Genomic Characterization of the Genus Nairovirus (Family Bunyaviridae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses
2.2. Genome Sequencing
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Detection of Reassortant Events
2.5. Sequence Analysis
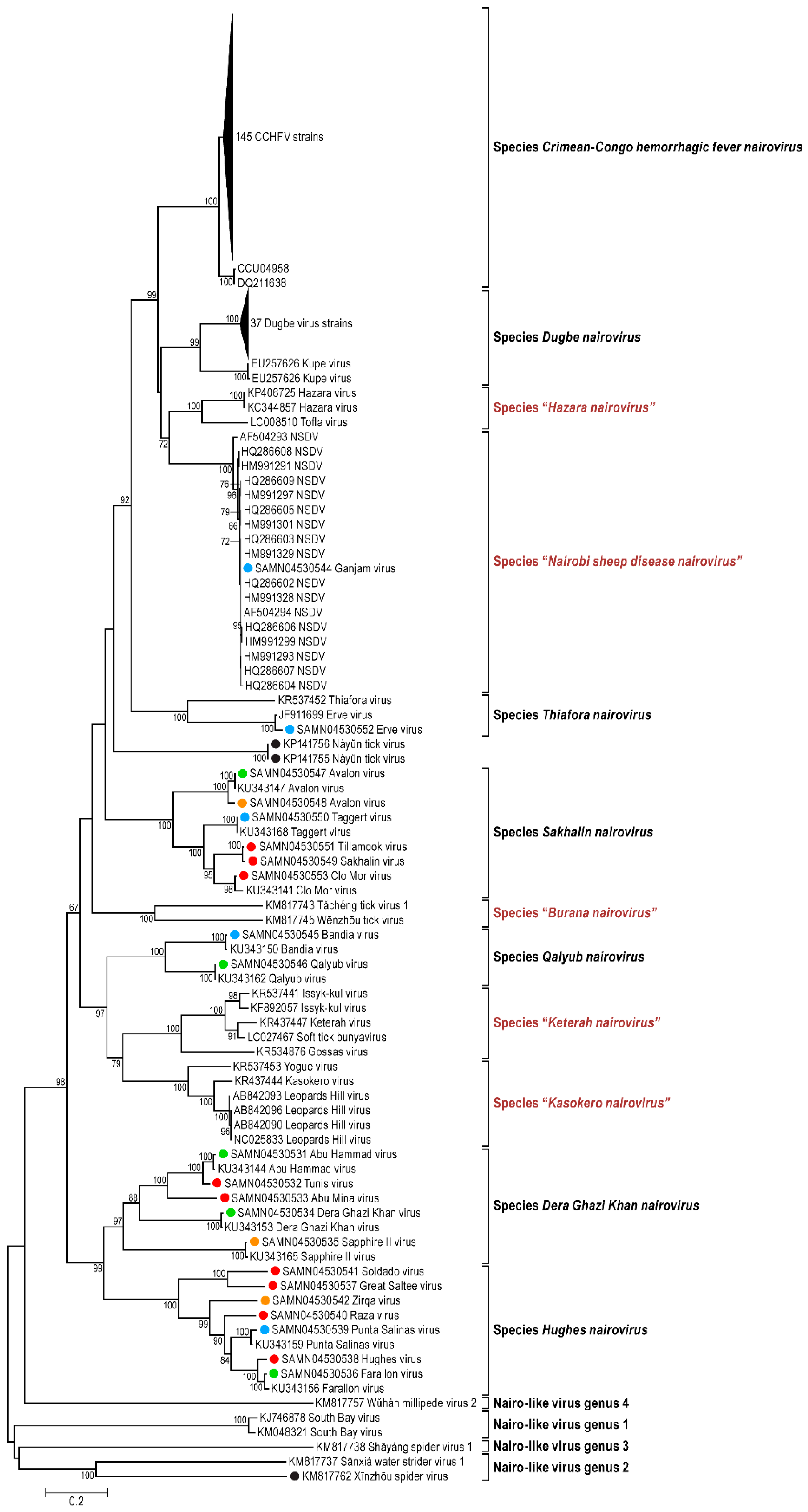
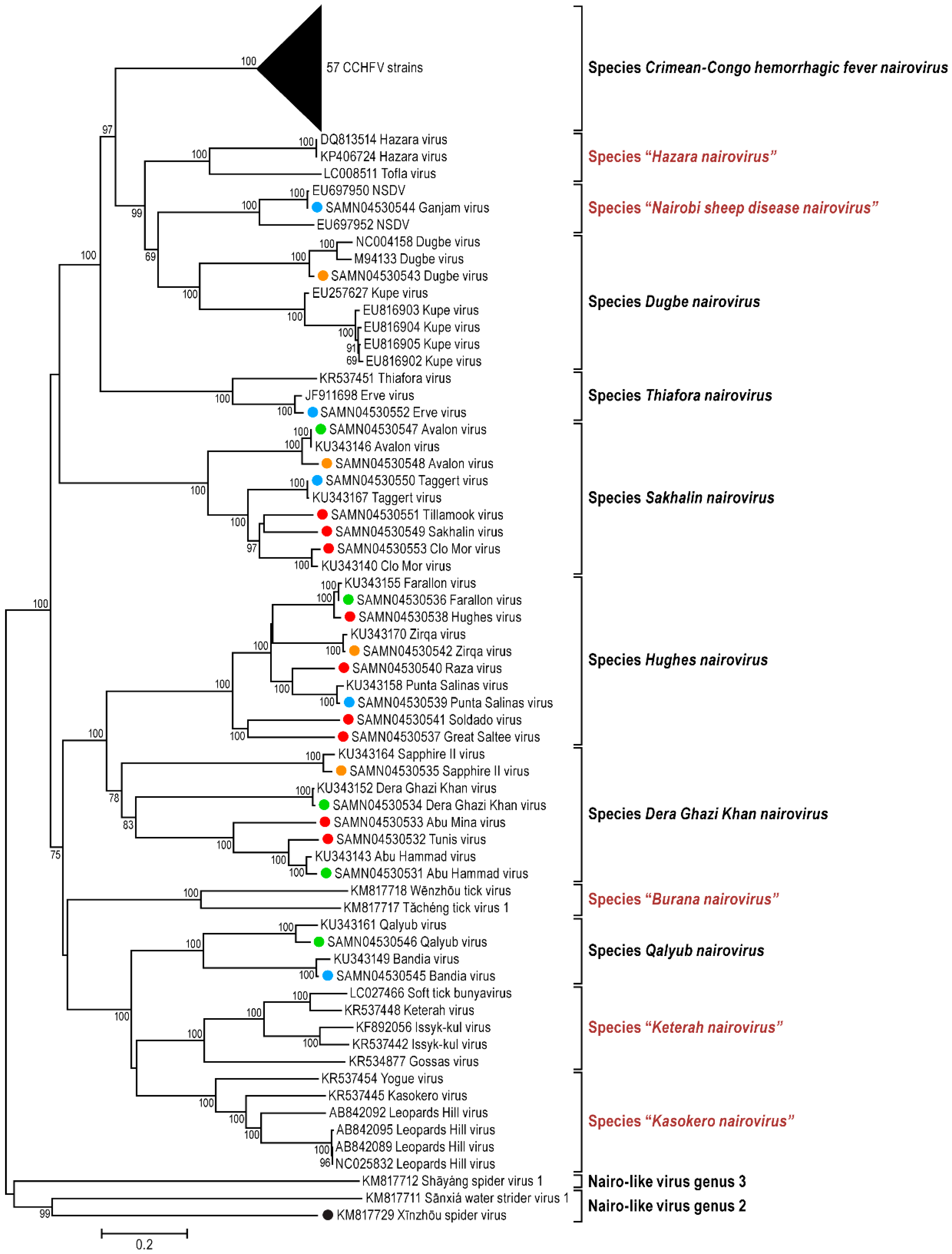
3. Results
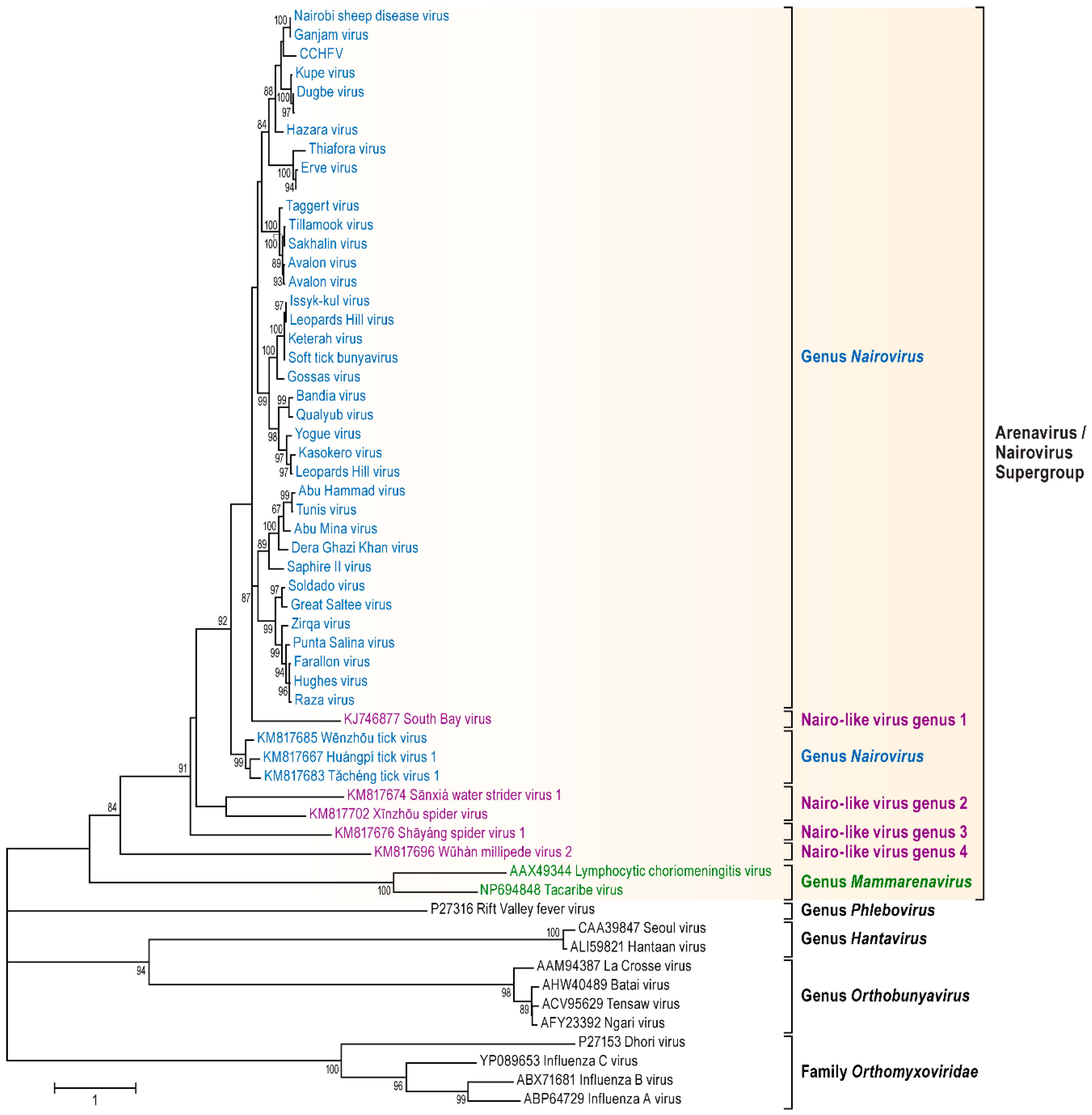
3.1. Genomic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis
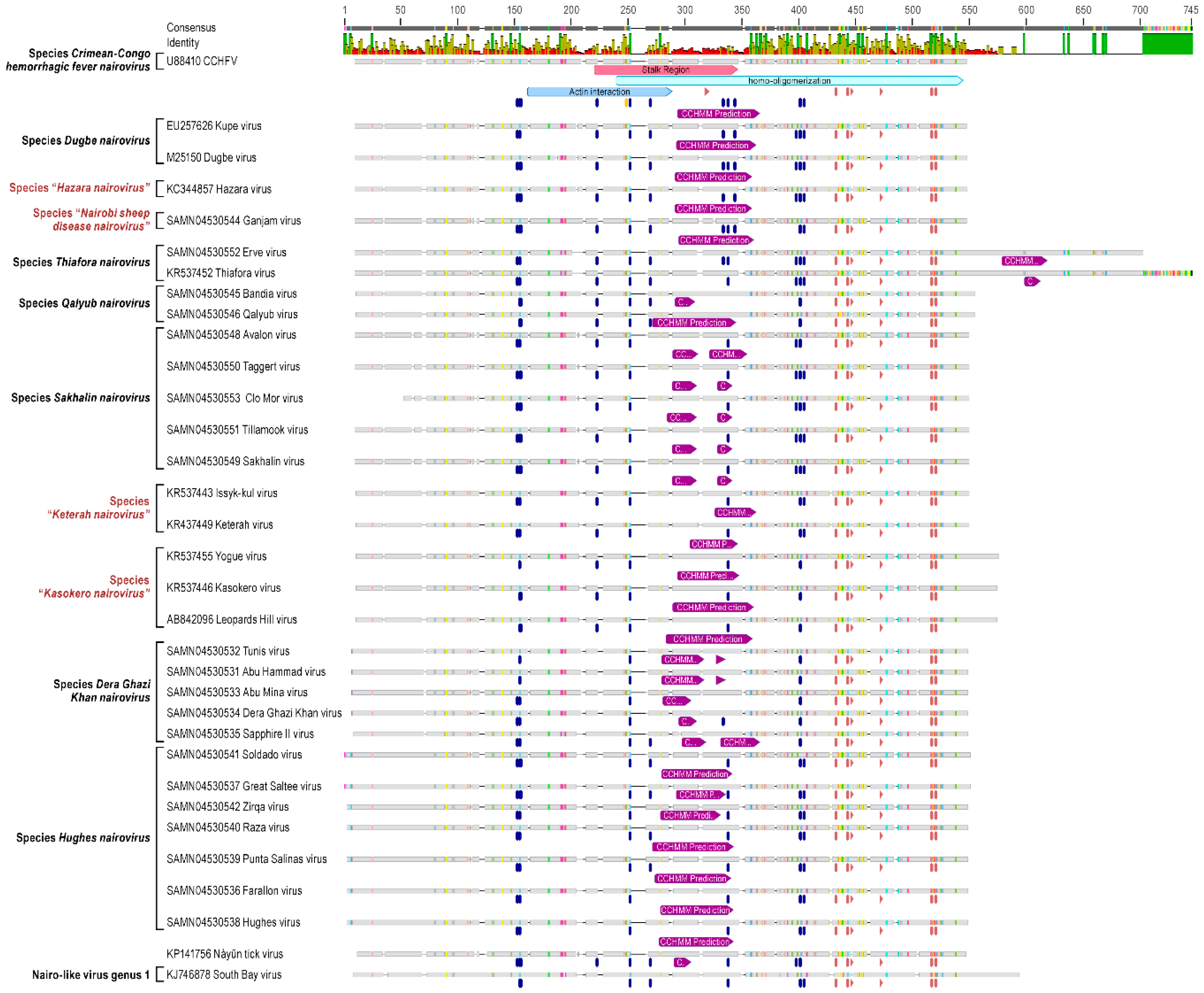
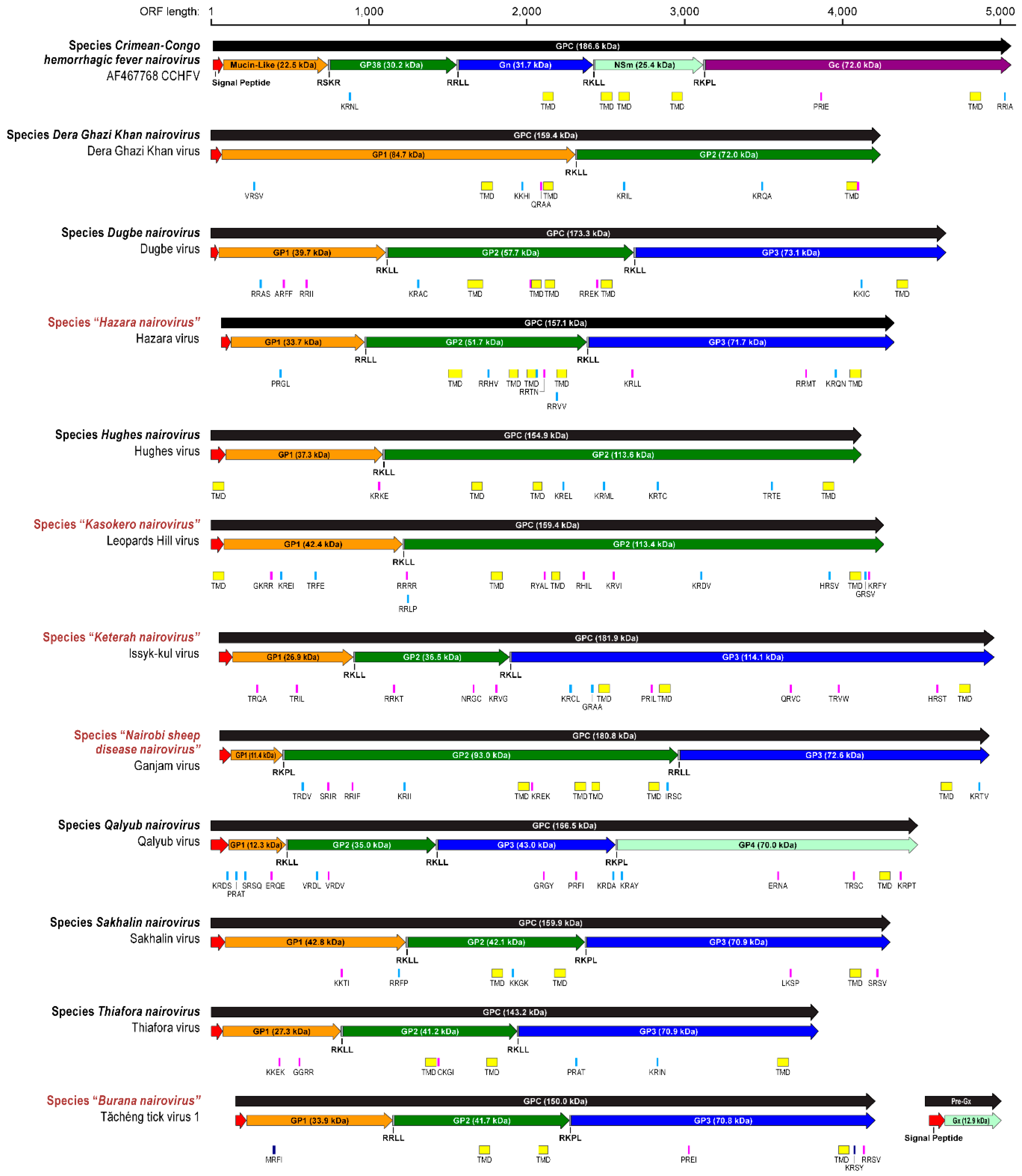
3.2. Open Reading Frames
3.2.1. Small (S) Segment—Nucleocapsid Protein
3.2.2. Medium (M) Segment—Glycoprotein Precursor
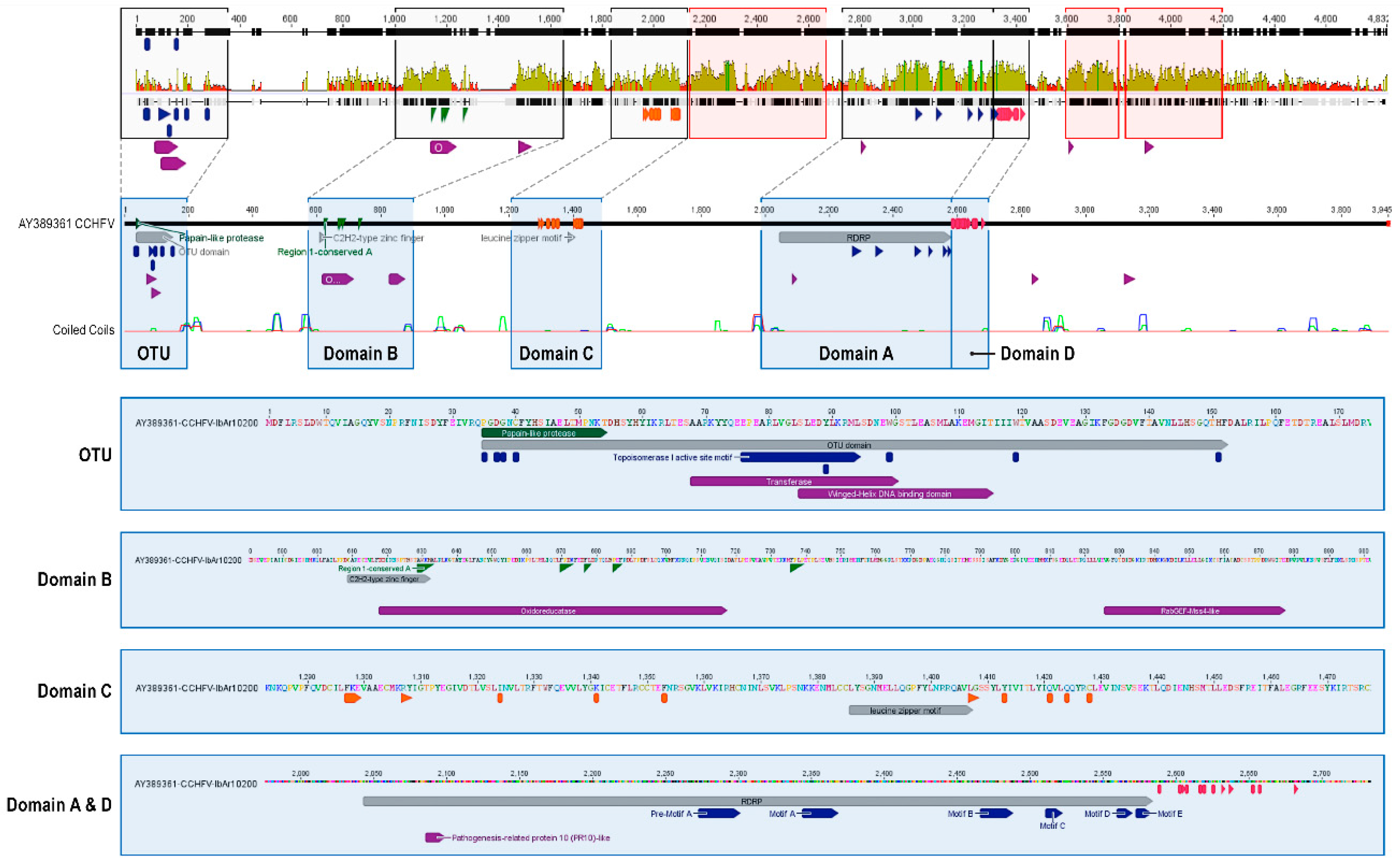
3.2.3. Large (L) Segment—RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plyusnin, A.; Beaty, B.J.; Elliott, R.M.; Goldbach, R.; Kormelink, R.; Lundkvist, A.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Tesh, R.B. Family Bunyaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy—Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 725–741. [Google Scholar]
- De Haan, P.; Wagemakers, L.; Peters, D.; Goldbach, R. The S RNA segment of tomato spotted wilt virus has an ambisense character. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, R.M.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Bunyaviridae. In Fields Virology, 7th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 1244–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, F.G.; Terpstra, C. Nairobi sheep disease. In Infectious Diseases of Livestock; Coetzer, J.A.W., Tustin, R.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1071–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Ladner, J.T.; Beitzel, B.; Chain, P.S.; Davenport, M.G.; Donaldson, E.F.; Frieman, M.; Kugelman, J.R.; Kuhn, J.H.; O’Rear, J.; Sabeti, P.C.; et al. Standards for sequencing viral genomes in the era of high-throughput sequencing. MBio 2014, 5, e01360-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, G.; Wiley, M.R.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Guzman, H.; Quiroz, E.; Savji, N.; Carrera, J.-P.; Bussetti, A.V.; Ladner, J.T.; Lipkin, W.I.; et al. Characterization of the Punta Toro species complex (genus Phlebovirus, family Bunyaviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, G.; Tesh, R.B.; Savji, N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Guzman, H.; Bussetti, A.V.; Desai, A.; Ladner, J.; Sanchez-Seco, M.; Lipkin, W.I. Characterization of the sandfly fever Naples species complex and description of a new Karimabad species complex (genus Phlebovirus, family Bunyaviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, G.; Tesh, R.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Savji, N.; Sze, W.; Jain, K.; Serge, R.; Guzman, H.; Guevara, C.; Nunes, M.R.T.; et al. Characterization of the Candiru antigenic complex (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus), a highly diverse and reassorting group of viruses affecting humans in tropical America. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3811–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, G.; Savji, N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Guzman, H.; Yu, X.; Desai, A.; Rosen, G.E.; Hutchison, S.; Lipkin, W.I.; Tesh, R. Characterization of the Uukuniemi virus group (Phlebovirus: Bunyaviridae): Evidence for seven distinct species. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, G.; Savji, N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Desai, A.; Sanchez-Seco, M.P.; Guzman, H.; Lipkin, W.I.; Tesh, R. Characterization of the Salehabad virus species complex of the genus Phlebovirus (Bunyaviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, G.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Savji, N.; Sze, W.; Wick, I.; Guzman, H.; Hutchison, S.; Tesh, R.; Lipkin, W.I. Aguacate virus, a new antigenic complex of the genus Phlebovirus (family Bunyaviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, K.; Weisend, C.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Anzick, S.L.; Dahlstrom, E.; Porcella, S.F.; Dorward, D.W.; Yu, X.-J.; Tesh, R.B.; Ebihara, H. Characterization of the Bhanja serogroup viruses (Bunyaviridae): A novel species of the genus Phlebovirus and its relationship with other emerging tick-borne phleboviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3719–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, K.; Weisend, C.; Kajihara, M.; Matysiak, C.; Williamson, B.N.; Simuunza, M.; Mweene, A.S.; Takada, A.; Tesh, R.B.; Ebihara, H. Comprehensive molecular detection of tick-borne phleboviruses leads to the retrospective identification of taxonomically unassigned bunyaviruses and the discovery of a novel member of the genus Phlebovirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Альховский, С.В.; Львов, Д.К.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Щетинин, А.М.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Самохвалов, Е.И.; Гительман, А.К.; Ботиков, А.Г. Таксономия вируса Хасан (Khasan, KHAV)—нового вируса рода Phlebovirus (сем. Bunyaviridae), изолированного из клещей Haemaphysalis longicornis (Neumann, 1901) в Приморском крае (Россия). Al’hovskij, S.V.; L’vov, D.K.; Ŝelkanov, M.Û.; Ŝetinin, A.M.; Derâbin, P.G.; Samohvalov, E.I.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Botikov, A.G. The taxonomy of the Khasan virus (KHAV), a new representative of the Phlebovirus genus (Bunyaviridae), isolated from Haemaphysalis longicornis (Neumann, 1901) ticks in the Maritime Territory. Vopr. Virusol. 2013, 58, 15–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell, T.B.; Heberlein-Larson, L.A.; Tan, Y.; Halpin, R.A.; Fedorova, N.; Katzel, D.A.; Smole, S.; Unnasch, T.R.; Kramer, L.D.; Das, S.R. First complete genome sequences of two Keystone viruses from Florida. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01255-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savji, N.; Palacios, G.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Hutchison, S.; Celone, C.; Hui, J.; Briese, T.; Calisher, C.H.; Tesh, R.B.; Lipkin, W.I. Genomic and phylogenetic characterization of Leanyer virus, a novel orthobunyavirus isolated in northern Australia. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, J.T.; Savji, N.; Lofts, L.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Wiley, M.R.; Gestole, M.C.; Rosen, G.E.; Guzman, H.; Vasconcelos, P.F.C.; Nunes, M.R.T.; et al. Genomic and phylogenetic characterization of viruses included in the Manzanilla and Oropouche species complexes of the genus Orthobunyavirus, family Bunyaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hontz, R.D.; Guevara, C.; Halsey, E.S.; Silvas, J.; Santiago, F.W.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Casanova, W.; Vasilakis, N.; Watts, D.M.; et al. Itaya virus, a novel Orthobunyavirus associated with human febrile illness, Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groseth, A.; Vine, V.; Weisend, C.; Ebihara, H. Complete genome sequence of Trivittatus virus. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2637–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groseth, A.; Mampilli, V.; Weisend, C.; Dahlstrom, E.; Porcella, S.F.; Russell, B.J.; Tesh, R.B.; Ebihara, H. Molecular characterization of human pathogenic bunyaviruses of the Nyando and Bwamba/Pongola virus groups leads to the genetic identification of Mojuí dos Campos and Kaeng Khoi virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchetinin, A.M.; Lvov, D.K.; Deriabin, P.G.; Botikov, A.G.; Gitelman, A.K.; Kuhn, J.H.; Alkhovsky, S.V. Genetic and phylogenetic characterization of Tataguine and Witwatersrand viruses and other orthobunyaviruses of the Anopheles A, Capim, Guama, Koongol, Mapputta, Tete, and Turlock serogroups. Viruses 2015, 7, 5987–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklewitz, M.; Zirkel, F.; Kurth, A.; Drosten, C.; Junglen, S. Evolutionary and phenotypic analysis of live virus isolates suggests arthropod origin of a pathogenic RNA virus family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7536–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklewitz, M.; Zirkel, F.; Rwego, I.B.; Heidemann, H.; Trippner, P.; Kurth, A.; Kallies, R.; Briese, T.; Lipkin, W.I.; Drosten, C.; et al. Discovery of a unique novel clade of mosquito-associated bunyaviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12850–12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, M.J.; Bruenn, J.A.; Hay, J.; Czechowski, D.; Taylor, D.J. Discovery and evolution of bunyavirids in arctic phantom midges and ancient bunyavirid-like sequences in insect genomes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8783–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Альховский, С.В.; Львов, Д.К.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Щетинин, А.М.; Самохвалов, Е.И.; Аристова, В.А.; Гительман, А.К.; Ботиков, А.Г. Генетическая характеристика вируса Узун-Агач (UZAV—Uzun-Agach virus) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus), изолированного в Казахстане от остроухой ночницы Myotis blythii oxygnathus Monticelli, 1885 (Chiroptera; Vespertilionidae). Al’hovskij, S.V.; L’vov, D.K.; Ŝelkanov, M.Û.; Derâbin, P.G.; Ŝetinin, A.M.; Samohvalov, E.I.; Aristova, V.A.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Botikov, A.G. Genetic characterization of Uzun-Agach virus (UZAV, Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus), isolated from Myotis blythii oxygnathus Monticelli, 1885 bats (Chiroptera; Vespertilionidae) in Kazakhstan. Vopr. Virusol. 2014, 59, 23–26. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Альховский, С.В.; Львов, Д.К.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Щетинин, А.М.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Гительман, А.К.; Ботиков, А.Г.; Самохвалов, Е.И.; Закарян, В.А. Таксономия вируса Арташат (ARTSV—Artashat virus) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus), изолированного из клещей Ornithodoros alactagalis Issaakjan, 1936 и O. verrucosus Olenev, Sassuchin et Fenuk, 1934 (Argasidae Koch, 1844), собранных в Закавказье. Al’hovskij, S.V.; L’vov, D.K.; Ŝelkanov, M.Û.; Ŝetinin, A.M.; Derâbin, P.G.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Botikov, A.G.; Samohvalov, E.I.; Zakarân, V.A. Taxonomic status of Artashat virus (ARTSV) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus) isolated from Ornithodoros alactagalis Issaakjan, 1936 and O. verrucosus Olenev, Sassuchin et Fenuk, 1934 ticks (Argasidae Koch, 1844) collected in Transcaucasia. Vopr. Virusol. 2014, 59, 24–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Альховский, С.В.; Львов, Д.К.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Щетинин, А.М.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Самохвалов, Е.И.; Гительман, А.К.; Ботиков, А.Г. Таксономия вируса Иссык-Куль (Issyk-kul virus, ISKV; Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus), возбудителя Иссык-Кульской лихорадки, изолированного от летучих мышей (Vespertilionidae) и клещей Argas (Carios) vespertilionis (Latreille, 1796). Al’hovskij, S.V.; L’vov, D.K.; Ŝelkanov, M.Û.; Ŝetinin, A.M.; Derâbin, P.G.; Samohvalov, E.I.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Botikov, A.G. Taxonomy of Issyk-kul virus (ISKV, Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus), the etiologic agent of Issyk-kul fever isolated from bats (Vespertilionidae) and Argas (Carios) vespertilionis (Latreille, 1796) ticks. Vopr. Virusol. 2013, 58, 11–15. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, B.; Marston, D.A.; Ellis, R.J.; Fooks, A.R.; Hewson, R. Complete genomic sequence of Issyk-kul virus. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00662-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.J.; Widen, S.G.; Firth, C.; Blasdell, K.R.; Wood, T.G.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. Genomic characterization of Yogue, Kasokero, Issyk-Kul, Keterah, Gossas, and Thiafora viruses: Nairoviruses naturally infecting bats, shrews, and ticks. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Львов, Д.К.; Альховский, С.В.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Щетинин, А.М.; Самохвалов, Е.И.; Аристова, В.А.; Гительман, А.К.; Ботиков, А.Г. Генетическая характеристика вируса Герань (GERV - Geran virus) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus, группа Кальюб), изолированного в Азербайджане от клещей Ornithodoros verrucosus Olenev, Zasukhin and Fenyuk, 1934 (Argasidae), собранных в норе краснохвостой песчанки (Meriones erythrourus Grey, 1842). L’vov, D.K.; Al’hovskij, S.V.; Ŝelkanov, M.Û.; Derâbin, P.G.; Ŝetinin, A.M.; Samohvalov, E.I.; Aristova, V.A.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Botikov, A.G. Genetic characterization of Geran virus (GERV, Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus, Qalyub group) isolated from Ornithodoros verrucosus Olenev, Zasukhin and Fenyuk, 1934 ticks (Argasidae) collected in the burrow of Meriones erythrourus Grey, 1842 in Azerbaijan. Vopr. Virusol. 2014, 59, 13–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Львов, Д.К.; Альховский, С.В.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Щетинин, А.М.; Аристова, В.А.; Гительман, А.К.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Ботиков, А.Г. Таксономия ранее негруппированного вируса Тамды (TAMV-Tamdy virus) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus), изолированного от иксодовых клещей Hyalomma asiaticum asiaticum Schülce et Schlottke, 1929 (Ixodidae, Hyalomminae) в Средней Азии и Закавказье. Lvov, D.K.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Shchelkanov, M.Yu.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Aristova, V.A.; Gitelman, A.K.; Deryabin, P.G.; Botikov, A.G. Taxonomy of previously unclassified Tamdy virus (TAMV) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus) isolated from Hyalomma asiaticum asiaticum Schülce et Schlottke, 1929 (Ixodidae, Hyalomminae) ticks in the Middle East and Transcaucasia. Vopr. Virusol. 2014, 59, 15–22. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Львов, Д.К.; Альховский, С.В.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Щетинин, А.М.; Аристова, В.А.; Морозова, Т.Н.; Гительман, А.К.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Ботиков, А.Г. Таксономия ранее не классифицированного вируса ЧИМ (CHIMV - Chim virus) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus, группа Кальюб), изолированного в Узбекистане и Казахстане из иксодовых (Acari: Ixodidae) и аргасовых (Acari: Argasidae) клещей, собранных в норах больших песчанок Rhombomys opimus Lichtenstein, 1823 (Muridae, Gerbillinae). L’vov, D.K.; Al’hovskij, S.V.; Shhelkanov, M.J.; Shhetinin, A.M.; Aristova, V.A.; Morozova, T.N.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Derjabin, P.G.; Botikov, A.G. Taxonomic status of Chim virus (CHIMV) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus, Qalyub group) isolated from Ixodidae and Argasidae ticks collected from great gerbil (Rhombomys opimus Lichtenstein, 1823) (Muridae, Gerbillinae) burrows in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. Vopr. Virusol. 2014, 59, 18–23. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Львов, Д.К.; Альховский, С.В.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Щетинин, А.М.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Гительман, А.К.; Аристова, В.А.; Ботиков, А.Г. Таксономический статус вируса Бурана (BURV—Burana virus) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus, группа Тамды), изолированного из клещей Haemaphysalis punctata Canestrini et Fanzago, 1877 и Haem. concinna Koch, 1844 (Ixodidae, Haemaphysalinae) в Кыргызстане. L’vov, D.K.; Al’hovskij, S.V.; Shhelkanov, M.J.; Shhetinin, A.M.; Derjabin, P.G.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Aristova, V.A.; Botikov, A.G. Taxonomic status of Burana virus (BURV) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus, Tamdy group) isolated from Haemaphysalis punctata Canestrini et Fanzago, 1877 and Haem. concinna Koch, 1844 ticks (Ixodidae, Haemaphysalinae) in Kyrgyzstan. Vopr. Virusol. 2014, 59, 10–15. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Львов, Д.К.; Альховский, С.В.; Щелканов, М.Ю.; Щетинин, А.М.; Дерябин, П.Г.; Самохвалов, Е.И.; Гительман, А.К.; Ботиков, А.Г. Генетическая характеристика вируса Каспий (CASV - Caspiy virus) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus), изолированного от чайковых (Laridae Vigors, 1825) и крачковых (Sternidae Bonaparte, 1838) птиц и аргасовых клещей Ornithodoros capensis Neumann, 1901 (Argasidae Koch, 1844) на западном и восточном побережьях Каспийского моря. L’vov, D.K.; Al’hovskij, S.V.; Shhelkanov, M.Ju.; Shhetinin, A.M.; Derjabin, P.G.; Samohvalov, E.I.; Gitel’man, A.K.; Botikov, A.G. Genetic characterization of Caspiy virus (CASV) (Bunyaviridae, Nairovirus) isolated from Laridae (Vigors, 1825) and Sternidae (Bonaparte, 1838) birds and Argasidae (Koch, 1844) Ornithodoros capensis Neumann, 1901, ticks form western and eastern coasts of the Caspian Sea. Vopr. Virusol. 2014, 59, 24–29. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dacheux, L.; Cervantes-Gonzalez, M.; Guigon, G.; Thiberge, J.-M.; Vandenbogaert, M.; Maufrais, C.; Caro, V.; Bourhy, H. A preliminary study of viral metagenomics of French bat species in contact with humans: Identification of new mammalian viruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, A.; Ueno, K.; Orba, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Moonga, L.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Mweene, A.S.; Umemura, T.; Ito, K.; Hall, W.W.; et al. A nairovirus isolated from African bats causes haemorrhagic gastroenteritis and severe hepatic disease in mice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Kang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J.; Qin, X.C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. Elife 2015, 4, e05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, M.; Omatsu, T.; Takano, A.; Fujita, H.; Sato, K.; Nakamoto, A.; Takahashi, M.; Takada, N.; Kawabata, H.; Ando, S.; et al. A novel Bunyavirus from the soft tick, Argas vespertilionis, in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Hu, C.; Zhang, D.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kou, Z.; Fan, Z.; Bente, D.; Zeng, C.; Li, T. Metagenomic profile of the viral communities in Rhipicephalus spp. ticks from Yunnan, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, S.; Aoki, K.; Nabeshima, T.; Fuxun, Y.; Kurosaki, Y.; Shiogama, K.; Onouchi, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Fuchigami, T.; et al. Tofla virus: A newly identified Nairovirus of the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever group isolated from ticks in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, R.; Williams, S.H.; Sameroff, S.; Sanchez Leon, M.; Jain, K.; Lipkin, W.I. Virome analysis of Amblyomma americanum, Dermacentor variabilis, and Ixodes scapularis ticks reveals novel highly divergent vertebrate and invertebrate viruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11480–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.J.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. A global genomic characterization of nairoviruses identifies nine discrete genogroups with distinctive structural characteristics and host-vector associations. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, M.A.; Imam, I.Z.E.; Omar, F.M. Complement-fixing antibodies against Abu Hammad and Abu Mina viruses in mammalian sera from Egypt. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 1976, 51, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quillien, M.C.; Monnat, J.Y.; Le Lay, G.; Le Goff, F.; Hardy, E.; Chastel, C. Avalon virus, Sakhalin group (Nairovirus, Bunyaviridae) from the seabird tick Ixodes (Ceratixodes) uriae White 1852 in France. Acta Virol. 1986, 30, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Main, A.J.; Downs, W.G.; Shope, R.E.; Wallis, R.C. Avalon and Clo Mor: Two new Sakhalin group viruses from the North Atlantic. J. Med. Entomol. 1976, 13, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brès, P.; Cornet, M.; Robin, Y. Le virus de la Forêt de Bandia (IPD/A 611), nouveau prototype d’arbovirus isolé au Sénégal [The Bandia Forest virus (IPD/A 611), a new arbovirus prototype isolated in Senegal]. Ann. Inst. Pasteur (Paris) 1967, 113, 739–747. (In French) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Begum, F.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr.; Casals, J. Tick-borne viruses of West Pakistan. III. Dera Ghazi Khan virus, a new agent isolated from Hyalomma dromedarii ticks in the D.G.Khan District of West Pakistan. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1970, 92, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The Subcommitee on Information Exchange of the American Commitee on Arthropod-borne Viruses, No. 226. Dugbe (DUG). Strain: AR 1792. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 1123–1124.
- Chastel, C.; Main, A.J.; Richard, P.; le Lay, G.; Legrand-Quillien, M.C.; Beaucournu, J.C. Erve virus, a probable member of Bunyaviridae family isolated from shrews (Crocidura russula) in France. Acta Viro 1989, 33, 270–280. [Google Scholar]
- Radovsky, F.J.; Stiller, D.; Johnson, H.N.; Clifford, C.M. Descriptive notes on Ornithodoros ticks from gull nests on the Farallon Islands and isolation of a variant of Hughes virus. J. Parasitol. 1967, 53, 890–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandawate, C.N.; Shah, K.V. Ganjam virus: A new arbovirus isolated from Ticks Haemaphysalis Intermedia Warburton and Nuttall, 1909 in Orissa, India. Indian J. Med. Res. 1969, 57, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keirans, J.E.; Yunker, C.E.; Clifford, C.M.; Thomas, L.A.; Walton, G.A.; Kelly, T.C. Isolation of a Soldado-like virus (Hughes group) from Ornithodorus maritimus ticks in Ireland. Experientia 1976, 32, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, L.E.; Clifford, C.M.; Thomas, L.A.; Denmark, H.A.; Philip, C.B. Isolation and characterization of a virus from soft ticks (Ornithodoros capensis group) collected on Bush Key, Dry Tortugas, Florida. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Philip, C.B. Hughes virus, a new arboviral agent from marine bird ticks. J. Parasitol. 1965, 51, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Converse, J.D.; Moussa, M.I.; Easton, E.R.; Casals, J. Punta Salinas virus (Hughes group) from Argas arboreus (Ixodoidea: Argasidae) in Tanzania. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Subcommitee on Information Exchange of the American Commitee on Arthropod-borne Viruses, No. 222. Qalyub (QYB). Strain: Ar 370. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 1115–1116.
- Clifford, C.M.; Thomas, L.A.; Hughes, L.E.; Kohls, G.M.; Philip, C.B. Identification and comparison of two viruses isolated from ticks of the genus Ornithodoros. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1968, 17, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lvov, D.K.; Timofeeve, A.A.; Gromashevski, V.L.; Chervonsky, V.I.; Gromov, A.I.; Tsynkin, Y.M.; Pogrebenko, A.G.; Kostyrko, I.N. ”Sakhalin” virus—A new arbovirus isolated from Ixodes (Ceratixodes) putus Pick.-Camb. 1878 collected on Tuleniy Island, Sea of Okhotsk. Arch. Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972, 38, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunker, C.E.; Clifford, C.M.; Thomas, L.A.; Cory, J.; George, J.E. Isolation of viruses from swallow ticks, Argas cooleyi, in the southwestern United States. Acta Virol. 1972, 16, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jonkers, A.H.; Casals, J.; Aitken, T.H.G.; Spence, L. Soldado virus, a new agent from Trinidadian Ornithodoros ticks. J. Med. Entomol. 1973, 10, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, R.L.; Carley, J.G.; Murray, M.D.; Main, A.J., Jr.; Kay, B.H.; Domrow, R. Isolation of arboviruses (Kemerovo group, Sakhalin group) from Ixodes uriae collected at Macquarie Island, Southern Ocean. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1975, 24, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.A.; Clifford, C.M.; Yunker, C.E.; Keirans, J.E.; Patzer, E.R.; Monk, G.E.; Easton, E.R. Tickborne viruses in western North America. I. Viruses isolated from Ixodes uriae in coastal Oregon in 1970. J. Med. Entomol. 1973, 10, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastel, C.; Bach-Hamba, D.; Karabatsos, N.; Bouattour, A.; le Lay, G.; le Goff, F.; Vermeil, C. Tunis virus: A new Phlebovirus from Argas reflexus hermanni ticks in Tunisia. Acta Virol. 1994, 38, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varma, M.G.; Bowen, E.T.; Simpson, D.I.; Casals, J. Zirga virus, a new arbovirus isolated from bird-infesting ticks. Nature 1973, 244, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djikeng, A.; Halpin, R.; Kuzmickas, R.; Depasse, J.; Feldblyum, J.; Sengamalay, N.; Afonso, C.; Zhang, X.; Anderson, N.G.; Ghedin, E.; et al. Viral genome sequencing by random priming methods. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisvert, S.; Raymond, F.; Godzaridis, E.; Laviolette, F.; Corbeil, J. Ray Meta: Scalable de novo metagenome assembly and profiling. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Tamura, K.; Nei, M. MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief. Bioinform. 2004, 5, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Rybicki, E. RDP: Detection of recombination amongst aligned sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, M.O.; Carr, J.K.; Burke, D.S.; McCutchan, F.E. Identification of breakpoints in intergenotypic recombinants of HIV type 1 by bootscanning. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1995, 11, 1423–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M. Analyzing the mosaic structure of genes. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Evaluation of methods for detecting recombination from DNA sequences: Computer simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13757–13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.C. Molecular epidemiology of dengue virus—The time for big science. Trop. Med. Int. Health 1998, 3, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP—Phylogeny inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 1989, 5, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GSL Biotech LLC. SnapGene: Software for Everyday Molecular Biology. Available online: http://www.snapgene.com/ (accessed on 31 May 2016).
- Von Heijne, G. Membrane protein structure prediction. Hydrophobicity analysis and the positive-inside rule. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 225, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claros, M.G.; von Heijne, G. TopPred II: An improved software for membrane protein structure predictions. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1994, 10, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahsay, R.Y.; Gao, G.; Liao, L. An improved hidden Markov model for transmembrane protein detection and topology prediction and its applications to complete genomes. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kall, L.; Krogh, A.; Sonnhammer, E.L. A combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction method. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, F.J.; Paweska, J.T.; Ashkettle, B.; Swanepoel, R. Genetic relationship in southern African Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus isolates: Evidence for occurrence of reassortment. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewson, R.; Gmyl, A.; Gmyl, L.; Smirnova, S.E.; Karganova, G.; Jamil, B.; Hasan, R.; Chamberlain, J.; Clegg, C. Evidence of segment reassortment in Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3059–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukashev, A.N. Evidence for recombination in Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedhals, D.; Bester, P.A.; Paweska, J.T.; Swanepoel, R.; Burt, F.J. Next-generation sequencing of southern African Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus isolates reveals a high frequency of M segment reassortment. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Deng, F.; Han, N.; Wang, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Rayner, S. Reassortment and migration analysis of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2536–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.D.; Surtees, R.; Walter, C.T.; Ariza, A.; Bergeron, É.; Nichol, S.T.; Hiscox, J.A.; Edwards, T.A.; Barr, J.N. Structure, function, and evolution of the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleocapsid protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10914–10923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayer, M.R.; Dayer, M.S.; Rezatofighi, S.E. Mechanism of preferential packaging of negative sense genomic RNA by viral nucleoproteins in Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic Fever virus. Protein J. 2015, 34, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajs, L.; Resman, K.; Avšič-Županc, T. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleoprotein suppresses IFN-beta-promoter-mediated gene expression. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Ji, W.; Deng, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleoprotein reveals endonuclease activity in bunyaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5046–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Structural and functional diversity of nairovirus-encoded nucleoproteins. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11740–11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dutta, S.; Karlberg, H.; Devignot, S.; Weber, F.; Hao, Q.; Tan, Y.J.; Mirazimi, A.; Kotaka, M. Structure of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleoprotein: Superhelical homo-oligomers and the role of caspase-3 cleavage. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12294–12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, I.; Bladh, L.; Mousavi-Jazi, M.; Magnusson, K.-E.; Lundkvist, Å.; Haller, O.; Mirazimi, A. Human MxA protein inhibits the replication of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlberg, H.; Tan, Y.J.; Mirazimi, A. Induction of caspase activation and cleavage of the viral nucleocapsid protein in different cell types during Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, C.M.; Filippis, I.; Kelley, L.A.; Sternberg, M.J. SuSPect: Enhanced prediction of single amino acid variant (SAV) phenotype using network features. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 2692–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, B.D.; Sakamoto, T.; Hong, M.S.; Sellers, J.R.; Takizawa, P.A. Myo4p is a monomeric myosin with motility uniquely adapted to transport mRNA. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, É.; Zivcec, M.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Nichol, S.T.; Albariño, C.G.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Recovery of Recombinant Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Reveals a Function for Non-structural Glycoproteins Cleavage by Furin. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.J.; Vincent, M.J.; Erickson, B.R.; Nichol, S.T. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoprotein precursor is cleaved by furin-like and SKI-1 proteases to generate a novel 38-kilodalton glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.J.; Sanchez, A.J.; Erickson, B.R.; Basak, A.; Chretien, M.; Seidah, N.G.; Nichol, S.T. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoprotein proteolytic processing by subtilase SKI-1. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8640–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyde, V.M.; Khristova, M.L.; Rollin, P.E.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Nichol, S.T. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus genomics and global diversity. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8834–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.J.; Vincent, M.J.; Nichol, S.T. Characterization of the glycoproteins of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 7263–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poch, O.; Sauvaget, I.; Delarue, M.; Tordo, N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3867–3874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.; Poch, O.; Delarue, M.; Bishop, D.H.L.; Bouloy, M. Rift Valley fever virus L segment: Correction of the sequence and possible functional role of newly identified regions conserved in RNA-dependent polymerases. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Arnold, E. Negative-strand RNA virus L proteins: one machine, many activities. Cell 2015, 162, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, J.; Gerlach, P.; Cusack, S. Towards a structural understanding of RNA synthesis by negative strand RNA viral polymerases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 36, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias-Staheli, N.; Giannakopoulos, N.V.; Kikkert, M.; Taylor, S.L.; Bridgen, A.; Paragas, J.; Richt, J.A.; Rowland, R.R.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Lenschow, D.J.; et al. Ovarian tumor domain-containing viral proteases evade ubiquitin- and ISG15-dependent innate immune responses. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, T.W.; Frias-Staheli, N.; Bacik, J.P.; Levingston Macleod, J.M.; Khajehpour, M.; García-Sastre, A.; Mark, B.L. Structural basis for the removal of ubiquitin and interferon-stimulated gene 15 by a viral ovarian tumor domain-containing protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capodagli, G.C.; Deaton, M.K.; Baker, E.A.; Lumpkin, R.J.; Pegan, S.D. Diversity of ubiquitin and ISG15 specificity among nairoviruses’ viral ovarian tumor domain proteases. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3815–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capodagli, G.C.; McKercher, M.A.; Baker, E.A.; Masters, E.M.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Pegan, S.D. Structural analysis of a viral ovarian tumor domain protease from the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in complex with covalently bonded ubiquitin. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, S.; Holzer, B.; Bridgen, A.; McMullan, G.; Quinn, D.G.; Baron, M.D. Dugbe virus ovarian tumour domain interferes with ubiquitin/ISG15-regulated innate immune cell signalling. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kasteren, P.B.; Beugeling, C.; Ninaber, D.K.; Frias-Staheli, N.; van Boheemen, S.; García-Sastre, A.; Snijder, E.J.; Kikkert, M. Arterivirus and nairovirus ovarian tumor domain-containing Deubiquitinases target activated RIG-I to control innate immune signaling. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, E.; Martin, S.G.; Grolla, A.; Czub, M.; Feldmann, H.; Flick, R. Sequence determination of the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus L segment. Virology 2004, 321, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landschulz, W.H.; Johnson, P.F.; McKnight, S.L. The leucine zipper: A hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science 1988, 240, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, H.C. Transcription factors. 1: bZIP proteins. Protein Profile 1994, 1, 123–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shugars, D.C.; Smith, M.S.; Glueck, D.H.; Nantermet, P.V.; Seillier-Moiseiwitsch, F.; Swanstrom, R. Analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nef gene sequences present in vivo. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4639–4650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Yadav, G.P.; Gupta, S.; Tripathi, A.K.; Ramachandran, R.; Tripathi, R.K. A novel dimer-tetramer transition captured by the crystal structure of the HIV-1 Nef. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, J.A.; McCulloch, R.J.; Spann, K.M.; Cadogan, L.C.; Walker, P.J. Preliminary molecular and biological characterization of Mourilyan virus (MoV): A new bunya-related virus of penaeid prawns. In Diseases in Asian Aquaculture V. Proceedings of the 5th Symposium on Diseases in Asian Aquaculture; Walker, P.J., Lester, R.G., Bondad-Reantaso, M.G., Eds.; Fish Health Section, Asian Fisheries Society: Manila, The Philippines, 2005; pp. 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mielke, N.; Muehlbach, H.P. A novel, multipartite, negative-strand RNA virus is associated with the ringspot disease of European mountain ash (Sorbus aucuparia L.). J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke-Ehret, N.; Mühlbach, H.-P. Emaravirus: A novel genus of multipartite, negative strand RNA plant viruses. Viruses 2012, 4, 1515–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakutani, T.; Hayano, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Minobe, Y. Ambisense segment 4 of rice stripe virus: Possible evolutionary relationship with phleboviruses and uukuviruses (Bunyaviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucher, E.; Sijen, T.; De Haan, P.; Goldbach, R.; Prins, M. Negative-strand tospoviruses and tenuiviruses carry a gene for a suppressor of gene silencing at analogous genomic positions. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, B.W.; Tsai, J.H. Biology and molecular biology of viruses in the genus Tenuivirus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1998, 36, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garry, C.E.; Garry, R.F. Proteomics computational analyses suggest that the carboxyl terminal glycoproteins of Bunyaviruses are class II viral fusion protein (beta-penetrenes). Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2004, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, J.; Weber, F.; Cusack, S. Bunyaviridae RNA polymerases (L-protein) have an N-terminal, influenza-like endonuclease domain, essential for viral cap-dependent transcription. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briese, T.; Calisher, C.H.; Higgs, S. Viruses of the family Bunyaviridae: Are all available isolates reassortants? Virology 2013, 446, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Chetvernin, V.; Tatusova, T. Improvements to pairwise sequence comparison (PASC): A genome-based web tool for virus classification. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Kapustin, Y.; Tatusova, T. Virus classification by Pairwise Sequence Comparison (PASC). In Encyclopedia of Virology, 3rd ed.; Mahy, B.W.J., Regenmortel, M.H.V., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 342–348. [Google Scholar]

| Virus Name (Abbreviation) | Strain Designation | Source | Date; Place of Isolation | Ref. | BioSampleID GenBank Accession Numbers | L 5′ NCR | L 3′ NCR | M 5′ NCR | M 3′ NCR | S 5′ NCR | S 3′ NCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abu Hammad virus (AHV) | Eg ArT 1194 | Ticks (Argas hermanni) collected from pigeon | 7 June 1971; Abu Hammad, al-Sharqia Governorate, Egypt | [43] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530531 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925436 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925435 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925434 | |||||||||||
| Abu Mina virus (AMV) | Eg An 4996-63 | European turtle dove (Streptopelia turtur) and associated ticks (Argas streptopelia) | 1 May 1963; Abu Mina, Matrouh Governorate, Egypt | [43] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530533 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925439 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925438 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925437 | |||||||||||
| Avalon virus (AVAV) | Brest/Ar T261 | Ticks (Ixodes uriae) | 1979; Brittany, France | [44] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530548 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925445 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925444 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925443 | |||||||||||
| Avalon virus (AVAV) | CanAr 173 | Ticks (Ixodes uriae) from European herring gull (Larus argentatus) | 31 July 1972; Great Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada | [45] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530547 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925442 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925441 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925440 | |||||||||||
| Bandia virus (BDAV) | IPD/A 611 | Rodent (Mastomys sp.) and ticks (Ornithodoros sonrai) collected from rodent burrow | 26 February 1965; Bandia Forest, Thiès Region, Senegal | [46] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530545 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| S: KU925448 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925447 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925446 | |||||||||||
| Clo Mor virus (C[L]MV) | ScotAr 7 | Ticks (Ixodes uriae) in nesting sites of common murees (Uria aalge) | 15 June 1973; Clo Mor, Cape Wrath, Scotland, UK | [45] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530553 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| S: KU925451 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925450 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925449 | |||||||||||
| Dera Ghazi Khan virus (DGKV) | JD 254 | Ticks (Hyalomma dromedarii) collected from a camelid | 4 April 1966; Dera Ghazi Khan District, Punjab Province, Pakistan | [47] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530534 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925454 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925453 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925452 | |||||||||||
| Dugbe virus (DUGV) | IbAr 1792 | Ticks (Amblyomma variegatum) collected from cattle | 14 October 1964; Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria | [48] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530543 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925457 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925456 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925455 | |||||||||||
| Erve virus (ERVEV) | Brest/An 221 (TVP21049) | Greater white-toothed shrew (Crocidura russula) | 5 May 1982; Saulges, Mayenne Départment, France | [49] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530552 | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925460 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925459 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925458 | |||||||||||
| Farallon virus (FARV) | Cal Ar846 | Ticks (Carios denmarki) | 20 July 1965; Farallon Islands, California, USA | [50] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530536 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925463 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925462 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925461 | |||||||||||
| Ganjam virus (GANV) | G 619 (TVP20486) | Ticks (Haemaphysalis intermedia) collected from a domestic goat | 6 November 1954; Bhanjanagar, Ganjam District, Orissa, India | [51] | Re-sequenced (Yadav et al., unpublished) SAMN04530544 | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| S: KU925466 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925465 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925464 | |||||||||||
| Great Saltee virus (GRSV) | RML 59972 | Ticks (Carios maritimus) collected from a seabird nest | 1972; Great Saltee Island, County Wexford, Ireland | [52] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530537 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925469 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925468 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925467 | |||||||||||
| Hughes virus (HUGV) | G2126 | Ticks (Carios denmarki) | January, 1962; Bush Key, Dry Tortugas, Florida, USA | [53,54] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530538 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925472 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925471 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925470 | |||||||||||
| Punta Salinas virus (PSV) | Cal Ar888 | Ticks (Carios amblus) | 14 October 1967; Punta Salinas, Huaura Province, Lima Region, Peru | [55] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530539 | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| S: KU925475 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925474 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925473 | |||||||||||
| Qalyub virus (QYBV) | Eg Ar 370 | Ticks (Carios erraticus) collected from a rat nest | 28 August 1952; Qalyub, al-Qalyubiyah Governorate, Egypt (British Protectorate) | [56] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530546 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925478 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925477 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925476 | |||||||||||
| Raza virus (RAZAV) | 829 | Ticks (Carios denmarki) | 20 May 1962; Raza Island, Baja California, Mexico | [57] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530540 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925481 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925480 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925479 | |||||||||||
| Sakhalin virus (SAKV) | LEIV-71C | Ticks (Ixodes uriae) collected from nesting sites of common murees (Uria aalge) | 21 November 1969; Tyuleniy Island, Sea of Okhotsk, Sakhalin Oblast, RSFSR, USSR | [58] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530549 | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| S: KU925484 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925483 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925482 | |||||||||||
| Sapphire II virus (SAPV) | RML 52323-14 | Ticks (Argas cooleyi) collected from a cliff swallow nest | August 1969; Garza County, Texas, USA | [59] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530535 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925487 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925486 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925485 | |||||||||||
| Soldado virus (SOLV) | TRVL 52214 | Ticks (Carios capensis) | 16 June 1963; Soldado Rock, Trinidad and Tobago | [60] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530541 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925490 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925489 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925488 | |||||||||||
| Taggert virus (TAGV) | Ml14850 | Ticks (Ixodes uriae) from seabird rookery | 1 January 1972; Macquarie Island, Tasmania, Australia | [61] | Re-sequenced [42]: SAMN04530550 | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925493 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925492 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925491 | |||||||||||
| Tillamook virus (TILLV) | RML 86 | Ticks (Ixodes uriae) | 1970; Oregon, USA | [62] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530551 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925496 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925495 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925494 | |||||||||||
| Tunis virus (TUNV) | Brest/Ar/T2756 | Ticks (Argas hermanni) | October 1989; El Kef, Kef Governorate, Tunisia | [63] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530532 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S: KU925499 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925498 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925497 | |||||||||||
| Zirqa virus (ZIRV) | POR7866 | Ticks (Carios muesebecki) | 2 November 1969; Zirku (Zirqa/Zarrakuh) Island, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates | [64] | Newly sequenced: SAMN04530542 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| S: KU925502 | |||||||||||
| M: KU925501 | |||||||||||
| L: KU925500 |
| Species | Virus Members |
|---|---|
| “Burana Nairovirus” | Huángpí tick virus 1 (HTV-1) |
| Tǎchéng tick virus 1 (TTV-1) | |
| Wēnzhōu tick virus (WTV) | |
| Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever nairovirus | Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) |
| Abu Hammad virus (AHV) including Tunis isolate | |
| Dera Ghazi Khan nairovirus | Abu Mina virus (AMV) |
| Dera Ghazi Khan virus (DGKV) | |
| Sapphire II virus (SAPV) | |
| Dugbe nairovirus | Dugbe virus (DUGV) |
| Kupe virus (KUPEV) | |
| “Hazara nairovirus” | Hazara virus (HAZV) |
| Tofla virus (TFLV) | |
| Hughes nairovirus | Caspiy virus (CASV) |
| Farallon virus (FARV) | |
| Great Saltee virus (GRSV) | |
| Hughes virus (HUGV) | |
| Punta Salinas virus (PSV) | |
| Raza virus (RAZAV) | |
| Soldado virus (SOLV) | |
| Zirqa virus (ZIRV) | |
| “Keterah nairovirus” | Gossas virus (GOSV) |
| Issyk-kul virus (ISKV) | |
| Keterah virus (KTRV) including soft tick isolate | |
| Uzun-Agach virus (UZAV) | |
| “Kasokero nairovirus” | Kasokero virus (KAS(O)V) |
| Leopards Hill virus (LPHV) | |
| Yogue virus (YOGV) | |
| “Nairobi sheep disease virus nairovirus” | Ganjam virus (GANV) |
| Nairobi sheep disease virus (NSDV) including Ganjam isolate | |
| Qalyub nairovirus | Bandia virus (BDAV) |
| Qalyub virus (QYBV) | |
| Sakhalin nairovirus | Avalon virus (AVAV) |
| Clo Mor virus (C(L)MV) | |
| Sakhalin virus (SAKV) | |
| Taggert virus (TAGB) | |
| Tillamook virus (TILLV) | |
| Thiafora nairovirus | Erve virus (ERVEV) |
| Thiafora virus (TFAV) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuhn, J.H.; Wiley, M.R.; Rodriguez, S.E.; Bào, Y.; Prieto, K.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Guzman, H.; Savji, N.; Ladner, J.T.; Tesh, R.B.; et al. Genomic Characterization of the Genus Nairovirus (Family Bunyaviridae). Viruses 2016, 8, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060164
Kuhn JH, Wiley MR, Rodriguez SE, Bào Y, Prieto K, Travassos da Rosa APA, Guzman H, Savji N, Ladner JT, Tesh RB, et al. Genomic Characterization of the Genus Nairovirus (Family Bunyaviridae). Viruses. 2016; 8(6):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060164
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuhn, Jens H., Michael R. Wiley, Sergio E. Rodriguez, Yīmíng Bào, Karla Prieto, Amelia P. A. Travassos da Rosa, Hilda Guzman, Nazir Savji, Jason T. Ladner, Robert B. Tesh, and et al. 2016. "Genomic Characterization of the Genus Nairovirus (Family Bunyaviridae)" Viruses 8, no. 6: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060164
APA StyleKuhn, J. H., Wiley, M. R., Rodriguez, S. E., Bào, Y., Prieto, K., Travassos da Rosa, A. P. A., Guzman, H., Savji, N., Ladner, J. T., Tesh, R. B., Wada, J., Jahrling, P. B., Bente, D. A., & Palacios, G. (2016). Genomic Characterization of the Genus Nairovirus (Family Bunyaviridae). Viruses, 8(6), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060164







