Nuclear Import of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids and Genome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nuclear Pores and Nuclear Import Receptors
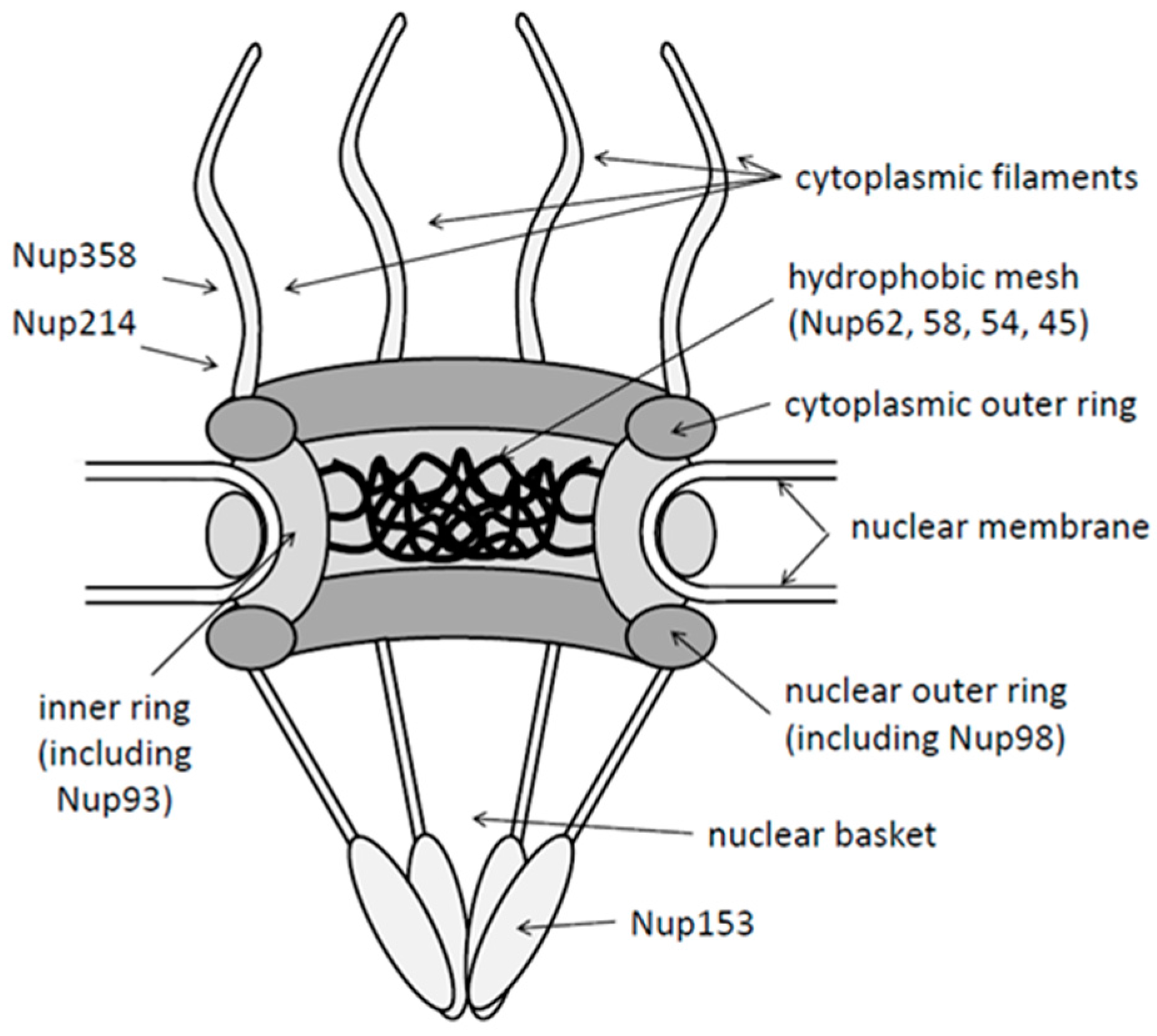
2.1. Structure of Nuclear Pores
2.2. Nuclear Import Receptors
3. Nuclear Import of Macromolecules
3.1. Nuclear Import Using Import Receptors
3.2. Import Receptor-Independent Pathways
4. Capsid Disassembly and Import of Other Viral Genomes
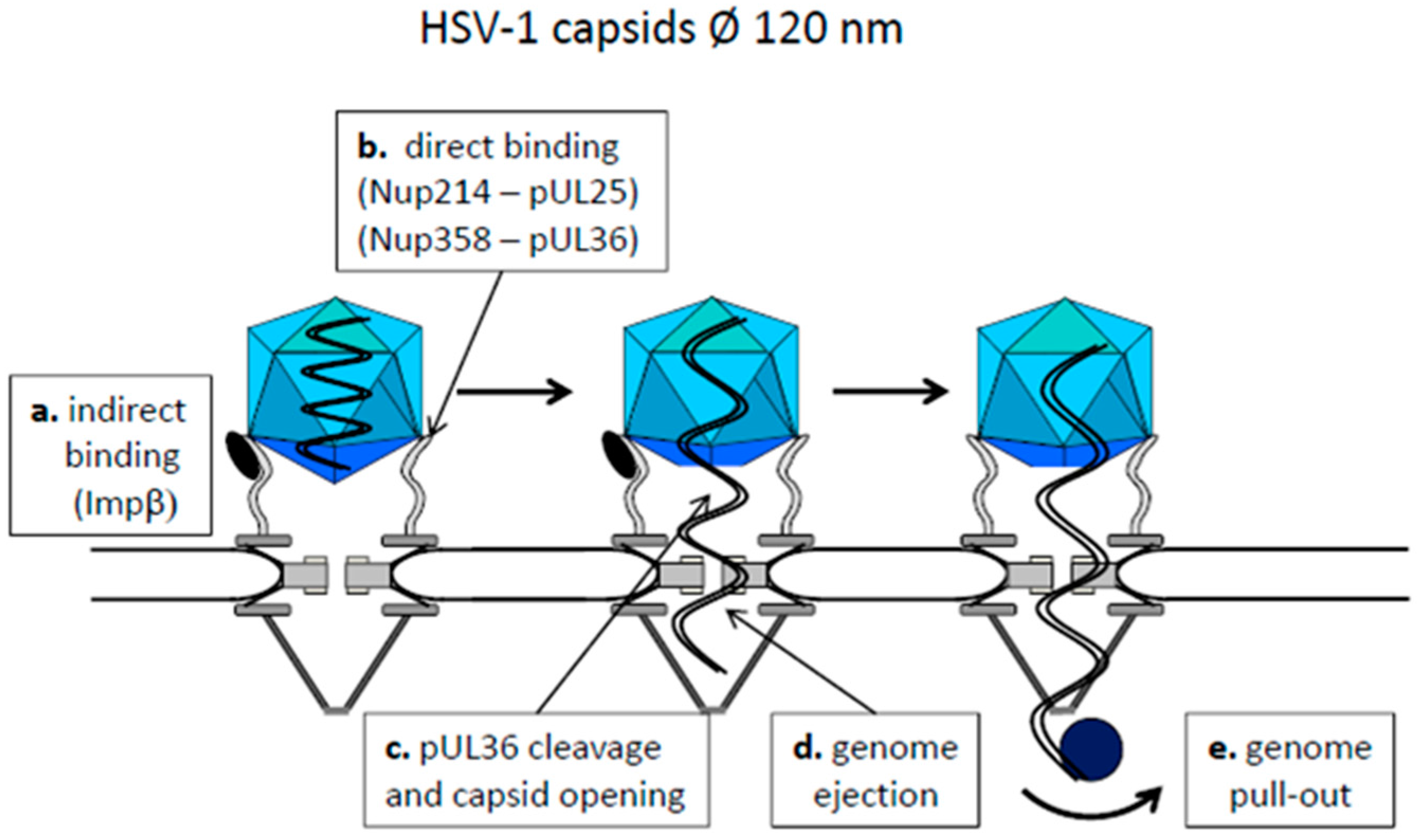
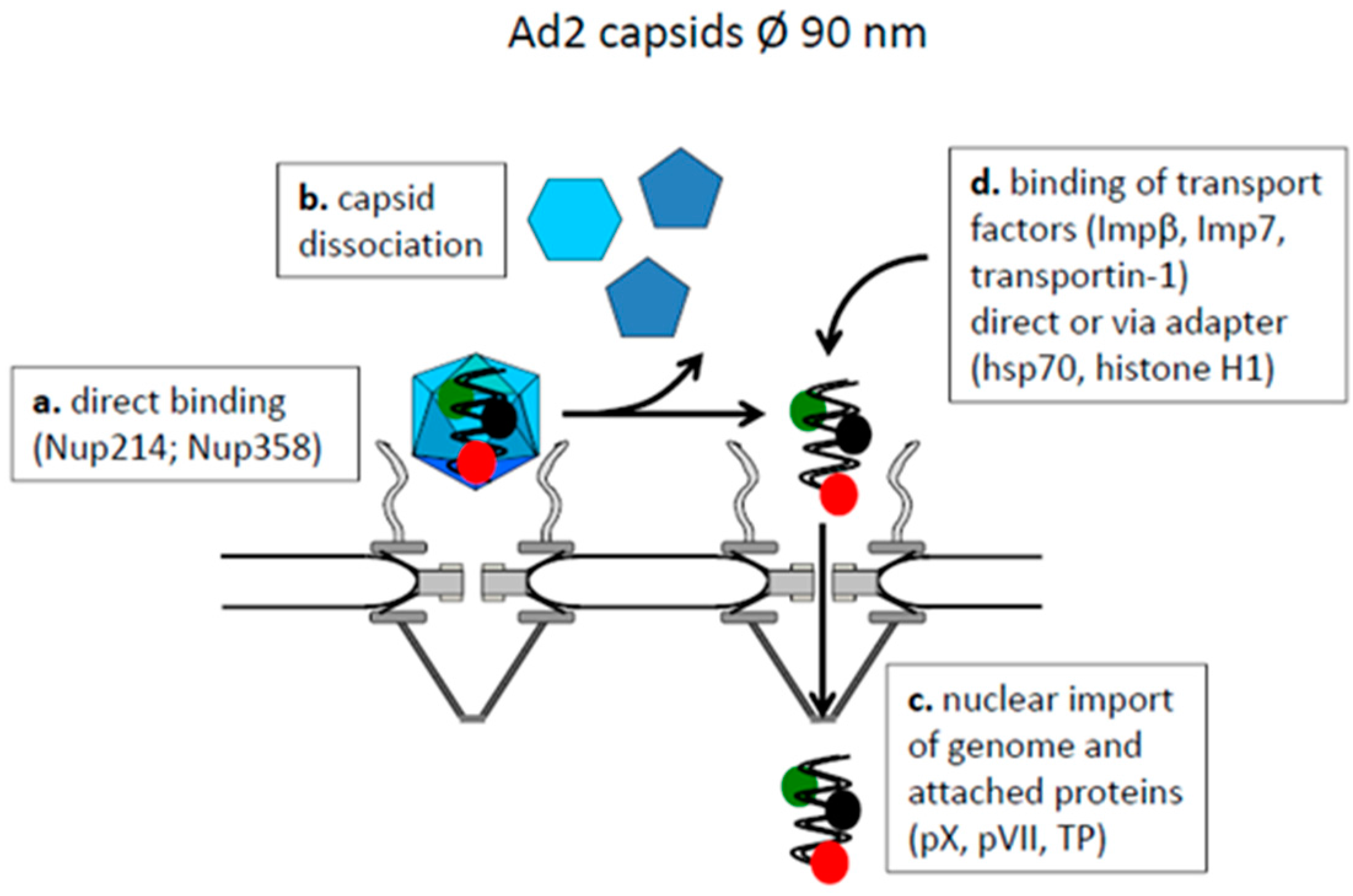
4.1. Capsids Larger than the Maximal Transport Diameter of the NPC
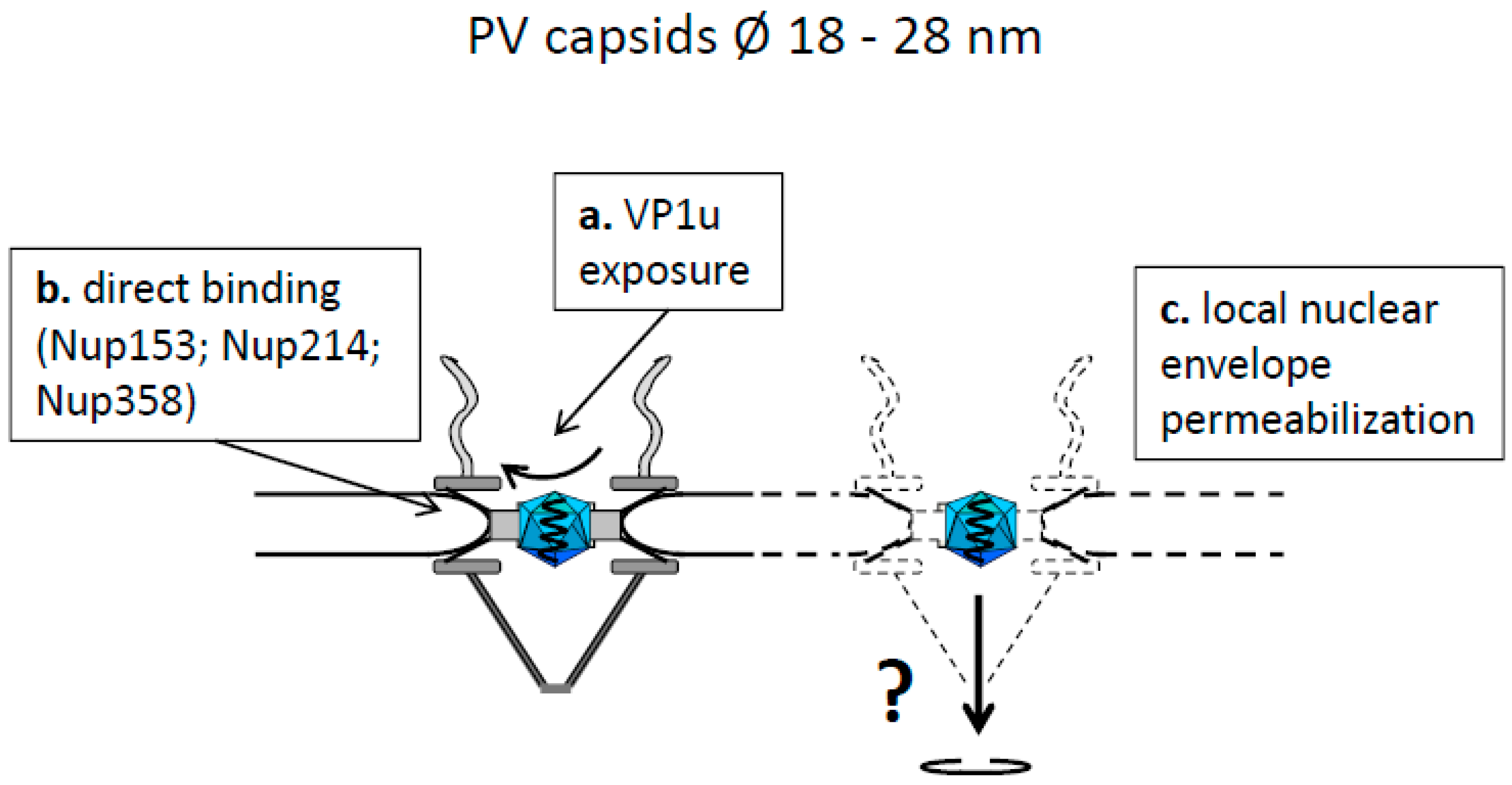
4.2. Capsids Smaller than the Maximal Transport Diameter of the NPC
5. Organization of HBV Core Proteins and Capsids
6. Intracellular HBV Capsid Localization
7. Transport of HBV Capsids and Genome
8. Transport and Release of the Hepadnaviral Genome
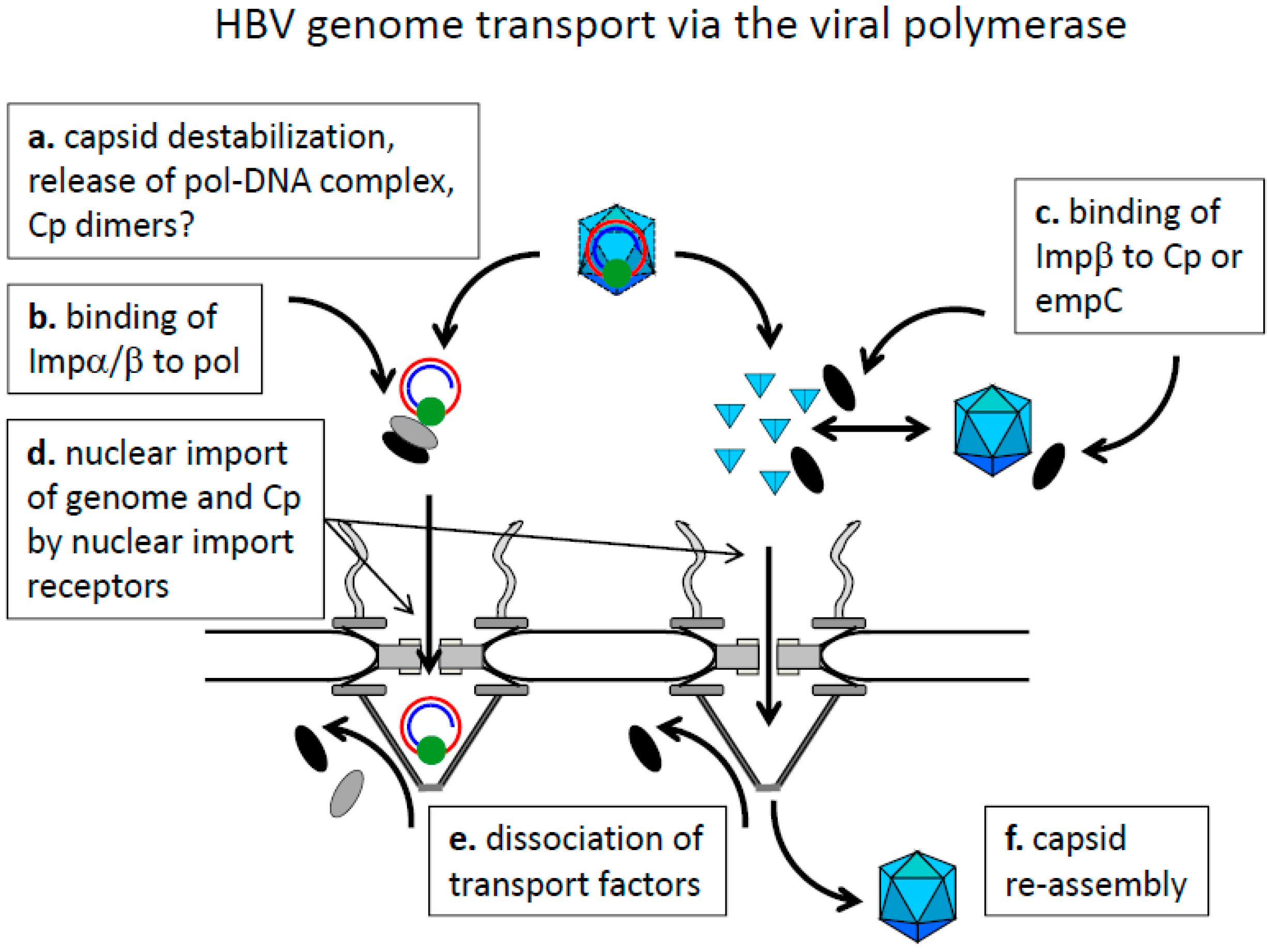
8.1. Cytoplasmic Genome Release and Genome Transport by the Viral Polymerase
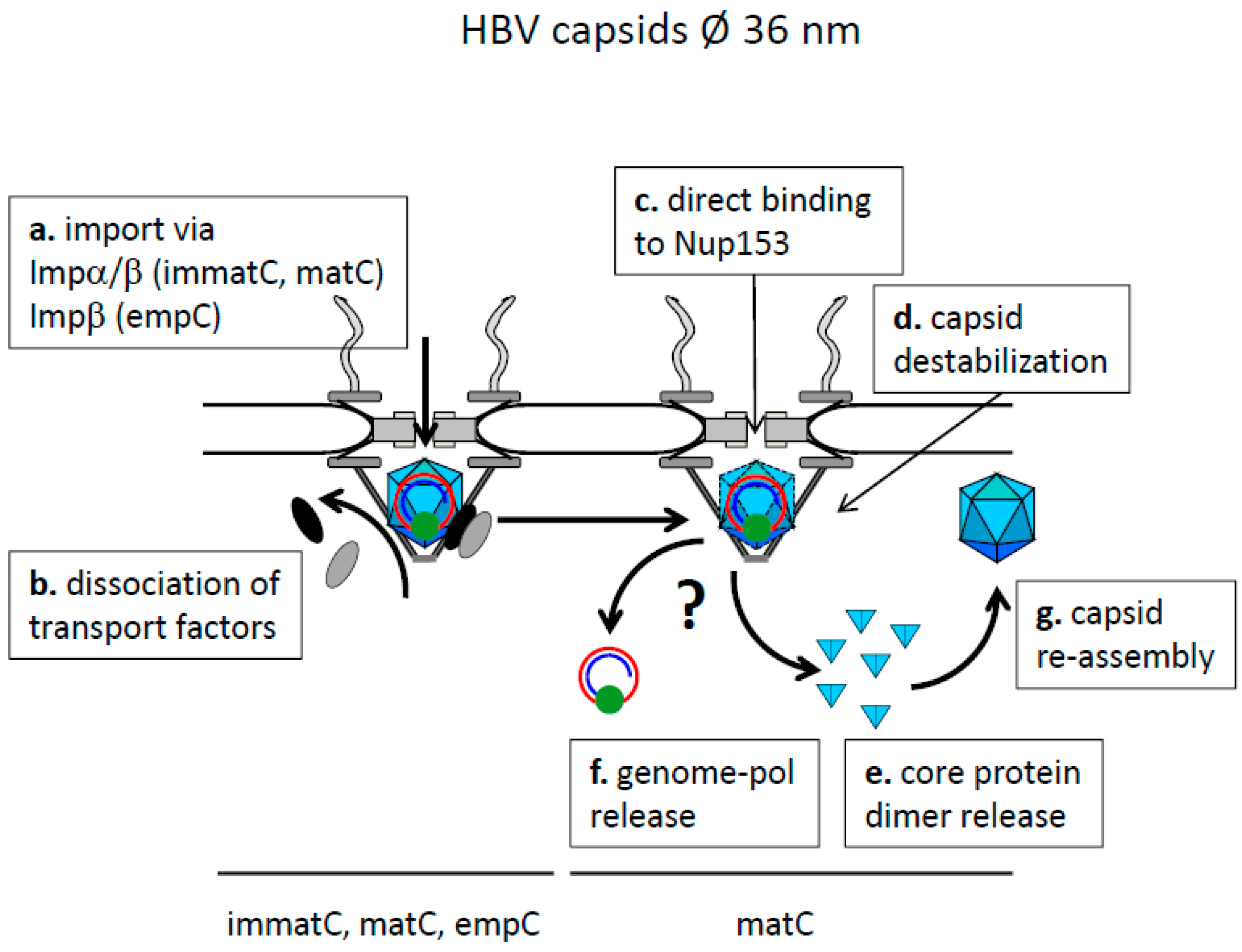
8.2. Nuclear Genome-Translocation in Intact Capsids and Nuclear Genome Release
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Königer, C.; Wingert, I.; Marsmann, M.; Rösler, C.; Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Involvement of the host DNA-repair enzyme TDP2 in formation of the covalently closed circular DNA persistence reservoir of hepatitis B viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4244–E4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, G.; Peng, B.; Liu, C.; Yan, H.; Yao, Q.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Tang, D.; et al. DNA Polymerase κ Is a Key Cellular Factor for the Formation of Covalently Closed Circular DNA of Hepatitis B Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerelsaikhan, T.; Tavis, J.E.; Bruss, V. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid envelopment does not occur without genomic DNA synthesis. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4269–4274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuttleman, J.S.; Pourcel, C.; Summers, J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell 1986, 47, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Smith, P.M.; Horwich, A.L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goff, S.P. Host factors exploited by retroviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, I.; Weber, S.; Snijder, B.; Ventayol, P.S.; Kühbacher, A.; Becker, M.; Day, P.M.; Schiller, J.T.; Kann, M.; Pelkmans, L.; et al. Large Scale RNAi Reveals the Requirement of Nuclear Envelope Breakdown for Nuclear Import of Human Papillomaviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clever, J.; Yamada, M.; Kasamatsu, H. Import of simian virus 40 virions through nuclear pore complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7333–7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Kasamatsu, H. Role of nuclear pore complex in simian virus 40 nuclear targeting. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, A.; Clever, J.; Yamada, M.; Li, P.P.; Kasamatsu, H. Association with capsid proteins promotes nuclear targeting of simian virus 40 DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, A.; Shum, D.; Morioka, H.; Otsuka, E.; Kasamatsu, H. Interaction of the Vp3 Nuclear Localization Signal with the Importin α2/β Heterodimer Directs Nuclear Entry of Infecting Simian Virus 40. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9368–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, A.; Itoh, N.; Li, P.P.; Handa, H.; Liddington, R.C.; Kasamatsu, H. Minor Capsid Proteins of Simian Virus 40 Are Dispensable for Nucleocapsid Assembly and Cell Entry but Are Required for Nuclear Entry of the Viral Genome. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3778–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butin-Israeli, V.; Ben-nun-Shaul, O.; Kopatz, I.; Adam, S.A.; Shimi, T.; Goldman, R.D.; Oppenheim, A. Simian virus 40 induces lamin A/C fluctuations and nuclear envelope deformation during cell entry. Nucleus 2011, 2, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Appen, A.; Beck, M. Structure Determination of the Nuclear Pore Complex with Three-Dimensional Cryo electron Microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alber, F.; Dokudovskaya, S.; Veenhoff, L.M.; Zhang, W.; Kipper, J.; Devos, D.; Suprapto, A.; Karni-Schmidt, O.; Williams, R.; Chait, B.T.; et al. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature 2007, 450, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabut, G.; Doye, V.; Ellenberg, J. Mapping the dynamic organization of the nuclear pore complex inside single living cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, E.J.; Wente, S.R. Dynamic Nuclear Pore Complexes: Life on the Edge. Cell 2006, 125, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, M.A.; Anderson, D.J.; Richard, E.; Hetzer, M.W. Nuclear Pores Form de Novo from Both Sides of the Nuclear Envelope. Science 2006, 312, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raices, M.; D’Angelo, M.A. Nuclear pore complex composition: A new regulator of tissue-specific and developmental functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.; Görlich, D. A Saturated FG-Repeat Hydrogel Can Reproduce the Permeability Properties of Nuclear Pore Complexes. Cell 2007, 130, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.S.; Belmont, B.J.; Sante, J.M.; Rexach, M.F. Natively Unfolded Nucleoporins Gate Protein Diffusion across the Nuclear Pore Complex. Cell 2007, 129, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strawn, L.A.; Shen, T.; Shulga, N.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Wente, S.R. Minimal nuclear pore complexes define FG repeat domains essential for transport. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, A.; van der Giessen, E.; Onck, P.R. Energetics of Transport through the Nuclear Pore Complex. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribbeck, K.; Görlich, D. Kinetic analysis of translocation through nuclear pore complexes. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucet, C.M.; Hetzer, M.W. Nuclear pore biogenesis into an intact nuclear envelope. Chromosoma 2010, 119, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Lafarga, M.; Berciano, M.T.; Hernandez, P.; Andres, M.A. Distribution of nuclear pores and chromatin organization in neurons and glial cells of the rat cerebellar cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989, 290, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshima, K.; Yahata, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Nakatomi, R.; Tachibana, T.; Hashikawa, T.; Imamoto, F.; Imamoto, N. Cell-cycle-dependent dynamics of nuclear pores: Pore-free islands and lamins. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 4442–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panté, N.; Kann, M. Nuclear Pore Complex Is Able to Transport Macromolecules with Diameters of ~39 nm. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cautain, B.; Hill, R.; de Pedro, N.; Link, W. Components and regulation of nuclear transport processes. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakielny, S.; Siomi, M.C.; Siomi, H.; Michael, W.M.; Pollard, V.; Dreyfuss, G. Transportin: Nuclear Transport Receptor of a Novel Nuclear Protein Import Pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 229, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siomi, H.; Dreyfuss, G. A nuclear localization domain in the hnRNP A1 protein. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 129, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lott, K.; Cingolani, G. The importin β binding domain as a master regulator of nucleocytoplasmic transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1578–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeri, D.; Malim, M.H. Importin β Can Mediate the Nuclear Import of an Arginine-Rich Nuclear Localization Signal in the Absence of Importin α. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalderon, D.; Roberts, B.L.; Richardson, W.D.; Smith, A.E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell 1984, 39, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Butel, J.S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell 1984, 37, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumroy, R.A.; Cingolani, G. Diversification of importin-α isoforms in cellular trafficking and disease states. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, D.A.; Ackermann, M.J.; Bischoff, J.R.; Beach, D.H.; Peters, R. p34cdc2-mediated phosphorylation at T124 inhibits nuclear import of SV-40 T antigen proteins. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 115, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Brown, K.; Siebenlist, U. Activation of NF-kappa B requires proteolysis of the inhibitor I kappa B-alpha: Signal-induced phosphorylation of I kappa B-alpha alone does not release active NF-kappa B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beals, C.R.; Clipstone, N.A.; Ho, S.N.; Crabtree, G.R. Nuclear localization of NF-ATc by a calcineurin-dependent, cyclosporin-sensitive intramolecular interaction. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingolani, G.; Lashuel, H.A.; Gerace, L.; Müller, C.W. Nuclear import factors importin α and importin β undergo mutually induced conformational changes upon association. FEBS Lett. 2000, 484, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Sekimoto, T.; Yamashita, E.; Nagoshi, E.; Nakagawa, A.; Imamoto, N.; Yoshimura, M.; Sakai, H.; Chong, K.T.; Tsukihara, T.; et al. The Structure of Importin-ß Bound to SREBP-2: Nuclear Import of a Transcription Factor. Science 2003, 302, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, M.P.; Aitchison, J.D.; Suprapto, A.; Hjertaas, K.; Zhao, Y.; Chait, B.T. The Yeast Nuclear Pore Complex. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.Y.H.; Huang, N.-P.; Köser, J.; Deng, J.; Lau, K.H.A.; Schwarz-Herion, K.; Fahrenkrog, B.; Aebi, U. Flexible phenylalanine-glycine nucleoporins as entropic barriers to nucleocytoplasmic transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9512–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, M.P.; Aitchison, J.D.; Magnasco, M.O.; Chait, B.T. Virtual gating and nuclear transport: The hole picture. Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.Y.H.; Fahrenkrog, B.; Köser, J.; Schwarz-Herion, K.; Deng, J.; Aebi, U. Nanomechanical Basis of Selective Gating by the Nuclear Pore Complex. Science 2007, 318, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.Y.H.; Köser, J.; Huang, N.; Schwarz-Herion, K.; Aebi, U. Nanomechanical interactions of phenylalanine–glycine nucleoporins studied by single molecule force–volume spectroscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 159, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.; Richter, R.P.; Görlich, D. FG-Rich Repeats of Nuclear Pore Proteins Form a Three-Dimensional Meshwork with Hydrogel-Like Properties. Science 2006, 314, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribbeck, K.; Görlich, D. The permeability barrier of nuclear pore complexes appears to operate via hydrophobic exclusion. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görlich, D.; Seewald, M.J.; Ribbeck, K. Characterization of Ran-driven cargo transport and the RanGTPase system by kinetic measurements and computer simulation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagstaff, K.M.; Jans, D.A. Importins and Beyond: Non-Conventional Nuclear Transport Mechanisms. Traffic 2009, 10, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argentaro, A.; Sim, H.; Kelly, S.; Preiss, S.; Clayton, A.; Jans, D.A.; Harley, V.R. A SOX9 Defect of Calmodulin-dependent Nuclear Import in Campomelic Dysplasia/Autosomal Sex Reversal. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33839–33847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holaska, J.M.; Black, B.E.; Love, D.C.; Hanover, J.A.; Leszyk, J.; Paschal, B.M. Calreticulin Is a Receptor for Nuclear Export. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alefantis, T.; Flaig, K.E.; Wigdahl, B.; Jain, P. Interaction of HTLV-1 Tax protein with calreticulin: Implications for Tax nuclear export and secretion. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2007, 61, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, C.F.; Neidig, J.A.; Freidinger, K.E.; Stankiewicz, T.A.; Weaver, B.S.; McGrew, J.; Allison, L.A. Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling of the Thyroid Hormone Receptorα. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grespin, M.E.; Bonamy, G.M.C.; Roggero, V.R.; Cameron, N.G.; Adam, L.E.; Atchison, A.P.; Fratto, V.M.; Allison, L.A. Thyroid Hormone Receptor α1 Follows a Cooperative CRM1/Calreticulin-mediated Nuclear Export Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25576–25588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen Recognition and Inflammatory Signaling in Innate Immune Defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arhel, N.J.; Souquere-Besse, S.; Munier, S.; Souque, P.; Guadagnini, S.; Rutherford, S.; Prévost, M.-C.; Allen, T.D.; Charneau, P. HIV-1 DNA Flap formation promotes uncoating of the pre-integration complex at the nuclear pore. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3025–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campadelli-Fiume, G.; Menotti, L.; Avitabile, E.; Gianni, T. Viral and cellular contributions to herpes simplex virus entry into the cell. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, E.E.; Stevenson, A.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Meredith, D.M. Differences in the intracellular localization and fate of herpes simplex virus tegument proteins early in the infection of Vero cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodeik, B.; Ebersold, M.W.; Helenius, A. Microtubule-mediated Transport of Incoming Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Capsids to the Nucleus. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 136, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, P.M.; Sodeik, B.; Ebersold, M.W.; Kutay, U.; Helenius, A. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Entry into Host Cells: Reconstitution of Capsid Binding and Uncoating at the Nuclear Pore Complex In Vitro. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4922–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasdeloup, D.; Blondel, D.; Isidro, A.L.; Rixon, F.J. Herpesvirus Capsid Association with the Nuclear Pore Complex and Viral DNA Release Involve the Nucleoporin CAN/Nup214 and the Capsid Protein pUL25. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6610–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, A.M.; Newcomb, W.W.; Brown, J.C. Herpes Simplex Virus Replication: Roles of Viral Proteins and Nucleoporins in Capsid-Nucleus Attachment. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liashkovich, I.; Hafezi, W.; Kühn, J.M.; Oberleithner, H.; Shahin, V. Nuclear delivery mechanism of herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovasevic, V.; Liang, L.; Roizman, B. Proteolytic Cleavage of VP1-2 Is Required for Release of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 DNA into the Nucleus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booy, F.P.; Newcomb, W.W.; Trus, B.L.; Brown, J.C.; Baker, T.S.; Steven, A.C. Liquid-crystalline, phage-like packing of encapsidated DNA in herpes simplex virus. Cell 1991, 64, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, V.; Hafezi, W.; Oberleithner, H.; Ludwig, Y.; Windoffer, B.; Schillers, H.; Kühn, J.E. The genome of HSV-1 translocates through the nuclear pore as a condensed rod-like structure. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molineux, I.J. No syringes please, ejection of phage T7 DNA from the virion is enzyme driven. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcomb, W.W.; Cockrell, S.K.; Homa, F.L.; Brown, J.C. Polarized DNA Ejection from the Herpesvirus Capsid. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 392, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greber, U.F.; Willetts, M.; Webster, P.; Helenius, A. Stepwise dismantling of adenovirus 2 during entry into cells. Cell 1993, 75, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotman, L.C.; Mosberger, N.; Fornerod, M.; Stidwill, R.P.; Greber, U.F. Import of adenovirus DNA involves the nuclear pore complex receptor CAN/Nup214 and histone H1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunze, S.; Trotman, L.C.; Boucke, K.; Greber, U.F. Nuclear Targeting of Adenovirus Type 2 Requires CRM1-mediated Nuclear Export. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 2999–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassany, A.; Ragues, J.; Guan, T.; Bégu, D.; Wodrich, H.; Kann, M.; Nemerow, G.R.; Gerace, L. Nuclear Import of Adenovirus DNA Involves Direct Interaction of Hexon with an N-Terminal Domain of the Nucleoporin Nup214. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunze, S.; Engelke, M.F.; Wang, I.-H.; Puntener, D.; Boucke, K.; Schleich, S.; Way, M.; Schoenenberger, P.; Burckhardt, C.J.; Greber, U.F. Kinesin-1-Mediated Capsid Disassembly and Disruption of the Nuclear Pore Complex Promote Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzer, M.J.; Visscher, K.; Block, S.M. Force production by single kinesin motors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weisel, J.W.; Shuman, H.; Litvinov, R.I. Protein–protein unbinding induced by force: Single-molecule studies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Fernandez, M.; Longshaw, S.V.; Kirby, I.; Santis, G.; Tobin, M.J.; Clarke, D.T.; Jones, G.R. Adenovirus Type-5 Entry and Disassembly Followed in Living Cells by FRET, Fluorescence Anisotropy, and FLIM. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greber, U.F.; Suomalainen, M.; Stidwill, R.P.; Boucke, K.; Ebersold, M.W.; Helenius, A. The role of the nuclear pore complex in adenovirus DNA entry. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5998–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Johnson, J.S.; Ornelles, D.A.; Lieberman, J.; Engel, D.A. Adenovirus Protein VII Functions throughout Early Phase and Interacts with Cellular Proteins SET and pp32. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saphire, A.C.S.; Guan, T.; Schirmer, E.C.; Nemerow, G.R.; Gerace, L. Nuclear Import of Adenovirus DNA in Vitro Involves the Nuclear Protein Import Pathway and hsc70. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4298–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindley, C.E.; Lawrence, F.J.; Matthews, D.A. A Role for Transportin in the Nuclear Import of Adenovirus Core Proteins and DNA. Traffic 2007, 8, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, R.A.; Berriman, J.A.; Curran, W.L.; Allan, G.M.; Todd, D. Comparison of the Structures of Three Circoviruses: Chicken Anemia Virus, Porcine Circovirus Type 2, and Beak and Feather Disease Virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13036–13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berns, K.I.; Parrish, C.R. Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 1768–1791. [Google Scholar]
- Snoussi, K.; Kann, M. Interaction of parvoviruses with the nuclear envelope. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2014, 54, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwal, M.; Cohen, S.; Snoussi, K.; Popa-Wagner, R.; Anderson, F.; Dugot-Senant, N.; Wodrich, H.; Dinsart, C.; Kleinschmidt, J.A.; Panté, N.; et al. Parvoviruses Cause Nuclear Envelope Breakdown by Activating Key Enzymes of Mitosis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riolobos, L.; Valle, N.; Hernando, E.; Maroto, B.; Kann, M.; Almendral, J.M. Viral Oncolysis That Targets Raf-1 Signaling Control of Nuclear Transport. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2090–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Marr, A.K.; Garcin, P.; Panté, N. Nuclear Envelope Disruption Involving Host Caspases Plays a Role in the Parvovirus Replication Cycle. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4863–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, M.; Sodeik, B.; Vlachou, A.; Gerlich, W.H.; Helenius, A. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of hepatitis B virus core particles to the nuclear pore complex. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haryanto, A.; Schmitz, A.; Rabe, B.; Gassert, E.; Vlachou, A.; Kann, M. Analysis of the nuclear localization signal of the hepatitis B virus capsid. Int. Res. J. Biochem. Bioinform. 2012, 2, 174–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.T.; Liaw, Y.F.; Ou, J.H. The arginine-rich domain of hepatitis B virus precore and core proteins contains a signal for nuclear transport. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 6141–6147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eckhardt, S.G.; Milich, D.R.; McLachlan, A. Hepatitis B virus core antigen has two nuclear localization sequences in the arginine-rich carboxyl terminus. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Ludgate, L.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, J. Regulation of Multiple Stages of Hepadnavirus Replication by the Carboxyl-Terminal Domain of Viral Core Protein in trans. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2918–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-C.; Huang, E.-Y.; Su, P.-Y.; Wu, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chang, W.-C.; Shih, C. Nuclear Export and Import of Human Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Protein and Particles. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, R.A.; Kiselev, N.A.; Böttcher, B.; Berriman, J.A.; Borisova, G.P.; Ose, V.; Pumpens, P. Three-dimensional structure of hepatitis B virus core particles determined by electron cryomicroscopy. Cell 1994, 77, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, B.; Wynne, S.A.; Crowther, R.A. Determination of the fold of the core protein of hepatitis B virus by electron cryomicroscopy. Nature 1997, 386, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, J.F.; Cheng, N.; Zlotnick, A.; Wingfield, P.T.; Stahl, S.J.; Steven, A.C. Visualization of a 4-helix bundle in the hepatitis B virus capsid by cryo-electron microscopy. Nature 1997, 386, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, S.A.; Crowther, R.A.; Leslie, A.G.W. The Crystal Structure of the Human Hepatitis B Virus Capsid. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseman, A.M.; Berriman, J.A.; Wynne, S.A.; Butler, P.J.G.; Crowther, R.A. A structural model for maturation of the hepatitis B virus core. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15821–15826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, K.A.; Wieland, S.F.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Gerin, J.L.; Chisari, F.V.; Yeager, M. Native Hepatitis B Virions and Capsids Visualized by Electron Cryomicroscopy. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stray, S.J.; Bourne, C.R.; Punna, S.; Lewis, W.G.; Finn, M.G.; Zlotnick, A. A heteroaryldihydropyrimidine activates and can misdirect hepatitis B virus capsid assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8138–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnick, A.; Johnson, J.M.; Wingfield, P.W.; Stahl, S.J.; Endres, D. A Theoretical Model Successfully Identifies Features of Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 14644–14652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnick, A.; Cheng, N.; Stahl, S.J.; Conway, J.F.; Steven, A.C.; Wingfield, P.T. Localization of the C terminus of the assembly domain of hepatitis B virus capsid protein: Implications for morphogenesis and organization of encapsidated RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9556–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Tavis, J.E.; Ganem, D. Relationship between viral DNA synthesis and virion envelopment in hepatitis B viruses. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6455–6458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greco, N.; Hayes, M.H.; Loeb, D.D. Snow Goose Hepatitis B Virus (SGHBV) Envelope and Capsid Proteins Independently Contribute to the Ability of SGHBV To Package Capsids Containing Single-Stranded DNA in Virions. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10705–10713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Nguyen, D.; Mentzer, L.; Adams, C.; Lee, H.; Ashley, R.; Hafenstein, S.; Hu, J. Secretion of Genome-Free Hepatitis B Virus—Single Strand Blocking Model for Virion Morphogenesis of Para-retrovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.H.; Tran, C.-T.; Robinson, W.S. Hepatitis B virus particles of plasma and liver contain viral DNA-RNA hybrid molecules. Virology 1984, 139, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, J.M.; vonBonsdorff, C.-H.; Nassal, M.; Fuller, S.D. Evolutionary conservation in the hepatitis B virus core structure: Comparison of human and duck cores. Structure 1995, 3, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.V.; Ong, S.-E.; Mann, M. Trypsin Cleaves Exclusively C-terminal to Arginine and Lysine Residues. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2004, 3, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, B.; Vlachou, A.; Panté, N.; Helenius, A.; Kann, M. Nuclear import of hepatitis B virus capsids and release of the viral genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9849–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selzer, L.; Kant, R.; Wang, J.C.-Y.; Bothner, B.; Zlotnick, A. Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein Phosphorylation Sites Affect Capsid Stability and Transient Exposure of the C-terminal Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28584–28593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melegari, M.; Bruss, V.; Gerlich, W.H. Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1991; pp. 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Akiba, T.; Nakayama, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kanno, A.; Ishii, M.; Ohori, H. Relationship between the Replication of Hepatitis B Virus and the Localization of Virus Nucleocapsid Antigen (HBcAg) in Hepatocytes. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.R.; Dhiman, R.K.; Chawla, Y.; Vasistha, R.K. Immunohistochemistry for core and surface antigens in chronic hepatitis. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2002, 23, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-J.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Chen, C.-L.; Cheng, H.-R.; Chen, P.-J.; Chen, T.-C.; Liu, C.-H.; Lai, M.-Y.; Chen, D.-S.; Kao, J.-H. Hepatitis B Virus Basal Core Promoter Mutation and DNA Load Correlate with Expression of Hepatitis B Core Antigen in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, T.; Nowoslawski, A. Crystalline Aggregates of Hepatitis B Core Particles in Cytoplasm of Hepatocytes. Intervirology 1982, 17, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.N.; Han, K.H.; Kim, K.S.; Chung, J.P.; Kim, S.; Park, C. Cytoplasmic expression of hepatitis B core antigen in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: Role of precore stop mutants. Liver Int. 1999, 19, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, M.A.; Pillot, J. HBc and HBe antigenicity and DNA-binding activity of major core protein P22 in hepatitis B virus core particles isolated from the cytoplasm of human liver cells. J. Virol. 1985, 53, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.-M.; Yeh, C.-T.; Sheen, I.-S.; Liaw, Y.-F. Subcellular localization of hepatitis B core antigen in relation to hepatocyte regeneration in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.M.; Yeh, C.T.; Chien, R.N.; Sheen, I.S.; Liaw, Y.F. The degrees of hepatocyte nuclear but not cytoplasmic expression of hepatitis B core antigen reflect the level of viral replication in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Cho, E.Y.; Oh, H.J.; Choi, C.S.; Kim, J.W.; Moon, H.B.; Kim, H.C. The Degrees of Hepatocyte Cytoplasmic Expression of Hepatitis B Core Antigen correlate with Histologic Activity of Liver Disease in the Young Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoumov, N.V.; Portmann, B.C.; Tedder, R.S.; Ferns, B.; Eddleston, A.L.; Alexander, G.J.; Williams, R. Detection of hepatitis B virus antigens in liver tissue. A relation to viral replication and histology in chronic hepatitis B infection. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H.; Goldmann, U.; Müller, R.; Stibbe, W.; Wolff, W. Specificity and localization of the hepatitis B virus-associated protein kinase. J. Virol. 1982, 42, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Martinez, V.; Loh, Y.T.; Rogler, C.E.; Chisari, F.V. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid particles do not cross the hepatocyte nuclear membrane in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5469–5475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Seyec, J.L.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deroubaix, A.; Osseman, Q.; Cassany, A.; Bégu, D.; Ragues, J.; Kassab, S.; Lainé, S.; Kann, M. Expression of viral polymerase and phosphorylation of core protein determine core and capsid localization of the human hepatitis B virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Tavis, J.E. Detection and characterization of cytoplasmic hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3353–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, E.; Gong, Y.; Chen, N.; Tavis, J.E. The Majority of Duck Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase in Cells Is Nonencapsidated and Is Bound to a Cytoplasmic Structure. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8648–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.C.-Y.; Pierson, E.E.; Keifer, D.Z.; Delaleau, M.; Gallucci, L.; Cazenave, C.; Kann, M.; Jarrold, M.F.; Zlotnick, A. Importin β Can Bind Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein and Empty Core-Like Particles and Induce Structural Changes. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardarelli, F.; Bizzarri, R.; Serresi, M.; Albertazzi, L.; Beltram, F. Probing Nuclear Localization Signal-Importin α Binding Equilibria in Living Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 36638–36646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-C.; Huang, E.-Y.; Li, H.-C.; Su, P.-Y.; Shih, C. Nuclear Export of Human Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein and Pregenomic RNA Depends on the Cellular NXF1-p15 Machinery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabit, H.; Knaust, A.; Breiner, K.M.; Schaller, H. Nuclear Localization of the Duck Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Protein: Detection and Functional Implications of Distinct Subnuclear Bodies in a Compartment Associated with RNA Synthesis and Maturation. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deres, K.; Schröder, C.H.; Paessens, A.; Goldmann, S.; Hacker, H.J.; Weber, O.; Krämer, T.; Niewöhner, U.; Pleiss, U.; Stoltefuss, J.; et al. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Drug-Induced Depletion of Nucleocapsids. Science 2003, 299, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C.; Fiaccadori, F.; Penna, A.; Margolskee, R.; Schlicht, H.J.; Fowler, P.; Guilhot, S.; Chisari, F.V. HLA class I-restricted human cytotoxic T cells recognize endogenously synthesized hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10445–10449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworetzky, S.I.; Lanford, R.E.; Feldherr, C.M. The effects of variations in the number and sequence of targeting signals on nuclear uptake. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uy, A.; Bruss, V.; Gerlich, W.H.; Köchel, H.G.; Thomssen, R. Precore sequence of hepatitis B virus inducing e antigen and membrane association of the viral core protein. Virology 1986, 155, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, A.; Schwarz, A.; Foss, M.; Zhou, L.; Rabe, B.; Hoellenriegel, J.; Stoeber, M.; Panté, N.; Kann, M. Nucleoporin 153 Arrests the Nuclear Import of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids in the Nuclear Basket. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, M.; Bischof, A.; Gerlich, W.H. In vitro model for the nuclear transport of the hepadnavirus genome. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tavis, J.E.; Ganem, D. Evidence for activation of the hepatitis B virus polymerase by binding of its RNA template. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5741–5750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tavis, J.E.; Massey, B.; Gong, Y. The Duck Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase Is Activated by Its RNA Packaging Signal ε. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5789–5796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, T.; Cuconati, A.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.-T. Characterization of the Intracellular Deproteinized Relaxed Circular DNA of Hepatitis B Virus: An Intermediate of Covalently Closed Circular DNA Formation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12472–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, B.; Glebe, D.; Kann, M. Lipid-Mediated Introduction of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids into Nonsusceptible Cells Allows Highly Efficient Replication and Facilitates the Study of Early Infection Events. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5465–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, B.; Delaleau, M.; Bischof, A.; Foss, M.; Sominskaya, I.; Pumpens, P.; Cazenave, C.; Castroviejo, M.; Kann, M. Nuclear entry of hepatitis B virus capsids involves disintegration to protein dimers followed by nuclear reassociation to capsids. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittkop, L.; Schwarz, A.; Cassany, A.; Grün-Bernhard, S.; Delaleau, M.; Rabe, B.; Cazenave, C.; Gerlich, W.; Glebe, D.; Kann, M. Inhibition of protein kinase C phosphorylation of hepatitis B virus capsids inhibits virion formation and causes intracellular capsid accumulation: HBV capsid phosphorylation by PKC. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, M.; Gerlich, W.H. Effect of core protein phosphorylation by protein kinase C on encapsidation of RNA within core particles of hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 7993–8000. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Ludgate, L.; Ning, X.; Hu, J. Maturation-Associated Destabilization of Hepatitis B Virus Nucleocapsid. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11494–11503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallucci, L.; Kann, M. Nuclear Import of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids and Genome. Viruses 2017, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9010021
Gallucci L, Kann M. Nuclear Import of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids and Genome. Viruses. 2017; 9(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallucci, Lara, and Michael Kann. 2017. "Nuclear Import of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids and Genome" Viruses 9, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9010021
APA StyleGallucci, L., & Kann, M. (2017). Nuclear Import of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids and Genome. Viruses, 9(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9010021




