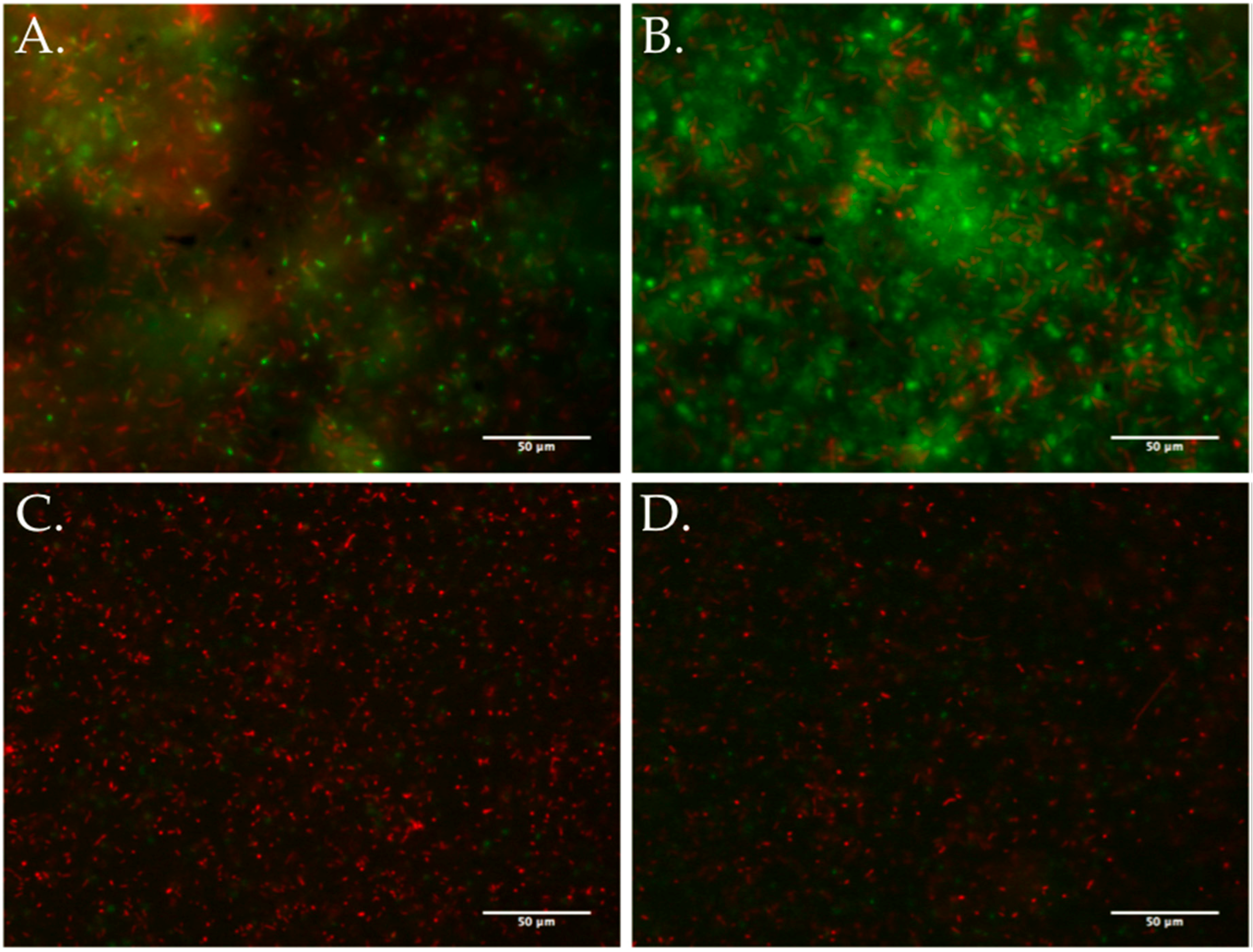
2.5. Biofilm Assays
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Cultivation and Genome Sequencing
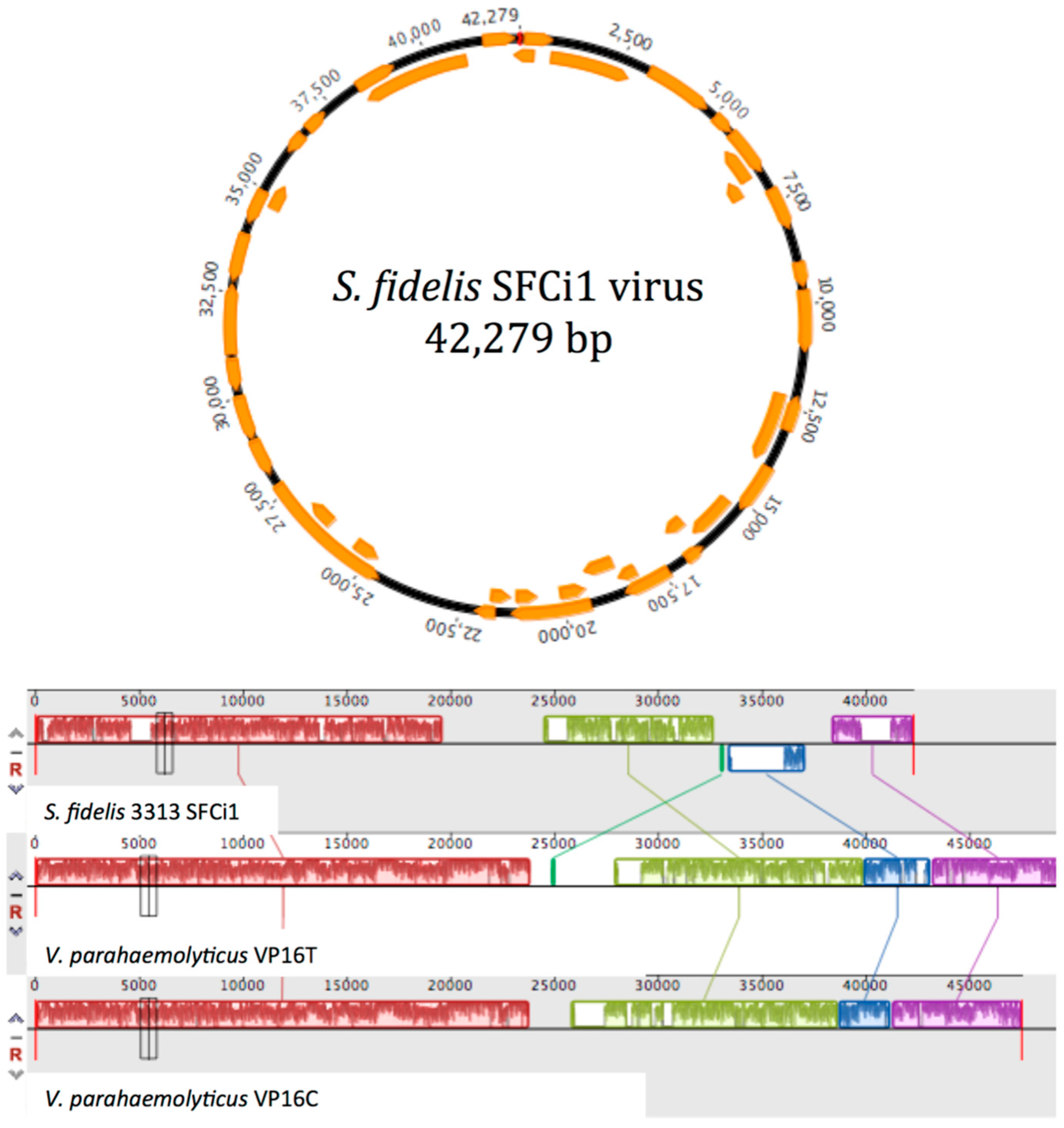
3.2. Prophage Induction and Genome Sequencing
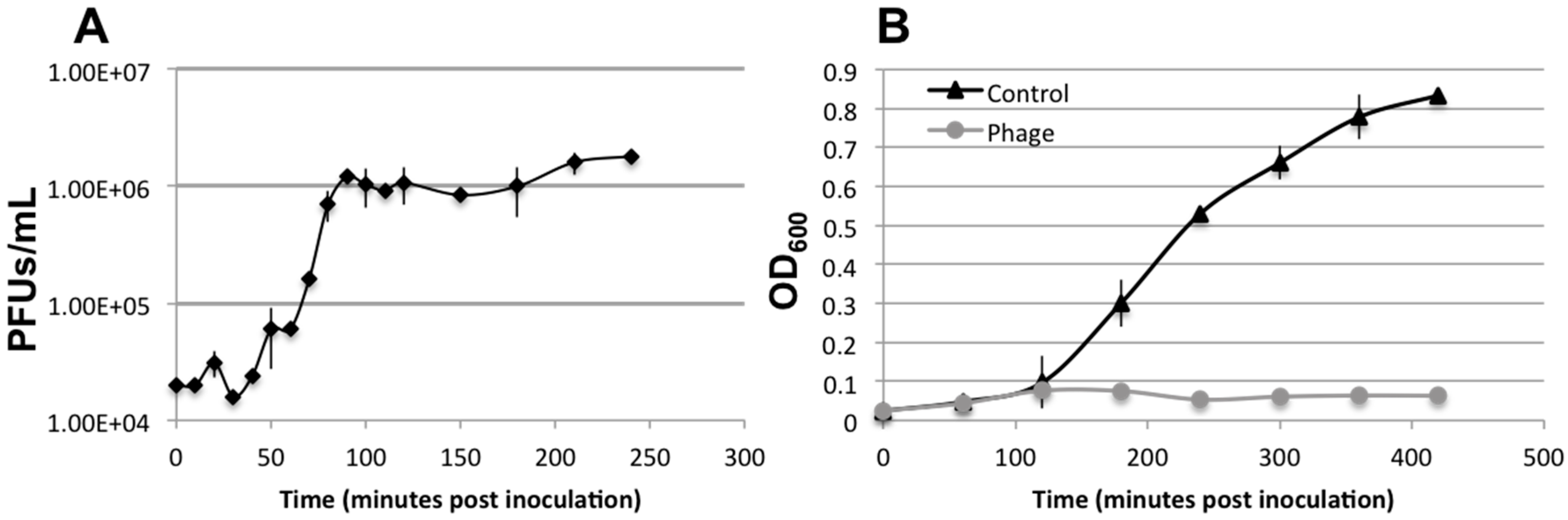
3.3. Lytic Phage Isolation and Genome Sequencing
3.4. Similarity to Vibrio Phages
3.5. Biofilm Development
3.6. GenBank Accession Numbers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brussow, H.; Hendrix, R.W. Phage genomics: Small is beautiful. Cell 2002, 108, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A. Viruses in the sea. Nature 2005, 437, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, S.; Tsai, P.; Bell, J.; Fromont, J.; Ilan, M.; Lindquist, N.; Perez, T.; Rodrigo, A.; Schupp, P.J.; Vacelet, J.; et al. Assessing the complex sponge microbiota: Core, variable and species-specific bacterial communities in marine sponges. ISME J. 2012, 6, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dishaw, L.J.; Flores-Torres, J.; Lax, S.; Gemayel, K.; Leigh, B.; Melillo, D.; Mueller, M.G.; Natale, L.; Zucchetti, I.; De Santis, R.; et al. The gut of geographically disparate Ciona intestinalis harbors a core microbiota. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzenburg, S.; Walter, J.; Kunzel, S.; Wang, J.; Baines, J.F.; Bosch, T.C.; Fraune, S. Distinct antimicrobial peptide expression determines host species-specific bacterial associations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3730–E3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Baik, K.S.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, B.M.; Shin, T.S.; Chung, G.H.; Rhee, M.S.; Seong, C.N. Shewanella haliotis sp. Nov., isolated from the gut microflora of abalone, Haliotis discus hannai. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, P.; Fruciano, C.; Frickey, T.; Jones, J.C.; Meyer, A. The gut microbial community of midas cichlid fish in repeatedly evolved limnetic-benthic species pairs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, P.; Espejo, R.T.; Romero, J. Molecular analysis of microbiota along the digestive tract of juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Microbial Ecol. 2009, 57, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, H.; Gu, J.D. Phylogenetic diversity and axial distribution of microbes in the intestinal tract of the polychaete Neanthes glandicincta. Microbial Ecol. 2009, 58, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrickson, J.K.; Romine, M.F.; Beliaev, A.S.; Auchtung, J.M.; Driscoll, M.E.; Gardner, T.S.; Nealson, K.H.; Osterman, A.L.; Pinchuk, G.; Reed, J.L.; et al. Towards environmental systems biology of Shewanella. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hau, H.H.; Gralnick, J.A. Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpinets, T.V.; Romine, M.F.; Schmoyer, D.D.; Kora, G.H.; Syed, M.H.; Leuze, M.R.; Serres, M.H.; Park, B.H.; Samatova, N.F.; Uberbacher, E.C. Shewanella knowledgebase: Integration of the experimental data and computational predictions suggests a biological role for transcription of intergenic regions. Database 2010, baq012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericsson, A.C.; Davis, D.J.; Franklin, C.L.; Hagan, C.E. Exoelectrogenic capacity of host microbiota predicts lymphocyte recruitment to the gut. Physiol. Genomics 2015, 47, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro-Quintero, A.; Deng, J.; Auchtung, J.; Brettar, I.; Hofle, M.G.; Klappenbach, J.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Unprecedented levels of horizontal gene transfer among spatially co-occurring Shewanella bacteria from the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, W.K.; Vu, T.T.; Lovendahl, K.N.; Llull, J.M.; Serres, M.H.; Romine, M.F.; Reed, J.L. Comparisons of Shewanella strains based on genome annotations, modeling, and experiments. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, C.; Moreno-Ventas, X.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Morinigo, M.A.; de La Banda, I.G. Dietary probiotic supplementation (Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11) modulates gut microbiota and promotes growth and condition in Senegalese sole larviculture. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhtanen, A.M.; Eronen-Rasimus, E.; Kaartokallio, H.; Rintala, J.M.; Autio, R.; Roine, E. Isolation and characterization of phage-host systems from the Baltic Sea ice. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, F. Role of filamentous phage SW1 in regulating the lateral flagella of Shewanella piezotolerans strain WP3 at low temperatures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7101–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Li, M.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Cao, L.; Khan, M.N. The novel Shewanella putrefaciens-infecting bacteriophage Spp001: Genome sequence and lytic enzymes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, F.; Li, Q.; Xiao, X. A novel filamentous phage from the deep-sea bacterium Shewanella piezotolerans WP3 is induced at low temperature. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7151–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godeke, J.; Paul, K.; Lassak, J.; Thormann, K.M. Phage-induced lysis enhances biofilm formation in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. ISME J. 2011, 5, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, J.H. Prophages in marine bacteria: Dangerous molecular time bombs or the key to survival in the seas? ISME J. 2008, 2, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, A.S.; Yamada, T.; Kristensen, D.M.; Kultima, J.R.; Sunagawa, S.; Koonin, E.V.; Bork, P. Classification and quantification of bacteriophage taxa in human gut metagenomes. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, K.K. What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H.; Stepankova, R.; Kozakova, H.; Hudcovic, T.; Vannucci, L.; Tuckova, L.; Rossmann, P.; Hrncir, T.; Kverka, M.; Zakostelska, Z.; et al. The role of gut microbiota (commensal bacteria) and the mucosal barrier in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer: Contribution of germ-free and gnotobiotic animal models of human diseases. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Backhed, F. The gut microbiota—Masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.A.; Tan, C.H.; Mikkelsen, P.J.; Kung, V.; Woo, J.; Tay, M.; Hauser, A.; McDougald, D.; Webb, J.S.; Kjelleberg, S. The biofilm life cycle and virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are dependent on a filamentous prophage. ISME J. 2009, 3, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kim, Y.; Ma, Q.; Hong, S.H.; Pokusaeva, K.; Sturino, J.M.; Wood, T.K. Cryptic prophages help bacteria cope with adverse environments. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrolo, M.; Frias, M.J.; Pinto, F.R.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M. Prophage spontaneous activation promotes DNA release enhancing biofilm formation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnenkade, L.; Teichmann, L.; Thormann, K.M. Iron triggers lambdaSo prophage induction and release of extracellular DNA in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5304–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16s ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.H. Bacteriophages; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1959; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Hyman, P.; Abedon, S.T. Practical methods for determining phage growth parameters. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 501, 175–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thurber, R.V.; Haynes, M.; Breitbart, M.; Wegley, L.; Rohwer, F. Laboratory procedures to generate viral metagenomes. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, H.-W.; Heldal, M. Basic electron microscopy of aquatic viruses. Man Aquatic Viral Ecol. 2010, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Naccache, S.N.; Ng, T.; Federman, S.; Li, L.; Chiu, C.Y.; Delwart, E.L. An ensemble strategy that significantly improves de novo assembly of microbial genomes from metagenomic next-generation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcher, A.L.; Bratke, K.A.; Powers, E.C.; Salzberg, S.L. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the rapid annotation of microbial genomes using subsystems technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goris, J.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Klappenbach, J.A.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 81–91, ANI Average Nucleotide Identity. Available online: http://enve-omics.ce.gatech.edu/ani/ (accessed on 12 May 2016). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinos, T. Bypassing cultivation to identify bacterial species. Microbe 2014, 9, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.; Enault, F.; Hurwitz, B.L.; Sullivan, M.B. VirSorter: Mining viral signal from microbial genomic data. PeerJ 2015, 3, e985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.C.; Paul, J.H. Significance of lysogeny in the marine environment: Studies with isolates and a model of lysogenic phage production. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Noble, R.T.; Steele, J.A.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Hewson, I.; Fuhrman, J.A. Virus and prokaryote enumeration from planktonic aquatic environments by epifluorescence microscopy with SYBR green I. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okshevsky, M.; Meyer, R.L. Evaluation of fluorescent stains for visualizing extracellular DNA in biofilms. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 105, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, J.H.; Kadouri, D.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Growing and analyzing static biofilms. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2005, 1B-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH image to ImageJ: 25 Years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Sawabe, T.; Hayashi, K.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Zhukova, N.V.; Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Mikhailov, V.V.; Nicolau, D.V.; Christen, R. Shewanella fidelis sp. Nov., isolated from sediments and sea water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Du, P.; Zheng, H.; Yu, W.; Wan, L.; Chen, C. Whole-genome sequence comparison as a method for improving bacterial species definition. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidelberg, J.F.; Paulsen, I.T.; Nelson, K.E.; Gaidos, E.J.; Nelson, W.C.; Read, T.D.; Eisen, J.A.; Seshadri, R.; Ward, N.; Methe, B.; et al. Genome sequence of the dissimilatory metal ion-reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauquet, C.M.; Maniloff, J.; Desselberger, U.; Ball, A. Virus Taxonomy: Viiith Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Seguritan, V.; Feng, I.W.; Rohwer, F.; Swift, M.; Segall, A.M. Genome sequences of two closely related Vibrio parahaemolyticus phages, VP16T and VP16C. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 6434–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. Progressive mauve: Multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Song, X.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Shao, H.; Jiang, Y. Complete genomic sequence of bacteriophage H188: A novel Vibrio kanaloae phage isolated from Yellow Sea. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sime-Ngando, T. Environmental bacteriophages: Viruses of microbes in aquatic ecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohwer, F.; Edwards, R. The phage proteomic tree: A genome-based taxonomy for phage. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucks, J.B.; Nelson, D.R.; Kudla, G.R.; Plotkin, J.B. Genome landscapes and bacteriophage codon usage. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chithambaram, S.; Prabhakaran, R.; Xia, X. Differential codon adaptation between dsDNA and ssDNA phages in Escherichia coli. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, B.A.; Liberti, A.; Dishaw, L.J. Generation of germ-free Ciona intestinalis for studies of gut-microbe interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Macpherson, A.J. Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Liu, C.H.; Tzianabos, A.O.; Kasper, D.L. An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell 2005, 122, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, K.E.; Slusher, N.A.; Cabana, M.D.; Lynch, S.V. Role of the gut microbiota in defining human health. Expert Rev. Anti Infect Ther. 2010, 8, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M. Marine viruses: Truth or dare. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, J.S.; Stock, C.A.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Bourouiba, L.; Coleman, M.L.; Buchan, A.; Follows, M.J.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Jover, L.F.; Lennon, J.T.; et al. A multitrophic model to quantify the effects of marine viruses on microbial food webs and ecosystem processes. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses—Major players in the global ecosystem. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvie, L.A.; Jones, B.V. The human gut virome: A multifaceted majority. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, A.; Mick, E.; Tirosh, I.; Sagy, O.; Sorek, R. CRISPR targeting reveals a reservoir of common phages associated with the human gut microbiome. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, P.; Leclerc, M.C.; Joossens, M.; Mondot, S.; Blottiere, H.M.; Raes, J.; Ehrlich, D.; Dore, J. A metagenomic insight into our gut’s microbiome. Gut 2013, 62, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, A.; Semenkovich, N.P.; Whiteson, K.; Rohwer, F.; Gordon, J.I. Going viral: Next-generation sequencing applied to phage populations in the human gut. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.R.; Lee, H.H.; Spina, C.S.; Collins, J.J. Antibiotic treatment expands the resistance reservoir and ecological network of the phage metagenome. Nature 2013, 499, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, M.A.; Chaconas, G. Three-site synapsis during Mu DNA transposition: A critical intermediate preceding engagement of the active site. Cell 1996, 85, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erauso, G.; Lakhal, F.; Bidault-Toffin, A.; Le Chevalier, P.; Bouloc, P.; Paillard, C.; Jacq, A. Evidence for the role of horizontal transfer in generating Pvt1, a large mosaic conjugative plasmid from the clam pathogen, Vibrio tapetis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerkop, B.A.; Clements, C.V.; Rollins, D.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Hooper, L.V. A composite bacteriophage alters colonization by an intestinal commensal bacterium. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17621–17626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okshevsky, M.; Meyer, R.L. The role of extracellular DNA in the establishment, maintenance and perpetuation of bacterial biofilms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberger, R.E.; Holden, P.A. Extracellular DNA in single- and multiple-species unsaturated biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5404–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Shen, P. Involvement of DNA in biofilm formation II: From bacterial adhesion to biofilm formation. J. Nat. Sci. Wuhan 2012, 17, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allesen-Holm, M.; Barken, K.B.; Yang, L.; Klausen, M.; Webb, J.S.; Kjelleberg, S.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1114–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramohan, L.; Ahn, J.S.; Weaver, K.E.; Bayles, K.W. An overlap between the control of programmed cell death in Bacillus anthracis and sporulation. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 4103–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, K.C.; Bayles, K.W. Death’s toolbox: Examining the molecular components of bacterial programmed cell death. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, J.S.; Thompson, L.S.; James, S.; Charlton, T.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Koch, B.; Givskov, M.; Kjelleberg, S. Cell death in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, A.M.; Thormann, K.; Frunzke, J. Impact of spontaneous prophage induction on the fitness of bacterial populations and host-microbe interactions. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Dahl, A.; Middelboe, M. Vibriophages differentially influence biofilm formation by Vibrio anguillarum strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinidoust, Z.; Tufenkji, N.; van de Ven, T.G. Formation of biofilms under phage predation: Considerations concerning a biofilm increase. Biofouling 2013, 29, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lacqua, A.; Wanner, O.; Colangelo, T.; Martinotti, M.G.; Landini, P. Emergence of biofilm-forming subpopulations upon exposure of Escherichia coli to environmental bacteriophages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoering, A.L.; Gilmore, M.S. Quorum sensing and DNA release in bacterial biofilms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, L.; Ramsdell, G. The effects of wall populations on coexistence of bacteria in the liquid phase of chemostat cultures. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1985, 131, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, J.J.; Auro, R.; Furlan, M.; Whiteson, K.L.; Erb, M.L.; Pogliano, J.; Stotland, A.; Wolkowicz, R.; Cutting, A.S.; Doran, K.S.; et al. Bacteriophage adhering to mucus provide a non-host-derived immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10771–10776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I. Biofilm exopolysaccharides: A strong and sticky framework. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moons, P.; Faster, D.; Aertsen, A. Lysogenic conversion and phage resistance development in phage exposed Escherichia coli biofilms. Viruses 2013, 5, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayles, K.W. Are the molecular strategies that control apoptosis conserved in bacteria? Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.D.; Parker, W. Cultivation of epithelial-associated microbiota by the immune system. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leigh, B.; Karrer, C.; Cannon, J.P.; Breitbart, M.; Dishaw, L.J. Isolation and Characterization of a Shewanella Phage–Host System from the Gut of the Tunicate, Ciona intestinalis. Viruses 2017, 9, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9030060
Leigh B, Karrer C, Cannon JP, Breitbart M, Dishaw LJ. Isolation and Characterization of a Shewanella Phage–Host System from the Gut of the Tunicate, Ciona intestinalis. Viruses. 2017; 9(3):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9030060
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeigh, Brittany, Charlotte Karrer, John P. Cannon, Mya Breitbart, and Larry J. Dishaw. 2017. "Isolation and Characterization of a Shewanella Phage–Host System from the Gut of the Tunicate, Ciona intestinalis" Viruses 9, no. 3: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9030060
APA StyleLeigh, B., Karrer, C., Cannon, J. P., Breitbart, M., & Dishaw, L. J. (2017). Isolation and Characterization of a Shewanella Phage–Host System from the Gut of the Tunicate, Ciona intestinalis. Viruses, 9(3), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9030060





